Progress of Ionogels in Flexible Pressure Sensors: A Mini-Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
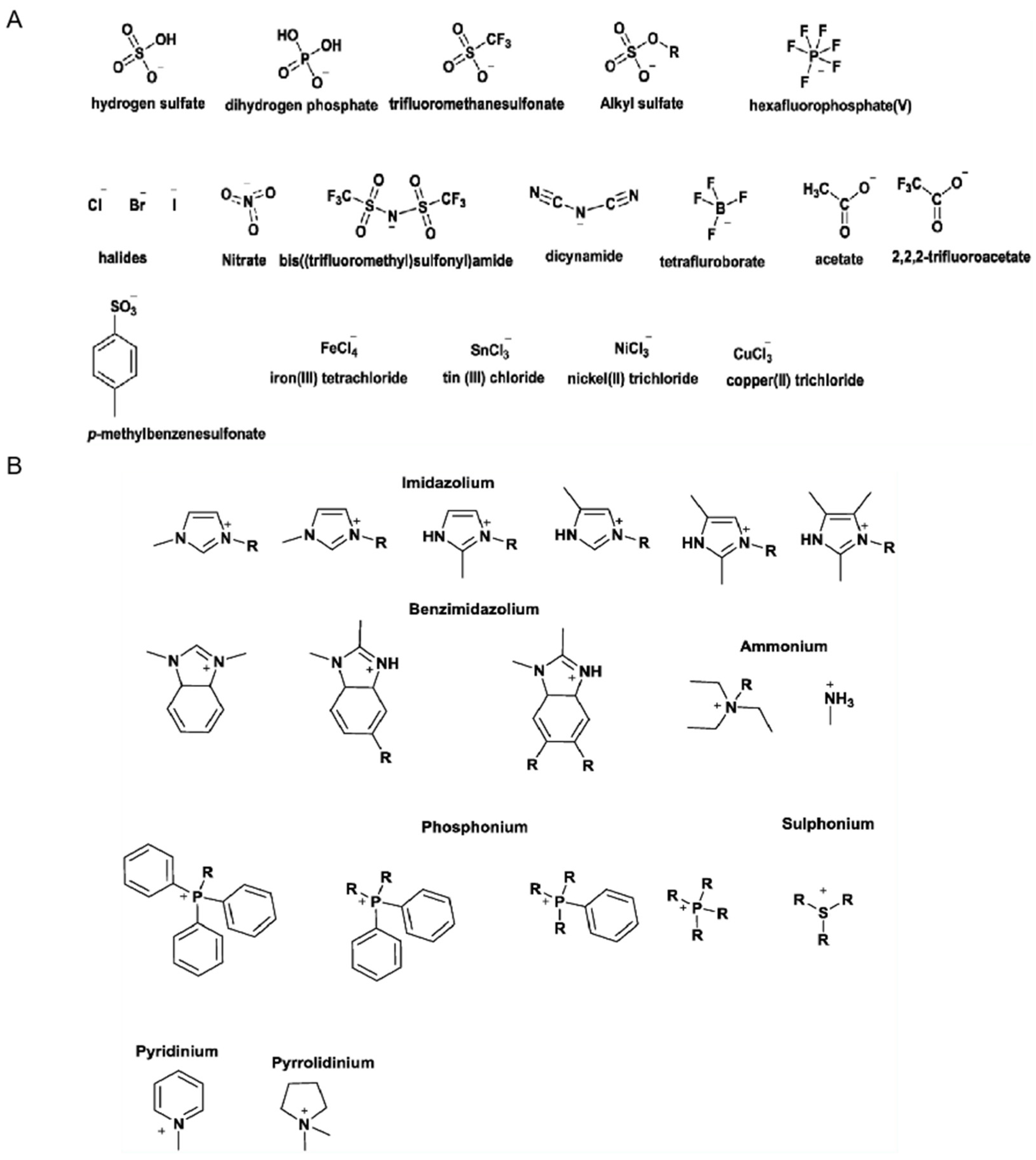
2. Classifications of Ionogels
2.1. Types of Ionic Liquid
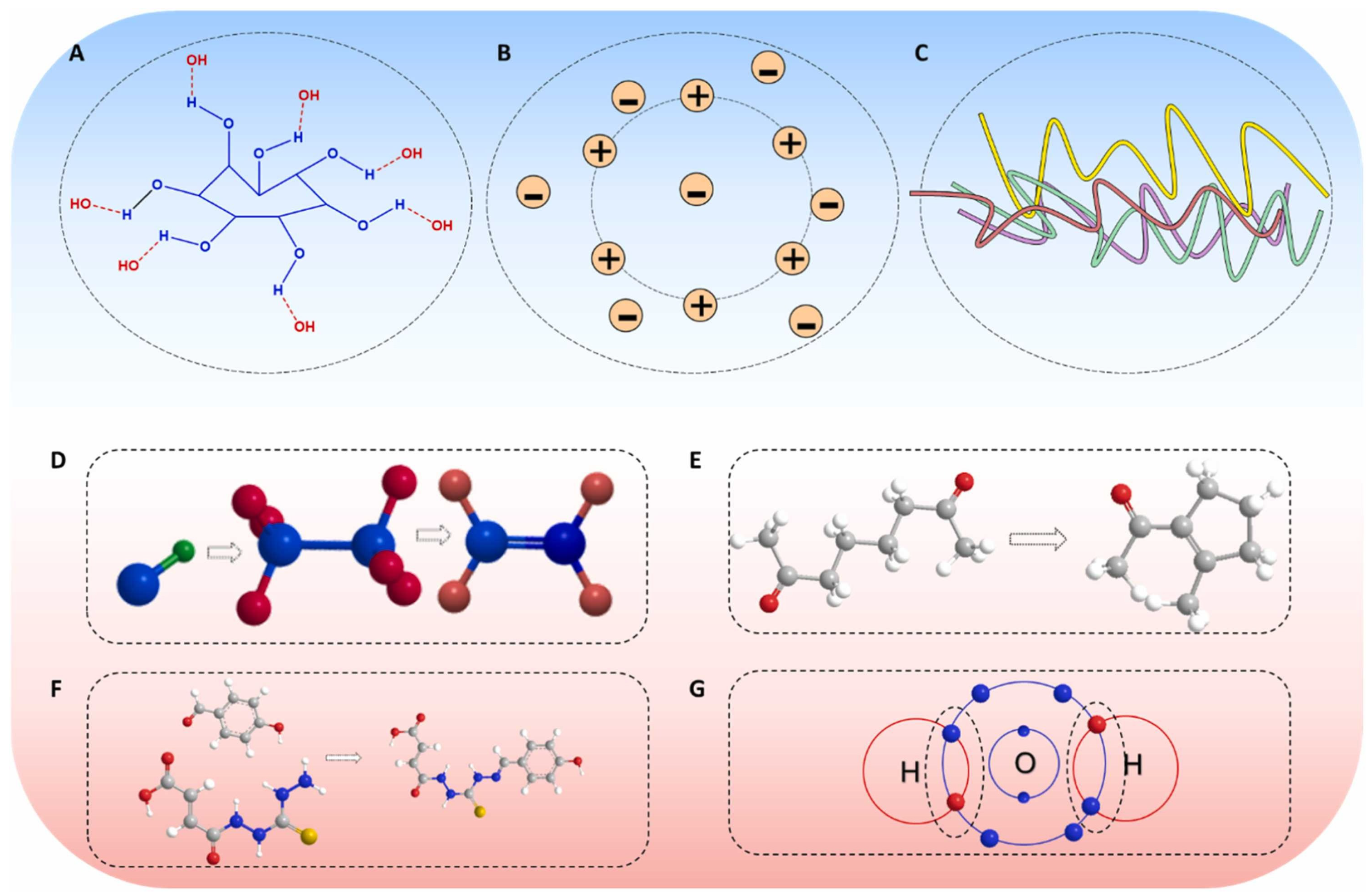
2.2. Types of Network Structures
2.3. Types of Design Strategy
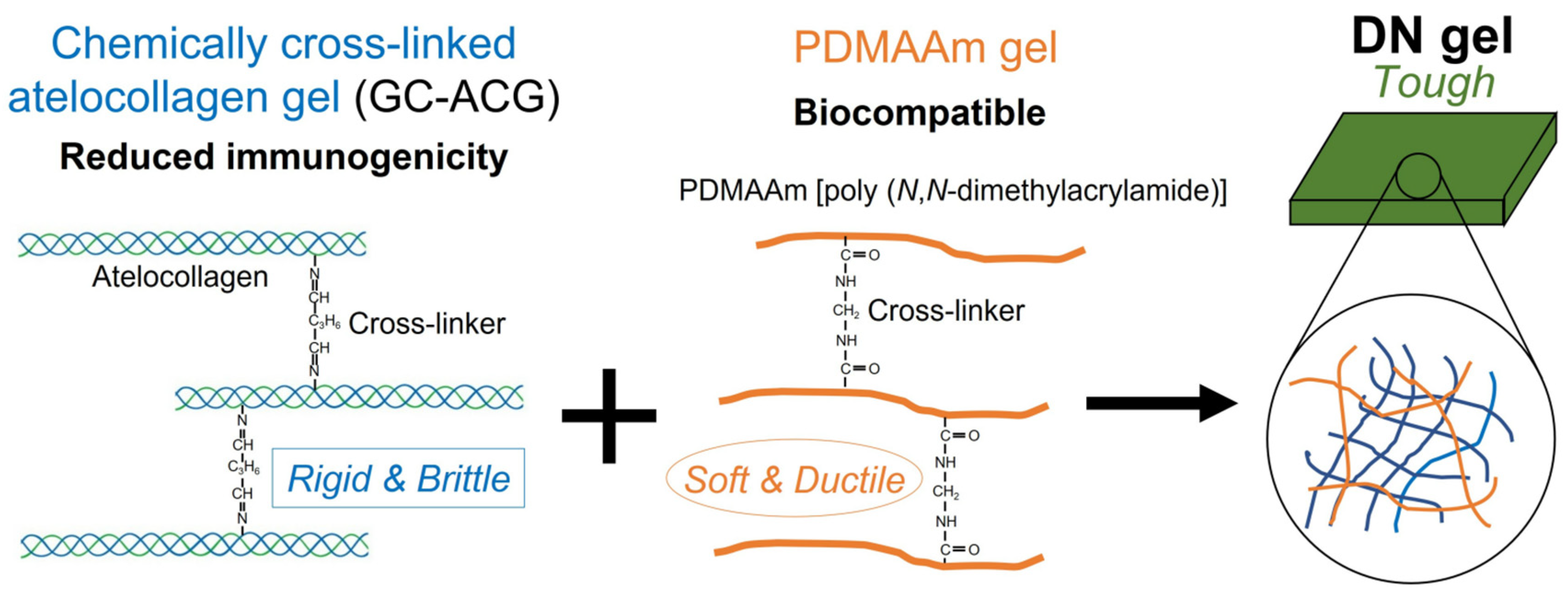
2.3.1. Double-Network Gels
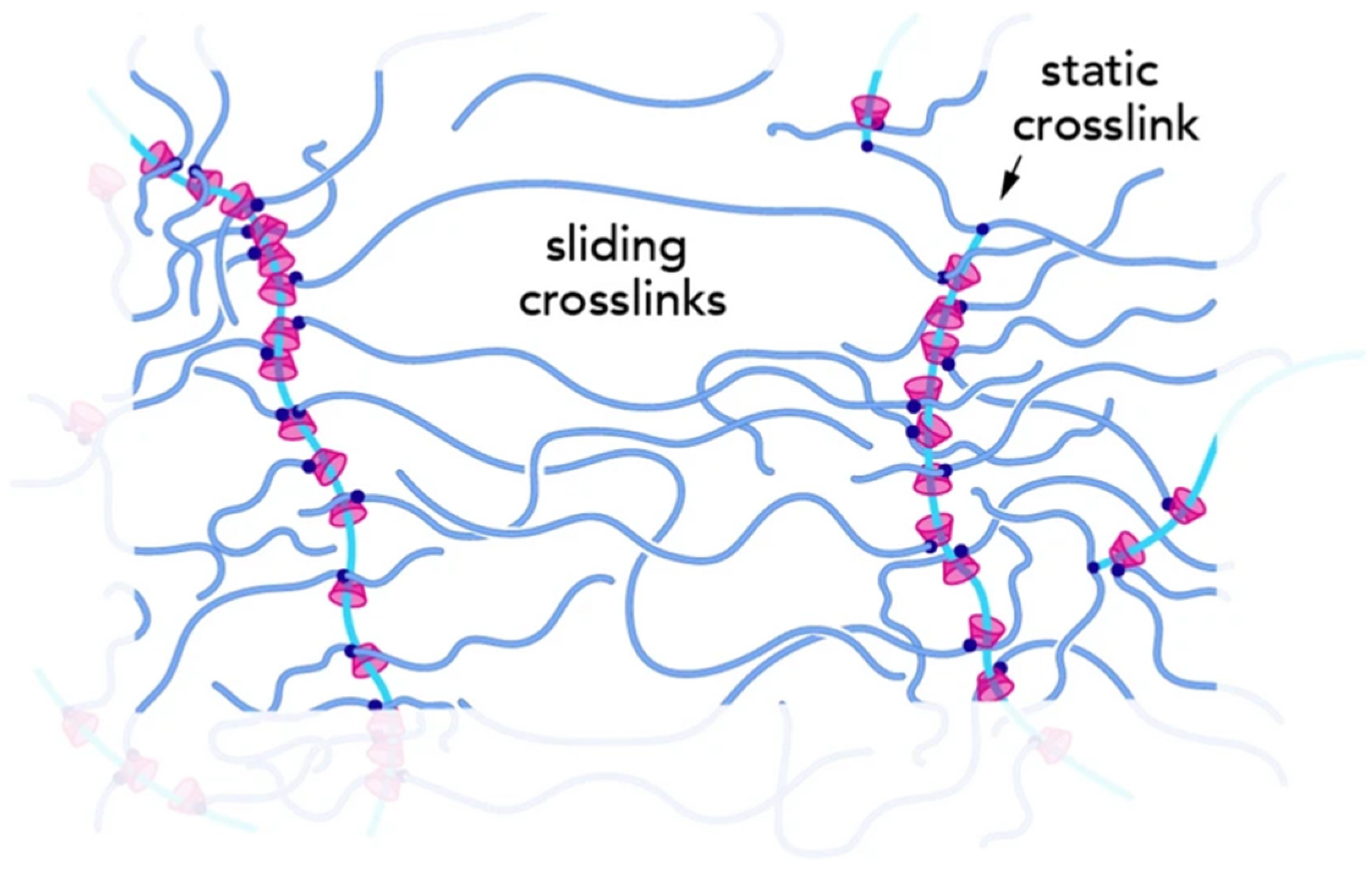
2.3.2. Slide-Ring Gels
2.3.3. Nanocomposite Gels
3. Preparations of Ionogels
3.1. Direct Mixing Method
3.2. In Situ Polymerization/Gel Method
3.3. Solvent Exchange Method
4. Properties and Modification Methods of Ionogels
4.1. Toughness
4.2. Conductivity
4.3. Hydrophobicity
4.4. Self-Healing
4.5. Adhesion
4.6. Freezing Resistance
5. Applications of Ionogels as Flexible Pressure Sensors
5.1. Classification and Key Parameters of Flexible Pressure Sensors
5.2. Applications in the Field of Wearable Electronic Devices
5.3. Applications in the Field of Intelligent Robots
5.4. Applications in the Field of Healthcare
6. Challenges of Ionogels as Flexible Pressure Sensors
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Néouze, M.-A.; Bideau, J.L.; Leroux, F.; Vioux, A. A Route to Heat Resistant Solid Membranes with Performances of Liquid Electrolytes. Chem. Commun. 2005, 8, 1082–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Susan, M.A.B.H.; Kaneko, T.; Noda, A.; Watanabe, M. Ion Gels Prepared by in Situ Radical Polymerization of Vinyl Monomers in an Ionic Liquid and Their Characterization as Polymer Electrolytes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 4976–4983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobashi, Y.; Yao, D.; Petel, Y.; Nguyen, T.N.; Sarwar, M.S.; Thabet, Y.; Ng, C.L.W.; Scabeni Glitz, E.; Nguyen, G.T.M.; Plesse, C.; et al. Piezoionic Mechanoreceptors: Force-Induced Current Generation in Hydrogels. Science 2022, 376, 502–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, T.; Jin, L.; Ao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Sun, Y.; Wang, S.; Qu, Y.; Huang, L.; Yang, T.; Deng, W.; et al. All-Polymer Piezo-Ionic-Electric Electronics. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 10876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Qi, Y.; Niu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Xiang, X.; Zhang, K.; He, P.; Dai, Y.; Niu, W.; Zhang, X. Highly Sensitive, Ultra-Reliable Flexible Piezoelectret Sensor for Non-Contact Sitting Motion Tracking and Physiological Signal Monitoring. Nano Energy 2023, 111, 108424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Li, W.; Yan, J.; Sun, J. Roles of Ionic Liquids in Adjusting Nature of Ionogels: A Mini Review. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2203988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhang, P.; Shamsi, M.; Thelen, J.L.; Qian, W.; Truong, V.K.; Ma, J.; Hu, J.; Dickey, M.D. Tough and Stretchable Ionogels by in Situ Phase Separation. Nat. Mater. 2022, 21, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, M.; Tang, Y.; Xu, C.; Li, C.Y.; Xia, K.; Xu, W.; Lin, J.; Jiang, Z.; Yang, J.; Zheng, S.Y. Developing Tough, Fatigue-Resistant and Conductive Hydrogels via in Situ Growth of Metal Dendrites. Mater. Horiz. 2025, 12, 1452–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, W.; Zhang, H.; Lyu, X.; Luo, Z.-Z.; Yu, Y.; Zou, Z. An Ultra-Tough and Super-Stretchable Ionogel with Multi Functions towards Flexible Iontronics. Sci. China Mater. 2023, 66, 1539–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marr, P.C.; Marr, A.C. Ionic Liquid Gel Materials: Applications in Green and Sustainable Chemistry. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 105–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, R.D.; Seddon, K.R. Ionic Liquids--Solvents of the Future? Science 2003, 302, 792–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Dong, Z.; Wu, M.; Duan, M.; Yin, S.; Jin, Q.; Chen, S.; Wang, X.; Zhou, D. Programmable Adhesive Ionogels Dominated by Temperature-Triggered Reversible Side-Chain Crystallization. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 498, 155513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, G.; Huo, R.; Ma, Z.; Strong, M.; Valiei, A.; Jiang, S.; Liu, S.; Mongeau, L.; Li, J. Ionotronic Tough Adhesives with Intrinsic Multifunctionality. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 37849–37861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Han, X.; Jiang, F. Cellulose Nanofibrils Enhanced, Strong, Stretchable, Freezing-Tolerant Ionic Conductive Organohydrogel for Multi-Functional Sensors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2003430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, R.; Yan, S.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, Y.; He, D.; Wang, K.; Zhou, D.; Jia, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhang, B.; et al. Ureido-Ionic Liquid Mediated Conductive Hydrogel: Superior Integrated Properties for Advanced Biosensing Applications. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, 2401869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, K.; Li, K.; Wang, Z.; Men, W.; Wu, X.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, J. An Unprecedented Strategy with Electric Double Layer and Adaptive Ionic Liquid in Fully Ionogel Fiber-Based TENG for Enhanced Output and Dynamic Stability. Nano Energy 2025, 135, 110658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.S.; Lee, C.Y.; Park, D.H.; Lee, J.E.; Cho, K.G.; Yang, S.; Lee, K.H. 3D Printable Double-Network Ionogels with a Multi-Angle Zigzag Pattern for Enhanced Linearity and Sensitivity of Stretchable Ionic Sensors. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 504, 158573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Bu, X.; Wang, L.; Wu, L.; Ma, X.; Diao, W.; Lu, D. Ultratough and Recoverable Ionogels Based on Multiple Interpolymer Hydrogen Bonding as Durable Electrolytes for Flexible Solid-state Supercapacitor. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 138, 50259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Chen, L.; Meng, H.; Wang, Y.; Ye, W.; Hu, B.; Gao, Z.; Wang, C. Multifunctional Janus-Type Self-Healing MXene/Polyionic Liquid Flexible Sensor. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2023, 243, 110240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Jiang, J.; Chen, W.; He, Y.; Lin, T.; Zhao, L. Radiation Synthesis of Rapidly Self-Healing, Durable, and Flexible Poly(Ionic Liquid)/MXene Gels with Anti-Freezing Property for Multi-Functional Strain Sensors. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 468, 143660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liang, L.; Hu, W.; Liao, H.; Zhang, Y. POSS Hybrid Poly(Ionic Liquid) Ionogel Solid Electrolyte for Flexible Lithium Batteries. J. Power Sources 2022, 542, 231766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Jiang, Y.; Hu, X. Ionogel-Based Membranes for Safe Lithium/Sodium Batteries. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2200945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Hu, J.; Dickey, M.D. Tough Ionogels: Synthesis, Toughening Mechanisms, and Mechanical Properties—A Perspective. JACS Au 2022, 2, 2645–2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Liu, S.; Jia, Z.; Koh, J.J.; Yeo, J.C.C.; Wang, C.-G.; Surat’man, N.E.; Loh, X.J.; Le Bideau, J.; He, C.; et al. Ionogels: Recent Advances in Design, Material Properties and Emerging Biomedical Applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2023, 52, 2497–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Liu, Y.; Yang, J.; Rehman, M.H.U.; Zhang, H.; Chen, L.; Li, J. Cellulose Ionogels: Recent Advancement in Material, Design, Performance and Applications. Resour. Chem. Mater. 2024, 100088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morozova, S.M. Recent Progress in the Design and Application of Polymer Based Ionogels as Proton Conducting Membranes for Fuel Cells. Mater. Today Commun. 2025, 42, 111390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Lin, L.; Zhang, T.; Wang, Z.; Liu, X.; Quan, Q.; Zhang, G.; Zhou, Y.; Li, J.; Zhou, X.; et al. High Toughness and Programmable Strength in Ion Gels via Hydrogen Bond-Induced Microphase Separation. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 505, 159608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomé, L.C.; Porcarelli, L.; Bara, J.E.; Forsyth, M.; Mecerreyes, D. Emerging Iongel Materials towards Applications in Energy and Bioelectronics. Mater. Horiz. 2021, 8, 3239–3265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, X.; Ma, S.L.; Li, P.; Wang, D.; Yang, J.; Liao, C.R. Spinning-Iongel Composite Structures for Iontronic Flexible Pressure Sensors with High-Sensitivity, Wide-Linearity. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE 3rd International Conference on Micro/Nano Sensors for AI, Healthcare, and Robotics (NSENS), Shenzhen, China, 2–3 March 2024; pp. 41–44. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Tan, S.; Wang, C.; Wu, Y. Lyotropic Ionic Liquid Crystal Gels Derived from Polyimidazolium Hydrogen Sulfate for Enhanced Proton Conductivity. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2024, 141, e55376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, V.; Das, E.; Bhargava, A.; Deshmukh, S.; Modi, A.; Srivastava, R. Ionogels for Flexible Conductive Substrates and Their Application in Biosensing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 254, 127736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K.; Savoy, A.W. Ionic Liquids Synthesis and Applications: An Overview. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 297, 112038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanasingha, N.; Dorishetty, P.; Dutta, N.; Choudhury, N. Polyelectrolyte Gels: Fundamentals, Fabrication and Applications. Gels 2021, 7, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Liu, Q.; Ke, Z.; Si, T.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, W.; Tang, S. Deep Eutectic Solvent-Based Ionogel: Innovative Potential as a Promising Chromatographic Separation Material. Anal. Chim. Acta 2025, 1342, 343673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Tang, L.; Kuang, G.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z.; Xing, G.; Jiang, X.; Chen, Z.; Tao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Supramolecular Ionogels Enable Highly Efficient Electrochromism. Mater. Horiz. 2025, 12, 1992–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Xu, L.; Zhang, W.; Wang, H. Large-Scale and Controllable Syntheses of Covalently-Crosslinked Poly(Ionic Liquid) Nanoporous Membranes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202302168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopson, C.; Villar-Chavero, M.M.; Domínguez, J.C.; Alonso, M.V.; Oliet, M.; Rodriguez, F. Cellulose Ionogels, a Perspective of the Last Decade: A Review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 274, 118663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, W.; Jiang, W.; Deng, X.; Tao, W.; Tang, J.; Li, Y.; Peng, J.; Chen, C.; Liu, K.; Fang, Y. Supramolecular Adhesives with Extended Tolerance to Extreme Conditions via Water-Modulated Noncovalent Interactions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202303506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, X.; Tang, J.; Guan, W.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Y.; Chen, H.-L.; Chen, C.-L.; Li, Y.; Liu, K.; et al. Strong Dynamic Interfacial Adhesion by Polymeric Ionic Liquids under Extreme Conditions. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 5303–5315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Dai, Y.; Xing, Y.; Wang, L.; Guo, C.; Chen, R.; Guo, S.; Wu, F. Biomimetic Ant-Nest Ionogel Electrolyte Boosts the Performance of Dendrite-Free Lithium Batteries. Energy Environ. Sci. 2017, 10, 1660–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nechausov, S.; Miriyev, A. 3D-Printable High-Mixed-Conductivity Ionogel Composites for Soft Multifunctional Devices. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 496, 153759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-A.; Ma, K.; Chen, K.-Z.; Qiao, S.-L. Flexible Wearable Ionogels: Classification, Fabrication, Properties and Applications. Sens. Actuators Phys. 2024, 372, 115325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.; Wang, H. High-Performance Polymeric Materials through Hydrogen-Bond Cross-Linking. Adv. Mater. 2019, 32, 1901244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Zhang, K.; Chen, G.; Su, B.; He, M. Stiff, Self-Healable, Transparent Polymers with Synergetic Hydrogen Bonding Interactions. Chem. Mater. 2021, 33, 5189–5196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, J.; Luo, H. Constructions and Properties of Physically Cross-Linked Hydrogels Based on Natural Polymers. Polym. Rev. 2022, 63, 574–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Larson, R.G.; Li, L.; Luo, H.; He, X.; Niu, Y.; Li, G. Influence of Chain Entanglement on Rheological and Mechanical Behaviors of Polymerized Ionic Liquids. Macromolecules 2023, 56, 2719–2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Inda, M.E.; Lai, Y.; Lu, T.K.; Zhao, X. Engineered Living Hydrogels. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2201326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; He, X.; Yang, B.; Lai, L.; Chen, N.; Hu, J.; Lu, Q. Dual Physically Cross-Linked Hydrogels Incorporating Hydrophobic Interactions with Promising Repairability and Ultrahigh Elongation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 31, 2008187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, Y.; Xia, Z.; Qi, Y.; Sumigawa, T.; Wu, J.; Šesták, P.; Lu, Y.; Håkonsen, V.; Li, T.; Wang, F.; et al. Simultaneously Toughening and Stiffening Elastomers with Octuple Hydrogen Bonding. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2008523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whba, R.; Su’ait, M.S.; Tian Khoon, L.; Ibrahim, S.; Mohamed, N.S.; Ahmad, A. Free-Radical Photopolymerization of Acrylonitrile Grafted onto Epoxidized Natural Rubber. Polymers 2021, 13, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, M.; Lv, Y.; Ge, J.; Zhang, B.; Wu, Y.; Shen, L.; Liu, Q.; Yan, M.; He, J. Hydrophobic and Multifunctional Strain, Pressure and Temperature Sensor Based on TPU/SiO2-ILs Ionogel for Human Motion Monitoring, Liquid Drop Monitoring, Underwater Applications. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 664, 131103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Li, Q.; He, X.; Wang, X.; Wen, Y.; Zeng, L.; Yu, W.; Hu, P.; Chen, H. A Multifunctional Hydrogel Based on Nature Polysaccharide Fabricated by Schiff Base Reaction. Eur. Polym. J. 2023, 197, 112330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Park, K.; Choi, H.; Son, D.; Shin, M. Self-Healing, Stretchable, Biocompatible, and Conductive Alginate Hydrogels through Dynamic Covalent Bonds for Implantable Electronics. Polymers 2021, 13, 1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.; Chen, Y.; Yu, X. Double-Network Ionogel Solid Electrolytes for Long-Cycling Supercapacitors. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2023, 812, 140259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Zhang, Q.; Yu, C.; Rao, S.; Yang, S.; Tian, H.; Qu, D. An Ultrastrong and Highly Stretchable Polyurethane Elastomer Enabled by a Zipper-Like Ring-Sliding Effect. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2000345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, T.D.; Trung, T.Q.; Le Mong, A.; Huynh, H.Q.; Lee, D.; Hong, S.J.; Vu, D.T.; Kim, M.; Lee, N.-E. Utilizing a High-Performance Piezoelectric Nanocomposite as a Self-Activating Component in Piezotronic Artificial Mechanoreceptors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 20813–20825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.P.; Katsuyama, Y.; Kurokawa, T.; Osada, Y. Double-Network Hydrogels with Extremely High Mechanical Strength. Adv. Mater. 2003, 15, 1155–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; King, D.R.; Sun, T.L.; Saruwatari, Y.; Nakajima, T.; Kurokawa, T.; Gong, J.P. Polyzwitterions as a Versatile Building Block of Tough Hydrogels: From Polyelectrolyte Complex Gels to Double-Network Gels. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 50068–50076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.-G.; Xu, Y.-C.; Fang, R.-C.; Liu, M.-J. Bioinspired Adaptive Gel Materials with Synergistic Heterostructures. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 2018, 36, 683–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuyukubo, A.; Kubota, R.; Sato, Y.; Fujimoto, I. The Toughness-Enhanced Atelocollagen Double-Network Gel for Biomaterials. Polymers 2024, 16, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, T.; Kawakami, R.; Namba, R.; Nakajima, T.; Gong, J.P. Mechanoresponsive Self-Growing Hydrogels Inspired by Muscle Training. Science 2019, 363, 504–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Lou, D.; Wang, H.; Jiang, D.; Fang, X.; Meng, J.; Sun, X.; Li, J. One-Pot Synthesis of Anti-Freezing Carrageenan/Polyacrylamide Double-Network Hydrogel Electrolyte for Low-Temperature Flexible Supercapacitors. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 435, 135057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zheng, H.; Tan, Y.J.; Tor, S.B.; Zhou, K. Development of an Ultrastretchable Double-Network Hydrogel for Flexible Strain Sensors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 12814–12823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, P.; Zhang, R.; Xu, K. Valorization of Waste Plastics to Prepare Tough, Stretchable and Highly Conductive Ionicgels. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 01, 148605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, A.; Li, J.; Kamachi, M. The Molecular Necklace: A Rotaxane Containing Many Threaded α-Cyclodextrins. Nature 1992, 356, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okumura, Y.; Ito, K. The Polyrotaxane Gel: A Topological Gel by Figure-of-Eight Cross-Links. Adv. Mater. 2001, 13, 485–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhode, A.R.; Montes De Oca, I.; Chabinyc, M.L.; Bates, C.M.; Pitenis, A.A. Sliding on Slide-Ring Gels. Tribol. Lett. 2024, 72, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noda, Y.; Hayashi, Y.; Ito, K. From Topological Gels to Slide-ring Materials. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131, app.40509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Liu, Q.; Yu, R.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, M.; Li, W.; Song, D.; Wang, R.; Xu, Z.; et al. Development and Optimization of a Nanocomposite Gel Foam for Inhibiting Coal Spontaneous Combustion. Combust. Sci. Technol. 2024, 196, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavrador, P.; Esteves, M.R.; Gaspar, V.M.; Mano, J.F. Stimuli-Responsive Nanocomposite Hydrogels for Biomedical Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 31, 2005941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; He, L.; Li, Y.; Chao, M.; Li, M.; Wan, P.; Zhang, L. Healable, Degradable, and Conductive MXene Nanocomposite Hydrogel for Multifunctional Epidermal Sensors. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 7765–7773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuchen, Z.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, D.; Dai, Y.; Xia, F.; Ma, X. Nanocomposite Adhesive Hydrogels: From Design to Application. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 6, 585–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, D.; Xing, L.; Xie, Y.; Li, P.; Yang, F. Hybrid Crosslinking Cellulose Nanofibers-Reinforced Zwitterionic Poly (Ionic Liquid) Organohydrogel with High-Stretchable, Anti-Freezing, Anti-Drying as Strain Sensor Application. Carbohydr. Polym. 2025, 353, 123253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.; Li, B.; Ma, Z.; Xu, J.; Wang, D.; Zeng, Z.; Ho, D. Ion-Selective Mobility Differential Amplifier: Enhancing Pressure-Induced Voltage Response in Hydrogels. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 64, e202415000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, S.; Wu, P. Adaptive Ionogel Paint from Room-Temperature Autonomous Polymerization of α-Thioctic Acid for Stretchable and Healable Electronics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2101494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, A.; Xia, Q.; Ju, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Wang, H.; Xie, Y. Cellulose Enhanced Highly Sensitive and Durable Dual-Network Ionogel Sensor for Human Motion Monitoring. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 499, 156608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.-L.; Liao, S.-W.; Guo, G.-S.; Shu, C.-M. Using TGA to Evaluate the Effect of Three Ionic Liquids on the Thermal Stability of Ionogel Membrane and Their Application in Synthesis. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2025, 150, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, S. Ionogel Adhesives: From Structural Design to Emerging Applications. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2025, 46, 2400973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhang, C.; Chen, J.; Lin, W.; Meng, J. A Tough Double-Network Ion Gel Membrane Based on Poly (Ionic Liquid) for Efficient Carbon Capture. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 331, 12551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Yang, Q.; Wu, Q.; Bu, X.; Wang, X.; Liu, W.; Han, C.; Hu, L.; Li, X.; Wang, X. In-Situ Copolymerization Ion-Gel-Based Flexible Sensor for Wearable Dimethyl Methylphosphonate Detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2024, 404, 135274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uz, M.; Jackson, K.; Donta, M.S.; Jung, J.; Lentner, M.T.; Hondred, J.A.; Claussen, J.C.; Mallapragada, S.K. Fabrication of High-Resolution Graphene-Based Flexible Electronics via Polymer Casting. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Tang, N.; Yu, X.; Li, M.-H. Strong and Tough Physical Eutectogels Regulated by the Spatiotemporal Expression of Non-Covalent Interactions. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 06305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.S.; Kim, J.H.; Yoo, H.; Yoon, D.-S.; Park, D.H.; Lee, C.Y.; Kim, S.J.; Choi, S.-B.; Hong, K.; Lee, K.H. Ultrastretchable, Tough, and Highly Conductive Ionogels for Multipurpose Motion Monitoring. ACS Mater. Lett. 2024, 6, 4658–4666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Guo, J.; Liu, Z.; Sun, Z.; Wu, Y.; Liu, L.; Yan, F. Ionic Liquid–Based Click-Ionogels. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaax0648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, X.; Wang, J.; Cong, Z.; Liu, C.; Cai, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, C.; Lan, S.; Niu, J. Strong and Tough Eutectogels with Broad-Range Tunable Mechanical Properties via the Hydrogen Bond Network-Specific Effect. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2025, 34, 2422464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.; Zhao, J.; Li, Q.; Sun, Y.; Du, G.; Tang, F.; Liu, Y.; Hu, Q.; Li, X.; Nie, S. A Strong and Tough Ion-gel Enabled by Hierarchical Meshing and Ion Hybridizations Collaboration. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 35, 2414682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Li, L.; Liu, Z.; Zheng, S.; Li, Q.; Yan, F. Supramolecular Ionogels Tougher than Metals. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2301383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Wei, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; Liu, C.; Diao, S.; Gao, Y.; Matyjaszewski, K.; Liu, H. Highly Processable Ionogels with Mechanical Robustness. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2211771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Li, W.; Liu, Z.; Zheng, S.; Hu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Guo, J.; Ou, X.; Li, Q.; Yu, J.; et al. Ionogels: Preparation, Properties and Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 34, 2314408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Yu, R.; Tao, X.; He, Y.; Li, X.; Tian, F.; Chen, X.; Huang, W. Mechanically Robust and Highly Conductive Ionogels for Soft Ionotronics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 33, 2208083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Luo, J.; Jia, T. Water-Resistant and Underwater Adhesive Ion-Conducting Gel for Motion- Robust Bioelectric Monitoring. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 431, 134012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Gan, D.; Wang, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, W.; Wang, Q.; Shao, J.; Dong, X. Ultra-Stretchable, Adhesive, and Anti-Swelling Ionogel Based on Fluorine-Rich Ionic Liquid for Underwater Reliable Sensor. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2023, 8, 2201566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Gao, S.; Guo, Q.; Wang, C.; Qiao, Y.; Qiu, D. A Solvent-Exchange Strategy to Regulate Noncovalent Interactions for Strong and Antiswelling Hydrogels. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2004579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Gao, G. Solvent-Resistant and Nonswellable Hydrogel Conductor toward Mechanical Perception in Diverse Liquid Media. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 13709–13717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Wang, M.; Prieto-López, L.O.; Deng, X.; Cui, J. Self-Hydrophobization in a Dynamic Hydrogel for Creating Nonspecific Repeatable Underwater Adhesion. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 30, 1907064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Fan, C.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Cui, C.; Liu, B.; Wu, T.; Zhang, X.; Liu, W. A Self-Thickening and Self-Strengthening Strategy for 3D Printing High-Strength and Antiswelling Supramolecular Polymer Hydrogels as Meniscus Substitutes. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2100462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Wang, J.; Gong, J.P. Barnacle Cement Proteins-Inspired Tough Hydrogels with Robust, Long-Lasting, and Repeatable Underwater Adhesion. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 31, 2009334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, X.; Sheng, Y.; Yao, L.; Li, X.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, S. Anti-Swelling Conductive Polyampholyte Hydrogels via Ionic Complexations for Underwater Motion Sensors and Dynamic Information Storage. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 463, 142439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, F.; Liu, J.; Gan, D.; Lei, B.; Shao, J.; Wang, W.; Wang, Q.; Dong, X. Underwater Self-Healing and Recyclable Ionogel Sensor for Physiological Signal Monitoring. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 28664–28674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.; He, Y.; Xu, Z.; Li, C.; Yang, C. Progress of Hydrophobic Ionogels: A Review. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2023, 44, 2200957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, T. A Fully Hydrophobic Ionogel Enables Highly Efficient Wearable Underwater Sensors and Communicators. Mater. Horiz. 2021, 8, 2761–2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Liu, F.; Abdiryim, T.; Liu, X. Self-Healing Hydrogels: From Synthesis to Multiple Applications. ACS Mater. Lett. 2023, 5, 1787–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamate, R.; Ueki, T. Adaptive Ion-Gel: Stimuli-Responsive, and Self-Healing Ion Gels. Chem. Rec. 2023, 23, e202300043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zuo, M.; Li, G.; Sha, J.; Zuo, X. Synthesis of Ammonium Persulfate Microcapsule with a Polyaniline Shell and Its Controlled Burst Release. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 138, 49695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, L.; Xin, Y.; Wu, X.; Ao, Q. Mechanism of Self-Healing Hydrogels and Application in Tissue Engineering. Polymers 2022, 14, 2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekeocha, J.; Ellingford, C.; Pan, M.; Wemyss, A.M.; Bowen, C.; Wan, C. Challenges and Opportunities of Self-Healing Polymers and Devices for Extreme and Hostile Environments. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2008052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Chen, L.; Xu, F.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Sun, J. Spontaneous Self-Healing Ionogels for Efficient and Reliable Carbon Dioxide Separation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2022, 10, 4695–4702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, J.W.; Keum, K.; Lee, H.; Jung, G.; Park, M.; Lee, Y.H.; Kim, S.; Ha, J.S. A Multi-Responsive Self-Healing and Air-Stable Ionogel for a Vertically Integrated Device Comprised of Flexible Supercapacitor and Strain Sensor. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 457, 141278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Duan, M.; Zou, X.; Gao, S.; Guo, J.; Wang, X.; Li, Q.; Li, W.; Wang, X.; Yan, F. Biocompatible Tough Ionogels with Reversible Supramolecular Adhesion. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 13903–13913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Xie, Q.; Pan, J.; Ma, C.; Zhang, G. Strong yet Tough Cross-Linked Oligosiloxane Elastomer with Impact-Resistant and Antifouling Properties. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 464, 142769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Xu, T.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Xie, R.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, Y. Tough Polyurethane Hydrogels with a Multiple Hydrogen-Bond Interlocked Bicontinuous Phase Structure Prepared by In Situ Water-Induced Microphase Separation. Adv. Mater. 2024, 37, 2412083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Song, H.; Chen, L.; Li, W.; Yang, D.; Cheng, P.; Duan, H. 3D Printed Ultrasensitive Graphene Hydrogel Self-Adhesive Wearable Devices. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2022, 4, 5199–5207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WANG, Z.; LIU, Z.; HAN, X.; WANG, T. Preparation and Underwater Adhesion Properties of Bi-Continuous Phases-Toughened Ionogel. J. Funct. Polym. 2024, 37, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Xu, J.; Liu, S.; Fu, L.; Wu, S.; Liu, Z.; Hou, T.; Liu, H.; Huang, D. Facile Synthesis of Ultratough Conductive Gels with Swelling and Freezing Resistance for Flexible Sensor Applications. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 7335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, J.; Pan, J.; Liu, X.; Yan, Y.; Shi, Y.; Yu, X.; Jia, X. A Flexible Solid-State Supercapacitor with Extreme Low-Temperature Tolerance Based on an Ion Conducting Ice Gel Electrolyte. J. Mater. Chem. A 2022, 10, 7036–7047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Dickey, M.D. Five-for-Five: Highlights from Five Recent Noteworthy Papers on Ionogels. J. Mater. Res. 2024, 39, 2237–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yang, N.; Chu, X.; Sun, F.; Ali, M.U.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, B.; Cai, Y.; Liu, M.; Gasparini, N.; et al. Wide-Humidity Range Applicable, Anti-Freezing, and Healable Zwitterionic Hydrogels for Ion-Leakage-Free Iontronic Sensors. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2211617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, W.; Wang, X.; Zou, X.; Zheng, S.; Liu, Z.; Li, Q.; Xia, Q.; Yan, F. Ultra-Tough and Recyclable Ionogels Constructed by Coordinated Supramolecular Solvents. Angew. Chem. 2022, 134, e202212512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Xu, K.; Shi, L.; Wu, J.; He, J.; Zhang, Z. Dual-Ionic Hydrogels with Ultralong Anti-Dehydration Lifespan and Superior Anti-Icing Performance. Appl. Mater. Today 2022, 26, 101367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Mao, Y.; Ji, D.; Wang, L.; Wang, L.; Chen, J.; Chang, X.; Zhu, Y. Transparent, Self-Adhesive, Highly Environmental Stable, and Water-Resistant Ionogel Enabled Reliable Strain/Temperature Sensors and Underwater Communicators. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 471, 144674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Cao, X.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, L.; Dong, J.; Qin, J.; Xuan, P.; Liu, L.; Sun, Y.; Fan, W.; et al. Human Skin-Mimicking Ionogel-Based Electronic Skin for Intelligent Robotic Sorting. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2024, 45, 2400379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Wu, P. Water-Resistant Ionogel Electrode with Tailorable Mechanical Properties for Aquatic Ambulatory Physiological Signal Monitoring. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2107226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.-Y.; Guo, C.-F. Department of Material Science and Engineering, Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen 518055, China Sensing mechanisms and applications of flexible pressure sensors. Acta Phys. Sin. 2020, 69, 178102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basarir, F.; Madani, Z.; Vapaavuori, J. Recent Advances in Silver Nanowire Based Flexible Capacitive Pressure Sensors: From Structure, Fabrication to Emerging Applications. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 9, 2200866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammock, M.L.; Chortos, A.; Tee, B.C.-K.; Tok, J.B.-H.; Bao, Z. 25th Anniversary Article: The Evolution of Electronic Skin (E-Skin): A Brief History, Design Considerations, and Recent Progress. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 5997–6038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolvanen, J.; Hannu, J.; Jantunen, H. Stretchable and Washable Strain Sensor Based on Cracking Structure for Human Motion Monitoring. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherumannil Karumuthil, S.; Singh, K.; Valiyaneerilakkal, U.; Akhtar, J.; Varghese, S. Fabrication of Poly (Vinylidene Fluoride-Trifluoroethylene)—Zinc Oxide Based Piezoelectric Pressure Sensor. Sens. Actuators Phys. 2020, 303, 111677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, F.; Xu, L.; He, Y.; Yan, H.; Liu, H. PVDF-Based Flexible Piezoelectric Tactile Sensors: Review. Cryst. Res. Technol. 2023, 58, 2300119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Wang, J.; Duan, L.; Gao, G. Highly Transparent Ionogel for Wearable Force Sensor and 3D Printing. Eur. Polym. J. 2025, 223, 113641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, H.; Pang, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhang, X.; Shang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Shi, Y.; Gui, Z.; Ye, Y.; et al. Ultrasensitive Iontronic Pressure Sensor Based on Microstructure Ionogel Dielectric Layer for Wearable Electronics. Nanotechnol. Precis. Eng. 2025, 8, 023010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Feng, H.; Yue, J.; Quan, G.; Wu, Y.; Yang, C.; Wang, K.; Xiao, L.; Liu, Y. Stretchable, Environmentally Stable, Multifunctional Ionogel with Self-Healing and Adhesive Properties for High-Performance Flexible Sensors. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 499, 156611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Huang, H.; Ding, Q.; Guo, Y.; Sun, W.; Wu, Z.; Qin, M.; Guan, Q.; You, Z. Highly Transparent, Stretchable, and Self-Healable Ionogel for Multifunctional Sensors, Triboelectric Nanogenerator, and Wearable Fibrous Electronics. Adv. Fiber Mater. 2021, 4, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.; Lee, S.; Kim, H.; Lee, W.; Chong, J.; You, I.; Kang, J. Self-Healing Electronic Skin with High Fracture Strength and Toughness. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 9763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, B.; Liu, K.; Wu, B.; Sun, S.; Wu, P. Low-Hysteresis and Tough Ionogels via Low-Energy-Dissipating Cross-Linking. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2408826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.; Zhi, X.; Guo, M.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, S.; Wang, X. Multimodal, Ultrasensitive, and Biomimetic Electronic Skin Based on Gradient Micro-Frustum Ionogel for Imaginary Keyboard and Haptic Cognition. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 35, 2414936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopilovic, B.; E Silva, F.A.; Pedro, A.Q.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Freire, M.G. Ionogels for Biomedical Applications. In Nanotechnology for Biomedical Applications; Gopi, S., Balakrishnan, P., Mubarak, N.M., Eds.; Materials Horizons: From Nature to Nanomaterials; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 391–425. ISBN 978-981-16-7482-2. [Google Scholar]
- Shukla, M.K.; Tiwari, H.; Verma, R.; Dong, W.-L.; Azizov, S.; Kumar, B.; Pandey, S.; Kumar, D. Role and Recent Advancements of Ionic Liquids in Drug Delivery Systems. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhamble, S.; Dighe, S.; Katari, O.; Yadav, V.; Ansari, M.M.; Jain, S. Ionic Liquid-Based Ionogel: A Novel Strategy to Improve Dermal Delivery and in Vivo Efficacy of Etodolac in Rheumatoid Arthritis Management. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 412, 125841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuddushi, M.; Ray, D.; Aswal, V.; Hoskins, C.; Malek, N. Poly(Vinyl Alcohol) and Functionalized Ionic Liquid-Based Smart Hydrogels for Doxorubicin Release. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2020, 3, 4883–4894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuddushi, M.; Patel, N.K.; Rajput, S.; Shah, A.; El Seoud, O.A.; Malek, N.I. Thermo-Switchable de Novo Ionic Liquid-Based Gelators with Dye-Absorbing and Drug-Encapsulating Characteristics. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 12068–12078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Yang, C.; Hu, J.; Pan, M.; Qiu, W.; Guo, Y.; Sun, K.; Xu, Y.; Li, P.; Peng, J.; et al. Wide-Range Linear Iontronic Pressure Sensor with Two-Scale Random Microstructured Film for Underwater Detection. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 43923–43933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, C.; Kim, D.; Lee, C.; Oh, J.H. Ultrasensitive Ionic Liquid Polymer Composites with a Convex and Wrinkled Microstructure and Their Application as Wearable Pressure Sensors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 13625–13636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M. Nanoscale Control of Morphologies Enables Robust and Elastic Ionogel for Sensitive and High-Resolution Pressure Sensing over Wide Linear Range. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 508, 160913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M. Emerging Applications of Tough Ionogels. NPG Asia Mater. 2023, 15, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keplinger, C.; Sun, J.-Y.; Foo, C.C.; Rothemund, P.; Whitesides, G.M.; Suo, Z. Stretchable, Transparent, Ionic Conductors. Science 2013, 341, 984–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Wang, M.; Chen, S.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, H.; Deng, Y.; Yang, G.; Fei, C.; Chen, B.; Lin, Y.; et al. Lead-Adsorbing Ionogel-Based Encapsulation for Impact-Resistant, Stable, and Lead-Safe Perovskite Modules. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabi8249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Shen, X.; Li, S.; Zhu, H.; Cheng, Y.; Lv, H.; Wang, Z.; Lou, C.; Song, H. Skin-Inspired Gradient Ionogels Induced by Electric Field for Ultrasensitive and Ultrafast-Responsive Multifunctional Ionotronics. J. Mater. Chem. A 2024, 12, 1036–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liang, S.; Li, F.; Ding, H.; Ding, L.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, L. Flexible Strain-Sensitive Sensors Assembled from Mussel-Inspired Hydrogel with Tunable Mechanical Properties and Wide Temperature Tolerance in Multiple Application Scenarios. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 50400–50412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Yang, C.; Guo, C.F. Creep-Free Polyelectrolyte Elastomer for Drift-Free Iontronic Sensing. Nat. Mater. 2024, 23, 1107–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.; Guo, F.; Li, Y.; Luo, X.; Luo, C.; Jin, Q.; Wu, H.; Fu, J.; Zhang, M.; Long, Y. A Novel 3D-Printed Self-Healing, Touchless, and Tactile Multifunctional Flexible Sensor Inspired by Cutaneous Sensory Organs. Compos. Commun. 2025, 54, 102287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Tang, W.; Chen, S.; Si, Y.; Liu, R.; Guo, X. Flexible Organic Polymer Gas Sensor and System Integration for Smart Packaging. Adv. Sens. Res. 2023, 2, 2300030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, Q.; Lin, Y.; Zheng, Z. Wearable Sweat Biosensors on Textiles for Health Monitoring. J. Semicond. 2023, 44, 021601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| # | Ionic Liquid | Solid Carrier Networks | Response Range (kPa) | Sensitivity (kPa−1) | Response, Relaxation Time (ms) | Low Detection Limit (Pa) | Strain (%) | Stress/ Compressive Stress (kPa) | Temperature (℃) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | BMP-NTf2 | TPU | 0.6~12 | 0.033 | 346, - | — | 2620 | 4.34 | 30 to 100 | [51] |
| 12~25 | 0.008 | |||||||||
| 2 | CE | PVA | 0.2 | 684.4 | 18.1, - | 0~1000 | 390 | 1220 | 25 | [74] |
| 3 | [EMIM][TFSI] | TPU | 0~20 | 3.744 | 100, - | — | — | — | 25 | [130] |
| 20~800 | 1.689 | |||||||||
| 4 | [EMIM][TFSI] | PVDF-HFP | 0.47 | 357.56 | 10, 20 | 0~500 | — | — | 25 | [135] |
| 5 | [EMIM][TFSI] | PVDF-HFP | 2.5 | 12.8 | 20, 30 | 0~1000 | — | — | 25 | [141] |
| 6 | [EMIM][TFSI] | PVDF-HFP | 0.5 | 12.8 | 60, 50 | 0~80 | — | — | 25 | [142] |
| 7 | [EMIm]OTf | AAm/DMAA | 8 | 1.2 | 52, 68 | 0.008~1000 | 97 | 990 | −30 to 150 | [143] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, H.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, M.; Wang, Q.; Yang, L.; Shuai, C. Progress of Ionogels in Flexible Pressure Sensors: A Mini-Review. Polymers 2025, 17, 1093. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17081093
Jiang H, Cheng Y, Zhang X, Li M, Wang Q, Yang L, Shuai C. Progress of Ionogels in Flexible Pressure Sensors: A Mini-Review. Polymers. 2025; 17(8):1093. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17081093
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Huaning, Yuqiang Cheng, Xingying Zhang, Mengqing Li, Qinqin Wang, Liang Yang, and Changgeng Shuai. 2025. "Progress of Ionogels in Flexible Pressure Sensors: A Mini-Review" Polymers 17, no. 8: 1093. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17081093
APA StyleJiang, H., Cheng, Y., Zhang, X., Li, M., Wang, Q., Yang, L., & Shuai, C. (2025). Progress of Ionogels in Flexible Pressure Sensors: A Mini-Review. Polymers, 17(8), 1093. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17081093







