Efficient Removal of Mercury Ions Stabilized by Gold Solution Using Chitosan–Guar Gum Polymer Blend in Basic Media
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
Preparation of Polymer Blend
2.3. Instrumentation
2.4. Adsorption Studies
2.4.1. Batch Equilibrium Studies
2.4.2. Influence of the Co-Existing Heavy Metal Ions
2.4.3. Batch Kinetic Studies
2.4.4. Desorption and Regeneration Studies
3. Results and Discussions
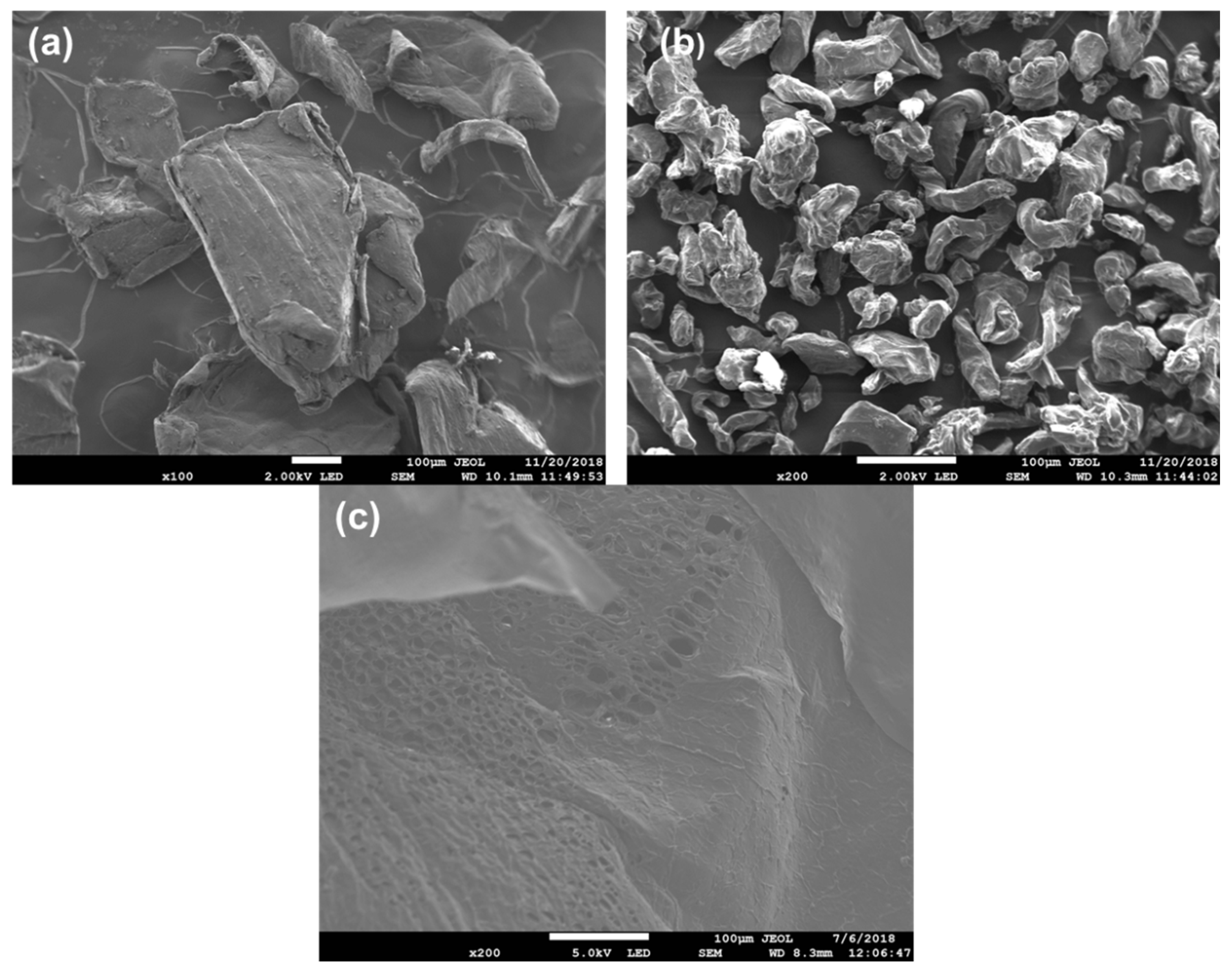
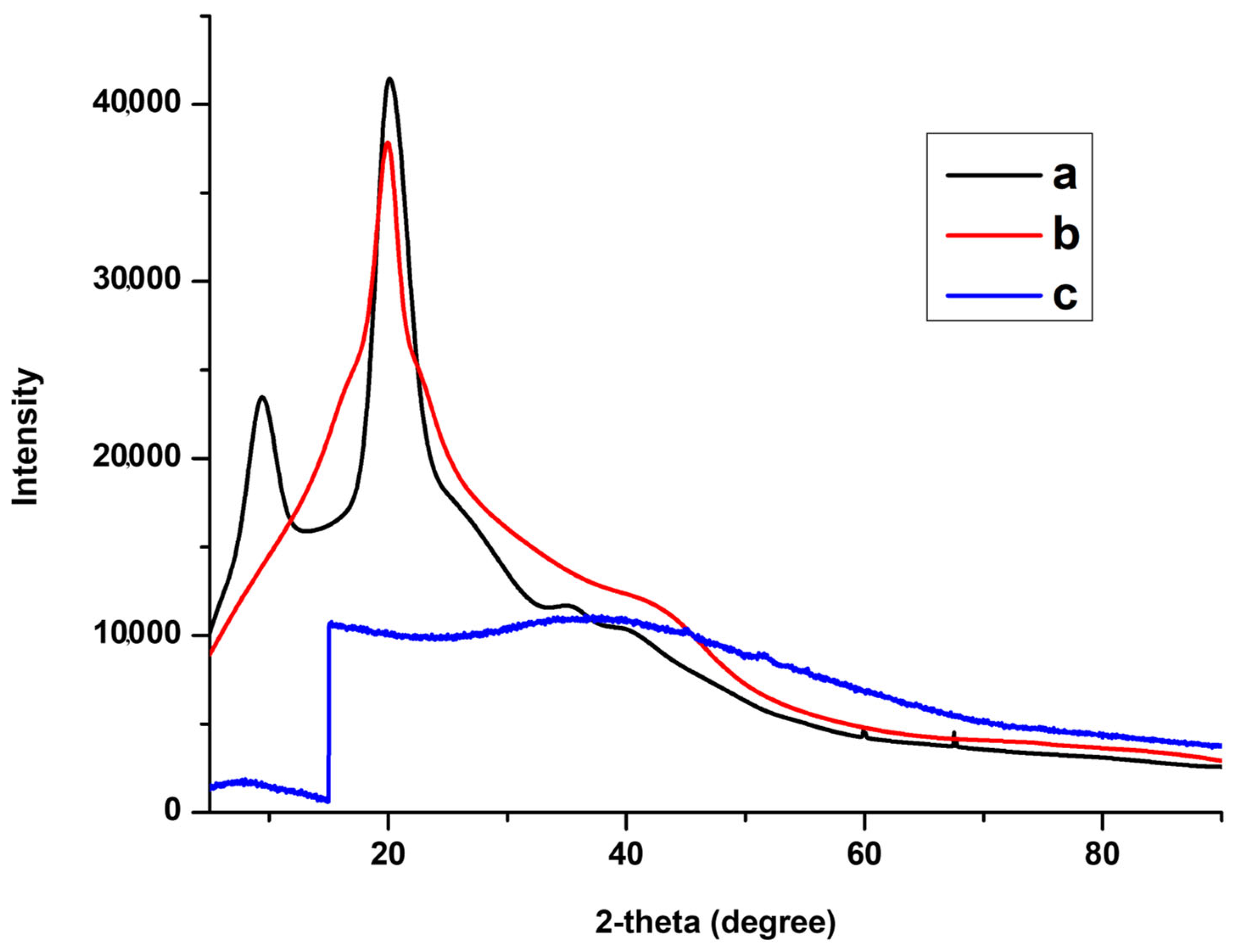
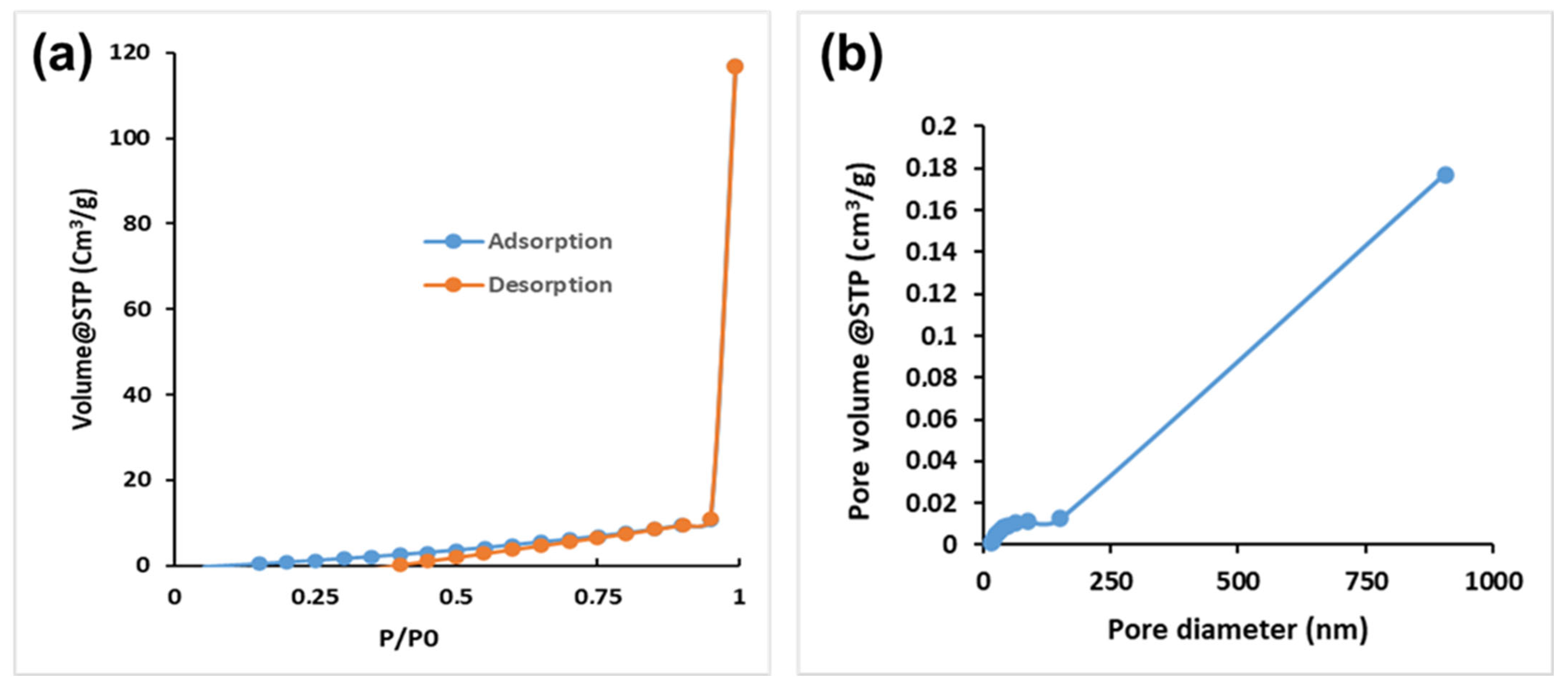
3.1. Characterisations of CS-GG Polymer Blend
3.2. Adsorption Studies
3.2.1. Effect of pH on Hg2+ Ion Removal by CS-GG Polymer Blend
3.2.2. Effect of Initial Metal Ion Concentration
3.2.3. Effect of Adsorbent Dosage
3.2.4. Effect of Contact Time
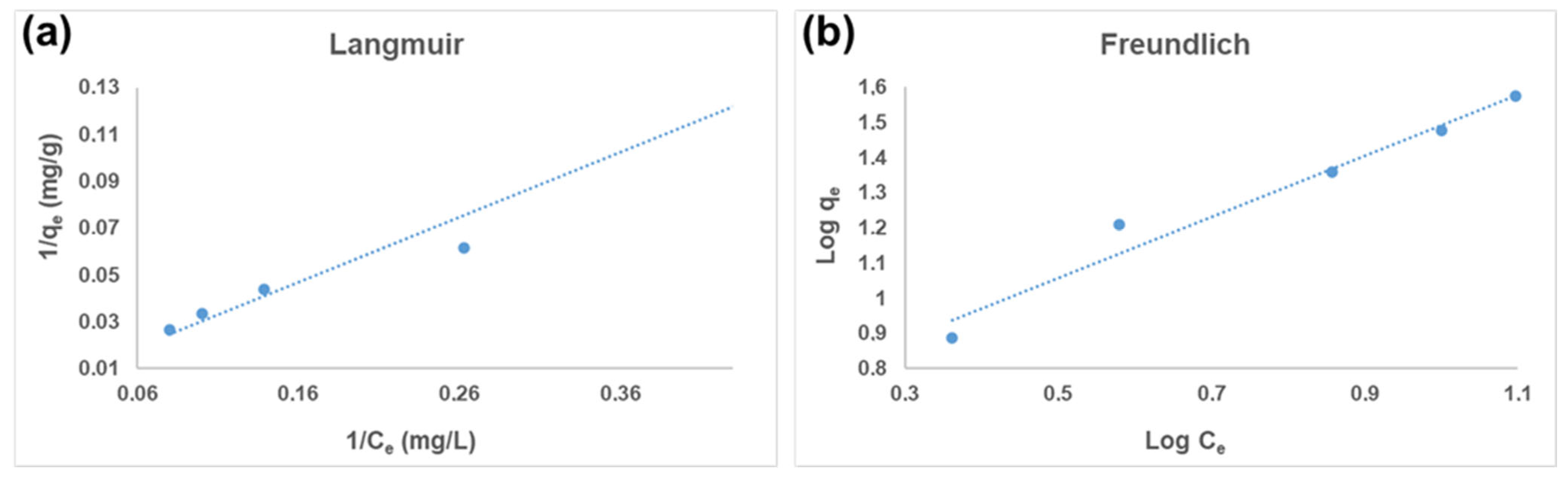
3.3. Adsorption Isotherms
3.3.1. Langmuir Isotherm Model
3.3.2. Freundlich Isotherm Model
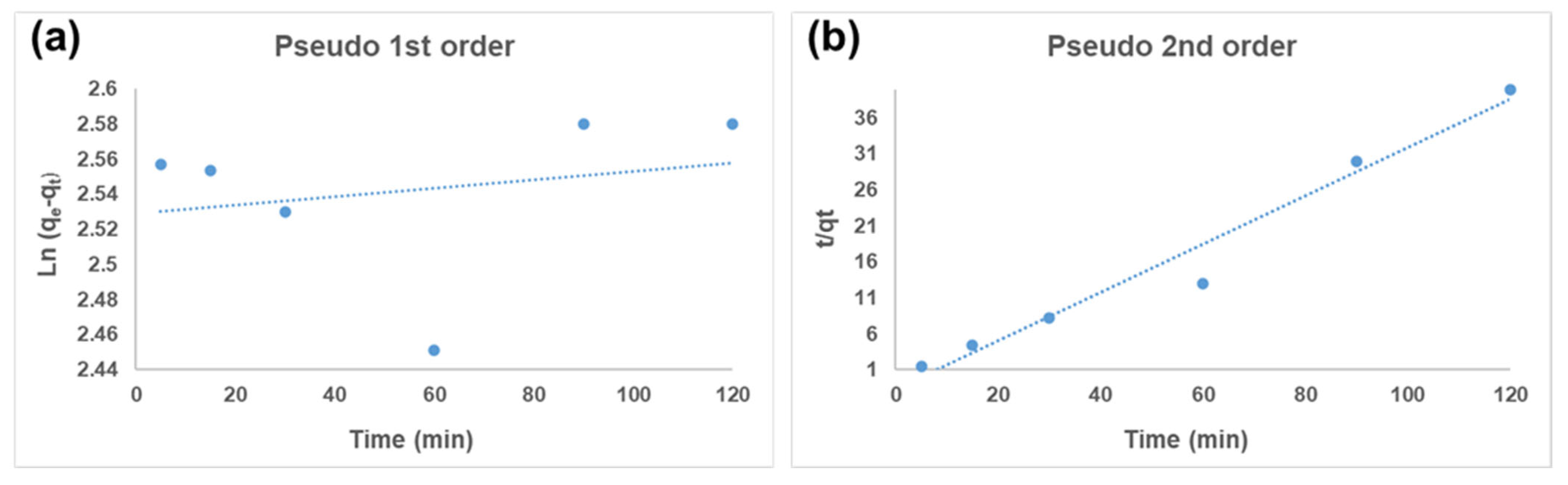
3.4. Kinetics Model Analysis
3.5. Influence of Co-Existing Ions
3.6. Comparison of Hg2+ Ion Adsorption on CS-GG Blend and Other Adsorbents
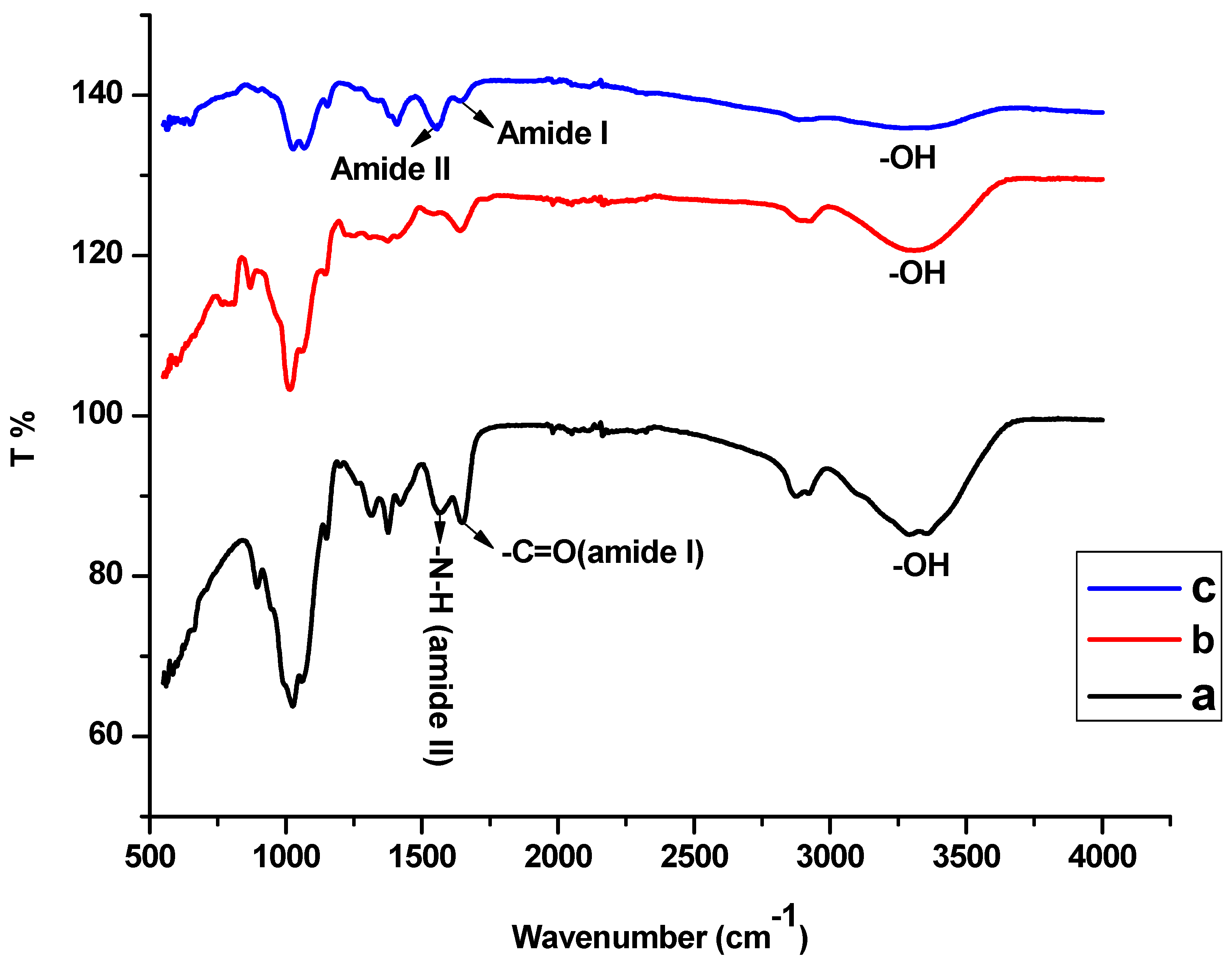
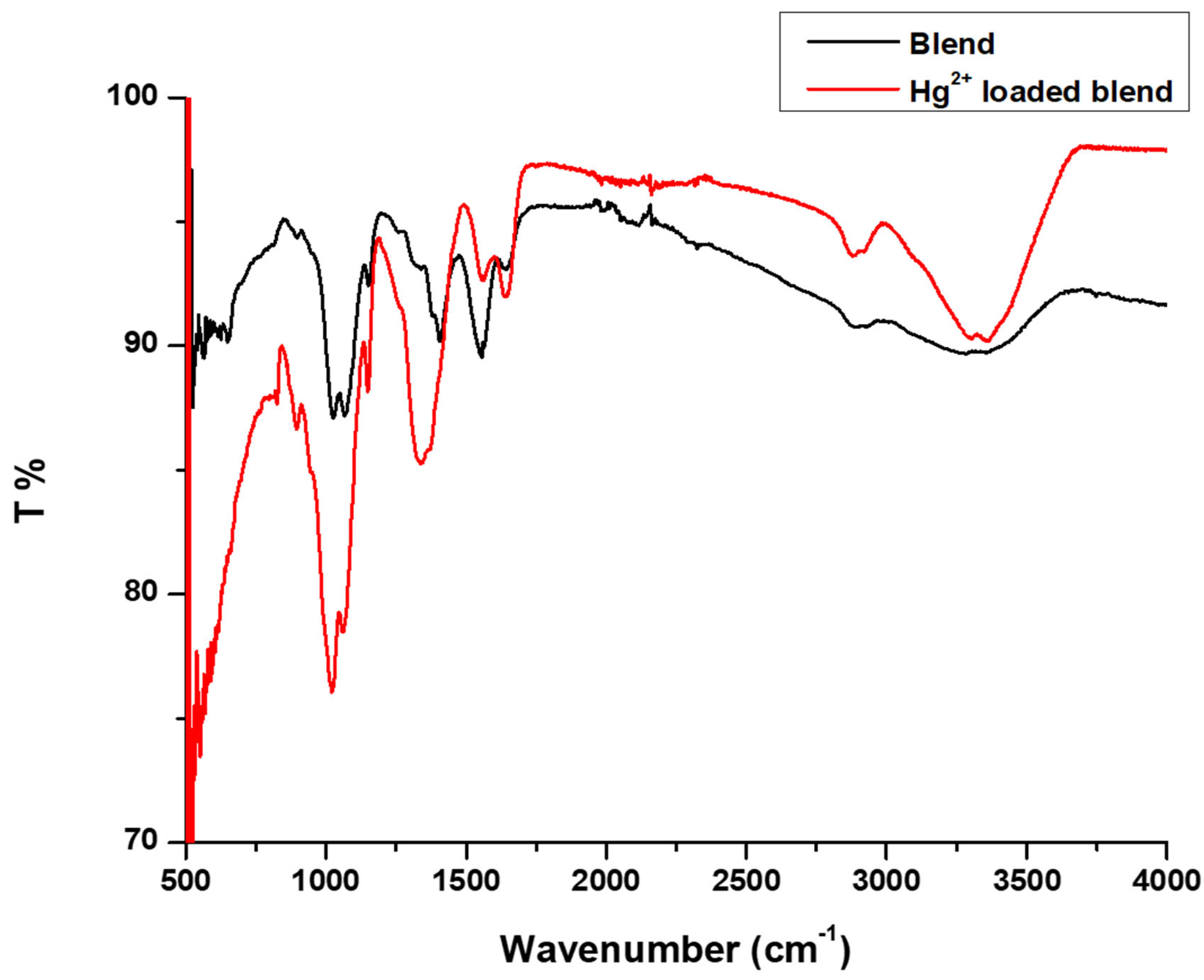
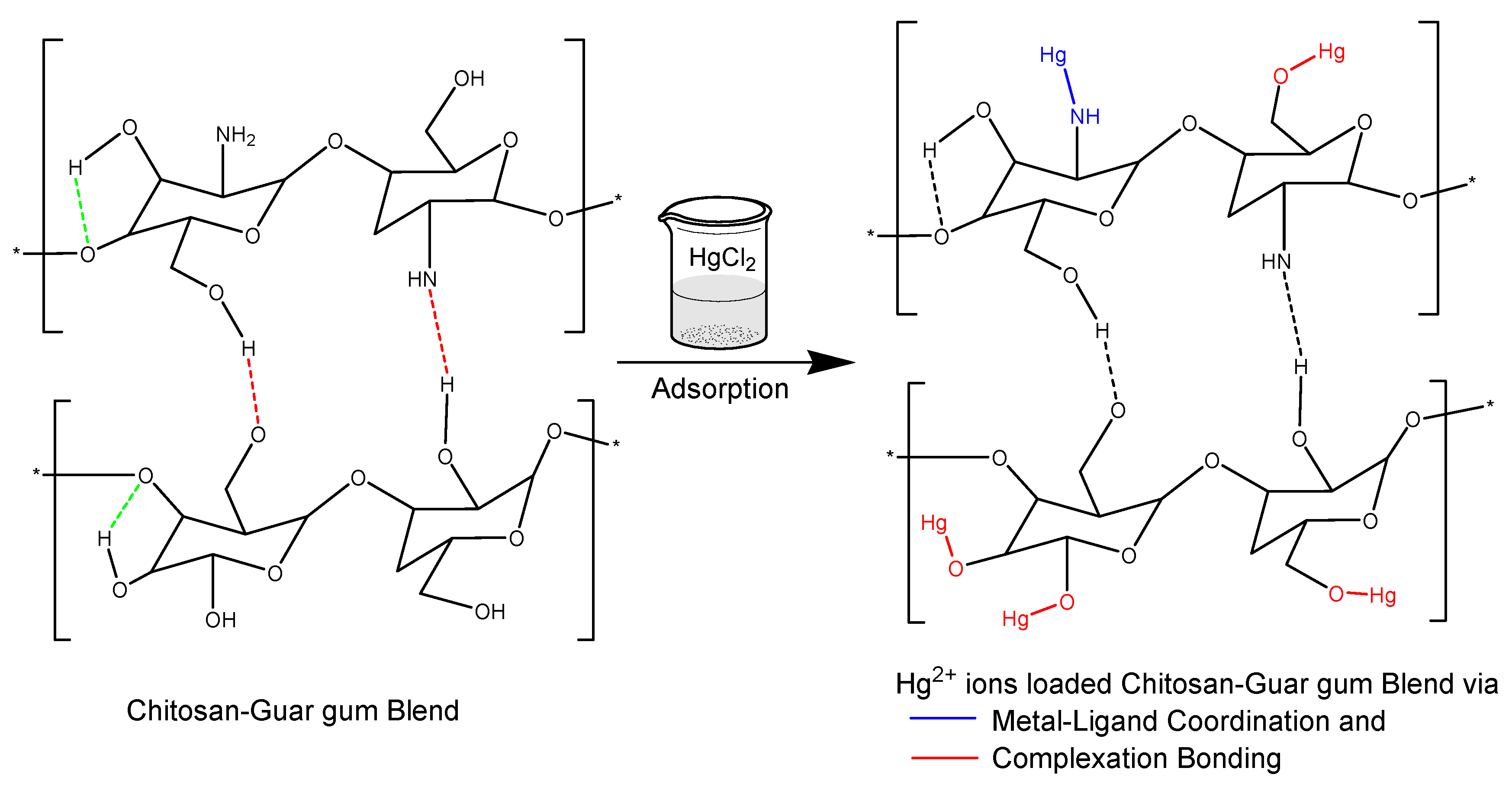
3.7. Adsorption Mechanism from FTIR
- (I)
- The -OH, amide I, and amide II absorption bands of the Hg2+ loaded CS-GG blend shifted to a higher frequency.
- (II)
- The Hg2+ loaded CS-GG blend OH stretching band showed an increase in intensity and narrowness.
- (III)
- There was an increase and reduction in the intensity of amide I and amide II bands in the Hg2+ loaded CS-GG blend, respectively.
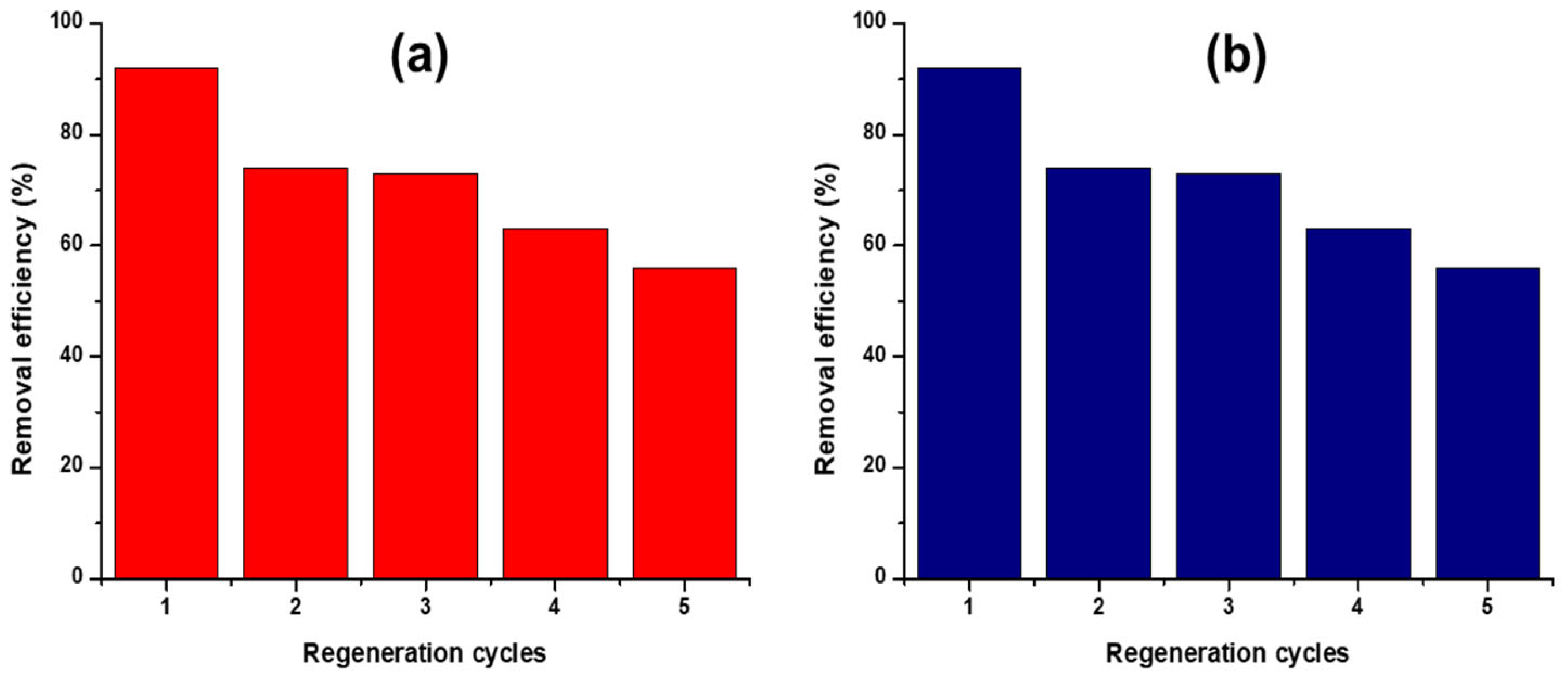
3.8. Desorption and Regeneration Cycles
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, C.; Hu, M.; Ke, Q.; Guo, C.; Guo, Y.; Guo, Y. Nacre-inspired hydroxyapatite/chitosan layered composites effectively remove lead ions in continuous-flow wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 386, 121999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liaw, B.; Chang, T.; Chang, H.; Liu, W.; Chen, P. Fish scale-extracted hydroxyapatite/chitosan composite scaffolds fabricated by freeze casting—An innovative strategy for water treatment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 382, 121082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Zheng, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, A. Preparation of Chitosan-g-Poly (Vinylimidazole-co-2-Acrylamido-2-Methyl Propane Sulfonic Acid) Granular Hydrogel for Selective Adsorption of Hg2+. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2016, 227, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmanzadeh, L.; Ghorbani, M.; Jahanshahi, M. Effective removal of hexavalent mercury from aqueous solution by modified polymeric nanoadsorbent. J. Water Environ. Nanotechnol. 2016, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Zhu, B.; Zhang, L.; Yuan, H.; Zhao, Q.; Yan, Z. Chitosan–gold nanocomposite and its functionalized paper strips for reversible visual sensing and removal of trace Hg2+ in practice. Analyst 2019, 144, 474–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Wang, L.; Zhang, D.; Wang, F.; Sharma, V.K.; Wang, C. Amido-functionalized carboxymethyl chitosan/montmorillonite composite for highly efficient and cost-effective mercury removal from aqueous solution. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 554, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Wang, L.; Zhang, D.; Yan, P.; Nie, J.; Sharma, V.K. Highly efficient and selective removal of mercury ions using hyperbranched polyethylenimine functionalized carboxymethyl chitosan composite adsorbent. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 358, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lata, S.; Samadder, S.R. Removal of arsenic from water using nano adsorbents and challenges: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 166, 387–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saberi, A.; Sadeghi, M.; Alipour, E. Design of AgNPs -Base Starch/PEG-Poly (Acrylic Acid) Hydrogel for Removal of Mercury (II). J. Polym. Environ. 2020, 28, 906–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnib, M.; Kabbani, A.; Holail, H.; Olama, Z. Heavy metals removal using activated carbon, silica and silica activated carbon composite. Energy Procedia 2014, 50, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, A.; Bakas, I.; Piquemal, J.; Nowak, S.; Abderrabba, M.; Chehimi, M.M. Mesoporous silica/polyacrylamide composite: Preparation by UV-graft photopolymerization, characterization and use as Hg (II) adsorbent. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 367, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahribesh, A.A.; Lazarević, S.; Janković-Častvan, I.; Jokić, B.; Spasojević, V.; Radetić, T.; Janaćković, Đ.; Petrović, R. Influence of the synthesis parameters on the properties of the sepiolite-based magnetic adsorbents. Powder Technol. 2017, 305, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahman, E.A.; Subaihi, A. Application of Geopolymers Modified with Chitosan as Novel Composites for Efficient Removal of Hg (II), Cd (II), and Pb (II) Ions from Aqueous Media. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2019, 30, 2440–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Wang, W.; Deng, Y.; Hou, B.; Wang, H.; Duan, J.; Ding, D.; Fan, H.; Liu, H. Bifunctional chitosan/tannin aerogel for gold recovery via electrostatic attraction and in-situ reduction. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 490, 137839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, Y.; Yuan, S.; Sheng, G.; Yu, H. Synthesis and characterization of a novel cationic chitosan-based flocculant with a high water-solubility for pulp mill wastewater treatment. Water Res. 2009, 43, 5267–5275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, J.; Yu, W.; Lang, T.; Chien, M. Evaluation of chitosan/PVA blended hydrogel membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 236, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corazzari, I.; Nisticò, R.; Turci, F.; Faga, M.G.; Franzoso, F.; Tabasso, S.; Magnacca, G. Advanced physico-chemical characterization of chitosan by means of TGA coupled on-line with FTIR and GCMS: Thermal degradation and water adsorption capacity. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2015, 112, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto-suárez, M.; López-quintela, M.A.; Lazzari, M. Preparation and characterization of crosslinked chitosan/gelatin scaffolds by ice segregation induced self-assembly. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 141, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhawade, P.P.; Jagtap, R.N. Characterization of the glass transition temperature of chitosan and its oligomers by temperature modulated differential scanning calorimetry. Adv. Appl. Sci. Res. 2012, 3, 1372–1382. [Google Scholar]
- Mnasri, N.; Moussaoui, Y.; Elaloui, E.; Salem, R.; Lagerge, S.; Douillard, J.M. Study of interaction between chitosan and active carbon in view of optimising composite gels devoted to heal injuries. EPJ Web Conf. 2012, 29, 00028. [Google Scholar]
- Thirugnanasambandham, K.; Sivakumar, V.; Maran, J.P.; Kandasamy, S. Chitosan based grey wastewater treatment—A statistical design approach. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 99, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salih, K.A.; Zhou, K.; Guibal, E.; Basiony, E.A.; Nassar, L.A.; Abdel-Rahman, A.A.-H.; Wei, Y.; Ning, S.; Hamza, M.F. Dual strategy for enhanced and selective uranium sorption by ion-imprinting functionalized chitosan–Fast and efficient recovery from processed acid ore leachate. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 505, 159469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngah, W.S.W.; Teong, L.C.; Hanafiah, M.A.K.M. Adsorption of dyes and heavy metal ions by chitosan composites: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 83, 1446–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Zheng, Y.; Shen, J.; Shi, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Che, J. Chitosan/Sodium Alginate Multilayer pH-Sensitive Films Based on Layer-by-Layer Self-Assembly for Intelligent Packaging. J. Renew. Mater. 2024, 12, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Ye, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, T.; Jiang, S.; Han, X. Functionalization of chitosan and its application in flame retardants: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 295, 139615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, Y.; Han, T.; Cheng, M.; Zhang, W.; Long, J. A biomimetic SiO2@chitosan composite as highly-efficient adsorbent for removing heavy metal ions in drinking water. Chemosphere 2019, 214, 738–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, S.S.; Rao, K.M.; Reddy, P.R.S.; Reddy, N.S.; Rao, K.S.V.K.; Subha, M.C.S. Synthesis and Characterisation of Guar Gum-g-Poly (Acrylamidoglycolic acid) by Redox Initiator. Indian J. Adv. Chem. Sci. 2012, 1, 28–32. [Google Scholar]
- Keshawy, M.; Kamal, R.S.; Abdelhamid, A.E.; Labena, A.; Amin, A.; Hasan, A.M.; Abdel-Raouf, M.E. Novel green sustainable hydrogel composites based on guar gum and algal species for wastewater remediation. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukhari, S.A.; Shahid, M.; Anjum, F.; Rasheed, A.; Munir, H. Purification, fragmentation and characterization of gum froM Cyamopsis tetragonolobus to enhance its nutraceutical attributes. Pak. J. Agric. Sci. 2014, 51, 1059–1067. [Google Scholar]
- Bhavya, B.B.; Shivakumar, H.R. Studies on miscibility and thermal properties of biocompatible polymer blends of pvp/guar gum. Int. J. Adv. Res. Sci. Eng. 2015, 8354, 1951–1960. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmoud, R.I. Investigation of Partially Methylolated Polyacrylamide Guar Gum by FTIR and Thermal Properties. Br. J. Appl. Sci. Technol. 2016, 17, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Wang, L.; Zeng, H.; Yan, P.; Nie, J.; Sharma, V.K.; Wang, C. A three-dimensional macroporous network structured chitosan/cellulose biocomposite sponge for rapid and selective removal of mercury(II) ions from aqueous solution. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 363, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allouche, F.N. Synergistic Effects on the Mercury Sorption Behaviors Using Hybrid Cellulose Fiber/Chitosan Foam. ChemistrySelect 2022, 7, e202202600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gihar, S.; Kumar, D.; Kumar, P. Facile synthesis of novel pH-sensitive grafted guar gum for effective removal of mercury (II) ions from aqueous solution. Carbohydr. Polym. Technol. Appl. 2021, 2, 100110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seney, C.S.; Kiefer, A.M.; Aljic, S. Determination of mercury solvation during cyanidation of artisanal & small-scale gold mining tailings via inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectroscopy in comparison to direct mercury analysis. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2019, 101, 2058–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Hong, P.; Liao, M.; Kong, S.; Huang, N.; Ou, C.; Li, S. Preparation and Characterization of chitosan-agarose composite films. Materials 2016, 9, 816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foroutan, R.; Peighambardoust, S.J.; Latifi, P.; Ahmadi, A.; Alizadeh, M.; Ramavandi, B. Carbon nanotubes/β-cyclodextrin/MnFe2O4 as a magnetic nanocomposite powder for tetracycline antibiotic decontamination from different aqueous environments. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawad, A.H.; Saber, S.E.M.; Abdulhameed, A.S.; Reghioua, A.; ALOthman, Z.A.; Wilson, L.D. Mesoporous activated carbon from mangosteen (Garcinia mangostana) peels by H3PO4 assisted microwave: Optimization, characterization, and adsorption mechanism for methylene blue dye removal. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2022, 129, 109389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajamani, M.; Rajendrakumar, K. Chitosan-boehmite desiccant composite as a promising adsorbent towards heavy metal removal. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 244, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandile, N.G.; Mohamed, H.M. Chitosan nanoparticle hydrogel based sebacoyl moiety with remarkable capability for metal ion removal from aqueous systems. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 122, 578–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ghouti, M.A.; Da’ana, D.; Abu-Dieyeh, M.; Khraisheh, M. Adsorptive removal of mercury from water by adsorbents derived from date pits. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azzam, E.M.S.; Eshaq, G.; Rabie, A.; Bakr, A.; Abd-Elaal, A.A.; El Metwally, A.; Tawfik, S.M. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules Preparation and characterization of chitosan-clay nanocomposites for the removal of Cu (II) from aqueous solution. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 89, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramesh, S.T.; Rameshbabu, N.; Gandhimathi, R.; Nidheesh, P.V.; Srikanth Kumar, M. Kinetics and equilibrium studies for the removal of heavy metals in both single and binary systems using hydroxyapatite. Appl. Water Sci. 2012, 2, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Pandey, J.; Khan, N.; Kumar, P.; Kundu, P.P. Synthesize and characterization of binary grafted psyllium for removing toxic mercury (II) ions from aqueous solution. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 104, 109900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Zhang, L.; Wang, B.; Yang, B.; Khan, I.; Khan, A.; Ni, Y. Multifunctional self-assembling hydrogel from guar gum. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 330, 1044–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, A.; Kalaee, M.; Moradi, O.; Mahmoodi, N.M.; Zaarei, D. Surface coated Guar gum biocomposite (Zeolite imidazolate framework (ZIF-8)-Guar gum–Polyvinylpyrrolidone) as an environmentally friendly adsorbent: Preparation, isotherm and kinetics of pollutant removal. J. Mol. Struct. 2024, 1304, 137642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshawy, M.; Samir, R.; Abdel-Raouf, M.E.S. Synthesis and Investigation of Green Hydrogels for Simultaneous Removal of Mercuric Cations and Methylene Blue from Aqueous Solutions. Egypt. J. Chem. 2022, 65, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkadir, O.K.A.; Al-Mashhadani, Z.I.; Aljeboree, A.M.; Alkaim, A.F. Comparison Between Pseudo-first-order and Pseudo-second-order of Linear and Nonlinear Equations Adsorption Kinetic Models for the Removal of Amoxicillin (AMX) onto Hydrogel. Int. J. Pharm. Qual. Assur. 2021, 12, 346–350. [Google Scholar]
- Revellame, E.D.; Fortela, D.L.; Sharp, W.; Hernandez, R.; Zappi, M.E. Adsorption kinetic modeling using pseudo-first order and pseudo-second order rate laws: A review. Clean. Eng. Technol. 2020, 1, 100032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, L.R.; Das, N. Removal of Hg (II) ions from aqueous environment using glutaraldehyde crosslinked nanobiocomposite hydrogel modified by TETA and β-cyclodextrin: Optimization, equilibrium, kinetic and ex situ studies. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 85, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandile, N.G.; Mohamed, H.M.; Mohamed, M.I. New heterocycle modified chitosan adsorbent for metal ions (II) removal from aqueous systems. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 72, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Xu, X.; Huang, Y.; Hu, J.; Chen, Q.; Wu, Y. Preparation of new diatomite–chitosan composite materials and their adsorption properties and mechanism of Hg (II). R. Soc. Open. Sci. 2017, 4, 170829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahmatpour, A.; Alijani, N. An all-biopolymer self-assembling hydrogel film consisting of chitosan and carboxymethyl guar gum: A novel bio-based composite adsorbent for Cu2+ adsorption from aqueous solution. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 242, 124878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, G.; Oliver, S.P. Adsorption of Hg (II) from aqueous solution using functionalized hydrogel loaded with hydrous manganese dioxide particles. Water Sci. Technol. 2017, 76, 747–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, A.F.; Hrdina, R. Chitosan/nanohydroxyapatite composite based scallop shells as an efficient adsorbent for mercuric ions: Static and dynamic adsorption studies. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 109, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Pore surface area (m2/g) | 11.843 |
| Pore volume (cm3/g) | 0.184 |
| Pore diameter (nm) | 17.072 |
| Langmuir Model | Freundlich Model | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| qmax (mg/g) | (L/mg) | (mg/g) | |
| R2 | R2 | ||
| 370.37 | 0.0097 | 0.8689 | 4.2072 |
| 0.9631 | 0.9663 | ||
| Kinetic Model | Constants | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Pseudo-first-order | qe (mg/g) 12.5422 | K1 (min−1) 0.0002 | R2 0.0507 |
| Pseudo-second-order | qe (mg/g) 2.9806 | K2 (g/mg/min) 0.1898 | R2 0.9687 |
| Adsorbent | pH | Adsorption Capacity (mg/g) | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diatomite-chitosan | 3 | 195.7 | [52] |
| Chitosan-g-poly granular hydrogel | 5.5 | 365.55 | [3] |
| Chitosan/carboxymethyl guar gum biopolymer | 6 | 151.51 | [53] |
| Hydrous manganese oxides onto acylamino and hydroxyl functionalized hydrogel | 8 | 131.2 | [54] |
| Chitosan–Guar gum polymer blend | 12 | 370.37 | This work |
| CS-GG Polymer Blend | Hg2+ Loaded CS-GG Polymer Blend |
|---|---|
| 3293.49—O-H stretching | 3320.87—O-H stretching |
| 2901.75—C-H stretching | 2894.91—C-H stretching |
| 1637.59—C=O stretching (amide I band) | 1638.47—C=O stretching (amide I band) |
| 1548.63—N-H stretching (amide II band) | 1555.47—N-H stretching (amide II band) |
| 1406.65—C-N stretching | 1339.93—C-N stretching |
| 1042.28—C-O-C stretching | 1021.75—C-O-C stretching |
| Desorbing Agent | Adsorption % | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st cycle | 2nd cycle | 3rd cycle | 4th cycle | 5th cycle | |
| EDTA | 92 | 74 | 73 | 63 | 56 |
| NaOH | 92 | 70 | 68 | 60 | 50 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tshikovhi, A.; Mishra, S.B.; Mishra, A.K.; Mochane, M.J.; Motaung, T.E. Efficient Removal of Mercury Ions Stabilized by Gold Solution Using Chitosan–Guar Gum Polymer Blend in Basic Media. Polymers 2025, 17, 985. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17070985
Tshikovhi A, Mishra SB, Mishra AK, Mochane MJ, Motaung TE. Efficient Removal of Mercury Ions Stabilized by Gold Solution Using Chitosan–Guar Gum Polymer Blend in Basic Media. Polymers. 2025; 17(7):985. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17070985
Chicago/Turabian StyleTshikovhi, Azwifunimunwe, Shivani B. Mishra, Ajay K. Mishra, Mokgaotsa J. Mochane, and Tshwafo E. Motaung. 2025. "Efficient Removal of Mercury Ions Stabilized by Gold Solution Using Chitosan–Guar Gum Polymer Blend in Basic Media" Polymers 17, no. 7: 985. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17070985
APA StyleTshikovhi, A., Mishra, S. B., Mishra, A. K., Mochane, M. J., & Motaung, T. E. (2025). Efficient Removal of Mercury Ions Stabilized by Gold Solution Using Chitosan–Guar Gum Polymer Blend in Basic Media. Polymers, 17(7), 985. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17070985







