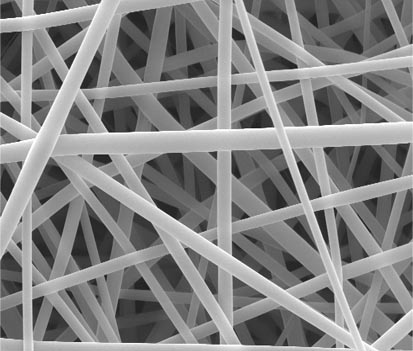
Tailoring Crystallinity of Electrospun Plla Fibres by Control of Electrospinning Parameters
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Kinematic Viscosity

2.2.2. Electrospinning

2.2.3. Characterisation of Electrospun Polymer Fibres
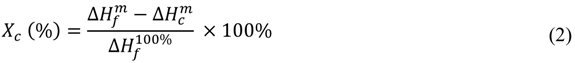
 = Heat of fusion (J·g−1),
= Heat of fusion (J·g−1),  = Heat of cold crystallization (J·g−1) and,
= Heat of cold crystallization (J·g−1) and,  = Heat of fusion for 100% crystalline material (93.6 J·g−1) [39].
= Heat of fusion for 100% crystalline material (93.6 J·g−1) [39].3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of Polymer Solution Parameters and Processing Conditions on the Electrospinning Process


3.2. Effect of Electrospinning on the Glass Transition Temperature (Tg)
3.3. Effect of Polymer Solution Concentration on Degree of Crystallinity

| PLLA electrospinning solution | Electrospinning parameters | Tg (°C) | Xc (%) | PLLA electrospinning solution | Electrospinning parameters | Tg (°C) | Xc (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NTCD (cm) | Voltage (kV) | 1st heating cycle | 2nd heating cycle | NTCD (cm) | Voltage (kV) | 1st heating cycle | 2nd heating cycle | ||||
| Granule | n/a | n/a | 67 | n/a | 37.4 | n/a | n/a | n/a | - | - | - |
| 5% | 7.5 | 15 | 52 | 56 | 45.3 | 8% | 7.5 | 15 | 61 | 61 | 37.3 |
| 20 | 54 | 54 | 45.1 | 20 | 64 | 61 | 43.8 | ||||
| 25 | 52 | 54 | 44.8 | 25 | 63 | 61 | 46.3 | ||||
| 10 | 15 | 53 | 54 | 43.9 | 10 | 15 | 60 | 61 | 30.5 | ||
| 20 | 52 | 55 | 42.2 | 20 | 60 | 61 | 36.7 | ||||
| 25 | 53 | 54 | 37.9 | 25 | 62 | 60 | 43.9 | ||||
| 12.5 | 15 | 55 | 54 | 45.5 | 12.5 | 15 | 60 | 61 | 33.4 | ||
| 20 | 53 | 55 | 43.7 | 20 | 58 | 61 | 36.9 | ||||
| 25 | 54 | 55 | 42.4 | 25 | 64 | 61 | 46.6 | ||||
| 15 | 15 | 52 | 55 | 46.6 | 15 | 15 | 60 | 61 | 31.2 | ||
| 20 | 55 | 54 | 28.4 | 20 | 60 | 61 | 34.7 | ||||
| 25 | 56 | 54 | 26.2 | 25 | 63 | 61 | 45.8 | ||||
3.4. Effect of Voltage during Electrospinning on the Degree of Crystallinity



3.5. Effect of NTCD on the Degree of Crystallinity
4. Conclusions
References
- Baji, A.; Mai, Y.W.; Wong, S.C.; Abtahi, M.; Chen, P. Electrospinning of polymer nanofibers: Effects on oriented morphology, structures and tensile properties. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2010, 70, 703–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kongkhlang, T.; Tashiro, K.; Kotaki, M.; Chirachanchai, S. Electrospinning as a new technique to control the crystal morphology and molecular orientation of polyoxymethylene nanofibers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 15460–15466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, J.S.; Chase, D.B.; Rabolt, J.F. Effect of the electrospinning process on polymer crystallization chain conformation in nylon-6 and nylon-12. Macromolecules 2004, 37, 877–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, H.W.; Wang, M. An investigation into the influence of electrospinning parameters on the diameter and alignment of poly(hydroxybutyrate-co-hydroxyvalerate) fibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2011, 120, 1694–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boland, E.D.; Wnek, G.E.; Simpson, D.G.; Pawlowski, K.J.; Bowlin, G.L. Tailoring tissue engineering scaffolds using electrostatic processing techniques: A study of poly(glycolic acid) electrospinning. J. Macromol. Sci. Pure Appl. Chem. 2001, 38, 1231–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukigara, S.; Gandhi, M.; Ayutsede, J.; Micklus, M.; Ko, F. Regeneration of bombyx mori silk by electrospinning-part 1: Processing parameters and geometric properties. Polymer 2003, 44, 5721–5727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.H.; Inai, R.; Kotaki, M.; Ramakrishna, S. Systematic parameter study for ultra-fine fiber fabrication via electrospinning process. Polymer 2005, 46, 6128–6134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Ma, Z.W.; Teo, W.E.; Dong, Y.X.; Robless, P.A.; Lim, T.C.; Ramakrishna, S. Tubular nanofiber scaffolds for tissue engineered small-diameter vascular grafts. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2009, 90A, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katta, P.; Alessandro, M.; Ramsier, R.D.; Chase, G.G. Continuous electrospinning of aligned polymer nanofibers onto a wire drum collector. Nano Lett. 2004, 4, 2215–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidoaki, S.; Kwon, I.K.; Matsuda, T. Mesoscopic spatial designs of nano- and microfiber meshes for tissue-engineering matrix and scaffold based on newly devised multilayering and mixing electrospinning techniques. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraf, A.; Lozier, G.; Haesslein, A.; Kasper, F.K.; Raphael, R.M.; Baggett, L.S.; Mikos, A.G. Fabrication of nonwoven coaxial fiber meshes by electrospinning. Tissue Eng. C Methods 2009, 15, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.C.; Zussman, E.; Yarin, A.L.; Wendorff, J.H.; Greiner, A. Compound core-shell polymer nanofibers by co-electrospinning. Adv. Mater. 2003, 15, 1929–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Lee, D.S. Thermal properties of electrospun polyesters. Polym. J. 2000, 32, 616–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Z.; Su, B.; Venugopal, J.; Ramakrishna, S.; Lim, C.T. Biomimetic and bioactive nanofibrous scaffolds from electrospun composite nanofibers. Int. J. Nanomed. 2007, 2, 623–638. [Google Scholar]
- Jagur-Grodzinski, J. Polymers for tissue engineering, medical devices, and regenerative medicine. Concise general review of recent studies. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2006, 17, 395–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacanti, J.; Vacanti, C.A. The History and Scope of Tissue Engineering. In Principles of Tissue Engineering, 3rd; Lanza, R., Langer, R., Vacanti, J., Eds.; Elsevier Academic Press: Burlington, VT, USA, 2007; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, P.X. Scaffolds for tissue fabrication. Mater. Today 2004, 7, 30–40. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, J.R. Scaffolds for Tissue Engineering. In Biomaterials, Artificial Organs and Tissue Engineering; Hench, L.L., Jones, J.R., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing Limited: Cambridge, UK, 2005; pp. 201–213. [Google Scholar]
- Middleton, J.C.; Tipton, A.J. Synthetic biodegradable polymers as orthopedic devices. Biomaterials 2000, 21, 2335–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bognitzki, M.; Czado, W.; Frese, T.; Schaper, A.; Hellwig, M.; Steinhart, M.; Greiner, A.; Wendorff, J.H. Nanostructured fibers via electrospinning. Adv. Mater. 2001, 13, 70–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, X.H.; Kim, K.; Fang, D.F.; Ran, S.F.; Hsiao, B.S.; Chu, B. Structure and process relationship of electrospun bioabsorbable nanofiber membranes. Polymer 2002, 43, 4403–4412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramdhanie, L.I.; Aubuchon, S.R.; Boland, E.D.; Knapp, D.C.; Barnes, C.P.; Simpson, D.G.; Wnek, G.E.; Bowlin, G.L. Thermal and mechanical characterization of electrospun blends of poly(lactic acid) and poly(glycolic acid). Polym. J. 2006, 38, 1137–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deitzel, J.M.; Kleinmeyer, J.D.; Hirvonen, J.K.; Beck Tan, N.C. Controlled deposition of electrospun poly(ethylene oxide) fibers. Polymer 2001, 42, 8163–8170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deitzel, J.M.; Kleinmeyer, J.; Harris, D.; Beck Tan, N.C. The effect of processing variables on the morphology of electrospun nanofibers and textiles. Polymer 2001, 42, 261–272. [Google Scholar]
- Buchko, C.J.; Chen, L.C.; Shen, Y.; Martin, D.C. Processing and microstructural characterization of porous biocompatible protein polymer thin films. Polymer 1999, 40, 7397–7407. [Google Scholar]
- Ayutsede, J.; Gandhi, M.; Sukigara, S.; Micklus, M.; Chen, H.-E.; Ko, F. Regeneration of bombyx mori silk by electrospinning. Part 3: Characterization of electrospun nonwoven mat. Polymer 2005, 46, 1625–1634. [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro, C.; Sencadas, V.; Miguel Costa, C.; Gomez Ribelles, J.L.; Lanceros-Mendez, S. Tailoring the morphology and crystallinity of poly(L-lactide acid) electrospun membranes. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2011, 12, 015001:1–015001:9. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.; Wu, X.; Wang, L.; Huang, Y. Electrospinning of ethyl-cyanoethyl cellulose/tetrahydrofuran solutions. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 91, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arinstein, A.; Burman, M.; Gendelman, O.; Zussman, E. Effect of supramolecular structure on polymer nanofibre elasticity. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2007, 2, 59–62. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, S.C.; Baji, A.; Leng, S.W. Effect of fiber diameter on tensile properties of electrospun poly(epsilon-caprolactone). Polymer 2008, 49, 4713–4722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kister, G.; Cassanas, G.; Bergounhon, M.; Hoarau, D.; Vert, M. Structural characterization and hydrolytic degradation of solid copolymers of D,L-lactide-co-epsilon-caprolactone by raman spectroscopy. Polymer 2000, 41, 925–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.X.; Liao, S.; Ngiam, M.; Chan, C.K.; Ramakrishna, S. Degradation behaviors of electrospun resorbable polyester nanofibers. Tissue Eng. B Rev. 2009, 15, 333–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollinger, J.O.; Battistone, G.C. Biodegradable bone repair materials-synthetic-polymers and ceramics. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1986, 290–305. [Google Scholar]
- Gomes, M.E.; Reis, R.L. Biodegradable polymers and composites in biomedical applications: From catgut to tissue engineering—part 1—available systems and their properties. Int. Mater. Rev. 2004, 49, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasal, R.M.; Janorkar, A.V.; Hirt, D.E. Poly(lactic acid) modifications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2010, 35, 338–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inai, R.; Kotaki, M.; Ramakrishna, S. Structure and properties of electrospun plla single nanofibres. Nanotechnology 2005, 16, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Electrospinz. Frequently Asked Questions. 2008. Available online: http://www.electrospinz.co.nz/faq.php (accessed on 12 January 2012).
- Mezghani, K.; Spruiell, J.E. High speed melt spinning of poly(L-lactic acid) filaments. J. Polym. Sci. B Polym. Phys. 1998, 36, 1005–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fambri, L.; Pegoretti, A.; Fenner, R.; Incardona, S.D.; Migliaresi, C. Biodegradable fibres of poly(l-lactic acid) produced by melt spinning. Polymer 1997, 38, 79–85. [Google Scholar]
- Wunderlich, B. Thermal Analysis of Polymeric Materials; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Shenoy, S.L.; Bates, W.D.; Frisch, H.L.; Wnek, G.E. Role of chain entanglements on fiber formation during electrospinning of polymer solutions: Good solvent, non-specific polymer-polymer interaction limit. Polymer 2005, 46, 3372–3384. [Google Scholar]
- Sill, T.J.; von Recum, H.A. Electro spinning: Applications in drug delivery and tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 1989–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, R.J. Introduction to Polymers; Chapman and Hall: New York, NY, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, W.G.; Li, X.H.; Zhu, X.L.; Yu, G.; Zhou, S.B.; Weng, J. Investigation of drug release and matrix degradation of electrospun poly(D,L-lactide) fibers with paracetanol inoculation. Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 1623–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, X.H.; Ran, S.F.; Kim, K.S.; Fang, D.F.; Hsiao, B.S.; Chu, B. Structure and morphology changes during in vitro degradation of electrospun poly(glycolide-co-lactide) nanofiber membrane. Biomacromolecules 2003, 4, 416–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrizales, C.; Pelfrey, S.; Rincon, R.; Eubanks, T.M.; Kuang, A.X.; McClure, M.J.; Bowlin, G.L.; Macossay, J. Thermal and mechanical properties of electrospun PMMA, PVC, Nylon 6, and Nylon 6,6. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2008, 19, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishna, S.; Fujihara, K.; Teo, W.; Lim, T.; Ma, Z. An Introduction to Electrospinning and Nanofibres; World Scientific Publishing Co. Ltd.: Singapore, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Jarusuwannapoom, T.; Hongrojjanawiwat, W.; Jitjaicham, S.; Wannatong, L.; Nithitanakul, M.; Pattamaprom, C.; Koombhongse, P.; Rangkupan, R.; Supaphol, P. Effect of solvents on electro-spinnability of polystyrene solutions and morphological appearance of resulting electrospun polystyrene fibers. Eur. Polym. J. 2005, 41, 409–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billmeyer, F.W. Textbook of Polymer Science, 3rd ed; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Singapore, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, X.X.; Yang, X.P.; Zhang, L.Q.; Waclawik, E.; Wu, S.Z. Stretching-induced crystallinity and orientation to improve the mechanical properties of electrospun pan nanocomposites. Mater. Des. 2010, 31, 1726–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Ero-Phillips, O.; Jenkins, M.; Stamboulis, A. Tailoring Crystallinity of Electrospun Plla Fibres by Control of Electrospinning Parameters. Polymers 2012, 4, 1331-1348. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym4031331
Ero-Phillips O, Jenkins M, Stamboulis A. Tailoring Crystallinity of Electrospun Plla Fibres by Control of Electrospinning Parameters. Polymers. 2012; 4(3):1331-1348. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym4031331
Chicago/Turabian StyleEro-Phillips, Olubayode, Mike Jenkins, and Artemis Stamboulis. 2012. "Tailoring Crystallinity of Electrospun Plla Fibres by Control of Electrospinning Parameters" Polymers 4, no. 3: 1331-1348. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym4031331
APA StyleEro-Phillips, O., Jenkins, M., & Stamboulis, A. (2012). Tailoring Crystallinity of Electrospun Plla Fibres by Control of Electrospinning Parameters. Polymers, 4(3), 1331-1348. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym4031331