Abstract
In this study, we present the synthesis and the characterization of novel functionalized arylene main-chain ionomers based on perfluoro-p-xylene (PFX). The polymers were prepared by polycondensation of PFX and 4,4'-dihydroxybiphenyl or bisphenol 2,2-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)-hexafluoropropane (bisphenol AF). After polymerization, the PFX unit was still able to undergo nucleophilic aromatic substitution reaction, which was used to introduce phosphonic acid groups into the polymer via a reaction with tris(trimethylsilyl)phosphite. Furthermore, electrophilic sulfonation of these polymers was possible in the bisphenol unit when using H2SO4/SO3 as the sulfonation agent. The so-obtained water-soluble PFX-based polyelectrolytes showed excellent chemical stability and were blended with polybenzimidazoles. The blend membranes formed flexible and mechanically robust films with excellent chemical and thermal stabilities.
1. Introduction
In recent years, the application of polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs) and direct methanol fuel cells (DMFCs) as power sources in automotive and portable electronic applications has attracted increasing attention in the scientific community [1]. Many different approaches have been investigated to substitute proton-conductive membrane materials based on perfluorinated sulfonic acids (PFSA), such as Nafion® [1]. While the PFSAs show excellent chemical, mechanical and thermal stability coupled with high proton conductivity, these materials unfortunately exhibit a high methanol permeability, which is a severe shortcoming for application in DMFCs. Additionally, a significant drop in proton conductivity occurs at temperatures above 80 °C, because of an increased drying-out of the PFSAs.
Several proton-conducting membrane materials have been investigated with different functionalized polymer families, e.g., sulfonated polysiloxanes [2], polyphosphazenes [3,4], styrene-grafted (partially) fluorinated polyolefins [5] and a significant variety of different aromatic main-chain polymers. When searching for new polymer materials for proton-conductive membranes, it was found that the perfluorinated xylene could serve as a promising building block for partially-fluorinated arylene ionomers. In principle, fluorinated ionomers are expected to have superior stability and increased acid strength, compared to their non-fluorinated analogues [6,7]. The focus of this study is the synthesis and characterization of a new partially-fluorinated and, therefore, electron-deficient arylene main-chain polymer prepared by a polycondensation reaction between perfluoro-p-xylene and bisphenols, like 2,2-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)-hexafluoropropane (bisphenol AF) or 4,4'-dihydroxybiphenyl. Due to the strongly electron-attracting C–F and CF3 groups, the perfluoroxylene building group is capable of undergoing nucleophilic substitution of the F. The reaction between poly(arylene ether perfluoroxylene) and tris(trimethylsilyl)phosphite followed by hydrolysis yielded a phosphonated polyelectrolyte. Moreover, the introduction of benzimidazole groups by nucleophilic substitution reaction was possible with 1-mercaptobenzimidazole (1H-benzo[d]imidazole-2-thiol) via the mercapto group. Additionally, the poly(aryl ether perfluoroxylene) backbone allowed electrophilic substitutions when using SO3/H2SO4 as a sulfonation agent, introducing the SO3H-group into the bisphenol portion of the aromatic polymer. The sulfonated and phosphonated main chain ionomers can subsequently be blended with base group-containing polymers, such as polybenzimidazoles, to obtain acid- or base-excess blend membranes.
Many types of ionically cross-linked acid-excess [8,9] and base-excess acid-base blend membranes and covalently cross-linked (blend) membranes, based on arylene main-chain ionomers, having high mechanical, chemical stability and low methanol permeability have been developed by the authors’ group during the last decade.
Since the acid-base blend membranes showed increased thermal and mechanical stability, compared to the pure polymers, which is due to the ionic cross-linking between the acidic and basic functional groups, acid-excess and base-excess blend membranes have been prepared from the novel perfluoroxylene polymers presented in this contribution.
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
Tetrafluoro-1,4-bis(trifluoromethyl)benzene, 4,4'-Dihydroxybiphenyl, 2,2-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)hexafluoropropane, tris(trimethylsilyl) phosphite, 2-mercaptobenzimidazole, decafluorobiphenyl, fuming sulfuric acid and sulfuric acid were purchased from ABCR GmbH (Karlsruhe, Germany) and Sigma-Aldrich Germany (Steinheim, Germany). All of the other chemicals used are HPLC (High Performance Liquid Chromatography) quality.
2.2. Synthesis
The typical polymerization for compounds 1–8 was carried out as follows:
(1) In a 250-mL three-neck round-bottom flask equipped with an argon inlet, magnetic stirrer and a reflux condenser, 1.8821 g (10.1074 mmol) of 4,4'-dihydroxybiphenyl and 1.8060 g (5.3711 mmol) of tetrafluoro-1,4-bis(trifluoromethyl)benzene were dissolved in 50 mL N,N-dimethylacetamide (DMAc) and an excess of 3 equivalents of potassium carbonate was added. The reaction mixture was heated to 110 °C and stirred for 3 h. Subsequently, the reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature for 30 min. The polymer was precipitated in water (1 L), filtered, washed with deionized water and dried. Yield: 2.23 g (81%); 1H-NMR (tetrahydrofurane (THF))-d8) δ: 7.02 (d, 2H, 3JHH = 8.82 Hz, CH); 7.50 (d, 2H, 3JHH = 8.82 Hz, CH); 19F-NMR (THF-d8) δ: −57.7 (d, 6F, 4JFF = 26.42 Hz, CF3); −128.6 (m, C–F); 13C{1H}-NMR (THF-d8) δ: 157.6 (s, C–O); 151.1 (d, 1JCF = 263 Hz, C–F); 139.3 (d, 2JCF = 17.3 Hz, C–O); 136.5 (s, CH); 128.7 (s, CH); 121.8 (q, 1JCF = 274 Hz, CF3); 118.7 (dd, 2JCF = 33.3 Hz, 2JCF = 10.3 Hz, C–CF3); 115.6 (s, CH); gel permeation chromatography (GPC) (eluent: N,N-dimethylacetamide containing 5 wt% LiBr; standard: polystyrene): Mw = 17.1 kg·mol−1, polydispersity index (PDI, PDI = Mw/Mn) = 1.45; thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) (heating rate 1 K·min−1; O2/N2 = 70/30): Tdecomposition = 509.4 °C.
(2) In a 250-mL three-neck round-bottom flask equipped with an argon inlet, magnetic stirrer and a reflux condenser, 4.2460 g (12.68 mmol) of bisphenol AF were dissolved in 50 mL DMAc, and an excess of 3 eq. of potassium carbonate was added. The reaction mixture was heated to 110 °C and stirred for 3 h. After cooling down to RT, 3.2788 g (13.88 mmol) of tetrafluoro-1,4-bis(trifluoromethyl)benzene were added to the reaction mixture. The reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature for 30 min. The polymer was precipitated in water (1 L), filtered, washed with deionized water and dried. Yield: 6.15 g (85%); 1H-NMR (DMSO-d6) δ: 7.12 (d, CH, 3JHH = 8.43 Hz); 7.35 (d, CH, 3JHH = 8,43 Hz); 19F-NMR (DMSO-d6) δ: −57.7 (d, 6F, 4JFF = 26.42 Hz, CF3); −64.8 (s, 6F) CF3); −128.6 (m, C–F); 13C{1H}-NMR (DMSO-d6) δ: 157.8 (s, C–O); 150.0 (d, 1JCF = 264 Hz, C–F); 138.9 (d, 2JCF = 17.25 Hz, C–O); 132.3 (s, CH); 128.9 (s, C–CCF3); 124.5 (d, 1JCF = 274 Hz, CF3); 121.8 (d, 1JCF = 274 Hz, CF3); 115.6 (s, CH); 63.9 (q, 2JCF = 24.6 Hz, CCF3); GPC (eluent: N,N-dimethylacetamide containing 5 wt% LiBr; standard: polystyrene): Mw = 51.4 kg·mol−1, PDI = 6.31; TGA (heating rate 1 K·min−1; O2/N2 = 70/30): Tdecomposition = 492.3 °C.
(3) Into a 250-mL round-bottom flask, 3.2610 g (7.54 mmol) of 1 in 30 ml 65% oleum were placed. The reaction mixture was heated to 120 °C and stirred for 3 h. Subsequently, the reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature for 30 min and precipitated into a water/ice (1 L) mixture. The mixture was then dialyzed (dialyzing tubes, molecular weight cutoff (MWCO) = 10,000 g·mol−1) for 3 days, exchanging the water twice a day. The dialyzed product was dried. Yield: 1.96 g (61%); 1H-NMR (dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO)-d6) δ: 8.46 (2H, broad line, CH); 8.33 (2H, broad line, CH); 8.05 (2H, broad line, CH); 19F-NMR (DMSO-d6) δ: −57.7 (d, CF3); −128.6 (m, C–F); 13C{1H}-NMR (DMSO-d6) δ: 154.5 (s, C–O); 150.9 (d, 1JCF = 263 Hz, C–F); 138.3 (s, C–O); 132.4 (s, C–SO3H); 128.8 (s, CH); 127.5 (s, CH); 122.8 (m, CF3); 120.1 (s, CCF3); 116.5 (s, CH); GPC (eluent: N,N-dimethylacetamide containing 5 wt% LiBr; standard: polystyrene): Mw = 27 kg·mol−1, PDI = 1.67; TGA (heating rate 1 K·min−1; O2/N2 = 70/30): Tdecomposition = 317.8 °C; ion-exchange capacities (IECs): IECdirect = 2.43 mmol·g−1; IECtotal = 2.80 mmol·g−1.
(4) Into a 250-mL round-bottom flask, 5.5074 g (9.46 mmol) of 2 in 50 mL 65% oleum were added. The reaction mixture was heated to 120 °C and stirred for 5 h. Subsequently, the reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature for 30 min and precipitated in a water/ice (1 L) mixture. The mixture was dialyzed (dialyzing tubes MWCO 10,000 g·mol−1) for 3 days, exchanging the water twice a day. The dialyzed product was dried. Yield: 3.47 g (63%); 1H-NMR (DMSO-d6) δ: 7.15 (4H, broad line, CH); 7.93 (2H, broad line, CH); 19F-NMR (DMSO-d6) δ: −56.5 (d, 6F, 4JFF = 14.05 Hz, CF3); −63.4 (s, 6F, CF3); −128.1 (CF, broad line); 13C{1H}-NMR (DMSO-d6) δ: 154.7 (s, C–O); 147.02 (C–F); 138.3 (m, C–O); 136.2 (s, C–SO3H); 132.4 (s, CH); 130.4 (s, CH); 126.5 (s, C–CCF3); GPC (eluent: N,N-dimethylacetamide containing 5 wt% LiBr; standard: polystyrene): Mw = 13.1 kg·mol−1, PDI = 1.87; TGA (heating rate 1 K·min−1; O2/N2 = 70/30): Tdecomposition = 217.5 °C; IECdirect = 2.01 mmol·g−1; IECtotal = 2.06 mmol·g−1.
(5) All of the glassware was dried (400 °C, argon) prior to use. Poly(arylene ether perfluoroxylene) (pPFX) 2.1330 g (4.93 mmol) and tris(trimethylsilyl)phosphite 20.96 g (70.2 mmol) were introduced into a round-bottom flask equipped with a magnetic stirrer, reflux condenser, argon in-/outlet system and an oil bath. The mixture was stirred, and the system was heated to 170 °C for 20 h. After cooling, the reaction mixture was refluxed with 10 mL of water for 30 min. The reaction mixture was dialyzed (dialyzing tubes MWCO 10,000 g·mol−1) for 3 days, exchanging the water twice a day. The product was obtained as a yellow solid and was dried at 120 °C. Yield: 2.7 g (45%); 1H-NMR (DMSO-d6) δ: 7.42 (2H, 3JHH = 8.66 Hz, CH); 6.85 (2H, 3JHH = 8.66 Hz, CH); 19F-NMR (DMSO-d6) δ: −52.9 (s, CF3); 13C{1H}-NMR (DMSO-d6) δ: 156.6 (s, CH); 131.7 (s, CH); 127.2 (d, 1JCP = 52.9 Hz); 127.4 (s, CH); 116.0 (s, CH); 31P-NMR (DMSO-d6) δ: 2.3 (d, 4JPF = 3.75 Hz, –PO3H2); TGA (heating rate 1 K·min−1; O2/N2 = 70/30): Tdecomposition = 271.1 °C; IECdirect = 0.67 mmol·g−1; IECtotal = 2.13 mmol·g−1.
(6) In a 250-mL three-neck round-bottom flask equipped with an argon inlet, magnetic stirrer and a reflux condenser, 1.0121 g (2.34 mmol) of 1 and 0.7385 g (4.91 mmol) 2-mercaptobenzimidazole were dissolved in 50 mL DMAc, and an excess of 3 eq. of potassium carbonate was added. The reaction mixture was heated at 100 °C and stirred for 3 h. Subsequently, the reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature for 30 min. The polymer was precipitated in water (1 L), filtered and dried. Yield: 0.94 g (73%); 1H-NMR (DMSO-d6) δ: 7.34 (2H, 3JHH = 8.66 Hz, CH); 7.20–7.05 (m, 4H, CH); 6.77 (2H, 3JHH = 8.66 Hz, CH); 19F-NMR (DMSO-d6) δ: −53.5 (s, CF3); 13C{1H}-NMR (DMSO-d6) δ: 138.4 (s, CO); 135.1 (s, CH); 132.7(s, C–C); 128.0 (s, CH); 122.7 (s, C–H); 119.9 (m, C–CF3); 116.0 (s, CH); 109.9 (s, CH); TGA (heating rate 1 K·min−1; O2/N2 = 70/30): Tdecomposition = 490.1 °C.
(7) In a 250-mL three-neck round-bottom flask equipped with an argon inlet, magnetic stirrer and a reflux condenser, 7.1180 g (38.22 mmol) of 4,4'-dihydroxy-biphenyl and 3 eq. of potassium carbonate were dissolved in 50 mL DMAc. The reaction mixture was heated to 100 °C and stirred for 3 h. After cooling of the reaction mixture down to 90 °C, 6.8891 g (24.08 mmol) perfluoro-p-xylene (PFX) and 5.3642 g (16.05 mmol) decafluorobiphenyl were added, and the mixture was refluxed for 15 min. The polymer was precipitated in water (1 L), filtered and dried. Yield: 6.86 g (78%); 1H-NMR (DMSO-d6) δ: 7.71 (2H, 3JHH = 7.37 Hz, CH); 7.32 (d, 2H, 3JHH = 7.37 Hz, CH); 19F-NMR (DMSO-d6) δ: −56.2 (s, CF3); −128.9 (m, CF); −138.2 (m, CF); −153.8 (m, CF); 13C{1H}-NMR (DMSO-d6) δ: 153.7 (s, C–O); 149.2 (d, 1JCF = 256 Hz, C–F); 141.6 (d, 1JCF = 256 Hz, C–F); 135.1 (s, CH); 132.7 (s, C–C); 128.8 (s, CH); 122.7 (s, CH); 118.9 (m, C–CF3); 116.0 (s, CH); 109.9 (s, CH); 100.9 (m, C–C); GPC (eluent: DMAc containing 5 wt% LiBr; standard: polystyrene): Mw = 33.6 kg·mol−1, PDI = 3.22; TGA (heating rate 1 K·min−1; O2/N2 = 70/30): Tdecomposition = 525 °C.
(8) In a 250-mL round-bottom flask, 1.391 g (1.59 mmol) of pPFX-decafluorobiphenyl (DFB)-polymer and a mixture of 70 mL sulfuric acid and 70 mL 65% oleum were added. The reaction mixture was stirred at RT for 24 h. Subsequently, the reaction mixture was precipitated in water/ice (1 L) mixture. The mixture was then dialyzed (dialyzing tubes MWCO 10,000 g·mol−1) for 3 days, exchanging to the water twice a day. The dialyzed product was dried. Yield: 0.9 g (65%); 1H-NMR (DMSO-d6) δ: 8.05 (2H, broad line, CH); 7.62 (2H, broad line, CH); 7.28 (2H, broad line, CH); 19F-NMR (DMSO-d6) δ: −56.2 (s, CF3); −128.9 (m, CF); −138.2 (m, CF); −153.8 (m, CF); 13C{1H}-NMR (DMSO-d6) δ: 153.7 (s, C–O); 152.4 (m, C–O); 149.2 (d, 1JCF = 256 Hz, C–F); 143.9 (d, 1JCF = 250.4 Hz, C–F); 141.6 (d, 1JCF = 256 Hz, C–F); 138.4 (s, CO); 137.5 (m, C–C); 135.1 (s, CH); 132.7 (s, C–C); 128.8 (s, CH); 127.2 (s, CH); 122.7 (s, CH); 118.9 (m, C–CF3); 116.0 (s, CH); 109.9 (s, CH); 100.9 (m, C–C).
2.3. Blend Membrane Preparation
The sulfonated pPFX-DFB in Na+-form was dissolved in DMSO to give a 40% solution. A 4 wt% solution of hexafluoroisopropylidene polybenzimidazole (F6-PBI) in DMSO was prepared and added to the sulfonated pPFX-DFB DMSO solution. The final ratio of sulfonated poly(arylene ether perfluoroxylene)/F6-PBI was adjusted to 30/70 (w/w). The mixed solution was poured onto glass plates and dried at T = 130 °C for 12 h. Subsequently, deionized water was spread on the polymer films to remove the membrane from the glass surface. To induce the formation of the ionic cross-linking in the membrane, the blend membrane was immersed in 10% HCl at 90 °C for 48 h followed by rinsing in water at 90 °C for 24 h.
2.4. Instrumentation
NMR spectra were recorded on a Bruker Avance 400 spectrometer at a resonance frequency of 250 MHz for 1H, 62.9 MHz for 13C, 235 MHz for 19F and 250 Hz for 1H, 13C-HSQC (heteronuclear single-quantum coherence) at 303 K. Chemical shifts were referenced to external TMS (1H, 13C). Coupling constants are given as absolute values. FTIR (Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy) spectra were obtained from samples as a KBr pellet on a Nicolet 6700 FTIR instrument (Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Waltham, MA, USA). The molecular weight distributions of the polymers and ionomers (Mn, PDI) were determined by gel permeation chromatography (GPC) using an Agilent Technology GPC system (Series 1200) (Agilent Technologies, Inc., Santa Clara, CA, USA) coupled with a viscosity detector (PSS ETA-2010 (Polymer Standards Service, Mainz, Germany)), a refractive index detector (Shodex RI71) (Showa Denko, Tokyo, Japan) and a static light-scattering detector (PSS SLD 7000). A set of three PSS GRAM columns (30, 3000, 3000 A) were used and calibrated with a series of polystyrene standards in N,N-dimethylacetamide containing 5 wt% LiBr. All of the samples were filtered through a Whatman syringe filter over a microporous polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) membrane (1.0 μm, Whatman 6878-2510 (Whatman plc, Maidstone, UK)) before injecting into the column system. The thermal stability of the polymers and membranes was determined by TGA (Netzsch GmbH & Co. KG, Selb, Germany), Model STA 449C) with a heating rate of 20 °C/min under an atmosphere enriched with oxygen (65%–70% O2, 35%–30% N2). Non-sulfonated polymers are compared by the temperature at which the sample has lost 5% of its initial weight (T5wt% loss). In the case of the sulfonated polymers the decomposition gases were further examined in a coupled FTIR spectrometer (Nicolet Nexus FTIR spectrometer) in order to identify the splitting-off temperature of the sulfonic acid group (TSO3H onset) for which the asymmetric stretching vibration of the S=O group at 1352–1342 cm−1 was used. Ion-exchange capacities (IECdirect and IECtotal) were determined by titration. Membranes in the H+ form were immersed in saturated sodium chloride solution (NaCl) for 24 h to convert them into the Na+ form. The exchanged H+ ions were then titrated with 0.1 M NaOH to the equivalent point (IECdirect). After that, a defined excess of NaOH was added, and this solution was back-titrated with 0.1 M HCl (IECtotal). For Fenton’s Test, a solution of 3 wt% H2O2 containing 4 ppm Fe2+ was used. Fe2+ was added as (NH4)2Fe(SO4)2·6H2O in order to accelerate the radical production. Membrane samples were immersed in Fenton’s Solution at 68 °C. After a certain period of time, the membrane samples were removed from the oxidizing solution, washed with water, dried at 120 °C for 2 h and weighed. For successive measurements, fresh Fenton’s Solutions were prepared and preheated every 24 h, in which the dried membrane samples were immersed continuously.
The H+ conductivity in the through plane was determined using the Membrane Test System (MTS 740) from Scribner Associates Inc. (Southern Pines, NC, USA) temperature and humidity sensors in the measuring cell ensure the appropriate temperature and relative humidity in the membrane. A detailed description and technical data are given elsewhere [10]. Gas-diffusion electrodes (GDE) (E-TEK ELAT GDE 140-HT) were glued with conductive carbon paint to the platinum electrode sandwiched with the membrane 3 cm × 1 cm in the middle. Porous gas diffusion layers (GDLs) served to facilitate gas-phase diffusion of water vapor to and from the membrane. For sufficient contact between the membrane, GDL and electrodes, the stack was kept under 1.4 MPa. A typical test procedure at relative humidity of 20% and T = 80–150 °C, respectively, with the pre-condition of the sample at 80 °C for 30 min, was followed by increasing the temperature with steps of 10 °C conditioning for 15 min followed by five electrochemical impedance (EIS) measurements. The specific conductivity was obtained by σ = l/(A × R), where l is the membrane thickness, A the overlapping area of the electrodes and R the resistance derived from the high-frequency intercept of the complex impedance with the real axis.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Polycondensation and Functionalization
3.1.1. Polycondensation of Tetrafluoro-1,4-bis(trifluoromethyl)-benzene,4,4'-Dihydroxybiphenyl and 2,2-Bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)-hexafluoropropane
Perfluorinated aromatics are suitable building blocks for nucleophilic displacement polycondensation (SN) reactions, as already shown by Day et al. [11]. Consequently, the PFX was transformed into perfluoroarylene polymers via an SN reaction with 4,4'-dihydroxybiphenyl and bisphenol AF. The presence of residual C–F bonds in the polymer main chain offers possibilities for further functionalization of this polymer by aromatic SN reactions.
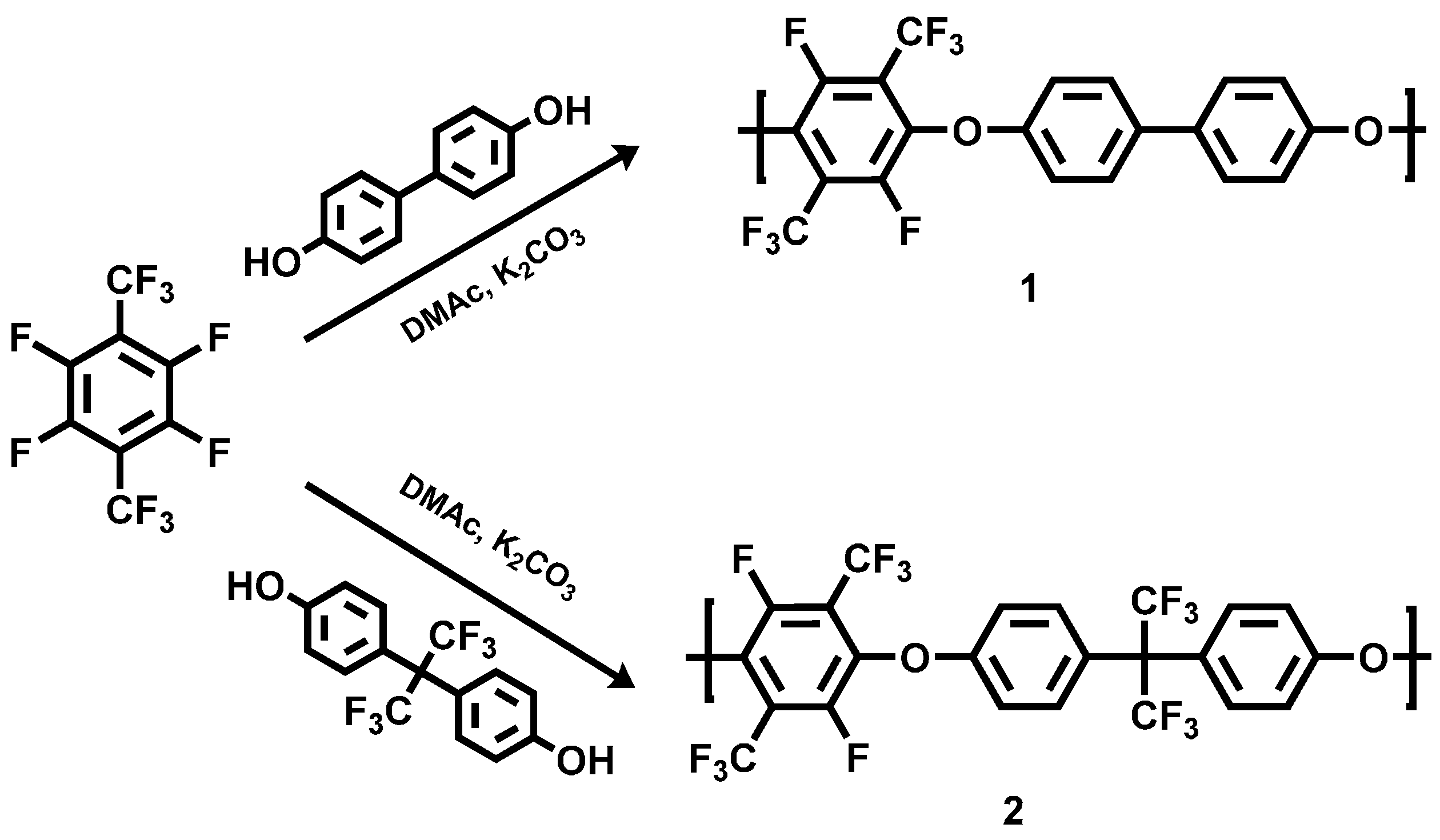
The polycondensation of PFX with 4,4'-dihydroxybiphenyl (DHB) and bisphenol AF was done for three hours at 90 °C under argon in a three-neck glass flask (see the Section 2.2 of this study). Potassium carbonate was utilized as deprotonation agent for the bisphenol (Scheme 1).
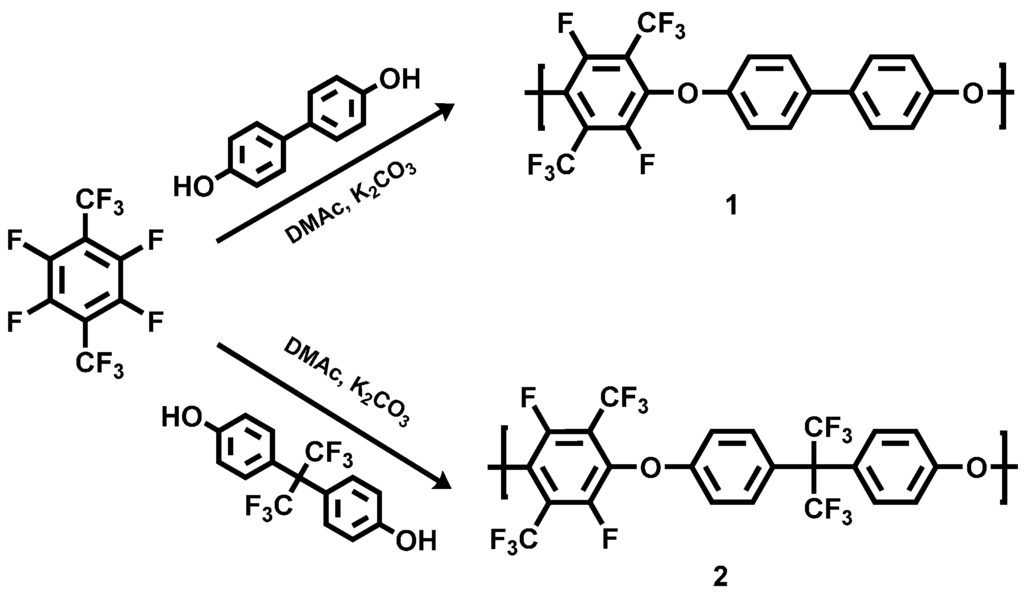
Scheme 1.
Reaction scheme of the polycondensation of poly(arylene ether perfluoroxylene) 1 and 2.
Scheme 1.
Reaction scheme of the polycondensation of poly(arylene ether perfluoroxylene) 1 and 2.
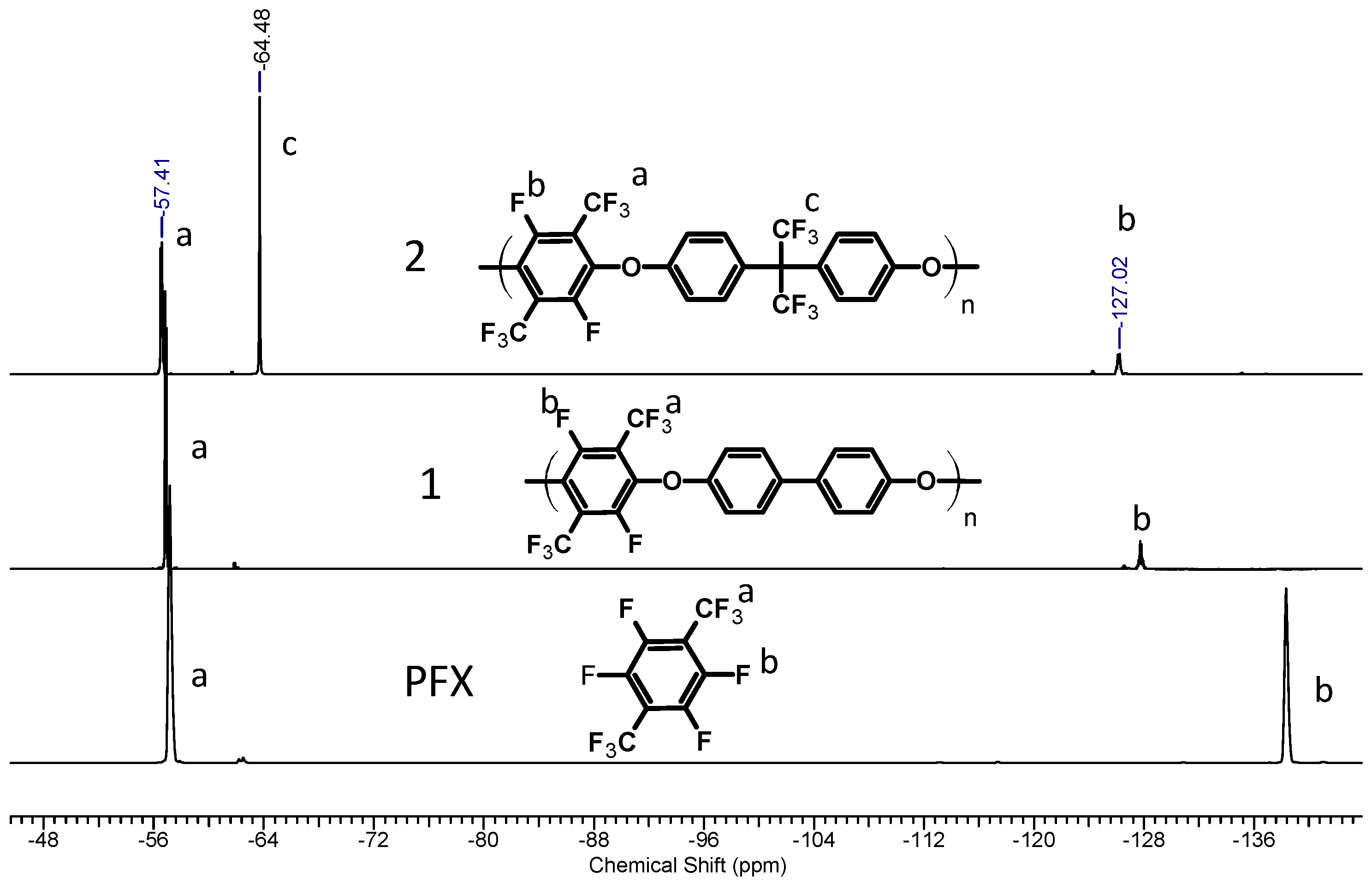
The structure of the synthesized poly(arylene ether perfluoroxylene) polymers (pPFX) 1, 2 was confirmed by 1H-, 13C- and 19F-NMR spectroscopy. The disappearance of the signals for the PFX meta-fluorine atoms at −139.2 ppm and the appearance of the new peak at −127 ppm in the 19F NMR spectra, revealed the completion of the reaction. The resonances with chemical shifts of −57, −127 ppm for 1 and −57, −64 and −128 ppm for 2 in the 19F NMR spectra were assigned to the ortho-fluorine atoms and the CF3-groups of the perfluoroxylene and bisphenol AF (see Figure 1). The linear structure of the polymer was confirmed by the existence of the two chemical equivalent fluorine atoms for the C–F and the CF3 group at −127 and −57 ppm for 1 and 2, respectively.
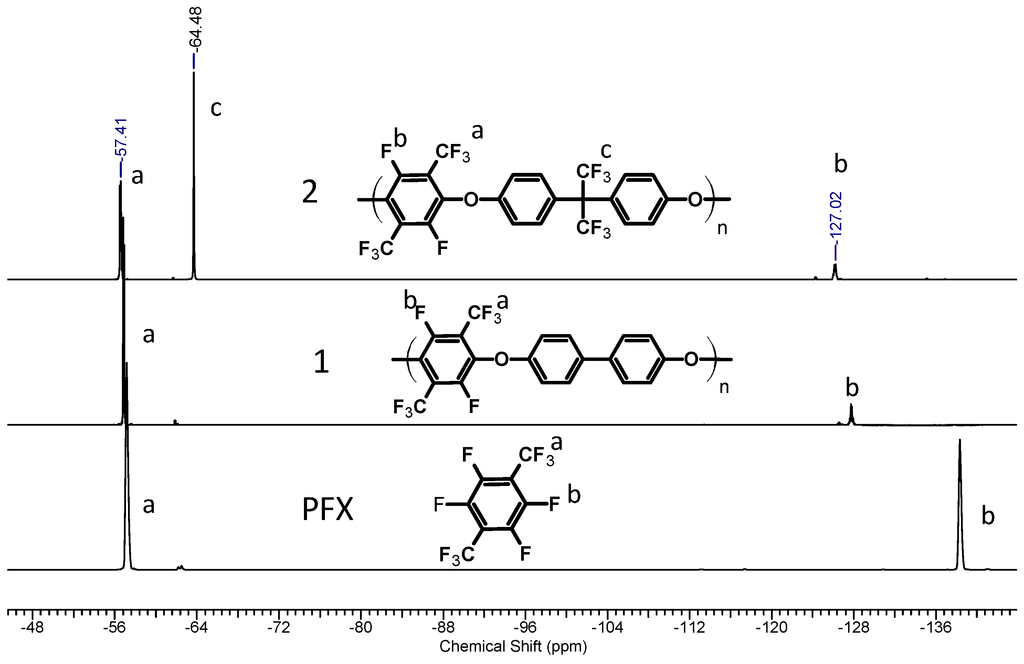
Figure 1.
19F-NMR spectra of perfluoro-p-xylene (PFX), 1 and 2.
Figure 1.
19F-NMR spectra of perfluoro-p-xylene (PFX), 1 and 2.
1H NMR measurements showed a down-field shift in the aromatic region with two doublets at 7.02 and 7.50 ppm for 1 and at 7.12 and 7.35 ppm for 2. Depending on the substituent in the polymer main chain, the 13C-NMR spectra showed chemical shifts at 115.6, 128.7, 136.5 and 157.6 ppm for 1. Similar chemical shifts were obtained at 63.9, 115.6, 121.8, 128, 132.3 and 157.8 ppm for 2. The related chemical shifts were observed for the perfluoroxylene group independent of the substituent.
The heat resistance of both polymers 1 and 2 was measured using thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) coupled with an FTIR sensor for analysis of the gaseous decomposition products forming during the TGA experiment (Figure 2). The polymers showed high thermal stability of Tdecomposition = 509 °C, indicated by the appearance of CO bands (between 2241 and 1991 cm−1) in the FTIR spectrum of 1 and Tdecomposition = 492 °C for 2. The high thermal stability makes the polymers suitable for high temperature polymer electrolyte membrane application. The weight loss at the TGA profile of 1 in the temperature range of 100–200 °C was attributed to water and residual solvent evaporation.
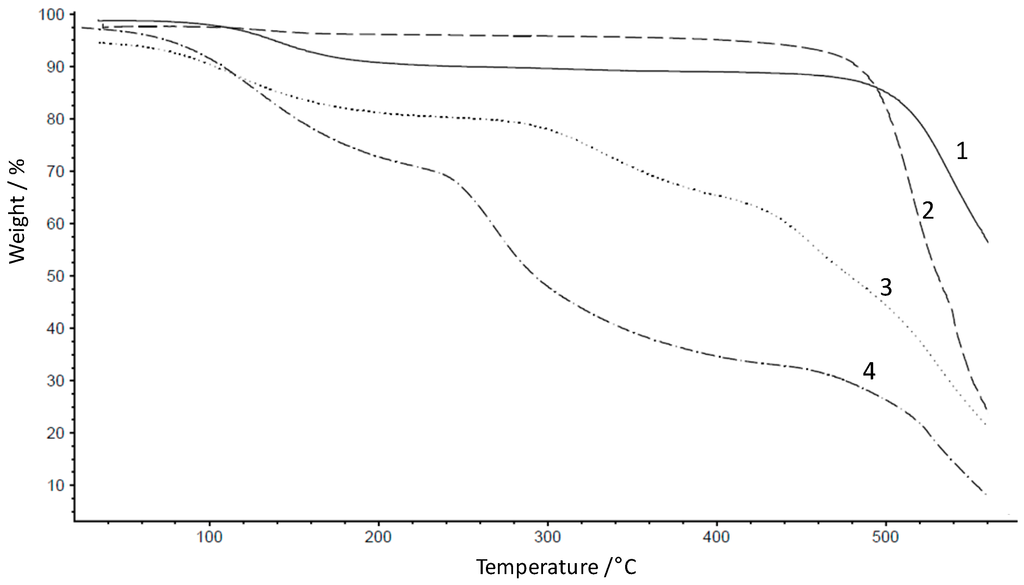
Figure 2.
Thermogravimetric analysis of 1, 2, 3 and 4.
Figure 2.
Thermogravimetric analysis of 1, 2, 3 and 4.
3.1.2. Sulfonation of Poly(arylene ether perfluoroxylene)s
The introduction of a sulfonic acid function of the biphenol and the bisphenol AF units of the pPFX was achieved via sulfonation with oleum at 120 °C for three and five hours respectively (see 3 and 4 in Scheme 2). The sulfonic acid groups served as the proton conductor in the acid-excess acid-base blend membranes or as an ionic cross-linker in the base-excess acid-base blend membranes.
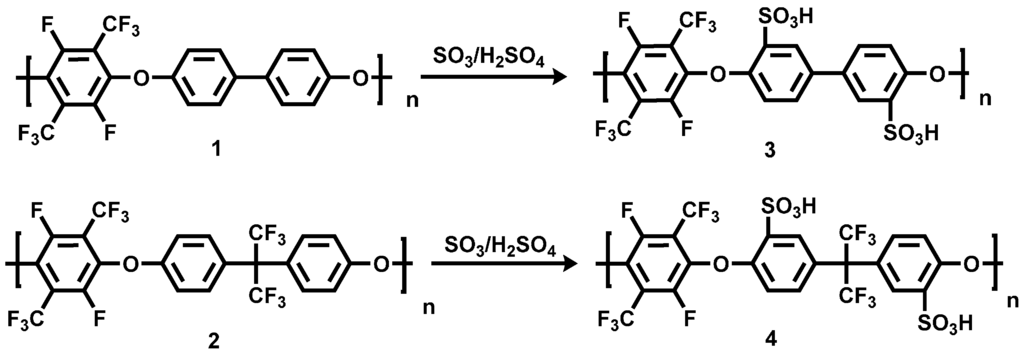
Scheme 2.
Sulfonation products of poly(arylene ether perfluoroxylene) (pPFX) 3 and 4.
Scheme 2.
Sulfonation products of poly(arylene ether perfluoroxylene) (pPFX) 3 and 4.
The structure of the sulfonated polymers was determined by 1H and 13C NMR spectroscopy. The disappearance of the symmetrical doublets, which are typical for aromatic protons of non-substituted bisphenols at 7.02 and 7.50 ppm and for biphenyl rings at 7.15 and 7.32 ppm, and the appearance of three different peaks in the 1H NMR spectra confirmed the substitution. Signals with chemical shifts at 8.05, 8.33 and 8.46 ppm for 3 and at 7.15, 7.21 and 7.93 ppm for 4 were observed. In the case of 4, the 1H-NMR chemical shifts of the protons adjust for the ortho sulfonation in the bisphenol AF unit showing similar values as has been presented in previous work [12]. The integration of the peaks of 4 was used to determine the number of protons. The 1H-NMR signals are too broad to show the typical pattern for the one fold-substituted aromatic ring with two doublets and one singlet peak. Due to the weak signals despite the high concentration, the exact position of the –SO3H groups could not be confirmed by heteronuclear single-quantum correlation measurements. According to the literature, it is expected that the SO3H group is introduced in the ortho position next to the ether-group [12,13].
The sulfonation degree was confirmed by 1H-NMR spectroscopy (see Figures S1 and S2 in Supplementary Materials). The integral ratio between the signals of the sulfonated and non-sulfonated units at the same position can be used to determine the sulfonation degree [12,13]. PFX is incompletely two-fold sulfonated, and all three degrees of substitution of the biphenyl unit can coexist in the polymer backbone (non-sulfonated, one-fold sulfonated and two-fold sulfonated). In the case of bisphenol AF, a sulfonation degree of 80% with a 20% non-sulfonated repeating unit was obtained. In the case of biphenol, the sulfonation degree of 50% was lower than in case of bisphenol AF. The sulfonation of the non-fluorinated aromatic rings was confirmed by 13C-NMR as the appearance of new signals with chemical shifts at 132.4 and 136.2 ppm for 3 and 4, respectively. Further evidence for sulfonation of pPFX was detected by FTIR measurement. Both of the sulfonated polymers showed absorption bands for the sulfone group found at 1334, 1151 and 1090 cm−1 for 3 and 1334, 1241, 1175 and 1088 cm−1 for 4 (see Figure S3 in Supplementary Materials). The IEC values reflected the partial sulfonation of the poly(arylene ether perfluoroxylene) polymer. The theoretical IEC was not achieved either in the case of 3 or 4 (see Table 1).

Table 1.
Ion-exchange capacity (IEC) data for polymers 3 and 4.
| pPFX (No.) | IECtheor (meq SO3H/g) | IECdirect (meq SO3H/g) | IECtotal (meq SO3H/g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 3.30 | 2.43 | 2.80 |
| 4 | 2.68 | 2.01 | 2.60 |
According to Figure 2, the thermal stability of the sulfonated products 3 and 4 is lower than that of the non-sulfonated polymers. A similar observation has been made for other arylene main chain polymers [12]. TGA-FTIR coupling experiments showed clearly that the sulfonated polymers split off –SO3H starting at 317 °C for 3 and 241 °C for 4. The thermal stability of 4 is almost 80 °C lower than that of 3, although 4 has higher fluorine content than 3, as already shown in the literature, that partially fluorinated aromatic polymers are more stable than their non-fluorinated analogues [7]. On the other hand, it has been found that the polymer stability can decrease if the aromatic system is too electron-deficient, as in the case for highly fluorinated oxadiazole polymers synthesized recently in the authors’ group [12].
The GPC measurements showed a decrease in molecular weights (30% and 46% for 3 and 4, respectively) after the sulfonation of 1 and 2. The degradation is common in view of the harsh reaction conditions required for the substitution reaction.
3.1.3. Phosphonation of Poly(arylene ether perfluoroxylene)
The nucleophilic substitution of a fluorine atom in perfluorinated aromatics is a well-established reaction in the literature [14,15,16,17]. Due to the presence of residual C–F groups in the PFX unit, –PO3H2 functions can be introduced via a nucleophilic substitution reaction using tris(trimethylsilyl)phosphite (P(OSiMe3)3, TMSP). This nucleophilic phosphonation reaction has been recently used to prepare poly(2,3,5,6-tetrafluorostyrene phosphonic acid) from pentafluorostyrene in our group [17]. To obtain the desired phosphonated polymer, pPFX 1 was reacted with TMSP at 170 °C for 24 h (see Scheme 3).
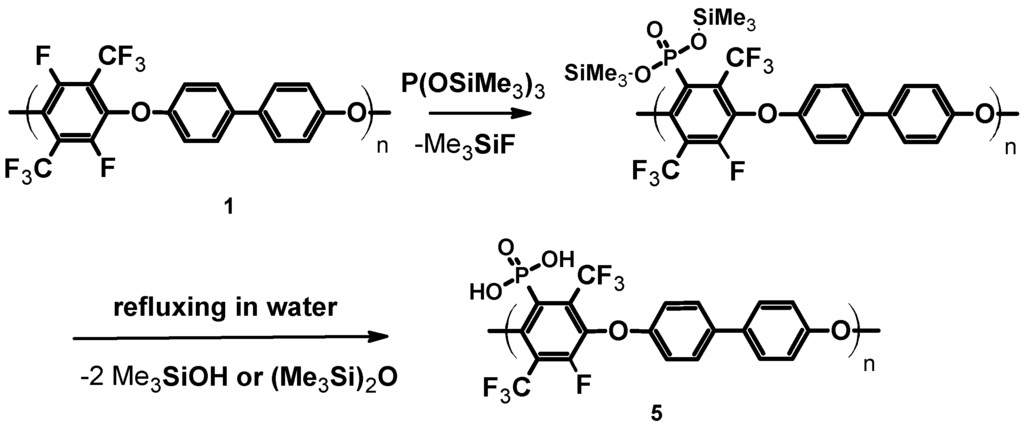
Scheme 3.
Phosphonation of pPFX 1.
Scheme 3.
Phosphonation of pPFX 1.
Disappearance of the fluorine signals of the C–F group at −57.7 ppm in the 19F NMR spectra (Figure 3) and appearance of the phosphorous signal 2.3 ppm in the 31P NMR spectra (Figure 4) confirmed the formation of the phosphonated polymer.
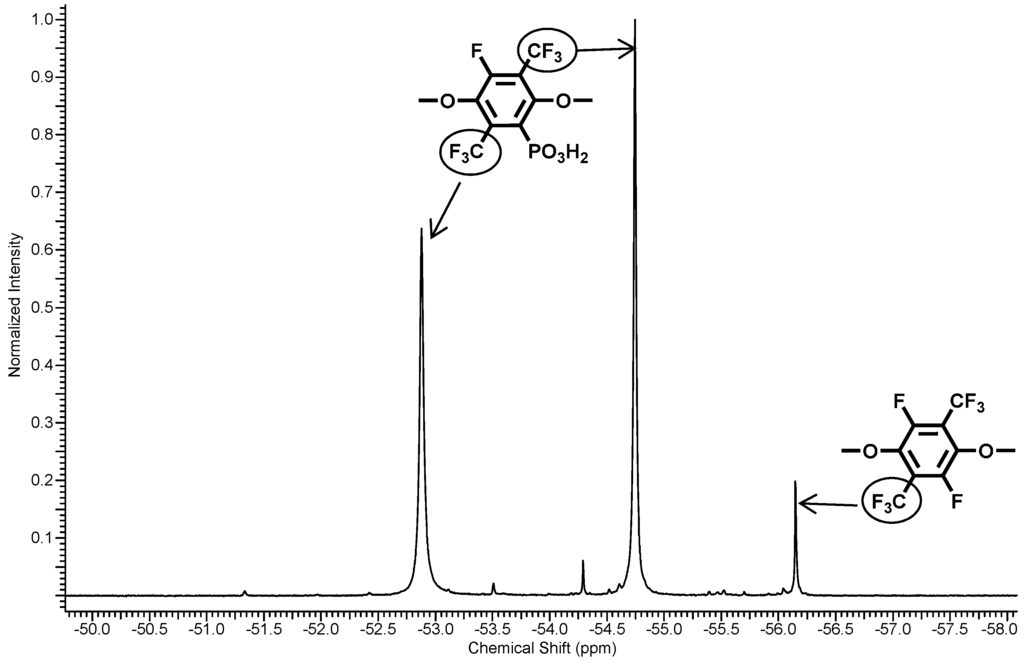
Figure 3.
19F-NMR spectra of polymer 5.
Figure 3.
19F-NMR spectra of polymer 5.
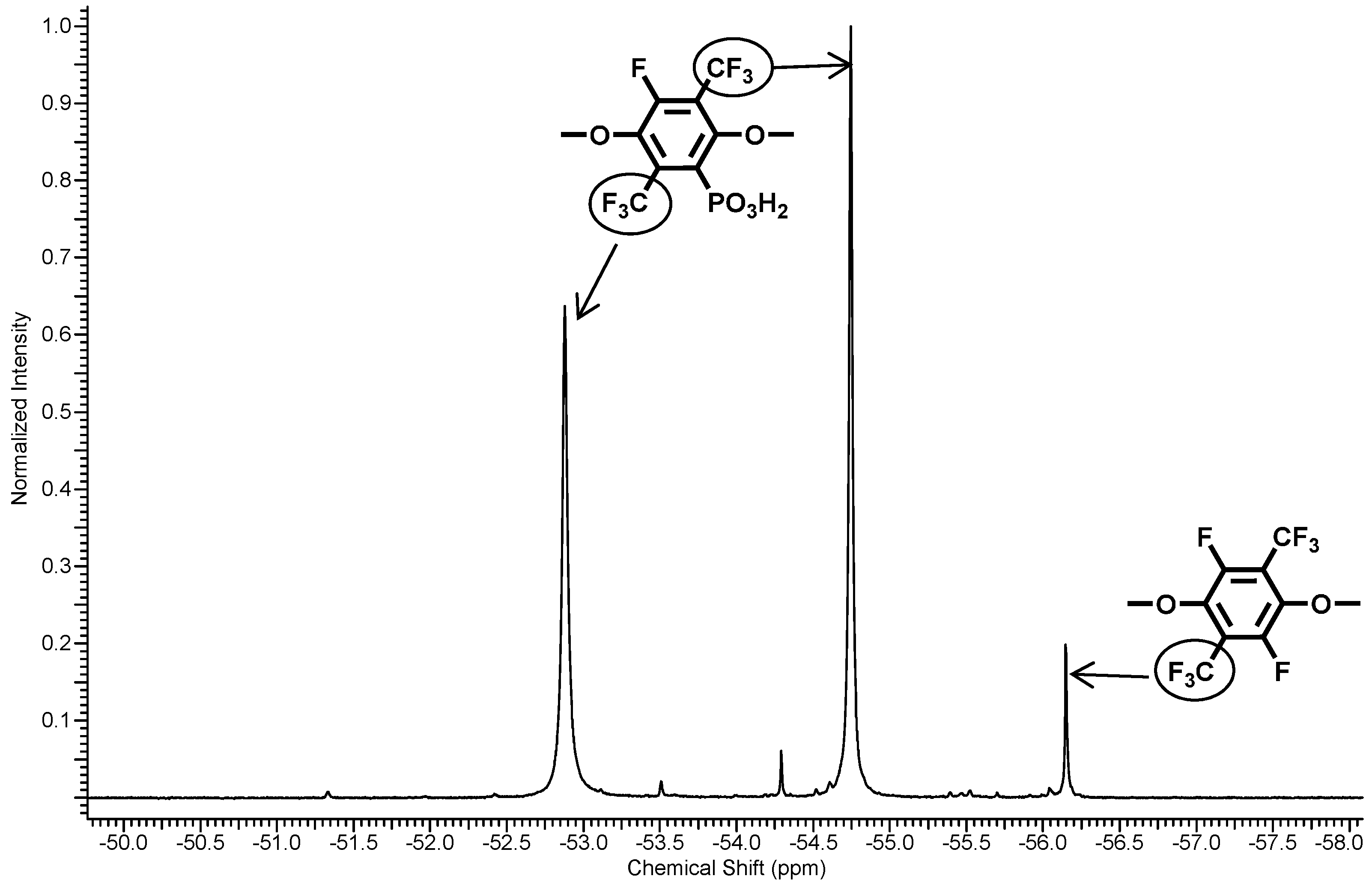
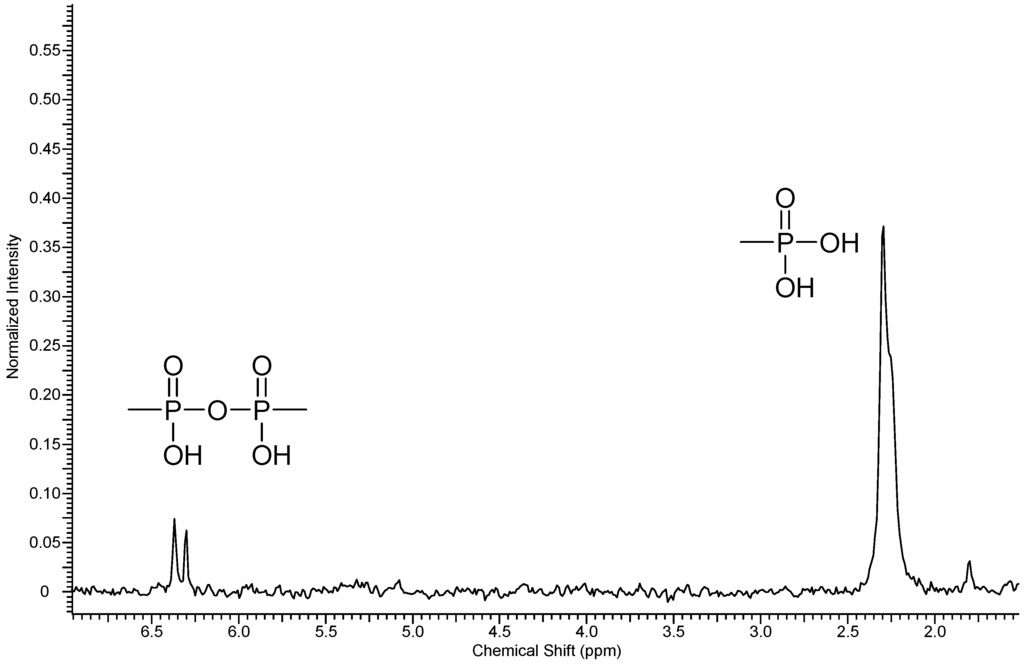
Figure 4.
31P-NMR spectra of polymer 5.
Figure 4.
31P-NMR spectra of polymer 5.
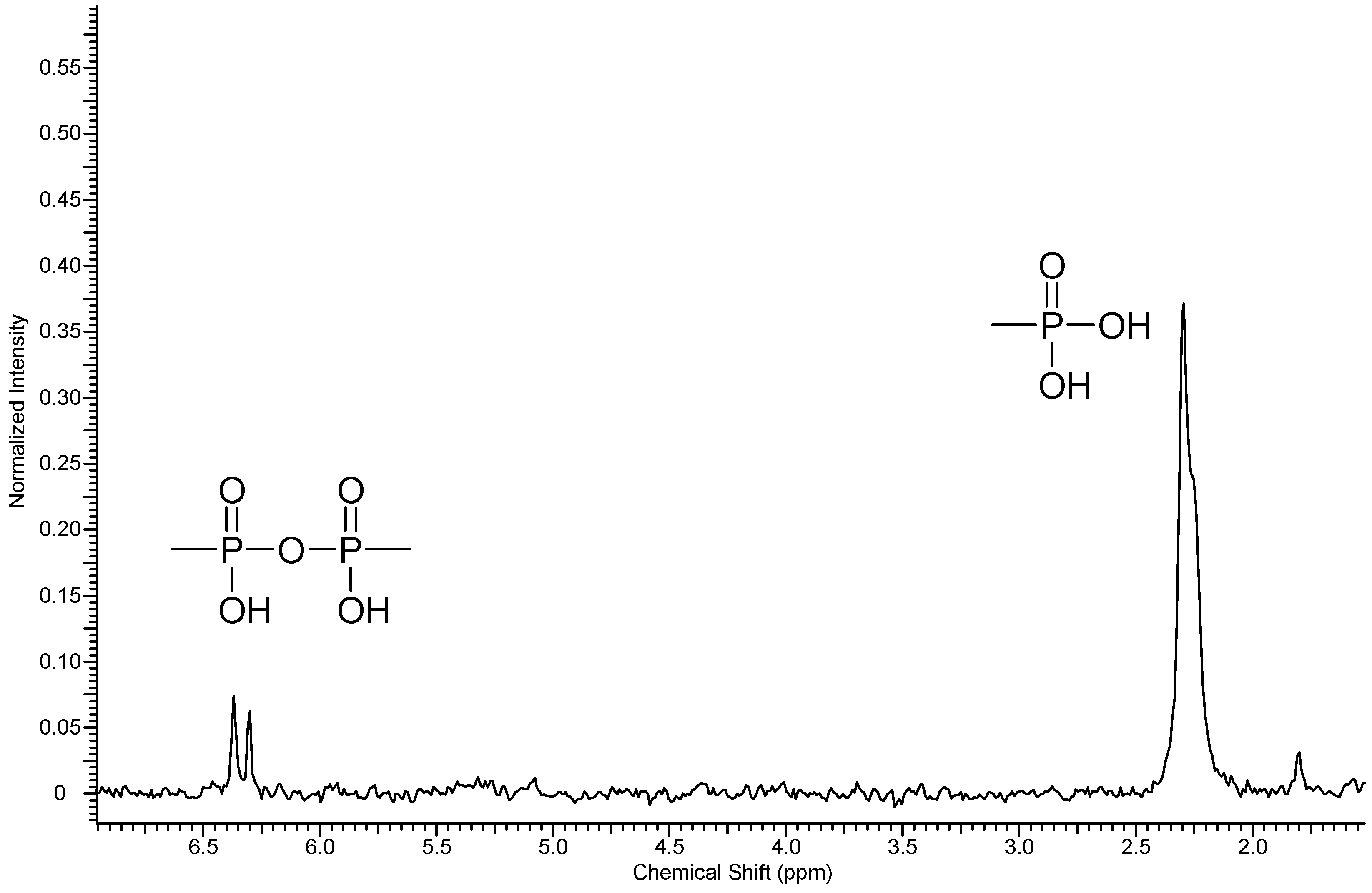
Three resonance signals corresponding to the CF3-groups of one-fold and non-substituted PFX were found in the 19F NMR spectrum of 5. The non-substituted PFX corresponds to the resonances at −56.2 ppm. The one-fold substituted PFX results in two resonances at −54.7 and −52.9 ppm. From the integral ratio between the non- and the one-fold substituted PFX, a phosphonation degree of about 95% was found.
A condensation reaction between the –PO3H2 groups, which has been shown previously for phosphonated polymers [18], was confirmed in the case of 5 by the 31P-NMR.
In the 31P-NMR spectrum of 5, two different phosphorus peaks were found at 2.27 ppm with a coupling constant of 4JPF = 4.8 Hz and at 6.33 ppm with a coupling constant of 2JPP = 6.9 Hz, respectively (Figure 4). The reason might be a condensation reaction between the two –PO3H2 groups during the hydrolysis reaction step [18,19].
The integral ratio between the free phosphonic acid functions and their anhydrides was resolved by 31P-NMR spectroscopy, yielding a condensation degree of the phosphonic acid groups of about 10%. The occurrences of condensed P–O–P groups decrease the attendance of the free –PO3H2 groups, which leads to lower ion exchange capacity.
The IEC value at 100% phosphonation (two protons) was calculated to be 3.36 mmol/g. However, the measured IEC was 0.67 mmol/g for IECdirect and 2.13 mmol/g for IECtotal. This is in agreement with the co-existence of the non-, one-fold-phosphonated and condensed phosphonic acid groups in the polymer.
Additionally, the structure of the phosphonated polymer 5 was confirmed by 1H- and 13C-NMR measurements. As expected, the 1H-NMR spectra showed two doublets for the protons in the aromatic rings of the bisphenol unit. The 13C-NMR spectra showed clear peaks representing the carbon atoms in the dihydroxy-biphenyl unit. A characteristic peak for the attendance of the C-P bond was delivered by the 13C-NMR with the chemical shift of 127.21 ppm and the coupling constant of 1JCP = 52.9 Hz. The phosphonation of the product was confirmed by FTIR measurement (see Figure S4 in Supplementary Materials). The –PO3H2 group is represented by several vibration bands, arising in the region 1244–1239, 1008–998, 924–903, 827–823 and 496–430 cm−1 [20]. The bands at 1243 and 1239 cm−1 are mainly due to the P=O stretching vibrations (P=O), whereas the 919 and 818 cm−1 bands are assigned to the P–O stretching mode (P–O).
The thermal stability of the phosphonated poly(arylene ether perfluoroxylene) is more than 100 °C lower than the non-phosphonated one. According to the TGA FTIR coupling measurements, the dephosphonation of the substituted polymer was observed at 308 °C. This decomposition temperature was confirmed by the appearance of the stretching vibration of the –PO3 group at 996 cm−1.
3.1.4. Functionalization of pPFX with Mercaptobenzimidazole
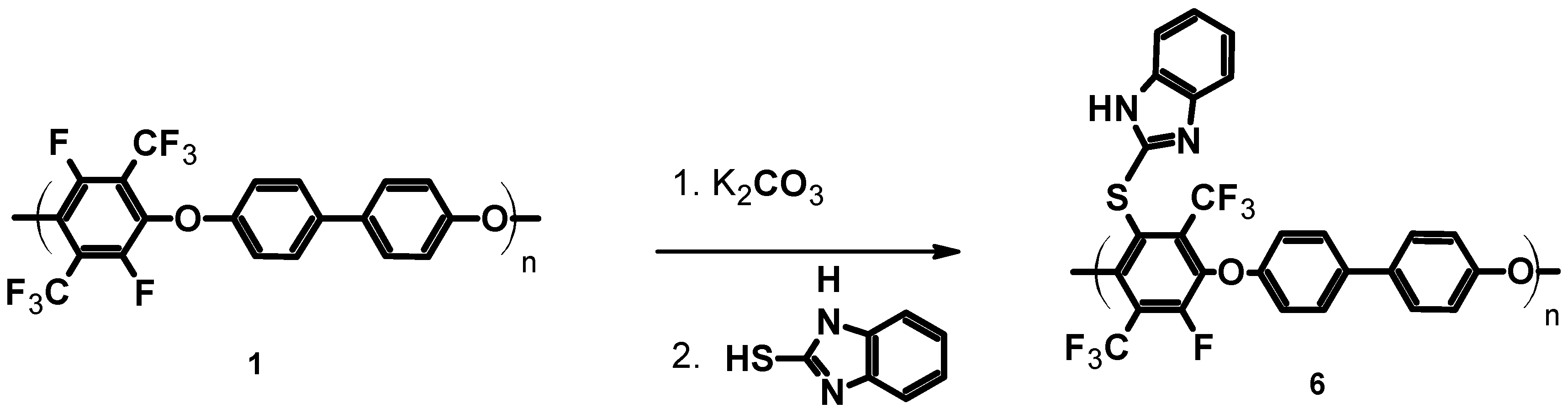
In order to introduce basic functionality, the pPFX was reacted with mercaptobenzimidazole (1H-benzo[d]imidazole-2-thiol). The mercaptobenzimidazole was reacted at T = 130 °C for four hours with potassium carbonate in order to deprotonate the S–H group, followed by the SN reaction of the thiolate with the C–F bond of the perfluorinated aromatic ring (see Scheme 4).
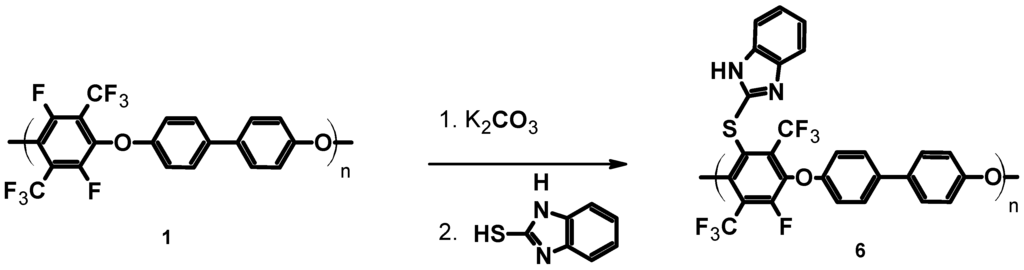
Scheme 4.
Thiolation of poly(arylene ether perfluoroxylene) 1–6.
Scheme 4.
Thiolation of poly(arylene ether perfluoroxylene) 1–6.
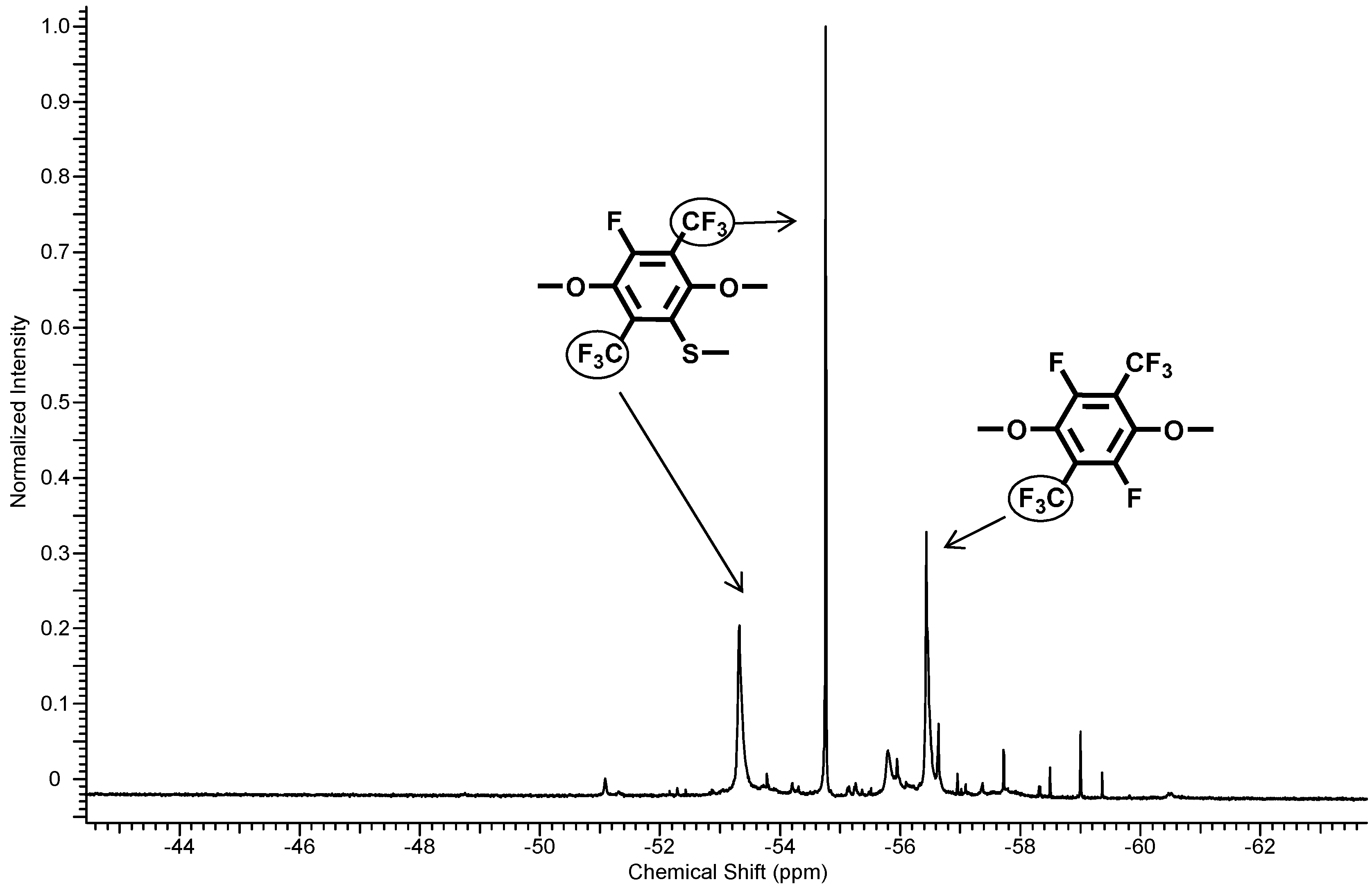
The structure of the thiolated polymer 6 was determined by means of 1H-, 13C-NMR and 19F-NMR. Direct evidence for the substitution could be found by the 19F-NMR assignments (see Figure 5). The disappearance of the C–F peak at −128.6 ppm in the perfluorinated aromatic unit indicates the completeness of the substitution reaction. In the 19F-NMR spectra, the typical peaks were found at −53.5 and −54.9 ppm for the one-fold-substituted PFX and a peak for the non-thiolated perfluoroxylene at −56.6 ppm. Integration of the fluorine signals revealed a ratio between one-fold: non-substituted = 1.8:1.1 (62% substitution).
The 1H-NMR spectra show a complex multiplet spin system in the aromatic region between 6.75 and 7.35 ppm. The multiplet may contain the signals of both the dihydroxy-biphenyl unit and the introduced mercaptobenzimidazole. The doublets for the four protons of the biphenyl group were detected at 6.84 and 7.42 ppm with a coupling constant of 3JHH = 8.1 Hz. The four protons of the aromatic rings in the substituted mercaptobenzimidazole unit have shown a typical four-spin-system with an AA'BB' pattern at 7.11 ppm.
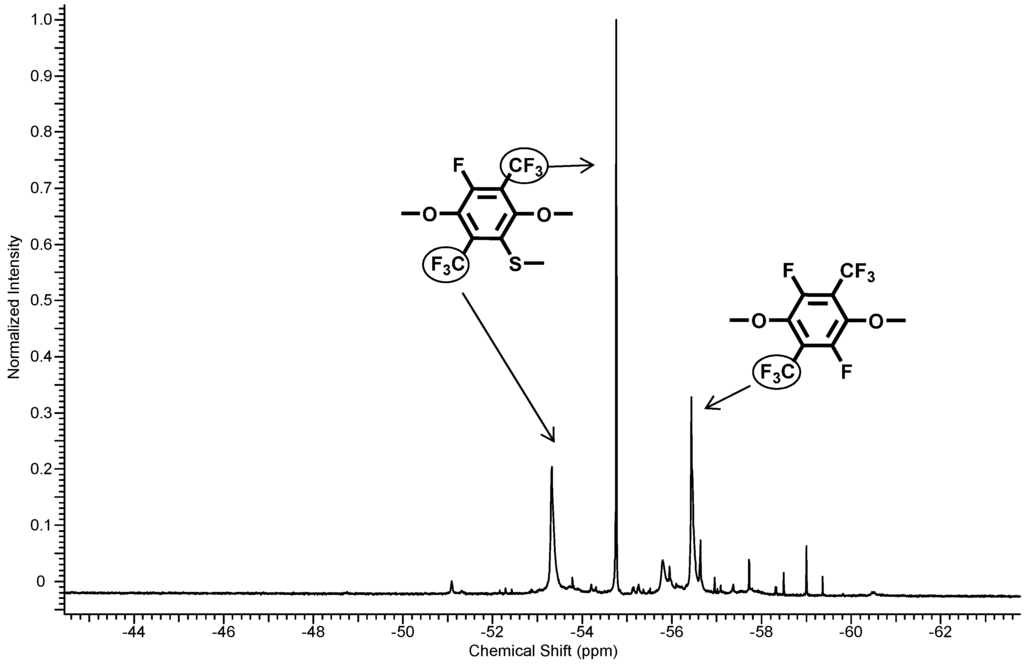
Figure 5.
19F-NMR spectra of polymer 6.
Figure 5.
19F-NMR spectra of polymer 6.
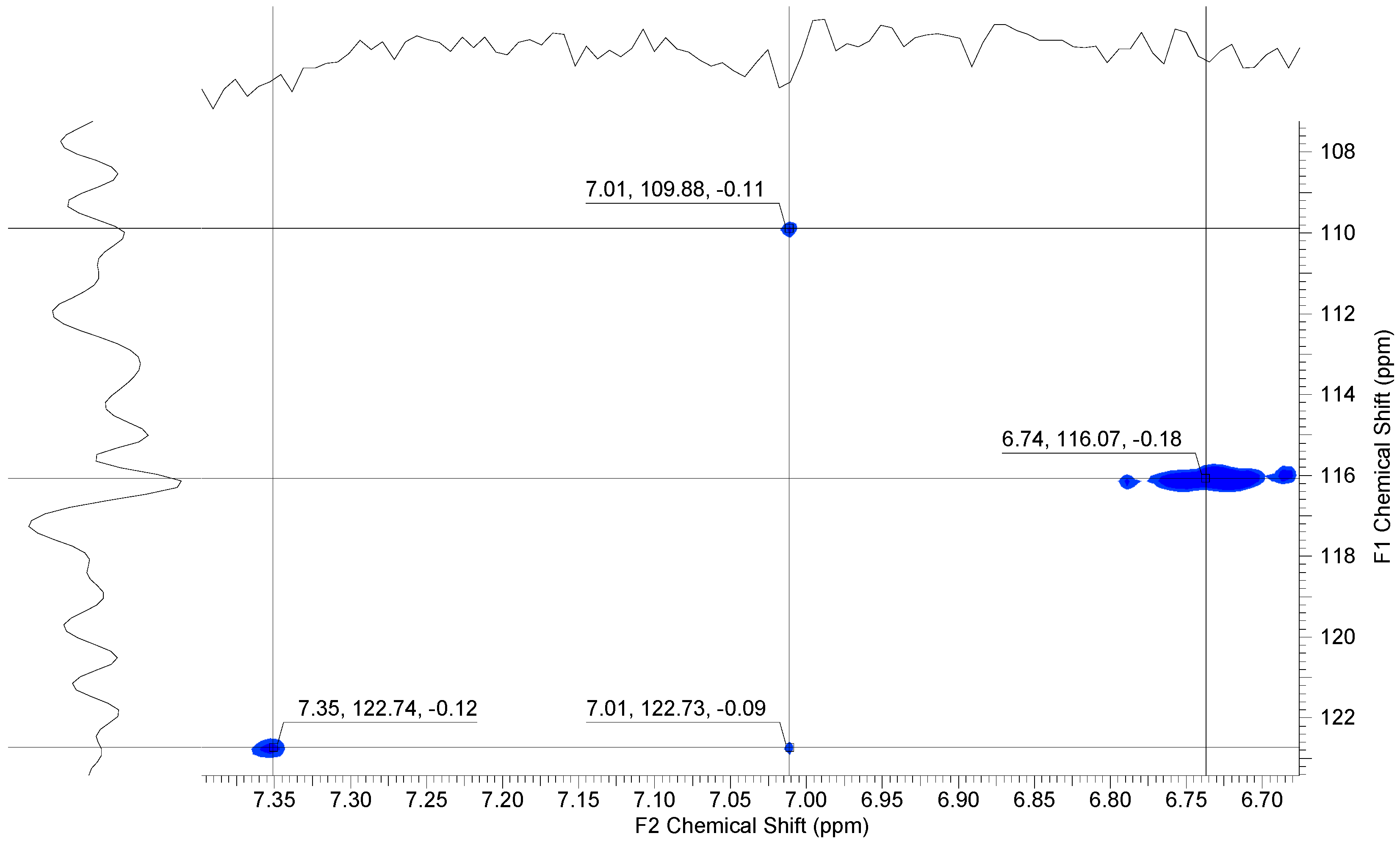
Heteronuclear single-quantum correlation (HSQC) measurements clearly showed four cross-peaks at 6.74 and 7.35 ppm for the coupling between C–H groups in the dihydroxy unit and at 7.01 for the coupling between the carbon and hydrogen atoms in the aromatic ring of the mercaptobenzimidazole side unit (see Figure 6).
Although a high concentration of the measured sample in the deuterated solvent was used, carbon peaks in the 13C-NMR spectra were only observed for the C–H bonds in the biphenyl unit at 156.63, 131.65, 127.44 and 116.0 ppm. In the FTIR spectra (see Figure S5 in Supplementary Materials), the band at 3239 cm−1 is characteristic for the C–N stretching. The C–S group shows several vibration bands between 824 and 600 cm−1, while the bands at 740 and 824 cm−1 were attributed to the S group. Supplementary bands were observed at 1628, 1571 and 1493 cm−1 and can be assigned to the aromatic stretching vibration.
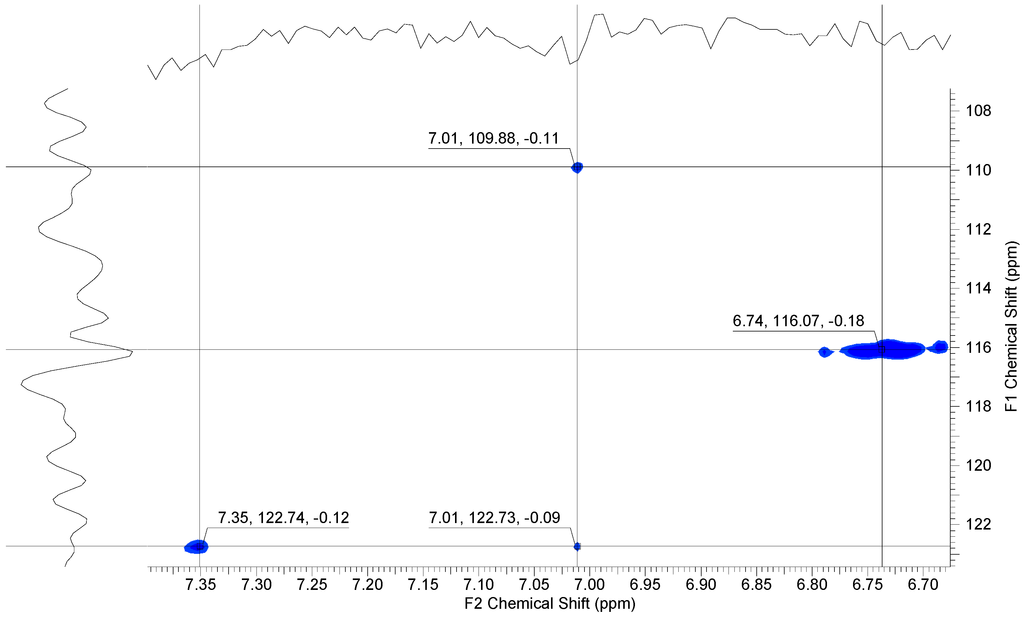
Figure 6.
1H, 13C-HSQC NMR spectrum of 6.
Figure 6.
1H, 13C-HSQC NMR spectrum of 6.
3.1.5. Terpolymer from PFX, Decafluorobiphenyl and 4,4'-Dihydroxy-biphenyl
To obtain an acid-excess acid-base blend membrane with good thermal and mechanical properties, a sulfonated random copolymer having a high C–F ratio in the polymer backbone was synthesized by polycondensation of DHB with both PFX and decafluorobiphenyl (DFBP). By the increase of the fluorine content in the polymer main chain, a better thermal and mechanical stability for the polymer compound was expected. The polycondensation reaction was conducted at 90 °C for 30 min (see Scheme 5).
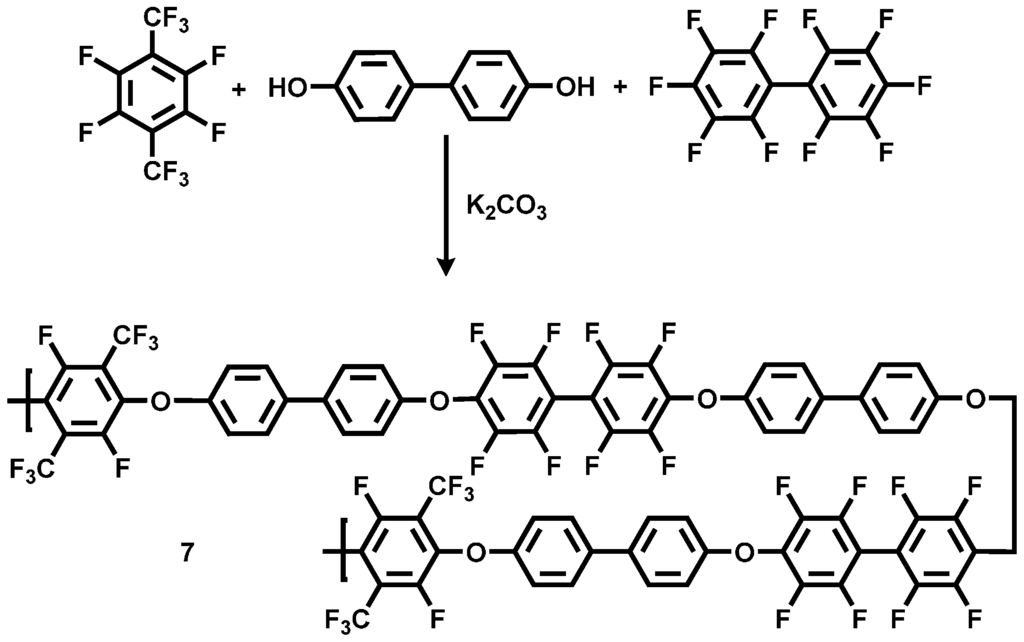
Scheme 5.
Reaction scheme of the polycondensation reaction for the preparation of the statistical copolymer poly(aryleneetherperfluoroxylene-co-decafluorobiphenyl) (pPFX-DBF) 7.
Scheme 5.
Reaction scheme of the polycondensation reaction for the preparation of the statistical copolymer poly(aryleneetherperfluoroxylene-co-decafluorobiphenyl) (pPFX-DBF) 7.
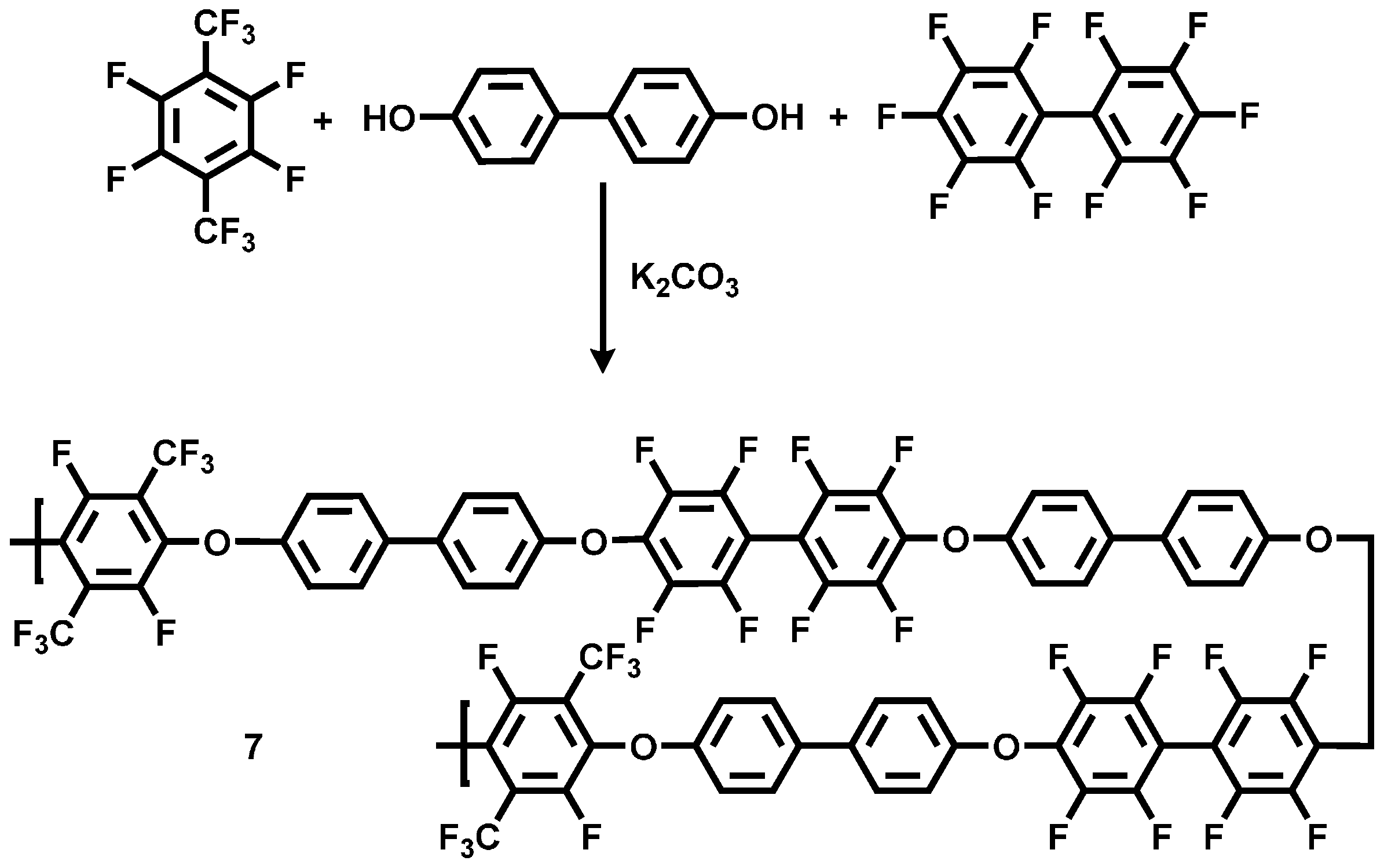
Due to the higher chemical reactivity of the DFBP, compared to the PFX, a molar ratio of PFX: DFBP = 60:40 was used in the reaction mixture to obtain a molar ratio of 50:50 in the polymer backbone. The obtained poly(arylene ether perfluoroxylene) (pPFX-DFB) 7 was characterized using 1H-, 13C- and 19F-NMR. The disappearance of the C–F peaks both for the meta-fluorine atoms at −139.2 ppm for the PFX and at −162.9 ppm for the DFBP revealed the completion of the reaction. The polymer shows chemical shifts of −56.3 and −128.3 ppm for PFX assigned to the CF3 and the CF groups, respectively. The signals at −139.5 and −154.4 were identified as fluorine atoms in the aromatic ring of the DFBP unit (see Figure 7).
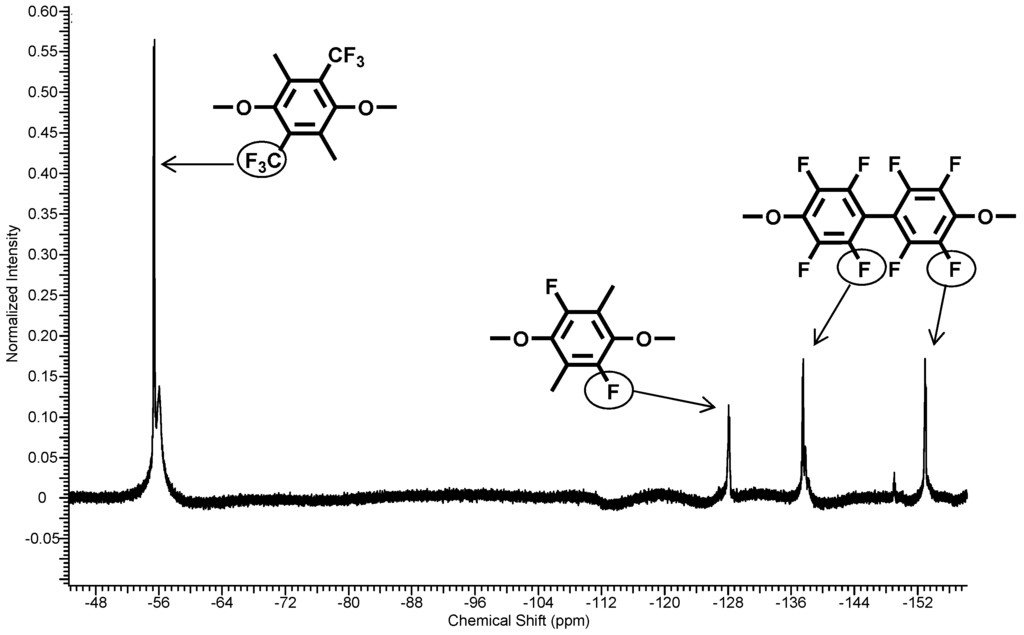
Figure 7.
19F-NMR spectra of polymer 7.
Figure 7.
19F-NMR spectra of polymer 7.
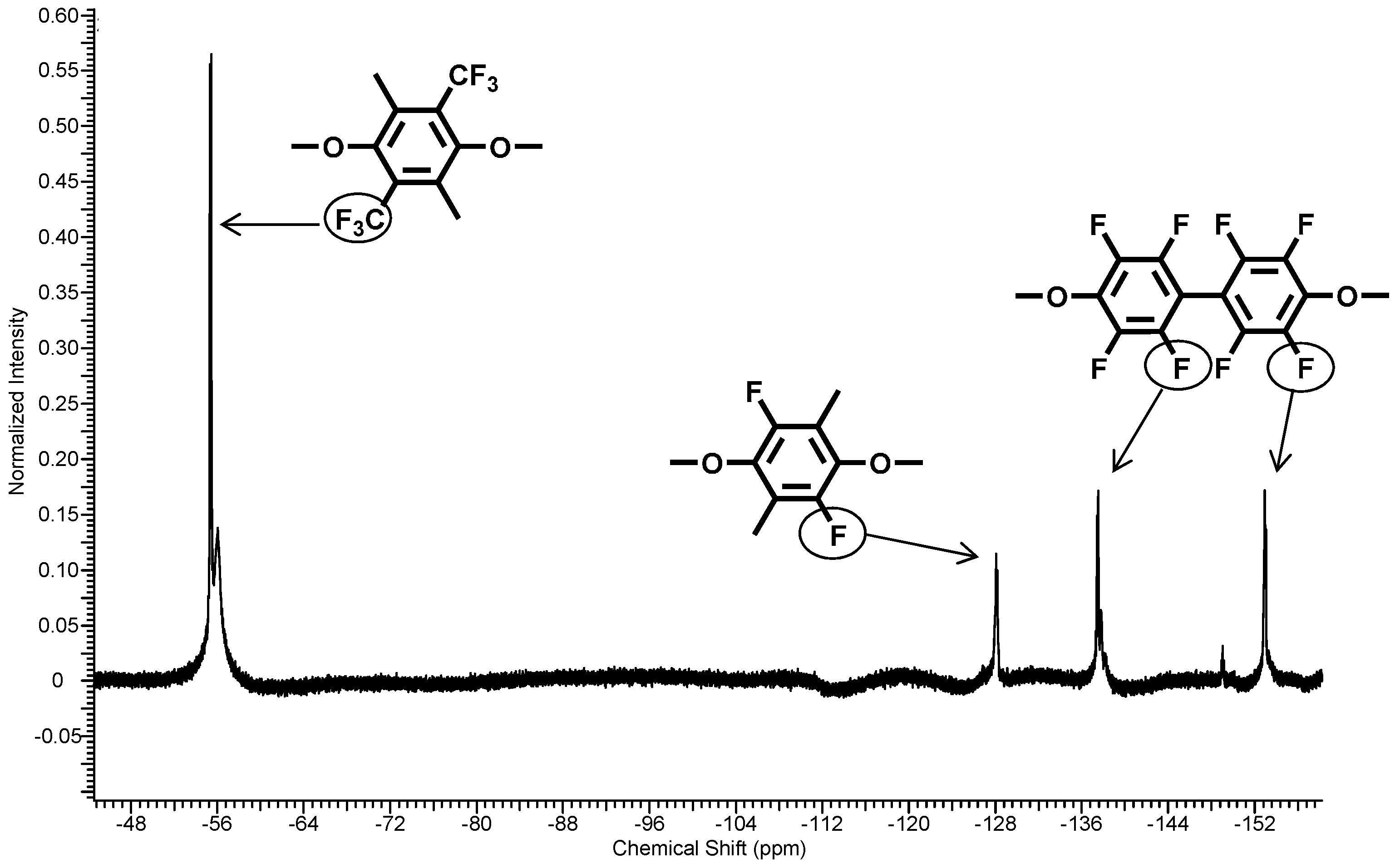
The 1H-NMR measurement showed the typical patterns for the aromatic protons of the dihydroxy-biphenyl ring at 7.33 ppm and 7.71 ppm with a coupling constant of 3JHH = 7.33 Hz.
The thermal stability measured by TGA revealed the highest value among the prepared pPFX polymers, showing a value of Tdecomposition = 525 °C (see Figure 8).
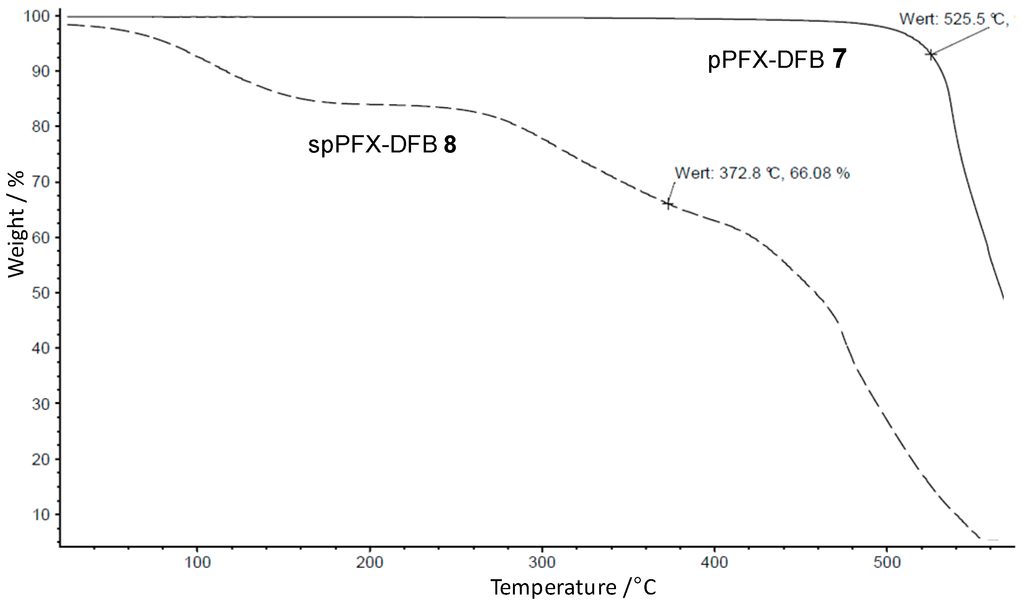
Figure 8.
Thermogravimetric analysis of pPFX-DFB 7 and sulfonated pPFX (spPFX)-DFB 8.
Figure 8.
Thermogravimetric analysis of pPFX-DFB 7 and sulfonated pPFX (spPFX)-DFB 8.
3.1.6. Sulfonation of pPFX-DFB with Fuming Sulfuric Acid
For the application in the blend membrane as an acidic compound, the pPFX-DFB polymer 7 was sulfonated. The introduction of the –SO3H group into the polymer backbone was realized by using H2SO4 with a SO3 content of 60% at RT for 24 h (see Scheme 6). The –SO3H group acts as proton conductor in acidic excess blend membranes or can serve as an ionic crosslinker in base-excess blend membranes.
The sulfonated pPFX-DFB 8 (spPFX-DFB) was characterized by1H-, 13C-, 19F- and HSQC NMR. Disappearance of the pattern of the aromatic protons of non-sulfonated bisphenol in the 1H-NMR at 7.73 and 7.31 ppm confirmed the substitution. Signals with chemical shifts at 7.27, 7.63 and 8.06 ppm were observed. Because of the broad signals in the proton spectra, the coupling constants of the 1H-atoms in the aromatic ring were difficult to determine.
Additionally, HSQC measurements yielded three cross-peaks for the coupling between the protons and carbon atoms in the dihydroxy unit at ppm 7.28, 7.62 and 8.05 ppm (see Figure 9).
Because of the numerous C–F groups in the polymer backbone and the substituted carbon atoms, the 13C-NMR spectrum was very complex in the aromatic region between 115 and 155 ppm. The existence of the sulfonated aromatic ring in the polymer backbone was confirmed by the four new peaks for the carbon atoms in the aromatic region. The sulfonation degree was determined from the integral ratio in the 1H-NMR spectra and yielded a of 1.8 SO3H groups per 4,4'-biphenylene unit in the random pPFX-DFB copolymer. As expected, the TGA of 8 (see Figure 8) revealed a lower thermal stability (Tdecomposition = 373 °C) than that of the non-sulfonated structure. However, this decomposition temperature is still 100 °C higher than that of the sulfonated pPFX 3 and 4, making spPFX-DBF a promising candidate for application in acid-excess blend membranes.
The IEC value (see Table 2) reflects the partial sulfonation of the pPFX-DFB polymer.
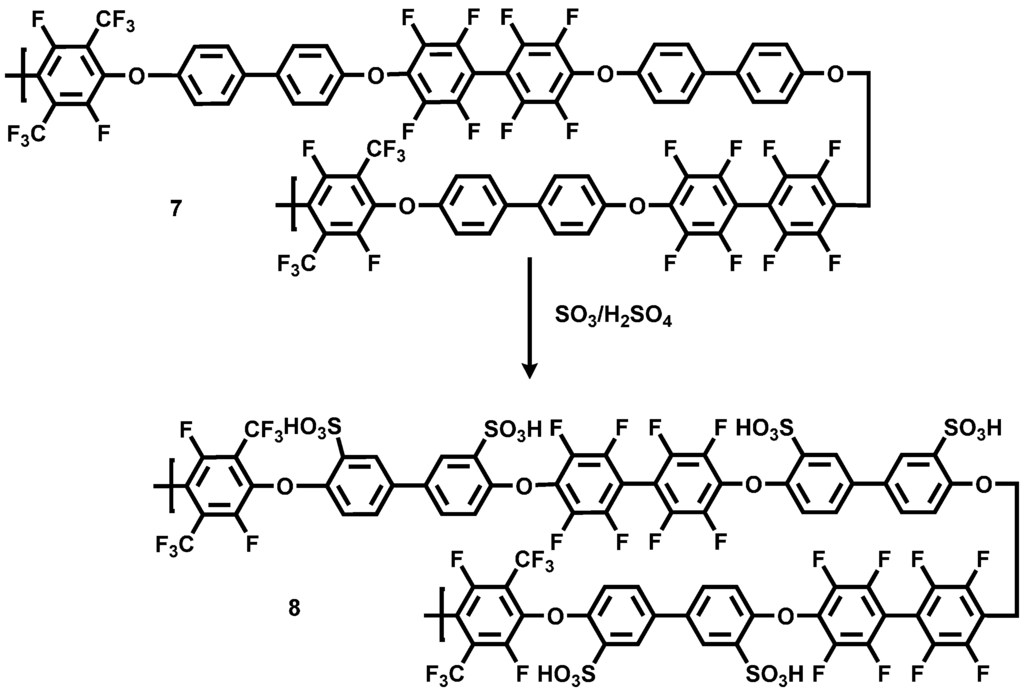
Scheme 6.
Reaction scheme of sulfonation of poly(arylene ether perfluoroxylene-co-decafluorobiphenyl) (pPFX)-DBF.
Scheme 6.
Reaction scheme of sulfonation of poly(arylene ether perfluoroxylene-co-decafluorobiphenyl) (pPFX)-DBF.
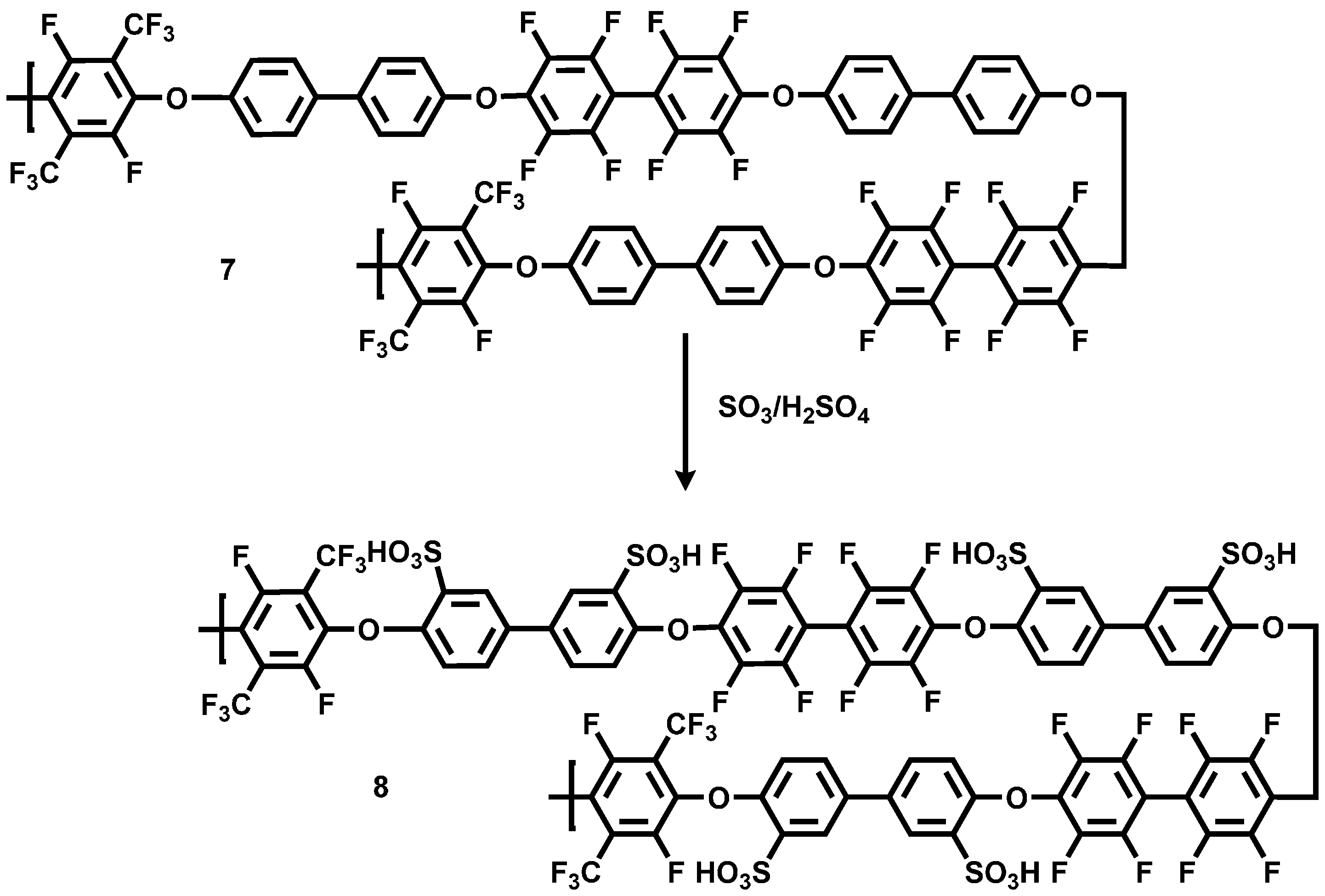
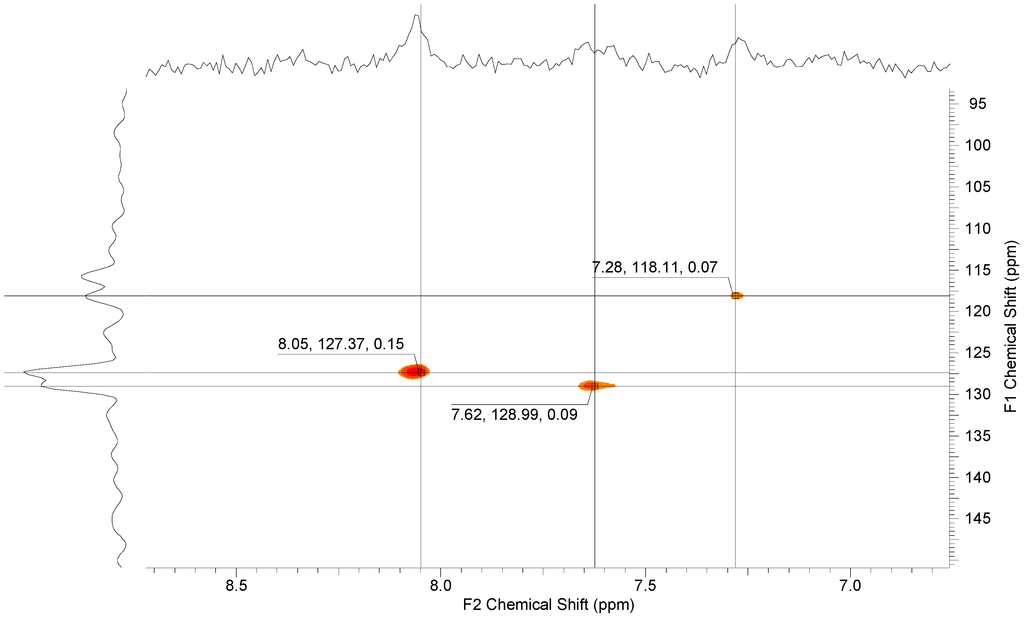
Figure 9.
1H, 13C-HSQC NMR spectrum of 8.
Figure 9.
1H, 13C-HSQC NMR spectrum of 8.
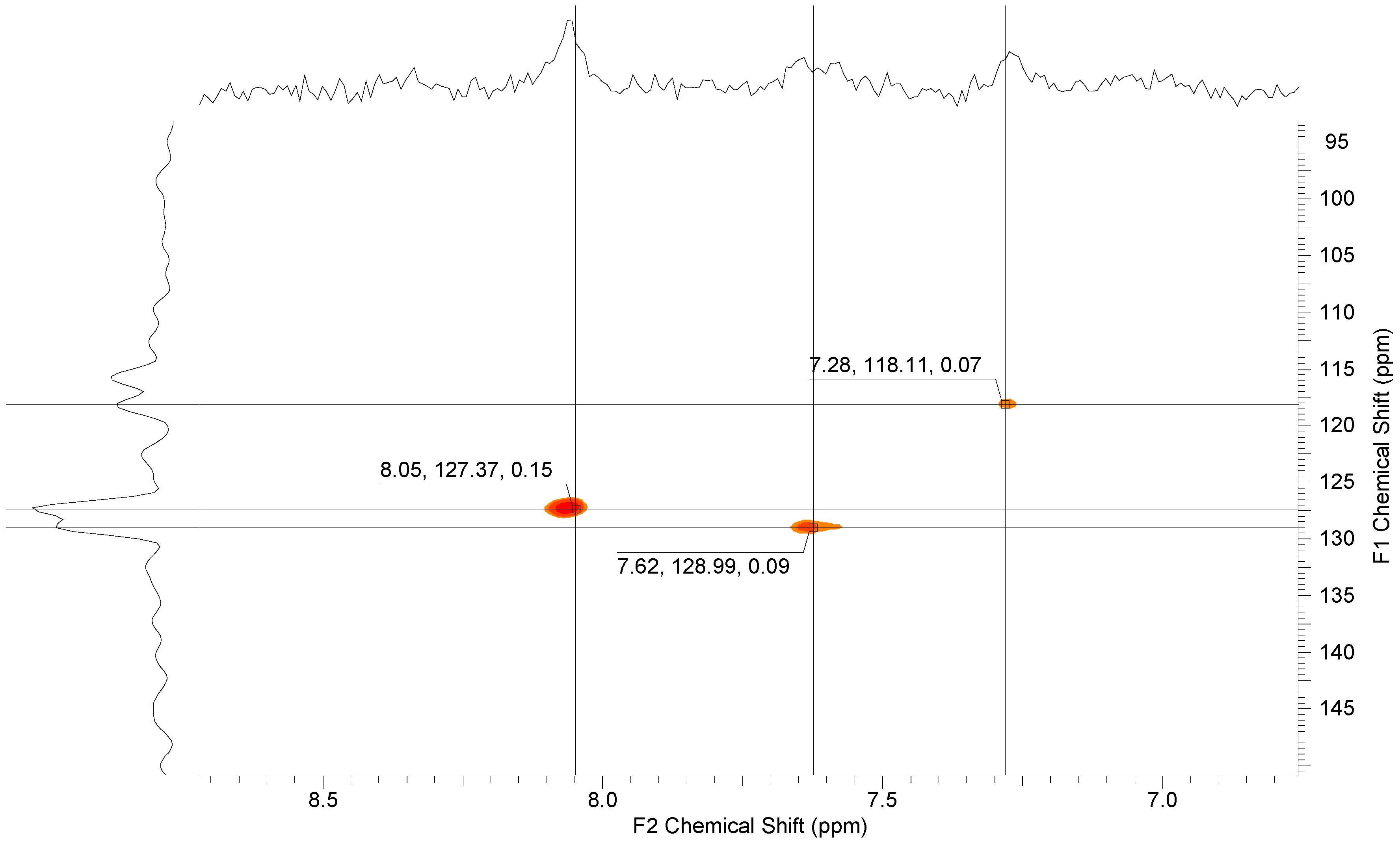

Table 2.
IEC data of the sulfonated polymer 8.
| pPFX (No.) | IECtheor (meq SO3H/g) | IECdirect (meq SO3H/g) | IECtotal (meq SO3H/g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 8 | 1.87 | 1.39 | 1.72 |
3.2. Preparation and Properties of Acid-Excess Acid-Base Blend Membranes MIH418
Due to the high thermal stability and suitable IEC value, the sulfonated pPFX-DFB polymer can serve as the proton-conducting blend component in acid-excess acid-base blend membranes with polybenzimidazole as the basic macromolecular cross-linker. In order to reach a significant excess of the acidic polymer in the membrane for sufficient proton-conductivity in the blend membrane, 80 wt% of the spPFX-DFB and 20 wt% of the F6PBI were mixed in DMSO. The blend membrane was dried at 130 °C, followed by rinsing with 10% HCl for 48 h at 90 °C and deionized water for 48 h at 60 °C. Characteristics of acid excess acid-base blend membrane MIH418 are collected in Table 3.

Table 3.
Data of the acid excess acid-base blend membrane MIH418. F6PBI, hexafluoroisopropylidene polybenzimidazole.
| Nr. | spPFX-DFB (wt%) | F6PBI (wt%) | Thickn. (nm) | IECdirect | IECtotal | Tdecomp. (°C) * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIH 418 | 80 | 20 | 160 | 1.33 | 1.83 | 424.5 |
Note: * Defined as first appearance of CO bands in the FTIR spectra coupled to the TGA.
Conductivity of the Acid Excess Acid-Base Blend Membrane MIH418
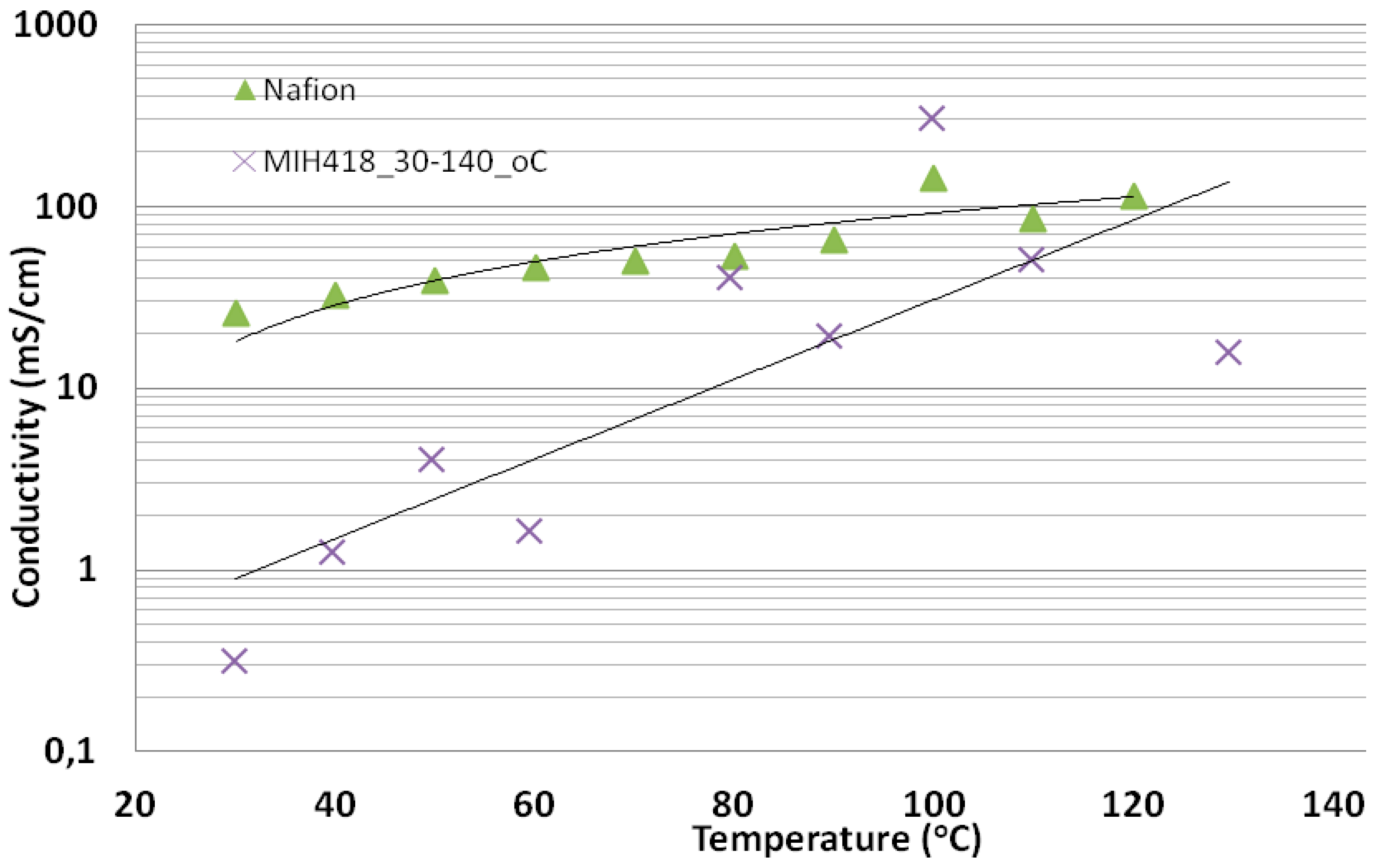
Figure 10 shows the H+-conductivity of the acid excess acid-base membrane MIH418 as a function of the temperature (30–130 °C) at constant relative humidity 90% ± 4%. For comparison, the standard PFSA membrane Nafion® 212 was given. Despite the higher IEC values of membrane MIH418, for most temperatures, lower conductivity was observed than for Nafion® 212. The reason for the strong deviation of the conductivity versus T curve from the correlation line observed for the MIH418 membrane is still unclear and requires further investigations.
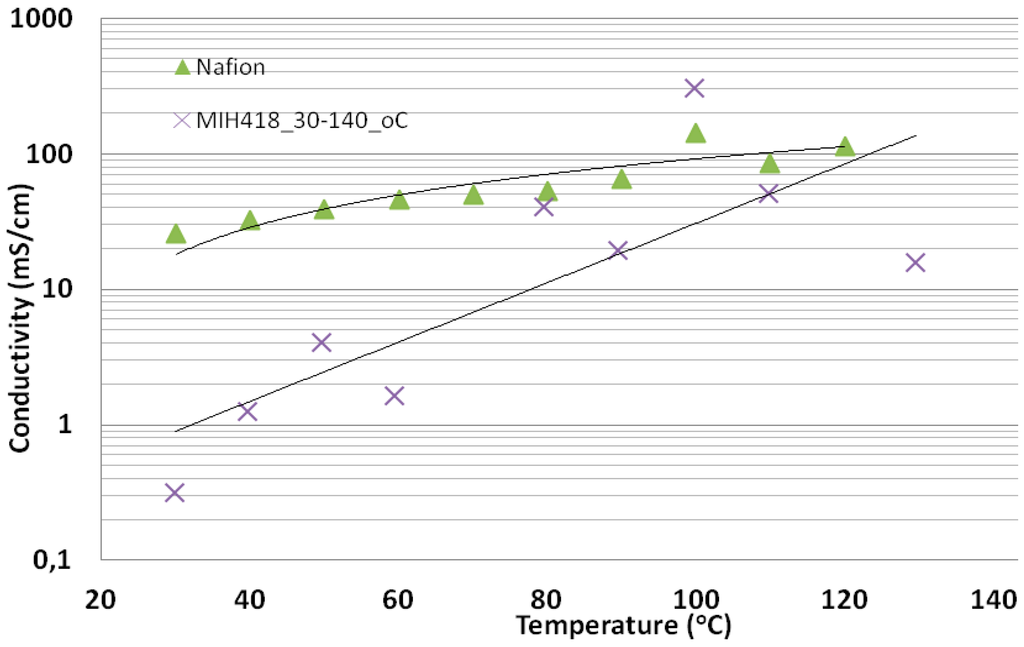
Figure 10.
Proton conductivity of the acid excess acid-base blend membrane, relative humidity (RH) = 90% ± 4%, T = 30–130 °C.
Figure 10.
Proton conductivity of the acid excess acid-base blend membrane, relative humidity (RH) = 90% ± 4%, T = 30–130 °C.
3.3. Preparation and Properties of Base-Excess Acid-Base Blend Membranes
Ionically cross-linked base-excess blend membranes for the application in intermediate-T fuel cells has been a research subject in the authors’ group for the past 10 years. The research in this field aims at the development of acidic ionomers, which could increase the mechanical stability of the polybenzimidazole membranes and reduce the swelling. Due to its high chemical and thermal stability, PFX-containing polymers were tested as acidic macromolecular cross-linkers for the partially-fluorinated polybenzimidazole F6-PBI. For the preparation of the base-excess blend membranes, the sulfonated poly(arylene ether perfluoroxylene) polymer 4 was blended with F6-PBI. To reach a sufficient molar excess of the basic polymer in the membrane, 70 wt% of the F6-PBI and 30 wt% of the 4 was mixed in DMSO and dried at 130 °C. The base-excess blend membranes were subsequently doped with H3PO4 to make them proton-conductive for application as intermediate-T fuel cell membranes.
3.3.1. Oxidative Stability of the Base-Excess Acid-Base Blend Membranes
Generally, the Fenton test (FT) can serve as a rapid oxidative-degradation test for ionomer membranes. In Fenton’s solution, which is composed of an aqueous 3% H2O2 solution with 4 ppm Fe2+ in the form of (NH4)2Fe(SO4)2·6H2O, high concentrations of OH– and •OOH-radicals are formed, which promote the oxidative radical attack on the membranes, leading to a cumulative decrease of the molecular weight of the membrane polymer(s). The molecular weight decrease leads to a significant loss of mechanical membrane stability. The abovementioned (undoped) base-excess F6PBI blend membrane was subjected to FT, and the mass loss of the membrane was determined. The weight loss vs. FT soaking time dependence of the membrane is presented in Figure 11. It can be concluded that the base excess acid-base-blend membrane shows a high resistance against radical attack, i.e., after 96 h of FT, the membrane still retained more than 86% of its original weight.
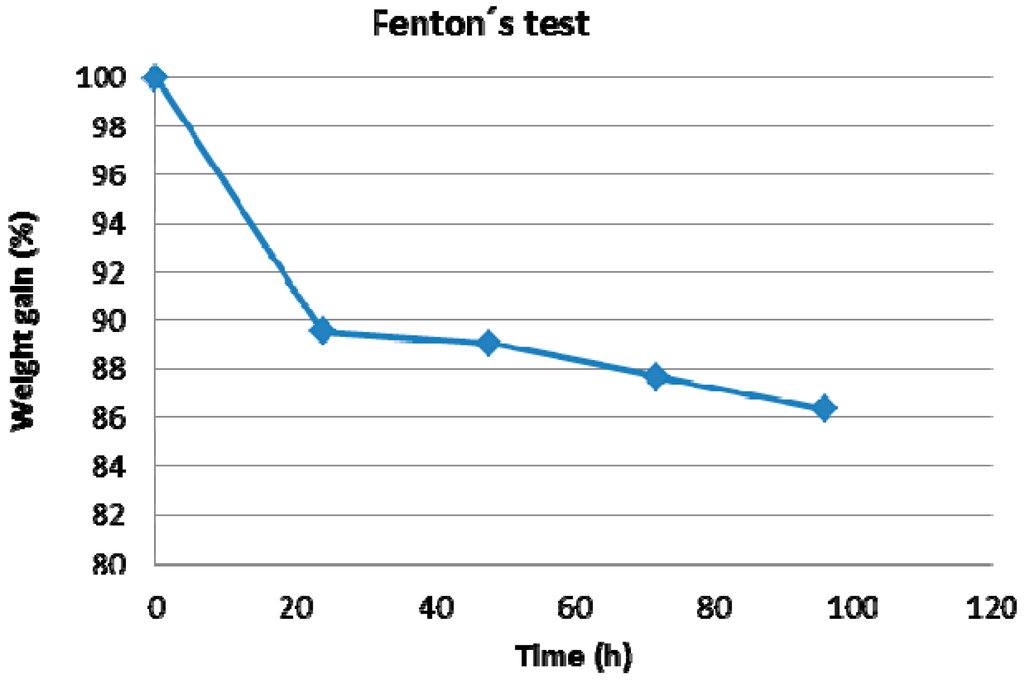
Figure 11.
Fenton’s test results for the base-excess blend membrane.
Figure 11.
Fenton’s test results for the base-excess blend membrane.
3.3.2. Phosphoric Acid Doping of the Base-Excess Blend Membrane
In order to optimize the doping level of the phosphoric acid doped base-excess blend membrane, a series of doped membranes were prepared. The membranes were immersed in concentrated phosphoric acid (85 wt% H3PO4) for given temperatures and times. The best result in terms of enough mechanical integrity at high doping degree was obtained at 240 wt%. This doping degree was reached at 120 °C for 30 min.
3.3.3. Conductivity of the H3PO4-Doped F6-PBI Blend Membranes
The conductivity of the phosphoric acid doped blend membrane was investigated using the Membrane Test Systems from Scribner Associates Inc. The measurement was done at 20% relative humidity in the temperatures range of 80–150 °C. According to Figure 12, the conductivity showed a typical Arrhenius behavior. As expected, the lowest conductivity in the investigated temperature range was observed at 80 °C, being 25.6 mS·cm−1. The highest conductivity was measured at 150 °C with a value of 91.8 mS·cm−1. The activation energy Ea of the blend membrane H+ conductivity could be derived from the Arrhenius plot, being 21.9 kJ/mol. The conductivity and activation energy values of this membrane are comparable to base-excess blend membranes prepared in our laboratories [11].
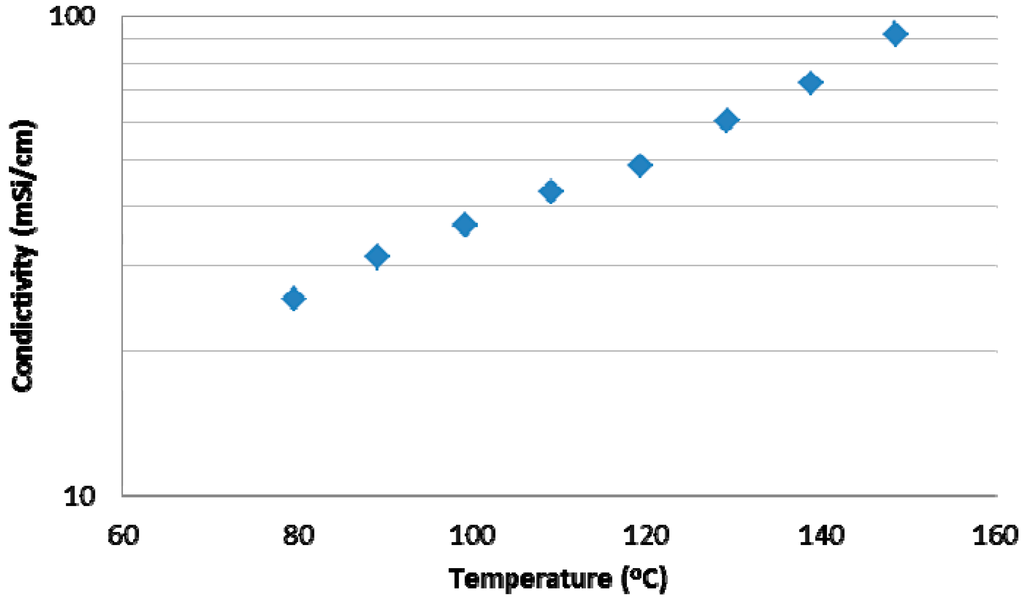
Figure 12.
Conductivity of base-excess acid-base blend membrane.
Figure 12.
Conductivity of base-excess acid-base blend membrane.
4. Conclusions
Partially-fluorinated poly(arylene ether) polymers with a perfluoro-p-xylene (PFX) building block were successfully synthesized and characterized. It was demonstrated that these polymers can be modified both nucleophilically (in the PFX unit, by nucleophilic exchange of F with other nucleophiles, such as mercaptans and phosphites) and electrophilically (SE sulfonation in the Ar–H of the polymer). Both the non-sulfonated and the sulfonated polymers showed high thermal stabilities up to 450 °C. The successful sulfonation of the pPFX makes it a suitable macromolecular H+-conducting ionomer in acid-excess acid-base blend membranes and a suitable acidic cross-linker in a base-excess blend membrane with the basic engineering polymer F6-PBI. The ionic cross-linking prohibits the dissolution of the membranes during the doping with phosphoric acid. The blend membranes showed higher thermal stability than the pure sulfonated polymers. Due to the doping with phosphoric acid, intermediate T blend membranes were obtained, which show a reasonable conductivity, confirming their suitability for intermediate-T fuel cell application.
In future work, the poly(arylene ether perfluoroxylene)s will be modified with further nucleophiles in the PFX unit to vary the polymer properties in a broader range. The novel sulfonated and phosphonated polymers will also be blended with basic polymers, such as PBIOO and PBI Celazole to yield base-excess blend membranes with a tailored property profile. The new blend membranes will be applied to intermediate T fuel cells, SO2-depolarized electrolysis, direct methanol fuel cells, PEM-electrolysis and redox-flow batteries.
Supplementary materials
Supplementary materials can be accessed at: http://www.mdpi.com/2073-4360/7/6/1066/s1.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge Inna Kharitonova and Galina Schumski (University of Stuttgart) for the TGA and the IEC analyses. Financial support was obtained from the AiF IGF Project 17955 BG) (AiF = Arbeitsgemeinschaft industrieller Forschungseinrichtungen, IGF = Industrielle Gemeinschaftsforschung).
Author Contributions
Imre Hajdok performed polymer and membrane syntheses, and characterizations, and wrote the paper, Vladimir Atanasov contributed to discussion and interpretation of results and contributed to edition of the paper, and Jochen Kerres provided the guidance of experiments, contributed to discussion and interpretation of results, contributed to edition of the paper, and was leader of the study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Liu, B.; Robertson, G.P.; Kim, D.S.; Guiver, M.D.; Hu, W.; Jiang, Z. Aromatic poly(ether ketone)s with pendant sulfonic acid phenyl groups prepared by a mild sulfonation method for proton exchange membranes. Macromolecules 2007, 40, 1934–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautier-Luneau, I.; Denoyelle, A.; Sanchez, J.Y.; Poinsignon, C. Organic-inorganic protonic polymer electrolytes as membrane for low-temperature fuel cell. Electrochim. Acta 1992, 37, 1615–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allcock, H.R.; Hofmann, H.A.; Ambler, C.M.; Morford, R.V. Phenylphosphonic acid functionalized Poly[aryloxyphosphazenes]. Macromolecules 2002, 35, 3484–3489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allcock, H.R.; Wood, R.M. Design and synthesis of ion-conductive polyphosphazenes for fuel cell applications: Review. J. Polym. Sci. B Polym. Phys. 2006, 44, 2358–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubler, R.; Beck, N.; Gürsel, S.A.; Hajbolouri, F.; Kramer, D.; Reiner, A.; Steiger, B.; Scherer, G.; Wokaun, A.; Rajesh, B.; et al. Materials for polymer electrolyte fuel cells. Chimia 2004, 58, 826–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schönberger, F.; Hein, M.; Kerres, J. Preparation and characterisation of sulfonated partially fluorinated statistical poly(arylene ether sulfone)s and their blends with PBI. Solid State Ion. 2007, 178, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerres, J.A.; Xing, D.; Schönberger, F. Comparative investigation of novel PBI blend ionomer membranes from nonfluorinated and partially fluorinated poly arylene ethers. J. Polym. Sci. B Polym. Phys. 2006, 44, 2311–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerres, J.; Ullrich, A.; Meier, F.; Häring, T. Synthesis and characterization of novel acid–base polymer blends for application in membrane fuel cells. Solid State Ion. 1999, 125, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerres, J.; Ullrich, A.; Häring, T.; Baldauf, M.; Gebhardt, U.; Preidel, W. Preparation, characterization and fuel cell application of new acid-base blend membranes. J. New Mater Electrochem. Syst. 2000, 3, 229–239. [Google Scholar]
- Cooper, K.R. Progress toward accurate through-plane ion transport resistance measurement of thin solid electrolytes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2010, 157, B1731–B1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Day, M. Novel highly fluorinated poly(arylene ether-1,3,4-oxadiazole)s, their preparation, and sensory properties to fluoride anion. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 6054–6062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajdok, I.; Bona, A.; Werner, H.; Kerres, J. Synthesis and characterization of fluorinated and sulfonated poly(arylene ether-1,3,4-Oxadiazole) derivatives and their blend membranes. Eur. Polym. J. 2014, 52, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerres, J.; Cui, W.; Reichle, S. New sulfonated engineering polymers via the metalation route. I. Sulfonated poly(ethersulfone) PSU Udel® via metalation-sulfination-oxidation. J. Polym. Sci. A Polym. Chem. 1996, 34, 2421–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beletskaya, I.P.; Artamkina, G.A.; Milchenko, A.Y.; Sazonov, P.K.; Shtern, M.M. Carbonylmetallates and carbanions in aromatic and vinylic nucleophilic substitution. J. Phys. Org. Chem. 1996, 9, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, A.O.; Furin, G.G. N-(polyfluoroaryl)-hydroxylamines. synthesis and properties. J. Fluor. Chem. 1987, 36, 247–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Parkin, S.R.; Watson, M.D. Benzodichalcogenophenes with perfluoroarene termini. Org. Lett. 2008, 10, 4420–4424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atanasov, V.; Kerres, J. Highly phosphonated polypentafluorostyrene. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 6416–6423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaltbeitzel, A.; Schauff, S.; Steininger, H.; Bingol, B.; Brunklaus, G.; Meyer, W.H.; Spiess, H.W. Water sorption of poly(vinylphosphonic acid) and its influence on proton conductivity. Solid State Ion. 2007, 178, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohms, G.; Großmann, G.; Schwab, B.; Schiefer, H. Synthesis and 31P and 13C NMR studies of pyrophosphonic acid. Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon 1992, 68, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piergies, N.; Proniewicz, E. Structure characterization of [N-Phenylamino(2-boronphenyl)-R-methyl]phosphonic acid by vibrational spectroscopy and density functional theory calculations. J. Spectrosc. 2014, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
