Preparation and Characterization of Chloroprene Latexes Modified with Vinyl-POSS
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
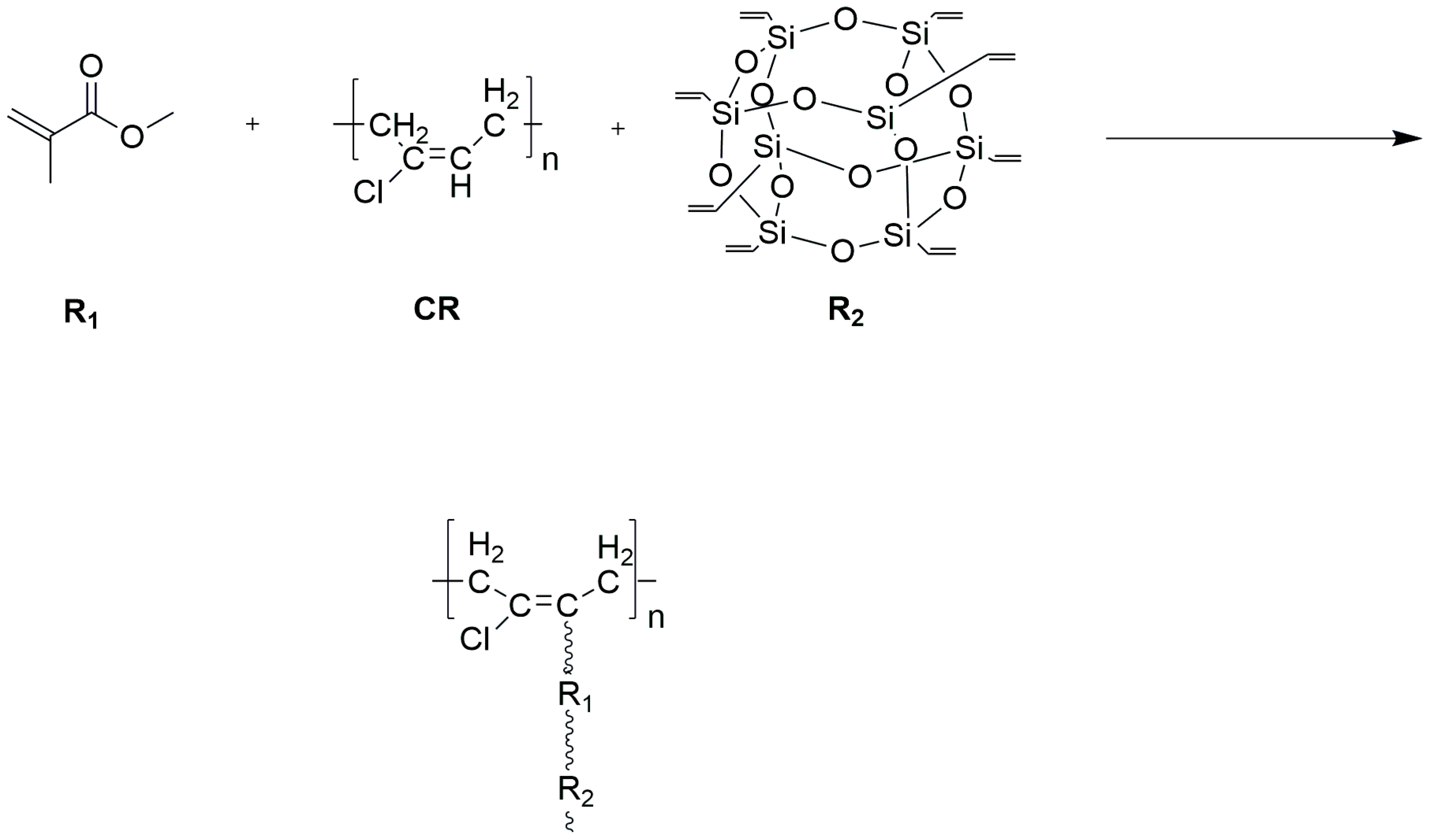
2.2. Preparation of Modified Aqueous Chloroprene Latex
2.3. Characterization
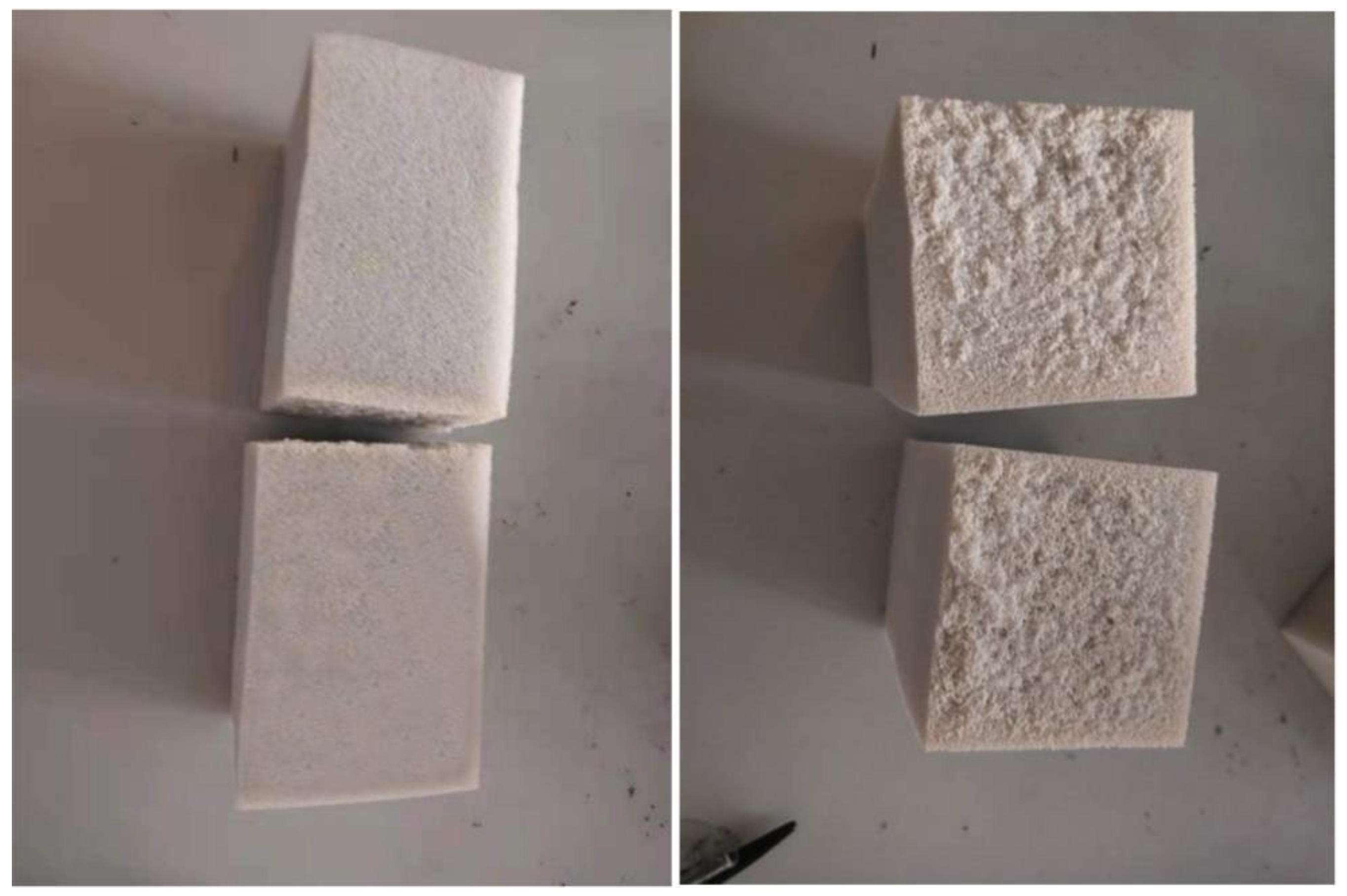
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
- (1)
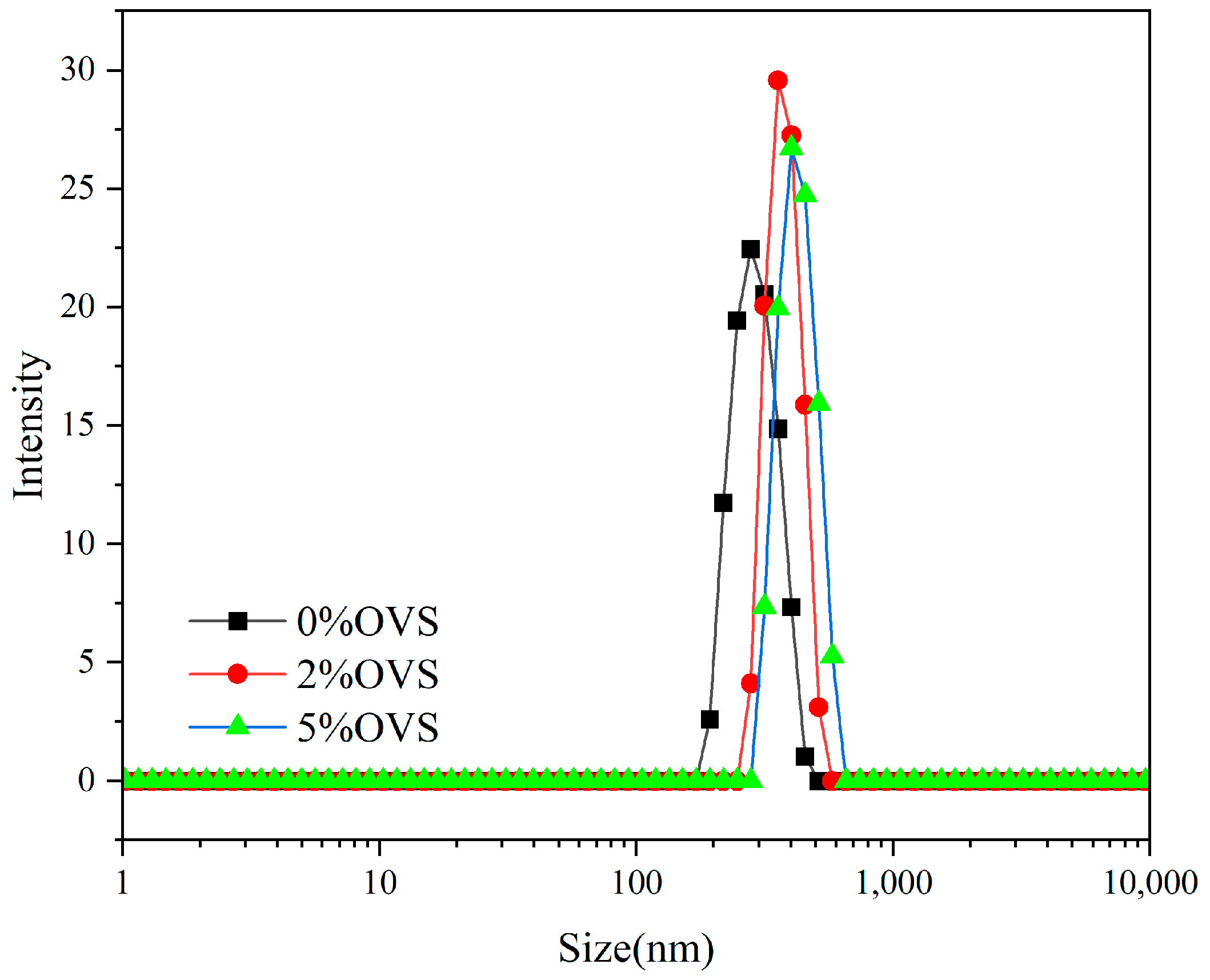
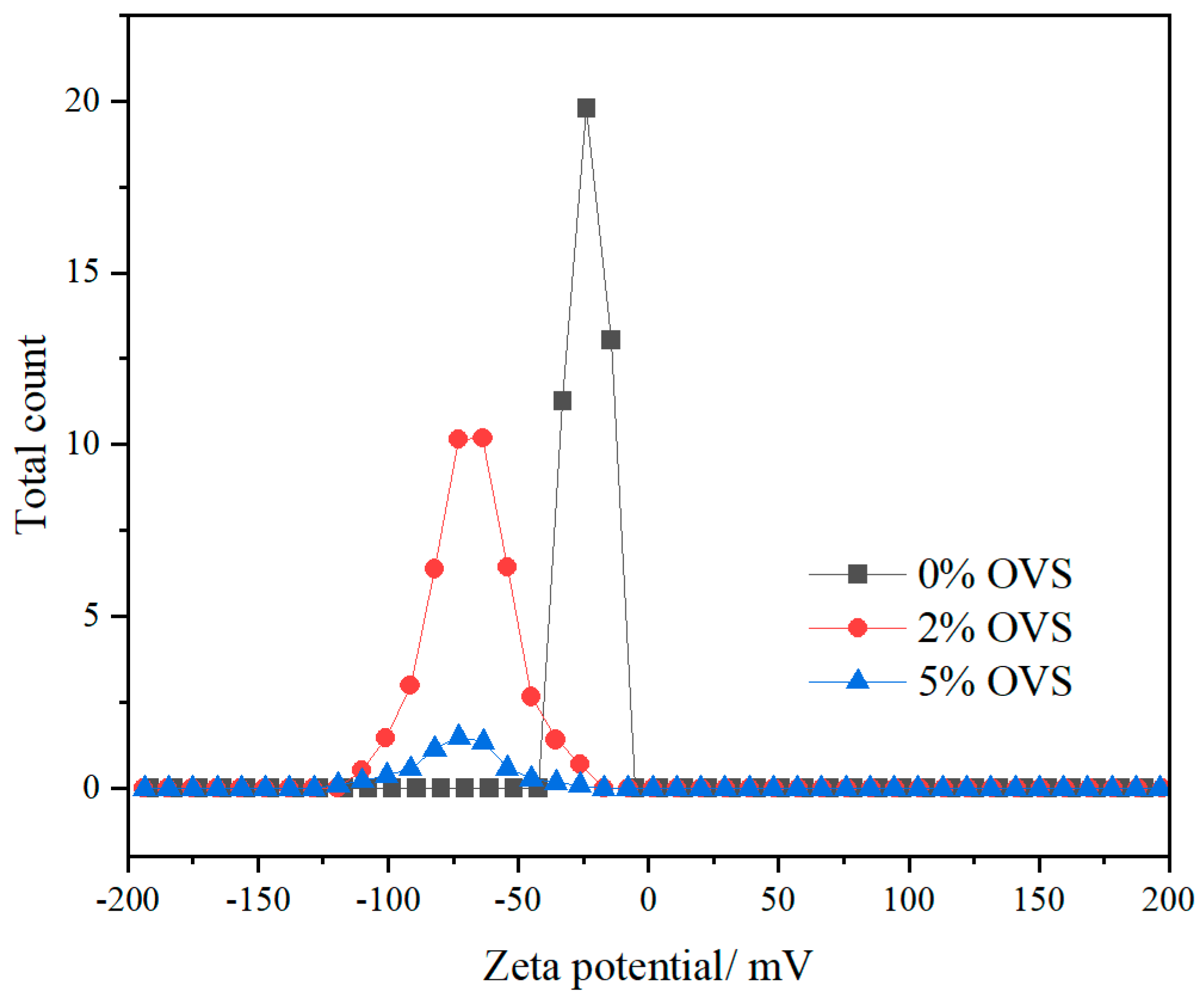
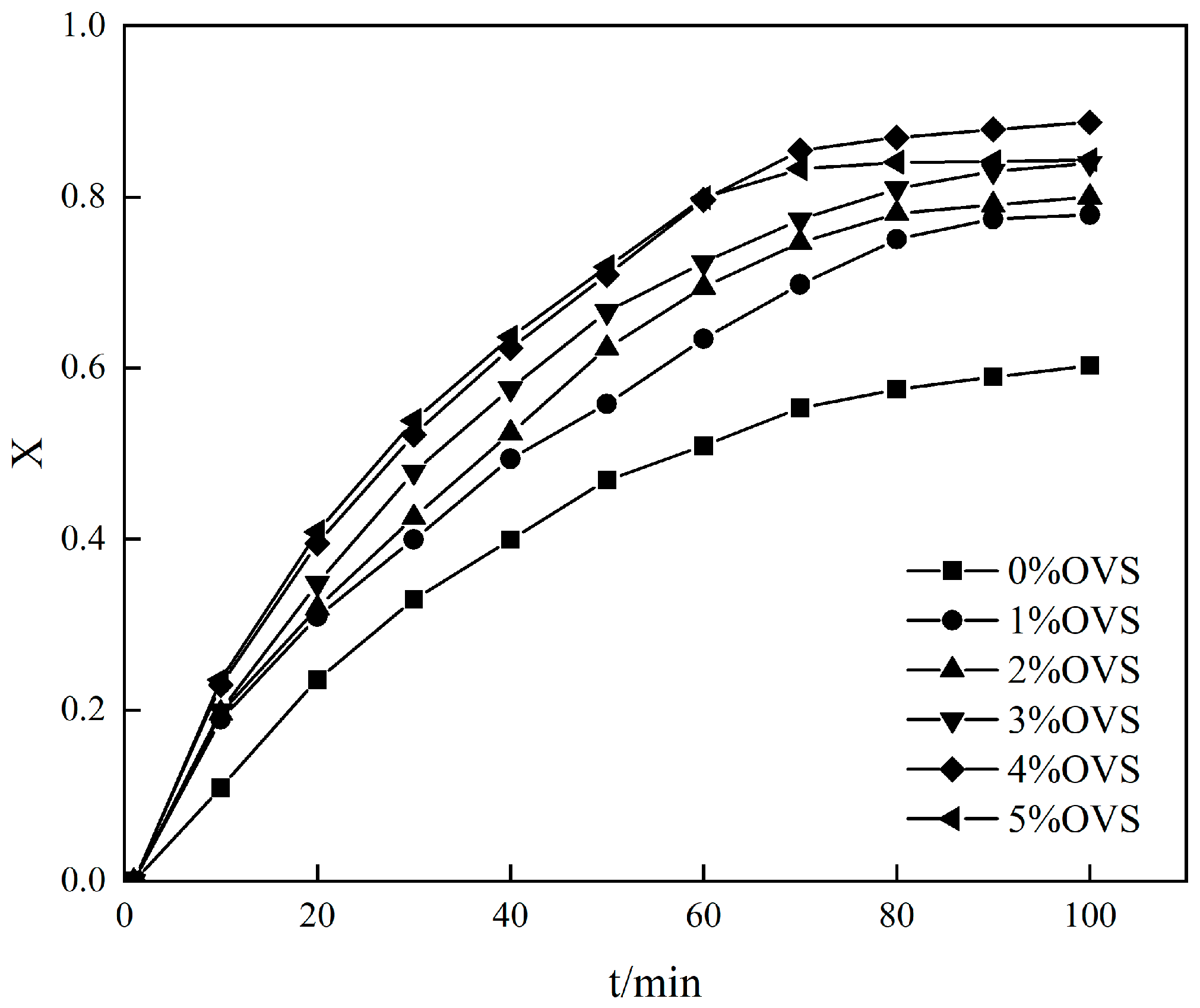
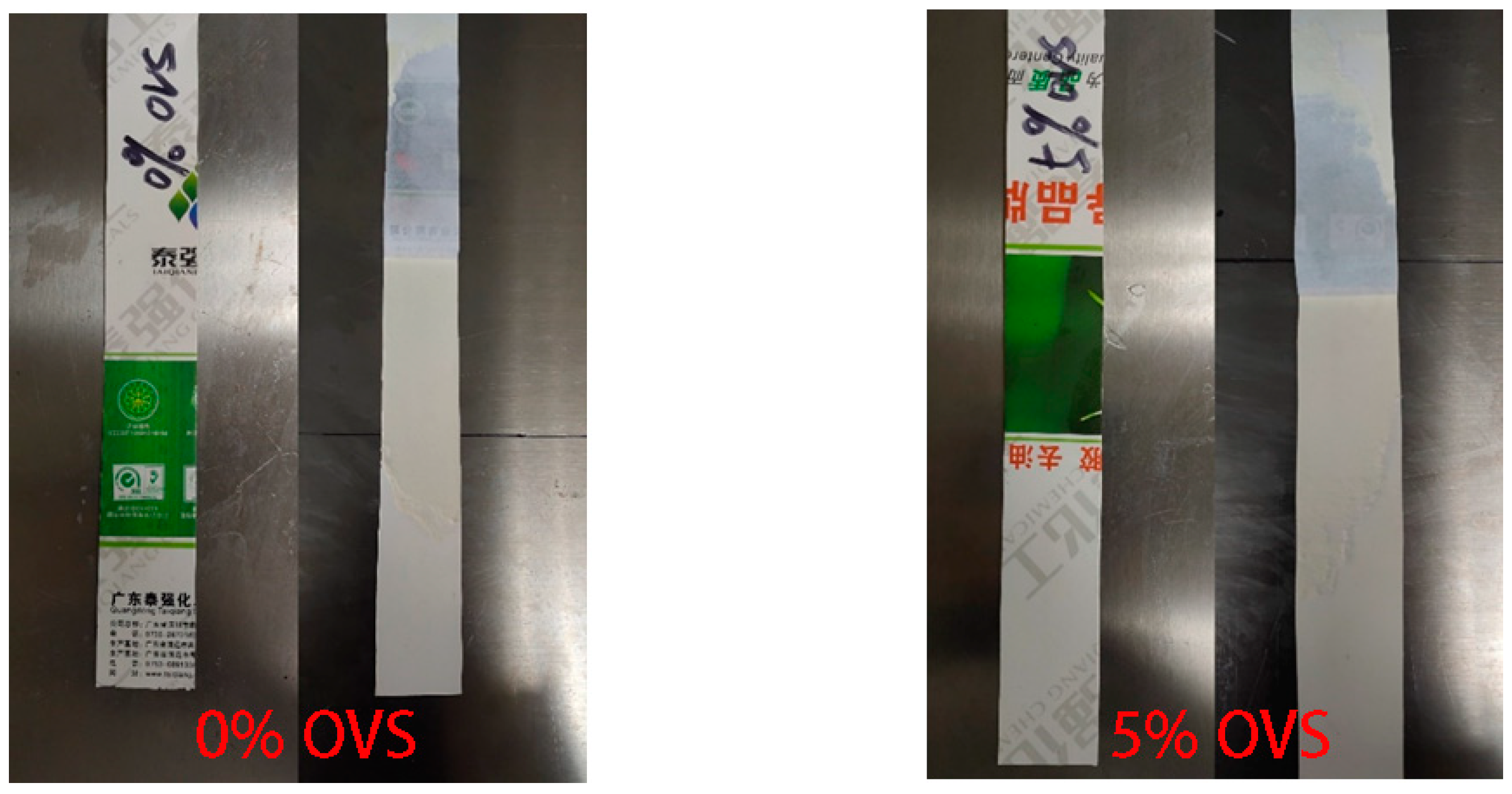
- Waterborne chloroprene latex modified with vinyl-POSS was prepared by emulsion polymerization using a redox initiator (TBHP/TEPA 0.5% of dry weight), an emulsifier (DSB 1% of total monomer) at a polymerization temperature of 50 °C, with a solid content of 30% controlled using deionized water and dropwise addition of the monomer methyl methacrylate and vinyl-POSS. The stability of the prepared aqueous chloroprene latex was good, with a small amount of gel appearing at 4% and 5% content for polymerization, and the best monomer conversion at 4% vinyl-POSS content. Infrared spectroscopic analysis demonstrated that MMA and OVS were grafted onto the chloroprene latex.
- (2)
- The OVS grafting CRL kinetic study showed that the relationship between the monomer reaction rate and reactant concentration was Rp = K[E]0.15[I]0.30[OVS]1.05 (K is a constant); the reaction mechanism deduced the rate equation Rp = kp(2kd/kt1)0.5[M][I2]0.5 and the free radical reaction mechanism of grafting polymerization is basically correct, but there is a deviation in the order of reaction because the actual experimental procedure deviates from the assumptions made in the theoretical derivation.
- (3)
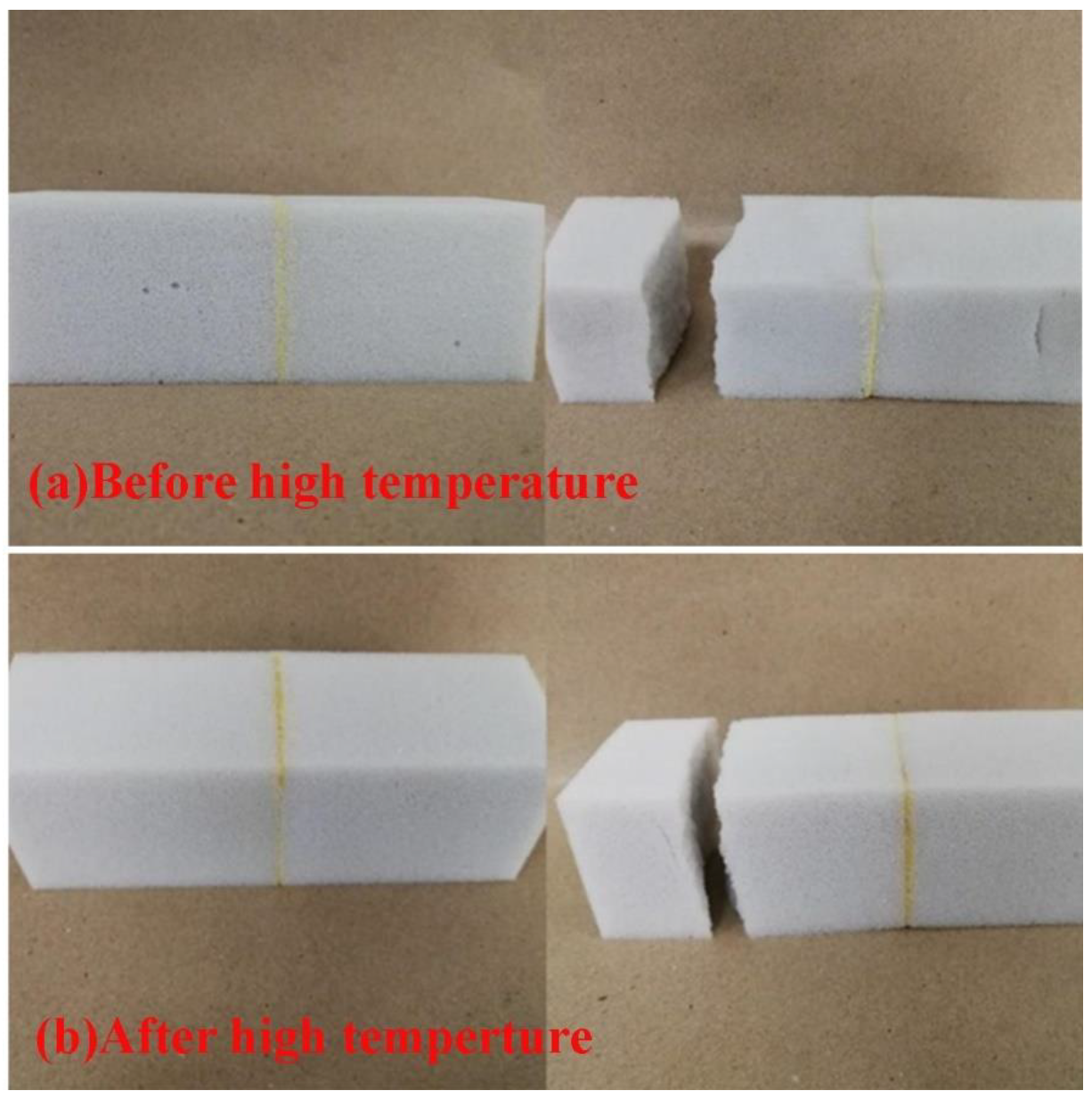
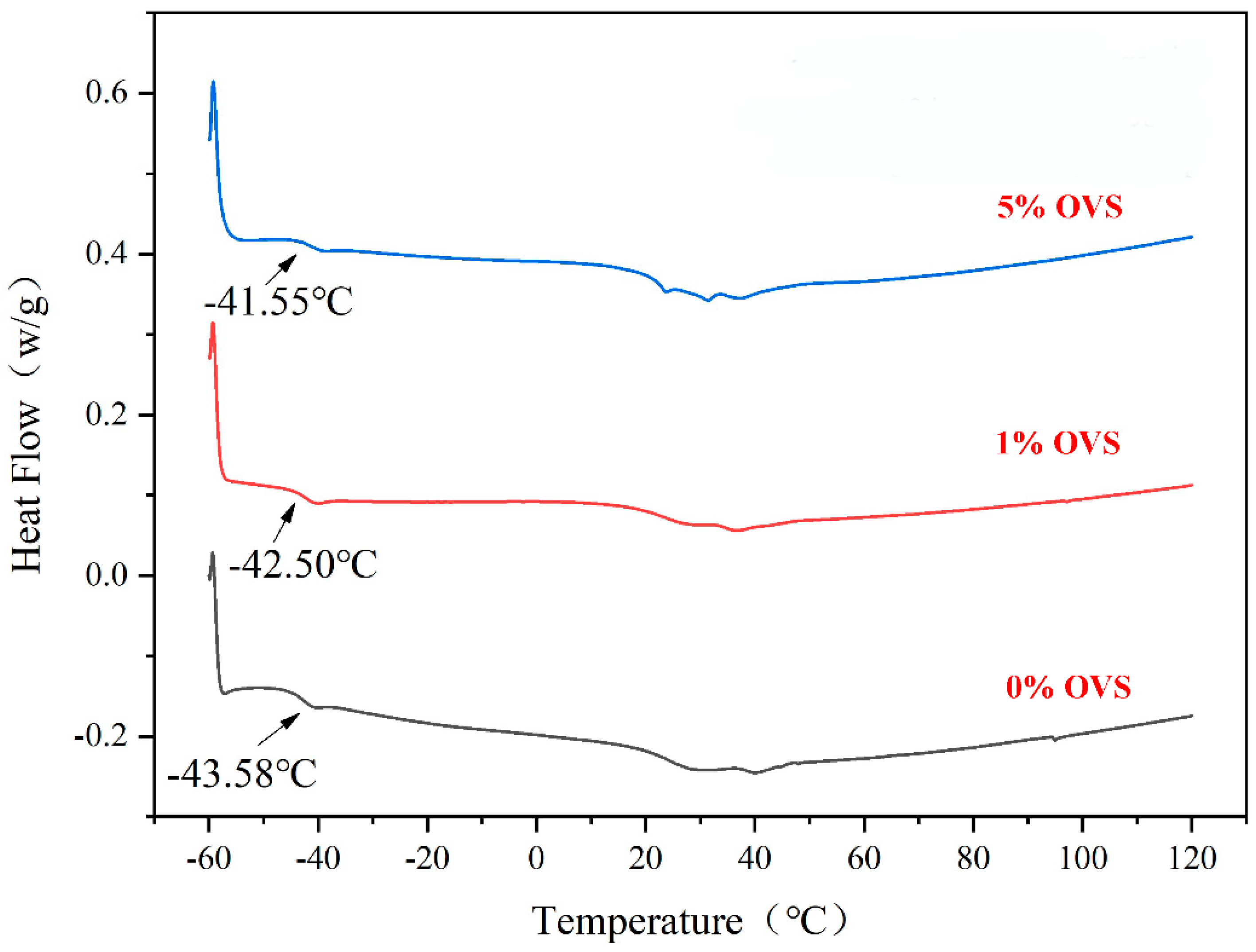
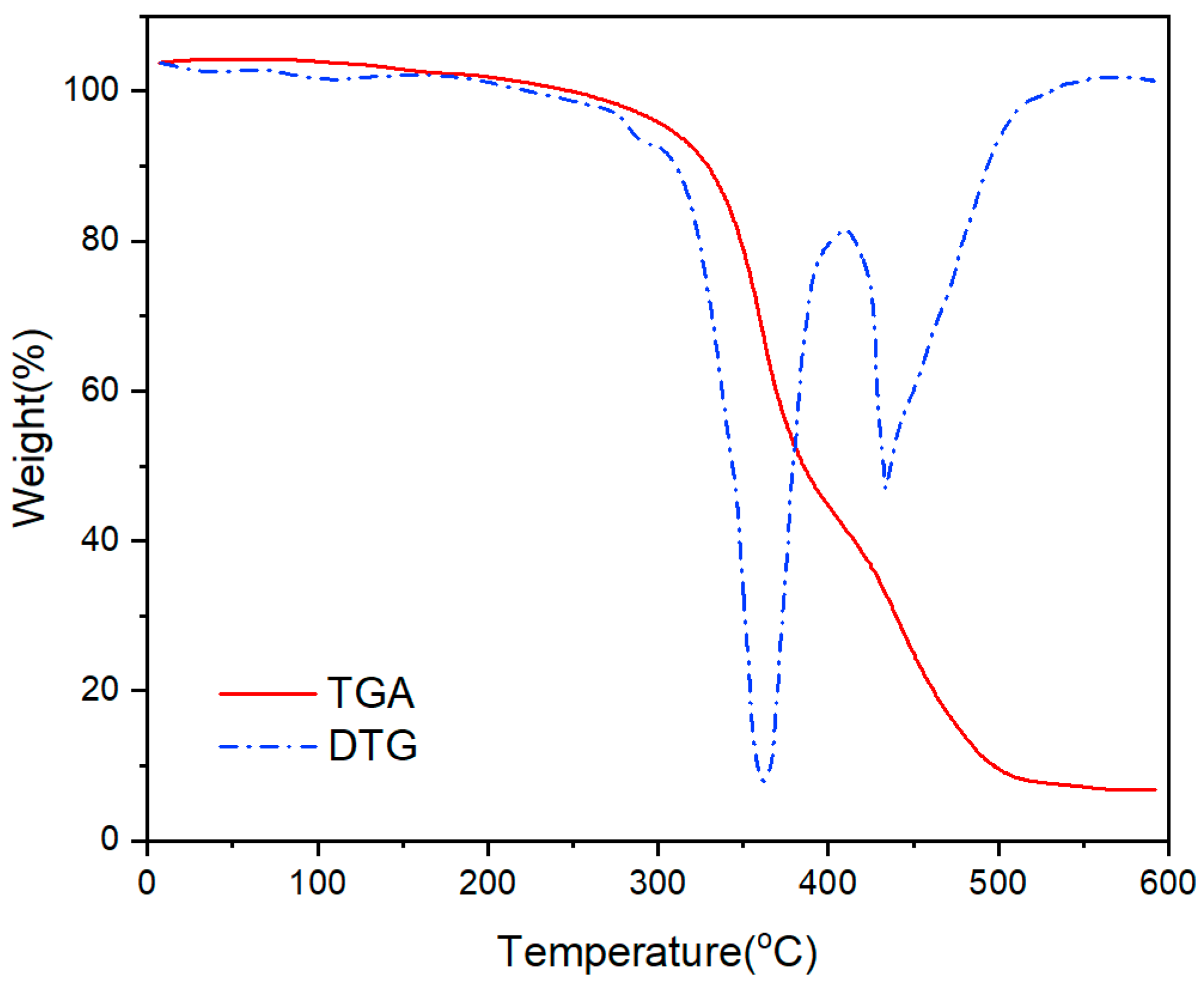
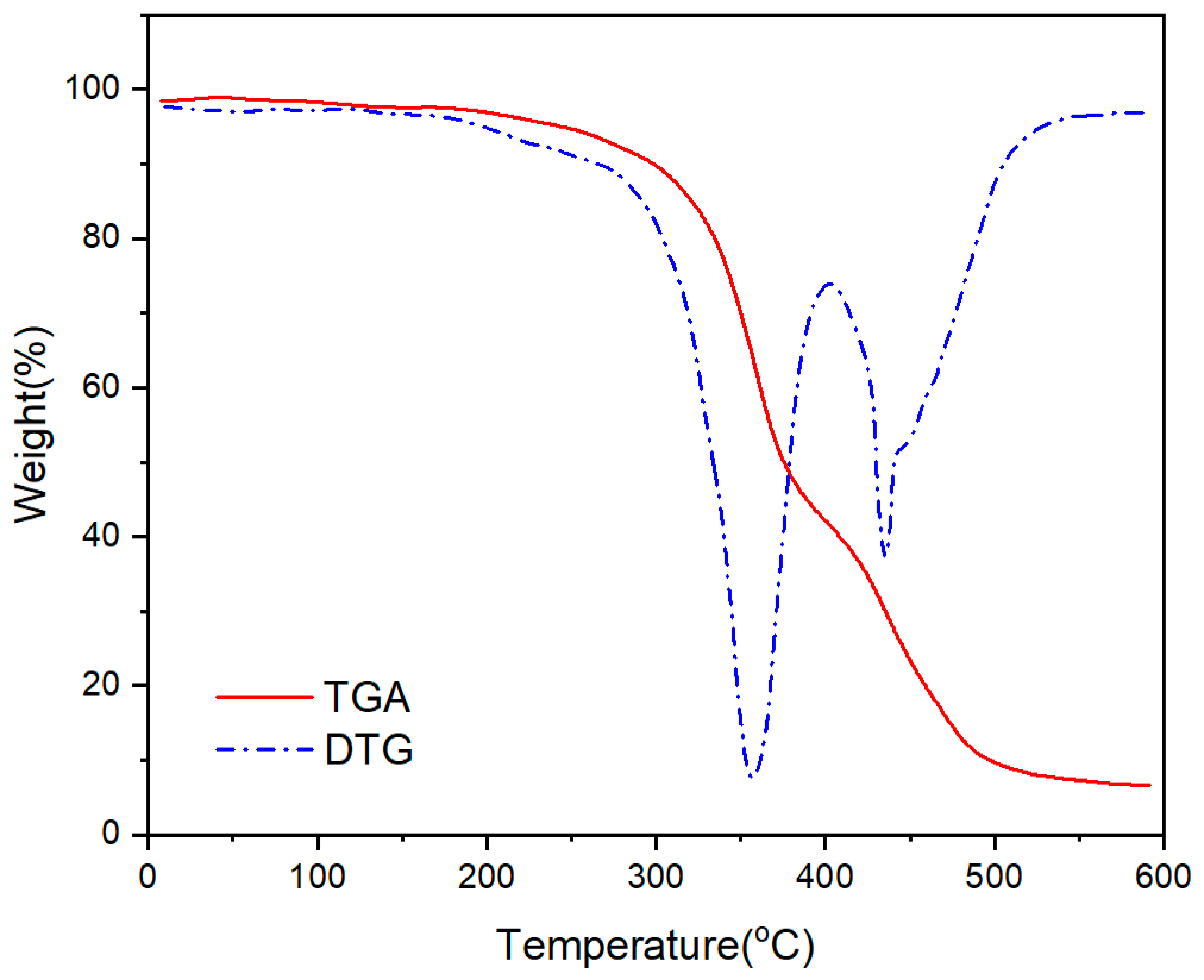
- As the addition of vinyl-POSS increased, the tensile strength of the chloroprene latex first increased and then decreased, and the thermal stability of the chloroprene latex increased.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Andersen, D.E.; Arnold, R.G. Aging Stability of Neoprene Latex. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1953, 45, 2727–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauterey, F. Production of Polychloroprene Latexes. U.S. Patent 5,322,886, 21 June 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Maron, S.H.; Levy-Pascal, A.E. Rheology of synthetic latex: VI. The flow behavior of neoprene latex. J. Colloid Sci. 1955, 10, 494–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, C.A., Jr.; Staff, U.B. Chloroprene. Kirk-Othmer Encycl. Chem. Technol. 2000, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yashima, H.; Mochizuki, K. Polychloroprene Latex, Process for the Production Thereof and Aqueous Adhesive Compositions. U.S. Patent 7,514,487, 7 April 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ozoe, S. Polychloroprene-Base Latex and Method for Producing it. U.S. Patent Application 11/946,201, 29 May 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Guggenberger, S.K. Neoprene (polychloroprene)-based solvent and latex adhesives. In Handbook of Adhesives; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1990; pp. 284–306. [Google Scholar]
- Minorikawa, N.; Takenoshita, Y.; Suzuki, E. Chloroprene Polymer Latex Composition and Use Thereof. U.S. Patent Application No. 13/512,540, 20 September 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ohnishi, T. Chloroprene Rubber-Based Polymer Latex Composition and Use Thereof. U.S. Patent 9,023,948, 5 May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Christell, L.A. High-Performance Water-Based Chloroprene Polymer Adhesive Composition. U.S. Patent No. 5,332,771, 26 July 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Onozuka, M.; Kiyofuji, G.; Hagiwara, S. Chloroprene Rubber Latex Adhesive Composition. U.S. Patent No. 11,479,698, 25 October 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Oba, H.; Tsuji, T.; Yamaguchi, M. Chloroprene Latex Composition, Process for Producing the Same, and Adhesive Composition Comprising the Same. U.S. Patent 6,525,132, 25 February 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Yashima, H.; Kishi, S.; Otsuka, K.; Ishigaki, Y. Chloroprene Rubber Composition and Adhesive Composition Using Said Chloroprene Rubber Composition. U.S. Patent 9,328,228, 3 May 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; Huang, C.B.; Shen, H.F.; Chen, H.Q. Modification of Polychloroprene Rubber Latex by Grafting Polymerization and Its Application as a Waterborne Contact Adhesive. J. Adhes. 2012, 88, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, N.; Konno, M.; Nagao, D.; Mashiko, Y.; Otsu, T. Method of Producing a Chloroprene-Based Polymer, Polychloroprene Latex and Adhesive Composition. U.S. Patent No. 9,493,683, 15 November 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Žukienė, K.; Jankauskaitė, V. The Effect of Surface Properties on the Adhesion of Modified Polychloroprene Used as Adhesive. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2005, 19, 627–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Huang, C.; Shen, H.; Chen, H. Grafting of methyl methacrylate and styrene onto polychloroprene latex for compatibilization of polychloroprene latex/styrene-acrylate emulsion blends. J. Adhes. 2015, 91, 419–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Shen, H.; Zhang, X.; Lan, R.H.; Chen, H.Q. Preparation and properties of a waterborne contact adhesive based on polychloroprene latex and styrene-acrylate emulsion blend. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2009, 23, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Soriano-Luna, M.; Núñez-Pérez, H.I.; Estrada, M.R. On the swelling of polychloroprene-MMT nanocomposite films. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 125, 2986–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rattanasom, N.; Kueseng, P.; Deeprasertkul, C. Improvement of the mechanical and thermal properties of silica-filled polychloroprene vulcanizates prepared from latex system. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 124, 2657–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salleh, S.; Ismail, H.; Ahmad, Z. Properties of natural rubber latex-compatibilized natural rubber/recycled chloroprene rubber blends. J. Elastomers Plast. 2016, 48, 640–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aneeq, F.; Shahid, M.; Saleem, M.; Awais, M.; Butt, M.S.; Adeel Umer, M. Enhancement in bonding strength and ageing resistance of polychloroprene solvent-base adhesives through graft copolymerization. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2021, 35, 1752–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, T.; Noon, Z.; Yasin, S.; Qaiser, A.A.; Ahmad, M.M. Temperature effects on grafting reaction to produce methyl methacrylate grafted polychloroprene adhesive. J. Pak. Inst. Chem. Eng. 2011, 39, 75–80. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, H.; Shah, S.M. Recent developments in nanostructured polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane-based materials via “controlled” radical polymerization. Polym. Int. 2014, 63, 835–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Deng, Y.Y.; Zhang, Q.; Han, D.; Fu, Q. Effect of POSS size on the porosity and adsorption performance of hybrid porous polymers. Macromolecules 2023, 56, 1243–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Li, B.; Zhao, Y.; Li, H.; Yuan, X. Functional POSS-containing polymers and their applications. Prog. Chem. 2014, 26, 394. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.; Nie, J.; Yi, S.; Wu, W.; Zhong, Y.; Liao, J.; Huang, C. Thermal behaviour and mechanical properties of novel RTV silicone rubbers using divinyl-hexa [(trimethoxysilyl) ethyl]-POSS as cross-linker. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2010, 95, 618–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, C.; Aprile, C.; Gruttadauria, M.; Giacalone, F. POSS nanostructures in catalysis. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2020, 10, 7415–7447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imoto, H.; Sato, Y.; Naka, K. Polymers and cyclic compounds based on a side-opening type cage silsesquioxane. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2019, 57, 2243–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karuppasamy, K.; Prasanna, K.; Vikraman, D.; Kim, H.S.; Kathalingam, A.; Mitu, L.; Rhee, H.W. A rapid one-pot synthesis of novel high-purity methacrylic phosphonic acid (PA)-based polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane (POSS) frameworks via thiol-ene click reaction. Polymers 2017, 9, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Ma, S.; Chen, L.; Xu, J.; Ou, J.; Ye, M. Porous styryl-linked polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane (POSS) polymers used as a support for platinum catalysts. Mater. Chem. Front. 2019, 3, 851–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Yi, S.; Wu, W.; Zhong, Y.; Liao, J.; Huang, C.; Shi, W. Synthesis and characterization of novel room temperature vulcanized (RTV) silicone rubbers using Vinyl-POSS derivatives as cross linking agents. Polymer 2010, 51, 3867–3878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Dong, Z.; Zhao, L. Radiation synthesis of polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxanes (POSS) gel polymers. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2022, 198, 110251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, F.; Xue, X. Synthesis and characterization of UV-cured epoxy acrylate/POSS nanocomposites. Prog. Org. Coat. 2013, 76, 863–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Ye, Q.; Xu, J. Polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane-based hybrid materials and their applications. Mater. Chem. Front. 2017, 1, 212–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kausar, A. State-of-the-Art overview on polymer/POSS nanocomposite. Polym.-Plast. Technol. Eng. 2017, 56, 1401–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pielichowski, K.; Njuguna, J.; Janowski, B.; Pielichowski, J. Polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxanes (POSS)-containing nanohybrid polymers. Supramol. Polym. Polym. Betains Oligomers 2006, 225–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.; Zhou, H.; Xu, J. Cubic polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane based functional materials: Synthesis, assembly, and applications. Chem. Asian J. 2016, 11, 1322–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, S.W.; Chang, F.C. POSS related polymer nanocomposites. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2011, 36, 1649–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.; Zou, L.; Zheng, S.; Zhao, L.; Huang, X.; Ye, L.; Zhong, G. Effects of colloidal silica on the properties of POSS-containing fluorinated poly (styrene–acrylate)/SiO2 composite materials. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2021, 18, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtenhan, J.D.; Pielichowski, K.; Blanco, I. POSS-based polymers. Polymers 2019, 11, 1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- So, J.I.; Kim, J.B.; Jeong, H.W.; Kim, C.H.; Choi, J.; Shim, S.E.; Qian, Y. One-pot synthesis of bifunctional polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane: Full spectrum ratio of vinyl groups from 0 to 100%. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2022, 113, 502–512. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Abbenhuis, H.C.L.; Yang, Q.; Wang, Y.-M.; Magusin, P.C.M.M.; Mezari, B.; van Santen, R.A.; Li, C. Mesoporous organic–inorganic hybrid materials built using polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane blocks. Angew. Chem. 2007, 119, 5091–5094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auner, N.; Weis, J. Organosilicon Chemistry III: From Molecules to Materials; John Wiley&Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Chin, J.M.; He, C.; Xu, J. Highly thermally resistant polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxanes lubricating oil prepared via a thiol-ene click reaction. Sci. Adv. Mater. 2014, 6, 1553–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 2794-2022; Determination of Viscosity of Adhesives, Single Cylinder Rotational Viscometer Method. Standardization Administration of China (SAC): Beijing, China, 2022.
- GB/T 2790-1995; Test Method for 180° Peel Strength of Adhesives Flexure to Rigidity. Standardization Administration of China (SAC): Beijing, China, 1995.
- GB/T 2909-2014; Cotton Grey Canvas for Rubber Industry. Standardization Administration of China (SAC): Beijing, China, 2015.
- Yeh, M.H.; Hwang, W.S.; Cheng, L.R. Microstructure and mechanical proper-ties of neoprene–montmorillonite nanocomposites. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2007, 253, 4777–4781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, T.; Jiang, N.; Zhang, T. Chemical modification of neoprene rubber by grafting cardanol, a versatile renewable material from cashew industry. J. Polym. Res. 2020, 27, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



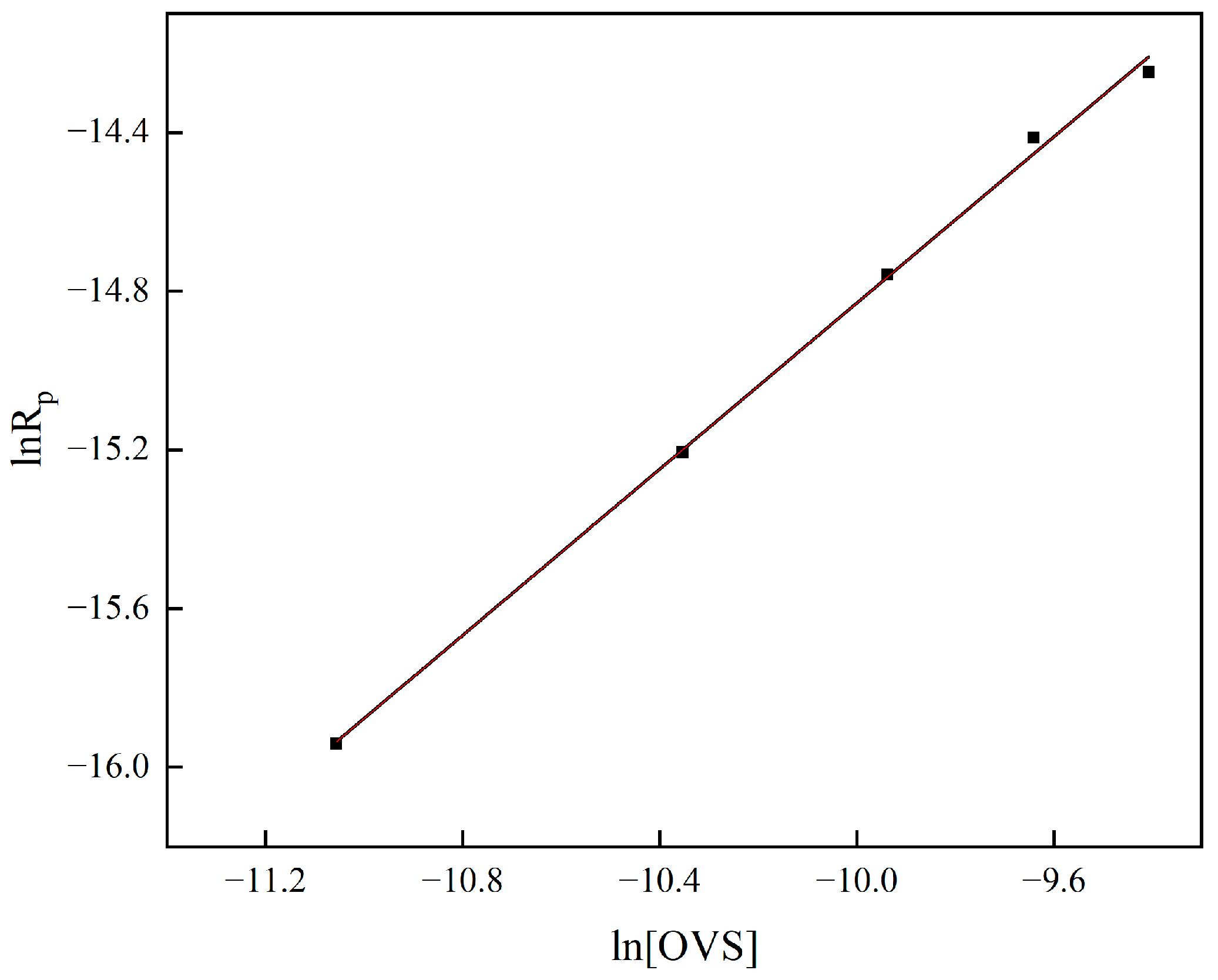


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, J.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Q.; Yang, C.; Chen, J.; Zhang, H.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, D.-Y.; Hao, X. Preparation and Characterization of Chloroprene Latexes Modified with Vinyl-POSS. Polymers 2024, 16, 462. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16040462
Chen J, Wu Z, Wang Q, Yang C, Chen J, Zhang H, Wu Y, Zhu D-Y, Hao X. Preparation and Characterization of Chloroprene Latexes Modified with Vinyl-POSS. Polymers. 2024; 16(4):462. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16040462
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Junhua, Zhenxian Wu, Qingwei Wang, Chuanghui Yang, Jinlian Chen, He Zhang, Yinping Wu, Dong-Yu Zhu, and Xiangying Hao. 2024. "Preparation and Characterization of Chloroprene Latexes Modified with Vinyl-POSS" Polymers 16, no. 4: 462. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16040462
APA StyleChen, J., Wu, Z., Wang, Q., Yang, C., Chen, J., Zhang, H., Wu, Y., Zhu, D.-Y., & Hao, X. (2024). Preparation and Characterization of Chloroprene Latexes Modified with Vinyl-POSS. Polymers, 16(4), 462. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16040462







