A Study of PLA Thin Film on SS 316L Coronary Stents Using a Dip Coating Technique
Abstract
1. Introduction
| Reference | Substrate | Coating | Concentration | Process Parameters | Coating Properties |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [24] | AZ31 Coronary stents (L = 10 mm, D = 3, 1.8 mm) | PCL with 1% of TiO2 | 10% | Entry speed: 125 mm min−1 Withdrawal speed: 125 mm min−1 Immersion Time: 5 s Cycles: 10 | Morphology Surface roughness (~1.5 μm Ra and ~10 μm Rz) Thickness (20–110 μm) Degradation |
| [29] | PCL-PLA Tube (D = 4 mm) | PLA and PCL | 3%, 5%, 7% (w/v) | Withdrawal speed: 50, 250, 450 mm min−1 Cycles: 40, 50, 60 | Morphology Surface Roughness Thickness (100 μm) |
| [31] | Nitinol Stents (L = 60 mm, D = 30 mm) | DTX and PU | DTX/PU loadings 1.92% and 2.79% (w/w) | Withdrawal speed: 390 mm min−1 Immersion Time: 60 s Cycles: 2 | Morphology Weight (559–563.93 mg/stent) In vitro release Cytotoxicity Cell behavior |
| [30] | 316L SS Square specimens (10 × 10 × 2 mm) | PCL-Gelatin composite | 50%, 70%, 90% (w) | Entry speed: 120 mm min−1 Withdrawal speed: 300 mm min−1 Immersion Time: 120 s Cycles: 5 | Morphology Surface roughness (4.778–6.518 μm) Coating attachment Chemical composition Electrochemical behavior |
| [32] | Zinc Wires | PLLA | 1.5, 5, and 15 g in 100 mL | Morphology (SEM pores of 12 μm) Thickness (1–12 μm) Electrochemical behavior Cytotoxicity Biocorrosion Biocompatibility | |
| [33] | SS stents | Fluorinated polyphosphazenes and polymethacrylates | 0.75% (w/v) | Morphology Stent implantation Quantitative coronary angiography |
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
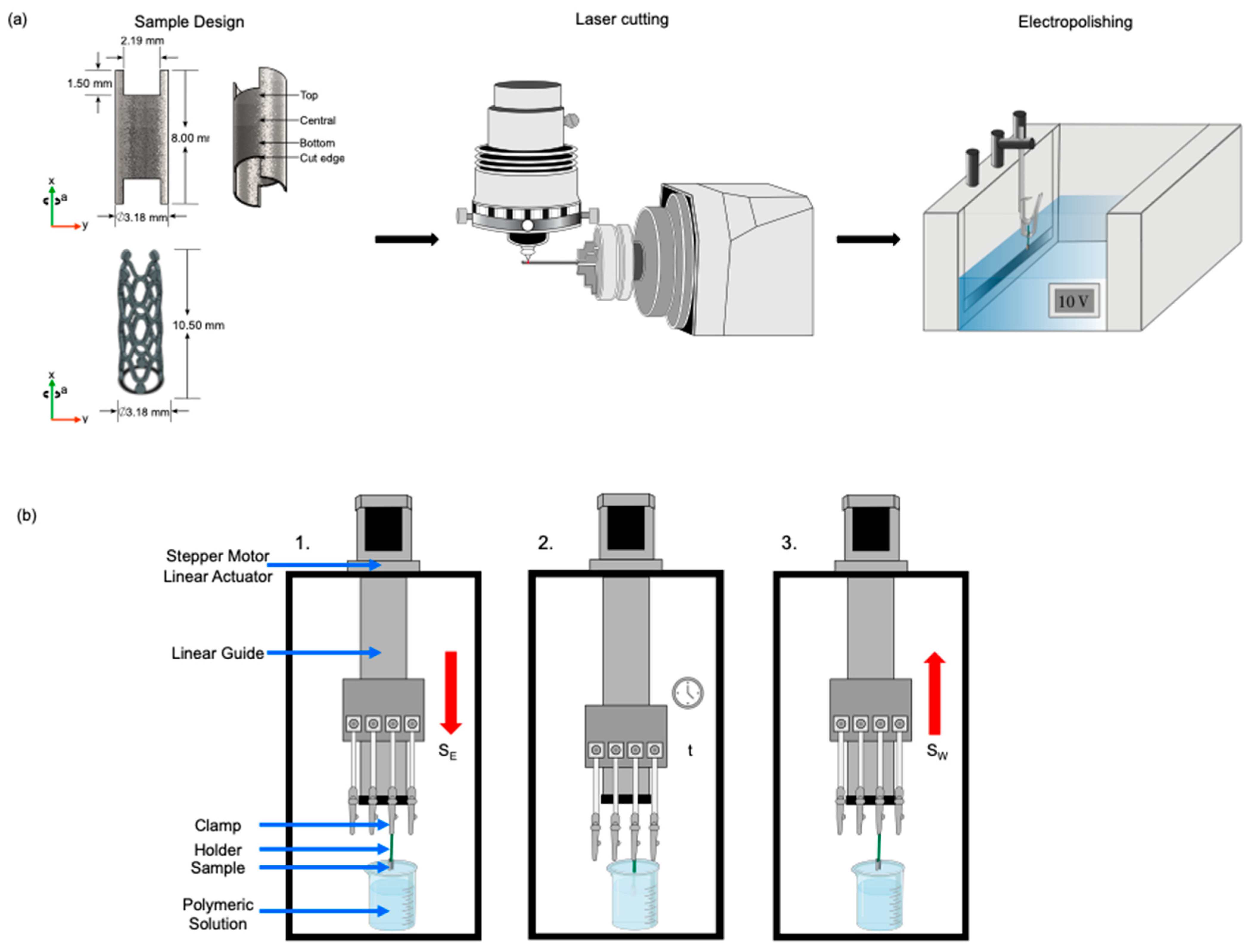
2.2. Fabrication of Samples
2.3. PLA Solutions Study
2.4. Dip Coating Process
2.5. Characterization of Dip-Coated Samples
2.6. Thin Film Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
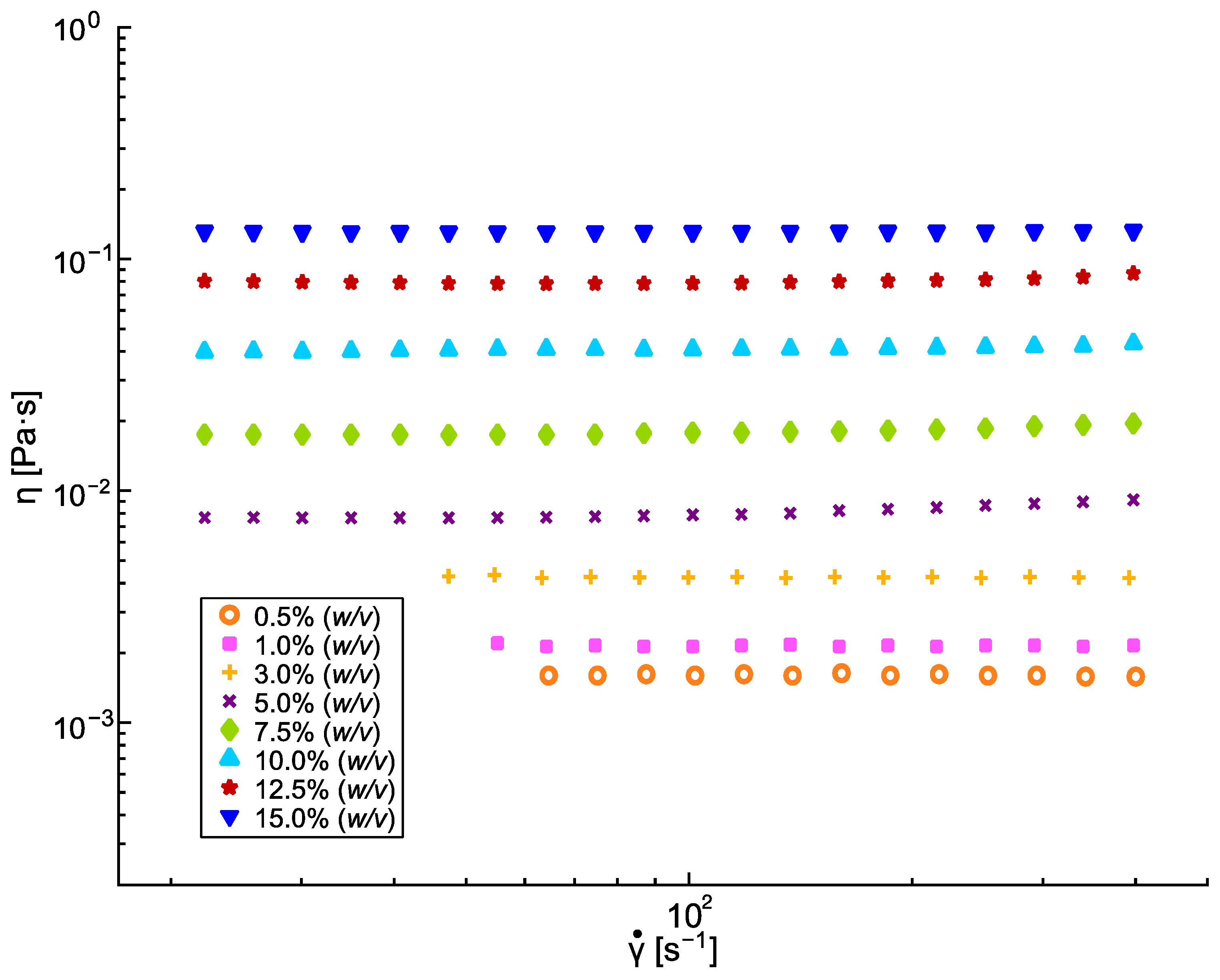
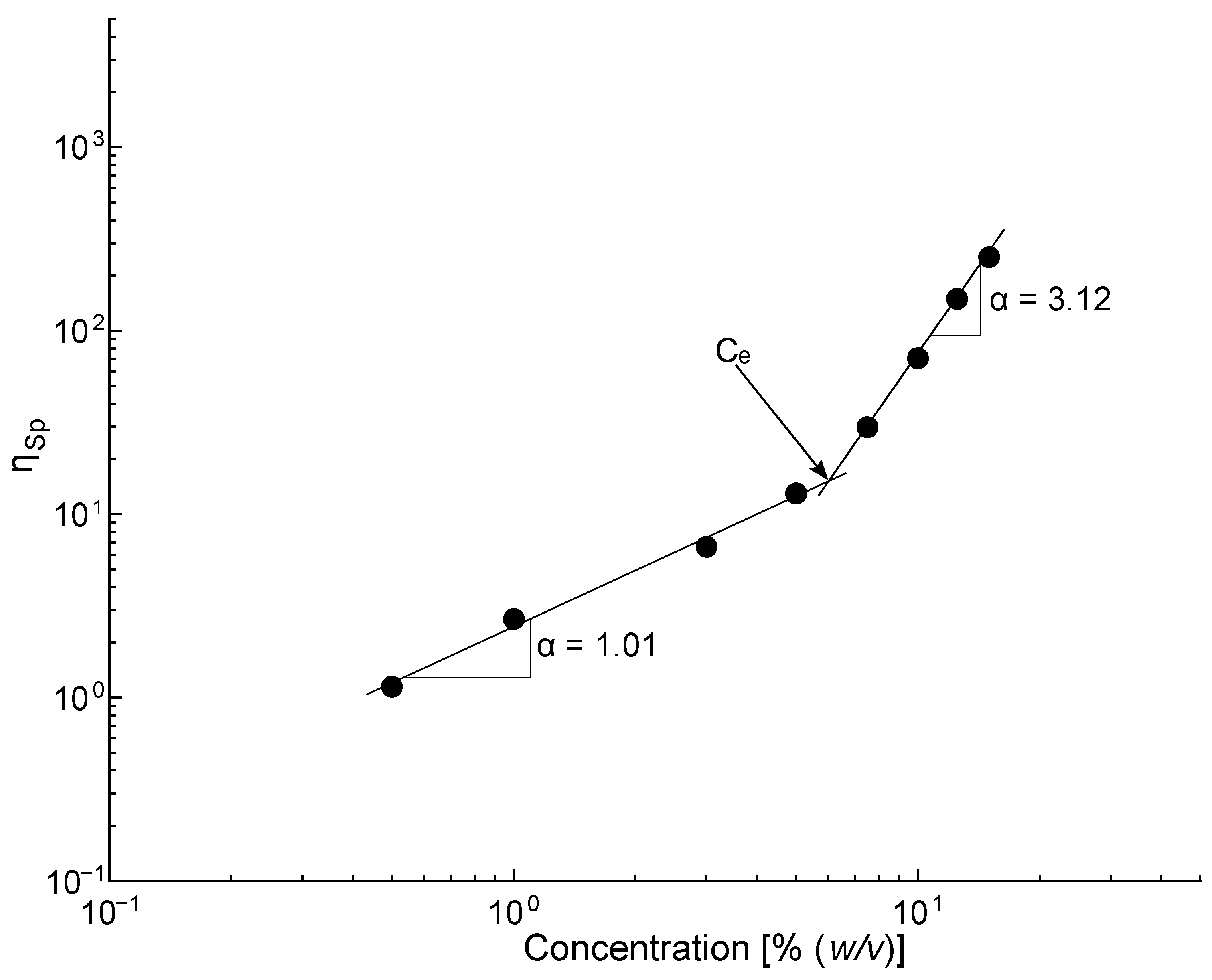
3.1. PLA Solutions Study
3.2. Dip Coating Parameters Study
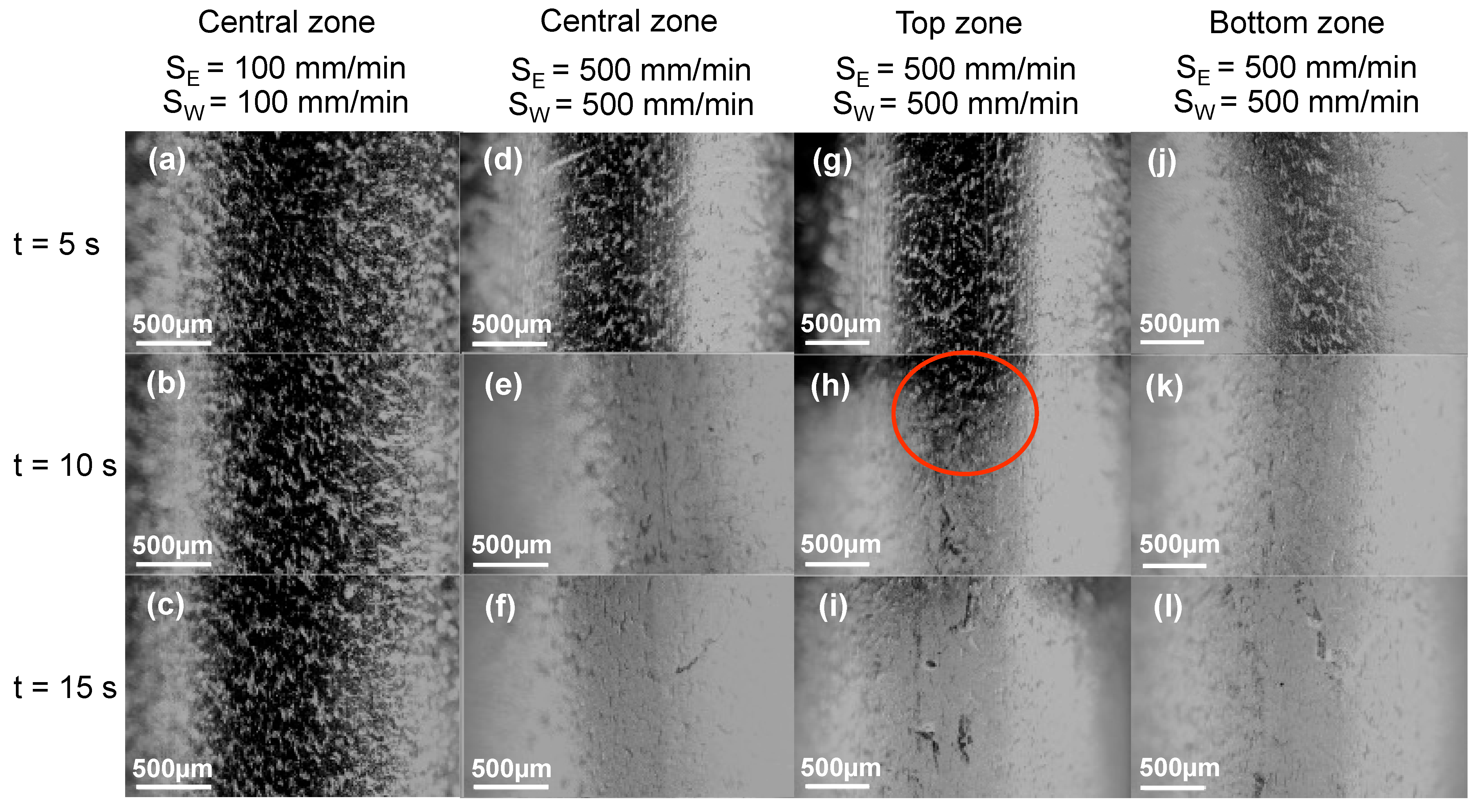
3.2.1. Process Window
3.2.2. Parameters Selected
3.2.3. Stents Coated
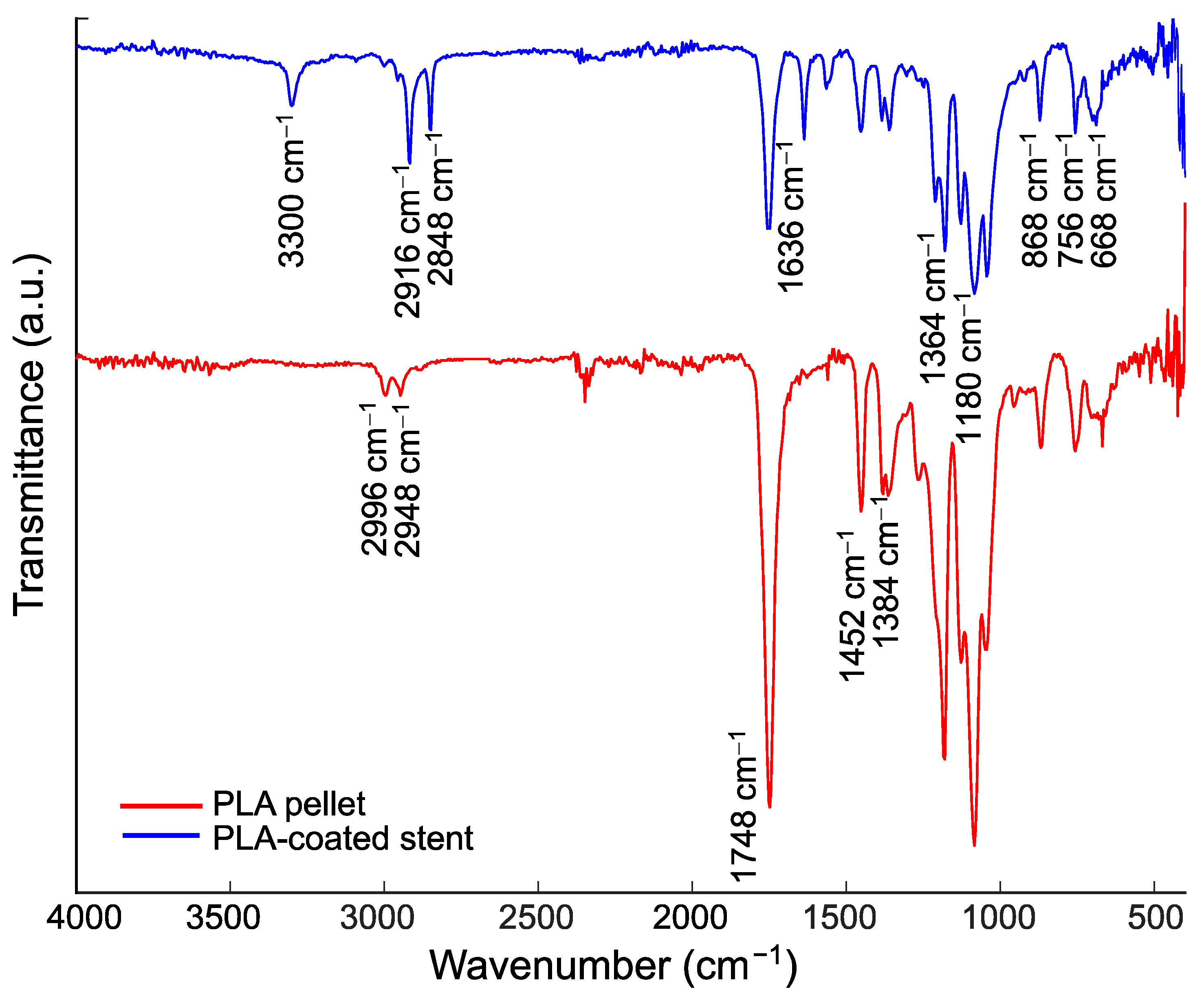
3.3. Thin Film Characterization
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Skorupski, W.J.; Grygier, M.; Lesiak, M.; Kałużna-Oleksy, M. Coronary Stent Thrombosis in COVID-19 Patients: A Systematic Review of Cases Reported Worldwide. Viruses 2022, 14, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahadi, F.; Azadi, M.; Biglari, M.; Bodaghi, M.; Khaleghian, A. Evaluation of Coronary Stents: A Review of Types, Materials, Processing Techniques, Design, and Problems. Heliyon 2023, 9, e13575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolas, J.; Pivato, C.A.; Chiarito, M.; Beerkens, F.; Cao, D.; Mehran, R. Evolution of Drug-Eluting Coronary Stents: A Back-and-Forth Journey from the Bench to Bedside. Cardiovasc. Res. 2022, 119, 631–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, S.; Patel, K.B.; Patel, Z.; Konat, A.; Patel, A.; Doshi, J.S.; Chokshi, P.; Patel, D.; Sharma, K.; Amdani, M.M.; et al. Evolving Coronary Stent Technologies—A Glimpse Into the Future. Cureus 2023, 15, e35651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, E.D.; Jun, E.J.; Yoo, H.S.; Lee, J.W. Analysis of Trends and Prospects Regarding Stents for Human Blood Vessels. Biomater. Res. 2018, 22, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, S.W.; Kim, D.S.; Song, D.H.; Kim, H.B.; Lee, S.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, J.K.; Hong, Y.J.; Park, C.G.; Han, D.K. Reduced Restenosis and Enhanced Re-Endothelialization of Functional Biodegradable Vascular Scaffolds by Everolimus and Magnesium Hydroxide. Biomater. Res. 2022, 26, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jian, Y.; Zhu, Y. Drug Release Property of Poly 3-Hydroxybutyrate 4-Hydroxybutyrate (P34HB) as Drug-Eluting Coatings on Metal Coronary Stents. Polymers 2022, 14, 3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, G.; Feldman, M.D.; Patel, D.; Agrawal, C.M. Coronary Stents: A Materials Perspective. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 1689–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherian, A.M.; Nair, S.V.; Maniyal, V.; Menon, D. Surface Engineering at the Nanoscale: A Way Forward to Improve Coronary Stent Efficacy. APL Bioeng. 2021, 5, 21508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.; Sung, J.S.; Choi, B.; Kim, H.; Sung, Y.K. Recent Trends on the Stent Research for Blood Arteries by Bibliometric Analysis. Biomater. Res. 2014, 18, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Yu, X.; Cui, J.; Yu, F.; Liu, M.; Chen, Y.; Wu, J.; Sun, B.; Mo, X. Development of Biodegradable Polymeric Stents for the Treatment of Cardiovascular Diseases. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beshchasna, N.; Saqib, M.; Kraskiewicz, H.; Wasyluk, Ł.; Kuzmin, O.; Duta, O.C.; Ficai, D.; Ghizdavet, Z.; Marin, A.; Ficai, A.; et al. Recent Advances in Manufacturing Innovative Stents. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, E.H.; Na, K. Polyurethane Membrane with Porous Surface for Controlled Drug Release in Drug Eluting Stent. Biomater. Res. 2014, 18, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.; Zhao, W.; Zhou, T.; Wang, L.; Qiu, T. A Review on Manufacturing and Post-Processing Technology of Vascular Stents. Micromachines 2022, 13, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koźlik, M.; Harpula, J.; Chuchra, P.J.; Nowak, M.; Wojakowski, W.; Gąsior, P. Drug-Eluting Stents: Technical and Clinical Progress. Biomimetics 2023, 8, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakhshi, R.; Darbyshire, A.; Evans, J.E.; You, Z.; Lu, J.; Seifalian, A.M. Polymeric Coating of Surface Modified Nitinol Stent with POSS-Nanocomposite Polymer. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2011, 86, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shafiq, N.; Malhotra, S.; Pandhi, P.; Grover, A.; Uboweja, A. A Meta-Analysis of Clinical Trials of Paclitaxel- and Sirolimus-Eluting Stents in Patients with Obstructive Coronary Artery Disease. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2005, 59, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Gu, X.; Mao, Z.; Ye, S.H.; Koo, Y.; Yun, Y.; Tiasha, T.R.; Shanov, V.; Wagner, W.R. Biodegradable, Elastomeric Coatings with Controlled Anti-Proliferative Agent Release for Magnesium-Based Cardiovascular Stents. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 144, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.X.; Wei, Q.Q.; Mo, H.L.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, W.; Lu, H.J.; Joung, Y.K. Challenges and Advances in Materials and Fabrication Technologies of Small-Diameter Vascular Grafts. Biomater. Res. 2023, 27, 58. [Google Scholar]
- Ishaque, N.; Naseer, N.; Abbas, M.A.; Javed, F.; Mushtaq, S.; Ahmad, N.M.; Khan, M.F.A.; Ahmed, N.; Elaissari, A. Optimize PLA/EVA Polymers Blend Compositional Coating for Next Generation Biodegradable Drug-Eluting Stents. Polymers 2022, 14, 3547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rykowska, I.; Nowak, I.; Nowak, R. Drug-eluting Stents and Balloons-Materials, Structure Designs, and Coating Techniques: A Review. Molecules 2020, 25, 4624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, I.H.; Jeong, M.H.; Park, D.S.; Lim, K.S.; Shim, J.W.; Kim, M.K.; Park, J.K. Mechanical and Physio-Biological Properties of Peptide-Coated Stent for Re-Endothelialization. Biomater. Res. 2020, 24, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Li, X.; Yang, R. The Surface Modification Methods for Constructing Polymer-Coated Stents. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2018, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuñez-Nava, M.; Vazquez, E.; Ortega-Lara, W.; Rodriguez, C.A.; García-López, E. An Assessment of Magnesium AZ31 Coronary Stents Manufacture. Mater. Res. Express 2021, 8, 3891686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheiban, I.; Villata, G.; Bollati, M.; Sillano, D.; Lotrionte, M.; Biondi-Zoccai, G. Next-Generation Drug-Eluting Stents in Coronary Artery Disease: Focus on Everolimus-Eluting Stent (Xience V®). Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2008, 4, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, M.A. Thin-Film Coating Methods: A Successful Marriage of High-Quality and Cost-Effectiveness—A Brief Exploration. Coatings 2022, 12, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felton, L.A. Mechanisms of Polymeric Film Formation. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 457, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavukkandy, M.O.; McBride, S.A.; Warsinger, D.M.; Dizge, N.; Hasan, S.W.; Arafat, H.A. Thin Film Deposition Techniques for Polymeric Membranes—A Review. J. Memb. Sci. 2020, 610, 118258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, A.J.; San, J.; Ciurana, J. Fabrication of PCL/PLA Composite Tube for Stent Manufacturing. Procedia CIRP 2017, 65, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojarad Shafiee, B.; Torkaman, R.; Mahmoudi, M.; Emadi, R.; Karamian, E. An Improvement in Corrosion Resistance of 316L AISI Coated Using PCL-Gelatin Composite by Dip-Coating Method. Prog. Org. Coat. 2019, 130, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouladian, P.; Jin, Q.; Arafat, M.; Song, Y.; Guo, X.; Blencowe, A.; Garg, S. Drug-Loaded, Polyurethane Coated Nitinol Stents for the Controlled Release of Docetaxel for the Treatment of Oesophageal Cancer. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shomali, A.A.; Guillory, R.J.; Seguin, D.; Goldman, J.; Drelich, J.W. Effect of PLLA Coating on Corrosion and Biocompatibility of Zinc in Vascular Environment. Surf. Innov. 2017, 5, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verweire, I.; Schacht, E.; Qiang, B.P.; Wang, K.; De Scheerder, I. Evaluation of Fluorinated Polymers as Coronary Stent Coating. J. Mater. Sci. 2000, 11, 207–212. [Google Scholar]
- Lemos, P.A.; Bienert, I. The Supralimus® Sirolimus-Eluting Stent. Expert. Rev. Med. Devices 2013, 10, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanini, G.G.; Taniwaki, M.; Windecker, S. Coronary Stents: Novel Developments. Heart 2014, 100, 1051–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abizaid, A.; Costa, J.R. New Drug-Eluting Stents an Overview on Biodegradable and Polymer-Free next-Generation Stent Systems. Circ. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2010, 3, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wykrzykowska, J.J.; Onuma, Y.; Serruys, P.W. Advances in Stent Drug Delivery: The Future is in Bioabsorbable Stents. Expert. Opin. Drug Deliv. 2009, 6, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, N.; Pacetti, S.D.; Tang, F.W.; Gada, M.; Roorda, W. XIENCE VTM Stent Design and Rationale. J. Interv. Cardiol. 2009, 22, S18–S27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhami, M.; Martin, N.K.; Maguire, C.; Courtenay, A.J.; Donnelly, R.F.; Domínguez-Robles, J.; Larrañeta, E. Drug Loaded Implantable Devices to Treat Cardiovascular Disease. Expert. Opin. Drug Deliv. 2023, 20, 507–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinker, C.J. Dip Coating. In Chemical Solution Deposition of Functional Oxide Thin Films; Springer-Verlag: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; Volume 9783211993118, pp. 233–261. ISBN 9783211993118. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, H.W.; Li, K.Y.; Su, T.L.; Yang, T.C.K.; Chang, J.S.; Lin, P.L.; Chang, W.C. Dip Coating Assisted Polylactic Acid Deposition on Steel Surface: Film Thickness Affected by Drag Force and Gravity. Mater. Lett. 2008, 62, 3739–3741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.I.; Su, T.L.; Lin, P.L.; Tseng, I.H.; Chang, C.H.; Fang, H.W. Fabrication of Porous Polylactic Acid Films Assisted by Dip-Coating and Template Leaching Techniques. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 124, 2333–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedijaberi, A.; Bhatara, G.; Eric, E.S.; Khomami, B. A Computational Study of the Influence of Viscoelasticity on the Interfacial Dynamics of Dip Coating Flow. J. Nonnewton Fluid. Mech. 2011, 166, 614–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrego, M.; Martín-Alfonso, J.E.; Valencia, C.; Sánchez Carrillo, M.D.C.; Franco, J.M. Developing Electrospun Ethylcellulose Nanofibrous Webs: An Alternative Approach for Structuring Castor Oil. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2022, 4, 7217–7227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yimsiri, P.; MacKley, M.R. Spin and Dip Coating of Light-Emitting Polymer Solutions: Matching Experiment with Modelling. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2006, 61, 3496–3505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Peng, F.; Kornev, K.G. The Thickness and Structure of Dip-Coated Polymer Films in the Liquid and Solid States. Micromachines 2022, 13, 982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, J.; Silveira Brichi, G.; Marconcini, J.M.; Mattoso, H.C.; Glenn, G.M.; Medeiros, S.; Oliveira, J. Effect of Solvent on The Physical and Morphological Properties of Poly(Lactic Acid) Nanofibers Obtained by Solution Blow Spinning. J. Eng. Fibers Fabr. 2014, 9, 155892501400900414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio-Valle, J.F.; Sánchez, M.C.; Valencia, C.; Martín-Alfonso, J.E.; Franco, J.M. Electrohydrodynamic Processing of Pvp-Doped Kraft Lignin Micro- and Nano-Structures and Application of Electrospun Nanofiber Templates to Produce Oleogels. Polymers 2021, 13, 2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colby, R.H. Structure and Linear Viscoelasticity of Flexible Polymer Solutions: Comparison of Polyelectrolyte and Neutral Polymer Solutions. Rheol. Acta 2010, 49, 425–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinker, C.J.; Frye, G.C.; Hurd, A.J.; Ashley, C.S. Fundamentals of sol-gel dip coating. Thin Solid Film. 1991, 201, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosso, D. How to Exploit the Full Potential of the Dip-Coating Process to Better Control Film Formation. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 17033–17038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.W.; Kwon, E.H.; Kim, M.; Park, Y.D. Uniform and Reliable Dip-Coated Conjugated Polymers for Organic Transistors as Obtained by Solvent Vapor Annealing. J. Phys. Chem. C 2019, 123, 23255–23263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strobel, C.; Kadow-Romacker, A.; Witascheck, T.; Schmidmaier, G.; Wildemann, B. Evaluation of Process Parameter of an Automated Dip-Coating. Mater. Lett. 2011, 65, 3621–3624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motealleh, A.; Eqtesadi, S.; Perera, F.H.; Pajares, A.; Guiberteau, F.; Miranda, P. Understanding the Role of Dip-Coating Process Parameters in the Mechanical Performance of Polymer-Coated Bioglass Robocast Scaffolds. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2016, 64, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izsó, I.; Asztalos, L. Development Options for Coronary Stent Coatings. Acta Mater. Transylvanica Magy. Kiadás 2020, 3, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haïdopoulos, M.; Turgeon, S.; Sarra-Bournet, C.; Laroche, G.; Mantovani, D. Development of an Optimized Electrochemical Process for Subsequent Coating of 316 Stainless Steel for Stent Applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2006, 17, 647–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voicu, M.E.; Ionita, D.; Buica, G.O.; Draganescu, D.; Anuta, V.; Raduly, F.M.; Demetrescu, I. Characterization of Two Types of Polylactic Acid Coating Loaded with Gentamicin Sulphate Deposed on AZ31 Alloy. Coatings 2023, 13, 1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buapool, S.; Thavarungkul, N.; Srisukhumbowornchai, N.; Termsuksawad, P. Modeling and Analysis of the Effect of Dip-Spin Coating Process Parameters on Coating Thickness Using Factorial Design Method. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 2017, 9639306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aditya, G.; Parmeshwar, D.; Mukty, S. Nanofiberous Coating for Bare Metal Stents: A Comparative Study of Coaxial and Monoaxial Modes. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 18, 1108–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, G.; Chandrasekar, B.; Feldman, M.D.; Patel, D.; Agrawal, C.M. Interaction of Endothelial Cells with Self-Assembled Monolayers for Potential Use in Drug-Eluting Coronary Stents. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2009, 90 B, 789–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Q.; Zhu, X.; Li, W.; Wu, M.; Cui, S.; Ling, Y.; Ma, X.; Wang, G.; Wang, L.; Zheng, W. Fabrication of Super-Hydrophilic and Highly Open-Porous Poly (Lactic Acid) Scaffolds Using Supercritical Carbon Dioxide Foaming. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 205, 740–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Murphy, A.; Scholz, D.; Geever, L.M.; Lyons, J.G.; Devine, D.M. Surface-Modified Halloysite Nanotubes Reinforced Poly(Lactic Acid) for Use in Biodegradable Coronary Stents. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 46521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadzadeh Asl, S.; Ganjali, M.; Karimi, M. Surface Modification of 316L Stainless Steel by Laser-Treated HA-PLA Nanocomposite Films toward Enhanced Biocompatibility and Corrosion-Resistance in Vitro. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2019, 363, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosseoglou, D.; Kokkinofta, R.; Sazou, D. FTIR Spectroscopic Characterization of Nafion®-Polyaniline Composite Films Employed for the Corrosion Control of Stainless Steel. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2011, 15, 2619–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.L.; Wu, Z.H.; Yang, W.; Yang, M.B. Thermal and Mechanical Properties of Chemical Crosslinked Polylactide (PLA). Polym. Test. 2008, 27, 957–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Davila, S.; González-Rodríguez, L.; Lama, R.; López-Álvarez, M.; Oliveira, A.L.; Serra, J.; Novoa, B.; Figueras, A.; González, P. 3D-Printed PLA Medical Devices: Physicochemical Changes and Biological Response after Sterilisation Treatments. Polymers 2022, 14, 4117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paragkumar, N.T.; Edith, D.; Six, J.L. Surface Characteristics of PLA and PLGA Films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2006, 253, 2758–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chieng, B.W.; Ibrahim, N.A.; Yunus, W.M.Z.W.; Hussein, M.Z. Poly(Lactic Acid)/Poly(Ethylene Glycol) Polymer Nanocomposites: Effects of Graphene Nanoplatelets. Polymers 2014, 6, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinavinijkul, P.; Riansuwan, K.; Kiratisin, P.; Srisang, S.; Nasongkla, N. Dip- and Spray-Coating of Schanz Pin with PLA and PLA Nanosphere for Prolonged Antibacterial Activity. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 65, 102667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuniarto, K.; Purwanto, Y.A.; Purwanto, S.; Welt, B.A.; Purwadaria, H.K.; Sunarti, T.C. Infrared and Raman Studies on Polylactide Acid and Polyethylene Glycol-400 Blend. AIP Conf. Proc. 2016, 1725, 020101. [Google Scholar]
- Cuiffo, M.A.; Snyder, J.; Elliott, A.M.; Romero, N.; Kannan, S.; Halada, G.P. Impact of the Fused Deposition (FDM) Printing Process on Polylactic Acid (PLA) Chemistry and Structure. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romashkin, A.V.; Struchkov, N.S.; Polikarpov, Y.A.; Petukhov, V.A.; Levin, D.D.; Nevolin, V.K. Polylactide Film Deposition onto Titanium Surface from Different Solutions. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2018, 1124, 031027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

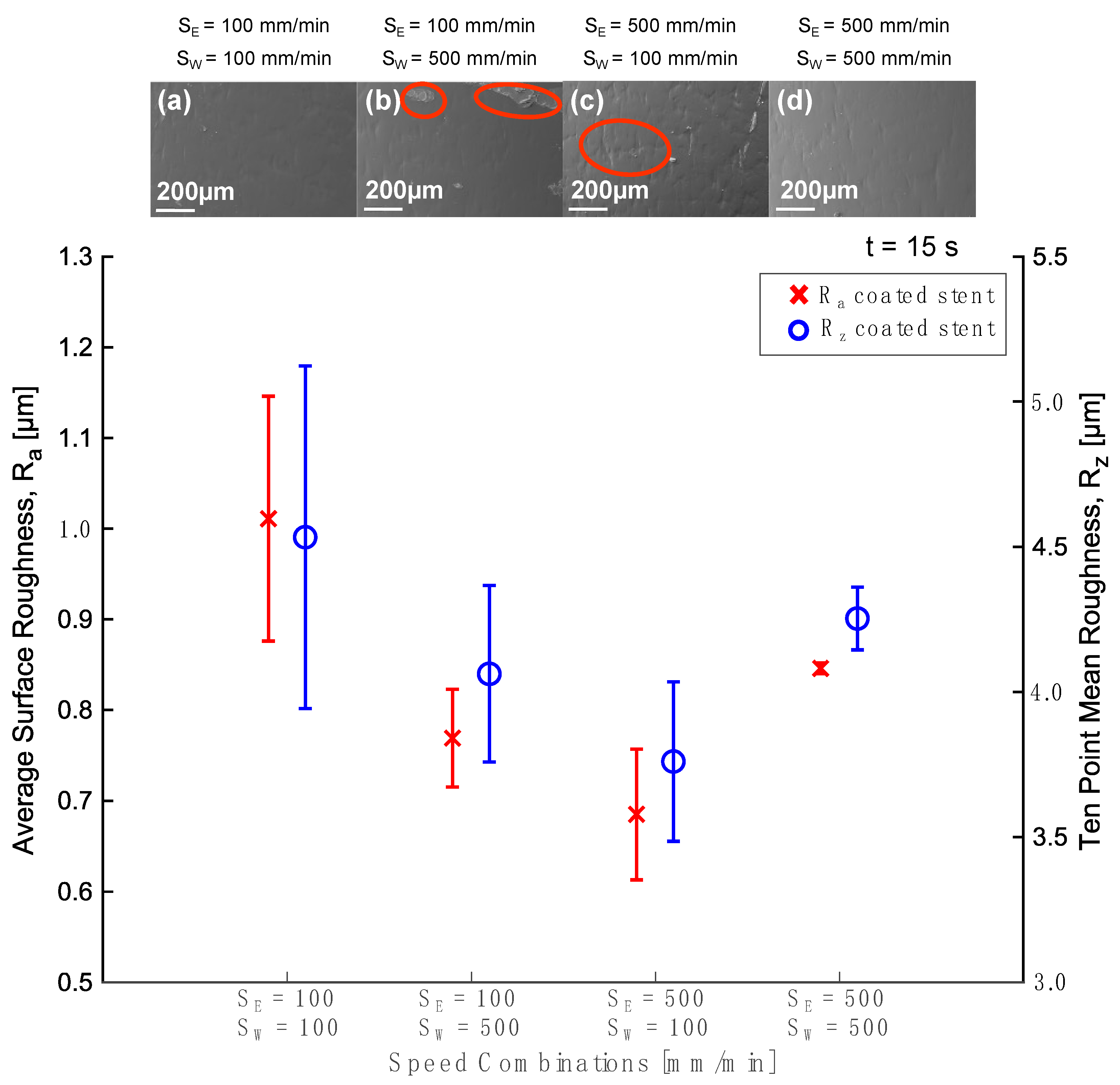

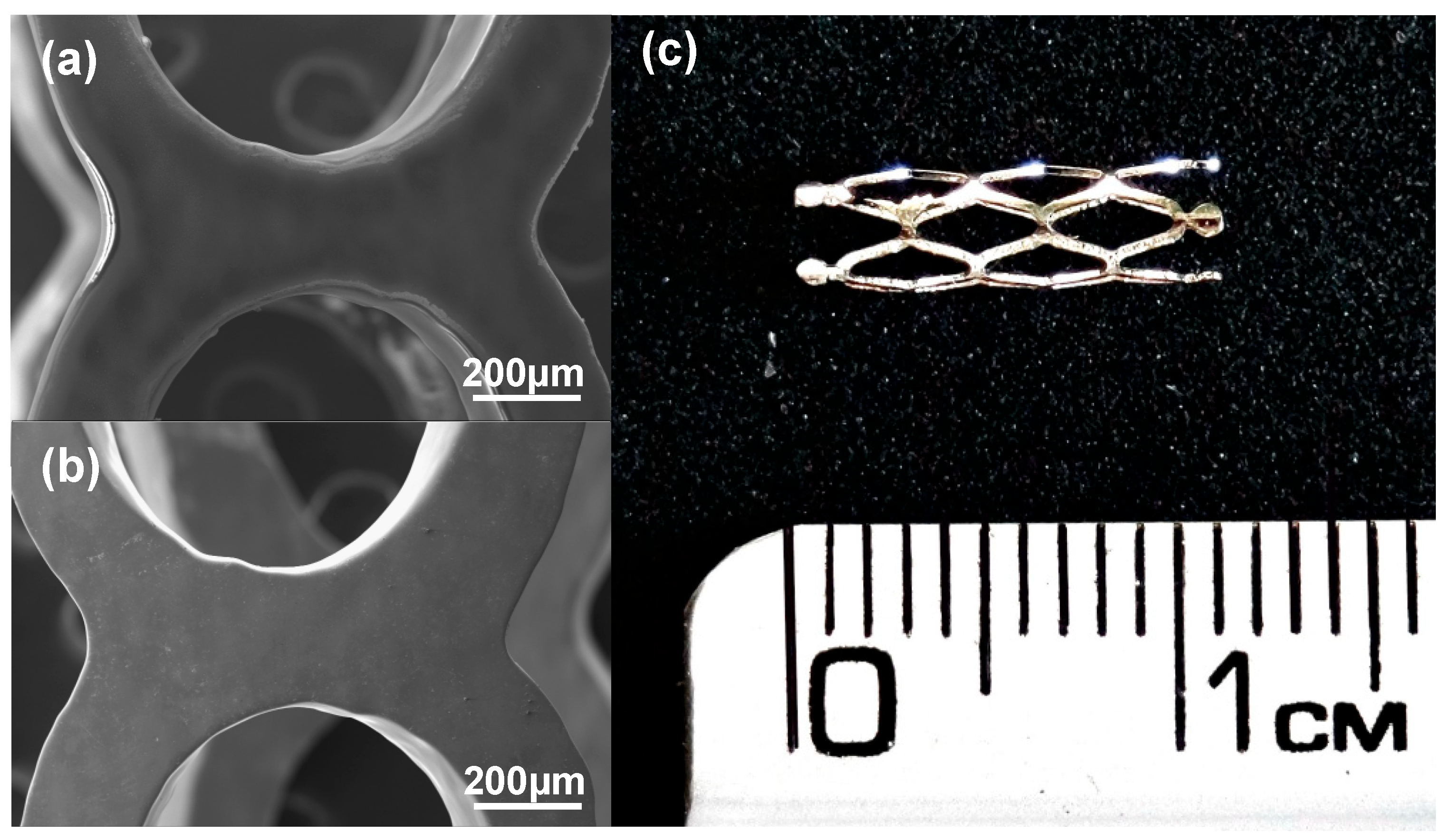
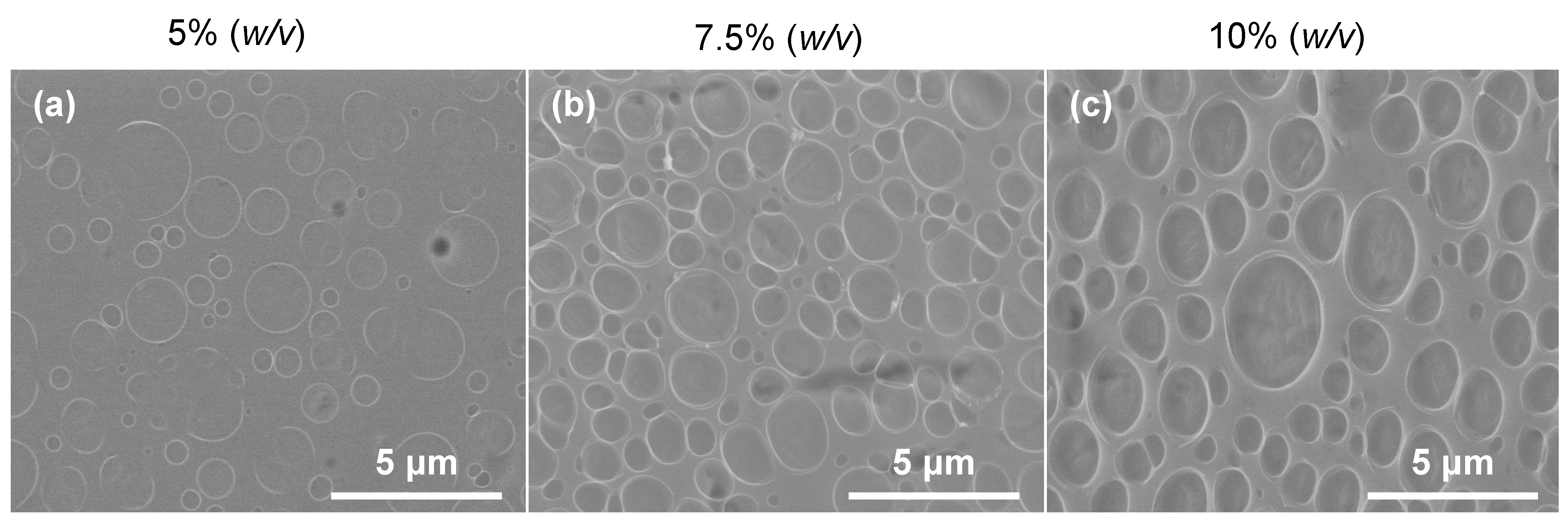
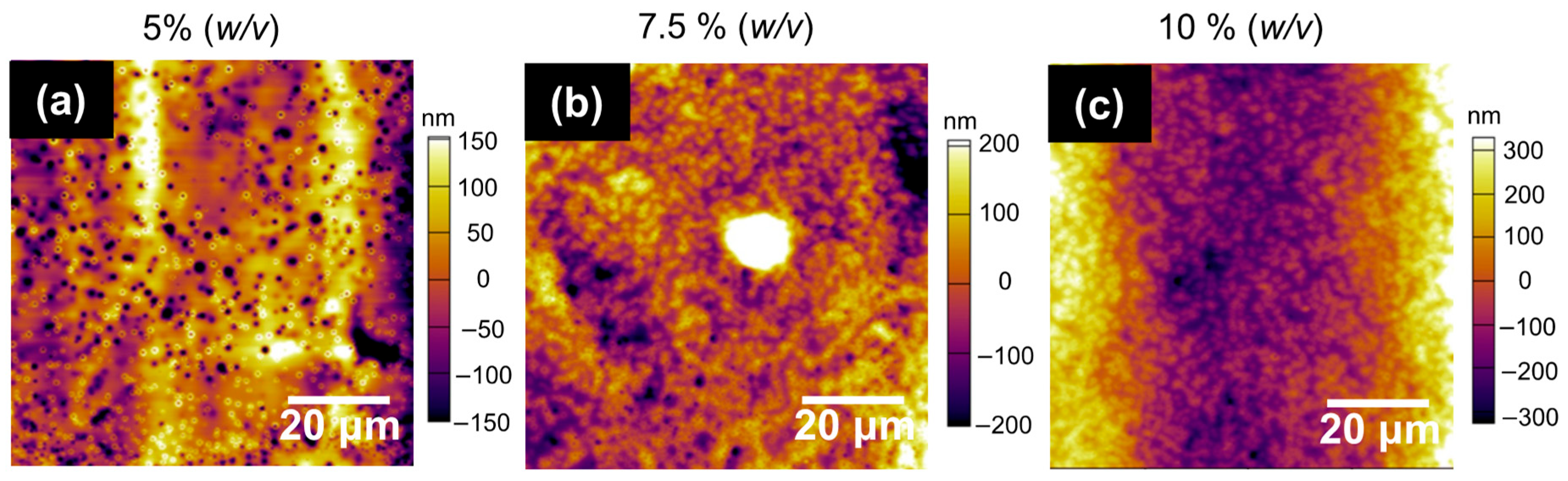

| Parameters | Values (Low, High) |
|---|---|
| Entry Speed, SE [mm min−1] | 100, 500 |
| Withdrawal Speed, SW [mm min−1] | 100, 500 |
| Immersion Time, t [s] | 5, 10, 15 |
| Cycles, C | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Macías-Naranjo, M.; Sánchez-Domínguez, M.; Rubio-Valle, J.F.; Rodríguez, C.A.; Martín-Alfonso, J.E.; García-López, E.; Vazquez-Lepe, E. A Study of PLA Thin Film on SS 316L Coronary Stents Using a Dip Coating Technique. Polymers 2024, 16, 284. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16020284
Macías-Naranjo M, Sánchez-Domínguez M, Rubio-Valle JF, Rodríguez CA, Martín-Alfonso JE, García-López E, Vazquez-Lepe E. A Study of PLA Thin Film on SS 316L Coronary Stents Using a Dip Coating Technique. Polymers. 2024; 16(2):284. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16020284
Chicago/Turabian StyleMacías-Naranjo, Mariana, Margarita Sánchez-Domínguez, J. F. Rubio-Valle, Ciro A. Rodríguez, J. E. Martín-Alfonso, Erika García-López, and Elisa Vazquez-Lepe. 2024. "A Study of PLA Thin Film on SS 316L Coronary Stents Using a Dip Coating Technique" Polymers 16, no. 2: 284. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16020284
APA StyleMacías-Naranjo, M., Sánchez-Domínguez, M., Rubio-Valle, J. F., Rodríguez, C. A., Martín-Alfonso, J. E., García-López, E., & Vazquez-Lepe, E. (2024). A Study of PLA Thin Film on SS 316L Coronary Stents Using a Dip Coating Technique. Polymers, 16(2), 284. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16020284








