Reinforcement and Deacidification for a Textile Scroll Painting (AD 1881) Using the CNF and MgO Suspensions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples
2.2. pH
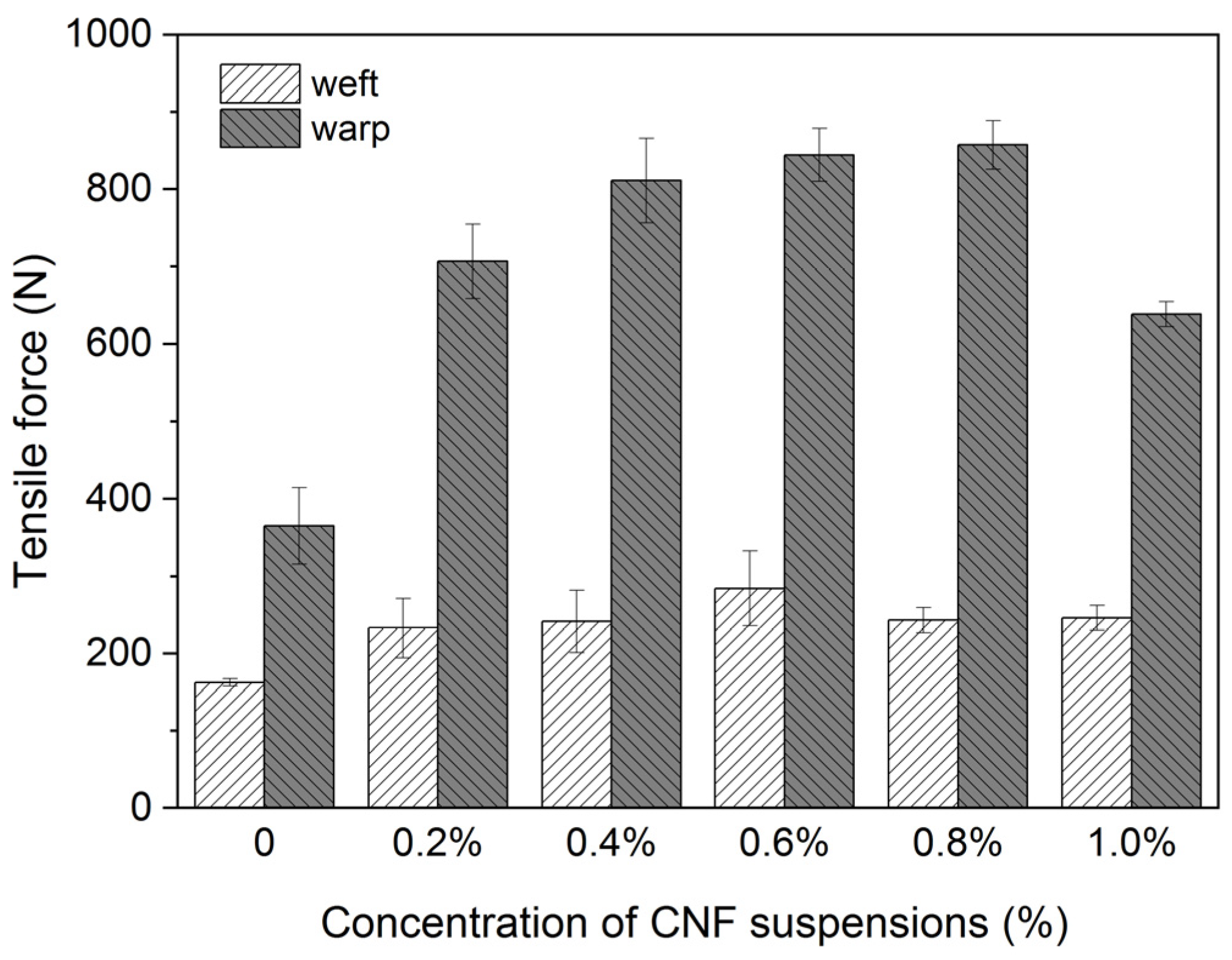
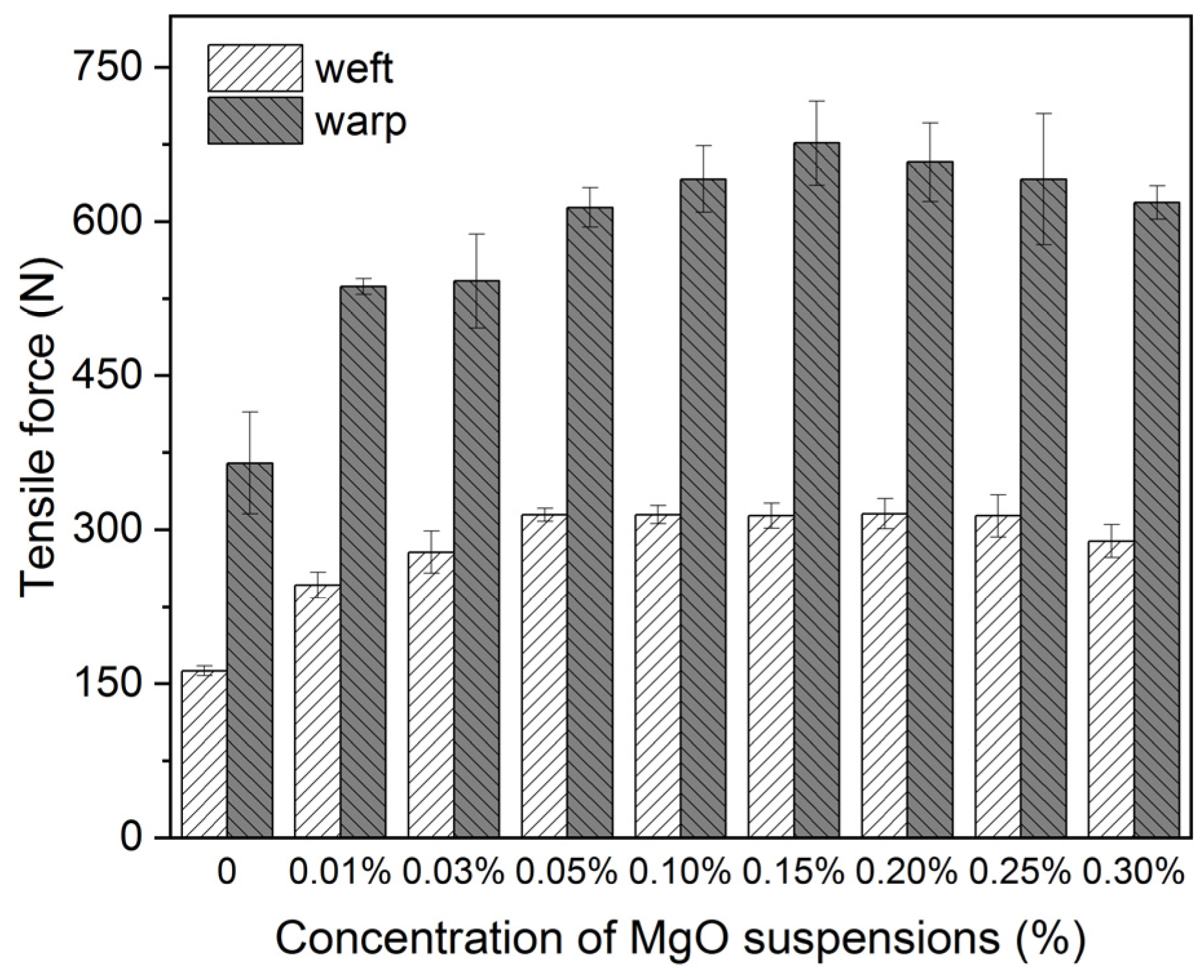
2.3. Mechanical Properties
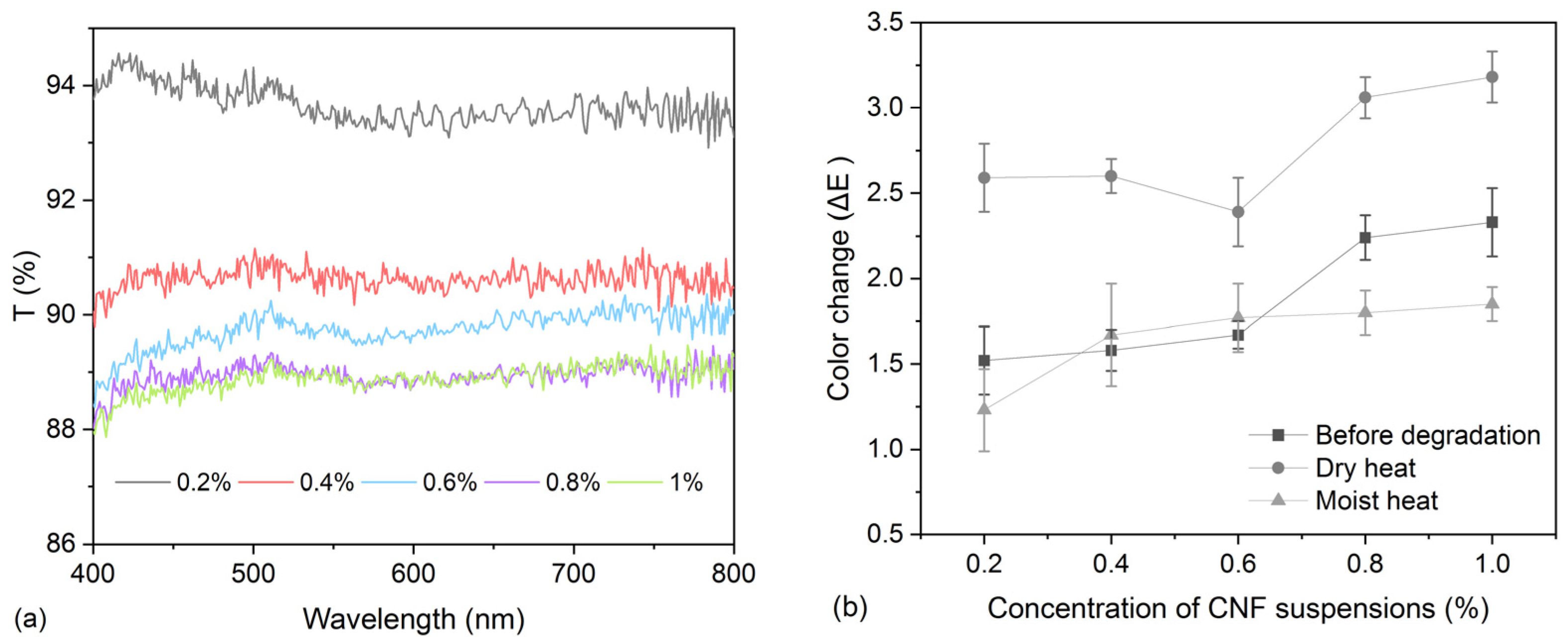
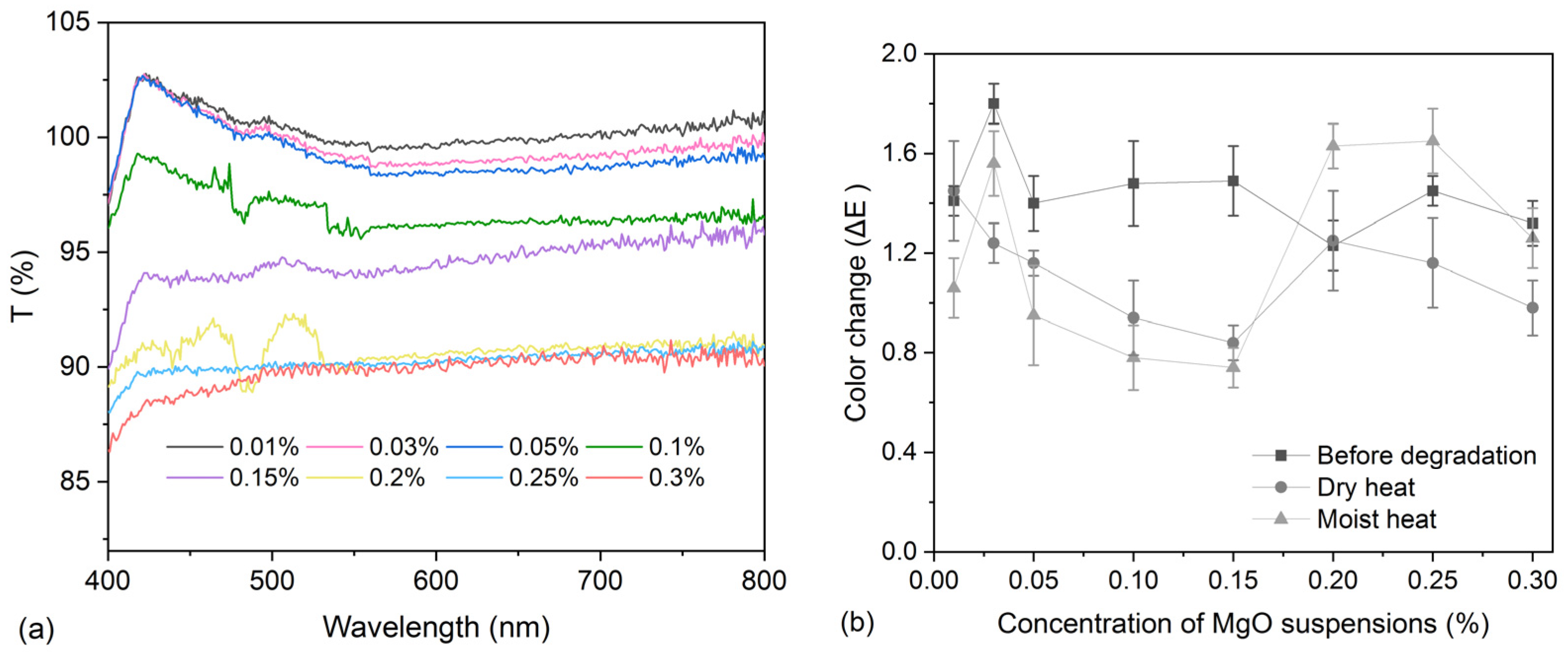
2.4. Colorimetry
2.5. Light Transmittance
2.6. Accelerated Degradation
2.7. Traditional Chinese Conservation Treatment
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Reinforcement for Model Samples
3.2. Deacidification for Model Samples
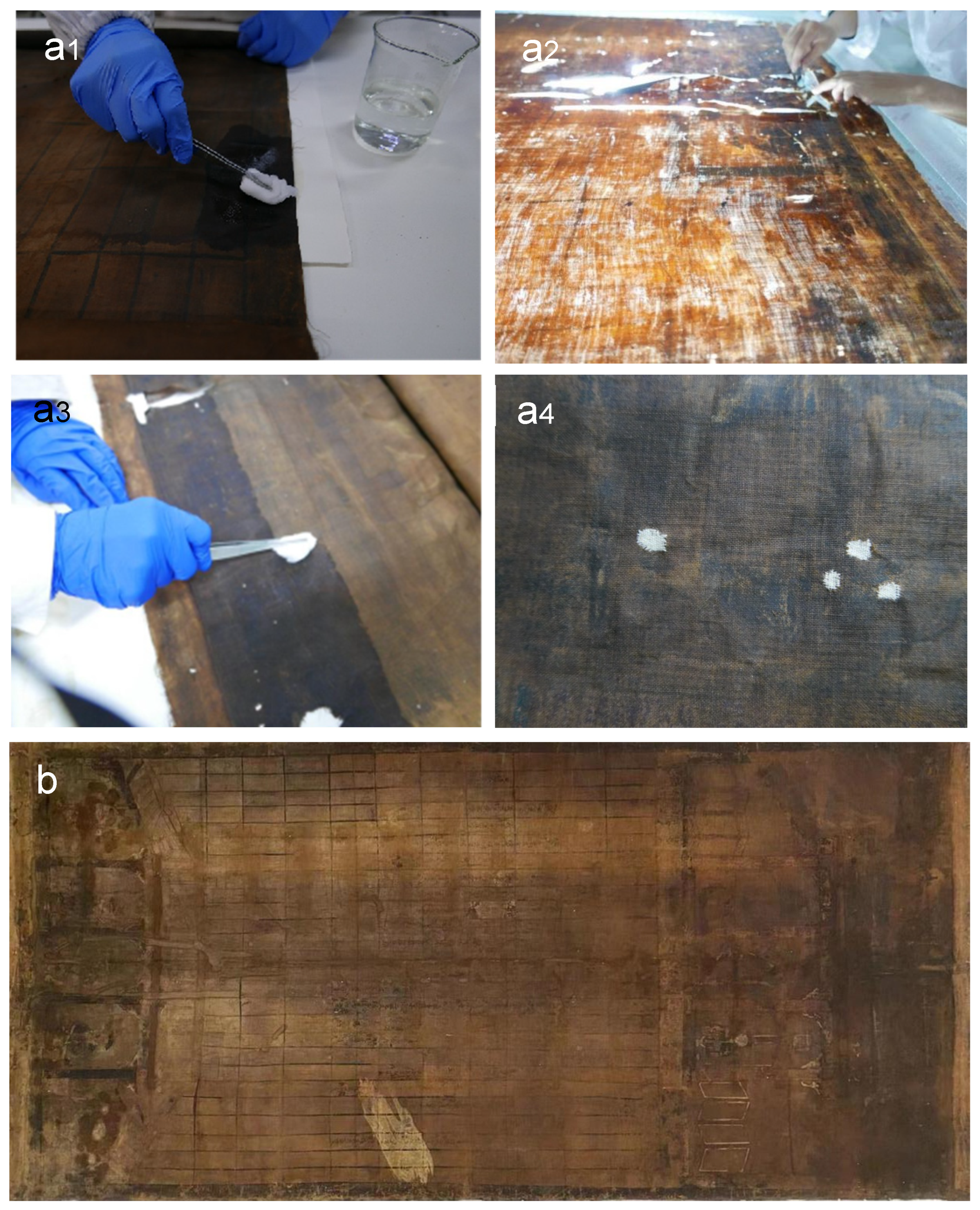
3.3. Conservation Treatment for the Scroll Painting
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, F.; Xing, H.; Wang, J.; Jia, Z.; Chao, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Li, Y. Analytical Investigation of Jiatang Scroll Paintings in the Seventh Year of the Guangxu Era. Coatings 2022, 12, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appelbaum, B. Conservation Treatment Methodology; CreateSpace Independent Publishing Platform: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, H.E.; Kolisis, F.N. An Investigation into the Removal of Starch Paste Adhesives from Historical Textiles by Using the Enzyme α-Amylase. J. Cult. Herit. 2011, 12, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Lin, H.; Chen, Y. Study on Aging Mechanism and Protection of Ancient Silk Textile. J. Soochow Univ. 2007, 27, 60–64. [Google Scholar]
- Schön, M. The Mechanical and Supporting Effect of Stitches in Textile Conservation; University of Gothenburg: Göteborg, Sweden, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, H.E.; Ziddan, Y.E. A New Approach for Conservation Treatment of a Silk Textile in Islamic Art Museum, Cairo. J. Cult. Herit. 2011, 12, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruickshank, P.; Delaunay, H.; Harrison, L. Painted Textiles and Canvas Paintings: A Collaborative Approach to Lining and Mounting. Conservator 2007, 30, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Hu, D.; Xing, H.; Chao, X.; Cao, J.; Jia, Z. A New Method for the Conservation of Ancient Colored Paintings on Ramie Textiles. Herit. Sci. 2021, 9, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Ooij, W.J. Van Surface Modification of Textile Fibers for Improvement of Adhesion to Polymeric Matrices: A Review. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2002, 16, 1715–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palladino, N.; Hacke, M.; Poggi, G.; Nechyporchuk, O.; Kolman, K.; Xu, Q.; Persson, M.; Giorgi, R.; Holmberg, K.; Baglioni, P.; et al. Nanomaterials for Combined Stabilisation and Deacidification of Cellulosic Materials-The Case of Iron-Tannate Dyed Cotton. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peacock, E.E. Deacidification of Degraded Linen. Stud. Conserv. 1983, 28, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbe, M.A.; Henniges, U.; Potthast, A.; Ahn, K.; Smith, R.D. Nonaqueous Solution Deacidification Treatments to Prolong the Storage Life of Acidic Books: A Review of Mechanistic and Process Aspects. BioResources 2019, 13, 7096–7136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, G.B.; Tang, L.C.; Krasnow, M.K. Methylmagnesium Carbonate—An Improved Nonaqueous Deacidification Agent. In Preservation of Paper and Textiles of Historic and Artistic Value; Advances in Chemistry; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1978; Volume 164, pp. 4–62. ISBN 9780841203600. [Google Scholar]
- Giorgi, R.; Dei, L.; Ceccato, M.; Schettino, C.; Baglioni, P. Nanotechnologies for Conservation of Cultural Heritage: Paper and Canvas Deacidification. Langmuir 2002, 18, 8198–8203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malešič, J.; Kadivec, M.; Kunaver, M.; Skalar, T.; Cigić, I.K. Nano Calcium Carbonate versus Nano Calcium Hydroxide in Alcohols as a Deacidification Medium for Lignocellulosic Paper. Herit. Sci. 2019, 7, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheradame, H.; Ipert, S.; Rousset, E. Mass Deacidification of Paper and Books. I: Study of the Limitations of the Gas Phase Processes. Restaurator 2003, 24, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodin, F.W.; Gregersen, Ø.W.; Syverud, K. Cellulose Nanofibrils: Challenges and Possibilities as a Paper Additive or Coating Material—A Review. Nord. Pulp Paper Res. J. 2014, 29, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osong, S.H.; Norgren, S.; Engstrand, P. Processing of Wood-Based Microfibrillated Cellulose and Nanofibrillated Cellulose, and Applications Relating to Papermaking: A Review. Cellulose 2016, 23, 93–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Li, L.; Coseri, S. Cellulose Nanofiber Extraction from Unbleached Kraft Pulp for Paper Strengthening. Cellulose 2023, 30, 3219–3235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biliuta, G.; Dascalu, A.; Stoica, I.; Baron, R.I.; Bejan, D.; Bercea, M.; Coseri, S. Structural and Rheological Insights of Oxidized Cellulose Nanofibers in Aqueous Suspensions. Wood Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 1443–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culica, M.E.; Chibac-Scutaru, A.-L.; Mohan, T.; Coseri, S. Cellulose-Based Biogenic Supports, Remarkably Friendly Biomaterials for Proteins and Biomolecules. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 182, 113170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Lee, S. Characterization of Carbon Nanofiber (CNF)/Polymer Composite Coated on Cotton Fabrics Prepared with Various Circuit Patterns. Fash. Text. 2018, 5, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamada, H.; Mitsuhashi, M. Effect of Cellulose Nanofibers as a Coating Agent for Woven and Nonwoven Fabrics. Nord. Pulp Paper Res. J. 2016, 31, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisuzzo, L.; Cavallaro, G.; Milioto, S.; Lazzara, G. Halloysite Nanotubes Filled with MgO for Paper Reinforcement and Deacidification. Appl. Clay Sci. 2021, 213, 106231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhme, N.; Anders, M.; Reichelt, T.; Schuhmann, K.; Bridarolli, A.; Chevalier, A. New Treatments for Canvas Consolidation and Conservation. Herit. Sci. 2020, 8, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W. The Effect of Aluminum Potassium Sulfate (PAS) on the Durability of Xuan Paper. Sci. Conserv. Archaeol. 2008, 20, 47–50. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 3071; Textiles—Determination of PH of Aqueous Extract. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020.
- ISO 13934-1; Textiles—Tensile Properties of Fabrics—Part 1: Determination of Maximum Force and Elongation at Maximum Force Using the Strip Method. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013.
- Mclaren, K. The Development of the CIE 1976 (L* A* B*) Uniform Colour Space and Colour-difference Formula. J. Soc. Dye. Colour. 1976, 92, 338–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 5631-2; Paper and Board—Determination of Colour by Diffuse Reflectance—Part 2: Outdoor Daylight Conditions (D65/10 Degrees). International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015.
- Larsson, P.T.; Lindström, T.; Carlsson, L.A.; Fellers, C. Fiber Length and Bonding Effects on Tensile Strength and Toughness of Kraft Paper. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 3006–3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichhorn, S.J.; Dufresne, A.; Aranguren, M.; Marcovich, N.E.; Capadona, J.R.; Rowan, S.J.; Weder, C.; Thielemans, W.; Roman, M.; Renneckar, S.; et al. Review: Current International Research into Cellulose Nanofibres and Nanocomposites. J. Mater. Sci. 2010, 45, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinga-Carrasco, G.; Averianova, N.; Gibadullin, M.; Petrov, V.; Leirset, I.; Syverud, K. Micro-Structural Characterisation of Homogeneous and Layered MFC Nano-Composites. Micron 2013, 44, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwiatkowska, A.; Wojech, R.; Wójciak, A. Paper Deacidification with the Use of Magnesium Oxide Nanoparticles. Ann. Wars. Univ. Life Sci.-SGGW For. Wood Technol. 2014, 148, 144–148. [Google Scholar]

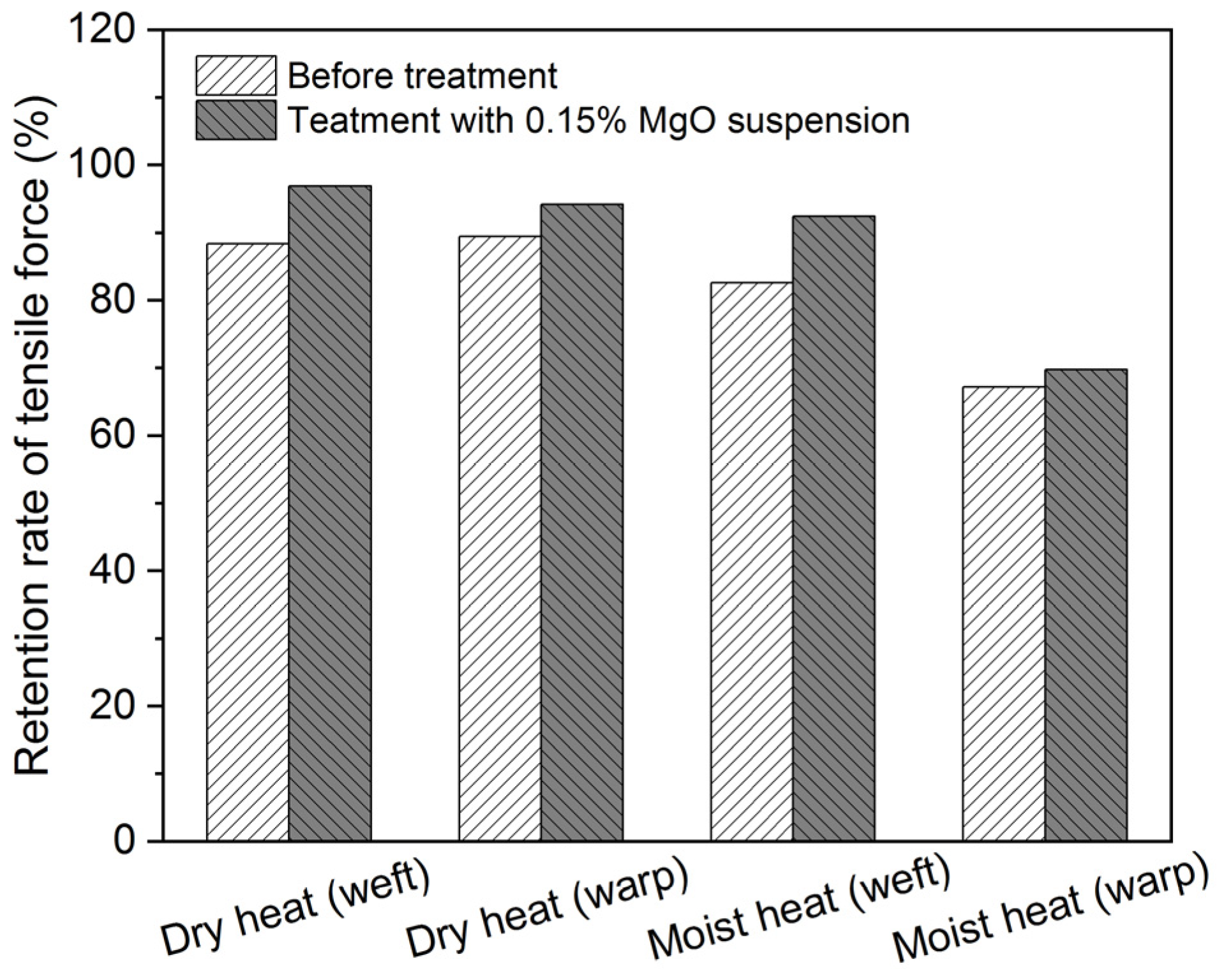
| Treatment Methods | Before Degradation | After Moist Heat | After Dry Heat | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model sample | 4.5 ± 0.1 | 4.4 ± 0.1 | 4.4 ± 0.1 | |
| pH of model samples treated CNF suspensions | 0.2% | 5.6 ± 0.1 | 5.9 ± 0.2 | 5.6 ± 0.1 |
| 0.4% | 5.6 ± 0.2 | 6.3 ± 0.2 | 5.6 ± 0.2 | |
| 0.6% | 5.9 ± 0.3 | 6.3 ± 0.2 | 5.9 ± 0.3 | |
| 0.8% | 6.0 ± 0.2 | 6.4 ± 0.3 | 6.0 ± 0.2 | |
| 1% | 6.1 ± 0.3 | 6.4 ± 0.2 | 6.1 ± 0.3 | |
| Treatment Methods | Before Degradation | After Moist Heat | After Dry Heat | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNF sample | 6.5 ± 0.3 | 6.3 ± 0.2 | 5.9 ± 0.3 | |
| The CNF sample treated with a series of concentrations of nanosized MgO suspensions | 0.01% MgO | 7.4 ± 0.2 | 6.8 ± 0.2 | 6.5 ± 0.1 |
| 0.03% MgO | 8.0 ± 0.1 | 7.6 ± 0.2 | 7.2 ± 0.2 | |
| 0.05% MgO | 8.4 ± 0.2 | 8.2 ± 0.1 | 8.2 ± 0.2 | |
| 0.1% MgO | 8.7 ± 0.1 | 8.7 ± 0.3 | 8.6 ± 0.2 | |
| 0.15% MgO | 9.4 ± 0.1 | 9.1 ± 0.2 | 9.2 ± 0.2 | |
| 0.2% MgO | 9.9 ± 0.2 | 9.6 ± 0.1 | 9.4 ± 0.3 | |
| 0.25% MgO | 9.8 ± 0.2 | 9.7 ± 0.2 | 9.6 ± 0.1 | |
| 0.3% MgO | 9.7 ± 0.2 | 9.6 ± 0.1 | 9.2 ± 0.1 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, H.; Zhao, F.; Qi, Y.; Jia, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Chao, X.; Shi, M.; Luo, Y.; Xing, H. Reinforcement and Deacidification for a Textile Scroll Painting (AD 1881) Using the CNF and MgO Suspensions. Polymers 2024, 16, 946. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16070946
Wei H, Zhao F, Qi Y, Jia Z, Zhou Y, Chao X, Shi M, Luo Y, Xing H. Reinforcement and Deacidification for a Textile Scroll Painting (AD 1881) Using the CNF and MgO Suspensions. Polymers. 2024; 16(7):946. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16070946
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Hanyu, Fangnan Zhao, Yunpeng Qi, Zhihui Jia, Yajun Zhou, Xiaolian Chao, Meirong Shi, Yujia Luo, and Huiping Xing. 2024. "Reinforcement and Deacidification for a Textile Scroll Painting (AD 1881) Using the CNF and MgO Suspensions" Polymers 16, no. 7: 946. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16070946
APA StyleWei, H., Zhao, F., Qi, Y., Jia, Z., Zhou, Y., Chao, X., Shi, M., Luo, Y., & Xing, H. (2024). Reinforcement and Deacidification for a Textile Scroll Painting (AD 1881) Using the CNF and MgO Suspensions. Polymers, 16(7), 946. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16070946






