Abstract
With the classical sulfonation method of polystyrene-based strongly acidic cation exchange resins, polystyrene/polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) alloy particles were sulfonated to obtain a cation exchange resin, which was then directly thermoformed to prepare a semi-interpenetrating polymer network (semi-IPN) cation exchange membrane. The effects of the swelling agent, sulfonation time and temperature and the relative contents of polystyrene and divinylbenzene (DVB) in the alloy particles on the feasibility of the membrane formation are discussed. The results indicate that a favorable sulfonation degree above 80% and a suitable ion exchange capacity of 1.5–2.4 mmol/g can be gained, with concentrated sulfuric acid as the sulfonation agent and 1,2-dichloroethane as the swelling agent. The running electrical resistance and desalination effect of the prepared cation exchange membrane were measured in a pilot-scale electrodialyser and not only obviously exceeded a commercial heterogeneous cation exchange membrane, but was also very close to a commercial homogenous membrane. In this way, the authors have combined the classical sulfonation method of polystyrene-based cation exchange resins with the traditional thermoforming manufacturing process of heterogeneous cation exchange membranes, to successfully develop a novel, low-price, but relatively high-performance polystyrene/PVDF cation exchange membrane with the semi-IPN structure.
1. Introduction
Since the 1960s, ion-exchange membrane separation technologies have been widely applied to numerous industrial fields, including drug, food, energy, chemical industry, biotechnology, waste water treatment, as well as the desalination of sea or brackish water, etc. [1,2,3]. Undoubtedly, the employed ion-exchange membrane is the most important “hardware” factor deciding whether the separation process is successful or not. According to the chemical structure or the connection of charge groups, ion exchange membranes can be classified into heterogeneous and homogenous membranes, in which the charged groups are physically mixed with or chemically bonded to the membrane matrix (base membrane), respectively [4]. Being different from homogenous membranes, heterogeneous membranes can be produced only by a fairly simple physical hot-processing, in which milling, blending, open milling and thermoforming with two pieces of reinforcing fabrics are usually involved. As a result, the cation or anion exchange resin particles are embedded in the membrane matrix material (e.g., poly(vinyl chloride), polypropylene or polyethylene) to form the so-called heterogeneous structure [5]. In this way, these two kinds of inexpensive membrane components and the relatively simple manufacturing process contribute to a very low cost for heterogeneous membranes. This allows heterogeneous membranes to remain competitive in industrial application markets, particularly in the primary electro-driven membrane processes, such as electro-deionization (EDI) and brackish water desalination [6,7].
However, there is an inherent structure drawback for heterogeneous membranes: the hydrophilic ion exchange resin particles are entirely incompatible with the inert membrane matrix material [8]. This inevitably brings the dropout of resin particles from the membrane and the subsequent formation of voids during the whole electro-driven process. Consequently, the membrane’s electrical resistance will gradually climb, while the ion permselectivity will accordingly decrease. If this effect cumulates to a large extent, the process will become uneconomic and have to be periodically interrupted to replace new membranes. Due to the short usage life, heterogeneous membranes are not suitable for other high-demand areas (e.g., a strongly acidic or alkaline situation).
To overcome this inherent drawback, a great quantity of work focusing on the preparation of several new membrane components (e.g., poly(ether sulfone) (PES) and sulfonated poly(phenylene sulfide) (SPPS) [9], sulfonated poly(ether ketone ketone) (SPEKK) [10] and sulfonated poly(styrene-ethylene/butylene-styrene) (SSEBS) [11]) or physical modification techniques (e.g., the ultrasonic dispersion [10], the addition of inorganic fillers [12] and surface coating [13]) have been made for the purpose of improving the compatibility of heterogeneous cation exchange membranes. However, the above mentioned improvements have the potential of increasing the membrane’s manufacturing cost because they mostly adopt the solution casting method, which involves inconvenient preparation processes and adds the extra cost of solvent consumption.
Considering that China has become the world’s largest production country for ion exchange resins [14] and the obvious cost advantage of traditional heterogeneous membranes, we had proposed a novel technical route for manufacturing polystyrene/ polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) cation exchange membranes [15], in which polystyrene/PVDF alloy particles were first sulfonated using the same method as that employed in the industrial production of polystyrene-based strongly acidic cation exchange resins and then directly thermoformed to prepare the cation exchange membrane. The technical route aimed at realizing the combination of the classical sulfonation method of the strongly acidic cation exchange resins with the traditional thermoforming process of the heterogeneous ion exchange membranes and bringing their manufacturing cost reduction into full play. The objective of this paper is to deal with the cation exchange membrane, starting from the sulfonation process, including the effects of the swelling agent, reaction time and temperature, as well as the contents of polystyrene and divinylbenzene (DVB) and ending with the desalination effect in a pilot-scale electrodialyser to point out its opportunity for developing a commercially-available membrane product.
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
Poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF) was purchased from Shanghai Sanaifu Co. (Shanghai, China). Styrene, divinylbenzene (DVB, 63.2 wt%) and benzoyl peroxide (BPO) were provided by Shangyu Pure Resin Co. Ltd. (Shangyu, China). The homogeneous cation exchange membrane (Type CMX) and anion exchange membrane (Type AMX) were purchased from Tokuyama Co. Ltd. (Osaka, Japan). The heterogeneous cation exchange membrane (Type QHC) was supplied by Zhejiang Qianqiu Water Treatment Co. (Hangzhou, China). All other reagents were of analytical reagent grade and purchased commercially.
2.2. Membrane Preparation [15]
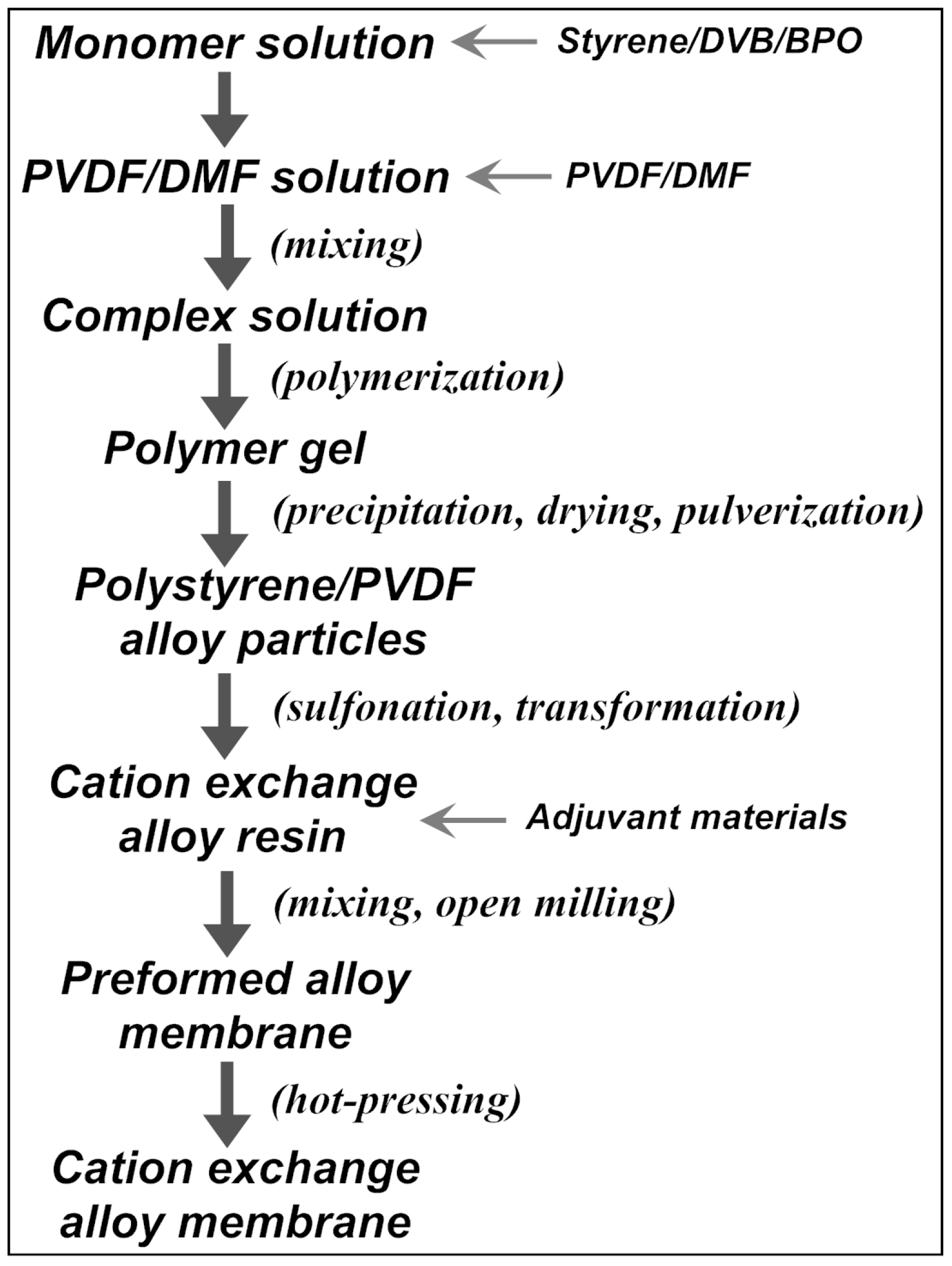
In a typical preparation, 281 g styrene, 19 g DVB (63.2 wt%) and 13 g benzoyl peroxide (BPO) were mixed magnetically in a 1000-mL triangular flask to form the monomer solution, which was then slowly dropped into a rapidly-stirred PVDF solution containing 300 g PVDF and 900 mL N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF), to form the homogeneous styrene/DVB/PVDF complex solution. In this case, the DVB content calculated as the net mass percentage of DVB in the total monomers (styrene and DVB) is 4.0%, while the mass ratio of the total monomers to PVDF in the complex solution (defined as RSt-DVB/PVDF) is 1.0. Polymerizing the complex solution under nitrogen atmosphere at 75 °C for 2 h and then at 85 °C for 12 h produced a jellylike gel, which was cut and cast into boiling water to suddenly precipitate into white particles. After being filtered, the material was dried at 120 °C until constant weight, then ground to 20–50 mesh sieve size, about 530 g polystyrene/PVDF alloy particles were synthesized. A mass of 100 g of alloy particles were sulfonated by adding 600 mL concentrated sulfuric acid (98 wt%) in a 1000-mL flask, with or without 1,2-dichloroethane (DCE) as the swelling agent. The reaction time and temperature are investigated in detail in Section 3. The sulfonated product was thoroughly washed with tap water and immersed into 1 N NaOH solution overnight to be transformed into the Na-form. After washing with water again, filtering out and drying at 105 °C until constant weight, the cation exchange resin was mixed with 0.1 wt% calcium stearate (as releasing agent) at 175–185 °C for 20 min in a CF-1L mixing machine (Dongwan Chang Feng Machinery Co., Dongwan, China). After that, a CF-120 open mill machine (Dongwan Chang Feng Machinery Co.) was used to manually form the membrane at 170–180 °C and control its thickness within 0.35–0.40 mm. Subsequently, the performed membrane was covered with two pieces of poly(ethylene terephthalate) (PET) protective film and then hot-pressed at 30 MPa and about 180 °C for 45 min with a column-form plate vulcanizing hot-press machine (Qingdao Yahua Machinery Co., Qingdao, China). Finally, the preparation process of the cation exchange membrane (shown in the chart in Figure 1) was completed, after cooling with freezing water, peeling the pressure and tearing off the PET film.
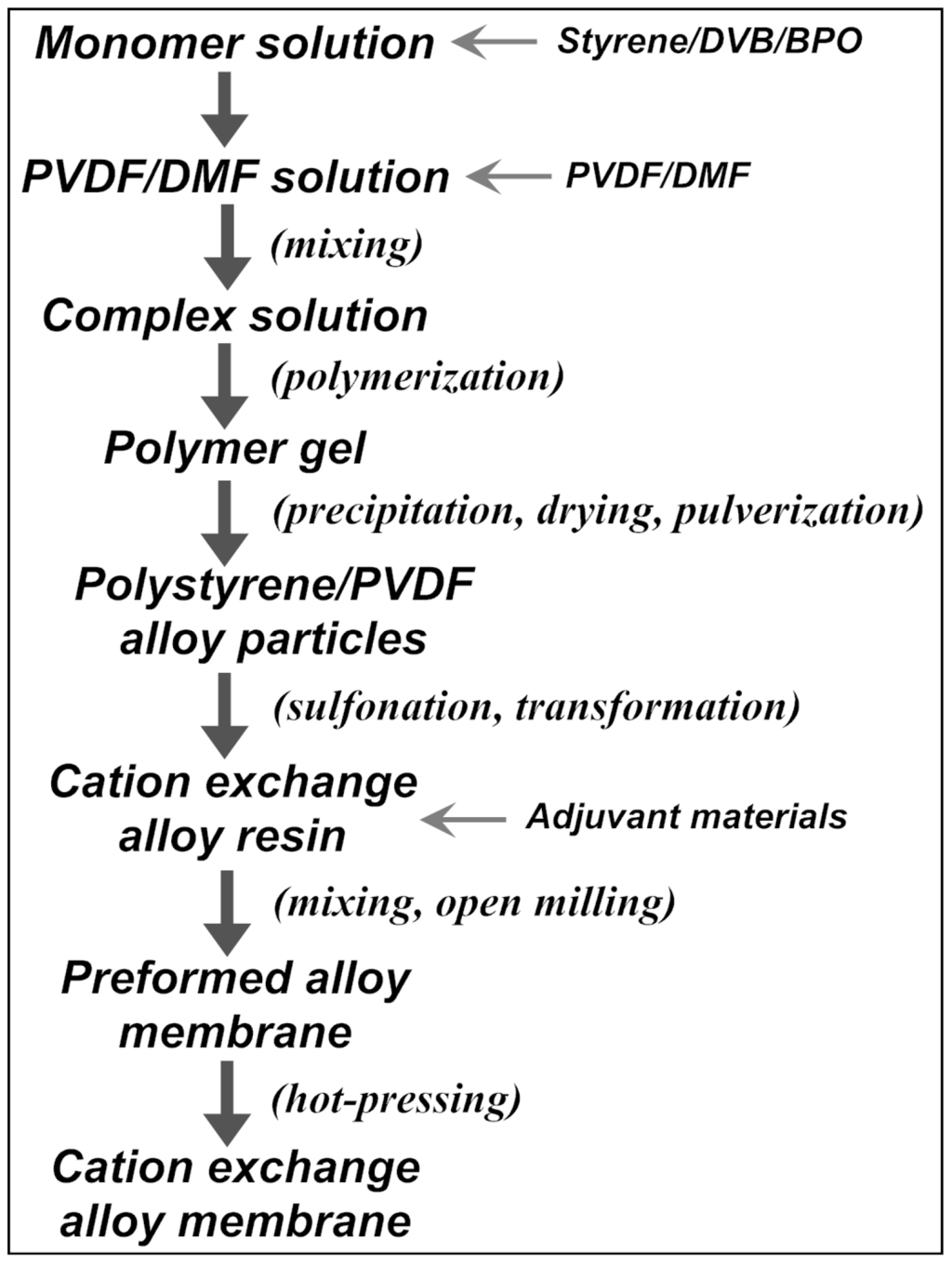
Figure 1.
Preparation of the polystyrene/poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF) cation exchange membrane. DVB, divinylbenzene; BPO, benzoyl peroxide.
Figure 1.
Preparation of the polystyrene/poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF) cation exchange membrane. DVB, divinylbenzene; BPO, benzoyl peroxide.
2.3. Sulfonation
The sulfonation degree was calculated by measuring the experimental ion exchange capacity (IECExperiment), which was determined by the back titration method [16]. From that, the dry H-form sulfonated resin (about 0.2 g) was equilibrated with 100 mL 0.01 N NaOH solution overnight, and then the back titration method with 0.01 N HCl solution was carried out. The IECExperiment (mmol/g) is equal to the net consumption of NaOH in millimolar per gram of the dry H-form resin. On the other hand, the theoretical ion exchange capacity (IECTheory) is calculated from Equation 1, by assuming that all polystyrene components in polystyrene/PVDF alloy particles are entirely sulfonated; in which case, RSt-DVB/PVDF is the mass ratio of the total monomers (styrene and DVB) to PVDF, PDVB the mass content of DVB in the total monomers (=19/(19 + 281) × 100% in the case of Section 2.2), 104.15 g/mol the molecular weight of styrene and 184.02 g/mol the molecular weight of p-styrene sulfonic acid. As a result, the sulfonation degree, =(IECExperiment/IECTheory) × 100%, can be simply calculated:
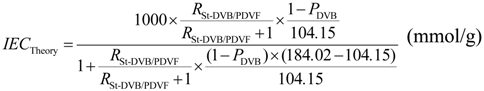
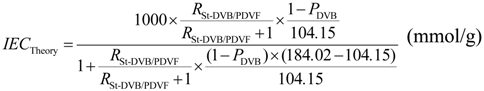
2.4. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) and Scanning Electron Microscope( SEM)
The components of polystyrene/PVDF alloy particles and cation exchange resin were analyzed by a Tensor 27 Fourier transform infrared spectrometer (FTIR) (Bruker Optics, Ettlingen, Germany). The inner morphology of the prepared membrane was observed by an Utral 55 scanning electron microscope (SEM) (Carl Zeiss, Jena, Germany).
2.5. Property Characterization
The electrochemical and physical properties of the tailor-made membrane, including water content (Wc), thickness, bursting pressure (P), ion exchange capacity (IEC), membrane area electric resistance (r) and apparent transport number (t+), were compared to the commercial homogeneous and heterogeneous membranes as controls. For the water content analysis, the Na-form dry membranes were completely soaked in deionized water overnight, the surface water was removed with filter paper and immediately weighed. After being dried under vacuum at 80 °C for at least 12 h, the water content was calculated as the mass percentage of soaked water per gram of dry sample, Wc = (Wwet – Wdry)/Wdry × 100%, in which Wdry and Wwet respectively denoted the weights of the dry and the wet samples. The thickness was directly recorded with a screw thread micrometer, and the average value of five data respectively at the four corners and the middle of a 30 × 50 mm rectangular sample was reported. To evaluate the bursting pressure, a circular membrane sample (50 mm in diameter) was fixed tightly at the bottom of a stainless steel column and then filled with glycerol. With the increase of the given air pressure from the column top, the membrane would break suddenly, where the bursting pressure was recorded. The average pressure from three tests was reported [17]. The membranes’ ion exchange capacities were also determined by the back titration method [16].
According to the classical test method [17,18,19], a two-compartment electrolytic cell system was employed to determine the cation apparent transport number (t+) and the area resistance (r). In this system, the geometric parameter of the cell (κ) was 1.0 cm−1, and the effective surface area of membrane sample (A) was 1.0 cm2. Therefore, the r was simplified to be the difference between 1/σ1 and 1/σ0, where σ0 and σ1 referred to the conductivities of the blank and the sample-loaded systems, respectively. As far as the cation apparent transport number was concerned, the system was loaded with a membrane sample to hold-off 0.1 N KCl and 0.01 N KCl solutions. After the electric potential between two sides was read by a digital multimeter, the membrane potential and the t+ value could be estimated by the Nernst equation.
2.6. Dimensional Stability [17]
Four 20 × 80 mm dry membrane samples were respectively immersed in deionized water, 4.0 wt% HCl, 4.0 wt% NaCl and 4.0 wt% NaOH solutions overnight, and then, their three-dimensional (3D) sizes were recorded with a digital micrometer. While x0, y0 and z0 were the 3D sizes of the dry sample, x1, y1 and z1 represented those values in the above single solution. Consequently, 3D changes were respectively calculated from (x1 − x0)/x0 × 100%, (y1 − y0)/y0 × 100% and (z1 − z0)/z0 × 100%.
2.7. Tests in the Electrodialyser
A pilot-scale electrodialyser was supplied by Ke-Yong Jin (Hangzhou Water Treatment Technology Development Center, Hangzhou, China) and used to determine the running electric resistance (I–V curves) and to evaluate the desalination effect. For the determination of the running electric resistance, five pieces of the same cation exchange membranes (cut into 11.0 × 17.0 cm) were assembled into the above electrodialyser. Three kinds of cation exchange membranes, including the prepared alloy CAM, the heterogeneous QHC and the homogeneous CMX, were tested under similar experimental conditions, and the running electric currents with the increase of the imposed voltage were recorded. As for the evaluation of desalination effect, six pieces of the same cation exchange membranes (QHC, CAM or CMX) and five pieces of AMX homogeneous anion exchange membranes were alternatively assembled into the electrodialyser. By recording the electrical conductivities of desalination stream at serial running times, the desalination degrees, =(C0 – C1)/C0 × 100%, where C0 was the initial conductivity and C1 the timely conductivity, were reported. All tests were carried out at 25 °C, with 5.0 wt% Na2SO4 as the system solution.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Sulfonation
With regard to the heterogeneous sulfonation process, the DVB-crosslinked polystyrene particles are so dense and hydrophobic that it is difficult for the hydrophilic sulfonation agent to enter the internal volume of the particles without the swelling agent. In the large-scale industrial production of polystyrene-based strongly acidic cation exchange resins, 1,2-dichloroethane (DCE) is the most widely used as the swelling agent to accelerate the reaction rate and to increase the sulfonation degree, especially when employing inexpensive concentrated sulfuric acid (usually 93–98 wt%) as the sulfonation agent. In view of the fact that China has become the world’s largest production country for ion exchange resins [14], the concentrated sulfuric acid (98 wt%) and DCE are still employed to sulfonate the polystyrene/PVDF alloy particles, in order to realize the relative “seamless combination” with the already existing industrial base of cation exchange resins.
Figure 2 investigated the effect of DCE as the swelling agent on the sulfonation efficiency, indicating that DCE was necessary for the polystyrene/PVDF alloy particles to obtain a satisfactory reaction degree, especially when the DVB content (which also represents the crosslinking degree) increased to 5% or 8%. For instance, DCE directly endowed the sulfonation degree with a more than a 100% increase (from 36% to 75%) for the 8% DVB case. In the absence of the suitable swelling agent, it was difficult for the concentrated sulfuric acid to rapidly permeate into the highly hydrophobic polystyrene-DVB beads, which led to the sulfonation mainly occurring at the outer surface rather than in the inner surface of the beads [20]. For the polystyrene/PVDF alloy particles, the hydrophobic PVDF component as the main matrix material will undoubtedly limit the concentrated sulfuric acid’s penetration into the alloy particles. Fortunately, Figure 2 has shown that DEC is still an effective swelling agent, and thus, the classical manufacturing method of polystyrene-based strongly acidic cation exchange resins is also available for the preparation of the polystyrene/PVDF cation exchange membrane.
Figure 3 shows the FTIR spectra of polystyrene-DVB particles (Figure 3a), PVDF powder (Figure 3b), the polystyrene/PVDF alloy particles (Figure 3c) and the polystyrene/PVDF-based cation exchange alloy resin (Figure 3d). In the spectrum for PVDF (Figure 3b), bands at 1400 and 1185 cm−1 are assigned to the deformation vibration of CH2 linked with CF2 and the stretching vibration of CF2, respectively. These two peaks were also observed in Figure 3c and Figure 3d, indicating the incorporation of PVDF both in the polystyrene/PVDF alloy particles and the cation exchange alloy resin. Similarly, the characteristic bands of polystyrene-DVB particles (Figure 3a) at 679, 1452 and 1493 cm−1 are present in Figure 3c. However, the bending vibration band of the benzene ring plane at 1028 cm−1 (in Figure 3a), had split into two independent peaks, respectively at 1009 and 1039 cm−1 (see Figure 3d). This was believed to be affected by the symmetric stretching vibration of the S=O bond affiliated with the SO3− group [21]. Also shown in Figure 3d, the fairly broad band at about 3460 cm−1 was assigned to the bending vibration of the OH group, which was probably caused by the drifting of its stretching vibration toward the low frequency direction, under the hydrogen bond interaction between the H2O molecule and the oxygen atom of the SO3− group [21]. Moreover, the aromatic C–H absorption peak was present at 1637 cm−1 (Figure 3d) and would strengthen and broaden with the increase of the sulfonation degree (not shown). Furthermore, the band at 1128 cm−1 should be assigned to the antisymmetric stretching vibration of the S=O bond [22]. Finally, the SO3− groups have been confirmed to have been introduced into the polystyrene/PVDF alloy particles by the FTIR spectra.
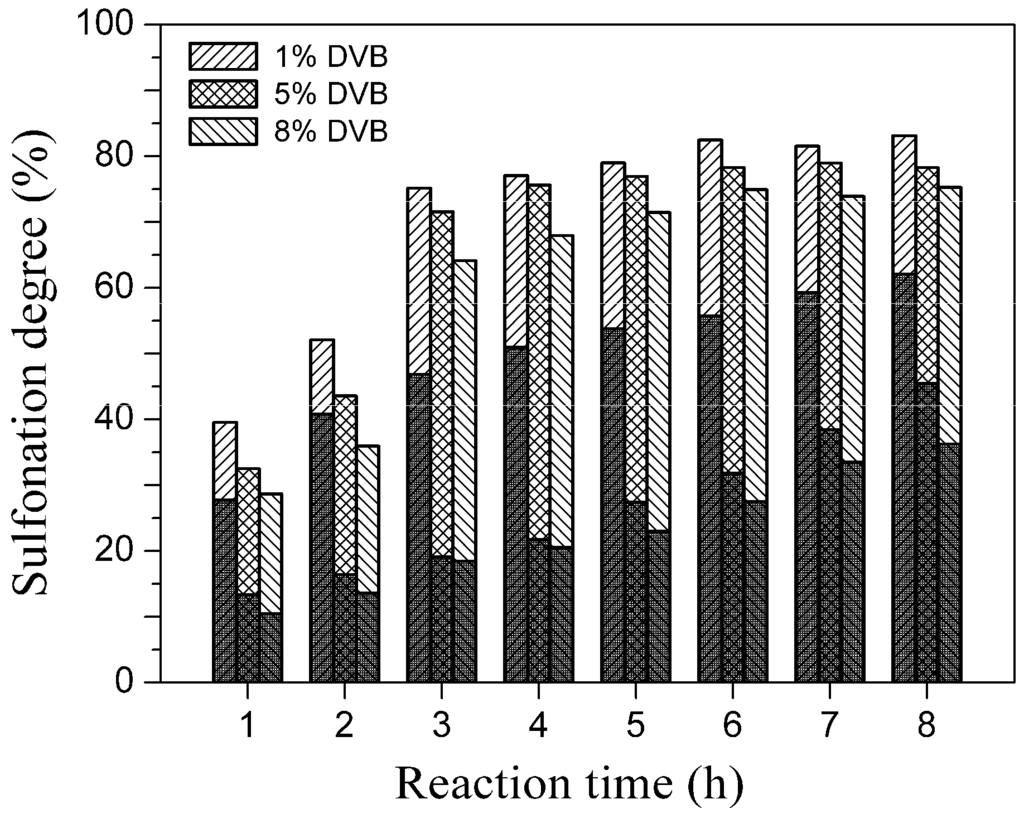
Figure 2.
The effect of the swelling agent on sulfonation. One hundred grams of polystyrene/PVDF alloy particles (RSt-DVB/PVDF = 0.8) were reacted with 600 mL of concentrated sulfuric acid at 80 °C. The upper bar indicates the addition of 100 mL of 1,2-dichloroethane (DCE) and the lower bar indicates the absence of DCE.
Figure 2.
The effect of the swelling agent on sulfonation. One hundred grams of polystyrene/PVDF alloy particles (RSt-DVB/PVDF = 0.8) were reacted with 600 mL of concentrated sulfuric acid at 80 °C. The upper bar indicates the addition of 100 mL of 1,2-dichloroethane (DCE) and the lower bar indicates the absence of DCE.
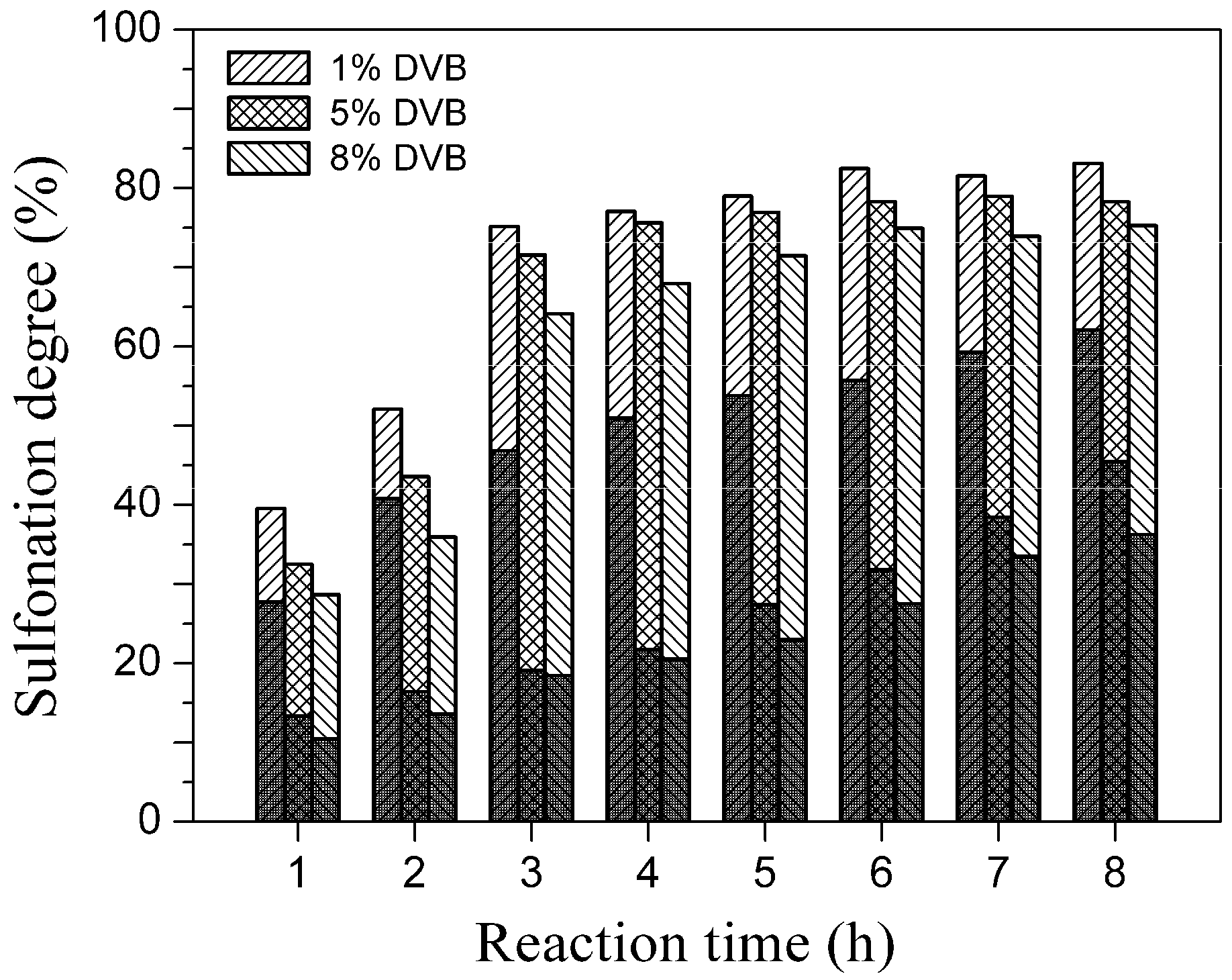
Figure 3.
FTIR spectra of (a) polystyrene-DVB particles, (b) PVDF powder, (c) polystyrene/PVDF alloy particles and (d) polystyrene/PVDF-based cation exchange alloy resin.
Figure 3.
FTIR spectra of (a) polystyrene-DVB particles, (b) PVDF powder, (c) polystyrene/PVDF alloy particles and (d) polystyrene/PVDF-based cation exchange alloy resin.
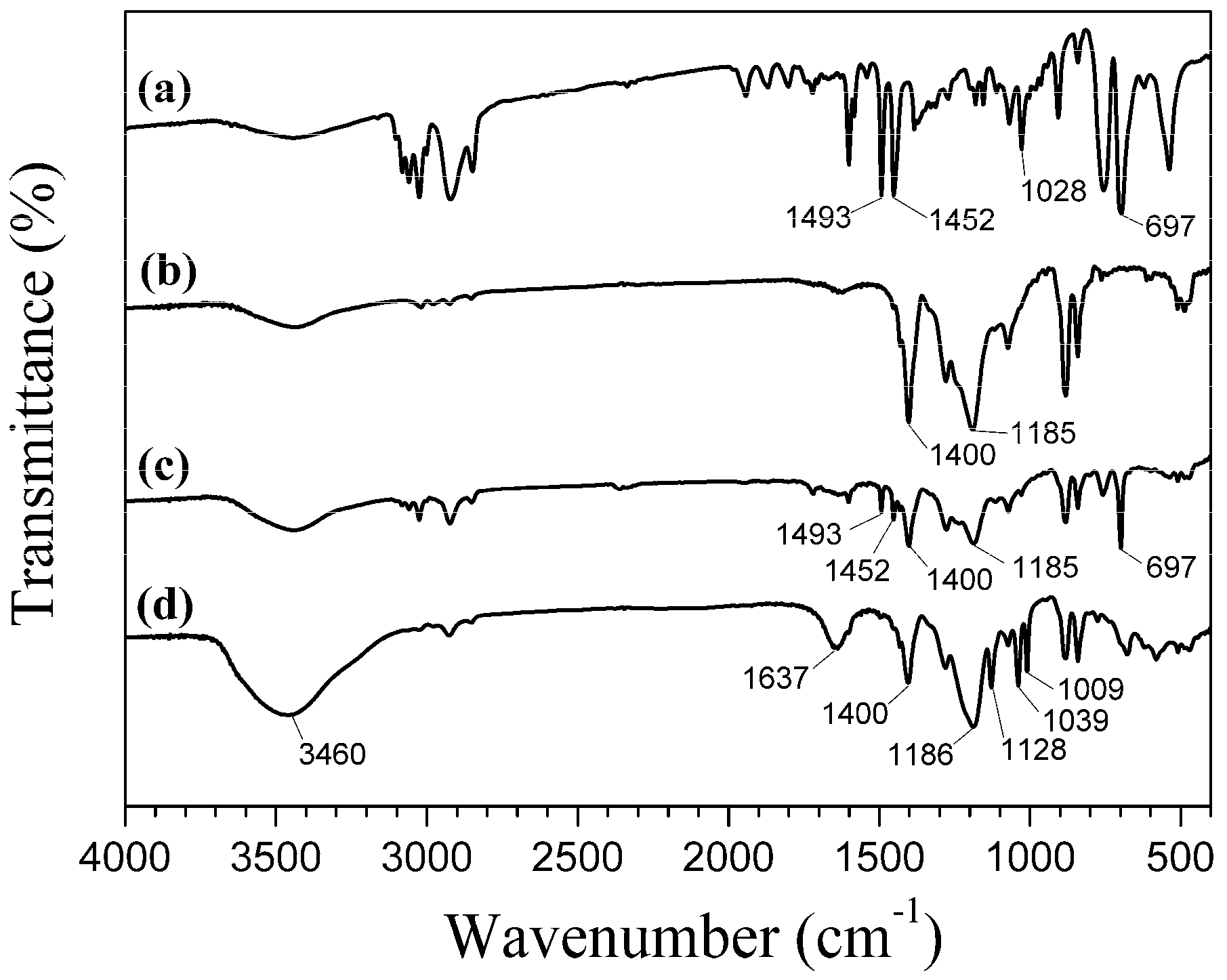
Figure 4 describes the effect of the reaction temperature on the sulfonation. As a result, the maximum sulfonation degree existed at about 80 °C, whether the PVDF content (Rst-DVB/PVDF) was high or not. On the one hand, raising the reaction temperature, e.g., from 60 to 80 °C, had promoted the rate and degree of sulfonation. However, on the other hand, too high of a sulfonation temperature, which was above the DCE’s boiling point (83.5 °C), e.g., 85 and 90 °C, would weaken the penetration of the concentrated sulfuric into the polystyrene/PVDF alloy particles. In addition, it was found that the sulfonated products at 85 and 90 °C had become brownish-black and lost their thermoplasticity for the alloy membrane formation. Therefore, we can propose that DCE acted as not only a swelling agent, but also a protectant for the sulfonation process of the polystyrene/PVDF alloy particles.
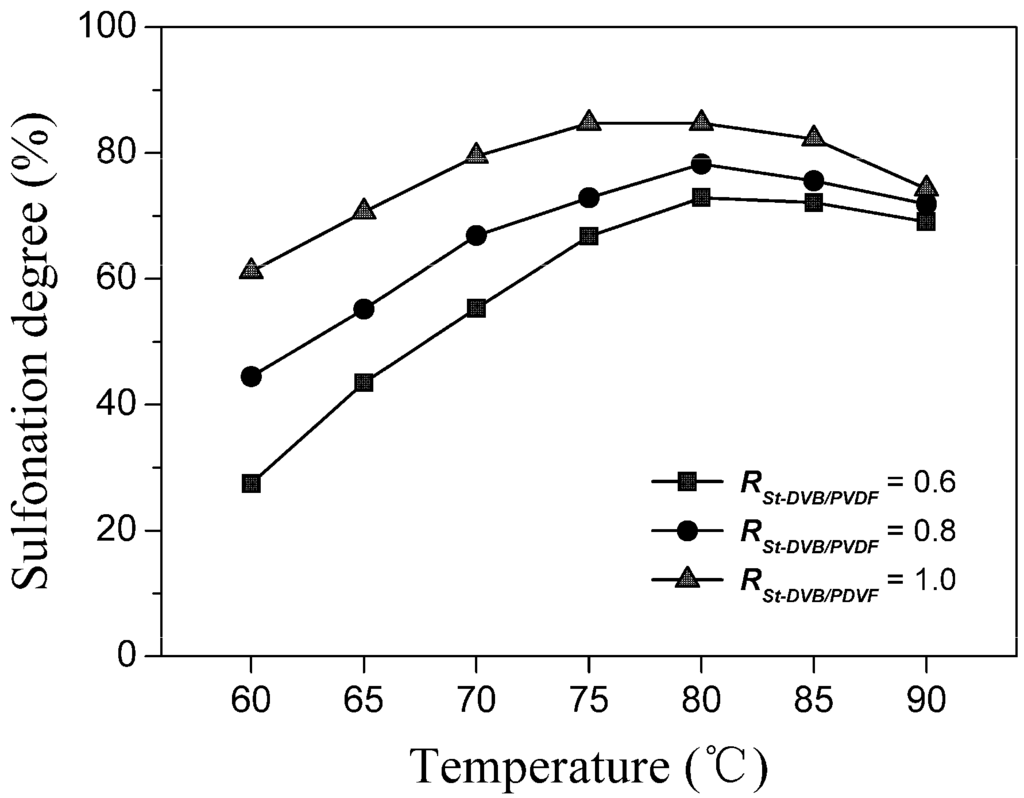
Figure 4.
The effect of the reaction temperature on sulfonation. One hundred grams of polystyrene/PVDF alloy particles (DVB content = 5%) were reacted with 100 mL of DCE and 600 mL of concentrated sulfuric acid for 8 h at serial temperatures.
Figure 4.
The effect of the reaction temperature on sulfonation. One hundred grams of polystyrene/PVDF alloy particles (DVB content = 5%) were reacted with 100 mL of DCE and 600 mL of concentrated sulfuric acid for 8 h at serial temperatures.
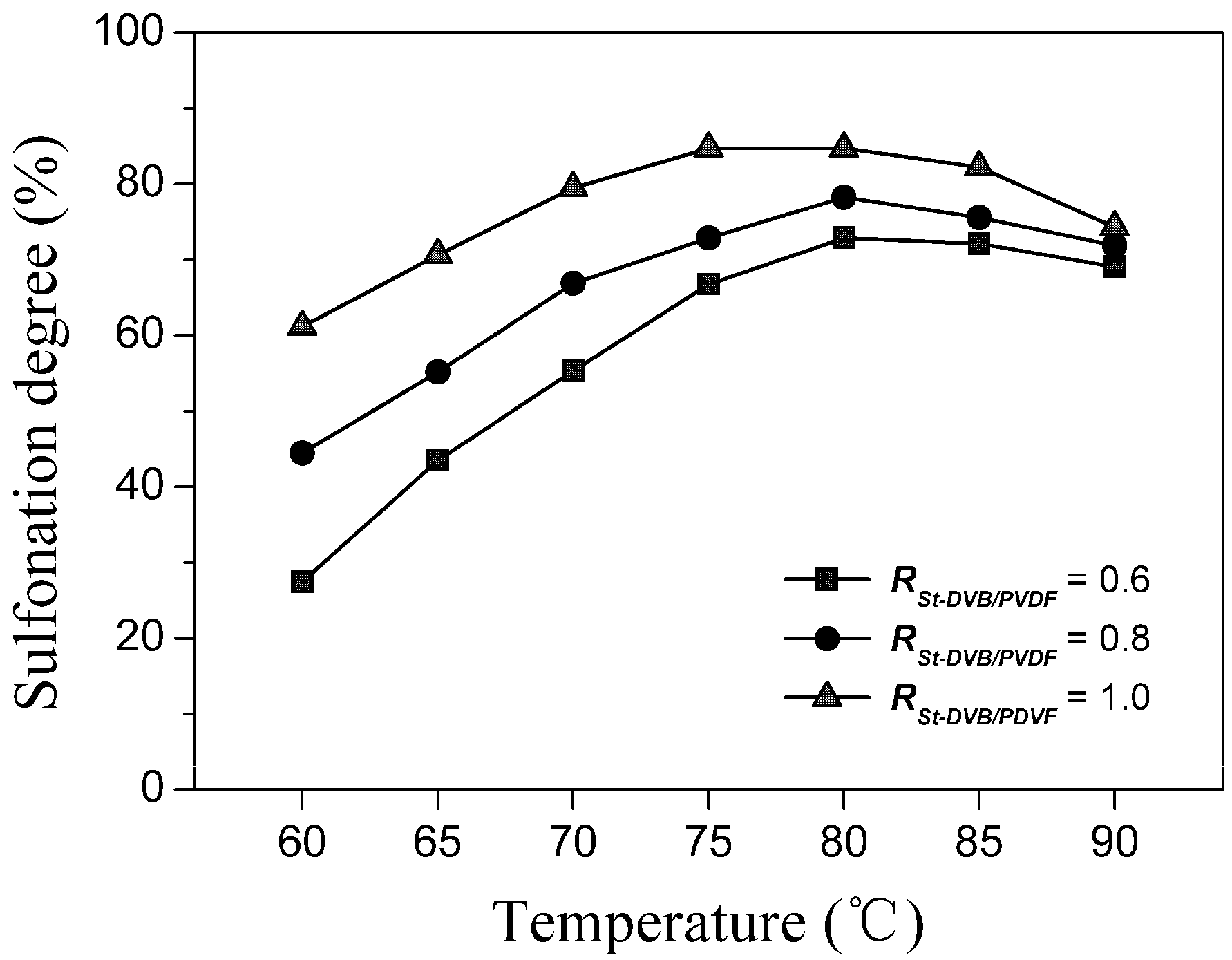
Figure 5 and Figure 6 demonstrate the effects of PVDF content (represented by Rst-DVB/PVDF) and DVB content in the polystyrene/PVDF alloy particles on the sulfonation degree, respectively. As shown in Figure 5, both the sulfonation degree and the experimental ion exchange capacity (IECExperiment) gradually increased with increasing Rst-DVB/PVDF. Especially from the changing trend of the sulfonation degree, we do have reason to believe that the interpenetration of the hydrophobic and inert PVDF had remarkably decreased the sulfonation accessibility of polystyrene-DVB component (from 85.5% to 69.7%). At the same time, the decrease of the sulfonation degree attributed to the increase of the DVB content was no more than 6% (from 83.1% to 77.3%), as shown in Figure 6. Taken as a whole, a favorable sulfonation degree (above 80%) and a suitable ion exchange capacity (1.5–2.4 mmol/g) can be achieved by simply adjusting the amount of styrene and/or DVB.
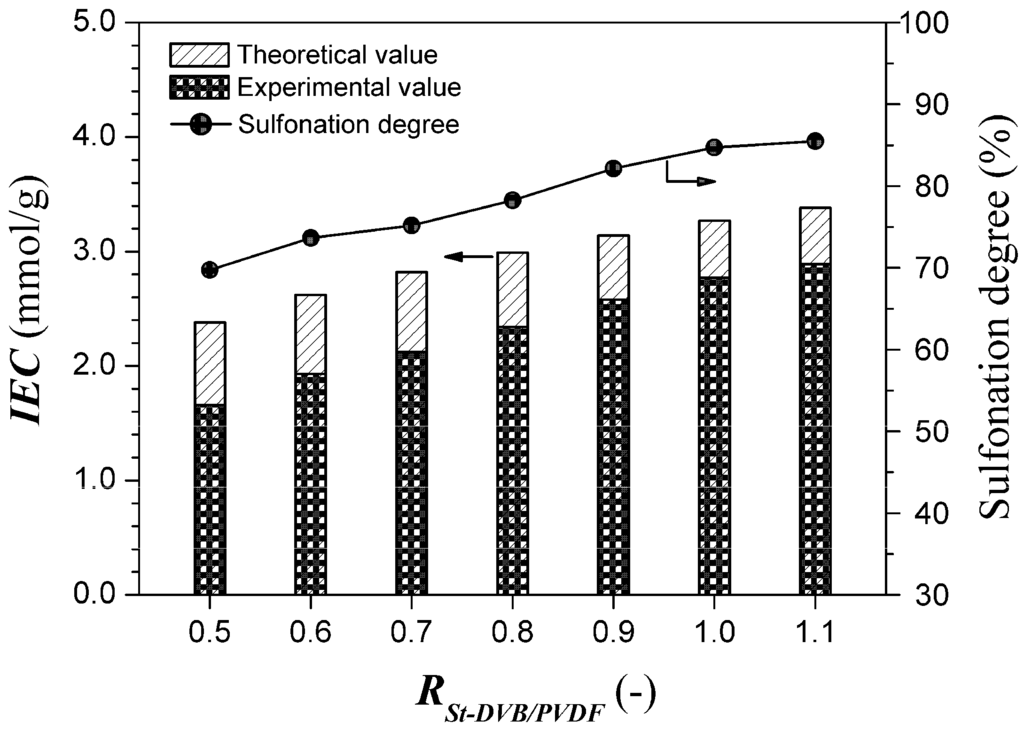
Figure 5.
Ion exchange capacities and sulfonation degrees at various Rst-DVB/PVDF values. One hundred grams of polystyrene/PVDF alloy particles (DVB content = 5%) were reacted with 100 mL of DCE and 600 mL of concentrated sulfuric acid at 80 °C for 8 h.
Figure 5.
Ion exchange capacities and sulfonation degrees at various Rst-DVB/PVDF values. One hundred grams of polystyrene/PVDF alloy particles (DVB content = 5%) were reacted with 100 mL of DCE and 600 mL of concentrated sulfuric acid at 80 °C for 8 h.
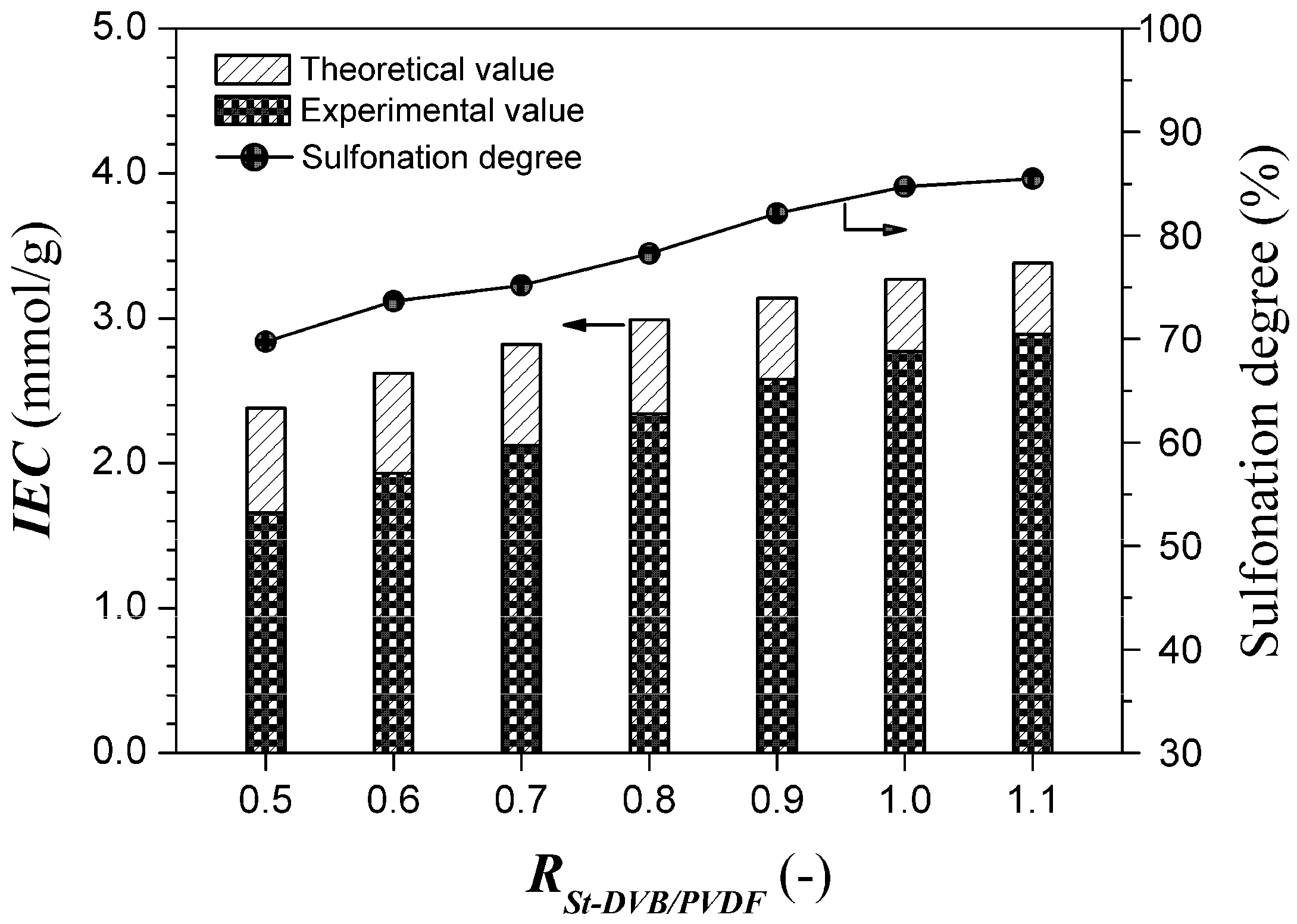
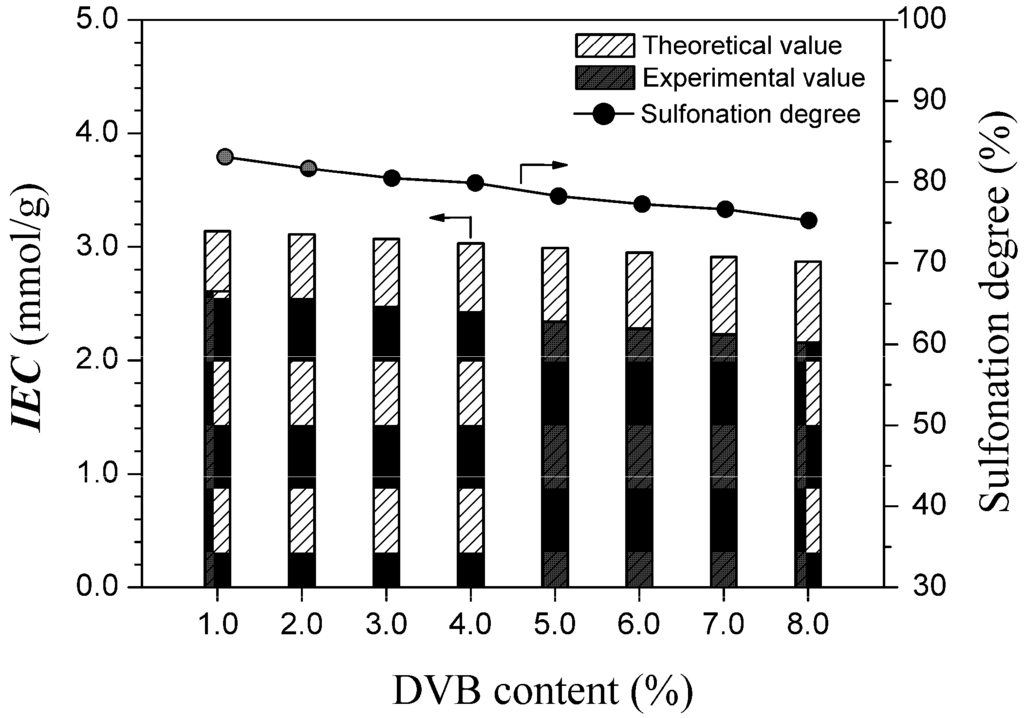
Figure 6.
Ion exchange capacities and sulfonation degrees at various DVB contents. One hundred grams of polystyrene/PVDF alloy particles (Rst-DVB/PVDF = 0.8) were reacted with 100 mL of DCE and 600 mL of concentrated sulfuric acid at 80 °C for 8 h.
Figure 6.
Ion exchange capacities and sulfonation degrees at various DVB contents. One hundred grams of polystyrene/PVDF alloy particles (Rst-DVB/PVDF = 0.8) were reacted with 100 mL of DCE and 600 mL of concentrated sulfuric acid at 80 °C for 8 h.
3.2. Membrane Morphology
Considering that the DVB-crosslinked polystyrene microspheres or beads have no thermoplasticity, even though the crosslinking degree is only 1%, we think that the thermoplasticity of polystyrene/PVDF alloy particles or the cation exchange alloy resin is chiefly attributable to its PVDF component. Furthermore, this indicates that the possibility of alloy membrane formation by the thermoforming process would increase at lower Rst-DVB/PVDF values, as summarized in Table 1. At the same time, Table 1 also shows that the higher DVB content (e.g., more than 8%) would limit the rheological behavior of the PVDF component and even make the membrane formation impossible. Making the comprehensive consideration from the sulfonation degree, IEC and the possibility of membrane formation, we chose the DVB content to be 5% and the Rst-DVB/PVDF value to be 0.8 to prepare the cation exchange alloy membrane (named CAM). The CAM’s morphology is shown in Figure 7, in which the white regions represent the C6H5SO3− functional clusters, and they were uniformly embedded in the honeycomb-like PVDF matrix. Consequently, the alloy membrane had formed the semi-interpenetrating polymer network (semi-IPN) structure.

Table 1.
The possibility of membrane formation by the thermoforming process a.
| DVB (wt%) | RSt-DVB/PVDF (−) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 1.0 | 1.1 | |
| 1.0 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 2.0 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 3.0 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 4.0 | + | + | + | + | + | + | − |
| 5.0 | + | + | + | + | + | + | − |
| 6.0 | + | + | + | + | − | − | − |
| 7.0 | + | + | − | − | − | − | − |
| 8.0 | + | − | − | − | − | − | − |
a “+” is possible, “−” is impossible.
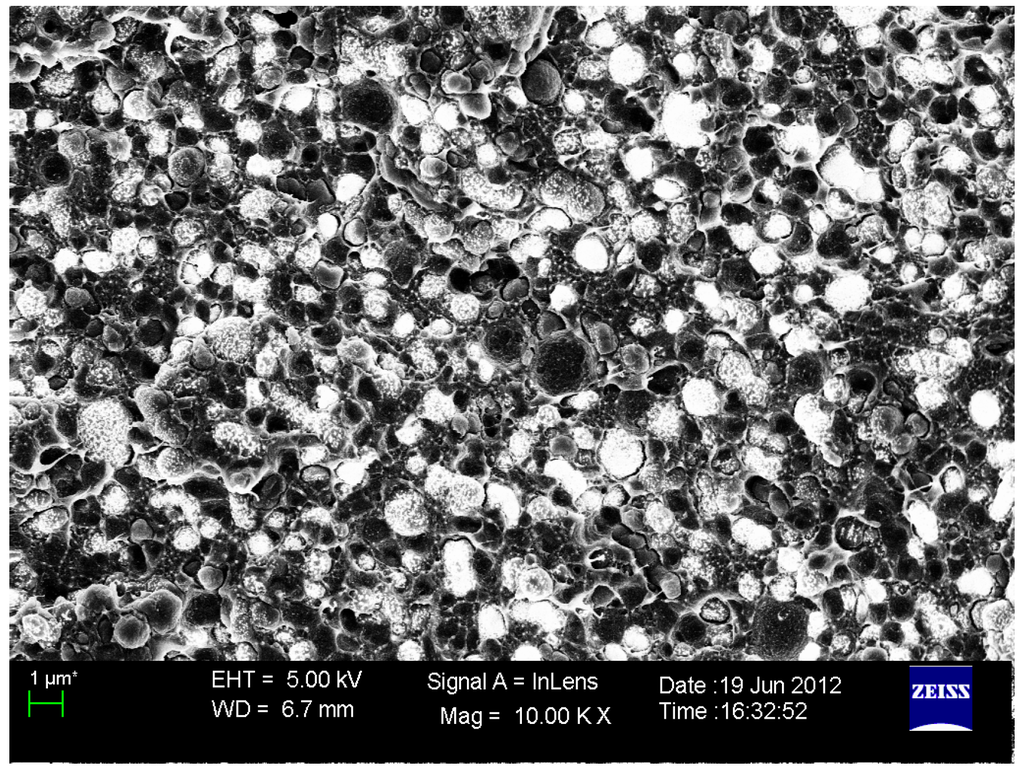
Figure 7.
SEM image of the prepared cation exchange membrane.
Figure 7.
SEM image of the prepared cation exchange membrane.
3.3. Dimensional Stability
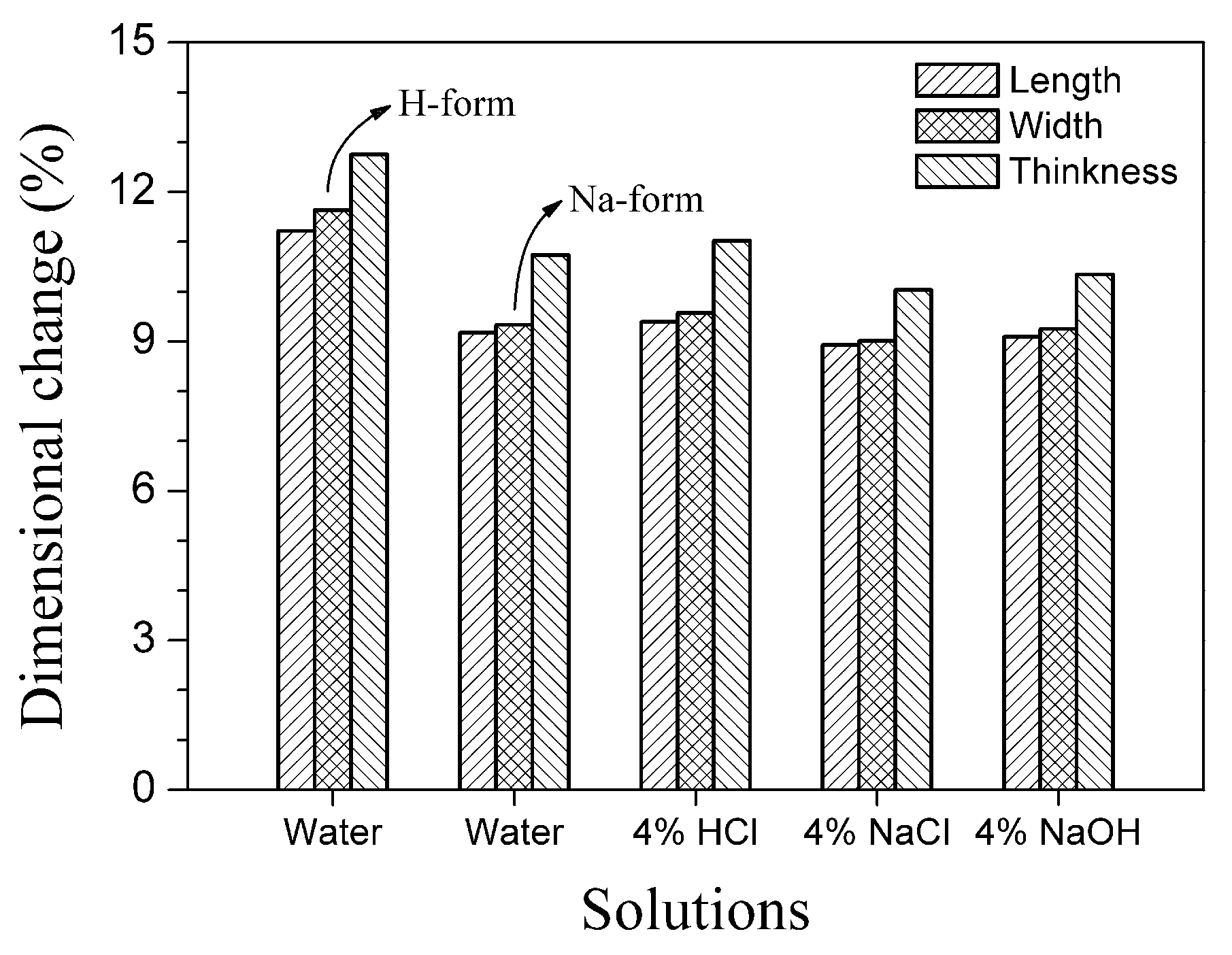
From a practical viewpoint, the dimensional stability in different electrolyte solutions is the key criteria for any commercial ion exchange membrane product. For this purpose, the 3D changes in four classical electrodialysis system solutions (deionized water, 4.0 wt% NaCl, 4.0% wt% HCl and 4.0 wt% NaOH) were compared. The results are displayed in Figure 8, in which a small downtrend of 3D changes for the Na-form CAM membrane was observed in the order of HCl, water, NaOH and NaCl solutions. Although the dry-wet change in length was close to 10%, the maximum difference in the four solutions was no more than 0.5% (from 8.93% in 4% NaCl to 9.39% in 4% HCl). This indicates that the alloy membrane has an outstanding dimensional ability in possible ED applications. On the other hand, 3D changes of the H-form CAM membrane in water exceeded 10%, and thus, the maximum length difference from 4% NaCl to water was up to 2.29%. However, the maximum 3D change criterion for the practical application of ion exchange membranes, particularly in length and in width, is generally believed to be less than 1%. A too large of a 3D change may lead the adopted membranes to puckering, breaching or even falling to pieces, particularly when the concentration or kind of running solution is suddenly alternated [23]. To overcome this drawback, it is necessary for the H-form CAM membrane to be transferred into the Na-form (e.g., using 4% NaCl solution) before washing with water.
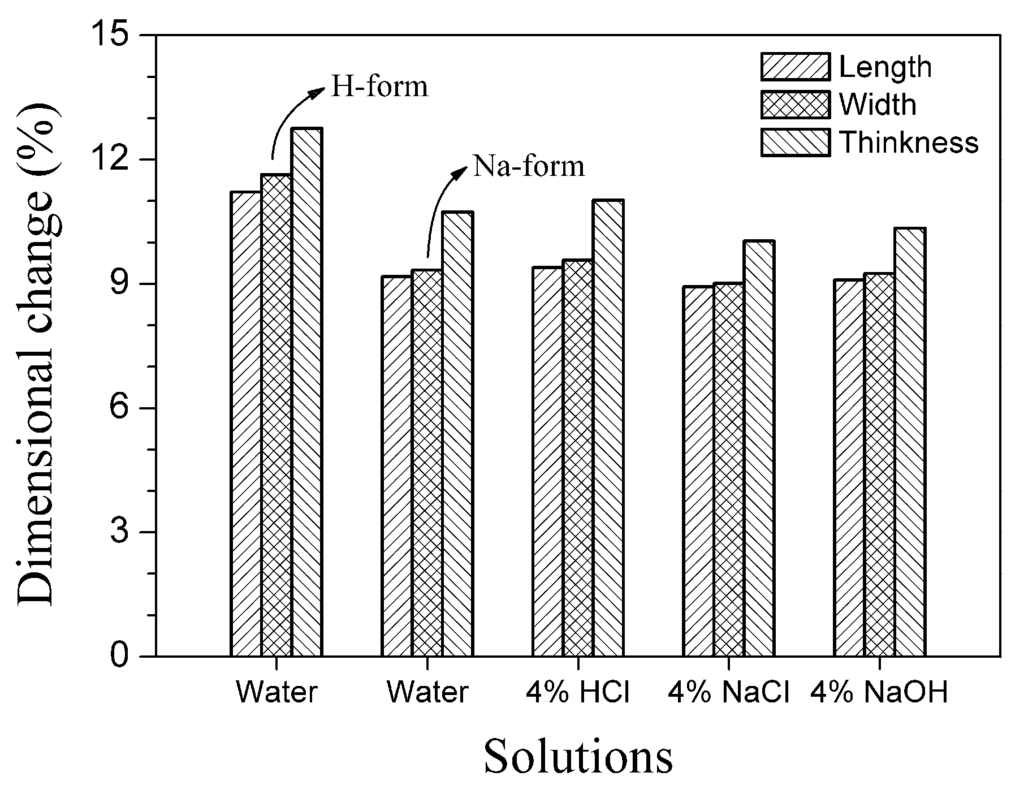
Figure 8.
3D changes of dry alloy membrane in various solutions.
Figure 8.
3D changes of dry alloy membrane in various solutions.
3.4. Physical and Electrochemical Properties
Table 2 lists the physical and electrochemical properties of the cation exchange alloy membrane (CAM), and the commercial heterogeneous membrane (QHC) and homogeneous membrane (CMX). Among the three membranes, CAM had the highest IEC (2.18 mmol/g), which partly contributed to the slightly higher water content (35.5%) compared to CMX (28.9%). With respect to the dose of inner compaction, the semi-interpenetrating network structure of CAM was relatively close to the homogeneous structure of CMX, but obviously denser than the heterogeneous structure of QHC. As a result, its apparent transport number (0.962) exceeded 0.95 and, thus, had a remarkable increase compared to QHC (0.908). Reducing the CAM’s thickness (e.g., to 0.25–0.3 mm) might reduce the area electric resistance, but also undoubtedly would decrease the mechanical strength (bursting pressure) and the apparent transport number. Furthermore, we had found that it was very difficult to control the membrane’s thickness below 0.3 mm. In the thermoforming process of alloy membranes, the space between two rollers of the open-mill machine should not be less than 0.2 mm, in order to avoid frequent mechanical collision and abrasion. On the other hand, the extensibility of the sulfonated polystyrene/PVDF alloy particles was still not enough at 170–180 °C, but a higher temperature or longer hot-pressing time would cause the decomposition of sulfonic acid groups [24]. These two aspects of the operating factors limited any further decrease of the alloy membrane’s thickness.

Table 2.
The properties of cation exchange membranes.
| Membrane | Thickness (mm) | P(MPa) | Wc(wt%) | IEC(mmol/g) | r (Ω·cm2 ) | t+(-) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QHC a | 0.43 | 0.65 | 50.2 | 2.06 | 10.12 | 0.908 |
| CAM b | 0.38 | 0.51 | 35.5 | 2.18 | 4.75 | 0.962 |
| CMX c | 0.19 | 0.42 | 28.9 | 1.73 | 2.78 | 0.987 |
a The heterogeneous cation exchange membrane from Qianqiu Water Treatment Co.; b The custom-made cation exchange alloy membrane (DVB content = 5%, Rst-DVB/PVDF = 0.8); c The homogeneous cation exchange membrane from Tokuyama Co. Ltd.
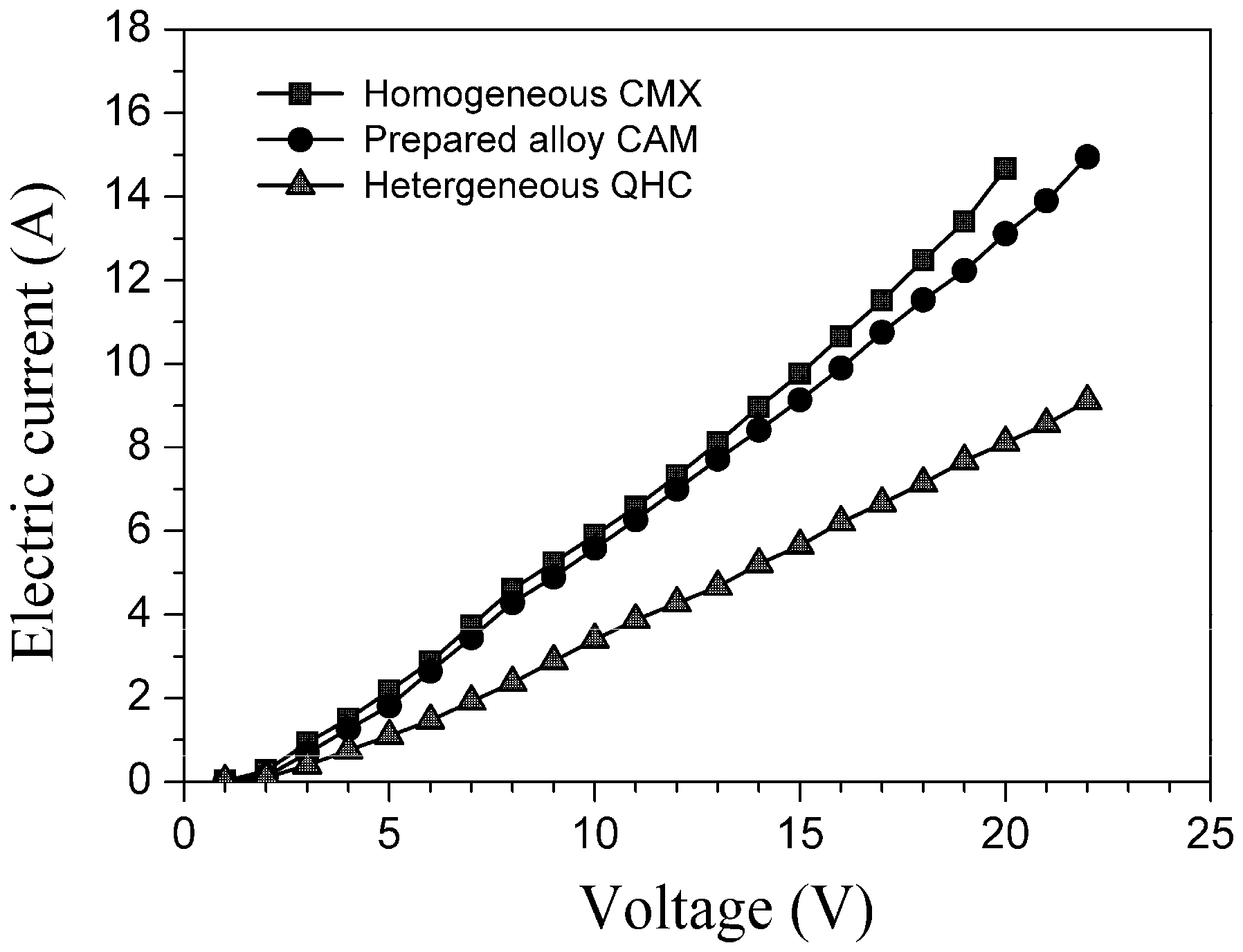
The overall running electric resistance in an electrodialyser not only directly depends on the intrinsic area electric resistance of the ion exchange membranes employed, but also is related to other system factors, including the material and quantity of clapboards, the electrolytic solution system and the degree of turbulence in the compartments. To compare the relative values of the area electric resistances, we carried out constant test conditions, only replacing the kind of cation exchange membranes and altering the voltage. Consequently, the running electric current through the electrodialyser increased almost linearly with the increase of the imposed voltage, as shown in Figure 9, in which the running electric resistance was roughly equal to the reciprocal value of the linear slope. Therefore, the I–V curves once again confirmed that the area electric resistance of the tailor-made alloy membrane was much lower than the commercial heterogeneous, but relatively close to the homogeneous membrane (also see Table 2).
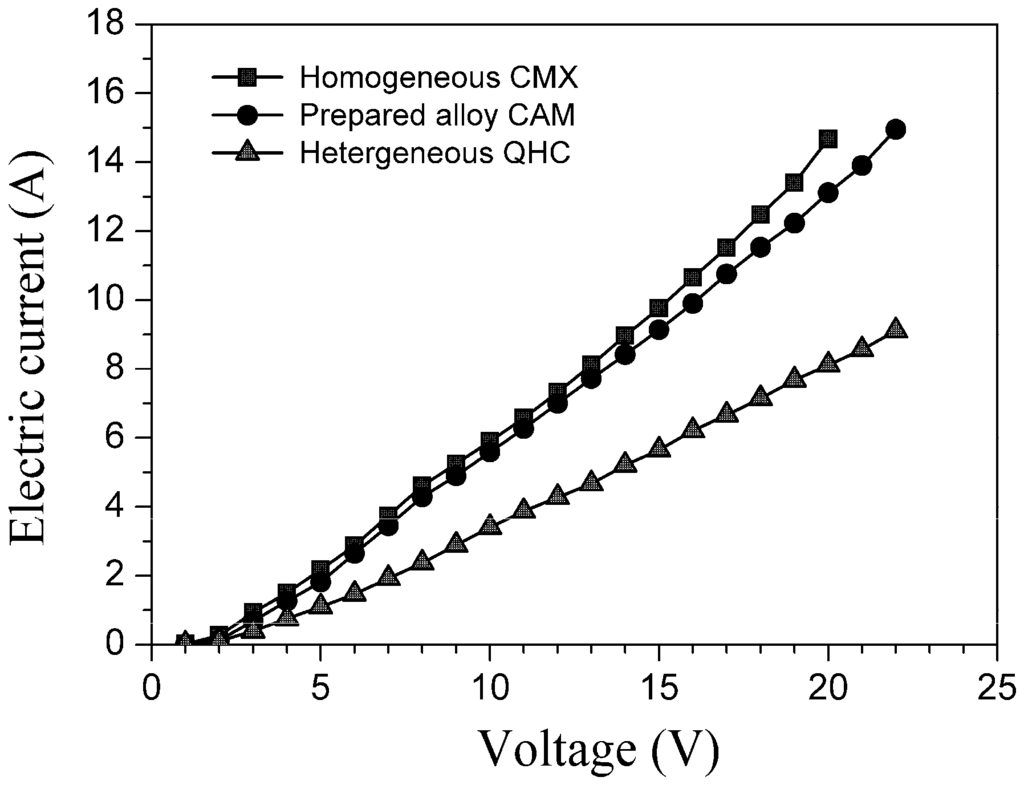
Figure 9.
I–V curves of the cation exchange membranes.
Figure 9.
I–V curves of the cation exchange membranes.
3.5. Desalination Effect
Figure 10 recorded the desalination degrees with the ED running times for three cation exchange membranes, and Table 3 summarized their desalination effects, by employing the same homogeneous anion exchange membrane (CMX) to match with the above-mentioned three membranes under similar test conditions. The results indicated that the CAM alloy membrane had the shortest desalination time (16 min), but could obtain a desalination degree (96.8%) close to the CMX homogeneous membrane (99.5%). For an ED process, the maximum desalination degree should arrive at the place where the ion transfer flux from the desalination side under the electric field is equal to the ion diffusion flux from the other side (or concentration side) under the difference of two-side salt concentrations. From the viewpoint of the relationship between the structure and the property, the lower area electric resistance could contribute to a stronger electric driving force and, thus, a larger ion transfer flux, while the denser membrane’s inner structure would limit and decrease the ion diffusion. Comparing these three kinds of cation exchange membranes, we can agree that the area electric resistance and the inner compact degree of the prepared alloy membrane were closer to those of the homogeneous membrane rather than the heterogeneous membrane. On the whole, the alloy membrane exhibited a remarkably superior desalination effect to the commercial heterogeneous membrane. Though there is a long way to gain the same area electric resistance and compaction degree as the homogeneous membrane, the result still illustrated that our cation exchange alloy membrane had shown great potential for applications in electro-driven membrane separation processes.
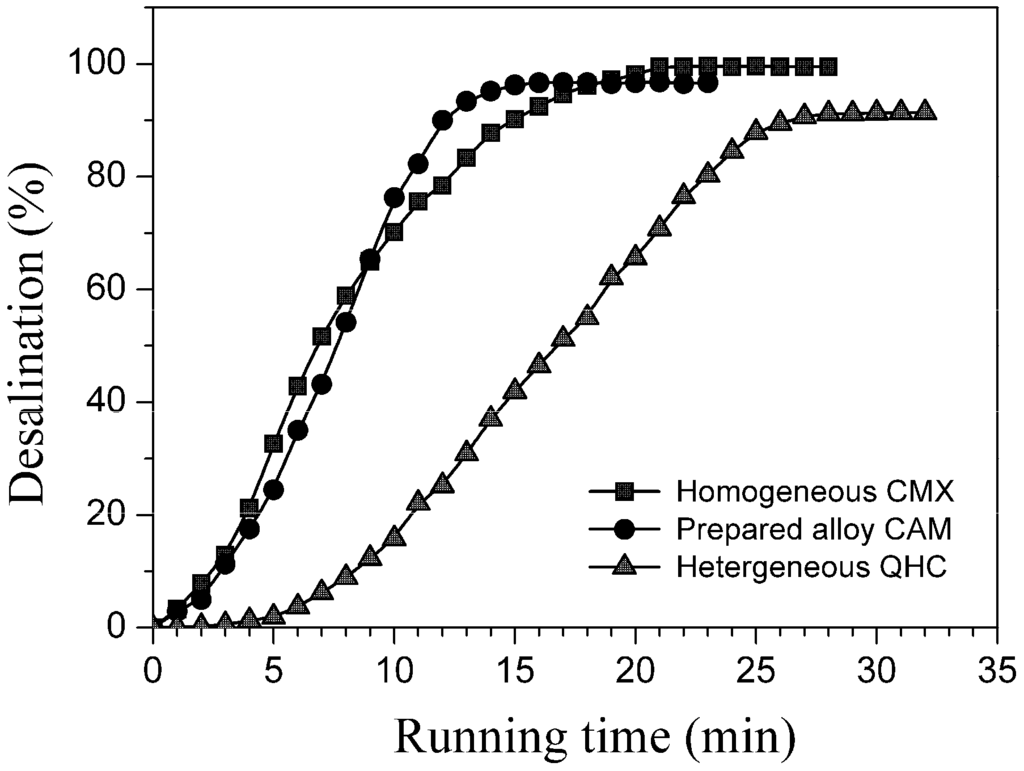
Figure 10.
Desalination curves of cation exchange membranes.
Figure 10.
Desalination curves of cation exchange membranes.
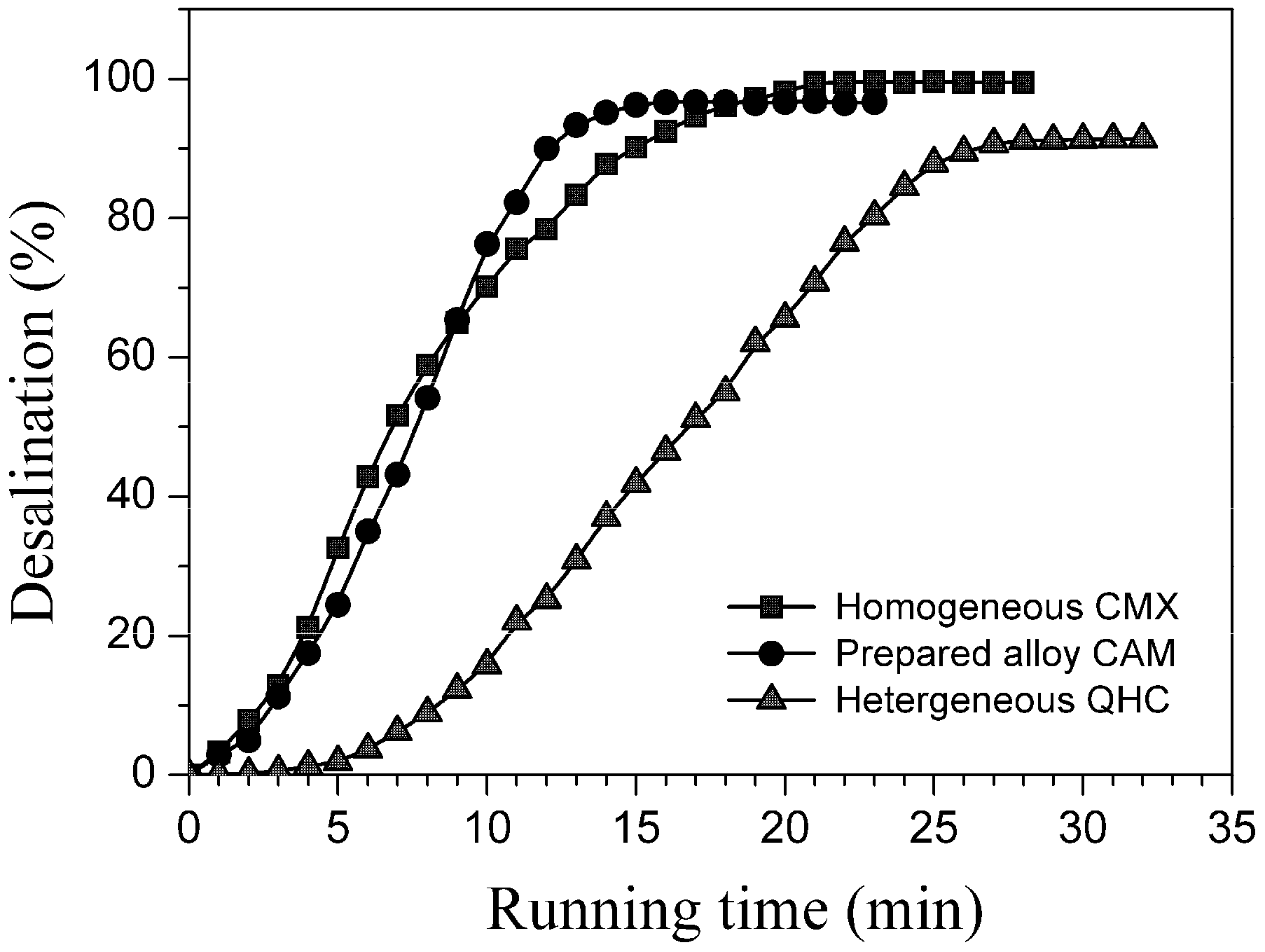

Table 3.
Desalination effects of the cation exchange membranes a.
| Membrane | QHC | CAM | CMX |
|---|---|---|---|
| Limiting conductivity (ms/cm) | 3.01 | 1.10 | 0.17 |
| Desalination degree (%) | 91.3 | 96.8 | 99.5 |
| Equilibrium time (min) | 28 | 16 | 21 |
a The initial conductivity is 34.6 ms/cm.
4. Conclusions
We have combined the classical sulfonation method of polystyrene-based cation exchange resins with the thermoforming manufacturing process of heterogeneous cation exchange membranes, to successfully develop a novel polystyrene/PVDF cation exchange alloy membrane with a semi-interpenetrating polymer network (semi-IPN) structure. For this purpose, a detailed study on sulfonating the polystyrene/PVDF alloy particles has confirmed that the classical sulfonation method is still effective, with a satisfactory sulfonation degree up to 85%. The prepared cation exchange alloy membrane exhibits excellent physical and electrochemical properties obviously exceeding a commercially available heterogeneous cation exchange membrane and a favorable dimensional stability (3D changes), regardless of whether in salt, acid or alkaline solutions. Moreover, the electrodialysis desalination tests confirm the low running electric resistance, high desalination degree and short operation time, with the CAM alloy membrane. Its desalination effect compares favorably with a commercial high-performance homogeneous membrane. Above all, the results encouraged the authors to keep on developing this kind of low-cost, but relatively high-performance, alloy membrane product and applying it to some specific electro-driven membrane separation processes.
Acknowledgments
We want to thank Xiao-cheng Sun and Wen-lan Chen for taking part in this work. Discussions with Jian-xiong Mo and Ke-yong Jin, both from Hangzhou Water Treatment Technology Development Center (Hangzhou, China), have been helpful and are appreciated. The study was financially supported by the National High Technology Research and Development Program (863 Program) (No. 2012AA03A605) and the Ningbo Municipal Science Foundation (No. 2009D10015).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Hickner, M.A.; Ghassemi, H.; Kim, Y.S.; Einsla, B.R.; McGrath, J.E. Alternative polymer systems for proton exchange membranes (PEMs). Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 4587–4612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kariduraganavar, M.Y.; Nagarale, R.K.; Kittur, A.A.; Kulkarni, S.S. Ion-exchange membranes: Preparative methods for electrodialysis and fuel cell applications. Desalination 2006, 197, 225–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarale, R.K.; Gohil, G.S.; Shahi, V.K. Recent developments on ion-exchange membranes and electro-membrane processes. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 119, 97–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.W. Ion exchange membranes: State of their development and perspective. J. Membr. Sci. 2005, 263, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mark, H.F.; Gaylord, N.G. Encyclopedia of Polymer Science and Technology; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Schauer, J.; Brožová, L. Heterogeneous ion-exchange membranes based on sulfonated poly (1,4-phenylene sulfide) and linear polyethylene: preparation, oxidation stability, methanol permeability and electrochemical properties. J. Membr. Sci. 2005, 250, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyas, P.V.; Shah, B.G.; Trivedi, G.S.; Ray, P.; Adhikary, S.K.; Rangarajan, R. Studies on heterogeneous cation-exchange membranes. React. Funct. Polym. 2000, 44, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schauer, J.; Llanos, J.; Zitka, J.; Hnat, J.; Bouzek, K. Cation-exchange membranes: Comparison of homopolymer, block copolymer, and heterogeneous membranes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 124, E66–E72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasa, J.V.; Boob, S.; Weiss, R.A.; Shaw, M.T. Proton-exchange membranes composed of slightly sulfonated poly (ether ketone ketone) and highly sulfonated crosslinked polystyrene particles. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 269, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.M.; Madaeni, S.S.; Khodabakhshi, A.R. Preparation and characterization of ABS/HIPS heterogeneous cation exchange membranes with various blend ratios of polymer binder. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 351, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.L.; Luo, Y.J.; Jin, Y.; Mo, J.X.; Tang, F.Y. Method for Manufacturing High-Selective Permeability Heterogeneous ion Exchange Membrane. CN Patent 102,512,974 A, 14 December 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Hosseini, S.M.; Madaeni, S.S.; Khodabakhshi, A.R. Preparation and characterization of PC/SBR heterogeneous cation exchange membrane filled with carbon nano-tubes. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 362, 550–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.M.; Madaeni, S.S.; Asiani, H.; Heidari, A.R. Preparation and electrochemical characterization of monovalent ion selective poly (vinyl chloride)-blend-poly (styrene-co-butadiene) heterogeneous cation exchange membrane coated with poly (methyl methacrylate). Sep. Sci. Technol. 2012, 47, 1443–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, Z.X.; Han, Q.Q.; Cao, S.A. Present situation and prospect of production and application of domestic ion exchange resin. Water Purif. Technol. 2012, 29, 11–26. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lei, Y.L.; Mo, J.X.; Sun, X.C.; Chen, F.; Luo, Y.J.; Liu, F.; Shen, L.Q.; Ye, J.R. Proudction of Polystyrene and Polyvinylidene Fluoride Composite Cation Exchange Membranes. CN Patent 102,814,125A, 25 July 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Khodabakhshi, A.R.; Madaeni, S.S.; Hosseini, S.M. Effect of polymers blend ratio binder on electrochemical and morphological properties of PC/S-PVC-based heterogeneous cation-exchange membranes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2011, 120, 644–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y. Ion Exchange Membranes Fundamentals and Applications, Membrane Science and Technology Series; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Hosseini, S.M.; Madaeni, S.S.; Khodabakhshi, A.R. Preparation and characterization of ABS/HIPS heterogeneous anion exchange membrane filled with activated carbon. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 118, 3371–3383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.W.; Yang, W.H. Fundamental studies of a new series of anion exchange membranes: Membrane preparation and characterization. J. Membr. Sci. 2001, 190, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JeřáBek, K. Distribution and catalytic activity of sulfonic acid groups in organic ion exchangers. J. Polym. Sci. Polym. Chem. Editor. 1980, 18, 65–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Xi, S.P.; Liu, Z.X.; Huang, Y.E. FTIR and fluorescence emission spectra of sulfonated PS and its Ionomers. Spectrosc. Spect. Anal. 1999, 19, 289–292. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, R.; Wei, R.Q.; Liu, X.N.; Lin, X. Poly(styrene-co-divinylbenzene)resins sulfonated by chlorosulfonic acid. J. Chem. Ind. Eng 2010, 61, 1047–1051. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.R. Electrodialysis Engineering; Science Press: Beijing ,China, 1995. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Singare, P.U.; Lokhande, R.S.; Madyal, R.S. Thermal degradation studies of some strongly acidic cation exchange resins. Open J. Phys. Chem. 2011, 1, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
