Accelerated Storage Induced Structural Evolution in Natural Rubber: A Comparative Study of Two Constant Viscosity Treatment Methods
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Sample Preparation
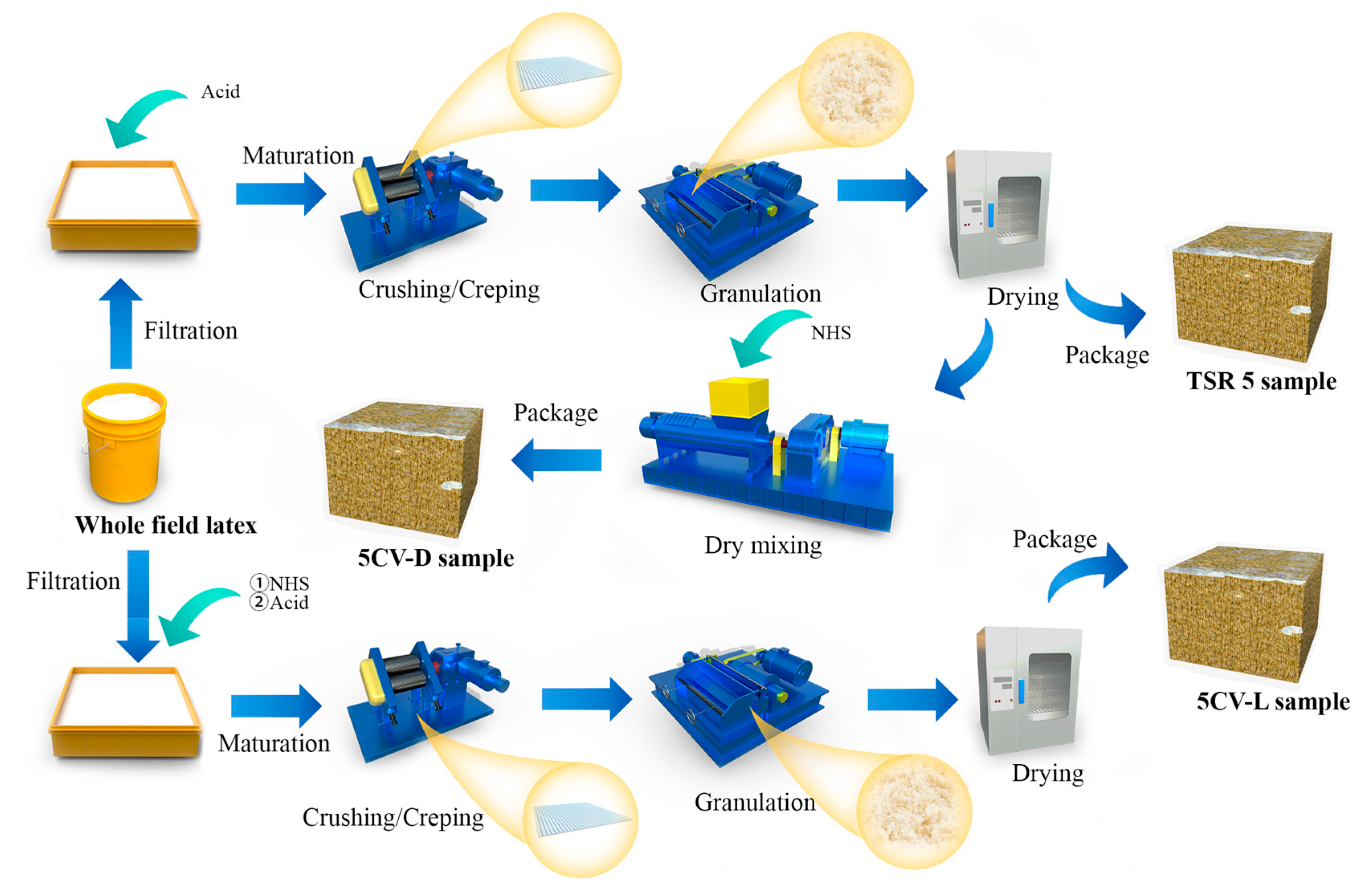
2.2.1. Preparation of Unaccelerated Storage Samples
2.2.2. Preparation of Accelerated Storage Samples
2.3. Testing and Characterization
2.3.1. Determination of Mooney Viscosity and P0
2.3.2. Determination of Mesostructure and Microstructure
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tang, C.; Yang, M.; Fang, Y.; Luo, Y.; Gao, S.; Xiao, X.; An, Z.; Zhou, B.; Zhang, B.; Tan, X.; et al. The rubber tree genome reveals new insights into rubber production and species adaptation. Nat. Plants 2016, 2, 16073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ejolle, E.E.; Elambo, N.G.; Frédéric, B. Mechanistic proposals for variations in the macrostructure of natural rubber. A review. Recent Res. Dev. Bioenergy 2006, 4, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Bonfils, F.; Doumbia, A.; Char, C.; Beuve, J.S. Evolution in the natural rubber native structure and plasticity retention index from the first tapping of clonal trees. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2005, 97, 903–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehabe, E.E.; Bonfils, F.; Sainte-Beuve, J.; Collet, A.; Schué, F. High-temperature mastication of raw natural rubber: Changes in macrostructure and mesostructure. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2005, 46, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noinart, J.; Vaysse, L.; Musigamart, N.; Sainte-Beuve, J.; Flori, A.; Liengprayoon, S.; Rattanaporn, K.; Granet, F.; Bonfils, F. Coagulation methods and drying step are the key drivers of the dynamics of structuration of natural rubber during the maturation of coagula. Express Polym. Lett. 2022, 16, 1161–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngolemasango, F.; Ehabe, E.; Aymard, C.; Sainte-Beuve, J.; Nkouonkam, B.; Bonfils, F. Role of short polyisoprene chains in storage hardening of natural rubber. Polym. Int. 2003, 52, 1365–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekhar, B. Degradation and crosslinking of polyisoprene in Hevea Brasiliensis latex during processing and storage. J. Polym. Sci. 1960, 48, 133–137. [Google Scholar]
- Sekhar, B. Inhibition of hardening in natural rubber. Rubber Chem. Technol. 1962, 35, 889–895. [Google Scholar]
- Nimpaiboon, A.; Sriring, M.; Sakdapipanich, J.T. Molecular structure and storage hardening of natural rubber: Insight into the reactions between hydroxylamine and phospholipids linked to natural rubber molecule. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 133, 43753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y.; Tarachiwin, L. Recent advances in structural characterization of natural rubber. Rubber Chem. Technol. 2009, 82, 283–314. [Google Scholar]
- Sakdapipanich, J.T.; Amnuaypornsri, S.; Nimpaiboon, A. Obstruction of Storage Hardening in Nr by Using Polar Chemicals. Rubber Chem. Technol. 2016, 89, 358–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Promhuad, K.; Smitthipong, W. The effect of hydroxylamine sulfate on the storage hardening of natural rubber. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 773, 012012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chollakup, R.; Suwanruji, P.; Tantatherdtam, R.; Smitthipong, W. New approach on structure-property relationships of stabilized natural rubbers. J. Polym. Res. 2019, 26, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayeemasae, N.; Soontaranon, S.; Masa, A. Structure—Property relationships of different natural rubber grades. Prog. Rubber Plast. Recycl. Technol. 2024, 41, 36–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noinart, J.; Bonfils, F.; Musigamart, N.; Sainte-Beuve, J.; Flori, A.; Liengprayoon, S.; Rattanaporn, K.; Granet, F.; Vaysse, L. Post-harvest maturation of Hevea brasiliensis latex coagula: Ranking of the key drivers of the mesostructure and physical properties of natural rubber. J. Rubber Res. 2022, 25, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saiwari, S.; Hayeemasae, N.; Soontaranon, S.; Kalkornsurapranee, E.; Jaratrotkamjorn, R.; Masa, A. Structure-Property relationships in natural rubber representing several clonal varieties of Hevea Brasiliensis. Prog. Rubber Plast. Recycl. Technol. 2022, 38, 295–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Sun, S.; Qin, L.; Li, Q. Microstructure and Meso-Mechanical Properties of Asphalt Mixture Modified by Rubber Powder under a Multi-Scale Effect. Coatings 2021, 11, 1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, L.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, F.; Luo, M.; Liao, S. The Role of Non-Rubber Components on Molecular Network of Natural Rubber during Accelerated Storage. Polymers 2020, 12, 2880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 289-1:2015; Rubber, Unvulcanized—Determinations Using a Shearing-Disc Viscometer—Part 1: Determination of Mooney Viscosity. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015.
- Nun-anan, P.; Wisunthorn, S.; Pichaiyut, S.; Nathaworn, C.D.; Nakason, C. Influence of nonrubber components on properties of unvulcanized natural rubber. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2020, 31, 44–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 2007:2007; Rubber, Unvulcanized—Determination of Plasticity—Rapid-Plastimeter Method. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007.
- Liengprayoon, S.; Char, C.; Vaysse, L.; Bonfils, F. A clearer understanding of the dynamic structuring of different natural rubber genotypes on a macroscopic and mesoscopic scale by asymmetrical-flow field-flow fractionation (A4F) analysis. Polym. Test. 2024, 140, 108614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojruthai, P.; Kantaram, T.; Sakdapipanich, J. Impact of non-rubber components on the branching structure and the accelerated storage hardening in Hevea rubber. J. Rubber Res. 2020, 23, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunyongwattanakorn, J.; Tanaka, Y.; Kawahara, S.; Klinklai, W.; Sakdapipanich, J. Effect of non-rubber components on storage hardening and gel formation of natural rubber during accelerated storage under various conditions. Rubber Chem. Technol. 2003, 76, 1228–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangpakdee. Characterization of Hevea Brazilian rubber from virgin trees: A possible role of cis-polyisoprene in unexploited tree. Rubber Chem. Technol. 1999, 72, 299–307. [Google Scholar]
- Cavallo, A.; Müller, M.; Wittmer, J.P.; Johner, A.; Binder, K. Single chain structure in thin polymer films: Corrections to Flory’s and Silberberg’s hypotheses. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2005, 17, S1697–S1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-H.; Wang, K.-L. Calculation of the Flory Exponent Using the Renormalization Theory. Polym. J. 1995, 27, 515–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burchard, W. Solution properties of branched macromolecules. Adv. Polym. Sci. 1999, 143, 113–194. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, C.; Morel, M.H.; Beuve, J.S.; Guilbert, S.; Collet, A.; Bonfils, F. Characterization of natural rubber using size-exclusion chromatography with online multi-angle light scattering. Study of the phenomenon behind the abnormal elution profile. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1213, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Beuve, J.S.; Guilbert, S.; Bonfils, F. Study of chain branching in natural rubber using size-exclusion chromatography coupled with a multi-angle light scattering detector (SEC-MALS). Eur. Polym. J. 2009, 45, 2249–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubascoux, S.; Thepchalerm, C.; Dubreucq, E.; Wisunthorn, S.; Vaysse, L.; Kiatkamjornwong, S.; Nakason, C.; Bonfils, F. Comparative study of the mesostructure of natural and synthetic polyisoprene by size exclusion chromatography-multi-angle light scattering and asymmetrical flow field flow fractionation-multi-angle light scattering. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1224, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sample | ML | P0 | Macrogel | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 h | 48 h | 0 h | 48 h | 0 h | 48 h | |
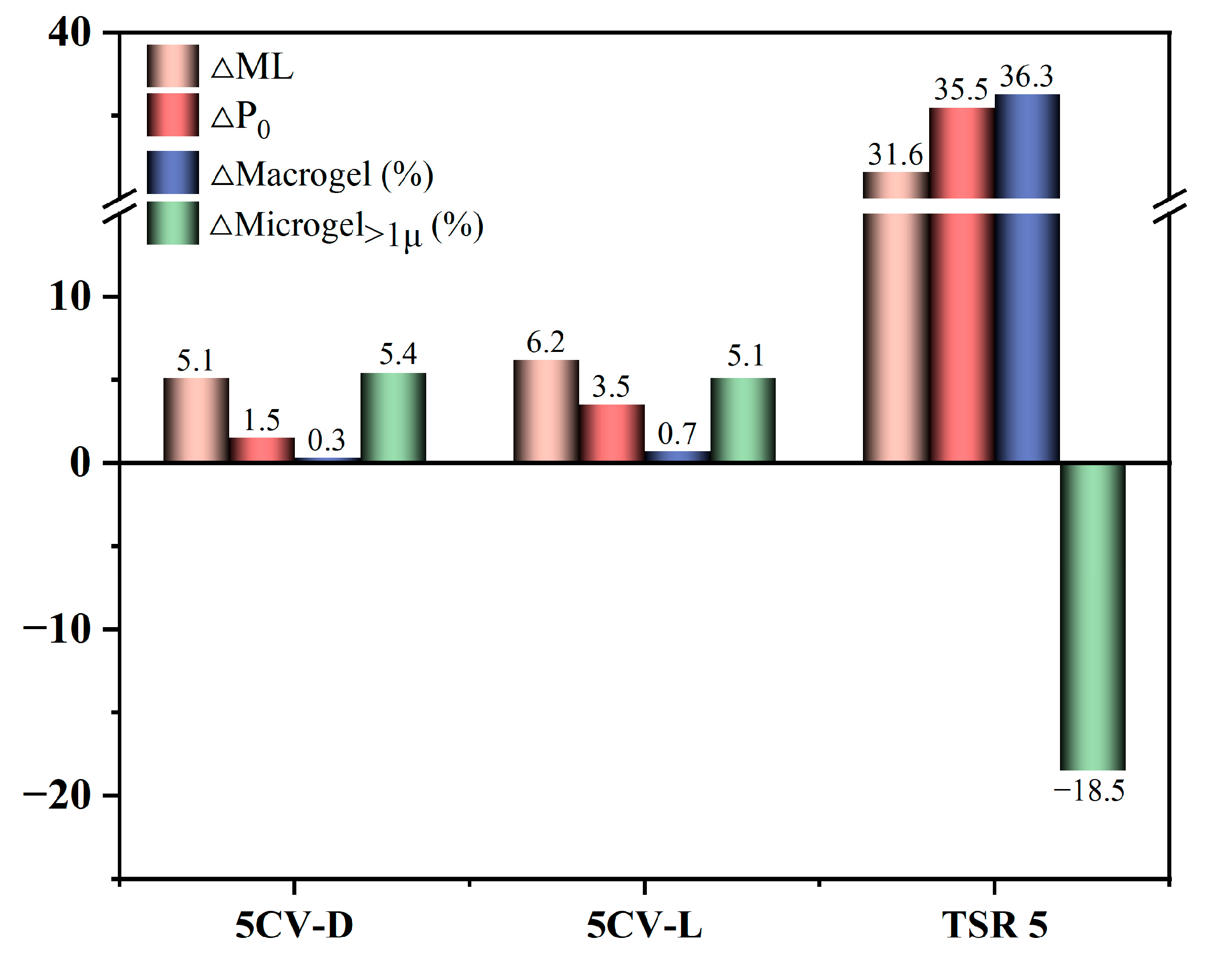
| 5CV-D | 67.7 | 72.8 | 34.0 | 35.5 | 10.8 | 11.1 |
| 5CV-L | 67.4 | 73.6 | 33.0 | 36.5 | 15.0 | 15.7 |
| TSR 5 | 83.6 | 115.2 | 45.5 | 81.0 | 19.5 | 55.8 |
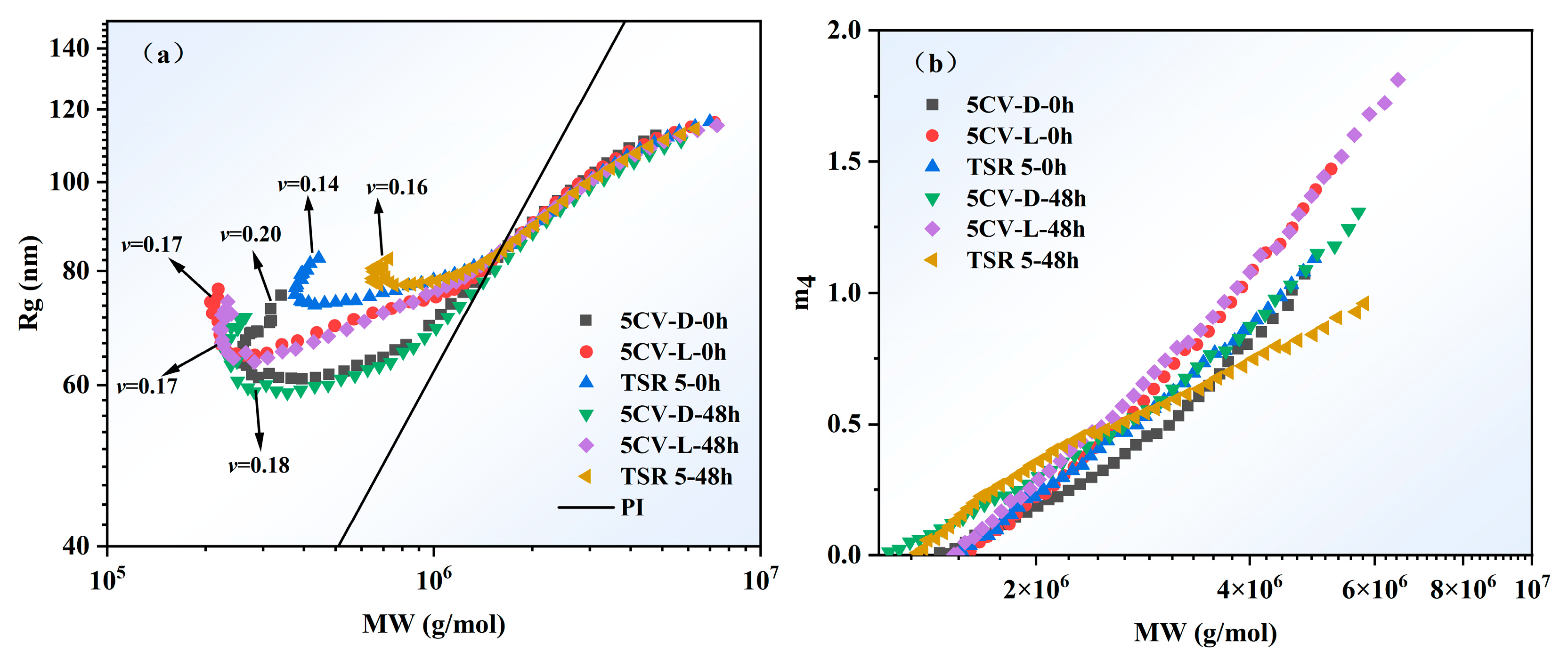
| Sample | Mw (g/mol), ×104 | Mn (g/mol), ×104 | PDI | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 h | 48 h | 0 h | 48 h | 0 h | 48 h | |
| 5CV-D | 126.4 | 130.2 | 59.4 | 59.4 | 2.1 | 2.2 |
| 5CV-L | 161.0 | 165.9 | 54.2 | 61.2 | 3.0 | 2.7 |
| TSR 5 | 171.8 | 191.0 | 88.1 | 137.3 | 2.0 | 1.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yun, D.; Peng, W.; Lin, H.; Liao, J.; Liao, L. Accelerated Storage Induced Structural Evolution in Natural Rubber: A Comparative Study of Two Constant Viscosity Treatment Methods. Polymers 2025, 17, 960. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17070960
Yun D, Peng W, Lin H, Liao J, Liao L. Accelerated Storage Induced Structural Evolution in Natural Rubber: A Comparative Study of Two Constant Viscosity Treatment Methods. Polymers. 2025; 17(7):960. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17070960
Chicago/Turabian StyleYun, Danhua, Wenfeng Peng, Hongtu Lin, Jianhe Liao, and Lusheng Liao. 2025. "Accelerated Storage Induced Structural Evolution in Natural Rubber: A Comparative Study of Two Constant Viscosity Treatment Methods" Polymers 17, no. 7: 960. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17070960
APA StyleYun, D., Peng, W., Lin, H., Liao, J., & Liao, L. (2025). Accelerated Storage Induced Structural Evolution in Natural Rubber: A Comparative Study of Two Constant Viscosity Treatment Methods. Polymers, 17(7), 960. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17070960





