Advancements in Cellulose-Based Materials for CO2 Capture and Conversion
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Cellulose Structure and Properties
2.1. Relationship Between Structure and Properties
2.2. Biodegradability and Sustainability
2.3. Abundance in Nature and Cost-Effectiveness
3. CO2 Capture Technologies
3.1. Post-Combustion Capture
3.2. Pre-Combustion Capture
3.3. Direct Air Capture (DAC) Technologies
3.4. Industrial Applications and Challenges
4. Need for Sustainable Adsorbents
Advantages of Cellulose-Based Materials
5. Design and Synthesis of Cellulose-Based Adsorbents
5.1. Chemical Functionalization
5.2. Modifications for Enhanced Performance
6. Synthesis Methods
Incorporation of Additives and Modifiers
7. Surface Modification for Selective CO2 Capture
7.1. Tailoring Surface Properties for Improved Adsorption
7.2. Functionalization Methods and Their Impact on Selectivity
8. Advances in Controlling Surface Chemistry
9. Applications of Cellulose-Based Materials in CO2 Capture
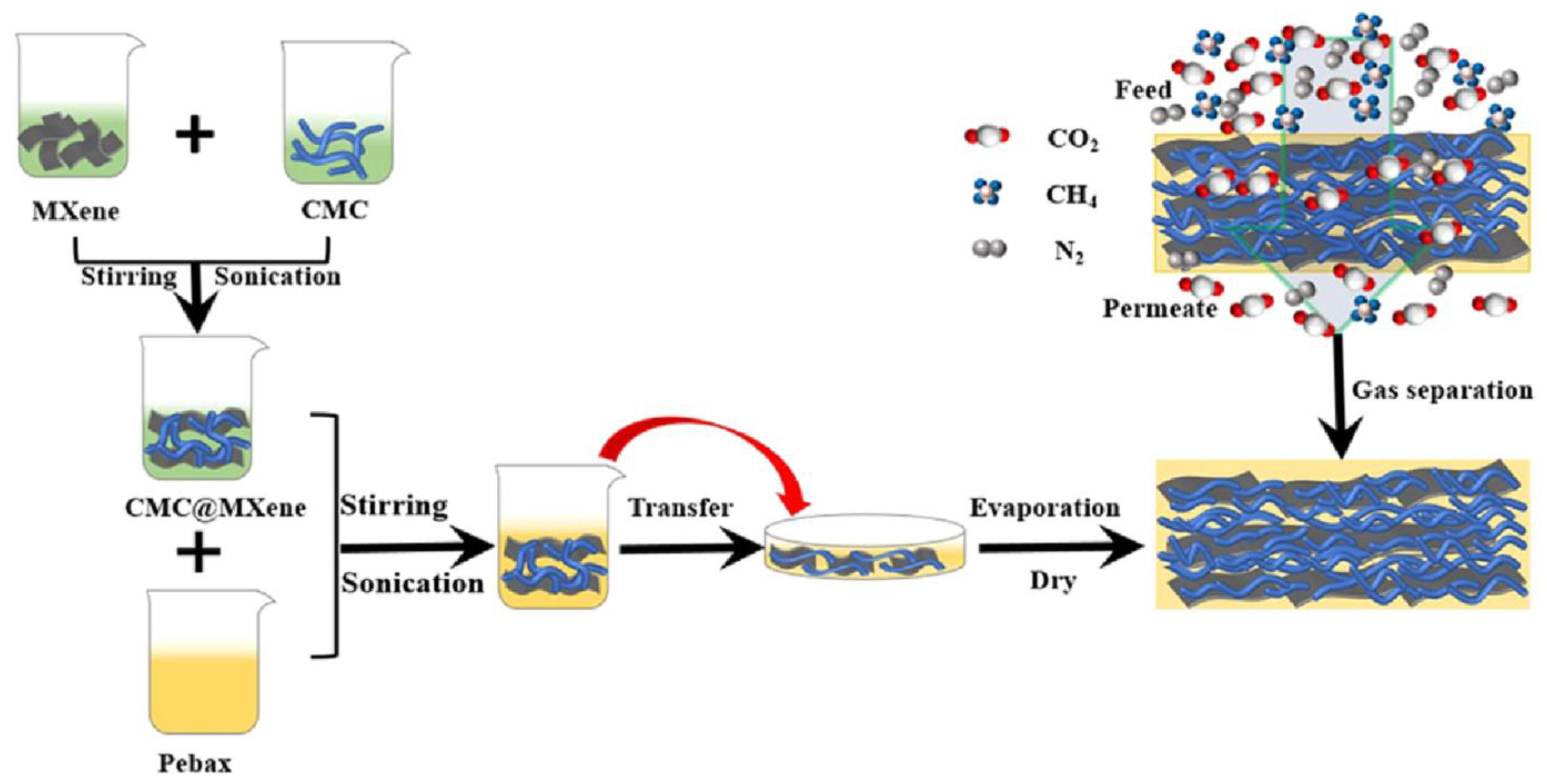
9.1. Composite Film
9.2. Composite Aerogel
9.3. Composite Solid Adsorbents
9.4. Technology Readiness Level (TRL) of Cellulose-Based Adsorbents
10. Cellulose Composites in Carbon Conversion
10.1. Carbonate Salts
10.2. Formic Acid and Methanol
10.3. Carbon Monoxide
11. Challenges and Future Directions
12. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pr Shukla, A.R.; Skea, J. Climate Change 2022 Mitigation of Climate Change-Summary for Policymakers Sixth Assessment Report (WG3). 2022. Available online: https://www.ipcc.ch/report/ar6/wg2/ (accessed on 1 January 2025).
- Rockström, J.; Gaffney, O.; Rogelj, J.; Meinshausen, M.; Nakicenovic, N.; Schellnhuber, H.J. A roadmap for rapid decarbonization. Science 2017, 355, 1269–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Yang, S.; Hu, L.; Cai, S.; Wu, L.; Kawi, S. Carbonaceous materials as adsorbents for CO2 capture: Synthesis and modification. Carbon Capture Sci. Technol. 2022, 3, 100039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hack, J.; Maeda, N.; Meier, D.M. Review on CO2 Capture Using Amine-Functionalized Materials. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 39520–39530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.W. Recent Developments in CO2 Capture and Conversion. JACS Au 2023, 3, 1536–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Gipson, R.; Wang, C.; Zhang, S.X.; Guddati, S.; Mui, S.; Nai, L. Emerging 3D-printed zeolitic gas adsorbents. Mater. Sci. Addit. Manuf. 2023, 2, 1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saqer, H.; El-fattah, A.A.; Kamel, A.H. Carbon Capture Materials in Post-Combustion: Adsorption and Absorption-Based Processes. J. Carbon Res. 2023, 9, 17. [Google Scholar]
- D’Alessandro, D.M.; Smit, B.; Long, J.R. Carbon dioxide capture: Prospects for new materials. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 6058–6082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhamid, H.N.; Sultan, S.; Mathew, A.P. Three-Dimensional Printing of Cellulose/Covalent Organic Frameworks (CelloCOFs) for CO2 Adsorption and Water Treatment. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 59795–59805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, M.; Flaig, R.W.; Jiang, H.L.; Yaghi, O.M. Carbon capture and conversion using metal-organic frameworks and MOF-based materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 2783–2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khdary, N.H.; Alayyar, A.S.; Alsarhan, L.M.; Alshihri, S.; Mokhtar, M. Metal Oxides as Catalyst/Supporter for CO2 Capture and Conversion, Review. Catalysts 2022, 12, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebald, C.; Wurzbacher, J.A.; Tingaut, P.; Steinfeld, A. Stability of amine-functionalized cellulose during temperature-vacuum-swing cycling for CO2 capture from air. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 10063–10070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anirudhan, T.S.; Jalajamony, S.; Divya, L. Efficiency of amine-modified poly(glycidyl methacrylate)-grafted cellulose in the removal and recovery of vanadium(V) from aqueous solutions. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2009, 48, 2118–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemm, D.; Heublein, B.; Fink, H.P.; Bohn, A. Cellulose: Fascinating biopolymer and sustainable raw material. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 3358–3393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samir, A.; Ashour, F.H.; Hakim, A.A.A.; Bassyouni, M. Recent advances in biodegradable polymers for sustainable applications. npj Mater. Degrad. 2022, 6, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Xu, T.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, K.; Liang, D.; Si, C. Cellulose-based materials for carbon capture and conversion. Carbon Capture Sci. Technol. 2023, 10, 100157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y. Catalytic transformation of cellulose and its derived carbohydrates into chemicals involving C-C bond cleavage. J. Energy Chem. 2015, 24, 595–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segneri, V.; Trinca, A.; Libardi, N.; Colelli, L.; Micciancio, M.; Vilardi, G. Nanoparticles used for CO2 Capture by Adsorption: A Review. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2023, 101, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sifat, N.S.; Haseli, Y. A critical review of CO2 capture technologies and prospects for clean power generation. Energies 2019, 12, 4143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keith, D.W.; Holmes, G.; St. Angelo, D.; Heidel, K. A Process for Capturing CO2 from the Atmosphere. Joule 2018, 2, 1573–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz-Pérez, E.S.; Murdock, C.R.; Didas, S.A.; Jones, C.W. Direct Capture of CO2 from Ambient Air. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 11840–11876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Fu, R.; Wen, S.; Ning, P.; Helal, M.H.; Salem, M.A.; Xu, B.B.; El-Bahy, Z.M.; Huang, M.; Guo, Z.; et al. Progress and current challenges for CO2 capture materials from ambient air. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2022; 5, 2721–2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McQueen, N.; Gomes, K.V.; McCormick, C.; Blumanthal, K.; Pisciotta, M.; Wilcox, J. A review of direct air capture (DAC): Scaling up commercial technologies and innovating for the future. Prog. Energy 2021, 3, 32001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Pauzi, M.M.; Azmi, N.; Lau, K.K. Emerging Solvent Regeneration Technologies for CO2 Capture through Offshore Natural Gas Purification Processes. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alivand, M.S.; Mazaheri, O.; Wu, Y.; Stevens, W.; Scholes, C.A.; Mumford, K.A. Catalytic Solvent Regeneration for Energy-Efficient CO2 Capture. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 18755–18788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.X.; Li, J.C.; Wang, Y.; Guo, Y.R.; Li, S.; Pan, Q.J. An environment-friendly technique for direct air capture of carbon dioxide via a designed cellulose and calcium system. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 307, 122774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Xu, Z.; Fan, M.; Gupta, R.; Slimane, R.B.; Bland, A.E.; Wright, I. Progress in carbon dioxide separation and capture: A review. J. Environ. Sci. 2008, 20, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Sun, Y.; Liu, L. Recent advances in biochar-based adsorbents for CO2 capture. Carbon Capture Sci. Technol. 2022, 4, 100059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussin, F.; Kiat, L.B.; Yusoff, R.; Aroua, M.K. A breakthrough adsorption study of modified activated carbon using different environmentally-friendly activating agents. Environ. Eng. Res. 2024, 29, 230005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Srivastava, R.; Koh, J. Utilization of zeolites as CO2capturing agents: Advances and future perspectives. J. CO2 Util. 2020, 41, 101251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaraweera, S.M.; Gunathilake, C.A.; Gunawardene, O.H.P.; Dassanayake, R.S.; Cho, E.B.; Du, Y. Carbon Capture Using Porous Silica Materials. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Zhou, S.; Strømme, M.; Xu, C. All-cellulose-based freestanding porous carbon nanocomposites and their versatile applications. Compos. Part B Eng. 2022, 232, 109602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Du, H.; Liu, H.; Xie, H.; Xu, T.; Zhao, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Si, C. Highly Efficient and Sustainable Preparation of Carboxylic and Thermostable Cellulose Nanocrystals via FeCl3-Catalyzed Innocuous Citric Acid Hydrolysis. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 16691–16700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, F.L.; Rodrigues, D.M.; Polesso, B.B.; Donato, A.J.; Seferin, M.; Chaban, V.V.; Vecchia, F.D.; Einloft, S. New cellulose based ionic compounds as low-cost sorbents for CO2 capture. Fuel Process. Technol. 2016, 149, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Du, H.; Liu, K.; Liu, H.; Xie, H.; Si, C.; Pang, B.; Zhang, X. Sustainable preparation of cellulose nanofibrils via choline chloride-citric acid deep eutectic solvent pretreatment combined with high-pressure homogenization. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 267, 118220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, Y.; Pudukudy, M.; Zhi, Y.; Miao, Y.; Shan, S.; Jia, Q.; Ni, Y. A facile method for in situ fabrication of silica/cellulose aerogels and their application in CO2 capture. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 236, 116079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, S.; Bernard, F.L.; Rodrigues, D.M.; Rojas, M.F.; Carreño, L.Á.; Chaban, V.V.; Einloft, S. Performance of metal-functionalized rice husk cellulose for CO2 sorption and CO2/N2 separation. Fuel 2019, 239, 737–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köse, K.; Mavlan, M.; Youngblood, J.P. Applications and impact of nanocellulose based adsorbents. Cellulose 2020, 27, 2967–2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Yang, H.; Liu, K.; Xu, T.; Chen, J.; Xie, H.; Du, H.; Dai, L.; Si, C. Cellulose nanofibril aerogels reinforcing polymethyl methacrylate with high optical transparency. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2023, 6, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunnarsson, M.; Bernin, D.; Östlund, Å.; Hasani, M. The CO2 capturing ability of cellulose dissolved in NaOH(aq) at low temperature. Green Chem. 2018, 20, 3279–3286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, N.A.D.; Leo, C.P. A review on the emerging applications of cellulose, cellulose derivatives and nanocellulose in carbon capture. Environ. Res. 2021, 197, 111100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
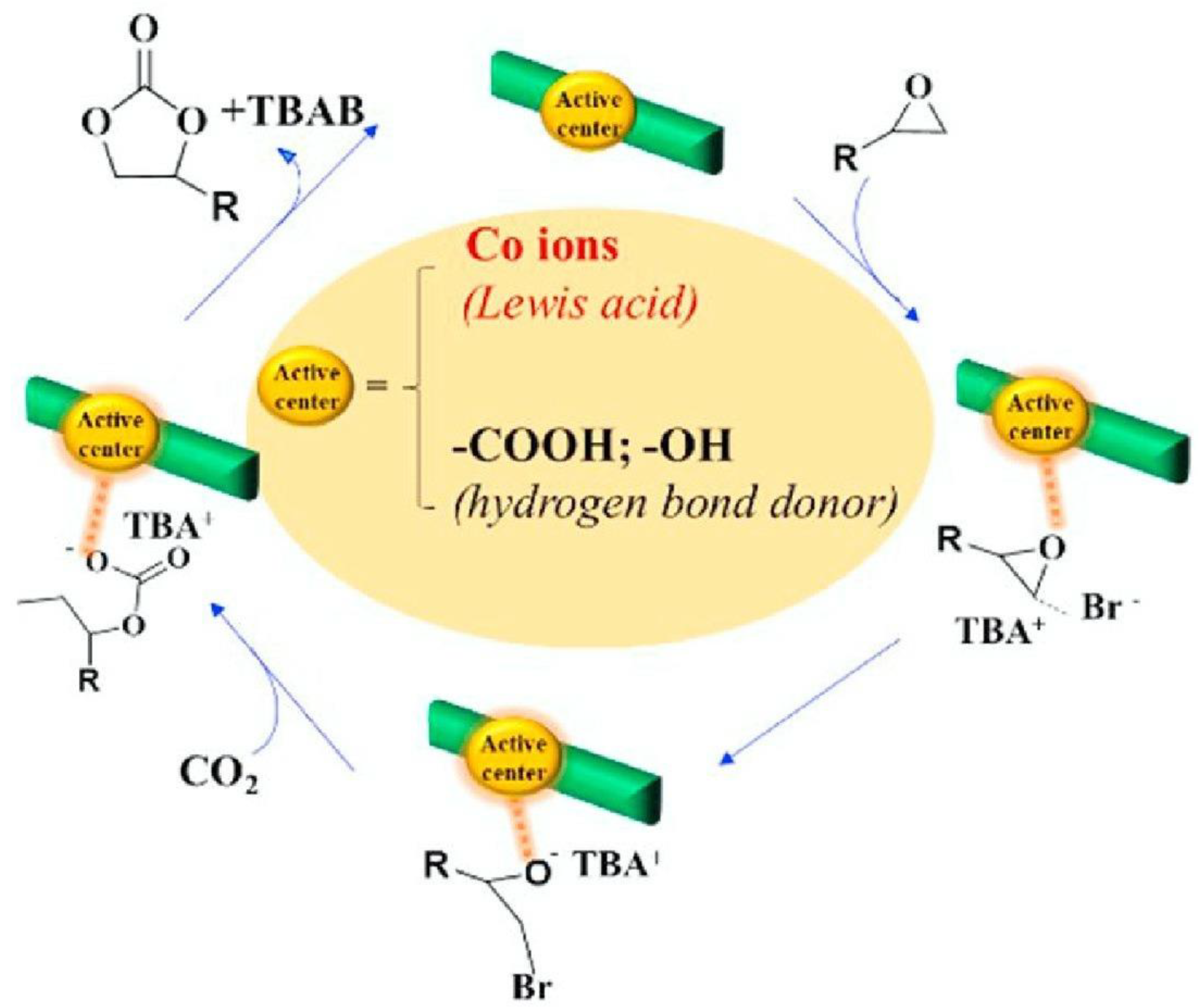
- Hu, L.; Xie, Q.; Tang, J.; Pan, C.; Yu, G.; Tam, K.C. Co (III)-Salen immobilized cellulose nanocrystals for efficient catalytic CO2 fixation into cyclic carbonates under mild conditions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 256, 117558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Liu, K.; Du, H.; Zheng, T.; Zhang, N.; Xu, T.; Pang, B.; Zhang, X.; Si, C.; Zhang, K. Cellulose Nanopaper: Fabrication, Functionalization, and Applications. Nano-Micro Lett. 2022, 14, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.F.; Ding, M.; Yao, J. In situ growth of amino-functionalized ZIF-8 on bacterial cellulose foams for enhanced CO2 adsorption. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 270, 118376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Liu, H.; Qian, L.; Meng, Q.; Wu, H.; Li, Z.; Zhou, H. Surface functionalization of cellulose fibers via aza-Michael addition for CO2-assisted water remediation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 554, 149593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Lijie, L.; Wang, B.; Feng, X.; Mao, Z.; Vancso, G.J.; Sui, X. Multifaceted applications of cellulosic porous materials in environment, energy, and health. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2020, 106, 101253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahfoudhi, N.; Boufi, S. Nanocellulose as a novel nanostructured adsorbent for environmental remediation: A review. Cellulose 2017, 24, 1171–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Xu, T.; Cai, C.; Liu, K.; Liu, W.; Zhang, M.; Du, H.; Si, C.; Zhang, K. Multifunctional Superelastic, Superhydrophilic, and Ultralight Nanocellulose-Based Composite Carbon Aerogels for Compressive Supercapacitor and Strain Sensor. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2113082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, M.W. Electrospinning cellulose and cellulose derivatives. Polym. Rev. 2008, 48, 378–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Singh, P.K.; Pattnaik, R.; Kumar, S.; Ojha, S.K.; Srichandan, H.; Parhi, P.K.; Jyothi, R.K.; Sarangi, P.K. Biochemistry, Synthesis, and Applications of Bacterial Cellulose: A Review. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 780409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, Y.; Xuan, Y.; Zhang, S. Synthesis and Applications of Carboxymethyl Cellulose Hydrogels. Gels 2022, 8, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, J.; Liu, S.; Yuan, Z.; Liu, X.; Liu, B.; Yi, X. A novel combining strategy of cellulose aerogel and hierarchically porous metal organic frameworks (HP-MOFs) to improve the CO2 absorption performance. Cellulose 2022, 29, 6783–6796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Song, Q.; Liu, K.; Liu, H.; Pan, J.; Liu, W.; Dai, L.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Y.; Si, C.; et al. Nanocellulose-Assisted Construction of Multifunctional MXene-Based Aerogels with Engineering Biomimetic Texture for Pressure Sensor and Compressible Electrode. Nano-Micro Lett. 2023, 15, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Shah, B.B.; Zhao, D. CO2 Capture in Metal–Organic Framework Adsorbents: An Engineering Perspective. Adv. Sustain. Syst. 2019, 3, 1800080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Xu, T.; Liang, Q.; Zhao, Q.; Zhao, D.; Si, C. Compressible cellulose nanofibrils/reduced graphene oxide composite carbon aerogel for solid-state supercapacitor. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2022, 5, 1168–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourenço, M.A.O.; Fontana, M.; Jagdale, P.; Pirri, C.F.; Bocchini, S. Improved CO2 adsorption properties through amine functionalization of multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 414, 128763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pita-Vilar, M.; Concheiro, A.; Alvarez-Lorenzo, C.; Diaz-Gomez, L. Recent advances in 3D printed cellulose-based wound dressings: A review on in vitro and in vivo achievements. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 321, 121298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Chuah, C.Y.; Tan, W.S.; Song, J.; Bae, T.H. 3D-printed monolithic porous adsorbents from a solution-processible, hypercrosslinkable, functionalizable polymer. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 427, 130883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauss, C.; Pickering, K.L.; Muthe, L.P. The use of cellulose in bio-derived formulations for 3D/4D printing: A review. Compos. Part C Open Access 2021, 4, 100113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phuong, H.T.; Thoa, N.K.; Tuyet, P.T.A.; Van, Q.N.; Hai, Y.D. Cellulose Nanomaterials as a Future, Sustainable and Renewable Material. Crystals 2022, 12, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morcillo-Martín, R.; Espinosa, E.; Rabasco-Vílchez, L.; Sanchez, L.M.; de Haro, J.; Rodríguez, A. Cellulose Nanofiber-Based Aerogels from Wheat Straw: Influence of Surface Load and Lignin Content on Their Properties and Dye Removal Capacity. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, A.M.S. 3D-Printed Adsorbents for CO2 Capture. Ph.D. Thesis, Khalifa University of Science, Abu Dhabi, UAE, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Motloung, M.T.; Magagula, S.I.; Kaleni, A.; Sikhosana, T.S.; Lebelo, K.; Mochane, M.J. Recent Advances on Chemically Functionalized Cellulose-Based Materials for Arsenic Removal in Wastewater: A Review. Water 2023, 15, 793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhamid, H.N.; Mathew, A.P. Cellulose-Based Materials for Water Remediation: Adsorption, Catalysis, and Antifouling. Front. Chem. Eng. 2021, 3, 790314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isa, E.D.M.; Shameli, K.; Ali, R.R.; Balasundram, V. Advances in Nanocellulose Based Materials as Adsorbent for Wastewater Treatment. J. Res. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2022, 5, 43–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, R.J.; Wang, T.; Lang, J.Q.; Zhou, N.; Ma, M.G. Multifunctional Cellulose and Cellulose-Based (Nano) Composite Adsorbents. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 891034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, T.; Farid, A.; Haq, F.; Kiran, M.; Ullah, A.; Zhang, K.; Li, C.; Ghazanfar, S.; Sun, H.; Ullah, R.; et al. A Review on the Modification of Cellulose and Its Applications. Polymers 2022, 14, 3206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, J.S.; Kim, B.J. Preparation of Cellulose-Based Activated Carbon Fibers with Improved Yield and Their Methylene Chloride Adsorption Evaluation. Molecules 2023, 28, 6997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasser Abdelhamid, H.; Mathew, A.P. Cellulose-zeolitic imidazolate frameworks (CelloZIFs) for multifunctional environmental remediation: Adsorption and catalytic degradation. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 426, 131733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerullis, S.; Pfuch, A.; Beier, O.; Kretzschmar, B.S.M.; Beyer, M.; Fischer, S. Plasma treatment of cellulose: Investigation on molecular changes using spectroscopic methods and chemical derivatization. Cellulose 2022, 29, 7163–7176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Shu, Q.; Ge, S.; Xuan, S. Plasma Treatment for Cellulose in Tobacco Paper-Base: The Improvement of Surface Hydrophilicity and Mechanical Property. Materials 2022, 15, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, A.H.; Liu, X.; Fan, C. Adsorptive separation of carbon dioxide at ambient temperatures in activated carbon. Carbon Capture Sci. Technol. 2022, 4, 100062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, H.R.; Jahan, Z.; Khan Niazi, M.B.; Noor, T.; Hou, H.; Rafiq, S. High–Selective Separation Performance of CO2 from CH4 by Interfacial Engineering of Ultra-low-dose Bimetallic Pyrazine-MOF based Mixed Matrix Membranes. Carbon Capture Sci. Technol. 2022, 3, 100048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Qu, Y.; Sun, J. Functionalized mesoporous SiO2 materials for CO2 capture and catalytic conversion to cyclic carbonates. Catal. Rev. 2024, 66, 2153–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbar, S.Q.; Janani, H.; Janani, H. Cellulose-Based Hybrid Composites Enabled by Metal Organic Frameworks for CO2 Capture: The Effect of Cellulosic Substrate. J. Polym. Environ. 2022, 30, 4210–4224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Niu, Z.; Mu, P.; Li, J. Pebax and CMC@MXene-Based Mixed Matrix Membrane with High Mechanical Strength for the Highly Efficient Capture of CO2. Macromolecules 2022, 55, 9851–9859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
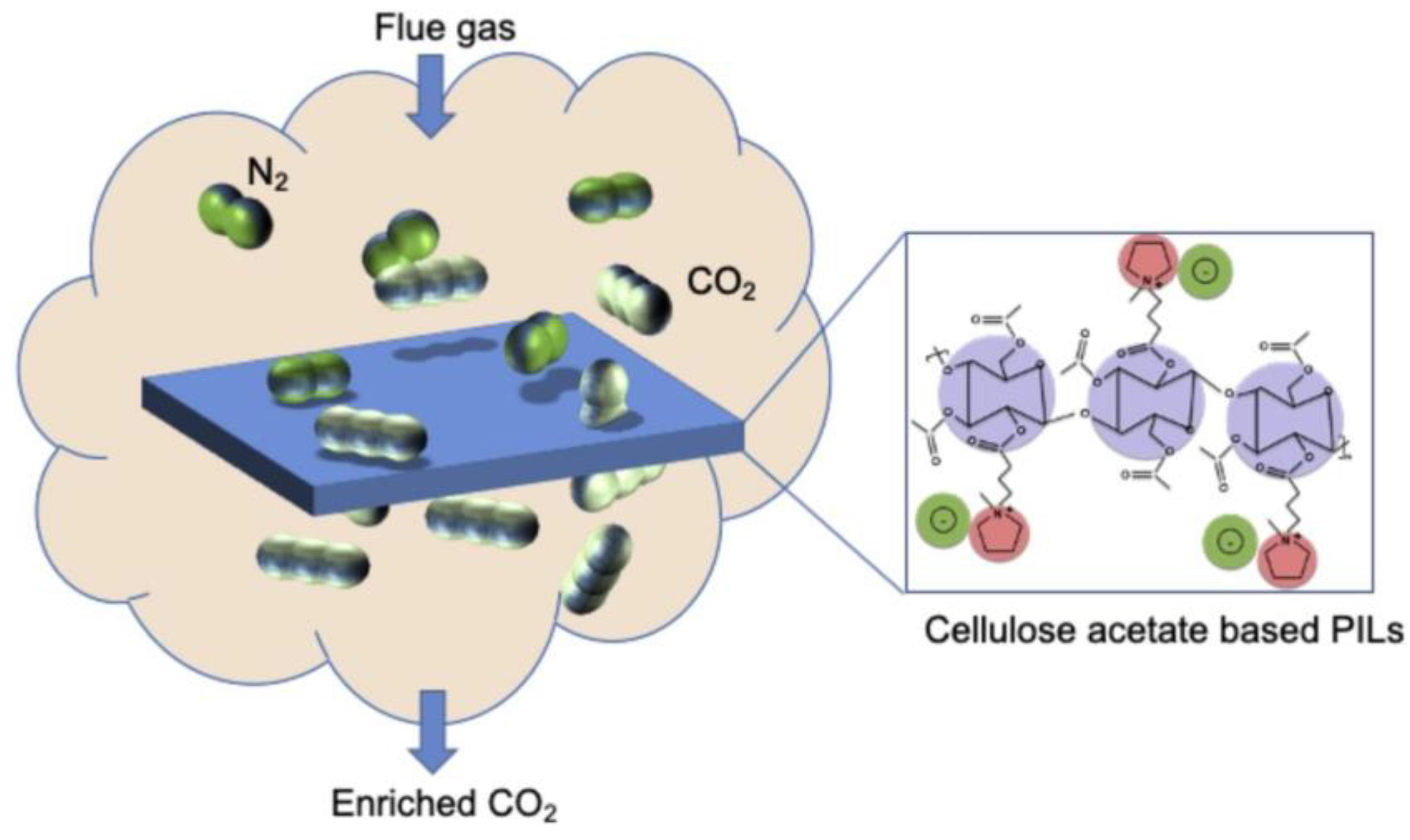
- Nikolaeva, D.; Verachtert, K.; Azcune, I.; Jansen, J.C.; Vankelecom, I.F.J. Influence of ionic liquid-like cationic pendants composition in cellulose based polyelectrolytes on membrane-based CO2 separation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 255, 117375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Wang, K.; Liu, R.; Tian, Y.; Kong, B.; Qi, G. Synthesis and CO 2 adsorption performance of TEPA-loaded cellulose whisker / silica composite aerogel. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 631, 127675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
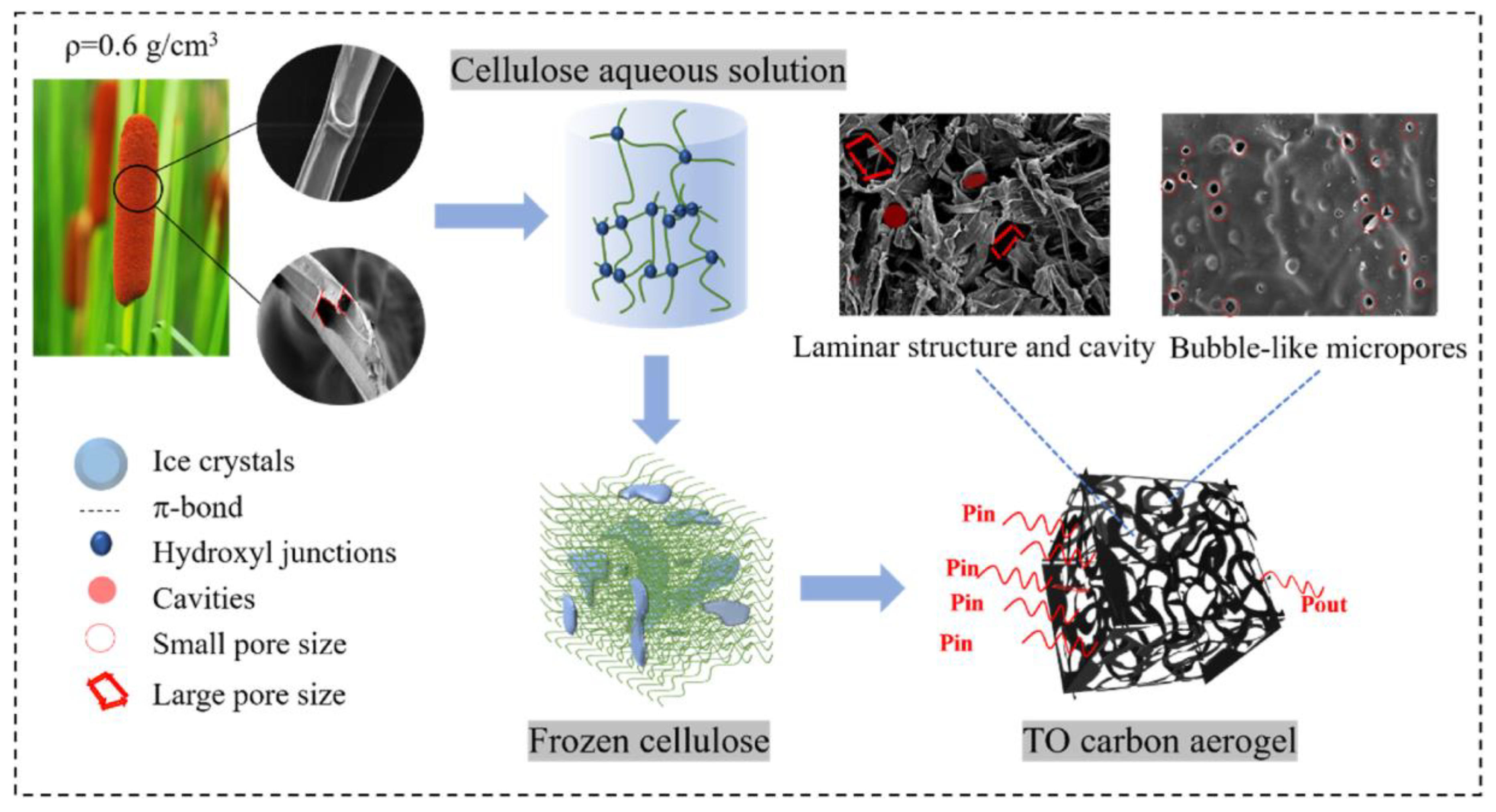
- Cheng, J.; Cheng, X.; Wang, Z.; Hussain, M.B.; Wang, M. Multifunctional carbon aerogels from typha orientalis for applications in adsorption: Hydrogen storage, CO2 capture and VOCs removal. Energy 2023, 263, 125984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, X.; Li, T.; Chen, J.; Fu, D. 3D-hierarchical porous functionalized carbon aerogel from renewable cellulose: An innovative solid-amine adsorbent with high CO2 adsorption performance. Energy 2023, 274, 127392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Long, Y.; Sun, J.; Bai, S.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, C. Core-in-Shell, Cellulose-Templated CaO-Based Sorbent Pellets for CO2Capture at Elevated Temperatures. Energy Fuels 2021, 35, 13215–13223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
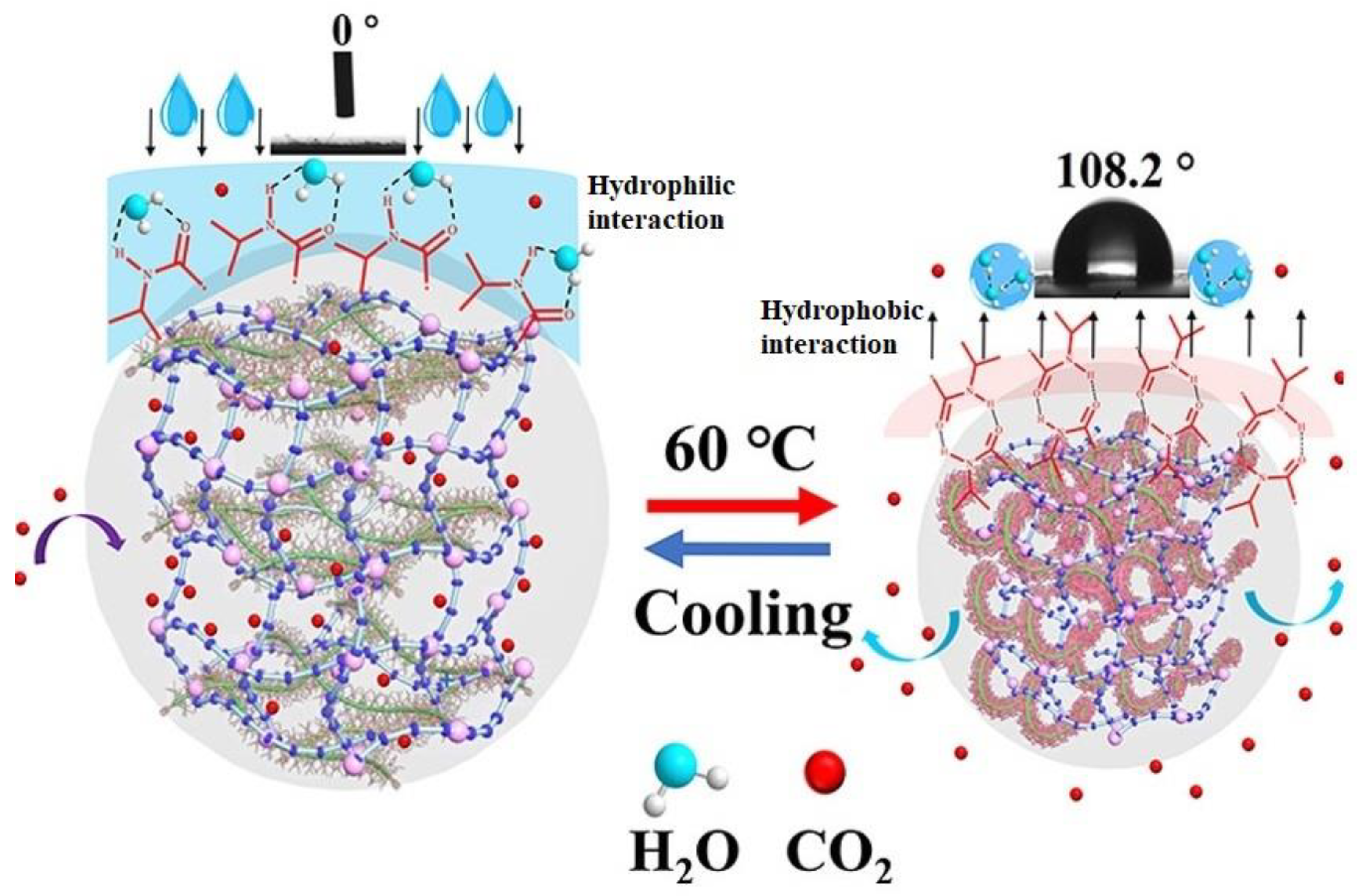
- Lu, W.; Shi, X.; Zhou, H.; Luo, W.; Wang, L.; He, H. Tailoring and properties of a novel solar energy-triggered regenerative bionic fiber adsorbent for CO2 capture. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 449, 137885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Lu, W.; Shi, X.; Lu, Q.; Wang, L.; He, H. Design of an Intelligent Nanofiber-Based Solid Amine Adsorbent with High CO2 Capture Capacity and an Ultralow Regeneration Temperature. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 10184–10195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Li, T.; Yang, X.; Li, C.; Mi, J.; Meng, H.; Jin, J. Hydrophobic carbon-based coating on metal tube with efficient and stable adsorption–desorption of CO2 from wet flue gas. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 307, 122798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Liu, H.; Yan, L.; Yang, H.; Dai, L.; Si, C. Lignin-Based Encapsulation of Liquid Metal Particles for Flexible and High-Efficiently Recyclable Electronics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 34, 2310653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
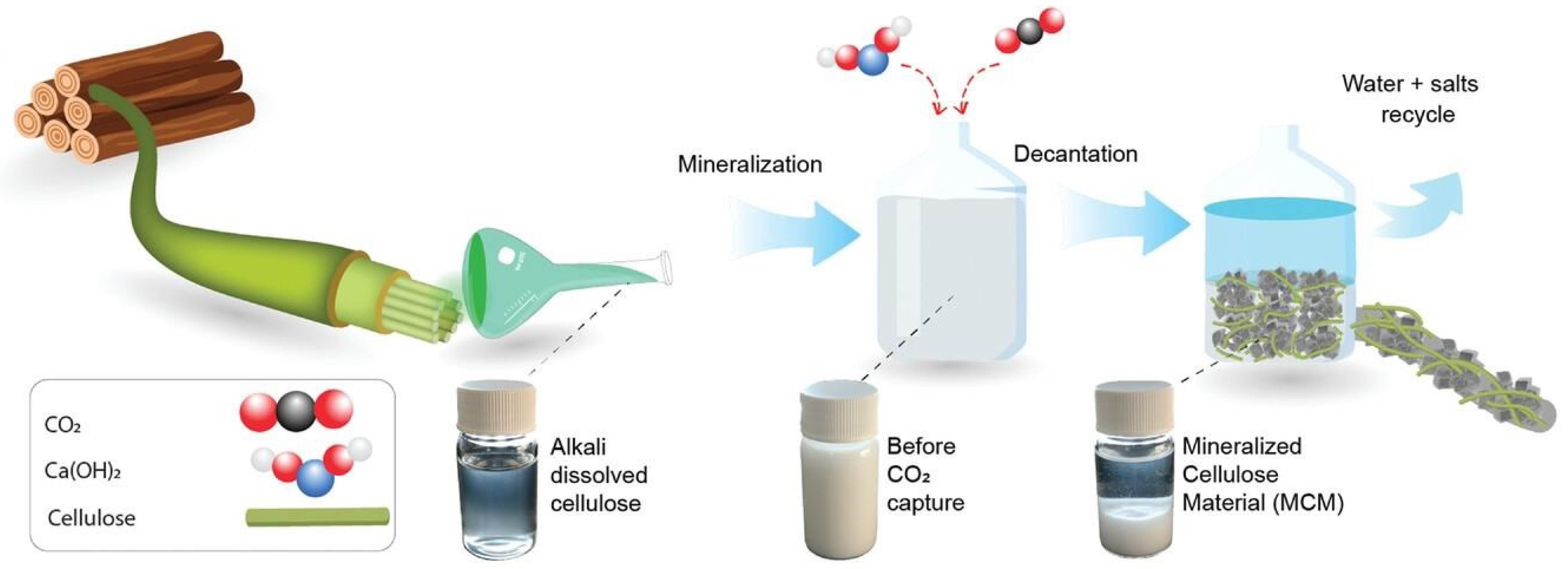
- Reyes, G.; Vega-Coloma, M.; Antonova, A.; Ajdary, R.; Jonveaux, S.; Flanigan, C.; Lautenbacher, N.; Rojas, O.J. Direct CO2 Capture by Alkali-Dissolved Cellulose and Sequestration in Building Materials and Artificial Reef Structures. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2209327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggrawal, S.; Sharma, R.; Mohanty, P. CuO immobilized paper matrices: A green catalyst for conversion of CO2 to cyclic carbonates. J. CO2 Util. 2021, 46, 101466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, T.; Zang, J.; Lv, C.; Zhao, G. Construction of alginate beads for efficient conversion of CO2 into vaterite CaCO3 particles. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 130, 107693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zeng, W.; Zhao, Y.; Tang, M.; Chang, X.; Xu, Y.; Li, R.; Liu, Z. Cellulose-Phytic Acid Composite Complexed Ru Catalyst for CO2 Hydrogenation to Free Formic Acid. ChemCatChem 2023, 15, e202201168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
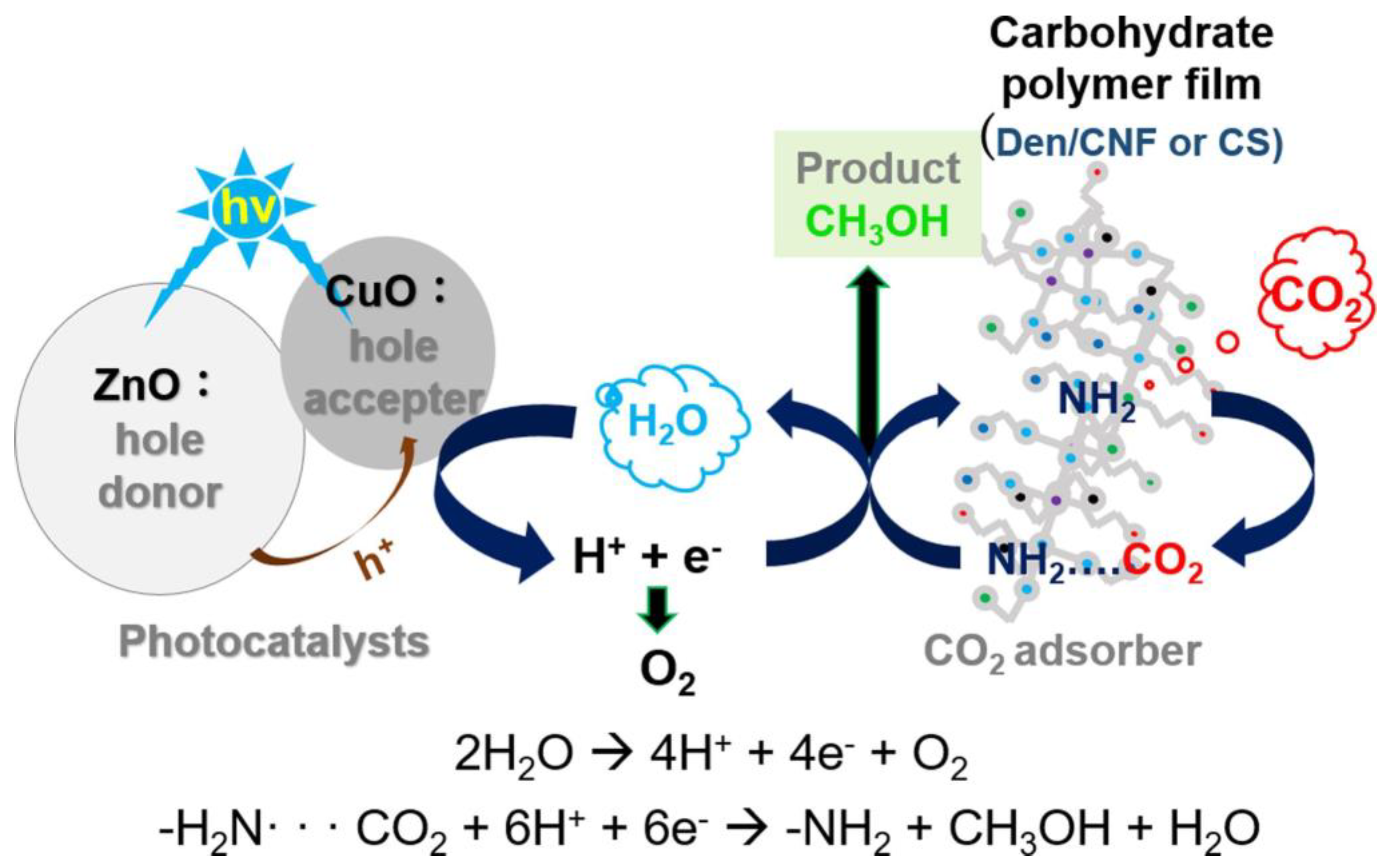
- Belay Getahun, M.; Budi Santiko, E.; Imae, T.; Chiang, C.L.; Lin, Y.G. Photocatalytic conversion of gaseous carbon dioxide to methanol on CuO/ZnO-embedded carbohydrate polymer films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 604, 154515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
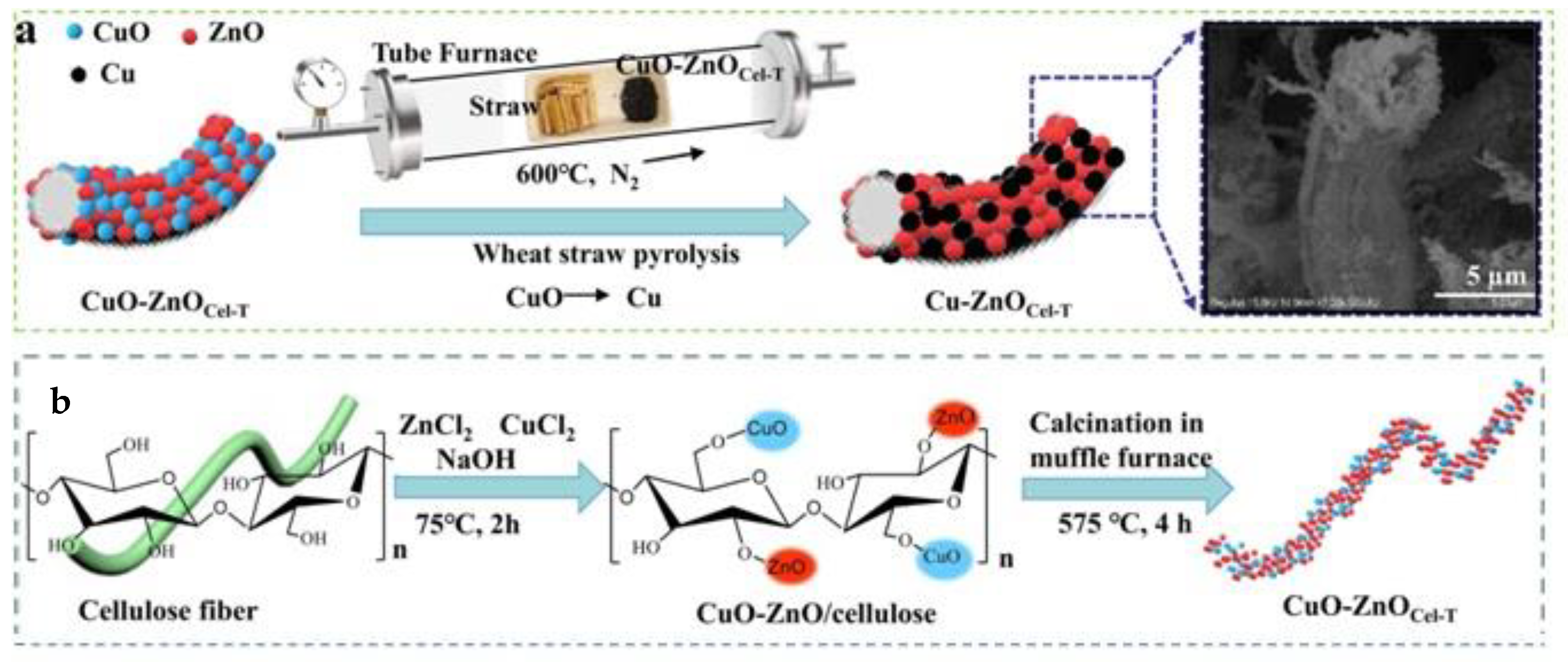
- Zhou, Y.; Guo, X.; Li, X.; Fu, J.; Liu, J.; Hong, F.; Qiao, J. In-situ growth of CuO/Cu nanocomposite electrode for efficient CO2 electroreduction to CO with bacterial cellulose as support. J. CO2 Util. 2020, 37, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Zhang, L.; Shi, Z.; Ma, J.; Wang, Z. Cellulose template designed porous ZnO based catalysts with different valence copper for solar photocatalytic CO2 conversion. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 186, 115223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Strømme, M. Sustainable porous carbon materials derived from wood-based biopolymers for CO2 capture. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Patra, N.; Ramesh, P.; Țălu, Ș. Advancements in Cellulose-Based Materials for CO2 Capture and Conversion. Polymers 2025, 17, 848. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17070848
Patra N, Ramesh P, Țălu Ș. Advancements in Cellulose-Based Materials for CO2 Capture and Conversion. Polymers. 2025; 17(7):848. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17070848
Chicago/Turabian StylePatra, Niranjan, Prathipati Ramesh, and Ștefan Țălu. 2025. "Advancements in Cellulose-Based Materials for CO2 Capture and Conversion" Polymers 17, no. 7: 848. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17070848
APA StylePatra, N., Ramesh, P., & Țălu, Ș. (2025). Advancements in Cellulose-Based Materials for CO2 Capture and Conversion. Polymers, 17(7), 848. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17070848







