Response Surface Methodology to Explore the Influence Mechanism of Fiber Diameter in a New Multi-Needle Electrospinning Spinneret
Abstract
:1. Introduction
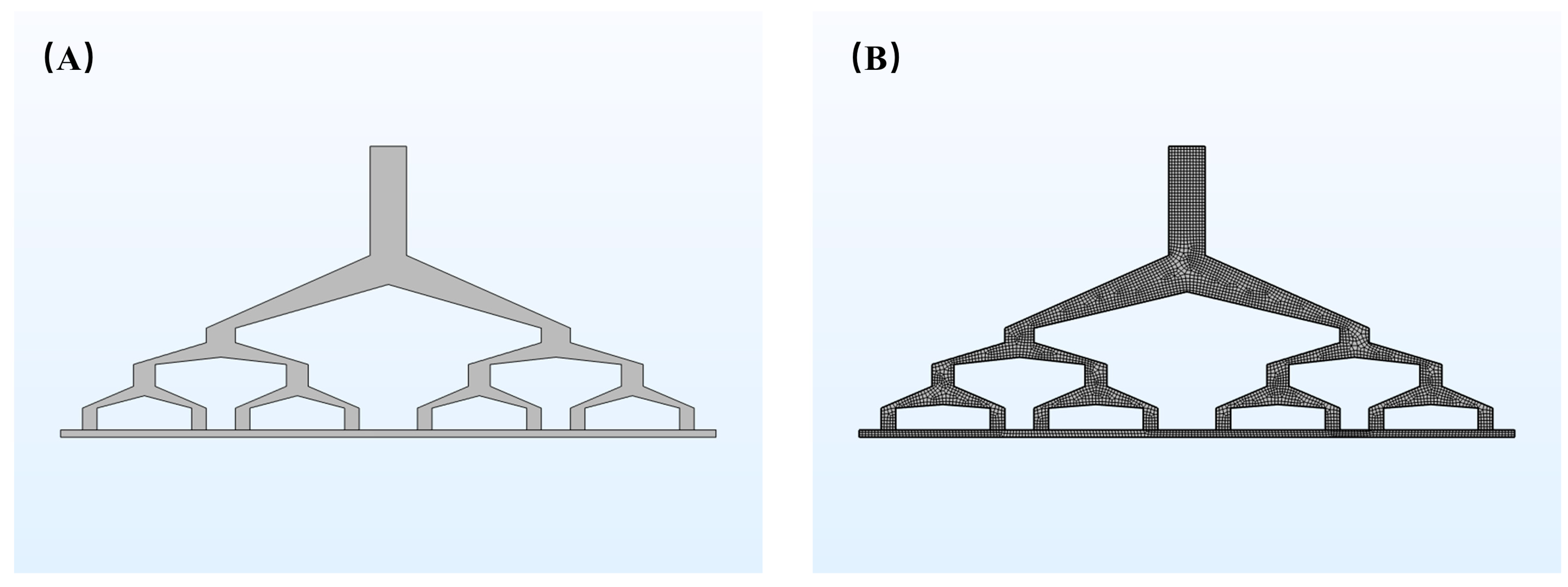
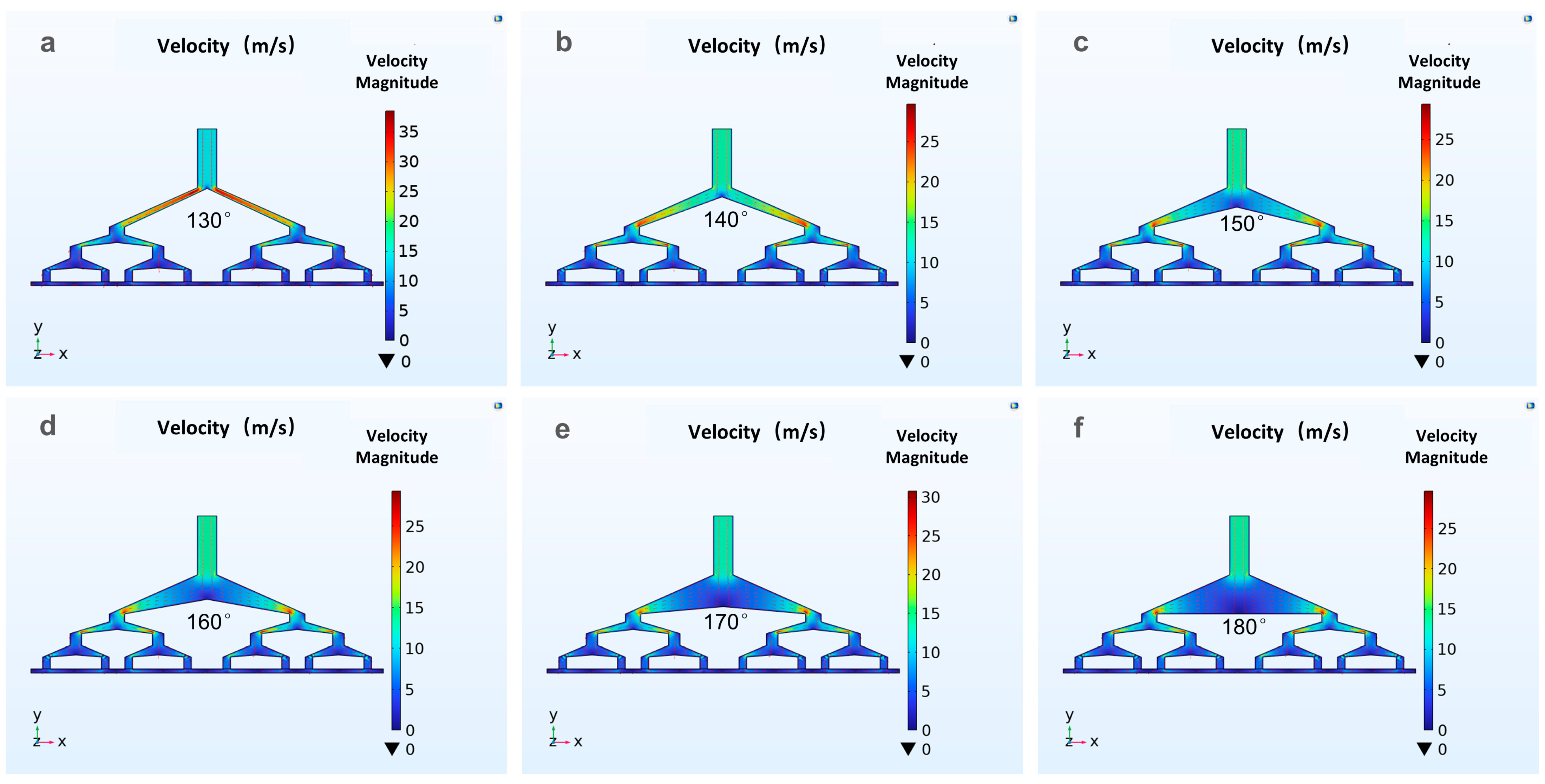
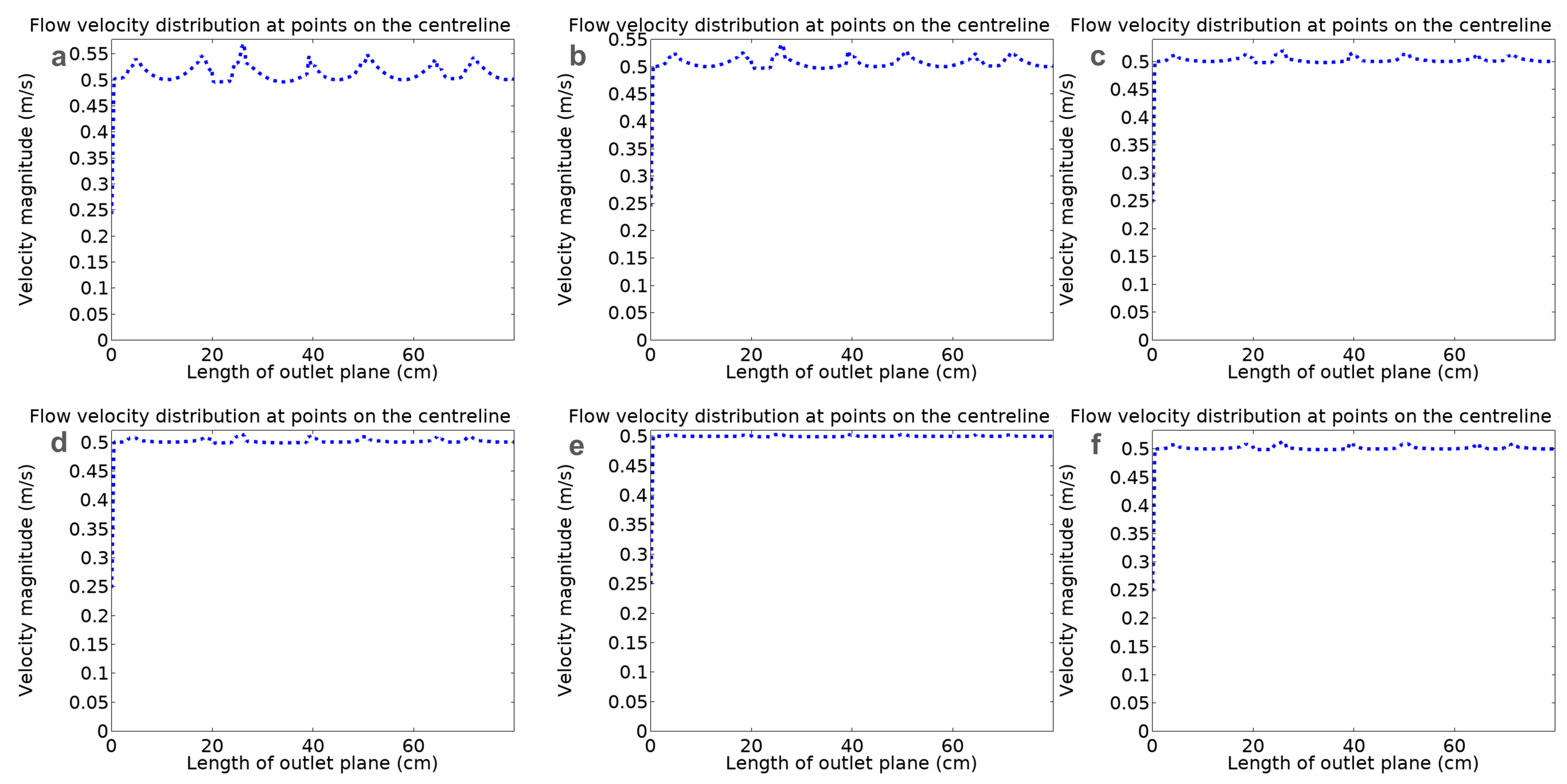
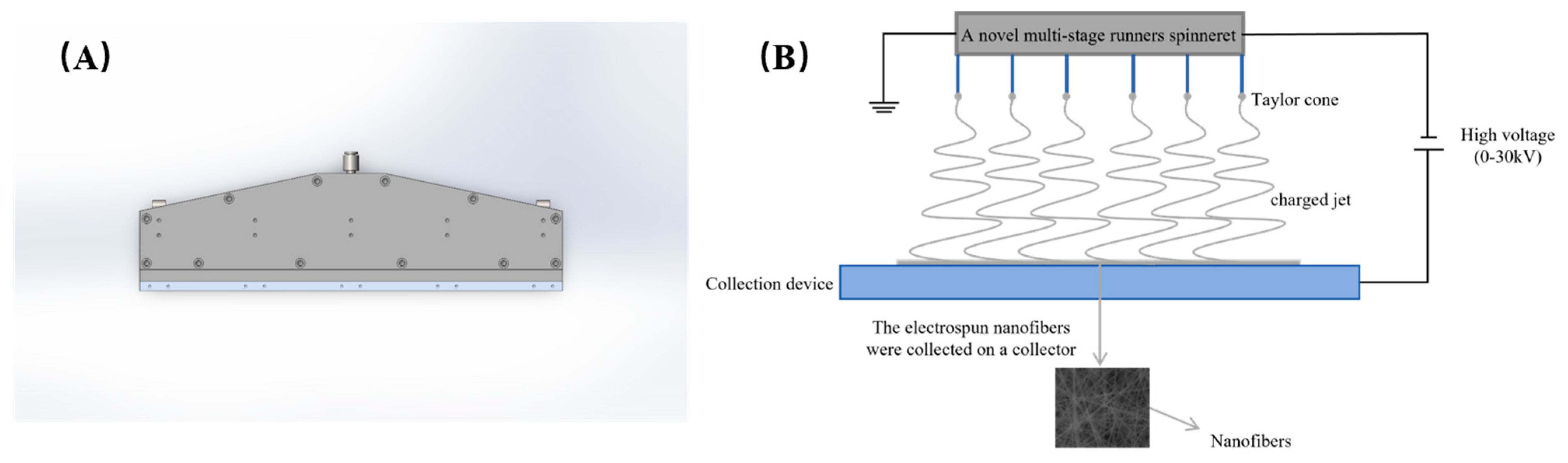
2. Design and Simulation of Spinneret
3. Experiment
3.1. Experimental Materials
3.2. Characterization
3.3. Experimental Design
4. Results and Discussion
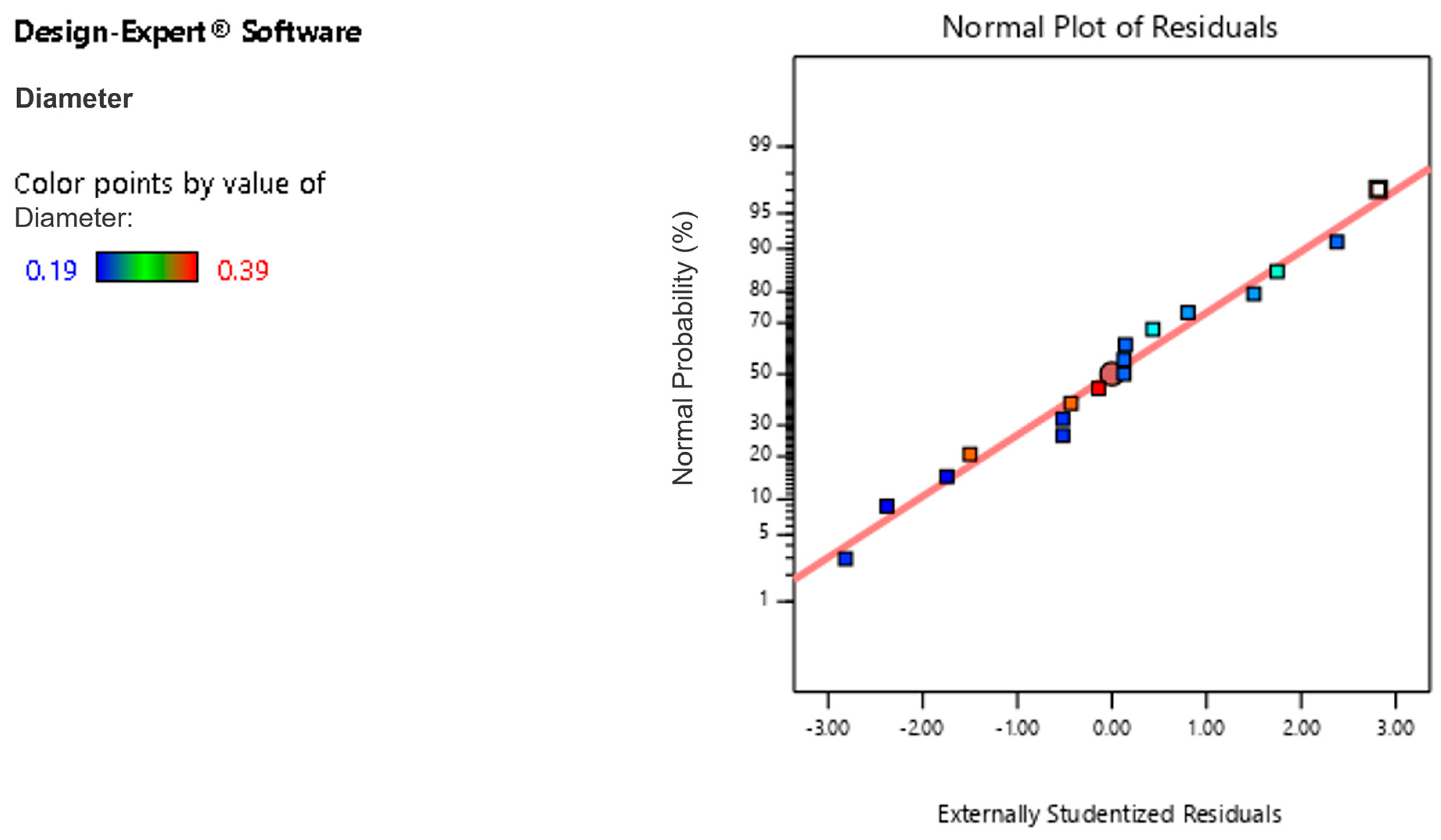
4.1. RSM Testing
4.2. Response Surface Analysis
4.3. Optimization and Validation
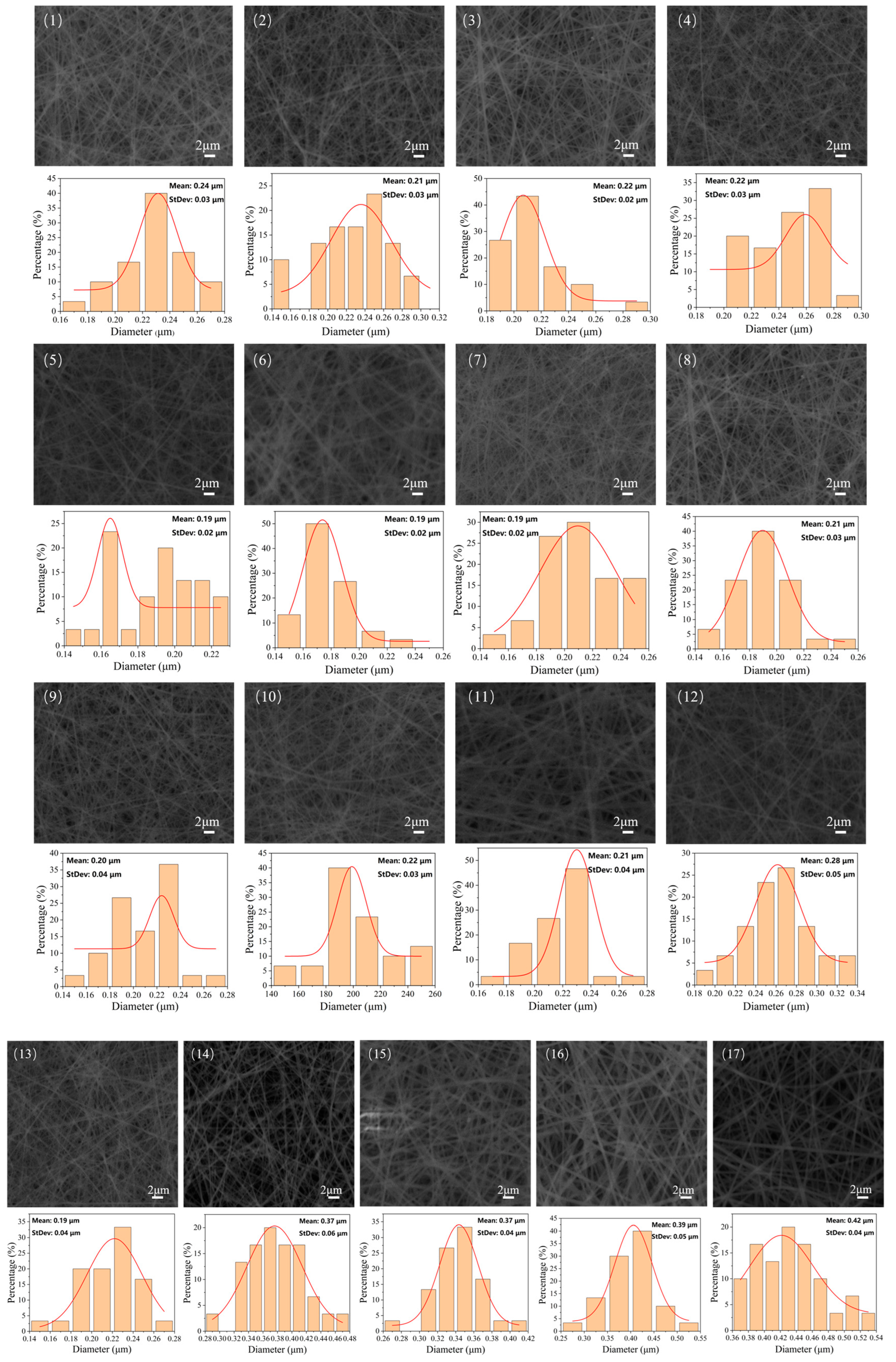
4.4. Microscopic Morphology
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bhagure, S.S.; Rao, A.R. A Review: Electrospinning and Electrospinning Nanofibre Technology, Process & Application. Int. J. Innov. Sci. Res. Technol. 2020, 5, 528–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xie, L.; Wang, X.; Shao, Z.; Kong, B. Electrospinning Super-Assembly of Ultrathin Fibers from Single- to Multi-Taylor Cone Sites. Appl. Mater. Today 2022, 26, 101272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xu, M.; Shi, R.; Zhang, A.; Zhang, J. Advances in Electrostatic Spinning of Polymer Fibers Functionalized with Metal-Based Nanocrystals and Biomedical Applications. Molecules 2022, 27, 5548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, X.; Hu, N.; Yan, F.; Wang, Y. Development and Applications of Electrospun Nanofiber-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2023, 112, 108444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakirov, S. (Ed.) Nano-Size Polymers; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; ISBN 978-3-319-39713-9. [Google Scholar]
- Partheniadis, I.; Nikolakakis, I.; Laidmäe, I.; Heinämäki, J. A Mini-Review: Needleless Electrospinning of Nanofibers for Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Applications. Processes 2020, 8, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SalehHudin, H.S.; Mohamad, E.N.; Mahadi, W.N.L.; Muhammad Afifi, A. Multiple-Jet Electrospinning Methods for Nanofiber Processing: A Review. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2018, 33, 479–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, P.; Shi, H.; Niu, P.; Lu, T.; Wang, W. Electric Field Analysis of Auxiliary Electrode in Needle-Free Electrostatic Spinning. Ferroelectrics 2019, 548, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, H.; Wang, X.; Lin, T. Needleless Electrospinning: Influences of Fibre Generator Geometry. J. Text. Inst. 2012, 103, 787–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Song, J.; Yang, C.; Long, Y.; Wu, H. Scalable Manufacturing and Applications of Nanofibers. Mater. Today 2019, 28, 98–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Jia, Z.; Li, Q.; Hou, L.; Liu, J.; Wang, L.; Guan, Z.; Zahn, M. A Shield Ring Enhanced Equilateral Hexagon Distributed Multi-Needle Electrospinning Spinneret. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2010, 17, 1592–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Zhou, Y. Multineedle electrospinning. In Electrospinning: Nanofabrication and Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 201–218. ISBN 978-0-323-51270-1. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Z.; Wu, P.; Wang, Z.; Xu, G.; Wang, H.; Chen, X.; Wang, R.; Huang, W.; Chen, R.; Chen, X.; et al. Optimization of Electric Field Uniformity of Multi-Needle Electrospinning Nozzle. AIP Adv. 2019, 9, 105104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, J.; Li, C.; Ko, F. Melt-Electrospinning Part I: Processing Parameters and Geometric Properties. Polymer 2004, 45, 7597–7603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beachley, V.; Wen, X. Effect of Electrospinning Parameters on the Nanofiber Diameter and Length. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2009, 29, 663–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zargham, S.; Bazgir, S.; Tavakoli, A.; Rashidi, A.S.; Damerchely, R. The Effect of Flow Rate on Morphology and Deposition Area of Electrospun Nylon 6 Nanofiber. J. Eng. Fibers Fabr. 2012, 7, 155892501200700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theron, S.A.; Zussman, E.; Yarin, A.L. Experimental Investigation of the Governing Parameters in the Electrospinning of Polymer Solutions. Polymer 2004, 45, 2017–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angammana, C.J.; Jayaram, S.H. The Effects of Electric Field on the Multijet Electrospinning Process and Fiber Morphology. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2011, 47, 1028–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Gong, R. Manufacturing Technologies of Polymeric Nanofibres and Nanofibre Yarns. Polym. Int. 2008, 57, 837–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maski, D.; Durairaj, D. Effects of Electrode Voltage, Liquid Flow Rate, and Liquid Properties on Spray Chargeability of an Air-Assisted Electrostatic-Induction Spray-Charging System. J. Electrost. 2010, 68, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Y.; Chen, N.; Zheng, X.; Shi, D.; Jiang, Z.; Song, S.; Shi, Y. Electric Field and Spraying Characteristics of Electrospray Using Concave Ground Electrode. J. Electrost. 2022, 115, 103662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, R.; Padhye, R. Nano Fibres by Electro Spinning: Properties and Applications. J. Text. Eng. Fash. Technol. 2017, 2, 486–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reneker, D.H.; Fong, H. (Eds.) Polymeric Nanofibers; ACS Symposium Series; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2006; Volume 918, ISBN 978-0-8412-3919-7. [Google Scholar]
- Younes, B.; Fotheringham, A. Factorial Optimisation of the Effects of Extrusion Temperature Profile and Polymer Grade on As-Spun Aliphatic–Aromatic Co-Polyester Fibres III: Mechanical Properties. J. Text. Inst. 2012, 103, 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Nam, Y.S.; Rhee, D.M.; Park, H.-S.; Park, W.H. Preparation and Characterization of Antimicrobial Polycarbonate Nanofibrous Membrane. Eur. Polym. J. 2007, 43, 3146–3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xiang, H.; Song, C.; Zhu, D.; Sui, J.; Liu, Q.; Long, Y. Highly Efficient Transparent Air Filter Prepared by Collecting-Electrode-Free Bipolar Electrospinning Apparatus. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 385, 121535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, X.H.; Liu, Q.; Ma, X.J.; Jia, C.H.; Yang, C.C. The Characteristics of Melt Flow in Composite Spinning Micropore. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 383–390, 2968–2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marla, V.T.; Shambaugh, R.L. Modeling of the Melt Blowing Performance of Slot Dies. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2004, 43, 2789–2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R. Melt Blown Dies: A Hot Innovation Spot. Int. Nonwovens J. 2002, 1558925002OS-01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tepper, M.; Eminoglu, Y.; Mehling, N.; Walorski, J.; Roth, H.; Wessling, M. Rotation-in-a-Spinneret Integrates Static Mixers inside Hollow Fiber Membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 656, 120599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadoosh, R.; Alwan, A.; Farhan, S.; Jassim, B.; Mahmood, A.; AlSaadi, L.; Abed, R. Examine Physicochemical Properties of PVC Thin Films Affected by Carbon Nanotubes to Prevent Photodegradation During UV Light Exposure. Prog. Color Color. Coat. 2024, 17, 307–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Design Variable | Denotations | Factor Level | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| −1 | 0 | 1 | ||
| Voltage (Kv) | A | 55 | 60 | 65 |
| Collection distance (cm) | B | 20 | 25 | 30 |
| Concentration (wt%) | C | 11 | 13 | 15 |
| Experimental Coding | Working Voltage A (Kv) | Collection Distance B (cm) | Solution Concentration C (wt%) | Nanofiber Average Diameter (μm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 60 | 30 | 11 | 0.24 0.03 |
| 2 | 60 | 25 | 13 | 0.21 |
| 3 | 65 | 25 | 11 | 0.22 |
| 4 | 60 | 25 | 13 | 0.22 |
| 5 | 55 | 25 | 15 | 0.37 |
| 6 | 65 | 30 | 13 | 0.19 |
| 7 | 55 | 20 | 13 | 0.20 |
| 8 | 60 | 25 | 13 | 0.21 |
| 9 | 60 | 25 | 13 | 0.19 |
| 10 | 60 | 25 | 13 | 0.20 |
| 11 | 60 | 20 | 11 | 0.21 |
| 12 | 60 | 30 | 15 | 0.42 |
| 13 | 60 | 20 | 15 | 0.37 |
| 14 | 65 | 20 | 13 | 0.19 |
| 15 | 55 | 30 | 13 | 0.28 |
| 16 | 55 | 25 | 11 | 0.22 |
| 17 | 65 | 25 | 15 | 0.39 |
| Source of Variance | Square Sum | Mean Square | F-Statistic | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 0.0864 | 0.0096 | 60.50 | <0.0001 | significant |
| A | 0.0003 | 0.0003 | 0.9117 | 0.3715 | not significant |
| B | 0.0010 | 0.0010 | 6.31 | 0.0402 | significant |
| C | 0.0512 | 0.0512 | 325.85 | <0.0001 | significant |
| AB | 0.0004 | 0.0004 | 2.87 | 0.1340 | not significant |
| AC | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0132 | 0.9119 | not significant |
| BC | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.3849 | 0.5546 | not significant |
| A2 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.1757 | 0.6877 | not significant |
| B2 | 0.0002 | 0.0002 | 1.27 | 0.2970 | not significant |
| C2 | 0.0330 | 0.0330 | 204.40 | <0.0001 | significant |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, J.; Chen, X.; Wang, H.; Ou, W.; He, J.; Liu, M.; Lu, Z.; Hu, J.; Zheng, G.; Wu, D. Response Surface Methodology to Explore the Influence Mechanism of Fiber Diameter in a New Multi-Needle Electrospinning Spinneret. Polymers 2024, 16, 2222. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16152222
Jiang J, Chen X, Wang H, Ou W, He J, Liu M, Lu Z, Hu J, Zheng G, Wu D. Response Surface Methodology to Explore the Influence Mechanism of Fiber Diameter in a New Multi-Needle Electrospinning Spinneret. Polymers. 2024; 16(15):2222. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16152222
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Jianmin, Xiaojie Chen, Han Wang, Weicheng Ou, Jiayi He, Maolin Liu, Zehui Lu, Jingyi Hu, Gaofeng Zheng, and Dezhi Wu. 2024. "Response Surface Methodology to Explore the Influence Mechanism of Fiber Diameter in a New Multi-Needle Electrospinning Spinneret" Polymers 16, no. 15: 2222. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16152222
APA StyleJiang, J., Chen, X., Wang, H., Ou, W., He, J., Liu, M., Lu, Z., Hu, J., Zheng, G., & Wu, D. (2024). Response Surface Methodology to Explore the Influence Mechanism of Fiber Diameter in a New Multi-Needle Electrospinning Spinneret. Polymers, 16(15), 2222. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16152222








