Magnetic Carbon Porous Polymer Prepared from a New Suspended Emulsion for the Absorption of Heavy Metal Ions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Starting Materials
2.2. Instruments
2.3. Synthesis of the Magnetic Carbon Nanopolymer
2.3.1. Formulation of Carbon Nanosuspensions
2.3.2. Synthesis of Magnetizable Carbon Nanoparticles
2.3.3. Fabrication of Carbon-Based Magnetic Polymer Nanocomposites
2.4. Adsorption Experiment
2.5. Regeneration Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
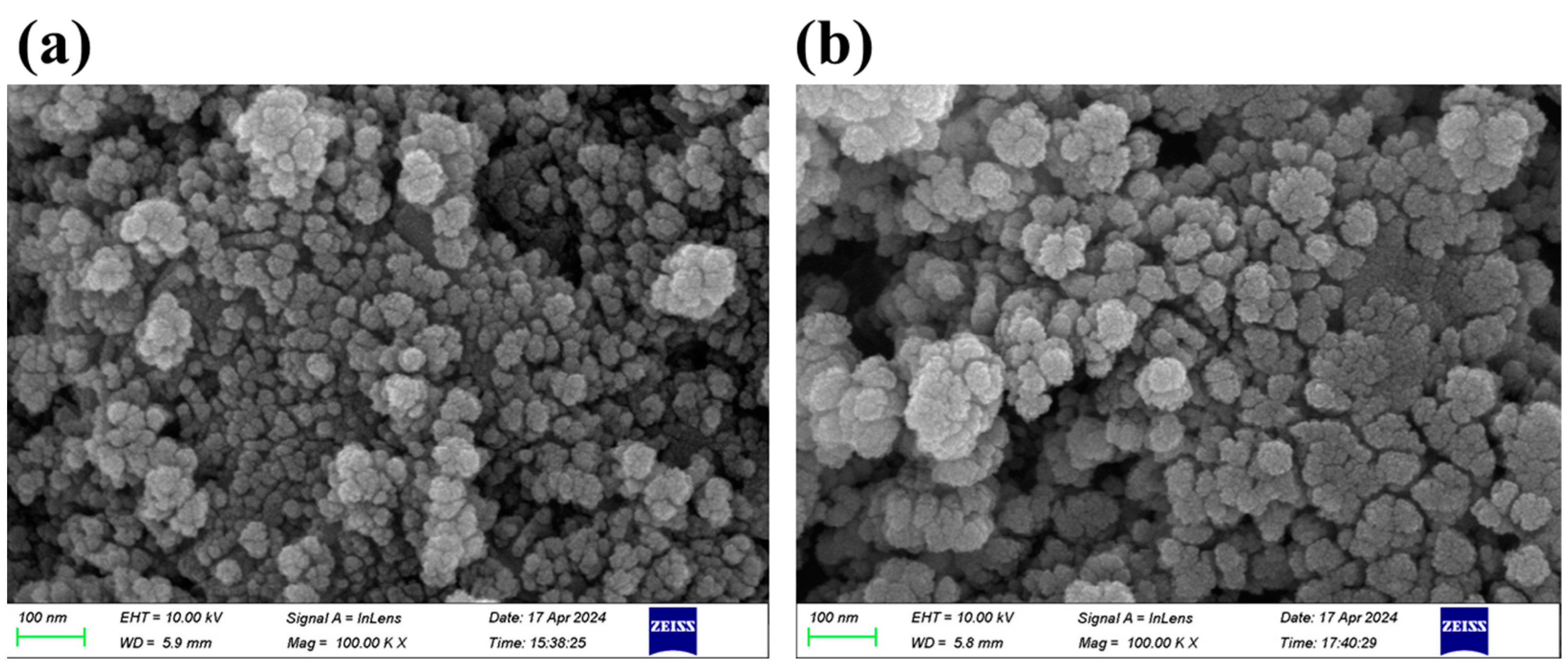
3.1. Characterization of Fe3O4/C and Fe3O4/C@PM
3.2. Adsorption of Fe3O4/C@PM
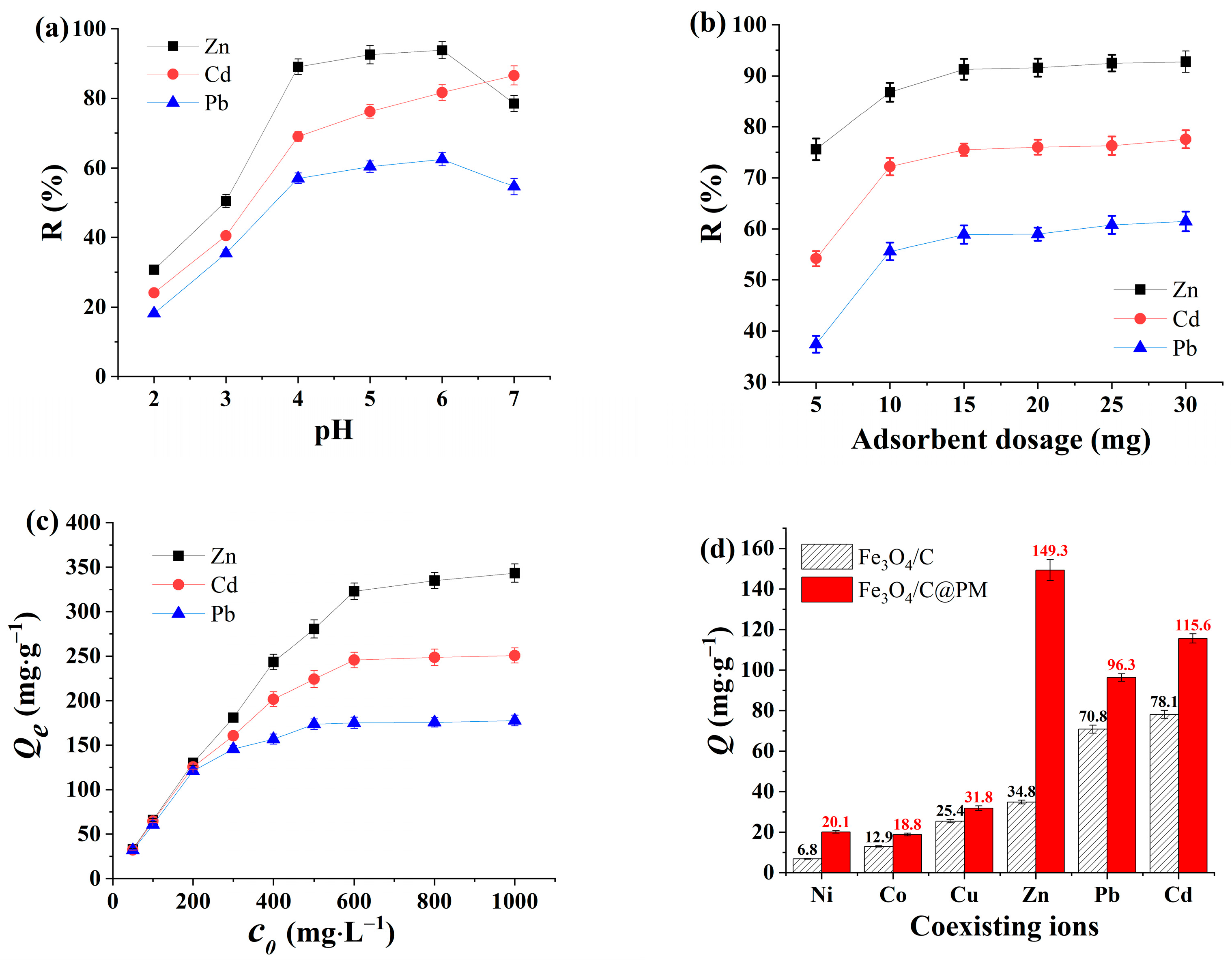
3.2.1. Influence of pH Value
3.2.2. Impact of Varying Concentrations of Fe3O4/C@PM on Removal Efficacy
3.2.3. Effect of Initial Concentration of Heavy Metal Pollutants
3.2.4. Selectivity of Adsorption
3.2.5. Analysis of Adsorption Isotherms
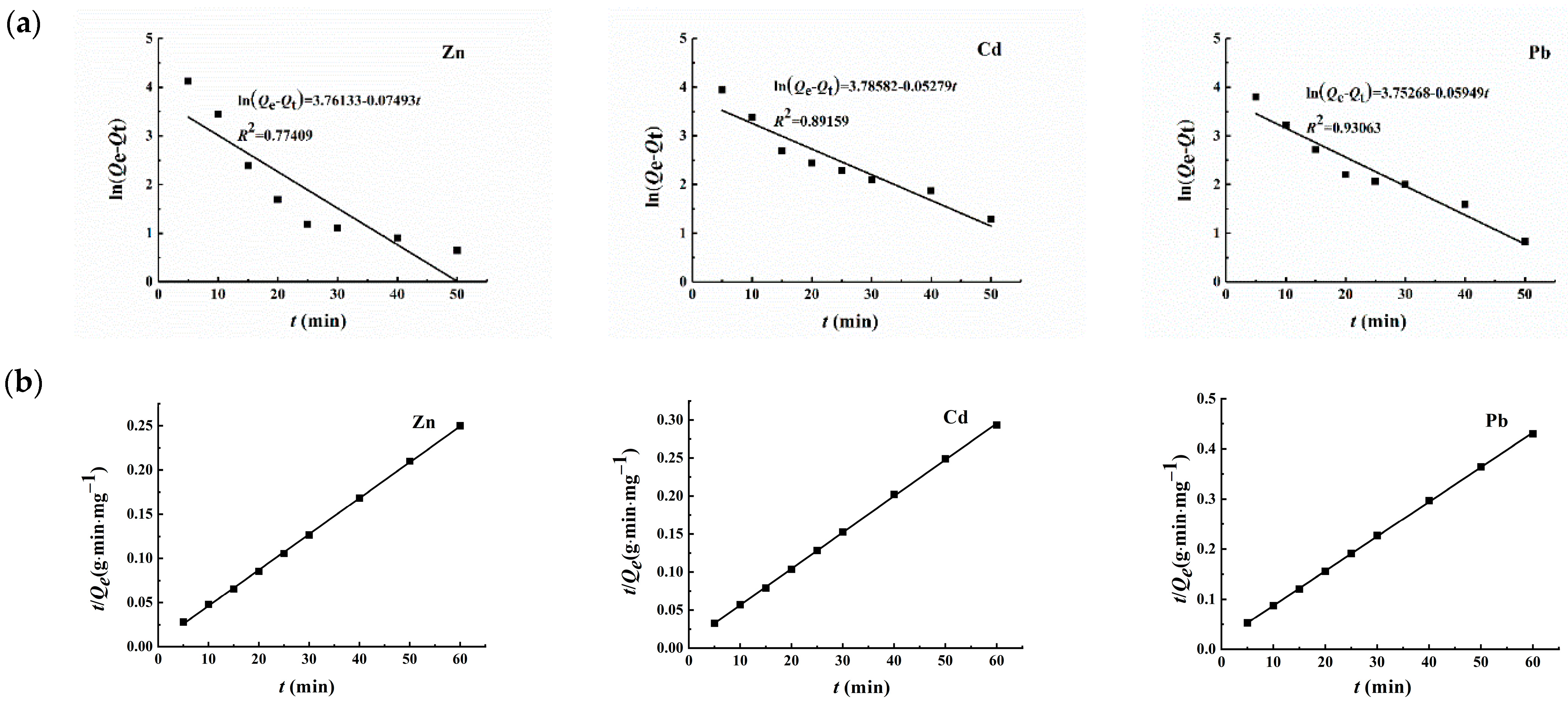
3.2.6. Analysis of Adsorption Kinetics
3.3. Desorption and Reuse
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dutta, D.; Arya, S.; Kumar, S. Industrial wastewater treatment: Current trends, bottlenecks, and best practices. Chemosphere 2021, 285, 131245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qasem, N.A.A.; Mohammed, R.H.; Lawal, D.U. Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewater: A comprehensive and critical review. NPJ Clean Water 2021, 4, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haidar, Z.; Fatema, K.; Shoily, S.S.; Sajib, A.A. Disease-associated metabolic pathways affected by heavy metals and metalloid. Toxicol. Rep. 2023, 10, 554–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Osman, M.; Yang, F.; Massey, I.Y. Exposure routes and health effects of heavy metals on children. BioMetals 2019, 32, 563–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benalia, M.C.; Youcef, L.; Bouaziz, M.G.; Achour, S.; Menasra, H. Removal of Heavy Metals from Industrial Wastewater by Chemical Precipitation: Mechanisms and Sludge Characterization. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2022, 47, 5587–5599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.-K.; Chiu, K.-F.; Lin, C.-Y.; Leu, H.-J. Electrochemical treatment of wastewater: Selectivity of the heavy metals removal process. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 27741–27748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.-J.; Jiang, S.-K.; Chao, X.-Y.; Zhang, C.-X.; Shi, Q.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Liu, M.-L.; Sun, S.-P. Removing miscellaneous heavy metals by all-in-one ion exchange-nanofiltration membrane. Water Res. 2022, 222, 118888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Wu, Y.; Chen, G.; Zheng, X.; Dai, M.; Peng, C. Metal-organic framework membranes: Recent development in the synthesis strategies and their application in oil-water separation. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 405, 127004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadila, C.R.; Othman, M.H.D.; Adam, M.R.; Takagi, R.; Yoshioka, T.; Khongnakorn, W.; Rahman, M.A.; Jaafar, J.; Ismail, A.F. Adsorptive membrane for heavy metal removal: Material, fabrication, and performance. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 65, 3037–3045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, S.A.; Bashir, O.; Ul Haq, S.A.; Amin, T.; Rafiq, A.; Ali, M.; Américo-Pinheiro, J.H.P.; Sher, F. Phytoremediation of heavy metals in soil and water: An eco-friendly, sustainable and multidisciplinary approach. Chemosphere 2022, 303, 134788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobielska, P.A.; Howarth, A.J.; Farha, O.K.; Nayak, S. Metal–organic frameworks for heavy metal removal from water. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2018, 358, 92–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MiarAlipour, S.; Friedmann, D.; Scott, J.; Amal, R. TiO2/porous adsorbents: Recent advances and novel applications. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 341, 404–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.; Li, H.; Liu, Y.; Song, S. A review on heavy metal ions adsorption from water by graphene oxide and its composites. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 230, 496–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassyouni, M.; Mansi, A.E.; Elgabry, A.; Ibrahim, B.A.; Kassem, O.A.; Alhebeshy, R. Utilization of carbon nanotubes in removal of heavy metals from wastewater: A review of the CNTs’ potential and current challenges. Appl. Phys. A 2019, 126, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, B.; Tao, X.; Wang, H.; Li, W.; Ding, X.; Chu, H. Biochar as a low-cost adsorbent for aqueous heavy metal removal: A review. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2021, 155, 105081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godwin, P.M.; Pan, Y.; Xiao, H.; Afzal, M.T. Progress in Preparation and Application of Modified Biochar for Improving Heavy Metal Ion Removal From Wastewater. J. Bioresour. Bioprod. 2019, 4, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, H.-X. Modified-biochar adsorbents (MBAs) for heavy-metal ions adsorption: A critical review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacinto, M.J.; Prescilio, I.C.; Abe, S.H.M. Magnetic-based adsorbing platforms for water and wastewater purification. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 21, 5865–5882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.S.A.; Mubarak, N.M.; Khalid, M.; Walvekar, R.; Abdullah, E.C.; Mazari, S.A.; Nizamuddin, S.; Karri, R.R. Magnetic nanoadsorbents’ potential route for heavy metals removal—A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 24342–24356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.-Z.; Xu, N.; Yang, X.-A.; Zhang, W.-B. Acoustic-Dependent Enhanced Functionalized Magnetic Nanomaterials for Purification of Chromium Containing Water. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2024, 7, 17512–17523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhu, Y.; Ma, L.; Hai, X.; Li, X.; Yang, Z.; Gao, Y.; Yuan, M.; Xiong, H.; Chen, M.; et al. Efficient removal of Chromium(VI) from wastewater based on magnetic multiwalled carbon nanotubes coupled with deep eutectic solvents. Chemosphere 2024, 362, 142732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervera-Gabalda, L.; Gómez-Polo, C. Magnetic carbon Fe3O4 nanocomposites synthesized via Magnetic Induction Heating. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 7244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, S.; Zhang, F.; Li, D.; Jiao, P. Highly efficient and selective removal of cadmium from aqueous solutions based on magnetic graphitic carbon nitride materials with molecularly imprinted polymers. J. Mol. Struct. 2020, 1221, 128887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokadem, Z.; Saidi-Besbes, S.; Lebaz, N.; Elaissari, A. Magnetic monolithic polymers prepared from high internal phase emulsions and Fe3O4 triazole-functionalized nanoparticles for Pb2+, Cu2+ and Zn2+ removal. React. Funct. Polym. 2020, 155, 104693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, F.; Wang, A. Monolithic supermacroporous hydrogel prepared from high internal phase emulsions (HIPEs) for fast removal of Cu2+ and Pb2+. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 284, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Qiu, T.; Guo, L.; Ye, J.; He, L.; Li, X. Polymerization induced shaping of Pickering emulsion droplets: From simple hollow microspheres to molecularly imprinted multicore microrattles. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 332, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.; Li, G.; Liu, Y.; Wei, S.; Wang, H.; Huang, X.; Luo, Z. Electrochemical detection of pyridoxal using a sonoelectrochemical prepared highly-oxidized carbon nanosheets modified electrode. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 274, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, B.; Duan, P. Preparation and characterization of floating porous graphite carbon monoliths produced from biomass and its application. E3S Web Conf. 2020, 194, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awokoya, K.N.; Okoya, A.A.; Elujulo, O. Preparation, characterization and evaluation of a styrene-based molecularly imprinted polymer for capturing pyridine and pyrrole from crude oil. Sci. Afr. 2021, 13, e00947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Lu, Y.; Luo, G. Ca(II) imprinted chitosan microspheres: An effective and green adsorbent for the removal of Cu(II), Cd(II) and Pb(II) from aqueous solutions. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 244, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poon, L.; Wilson, L.D.; Headley, J.V. Chitosan-glutaraldehyde copolymers and their sorption properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 109, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Zhan, X.; Wen, C.; Xu, F.; Luo, L. Amino-functionalized magnetic bacterial cellulose/activated carbon composite for Pb2+ and methyl orange sorption from aqueous solution. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2018, 34, 855–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Geng, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Ren, L.; Tao, T.; Yang, R.; Guo, Z. Synthesis of Magnetic Fe3O4@C Nanoparticles Modified with –SO3H and –COOH Groups for Fast Removal of Pb2+, Hg2+, and Cd2+ Ions. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 2014, 3172–3177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzoor, Q.; Farrukh, M.A.; Qamar, M.T.; Sajid, A.; Aldossari, S.A.; Manikandan, A.; Iqbal, M. Polymer-assisted synthesis of ternary magnetic graphene oxide nanocomposite for the adsorptive removal of Cr(VI) and Pb(II) ions. Heliyon 2024, 10, e35204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habila, M.A.; ALOthman, Z.A.; El-Toni, A.M.; Labis, J.P.; Khan, A.; Al-Marghany, A.; Elafifi, H.E. One-Step Carbon Coating and Polyacrylamide Functionalization of Fe3O4 Nanoparticles for Enhancing Magnetic Adsorptive-Remediation of Heavy Metals. Molecules 2017, 22, 2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, A.; Rais, S. A facile approach for grafting ion imprinted polymer onto magnetic multi-walled carbon nanotubes for selective removal and preconcentration of cadmium in food and wastewater samples prior to atomic spectrometric determination. Food Chem. 2023, 405, 134751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



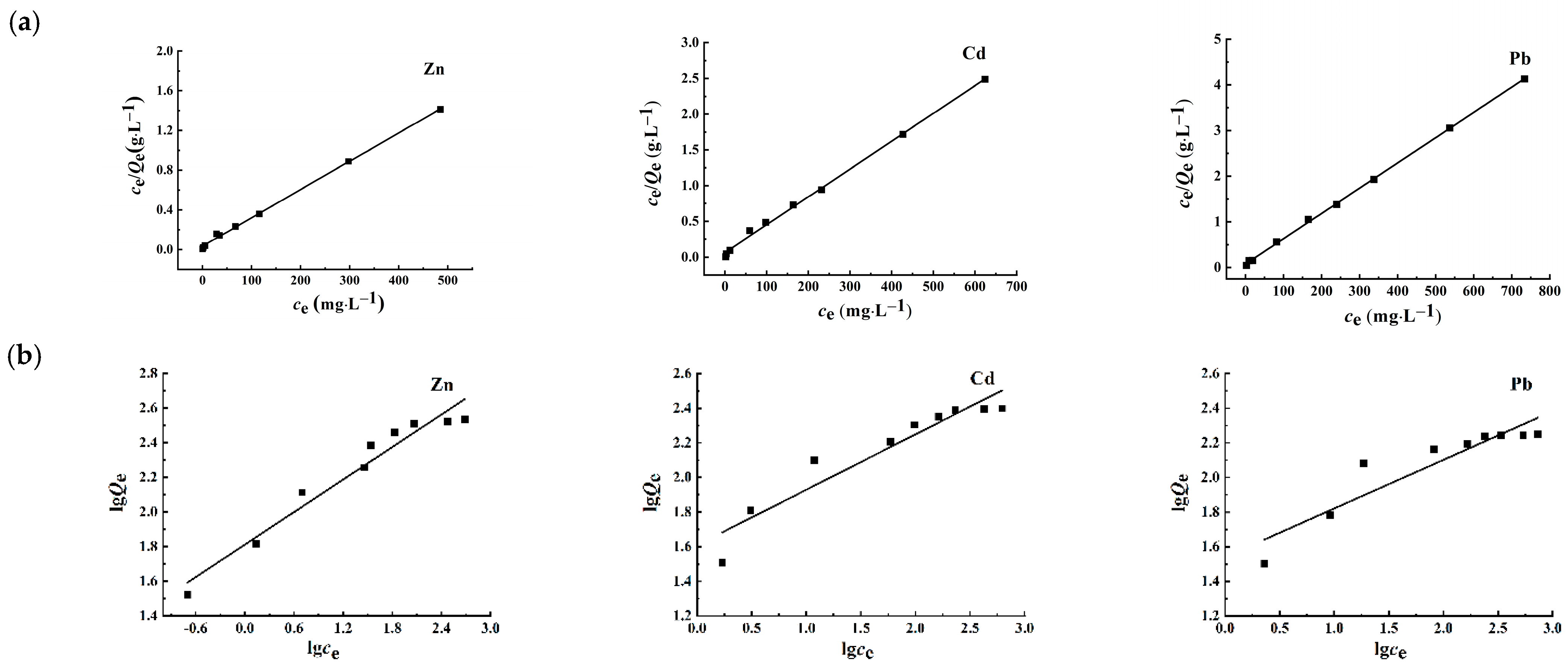

| Metal Ion | Langmuir | Freundlich | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qm/(mg·g−1) | KL/(min−1) | R2 | 1/n | KF/(mg·g−1·min−1) | R2 | |
| Zn2+ | 349.65 | 0.0853 | 0.9980 | 0.31315 | 64.916 | 0.9488 |
| Cd2+ | 256.41 | 0.0619 | 0.9972 | 0.32003 | 40.635 | 0.8922 |
| Pb2+ | 180.83 | 0.0702 | 0.9994 | 0.28106 | 34.657 | 0.8401 |
| Adsorbent | Preparation Method | Qm (mg·g−1) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Magnetic graphitic carbon nitride | Multi-step and surface imprinting technology | 258.35 for Cd2+ | [23] |
| Fe3O4/BC/AC | Multi-step reaction | 161.78 for Pb2+ | [32] |
| Fe3O4@C nanoparticles modified with–SO3H and –COOH Groups | Multi-step reaction | 90.7, 83.1 and 39.7 mg·g−1 for Pb2+, Hg2+ and Cd2+ | [33] |
| mGO/CS mGO/PA | Multi-step reaction | 110.84 and 118.44 mg·g−1 for Pb2+ were obtained for mGO/CS and mGO/PA | [34] |
| Carbon coating and polyacrylamide functionalization of Fe3O4 nanoparticles | Hydrothermal technique | 231.7 mg·g−1 for Cd2+ | [35] |
| 3D Fe3O4@MWCNT-CdIIP | Multi-step reaction | 109 mg·g−1 for Cd2+ | [36] |
| Fe3O4/C@PM | Suspension polymerization | 349.65, 256.41, 180.83 mg·g−1 for Zn2+, Cd2+, Pb2+ | This work |
| Metal Ion | Quasi-First-Order | Quasi-Second-Order | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qe (mg·g−1) | K1 (min−1) | R2 | Qe (mg·g−1) | K2 (mg·g−1·min−1) | R2 | |
| Zn2+ | 42.98 | 0.07493 | 0.77409 | 246.3 | 0.00291 | 0.99959 |
| Cd2+ | 44.04 | 0.05279 | 0.89159 | 209.2 | 0.00260 | 0.99975 |
| Pb2+ | 42.60 | 0.05949 | 0.93063 | 144.9 | 0.00258 | 0.99983 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, S.; Huang, S.; Zhou, J.; Xiao, C.; Cao, J.; Xiao, J.; Xie, C. Magnetic Carbon Porous Polymer Prepared from a New Suspended Emulsion for the Absorption of Heavy Metal Ions. Polymers 2025, 17, 257. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17030257
Wei S, Huang S, Zhou J, Xiao C, Cao J, Xiao J, Xie C. Magnetic Carbon Porous Polymer Prepared from a New Suspended Emulsion for the Absorption of Heavy Metal Ions. Polymers. 2025; 17(3):257. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17030257
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Shoulian, Shenwei Huang, Jun Zhou, Chun Xiao, Jiangfei Cao, Jibo Xiao, and Chunsheng Xie. 2025. "Magnetic Carbon Porous Polymer Prepared from a New Suspended Emulsion for the Absorption of Heavy Metal Ions" Polymers 17, no. 3: 257. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17030257
APA StyleWei, S., Huang, S., Zhou, J., Xiao, C., Cao, J., Xiao, J., & Xie, C. (2025). Magnetic Carbon Porous Polymer Prepared from a New Suspended Emulsion for the Absorption of Heavy Metal Ions. Polymers, 17(3), 257. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17030257






