The Properties of Thin Films Based on Chitosan/Konjac Glucomannan Blends
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Chitosan/Konjac Glucomannan Films Preparation
2.3. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.4. Mechanical Testing
2.5. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.6. Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM)
2.7. Thermogravimetric Analysis
2.8. Swelling and Degradation Properties
- mt—the weight of the material after immersion in PBS [g];
- m0—the initial weight of the material [g].
2.9. Contact Angle and Surface Free Energy
3. Results
3.1. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
FTIR After 6 Months of Storage
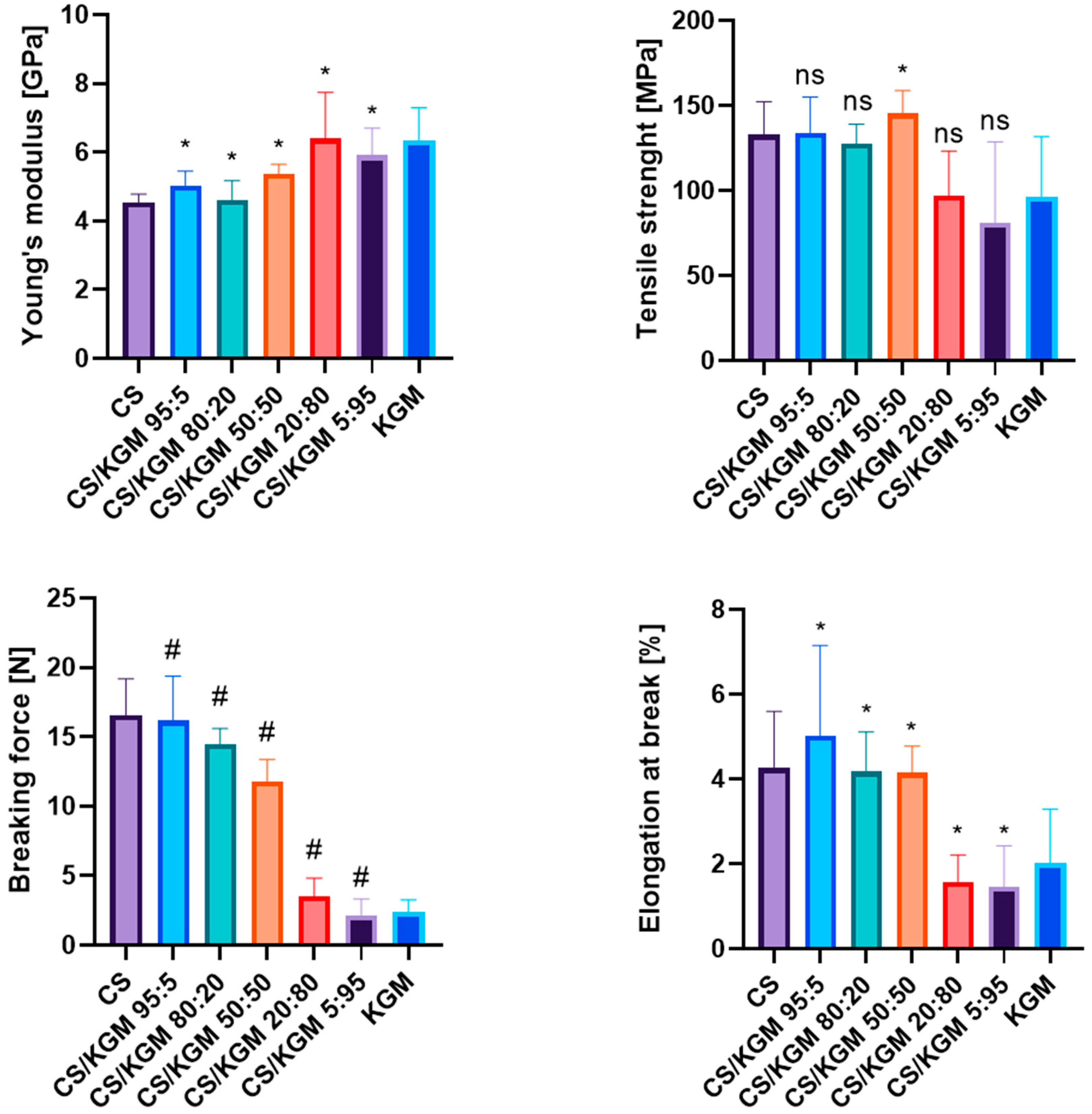
3.2. Mechanical Testing
Mechanical Testing After 6 Months of Storage
3.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
3.4. Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM)
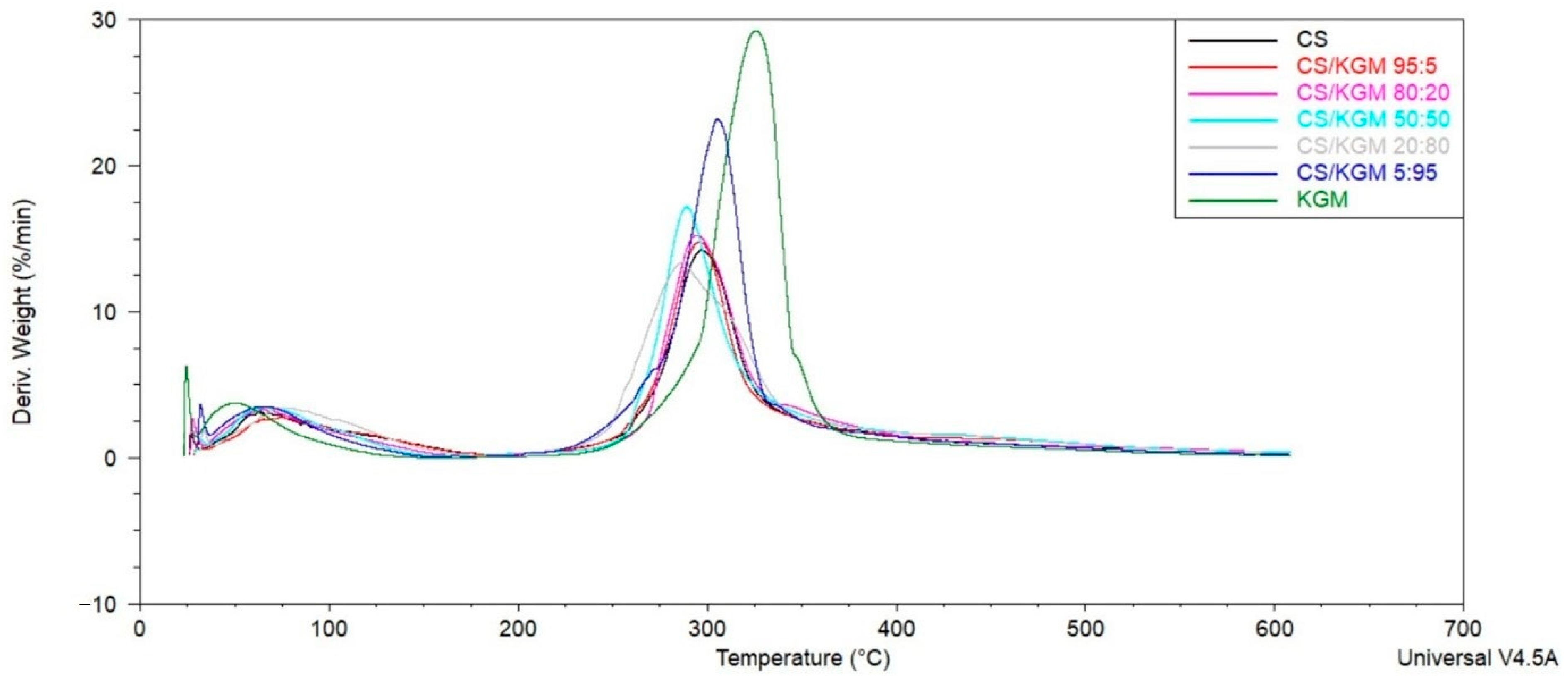
3.5. Thermogravimetric Analysis
3.6. Swelling and Degradation Properties
Swelling and Degradation Properties After 6 Months of Storage
3.7. Contact Angle and Surface Free Energy
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barnawal, J.; Barse, B.; Fais, A.; Delogu, G.L.; Kumar, A. Biopolymer: A Sustainable Material for Food and Medical Applications. Polymers 2022, 14, 983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, A.; Ringu, T.; Ghosh, S.; Pramanik, N.A. Comprehensive review on recent advances in preparation, physicochemical applications of biopolymers. Polym. Bull. 2023, 80, 7249–7312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabska-Zielińska, S.; Sionkowska, A. How to Improve Physico-Chemical Properties of Silk Fibroin Materials for Biomedical Applications?—Blending and Cross-linking of Silk Fibroin—A Review. Materials 2021, 14, 1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogovina, S.Z.; Vikhoreva, G.A. Polysaccharide-based polymer blends: Method of their production. Glycoconj. J. 2006, 23, 611–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daud, H.; Ghani, A.; Iqbal, D.N.; Ahmad, N.; Nazir, S.; Muhammad, M.J.; Hussain, E.A.; Nazir, A.; Iqbal, M. Preparation and characterization of guar gum based biopolymeric hydrogels for controlled release of antihypertensive drug. Arab. J. Chem. 2021, 14, 103111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feijoo, P.; Samaniego-Aguilar, K.; Sanchez-Safont, E.; Torres-Giner, S.; Lagaron, J.M.; Gamez-Perez, J.; Cabedo, L. Development and Characterization of Fully Renewable and Biodegradable Polyhydroxyalkanoate Blends with Improved Thermoformability. Polymers 2022, 14, 2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyas, R.A.; Aisyah, H.A.; Nordin, A.H.; Ngadi, N.; Zuhri, M.Y.M.; Asyraf, M.R.M. Natural-Fiber-Reinforced Chitosan, Chitosan Blends and Their Nanocomposites for Various Advances Applications. Polymers 2022, 14, 874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitura, S.; Sionkowska, A.; Jaiswal, A. Biopolymers for hydrogel in cosmetics: Review. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2020, 31, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kedir, W.M.; Abdi, G.F.; Goro, M.M.; Tolesa, L.D. Pharmaceutical and drug delivery applications of chitosan biopolymer and its modified nanocomposite: A review. Heliyon 2022, 8, e10196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhuang, S. Antibacterial activity of chitosan and its derivatives and their interaction mechanism with bacteria: Current state and perspectives. Eur. Polym. J. 2020, 138, 109984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthu, M.; Gopal, J.; Chun, S.; Devadoss, A.J.P.; Hasan, N.; Sivanesan, I. Crustean Waste-Derived Chitosan: Antioxidant Properties and Future Perspective. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellis, A.; Guebits, G.M.; Myanhongo, G.S. Chitosan: Sources, Processing and Modification Techniques. Gels 2022, 8, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulka-Kamińska, K.; Sionkowska, A. Chitosan Based Materials in Cosmetic Applications: A Review. Molecules 2023, 28, 1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seidi, F.; Yazdi, M.K.; Jouyandeh, M.; Dominic, M.; Naeim, H.; Nezhad, M.N.; Bagheri, B.; Habibzadeh, S.; Zarrintaj, P.; Saeb, M.R.; et al. Chitosan-based blends for biomedical applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 183, 1818–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.H.; Kim, S.T.; Bin, B.H.; Park, P.J. Effect of Konjac Glucomannan (KGM) on the Reconstitution of the Dermal Environment against UVB-Induced Condition. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Xie, W.; Zhao, Y.; Lv, X.; Yang, H.; Zeng, Q.; Zheng, Z.; Yang, X. Synthesis, Antimicrobial, moisture Absorption and Retention Activities of Kojic Acid-Grafted Konjac Glucomannan Oligosaccharides. Polymers 2019, 11, 1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Jiang, R.; Perkins, W.S.; Cheng, Y. Morphology evaluation and gelation mechanism of alkali induced konjac glucomannan hydrogel. Food Chem. 2019, 269, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neto, R.J.G.; Genevro, G.M.; Paulo, L.A.; Lopes, P.S.; de Moraes, M.A.; Beppu, M.M. Characterization and in vitro evaluation of chitosan/konjac glucomannan bilayer film as a wound dressing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 212, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, D.; Xie, X.; Zhou, H.; Wu, Z.; Liu, R.; Pang, J. Review of Konjac Glucomannan Structure, Properties, Gelation Mechanism, and Application in Medical Biology. Polymer 2023, 15, 1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, D.F.; Ferreira, S.B.; Bruschi, M.L.; Britten, M.; Matumoto-Pintro, P.T. Effect of commercial konjac glucomannan and konjac flours on textural, rheological and microstructural properties of low fat processed cheese. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 60, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, A.; Miguel, S.P.; Araujo, A.R.T.S.; de Jesús Valle, M.J.; Navarro, A.S.; Correia, I.J.; Ribeiro, M.P.; Coutinho, P. Xanthan Gum-Konjac Glucomannan Blend Hydrogel for Wound Healing. Polymers 2020, 12, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, C.; Gao, S.; Wang, H.; Zhang, L. Blend Film from Chitosan and Konjac Glucomannan Solutions. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2000, 76, 506–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Sande, M.; Cuna, M.; Remunan-Lopez, C.; Teijeiro-Osorio, D.; Alonso-Lebrero, J.L.; Alonso, M.J. Formation of New Glucomannan-Chitosan Nanoparticles and Study of Their Ability to Associate and Deliver Proteins. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 4152–4158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Li, Q.; Zhu, T. New chitosan/Konjac glucomannan blending membrane for application in pervaporation dehydration of caprolactam solution. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2012, 18, 934–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Kennedy, J.F.; Li, B.; Xie, B.J. Condensed state structure and biocompatibility of the konjac glucomannan blend films. Carbohydr. Polym. 2006, 64, 532–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Li, J.; Xia, J.; Kennedy, J.F.; Yie, X.; Liu, T.G. Effect of gamma irradiation on the condensed state structure and mechanical properties of konjac glucomannan/chitosan blend films. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 83, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sionkowska, A.; Michalska-Sionkowska, M.; Walczak, M. Preparation and characterization of collagen/hyaluronic acid/chitosan film crosslinked with dialdehyde starch. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 149, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulka, K.; Szmejkowska, A.; Sionkowska, A.; Wypij, M.; Golińska, P. Materials based on chitosan enriched with zinc nanoparticles for potential applications on the skin. Eng. Biomater. 2022, 167, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szulc, M.; Lewandowska, K. Characterization of Chitosan Films Modified Using Caffeic Acid and a Neutralization Process. Materials 2023, 16, 5038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, D.F.; Ogawa, C.Y.L.; Sato, F.; Neto, A.M.; Larsen, F.H.; Matumoto-Pintro, P.T. Chemical and physical characterization of Konjac glucomannan-based powders by FTIR and 13C MAS NMR. Powder Technol. 2020, 361, 610–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jena, K.; Ananta, S.; Akthar, J.; Patnaik, A.; Das, S.; Singh, J.; Sathyanarayana, K.; Kar, P.K.; Das, B.K.; Hassan, A.; et al. Physical, biochemical and antimicrobial characterization of chitosan prepared from tasar silkworm pupae waste. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2023, 31, 103200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakubowska, E.; Gierszewska, M.; Szydłowska-Czerniak, A.; Nowaczyk, J.; Olewnik-Kruszkowska, E. Development and characterization of active packaging films based on chitosan, plasticizer, and quercetin for repassed oil storage. Food Chem. 2023, 399, 135617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Y.; Yuan, C.; Cui, B.; Liu, P.; Wu, Z.; Zhao, H. Formation of high amylose corn starch/konjac glucomannan composite film with improved mechanical and barrier properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 251, 117039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Thi Dao, U.T.; Thi Bui, Q.P.; Bach, G.L.; Ha Thuc, C.N.; Ha Thuc, H. Enhanced antimicrobial activities and physicochemical properties of edible film based on chitosan incorporated with Sonneratia caseolaris (L.) Engl. Leaf extract. Prog. Org. Coat. 2020, 140, 105487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queiroz, M.F.; Melo, K.R.T.; Sabry, D.A.; Sassaki, G.L.; Rocha, H.A.O. Does the Use of Chitosan Contribute to Oxalate Kidney Stone Formation. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 141–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, P.; Demirhan, E.; Ozbek, B. Development of Ficus carica Linn leaves extract incorporated chitosan films for active food packaging materials and investigation of their properties. Food Biosci. 2022, 46, 101542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, T.; Yin, J.-Y.; Nie, S.-P.; Xie, M.-Y. Applications of infrared spectroscopy in polysaccharide structural analysis: Progress, challenge and perspective. Food Chem. X 2021, 12, 100168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Ni, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, D.; Pang, J. Physicochemical properties of degraded konjac glucomannan prepared by laser assisted with hydrogen peroxide. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 129, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, H.; Tian, S. Plasma Depolymerization of Chitosan in the Presence of Hydrogen Peroxide. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 7788–7797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Li, B.; Kennedy, J.F.; Xie, B.J.; Huang, M. Characterization of konjac glucomannan-gellan gum blend films and their suitability for release of nisin incorporated therein. Carbohydr. Polym. 2007, 70, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, S.C.L.; Boyadzhieva, S.; Hensel, R.; Kruttwig, K.; Arzt, E. Adhesion and relaxation of a soft elastomer on surfaces with skin like roughness. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2018, 80, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jagodzińska, S.; Pałys, B.; Wawro, D. Effect of chitosan film Surface structure on the contact angle. Prog. Chem. Appl. Chitin Deriv. 2021, 26, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristó, K.; Módra, S.; Hornok, V.; Süvegh, K.; Ludasi, K.; Aigner, Z.; Kelemen, A.; Sovány, T.; Pintye-Hódi, K.; Regdon, G. Investigation of Surface Properties and Free Volumes of Chitosan-Based Buccal Mucoadhesive Drug Delivery Films Containing Ascorbic Acid. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamiak, K.; Sionkowska, A. The influence of UV irradiation on fish skin collagen films in the presence of xanthohumol and propanediol. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2022, 282, 121652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choundhary, P.; Ramalingam, B.; Das, S.K. Rational design of antimicrobial peptide conjugated graphene-silver nanoparticle loaded chitosan wound dressing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 246, 125347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruocco, N.; Costantini, S.; Guariniello, S.; Costantini, M. Polysaccharides from the Marine Environment with Pharmacological, Cosmeceutical and Nutriceutical Potential. Molecules 2016, 21, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, S. Polysaccharide-Based Multifunctional Hydrogel Bio-Adhesives for Wound Healing: A Review. Gels 2023, 9, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, D.; Fang, Y.; Yao, K. Water vapor and mechanical properties of konjac glucomannan-chitosan-soy protein isolate edible films. Food Bioprod. Process. 2009, 87, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Shi, S.; Zhu, W.; Wang, R. Advanced konjac glucomannan-based films in food packaging: Classification, preparation, formation mechanism and function. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 152, 112338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanowska, K.; Woźniak, M.; Dobrucka, R.; Ratajczak, I. Chitosan with Natural Additives as a Potential Food Packaging. Materials 2023, 16, 1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Tong, X.; Pan, W.; Zeng, Q.; You, S.; Shen, J. Recent advances in polysaccharide-based adsorbents for wastewater treatment. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 315, 128221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flórez, M.; Guerra-Rodríguez, E.; Cazón, P.; Vázquez, M. Chitosan for food packaging: Recent advances in active and intelligent films. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 124, 107328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Kennedy, J.F.; Peng, J.L.; Yie, X.; Xie, B.J. Preparation and performance evaluation of glucomannan-chitosan-nisin antimicrobial blend film. Carbohydr. Polym. 2006, 65, 488–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, J.; Liu, H.; Qi, C.; Chen, X.; Guo, K. Physical, mechanical properties, and structural characterization of konjac glucomannan-chitosan-polypeptide adhesive blends. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2015, 29, 2334–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Zheng, H.; Xu, J.; Huang, J.; Zhang, C. Preparation and properties of Chitosan/Konjac Glucomannan Blend Fibers. J. Macromol. Sci. 2007, 44, 439–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, S.; Yang, C.; Zhang, L.; Li, Z.; Jiang, S.; Bai, R.; Ye, X.; Ding, W. Chitosan/konjac glucomannan bilayer films: Physical, structural, and thermal properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 257, 128660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, S.B.; Alummoottil, N.J.; Moothandasserry, S.S. Chitosan-konjac glucomannan cassava starch-nanosilver composite films with moisture resistant and antimicrobial properties for food packaging applications. Starch/Starke 2017, 69, 1600210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghomi, E.R.; Khalili, S.; Khorsani, S.N.; Neisiany, R.E.; Ramakrishna, S. Wound dressings: Current advances and future directions. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136, 47738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Z.; Yu-min, D. Preparation and Characterization of Chitosan/Carboxymethylated Konjac Glucomannan Blend Films. Wuhan Univ. J. Nat. Sci. 2002, 7, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koroskenyi, B.; McCarthy, S.P. Synthesis of Acetylated Konjac Glucomannan and Effect of Degree of Acetylation on Water Absorbency. Biomacromolecules 2001, 2, 824–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Deng, X.; Lin, X. Swelling characteristics of konjac glucomannan superabsorbent synthesized by radiation-induced graft copolymerization. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2013, 83, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkongchai, K.; Chuysinuan, P.; Thanyacharoen, T.; Techasakul, S.; Ummartyotin, S. Integration of collagen into chitosan blend film composites physicochemical property aspects for pharmaceutical materials. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strnad, S.; Oberhollenzer, Z.; Šauperl, O.; Kreže, T.; Zemljič, L.F. Modifying properties of father keratin bioplastic films using konjac glucomannan. Cell. Chem. Technol. 2019, 53, 1017–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Xiao, M.; Wang, S.; Peng, C.; Wu, X.; Jiang, F. Effect of drying temperature on microstructural, mechanical, and water barrier properties of konjac glucomannan/agar film produced at industrial scale. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 173, 114275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvipriya, K.S.; Kumar, K.K.; Bhat, A.R.; Kumar, D.B.; John, A.; Iakshamanan, P. Collagen: Animal Sources and Biomedical Application. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 5, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Cheng, N.; Fang, D.; Wang, H.; Rahman, F.-U.; Hao, H.; Zhang, Y. Recent advances on application of polysaccharides in cosmetics. J. Dermatol. Sci. Cosm. Technol. 2024, 1, 100004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, V.P.; Marques, N.S.S.; Maia, P.C.S.V.; Lima, M.A.B.; Franco, L.O.; Campos-Takaki, G.M. Seafood Waste as Attractive Source of Chitin and Chitosan Production and Their Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afonso, C.R.; Hirano, R.S.; Gaspar, A.L.; Chagas, E.G.L.; Carvalho, R.A.; Silva, F.V.; Leonardi, G.; Lopes, P.; Silva, C.; Yoshida, C. Biodegradable antioxidant chitosan films useful as an anti-aging skin mask. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 132, 1262–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzman, E.; Ortega, F.; Rubio, G.R. Chitosan: A Promising Multifunctional Cosmetic Ingredient for Skin and Hair Care. Cosmetics 2022, 9, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspar, A.L.; Gaspar, A.B.; Contini, L.R.F.; Silva, M.F.; Chagas, E.G.L.; Bahu, J.O.; Concha, V.O.; Carvalho, R.A.; Severino, P.; Souto, E.B.; et al. Lemongrass (Cymbopogon citratus)-incorporated chitosan bioactive films for potential skincare applications. Int. J. Phram. 2022, 628, 122301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sionkowska, A.; Lewandowska, K.; Kurzawa, M. Chitosan-Based Films Containing Rutin for Potential Cosmetic Applications. Polymers 2023, 15, 3224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kodolova-Chukontseva, V.V.; Rozova, E.Y.; Dresvyanina, E.N.; Naschekina, Y.A.; Dobrovol’skaya, I.P.; Vlasova, E.N.; Bystrov, S.G.; Popova, E.N.; Maslennikova, T.P.; Yudin, V.E.; et al. New Composite Materials Based on Chitosan Films Reinforced with Chitin Nanofibrils for Cosmetic Applications. Cosmetics 2023, 10, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, N.; Zheng, S.; Xie, W.; Cao, G.; Wang, L.; Pang, J. Konjac glucomannan: A review of structure, physicochemical properties, and wound dressing applications. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2022, 139, e51780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liang, X.; Chen, Y.; Liu, K.; Fu, X.; Zhang, C.; Wang, X.; Yang, J. Synergy of antioxidant and M2 polarization in polyphenol-modified konjac glucomannan dressing for remodelling wound healing microenvironement. Bioeng. Transl. Med. 2023, 8, e10398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-C.; Chu, H.-W.; Huang, C.-C.; Wu, W.-C.; Tsai, J.-S. Alkali-treated konjac glucomannan film as a novel wound dressing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 117, 778–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genesi, B.P.; Barbosa, R.M.; Severino, P.; Rodas, A.C.D.; Yoshida, C.M.P.; Mathor, M.B. Aloe vera copaiba oleoresin-loaded chitosan films for wound dressings: Microbial permeation, cytotoxicity, and in vivo proof of concept. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 634, 122648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colobiatu, L.; Gavan, A.; Potarniche, A.-V.; Rus, V.; Diaconeasa, Z.; Mocan, A.; Tomuta, I.; Mirel, S.; Mihaiu, M. Evaluation of bioactive compounds-loaded chitosan films as a novel and potential diabetic wound dressing material. React. Funct. Polym. 2019, 145, 104369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eulalio, H.Y.C.; Vieira, M.; Fideles, T.B.; Tomas, H.; Silva, S.M.L.; Peniche, C.A.; Fook, M.V.L. Physicochemical Properties and Cell Viability of Shrimp Chitosan Films as Affected by Film Casting Solvents. I-Potential Use as Wound Dressing. Materials 2020, 13, 5005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Qian, Y.; Huang, Y.; Ding, F.; Qi, W.; Shen, J. Polydopamine nanoparticle-dotted food gum hydrogel with excellent antibacterial activity and rapid shape adaptability for accelerated bacteria-infected wound healing. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 6, 2647–2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Huang, J.; Wu, X.; Ren, Y.; Li, Z.; Ren, J. Controlled release of silver ions from AgNPs using a hydrogel based on konjac glucomannan and chitosan for infected wounds. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 149, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Ju, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, Z.; Liu, H.; Yang, M.; Chen, X.; Lei, L.; Fang, B. Natural self-healing injectable hydrogels loaded with exosomes and berberine for infected wound healing. Mater Today Bio 2023, 23, 100875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, D.; Zhang, A.; Wang, N.; Yao, Y.; Chen, X.; Liu, Y. Hydroxybutyl chitosan/oxidized glucomannan self-healing hydrogels as BMSCs-derived exosomes carriers for advanced stretchable wounds. Appl. Mater. Today 2022, 26, 101342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, L.; Guo, Y.; Chen, L.; Hu, K.; Ruan, L.; Li, P.; Cai, X.; Li, B.; Shou, Q.; Jiang, G. Injectable Zn2+ and Paeoniflorin Release Hydrogel for Promoting Wound Healing. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2023, 6, 2184–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Cheng, C.; Qiao, Y.; Li, F.; Li, W.; Wu, H.; Ren, B. GNPs-CS/KGM as Hemostatic First Aid Wound Dressing with Antibiotic Effect: In Vitro and In Vivo Study. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Yan, S.; You, J.; Wu, X. Antibacterial Micelles-Loaded Carboxymethyl Chitosan/Oxidized Konjac Glucomannan Composite Hydrogels for Enhanced Wound Repairing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 13563–13572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, L.; Yi, J.; Tong, J.; Zhou, X.; Ge, H.; Zou, S.; Wen, H.; Nie, M. Preparation and characterization of oxidized konjac glucomannan/carboxymethyl chitosan/graphene oxide hydrogel. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 91, 358–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chellathurai, M.S.; Chung, L.Y.; Hilles, A.R.; Sofian, Z.M.; Singha, S.; Ghosal, K.; Mahmood, S. Pharmaceutical chitosan hydrogels: A review on its design and applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 280, 135775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, B.; Liu, J. Smart stimuli-responsive chitosan hydrogel for drug delivery: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 235, 123902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
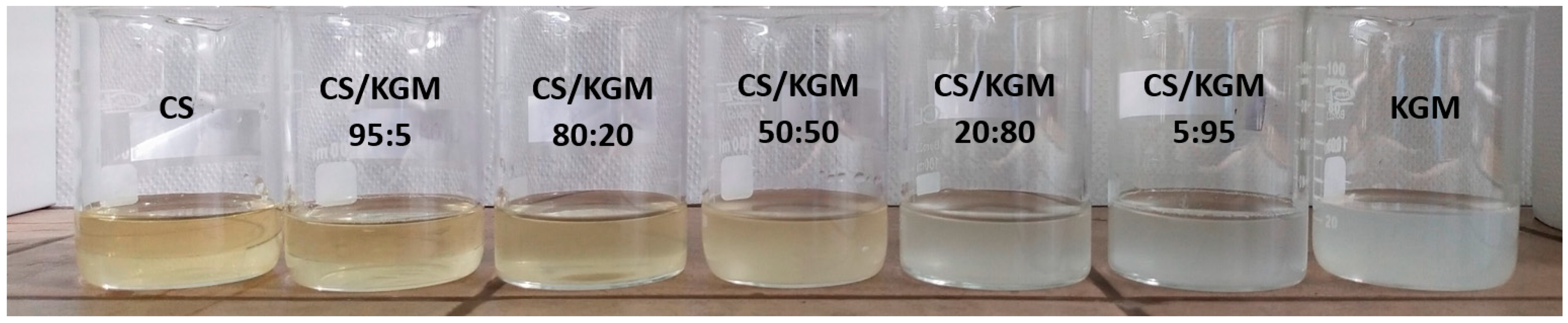






| CS | CS/KGM, 95:5 | CS/KGM, 80:20 | CS/KGM 50:50 | CS/KGM 20:80 | CS/KGM 5:95 | KGM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |  |  |  |  |  |  |
 |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| Sample | Rq [nm] | Ra [nm] |
|---|---|---|
| CS | 5.64 ± 1.25 | 4.50 ± 0.97 |
| CS/KGM 95:5 | 9.60 ± 2.85 | 6.35 ± 1.04 |
| CS/KGM 80:20 | 12.60 ± 1.14 | 9.88 ± 0.77 |
| CS/KGM 50:50 | 5.95 ± 2.48 | 4.69 ± 1.92 |
| CS/KGM 20:80 | 6.57 ± 0.84 | 4.96 ± 0.46 |
| CS/KGM 5:95 | 6.17 ± 0.75 | 4.86 ± 0.50 |
| KGM | 6.87 ± 0.94 | 5.68 ± 0.98 |
| Sample | Tmax1 [°C] | Tmax2 [°C] |
|---|---|---|
| CS | 62.87 | 296.72 |
| CS/KGM 95:5 | 74.31 | 296.01 |
| CS/KGM 80:20 | 65.02 | 293.86 |
| CS/KGM 50:50 | 67.16 | 288.86 |
| CS/KGM 20:80 | 75.74 | 285.99 |
| CS/KGM 5:95 | 65.73 | 305.30 |
| KGM | 50.00 | 326.04 |
| Specimen | 0.25 h [%] | 1 h [%] | 2 h [%] | 4 h [%] | 8 h [%] | 24 h [%] | 48 h [%] | 72 h [%] | 168 h [%] | 336 h [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CS | 270 ± 23 | 279 ± 36 | 235 ± 16 | 207 ± 11 | 189 ± 10 | 184 ± 5.0 | 166 ± 9.0 | 148 ± 5.0 | 137 ± 4.0 | 128 ± 7.0 |
| CS/KGM 95:5 | 236 ± 82 | 241 ± 100 | 198 ± 15 | 173 ± 10 | 159 ± 12 | 141 ± 11 | 134 ± 9.0 | 124 ± 7.0 | 119 ± 20 | 107 ± 20 |
| CS/KGM 80:20 | 296 ± 44 | 269 ± 33 | 230 ± 17 | 218 ± 10 | 189 ± 16 | 177 ± 8.0 | 152 ± 13 | 149 ± 9.0 | 141 ± 3.0 | 124 ± 8.0 |
| CS/KGM 50:50 | 162 ± 21 | 159 ± 27 | 149 ± 24 | 144 ± 8.0 | 144 ± 10 | 138 ± 9.0 | 125 ± 15 | 123 ± 5.0 | 120 ± 10 | 122 ± 12 |
| CS/KGM 20:80 | 310 ± 184 | 265 ± 117 | 256 ± 112 | 238 ± 97 | 242 ± 91 | 255 ± 107 | 247 ± 108 | 242 ± 109 | 233 ± 114 | 229 ± 101 |
| CS/KGM 5:95 | 946 ± 178 | 938 ± 95 | 886 ± 45 | 841 ± 54 | 825 ± 52 | 765 ± 41 | 761 ± 35 | 670 ± 51 | 636 ± 60 | 587 ± 24 |
| KGM | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Specimen | 0.25 h [%] | 1 h [%] | 2 h [%] | 4 h [%] | 8 h [%] | 24 h [%] | 48 h [%] | 72 h [%] | 168 h [%] | 336 h [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CS | 54 ± 12 | 76 ± 20 | 78 ± 36 | 78 ± 17 | 69 ± 13 | 69 ± 15 | 72 ± 26 | 61 ± 15 | 61 ± 19 | 62 ± 25 |
| CS/KGM 95:5 | 87 ± 16 | 87 ± 3.0 | 87 ± 4.0 | 83 ± 3.0 | 82 ± 3.0 | 77 ± 4.0 | 81 ± 1.0 | 73 ± 4.0 | 67 ± 2.0 | 70 ± 5.0 |
| CS/KGM 80:20 | 85 ± 4.0 | 87 ± 5.0 | 87 ± 1.0 | 82 ± 3.0 | 84 ± 5.0 | 84 ± 5.0 | 78 ± 4.0 | 76 ± 4.0 | 77 ± 1.0 | 73 ± 3.0 |
| CS/KGM 50:50 | 99 ± 3.0 | 89 ± 4.0 | 99 ± 10 | 105 ± 8.0 | 102 ± 7.0 | 83 ± 2.0 | 88 ± 5.0 | 96 ± 7.0 | 86 ± 5.0 | 90 ± 4.0 |
| CS/KGM 20:80 | 187 ± 74 | 168 ± 30 | 149 ± 14 | 135 ± 12 | 137 ± 16 | 130 ± 3.0 | 125 ± 5.0 | 126 ± 8.0 | 116 ± 6.0 | 126 ± 8.0 |
| CS/KGM 5:95 | 373 ± 22 | 413 ± 45 | 431 ± 21 | 430 ± 22 | 413 ± 26 | 398 ± 18 | 410 ± 18 | 387 ± 23 | 379 ± 19 | 367 ± 17 |
| KGM | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Specimen | ΘG | ΘD | γs [mJ/m2] | γsd [mJ/m2] | γsp [mJ/m2] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CS | 90.08 ± 2.93 | 47.33 ± 9.46 | 35.50 ± 5.13 | 35.23 ± 5.41 | 0.40 ± 0.1 |
| CS/KGM 95:5 | 97.82 ± 3.00 | 64.52 ± 2.48 | 25.97 ± 1.14 | 25.62 ± 0.89 | 0.35 ± 0.25 |
| CS/KGM 80:20 | 89.33 ± 2.87 | 52.07 ± 6.40 | 32.73 ± 3.59 | 31.94 ± 3.56 | 0.79 ± 0.04 |
| CS/KGM 50:50 | 81.83 ± 3.53 | 29.54 ± 7.94 | 43.88 ± 2.99 | 43.12 ± 2.73 | 0.77 ± 0.26 |
| CS/KGM 20:80 | 75.19 ± 6.94 | 39.57 ± 8.63 | 39.30 ± 4.54 | 35.86 ± 3.14 | 3.43 ± 1.40 |
| CS/KGM 5:95 | 76.11 ± 2.57 | 43.94 ± 3.34 | 37.32 ± 1.94 | 33.76 ± 1.51 | 3.55 ± 0.45 |
| KGM | 56.27 ± 3.74 | 35.24 ± 1.30 | 45.35 ± 1.69 | 35.58 ± 0.20 | 11.77 ± 1.89 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kulka-Kamińska, K.; Sionkowska, A. The Properties of Thin Films Based on Chitosan/Konjac Glucomannan Blends. Polymers 2024, 16, 3072. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16213072
Kulka-Kamińska K, Sionkowska A. The Properties of Thin Films Based on Chitosan/Konjac Glucomannan Blends. Polymers. 2024; 16(21):3072. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16213072
Chicago/Turabian StyleKulka-Kamińska, Karolina, and Alina Sionkowska. 2024. "The Properties of Thin Films Based on Chitosan/Konjac Glucomannan Blends" Polymers 16, no. 21: 3072. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16213072
APA StyleKulka-Kamińska, K., & Sionkowska, A. (2024). The Properties of Thin Films Based on Chitosan/Konjac Glucomannan Blends. Polymers, 16(21), 3072. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16213072










