Magnetic Nanoparticles in Biopolymer Fibers: Fabrication Techniques and Characterization Methods
Abstract
:1. Introduction
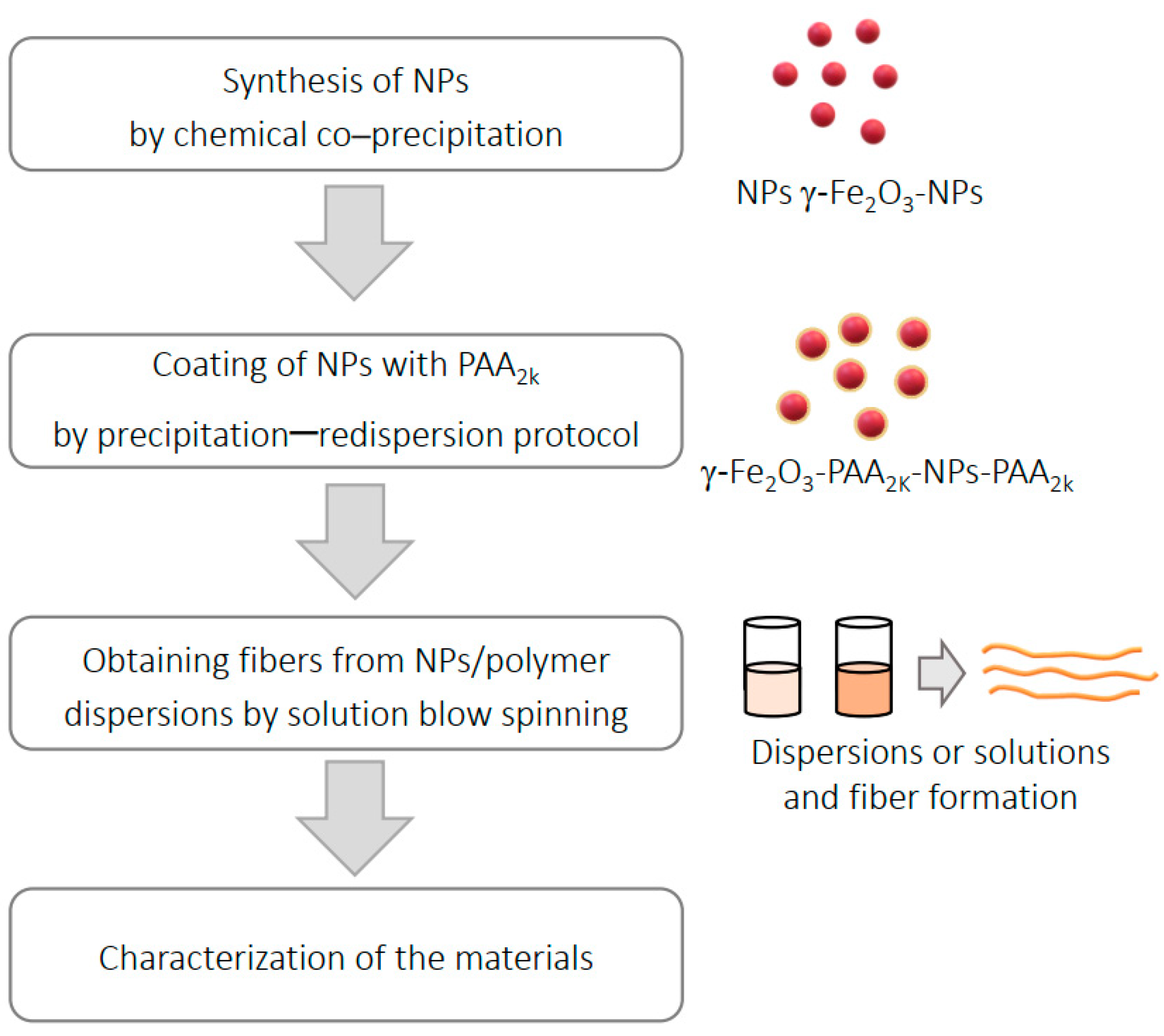
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials Preparation
2.1.1. Synthesis of Iron Oxide (γ-Fe2O3) Nanoparticles (NPs)
2.1.2. Coating of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles
2.1.3. Polymeric Solutions and Nanoparticles Behavior in Dispersions
2.2. Obtaining Fibers Incorporated with NPs
2.3. Characterization
2.3.1. Analysis by Dynamic Light Scattering and Zeta Potential
2.3.2. Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.3.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.3.4. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
2.3.5. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.3.6. X-ray Diffraction Analysis (XRD)
3. Results
3.1. Nanoparticles and Individual Polymers Characterization
3.1.1. Size and Surface Charge of Particles
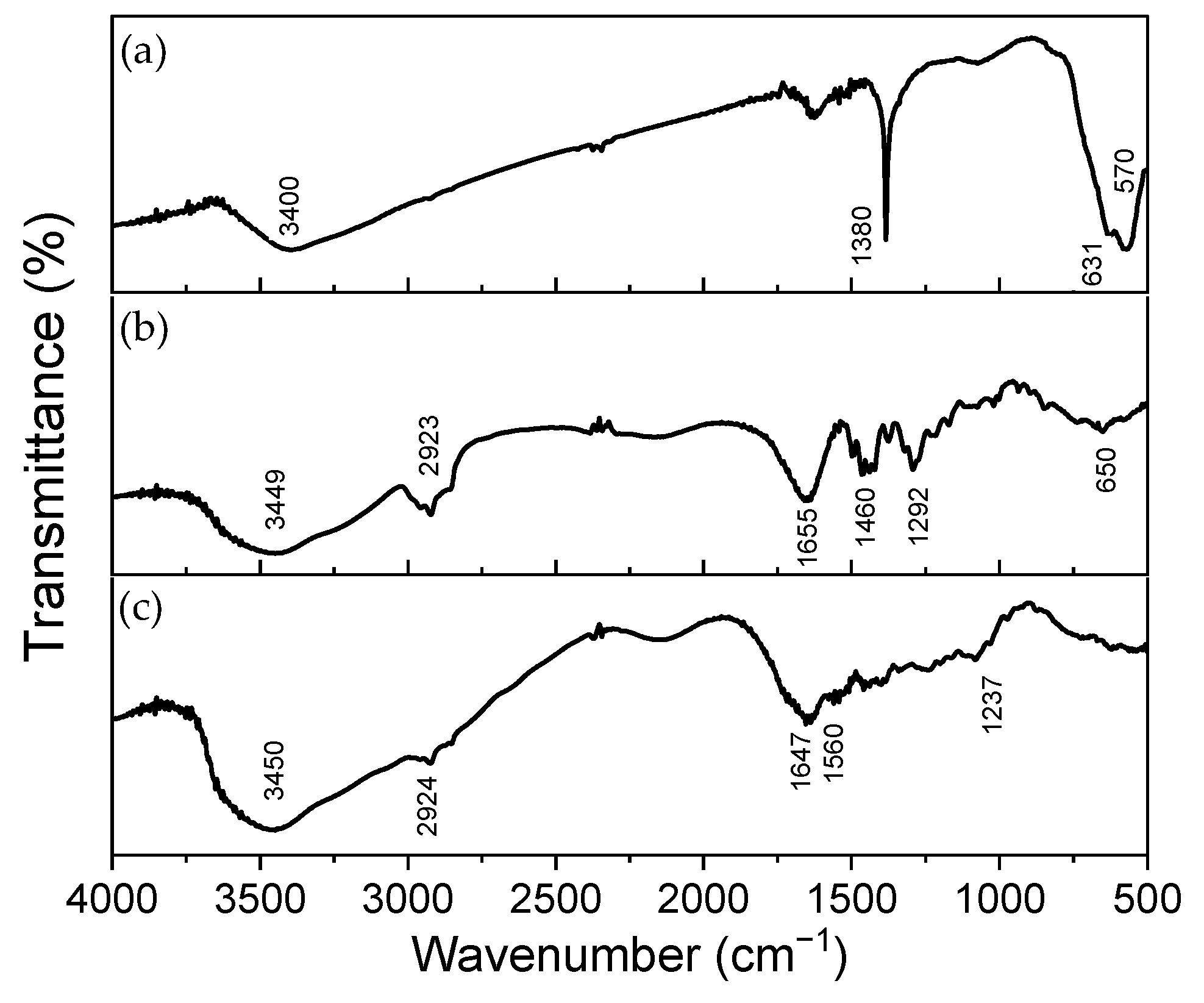
3.1.2. Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) of the NPs and Individual Polymers
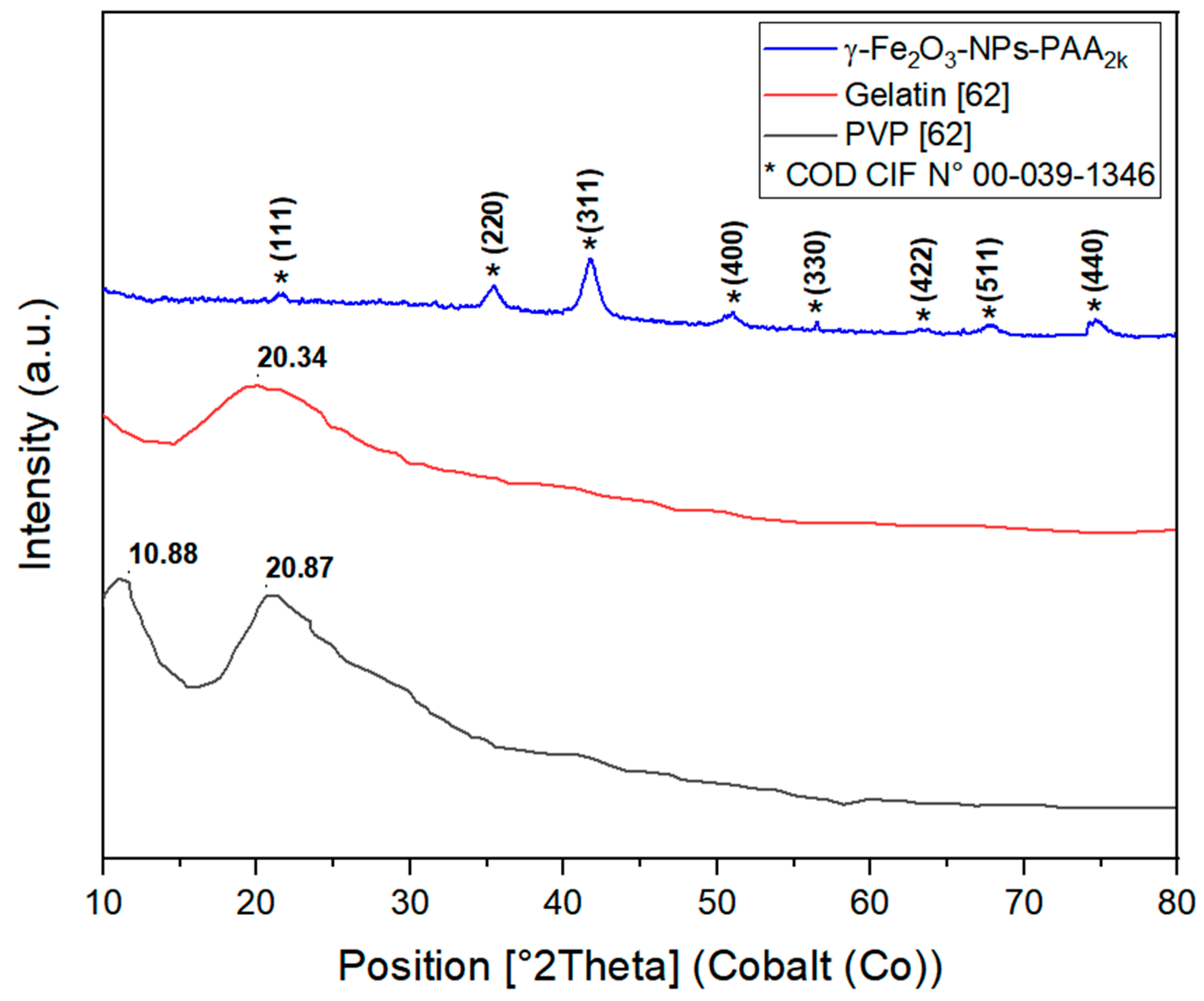
3.1.3. Structural Characterization of γ-Fe2O3-NPs-PAA2k
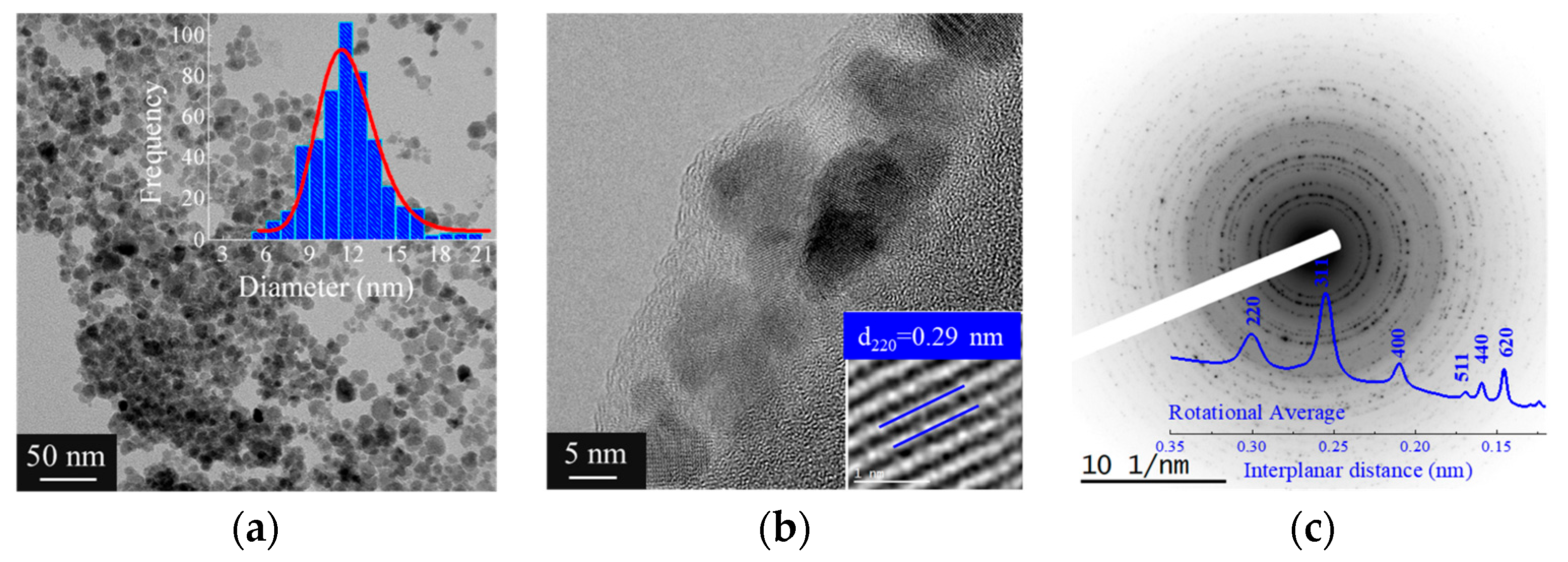
3.1.4. Morphological Analysis of γ-Fe2O3-NPs-PAA2k
3.2. Nanocomposite Polymer Fiber Materials Characterization
3.2.1. Obtaining Polymeric Fibers
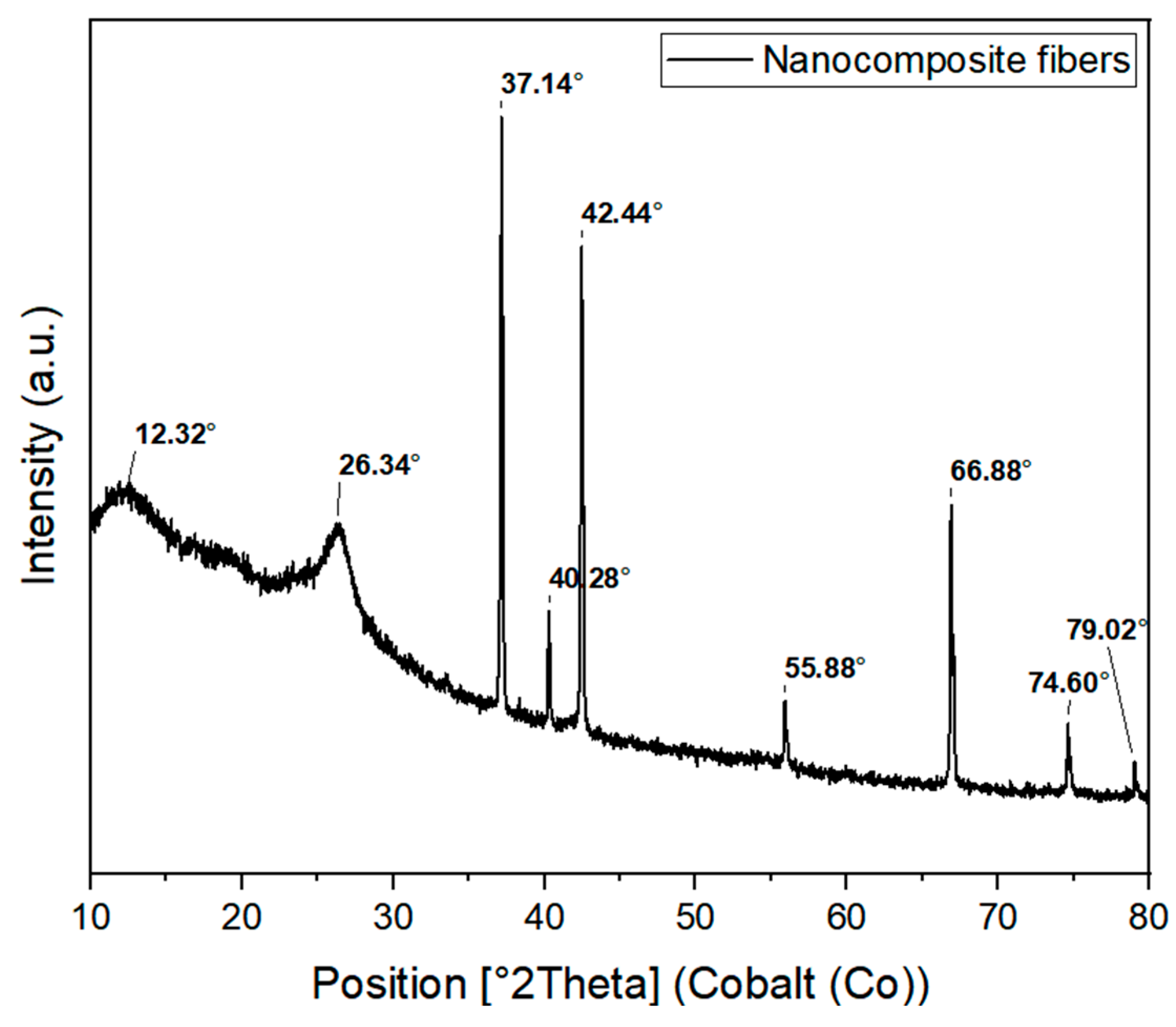
3.2.2. Structural Characterization of the Nanocomposite Fibers
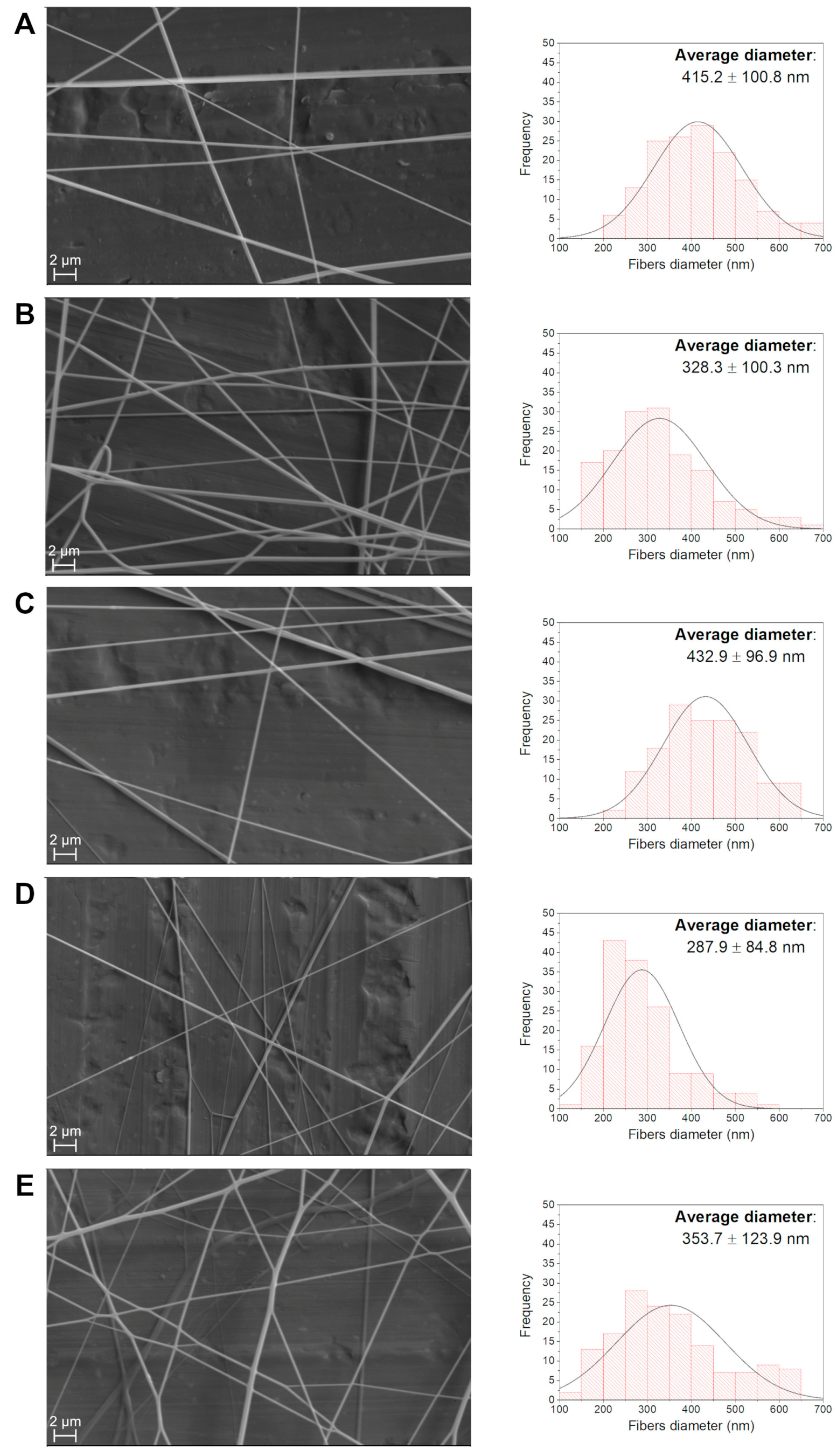
3.2.3. Morphological Analysis of Polymer Nanocomposite Fibers
3.2.4. Thermal Analysis of the Polymer Nanocomposite Fibers
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saleh, T.A. Nanomaterials: Classification, properties and environmental toxicities. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 20, 101067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joudeh, N.; Linke, D. Nanoparticle classification, physicochemical properties, characterization and applications: A comprehensive review for biologists. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 20, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, R.D.; Prasad, R.S.; Prasad, R.B.; Prasad, S.R.; Singha, S.B.; Singha, D.; Navathe, G.J. A review on modern characterization techniques for analysis of nanomaterials and biomaterials. ES Energy Environ. 2024, 23, 1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulusoy, U. A review of particle shape effects on material properties for various engineering applications: From macro to nanoscale. Minerals 2023, 13, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idumah, C.I.; Obele, C.M. Understanding interfacial influence on properties of polymer nanocomposites. Surf. Interfaces 2021, 22, 100879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafeeq, H.; Hussain, A.; Ambreen, A.; Waqas, M.; Bilal, M.; Iqbal, H.M. Functionalized nanoparticles and their environmental remediation potential: A review. J. Nanostruct. Chem. 2022, 12, 1007–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Choudhary, P.; Kumar, A.; Camargo, P.H.; Krishnan, V. Recent advances in plasmonic photocatalysis based on TiO2 and noble metal nanoparticles for energy conversion, environmental remediation and organic synthesis. Small 2022, 18, 2101638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.W.; Yan, S.; Shang, G.; Wang, S.; Zhong, C.J. Strain sensors fabricated by surface assembly of nanoparticles. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 186, 113268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Agarwal, P.; Sebghatollahi, Z.; Mahato, N. Functional nanostructured materials in the cosmetics industry: A review. ChemEngineering 2023, 7, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.H.; Hsiao, J.K. Diagnostic and therapeutic roles of iron oxide nanoparticles in biomedicine. Tzu Chi Med. J. 2023, 35, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MubarakAli, D.; Kim, H.; Venkatesh, P.S.; Kim, J.W.; Lee, S.Y. A systemic review on the synthesis, characterization and applications of palladium nanoparticles in biomedicine. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2023, 195, 3699–3718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Song, W.; Tang, Y.; Xu, X.; Huang, Y.; Yu, D. Polymer-based nanofiber–nanoparticle hybrids and their medical applications. Polymers 2022, 14, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, P.I.; Borges, J.P. Recent advances in magnetic electrospun nanofibers for cancer theranostics application. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 2021, 31, 835–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustamante-Torres, M.; Romero-Fierro, D.; Estrella-Nuñez, J.; Arcentales-Vera, B.; Chichande-Proaño, E.; Bucio, E. Polymeric composite of magnetite iron oxide nanoparticles and their application in biomedicine: A review. Polymers 2022, 14, 752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kush, P.; Kumar, P.; Singh, R.; Kaushik, A. Aspects of high-performance and bio-acceptable magnetic nanoparticles for biomedical application. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 16, 704–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, N.D. Smart Textiles: Wearable Nanotechnology, 1st ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Barros, L.N.L.C.; Araujo, R.N.D.; Nascimento, E.P.D.; Gama, A.J.D.A.; Neves, G.A.; Torres, M.A.M.; Menezes, R.R. Influence of fast drying on the morphology of α-Fe2O3 and FeMnO3/α-Fe2O3 fibers produced by solution blow spinning. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xia, J.; Pang, X.; Zhao, M.; Wang, B.; Yang, L.; Fu, S. Magnetic nanoparticle-loaded electrospun polymeric nanofibers for tissue engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 73, 537–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oun, A.A.; Shankar, S.; Rhim, J.W. Multifunctional nanocellulose/metal and metal oxide nanoparticle hybrid nanomaterials. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 435–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadehnazari, A. Metal oxide/polymer nanocomposites: A review on recent advances in fabrication and applications. Polym. Plast. Technol. Mater. 2023, 62, 655–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, M.F.; Neves, G.A.; Nascimento, E.P.; Loureiro, F.J.; Araújo, A.J.; Raimundo, R.A.; Menezes, R.R. Solution blow spinning of Co3O4 nanofibers as electrocatalyst for oxygen evolution processes. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 25140–25149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Kayal, T.; Giuntoli, G.; Cavallo, A.; Pisani, A.; Mazzetti, P.; Fonnesu, R.; Losi, P. Incorporation of copper nanoparticles on electrospun polyurethane membrane fibers by a spray method. Molecules 2023, 28, 5981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdullah, J.A.A.; Perez-Puyana, V.; Guerrero, A.; Romero, A. Novel hybrid electrospun poly (ε-caprolactone) nanofibers containing green and chemical magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2023, 140, e54345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawant, S.R.; Kalla, S.; Murthy, Z.V.P. Nanomaterial-incorporated membrane distillation membranes: Characteristics, fabrication techniques and applications. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2023, 46, 1982–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voorhis, C.; González-Benito, J.; Kramar, A. “Nano in Nano”—Incorporation of ZnO Nanoparticles into Cellulose Acetate–Poly (Ethylene Oxide) Composite Nanofibers Using Solution Blow Spinning. Polymers 2024, 16, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakoria, A.; Sinha-Ray, S. A Review on biopolymer-based fibers via electrospinning and solution blowing and their applications. Fibers 2018, 6, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramar, A.; González-Benito, J. Preparation of cellulose acetate film with dual hydrophobic-hydrophilic properties using solution blow spinning. Mater. Des. 2023, 227, 111788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsinas, Z.; Tao, R.; Forster, A.L. Solution blow spinning of polymeric nano-composite fibers for personal protective equipment. J. Vis. Exp. 2021, 169, e62283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, J.E.; Mattoso, L.H.C.; Orts, W.J.; Medeiros, E.S. Structural and Morphological Characterization of Micro and Nanofibers Produced by Electrospinning and Solution Blow Spinning: A Comparative Study. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2013, 2013, 409572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaffaro, R.; Settanni, L.; Gulino, E.F. Release Profiles of Carvacrol or Chlorhexidine of Pla/Graphene Nanoplatelets Membranes Prepared Using Electrospinning and Solution Blow Spinning: A Comparative Study. Molecules 2023, 28, 1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilches, J.L.; Filho, M.D.S.M.D.S.; Rosa, M.D.F.; Sanches, A.O.; Malmonge, J.A. Fabrication of fish gelatin microfibrous mats by solution blow spinning. Mater. Res. 2019, 22, e20190158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eticha, A.K.; Akgul, Y. Optimization of gelatin nanofibrous webs fabricated via electrically assisted solution blow spinning for air filtration applications. Int. J. Sci. Environ. Technol. 2024, 21, 7135–7152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardareh, E.A.; Shahzeidi, M.; Ardestani, M.T.A.; Mousavi-Khattat, M.; Zarepour, A.; Zarrabi, A. Antimicrobial activity of blow spun PLA/gelatin nanofibers containing green synthesized silver nanoparticles against wound infection-causing bacteria. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kołodziejek, D.; Łopianiak, I.; Tadko, O.; Drozd, M.; Wojasiński, M.; Jastrzębska, E. Magnetic polyurethane nanomaterials: A novel approach for in vitro cardiac cell maturation and culture. Polym. Test 2023, 127, 108190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khdary, N.H.; Almuarqab, B.T.; El Enany, G. Nanoparticle-embedded polymers and their applications: A review. Membranes 2023, 13, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araujo, R.N.; Nascimento, E.P.; Raimundo, R.A.; Macedo, D.A.; Mastelaro, V.R.; Neves, G.A.; Menezes, R.R. Hybrid hematite/calcium ferrite fibers by solution blow spinning: Microstructural, optical and magnetic characterization. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 33363–33372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraj, S.; Thangam, R.; Fathima, N.N. Electrospinning of casein nanofibers with silver nanoparticles for potential biomedical applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 120, 1674–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowsalya, E.; MosaChristas, K.; Balashanmugam, P.; Rani, J.C. Biocompatible silver nanoparticles/poly (vinyl alcohol) electrospun nanofibers for potential antimicrobial food packaging applications. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2019, 21, 100379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aamer, H.; Kim, S.B.; Oh, J.M.; Park, H.; Jo, Y.M. ZnO-impregnated polyacrylonitrile nanofiber filters against various phases of air pollutants. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berret, J.-F.; Sandre, O.; Mauger, A. Size Distribution of superparamagnetic particles determined by magnetic sedimentation. Langmuir 2007, 23, 2993–2999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safi, M.; Courtois, J.; Seigneuret, M.; Conjeaud, H.; Berret, J.F. The effects of aggregation and protein corona on the cellular internalization of iron oxide nanoparticles. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 9353–9363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitorazi, L.; Berret, J.F. Mixing order asymmetry in nanoparticle-polymer complexation and precipitation revealed by isothermal titration calorimetry. J. Phys. Chem. B 2024, 128, 7859–7870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Ma, M.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, N. Synthesis of Nanometer-Size Maghemite Particles from Magnetite. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2004, 245, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bee, A.; Massart, R.; Neveu, S. Synthesis of very fine maghemite particles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1995, 149, 6–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Q.; Zhou, C.; Rehman, A.; Qayum, A.; Liu, Y.; Ren, X. Improvement of physicochemical properties, microstructure and stability of lotus root starch/xanthan gum stabilized emulsion by multi-frequency power ultrasound. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2023, 101, 106687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pochapski, D.J.; Santos, C.C.; Leite, G.W.; Pulcinelli, S.H.; Santilli, C.V. Zeta potential and colloidal stability predictions for inorganic nanoparticle dispersions: Effects of experimental conditions and electrokinetic models on the interpretation of results. Langmuir 2021, 37, 13379–13389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fresnais, J.; Yan, M.; Courtois, J.; Bostelmann, T.; Bée, A.; Berret, J.F. Poly(acrylic acid)-coated iron oxide nanoparticles: Quantitative evaluation of the coating properties and applications for the removal of a pollutant dye. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 395, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadfar, S.M.; Camozzi, D.; Darguzyte, M.; Roemhild, K.; Varvarà, P.; Metselaar, J.; Lammers, T. Size-isolation of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles improves MRI, MPI and hyperthermia performance. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2020, 18, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guibert, C.; Dupuis, V.; Fresnais, J.; Peyre, V. Controlling nanoparticles dispersion in ionic liquids by tuning the pH. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 454, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.; Fresnais, J.; Berret, J.F. Growth mechanism of nanostructured superparamagnetic rods obtained by electrostatic co-Assembly. Soft Matter 2010, 6, 1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandhu, A.; Sutradhar, S.; Mukherjee, S.; Greneche, J.M.; Chakrabarti, P.K. Synthesis, characterization and magnetic property of maghemite (γ-Fe2O3) nanoparticles and their protective coating with pepsin for bio-functionalization. Mater. Res. Bull. 2015, 70, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shayan, N.N.; Mirzayi, B. Adsorption and removal of asphaltene using synthesized maghemite and hematite nanoparticles. Energy Fuels 2015, 29, 1397–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverstein, R.M.; Webster, F.X.; Kiemle, D.J. Spectrometric Identification of Organic Compounds, 7th ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Campos, E.A.; Pinto, D.V.; Oliveira, J.I.; Mattos, E.D.; Dutra, R.D. Synthesis, characterization and applications of iron oxide nanoparticles-a short review. J. Aerosp. Technol. Manag. 2015, 7, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, A.F.; Mendo, S.G.; Ferreira, L.P.; Mendonça, M.H.; Ferreira, P.; Godinho, M.; Cruz, M.M.; Carvalho, M.D. Gelatine-assisted synthesis of magnetite nanoparticles for magnetic hyperthermia. J. Nanopart. Res. 2016, 18, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhavsar, V.; Tripathi, D. Structural, optical and aging studies of biocompatible PVC-PVP blend films. J. Polym. Eng. 2017, 38, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winsett, J.; Moilanen, A.; Paudel, K.; Kamali, S.; Ding, K.; Cribb, W.; Seifu, D.; Neupane, S. Quantitative determination of magnetite and maghemite in iron oxide nanoparticles using Mössbauer spectroscopy. Disco Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dar, M.I.; Shivashankar, S.A. Single crystalline magnetite, maghemite and hematite nanoparticles with rich coercivity. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 4105–4113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koczkur, K.M.; Mourdikoudis, S.; Polavarapu, L.; Skrabalak, S.E. Polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) in nanoparticle synthesis. Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 17883–178905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, M.P.; Suguna, P.R.; Prasad, K.A.; Vijaylakshmi, J.V.; Renuka, M. Extraction and characterization of gelatin: A functional biopolymer. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 9, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, T.A.T.; Ismail, A.I.; Ahmad, S.A.; Khalil, K.A.; Awad, E.A.E.; Leo, T.K.; Imlan, J.C.; Sazili, A.Q. Characterization of gelatin from bovine skin extracted using ultrasound subsequent to bromelain pretreatment. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 80, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, R.; Varshney, R.; Das, N.; Sircar, D.; Roy, P. Synthesis and characterization of gelatin-PVP polymer composite scaffold for potential application in bone tissue engineering. Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 119, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salles, T.H.C.; Lombello, C.B.; D’ávila, M.A. Electrospinning of Gelatin/Poly(Vinyl Pyrrolidone) Blends from Water/Acetic Acid Solutions. Mater. Res. 2015, 18, 509–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| NP Content (%) | Feeding Rate (mL/h) | Air Pressure (kg/cm2) | Needle–Collector Distance (cm) | Relative Humidity (% H2O) | Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1.70 | 1.00 | 35 | 50 | 23.2 |
| 1.00 | 1.80 | 1.00 | 30 | 57 | 20.9 |
| 1.25 | 1.80 | 1.00 | 35 | 51 | 22.5 |
| 1.50 | 1.80 | 1.00 | 25 | 58 | 21.0 |
| 1.70 | 1.80 | 1.00 | 28 | 55 | 21.2 |
| R (%) | Hydrodynamic Diameter (nm) | Zeta Potential (mV) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 93 ± 11 | +26.3 ± 1.3 |
| 0.25 | 54 ± 1 | +32.2 ± 1.1 |
| 0.50 | 73 ± 1 | +29.5 ± 1.4 |
| 0.75 | 60 ± 7 | +32.8 ± 1.6 |
| 1.00 | 48 ± 1 | +21.6 ± 1.1 |
| 2.00 | 89 ± 5 | +30.4 ± 1.4 |
| 3.00 | 83 ± 5 | +34.4 ± 1.5 |
| 3.50 | 124 ± 4 | +30.9 ± 1.3 |
| γ-Fe2O3-NPs | PVP Polymer | Gelatin Polymer | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Band (cm−1) | Chemical Group | Band (cm−1) | Chemical Group | Band (cm−1) | Chemical Group |
| 3400 | Stretching O-H | 3449 | Stretching O-H | 3450 | Amide A |
| 1380 | Angular deformation H-OH | 2923 | Stretching C-H of CH2 group | 2924 | Amide B |
| 631 | Vibration Fe-O | 1655 | Stretching C=O of the ring | 1647 | Amide I |
| 570 | Vibration Fe-O | 1460 | Angular deformation CH2 | 1560 | Amide II |
| - | - | 1292 | Stretching C-N | 1237 | Amide III |
| - | - | 650 | Angular deformation C-H | - | - |
| NP Content (%) | Average Fiber Diameter (nm) | Standard Deviation (nm) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 415.2 | 100.8 |
| 1.00 | 328.3 | 106.5 |
| 1.25 | 432.9 | 96.9 |
| 1.50 | 287.9 | 84.8 |
| 1.70 | 353.7 | 123.9 |
| II | III | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tonset (°C) | Δm (%) | TD (°C) | Tonset (°C) | Δm (%) | TD (°C) | |
| 0% | 306 | 13.30 | 329 | 402 | 65.25 | 423 |
| 1.70% | 304 | 11.60 | 327 | 401 | 62.16 | 424 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bianchini Silva, M.; Costa, U.O.; Mattoso, L.H.C.; Monteiro, S.N.; de Souza, M.L.; Vitorazi, L. Magnetic Nanoparticles in Biopolymer Fibers: Fabrication Techniques and Characterization Methods. Polymers 2024, 16, 2805. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16192805
Bianchini Silva M, Costa UO, Mattoso LHC, Monteiro SN, de Souza ML, Vitorazi L. Magnetic Nanoparticles in Biopolymer Fibers: Fabrication Techniques and Characterization Methods. Polymers. 2024; 16(19):2805. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16192805
Chicago/Turabian StyleBianchini Silva, Mariana, Ulisses Oliveira Costa, Luiz Henrique Capparelli Mattoso, Sergio Neves Monteiro, Michele Lemos de Souza, and Letícia Vitorazi. 2024. "Magnetic Nanoparticles in Biopolymer Fibers: Fabrication Techniques and Characterization Methods" Polymers 16, no. 19: 2805. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16192805
APA StyleBianchini Silva, M., Costa, U. O., Mattoso, L. H. C., Monteiro, S. N., de Souza, M. L., & Vitorazi, L. (2024). Magnetic Nanoparticles in Biopolymer Fibers: Fabrication Techniques and Characterization Methods. Polymers, 16(19), 2805. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16192805







