Application of Collagen Scaffold in Tissue Engineering: Recent Advances and New Perspectives
Abstract
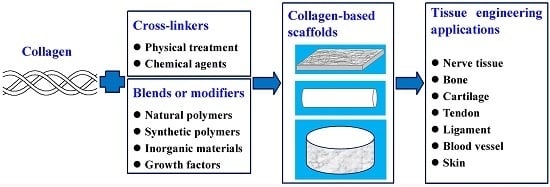
:1. Introduction
2. Characterization of Collagen as a Biomaterial
2.1. Structure of Collagen
2.2. Biological Characteristics of Collagen
| Type | Composition | Distribution |
|---|---|---|
| I | (α1(I))2α2(I) | Skin, tendon, ligament, bone, cornea, cartilage, large vessels, dermis, intestine, uterus, dentin, nerve |
| II | (α1(II))3 | Cartilage, vitreous, nucleus pulposus, notochord |
| III | (α1(III))3 | Large vessels, uterine wall, dermis, intestine, heart valve, gingival, skin, nerve |
| IV | (α1(IV))2α2(IV) α3(IV)α4(IV)α5(IV) (α5(IV))2α6(IV) | Basement membranes, nerve |
| V | α1(V)α2(V)α3(V) (α1(V))2α2(V) (α1(V))3 | Cornea, placental membranes, bone, large vessels, hyaline cartilage, gingival, dermis, nerve |
| VI | α1(VI)α2(VI)α3(VI) α1(VI)α2(VI)α4(VI) | Descemet‘s membrane, skin, nucleus pulposus, heart muscle |
| VII | (α1(VII))3 (α1(VII))2α2(VII) | Skin, placenta, lung, cartilage, cornea, dermis, bladder |
| VIII | (α1(VIII))3 (α2(VIII))3 (α1(VIII))2α2(VIII) | Dermis, brain, heart, kidney |
| IX | α1(IX)α2(IX) α3(IX) | Cartilage, cornea, vitreous |
| X | (α1(X))3 | Hypertrophic and mineralizing cartilage |
| XI | 1α2α3α1 α1(XI)α2(XI)α3(XI) | Cartilage, intervertebral disc, vitreous humor |
| XII | (α1(XII))3 | Tendon, ligament, dermis |
| XIII | Unknown | Skin, bone, intestinal mucosa, endothelial cells, dermis, eye, heart |
| XIV | (α1(XIV))3 | Bone, dermis, cartilage |
| XV | Unknown | Capillaries, testis, kidney, heart, |
| XVI | Unknown | Dermis, kidney |
| XVII | (α1(XVII))3 | Hemidesmosomes in epithelia |
| XVIII | Unknown | Basement membrane, liver |
| XIX | Unknown | Basement membrane |
| XX | Unknown | Cornea (chick) |
| XXI | Unknown | Stomach, kidney |
| XXII | Unknown | Tissue junctions |
| XXIII | Unknown | Heart, retina |
| XXIV | Unknown | Bone, cornea |
| XXV | Unknown | Brain, heart, testis |
| XXVI | Unknown | Testis, ovary |
| XXVII | Unknown | Cartilage |
| XXVIII | Unknown | Dermis, sciatic nerve, skin and calvaria. In zebrafish 1: nervous system, liver, thymus, muscle, intestine and skin |
2.3. Extraction and Purification of Collagen
2.4. Recombination of Collagen
3. Collagen-Based Scaffolds for Tissue Engineering
3.1. Pure Collagen Scaffold
3.2. Collagen/Natural Polymer Blend Scaffold
3.3. Collagen/Synthetic Polymer Blend Scaffold
3.4. Collagen/Inorganic Hybrid Scaffold
3.5. Collagen Scaffold Modified with Growth Factors
4. Typical Applications of Collagen-Based Scaffold in Tissue Engineering
4.1. Nerve Tissue
4.2. Bone/Cartilage Tissue

4.3. Tendon/Ligament Tissue
4.4. Vascular Grafts
4.5. Skin
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, B.S.; Park, I.K.; Hoshiba, T.; Jiang, H.L.; Choi, Y.J.; Akaike, T.; Cho, C.S. Design of artificial extracellular matrices for tissue engineering. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2011, 36, 238–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cen, L.; Liu, W.; Cui, L.; Zhang, W.; Cao, Y. Collagen tissue engineering: Development of novel biomaterials and applications. Pediatr. Res. 2008, 63, 492–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guarino, V.; Cirillo, V.; Altobelli, R.; Ambrosio, L. Polymer-based platforms by electric field-assisted techniques for tissue engineering and cancer therapy. Expert Rev. Med. Devices 2015, 12, 113–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aszódi, A.; Legate, K.R.; Nakchbandi, I.; Fässler, R. What mouse mutants teach us about extracellular matrix function. Annu. Rev. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2006, 22, 591–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelse, K.; Pöschl, E.; Aigner, T. Collagens-structure, function, and biosynthesis. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2003, 55, 1531–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgeson, R.E.; Nimni, M.E. Collagen types. Molecular structure and tissue distribution. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1992, 282, 250–272. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chevallay, B.; Herbage, D. Collagen-based biomaterials as 3D scaffold for cell cultures: Applications for tissue engineering and gene therapy. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2000, 38, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, K.; Alexander, S.; Schacht, V.; Coussens, L.; von Andrian, U.H.; van Rheenen, J.; Deryugina, E.; Friedl, P. Collagen-based cell migration models in vitro and in vivo. Semin. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2009, 20, 931–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friess, W. Collagen-biomaterial for drug delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 1998, 45, 113–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meimandi-Parizi, A.; Oryan, A.; Moshiri, A. Role of tissue engineered collagen based tridimensional implant on the healing response of the experimentally induced large Achilles tendon defect model in rabbits: A long term study with high clinical relevance. J. Biomed. Sci. 2013, 20, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inzana, J.A.; Olvera, D.; Fuller, S.M.; Kelly, J.P.; Graeve, O.A.; Schwarz, E.M.; Kates, S.L.; Awad, H.A. 3D printing of composite calcium phosphate and collagen scaffolds for bone regeneration. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 4026–4034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.; Meng, D.; Cao, J.; Xiao, Z.; Cui, Y.; Fan, J.; Cui, X.; Chen, B.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Collagen scaffolds combined with collagen-binding ciliary neurotrophic factor facilitate facial nerve repair in mini-pigs. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2015, 103, 1669–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghazanfari, S.; Driessen-Mol, A.; Strijkers, G.J.; Baaijens, F.P.; Bouten, C.V. The evolution of collagen fiber orientation in engineered cardiovascular tissues visualized by diffusion tensor imaging. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0127847. [Google Scholar]
- Ricard-Blum, S. The collagen family. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2011, 3, a004978. [Google Scholar]
- Mienaltowski, M.J.; Birk, D. Structure, physiology, and biochemistry of collagens. In Progress in heritable soft connective tissue diseases; Halper, J., Ed.; Springer-Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 2014; Volume 802, pp. 5–29. [Google Scholar]
- Burgeson, R.E. Genetic heterogeneity of collagens. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1982, 79, 25s–30s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Rest, M.; Garrone, R. Collagen family of proteins. FASEB J. 1991, 5, 2814–2823. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ricard-Blum, S.; Ruggiero, F. The collagen superfamily: From the extracellular matrix to the cell membrane. Pathol. Biol. 2005, 53, 430–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, M.K.; Hahn, R.A. Collagens. Cell. Tissue Res. 2010, 339, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthews, J.A.; Wnek, G.E.; Simpson, D.G.; Bowlin, G.L. Electrospinning of collagen nanofibers. Biomacromolecules 2002, 3, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sell, S.A.; Wolfe, P.S.; Garg, K.; McCool, J.M.; Rodriguez, I.A.; Bowlin, G.L. The use of natural polymers in tissue engineering: A focus on electrospun extracellular matrix analogues. Polymers 2010, 2, 522–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynn, A.K.; Yannas, I.V.; Bonfield, W. Antigenicity and immunogenicity of collagen. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B 2004, 71, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoulders, M.D.; Raines, R.T. Collagen structure and stability. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2009, 78, 929–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koopmans, G.; Hasse, B.; Sinis, N. The role of collagen in peripheral nerve repair. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2009, 87, 363–379. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gebauer, J.M.; Kobbe, B.; Paulsson, M.; Wagener, R. Structure, evolution and expression of collagen XXVIII: Lessons from the zebrafish. Matrix Biol. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, S.; Vavken, P.; Kevy, S.; Jacobson, M.; Zurakowski, D.; Murray, M.M. Platelet activation by collagen provides sustained release of anabolic cytokines. Am. J. Sports Med. 2011, 39, 729–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadjipanayi, E.; Kuhn, P.H.; Moog, P.; Bauer, A.T.; Kuekrek, H.; Mirzoyan, L.; Hummel, A.; Kirchhoff, K.; Salgin, B.; Isenburg, S.; et al. The fibrin matrix regulates angiogenic responses within the hemostatic microenvironment through biochemical control. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujii, K.; Tsuji, M.; Murota, K. Isolation of peripheral nerve collagen. Neurochem. Res. 1986, 11, 1439–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spira, M.; Liu, B.; Xu, Z.; Harrell, R.; Chahadeh, H. Human amnion collagen for soft tissue augmentation-biochemical characterizations and animal observations. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1994, 28, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, S.; Yamamoto, K.; Ikeda, T.; Yanagiguchi, K.; Hayashi, Y. Potency of fish collagen as a scaffold for regenerative medicine. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 302932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adachi, T.; Tomita, M.; Shimizu, K.; Ogawa, S.; Yoshizato, K. Generation of hybrid transgenic silkworms that express Bombyx mori prolyl-hydroxylase alpha-subunits and human collagens in posterior silk glands: Production of cocoons that contained collagens with hydroxylated proline residues. J. Biotechnol. 2006, 126, 205–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uitto, J.; Booth, B.A.; Polak, K.L. Collagen biosynthesis by human skin fibroblasts. II. Isolation and further characterization of type I and type III procollagens synthesized in culture. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1980, 624, 545–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; An, B.; Ramshaw, J.A.; Brodsky, B. Bacterial collagen-like proteins that form triple-helical structures. J. Struct. Biol. 2014, 186, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myllyharju, J.; Nokelainen, M.; Vuorela, A.; Kivirikko, K.I. Expression of recombinant human type I-III collagens in the yeast pichia pastoris. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2000, 28, 353–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.Y.; Stoichevska, V.; Madsen, S.; Howell, L.; Dumsday, G.J.; Werkmeister, J.A.; Ramshaw, J.A. A simple cost-effective methodology for large-scale purification of recombinant non-animal collagens. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 1807–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, P.X. Biomimetic materials for tissue engineering. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2008, 60, 184–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zander, N.E. Hierarchically structured electrospun fibers. Polymers 2013, 5, 19–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, J.; Lizu, M.; Stewart, M.; Zygula, K.; Lu, Y.; Chauhan, R.; Yan, X.; Guo, Z.; Wujcik, E.K.; Wei, S. Multifunctional nanofibers towards active biomedical therapeutics. Polymers 2015, 7, 186–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuber, M.; Zia, F.; Zia, K.M.; Tabasum, S.; Salman, M.; Sultan, N. Collagen based polyurethanes—A review of recent advances and perspective. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 80, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shields, K.J.; Beckman, M.J.; Bowlin, G.L.; Wayne, J.S. Mechanical properties and cellular proliferation of electrospun collagen type II. Tissue Eng. 2004, 10, 1510–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boland, E.D.; Matthews, J.A.; Pawlowski, K.J.; Simpson, D.G.; Wnek, G.E.; Bowlin, G.L. Electrospinning collagen and elastin: Preliminary vascular tissue engineering. Front. Biosci. 2004, 9, 1422–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, C.P.; Pemble, C.W.; Brand, D.D.; Simpson, D.G.; Bowlin, G.L. Cross-linking electrospun type II collagen tissue engineering scaffolds with carbodiimide in ethanol. Tissue Eng. 2007, 13, 1593–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sell, S.A.; Francis, M.P.; Garg, K.; McClure, M.J.; Simpson, D.G.; Bowlin, G.L. Cross-linking methods of electrospun fibrinogen scaffolds for tissue engineering applications. Biomed. Mater. 2008, 3, 045001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sell, S.A.; McClure, M.J.; Garg, K.; Wolfe, P.S.; Bowlin, G.L. Electrospinning of collagen/biopolymers for regenerative medicine and cardiovascular tissue engineering. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2009, 61, 1007–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, A.; Zhang, K.; McClure, M.J.; Huang, C.; Wu, J.; Fang, J.; Mo, X.; Bowlin, G.L.; AI Deyab, S.S.; EI-Newehy, M. Electrospinning collagen/chitosan/poly(l-lactic acid-co-ε-caprolactone) to form a vascular graft: mechanical and biological characterization. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2013, 101, 1292–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Wu, J.; Liu, X.; Chen, D.; Bowlin, G.L.; Cao, L.; Lu, J.; Li, F.; Mo, X.; Fan, C. Osteochondral regeneration using an oriented nanofiber yarn-collagen type I/hyaluronate hybrid/TCP biphasic scaffold. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2015, 103, 581–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Offeddu, G.S.; Ashworth, J.C.; Cameron, R.E.; Oyen, M.L. Multi-scale mechanical response of freeze-dried collagen scaffolds for tissue engineering applications. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2015, 42, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, R.; Ni, Y. Physical crosslinkings of edible collagen casing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 81, 920–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takitoh, T.; Bessho, M.; Hirose, M.; Ohgushi, H.; Mori, H.; Hara, M. Gamma-cross-linked nonfibrillar collagen gel as a scaffold for osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2015, 119, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maslennikova, A.; Kochueva, M.; Ignatieva, N.; Vitkin, A.; Zakharkina, O.; Kamensky, V.; Sergeeva, E.; Kiseleva, E.; Bagratashvili, V. Effects of gamma irradiation on collagen damage and remodeling. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2015, 91, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suchý, T.; Šupová, M.; Sauerová, P.; Verdánová, M.; Sucharda, Z.; Rýglová, Š.; Žaloudková, M.; Sedláček, R.; Kalbáčová, M.H. The effects of different cross-linking conditions on collagen-based nanocomposite scaffolds-an in vitro evaluation using mesenchymal stem cells. Biomed. Mater. 2015, 10, 065008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshioka, S.A.; Goissis, G. Thermal and spectrophotometric studies of new crosslinking method for collagen matrix with glutaraldehyde acetals. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2008, 19, 1215–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vrana, N.E.; Builles, N.; Kocak, H.; Gulay, P.; Justin, V.; Malbouyres, M.; Ruggiero, F.; Damour, O.; Hasirc, V. EDC/NHS cross-linked collagen foams as scaffolds for artificial corneal stroma. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2007, 18, 1527–1545. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Arafat, M.T.; Tronci, G.; Yin, J.; Wood, D.J.; Russell, S.J. Biomimetic wet-stable fibres via wet spinning and diacid-based crosslinking of collagen triple helices. Polymer 2015, 77, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Wang, Z. Collagen crosslinking of porcine sclera using genipin. Acta. Ophthalmol. 2013, 91, e253–e257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagaoka, H.; Nagaoka, H.; Walter, R.; Boushell, L.W.; Miguez, P.A.; Burton, A.; Ritter, A.V.; Yamauchi, M. Characterization of genipin-modified dentin collagen. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 702821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilsen-Nygaard, J.; Strand, S.P.; Vårum, K.M.; Draget, K.I.; Nordgård, C.T. Chitosan: Gels and interfacial properties. Polymers 2015, 7, 552–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, A.; Blanco, M.D.; Davidenko, N.; Cameron, R.E. Tailoring chitosan/collagen scaffolds for tissue engineering: Effect of composition and different crosslinking agents on scaffold properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 132, 606–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, F.; Yue, W.; Zhang, Y.; Mao, G.; Gao, K.; Zuo, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, H. Chitosan-collagen porous scaffold and bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for ischemic stroke. Neural. Regen. Res. 2015, 10, 1421–1426. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kasoju, N.; Bora, U. Silk fibroin in tissue engineering. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2012, 1, 393–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, K.; Li, H.; Li, R.; Nian, Z.; Li, D.; Xu, C. Silk fibroin/collagen and silk fibroin/chitosan blended three-dimensional scaffolds for tissue engineering. Eur. J. Orthop. Surg. Traumatol. 2015, 25, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Z.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, F.; Zuo, B.; Lu, Q.; Wu, P.; Xie, Z.; Dong, Q.; Zhang, H. Control of olfactory ensheathing cell behaviors by electrospun silk fibroin fibers. Cell Transplant. 2013, 22 Suppl. 1, S39–S50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Felice, V.; Serradifalco, C.; Rizzuto, L.; De Luca, A.; Rappa, F.; Barone, R.; Di Marco, P.; Cassata, G.; Puleio, R.; Verin, L.; et al. Silk fibroin scaffolds enhance cell commitment of adult rat cardiac progenitor cells. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2015, 9, E51–E64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, K.; Liu, Y.; Li, W.; Wang, L.; Liu, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Ren, L. Improving the mechanical properties of collagen-based membranes using silk fibroin for corneal tissue engineering. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2015, 103, 1159–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kontturi, L.S.; Järvinen, E.; Muhonen, V.; Collin, E.C.; Pandit, A.S.; Kiviranta, I.; Yliperttula, M.; Urtti, A. An injectable, in situ forming type II collagen/hyaluronic acid hydrogel vehicle for chondrocyte delivery in cartilage tissue engineering. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2014, 4, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bornes, T.D.; Jomha, N.M.; Mulet-Sierra, A.; Adesida, A.B. Hypoxic culture of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal stem cells differentially enhances in vitro chondrogenesis within cell-seeded collagen and hyaluronic acid porous scaffolds. Stem Cell. Res. Ther. 2015, 6, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, L.; Jiang, X.; Chen, X.; Fan, H.; Zhang, X. Evaluation of novel in situ synthesized nano-hydroxyapatite/collagen/alginate hydrogels for osteochondral tissue engineering. Biomed. Mater. 2014, 9, 065004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Lv, S.; Lu, J.; Jiang, S.; Lin, L. Characterization of polycaprolactone/collagen fibrous scaffolds by electrospinning and their bioactivity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 76, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.S.; Lee, S.J.; Christ, G.J.; Atala, A.; Yoo, J.J. The influence of electrospun aligned poly (ε-caprolactone)/collagen nanofiber meshes on the formation of self-aligned skeletal muscle myotubes. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 2899–2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haaparanta, A.M.; Järvinen, E.; Cengiz, I.F.; Ellä, V.; Kokkonen, H.T.; Kiviranta, I.; Kellomäki, M. Preparation and characterization of collagen/PLA, chitosan/PLA, and collagen/chitosan/PLA hybrid scaffolds for cartilage tissue engineering. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2014, 25, 1129–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, L.; Prabhakaran, M.P.; Qin, X.; Ramakrishna, S. Stem cell differentiation on electrospun nanofibrous substrates for vascular tissue engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2013, 33, 4640–4650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Lee, Y.J.; Cho, H.J.; Shin, H. Guidance of in vitro migration of human mesenchymal stem cells and in vivo guided bone regeneration using aligned electrospun fibers. Tissue Eng. Part. A 2014, 20, 2031–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, C.; Ma, X.; Xian, L.; Zhou, Y.; Fan, D. Characterization of a co-electrospun scaffold of HLC/CS/PLA for vascular tissue engineering. Biomed. Mater. Eng. 2014, 24, 1999–2005. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hardy, J.G.; Lin, P.; Schmidt, C.E. Biodegradable hydrogels composed of oxime crosslinked poly(ethylene glycol), hyaluronic acid and collagen: A tunable platform for soft tissue engineering. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2015, 26, 143–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shim, J.H.; Kim, A.J.; Park, J.Y.; Yi, N.; Kang, I.; Park, J.; Rhie, J.W.; Cho, D.W. Effect of solid freeform fabrication-based polycaprolactone/poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid)/collagen scaffolds on cellular activities of human adipose-derived stem cells and rat primary hepatocytes. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2013, 24, 1053–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyazaki, T.; Ishikawa, K.; Shirosaki, Y.; Ohtsuki, C. Organic-inorganic composites designed for biomedical applications. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2013, 36, 1670–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyazaki, T.; Sugawara-Narutaki, A.; Ohtsuki, C. Organic-inorganic composites toward biomaterial application. Front. Oral Biol. 2015, 17, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ngiam, M.; Liao, S.; Patil, A.J.; Cheng, Z.; Yang, F.; Gubler, M.J.; Ramakrishna, S.; Chan, C.K. Fabrication of mineralized polymeric nanofibrous composites for bone graft materials. Tissue Eng. Part. A 2009, 15, 535–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balaji Raghavendran, H.R.; Puvaneswary, S.; Talebian, S.; Murali, M.R.; Naveen, S.V.; Krishnamurithy, G.; McKean, R.; Kamarul, T. A comparative study on in vitro osteogenic priming potential of electron spun scaffold PLLA/HA/Col, PLLA/HA, and PLLA/Col for tissue engineering application. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e104389. [Google Scholar]
- Sarikaya, B.; Aydin, H.M. Collagen/beta-tricalcium phosphate based synthetic bone grafts via dehydrothermal processing. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 576532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MatéSánchez de Val, J.E.; Calvo Guirado, J.L.; Ramírez Fernández, M.P.; Delgado Ruiz, R.A.; Mazón, P.; De Aza, P.N. In vivo behavior of hydroxyapatite/β-TCP/collagen scaffold in animal model. Histological, histomorphometrical, radiological, and SEM analysis at 15, 30, and 60 days. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perumal, S.; Ramadass, S.K.; Gopinath, A.; Madhan, B.; Shanmugam, G.; Rajadas, J.; Mandal, A.B. Altering the concentration of silica tunes the functional properties of collagen-silica composite scaffolds to suit various clinical requirements. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2015, 52, 131–138. [Google Scholar]
- Venkatesan, J.; Pallela, R.; Kim, S.K. Applications of carbon nanomaterials in bone tissue engineering. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2014, 10, 3105–3123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Lee, J.Y.; Yang, S.H.; Lee, E.J.; Kim, H.W. Carbon nanotube-collagen three-dimensional culture of mesenchymal stem cells promotes expression of neural phenotypes and secretion of neurotrophic factors. Acta. Biomater. 2014, 10, 4425–4436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.; Sridharan, I.; Zhu, B.; Orgel, J.; Wang, R. Effect of CNT on collagen fiber structure, stiffness assembly kinetics and stem cell differentiation. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 49, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talukdar, Y.; Rashkow, J.T.; Lalwani, G.; Kanakia, S.; Sitharaman, B. The effects of graphene nanostructures on mesenchymal stem cells. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 4863–4877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, S.; Yin, P.T.; Uehara, T.M.; Chueng, S.T.; Yang, L.; Lee, K.B. Guiding stem cell differentiation into oligodendrocytes using graphene-nanofiber hybrid scaffolds. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 3673–3780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.Y.; Pang, D.W.; Hwang, S.M.; Tuan, H.Y.; Hu, Y.C. A graphene-based platform for induced pluripotent stem cells culture and differentiation. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 418–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanayama, I.; Miyaji, H.; Takita, H.; Nishida, E.; Tsuji, M.; Fugetsu, B.; Sun, L.; Inoue, K.; Ibara, A.; Akasaka, T.; et al. Comparative study of bioactivity of collagen scaffolds coated with graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 3363–3373. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, Y.C.; Lee, J.H.; Jin, L.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, Y.J.; Hyun, J.K.; Jung, T.G.; Hong, S.W.; Han, D.W. Stimulated myoblast differentiation on graphene oxide-impregnated PLGA-collagen hybrid fibre matrices. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2015, 13, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajimiri, M.; Shahverdi, S.; Kamalinia, G.; Dinarvand, R. Growth factor conjugation: Strategies and applications. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2015, 103, 819–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Lv, Y. Immobilization and application of electrospun nanofiber scaffold-based growth factor in bone tissue engineering. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2015, 21, 1967–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roelofs, L.A.; Oosterwijk, E.; Kortmann, B.B.; Daamen, W.F.; Tiemessen, D.M.; Brouwer, K.M.; Eggink, A.J.; Crevels, A.J.; Wijnen, R.M.; van Kuppevelt, T.H.; et al. Bladder regeneration using a smart acellular collagen scaffold with growth factors VEGF, FGF2 and HB-EGF. Tissue Eng. Part. A 2015, 22, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Liang, H.; Sun, J.; Zhuang, Y.; Xu, B.; Dai, J. Electrospun collagen fibers with spatial patterning of SDF1α for the guidance of neural stem cells. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2015, 4, 1869–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Arinzeh, T.L. Electrospun nanofibrous materials for neural tissue engineering. Polymers 2011, 3, 413–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Houle, J.D.; Xu, J.; Chan, B.P.; Chew, S.Y. Nanofibrous collagen nerve conduits for spinal cord repair. Tissue Eng. Part. A 2012, 18, 1057–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boecker, A.H.; van Neerven, S.G.; Scheffel, J.; Tank, J.; Altinova, H.; Seidensticker, K.; Deumens, R.; Tolba, R.; Weis, J.; Brook, G.A.; et al. Pre-differentiation of mesenchymal stromal cells in combination with a microstructured nerve guide supports peripheral nerve regeneration in the rat sciatic nerve model. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozkurt, A.; Boecker, A.; Tank, J.; Altinova, H.; Deumens, R.; Dabhi, C.; Tolba, R.; Weis, J.; Brook, G.A.; Pallua, N.; et al. Efficient bridging of 20 mm rat sciatic nerve lesions with a longitudinally micro-structured collagen scaffold. Biomaterials 2016, 75, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Lu, C.; Meng, D.; Xiao, Z.; Hou, X.; Ding, W.; Kou, D.; Yao, Y.; Chen, B.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Collagen scaffolds modified with CNTF and bFGF promote facial nerve regeneration in minipigs. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 7819–7827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koppes, A.N.; Nordberg, A.L.; Paolillo, G.M.; Goodsell, N.M.; Darwish, H.A.; Zhang, L.; Thompson, D.M. Electrical stimulation of schwann cells promotes sustained increases in neurite outgrowth. Tissue Eng. Part. A 2014, 20, 494–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kavet, R. Dosimetric uncertainties: Magnetic field coupling to peripheral nerve. Health Phys. 2015, 109, 556–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, Y.; Nan, P.; Chen, G.; Sha, Y.; Xia, B.; Yang, L. In vivo repair of rat transected sciatic nerve by low-intensity pulsed ultrasound and induced pluripotent stem cells-derived neural crest stem cells. Biotechnol. Lett. 2015, 37, 2497–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ristić, D.; Ellrich, J. Innocuous peripheral nerve stimulation shifts stimulus-response function of painful laser stimulation in man. Neuromodulation 2014, 17, 686–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Lv, Y.; Dong, C.; Yang, L. Effect of internal structure of collagen/hydroxyapatite scaffold on the osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Curr. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2015, 8, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Lv, Y.; Guo, P.; Lin, C.; Zhang, X.; Yang, L.; Xu, Z. Matrix mechanics and fluid shear stress control stem cells fate in three dimensional microenvironment. Curr. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2013, 10, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Dong, C.; Yang, L.; Lv, Y. 3D scaffolds with different stiffness but the same microstructure for bone tissue engineering. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 15790–15802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Yang, L.; Lv, Y. Cell-free scaffolds with different stiffness but same microstructure promote bone regeneration in rabbit large bone defect model. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Wang, W.; Liu, S.; Wu, J.; Li, F.; Cao, L.; Liu, X.D.; Mo, X.; Fan, C. Enhancement of chondrogenic differentiation of rabbit mesenchymal stem cells by oriented nanofiber yarn-collagen type I/hyaluronate hybrid. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 58, 1071–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhonen, V.; Salonius, E.; Haaparanta, A.M.; Järvinen, E.; Paatela, T.; Meller, A.; Hannula, M.; Björkman, M.; Pyhältö, T.; Ellä, V.; et al. Articular cartilage repair with recombinant human type II collagen/polylactide scaffold in a preliminary porcine study. J. Orthop. Res. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willers, C.; Chen, J.; Wood, D.; Xu, J.; Zheng, M.H. Autologous chondrocyte implantation with collagen bioscaffold for the treatment of osteochondral defects in rabbits. Tissue Eng. 2005, 11, 1065–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berninger, M.T.; Wexel, G.; Rummeny, E.J.; Imhoff, A.B.; Anton, M.; Henning, T.D.; Vogt, S. Matrix-assisted autologous chondrocyte transplantation for remodeling and repair of chondral defects in a rabbit model. J. Vis. Exp. 2013, 75, e4422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffin, D.J.; Bonnevie, E.D.; Lachowsky, D.J.; Hart, J.C.; Sparks, H.D.; Moran, N.; Matthews, G.; Nixon, A.J.; Cohen, I.; Bonassar, L.J. Mechanical characterization of matrix-induced autologous chondrocyte implantation (MACI®) grafts in an equine model at 53 weeks. J. Biomech. 2015, 48, 1944–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basad, E.; Wissing, F.R.; Fehrenbach, P.; Rickert, M.; Steinmeyer, J.; Ishaque, B. Matrix-induced autologous chondrocyte implantation (MACI) in the knee: Clinical outcomes and challenges. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2015, 23, 3729–3735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gigante, A.; Busilacchi, A.; Lonzi, B.; Cecconi, S.; Manzotti, S.; Renghini, C.; Giuliani, A.; Mattioli-Belmonte, M. Purified collagen I oriented membrane for tendon repair: An ex vivo morphological study. J. Orthop. Res. 2013, 31, 738–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardwell, R.D.; Dahlgren, L.A.; Goldstein, A.S. Electrospun fibre diameter, not alignment, affects mesenchymal stem cell differentiation into the tendon/ligament lineage. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2014, 8, 937–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yunoki, S.; Hatayama, H.; Ebisawa, M.; Kondo, E.; Yasuda, K. A novel fabrication method to create a thick collagen bundle composed of uniaxially aligned fibrils: An essential technology for the development of artificial tendon/ligament matrices. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2015, 103, 3054–3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.J.; Liu, J.; Oh, S.H.; Soker, S.; Atala, A.; Yoo, J.J. Development of a composite vascular scaffolding system that withstands physiological vascular conditions. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 2891–2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Liu, S.; Zhang, K.; Chen, J.; Huang, N. Endothelialization of implanted cardiovascular biomaterial surfaces: The development from in vitro to in vivo. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2014, 102, 3754–3772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, C.; Fan, D.; Wang, Y. Human-like collagen/hyaluronic acid 3D scaffolds for vascular tissue engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2014, 34, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heo, Y.; Shin, Y.M.; Lee, Y.B.; Lim, Y.M.; Shin, H. Effect of immobilized collagen type IV on biological properties of endothelial cells for the enhanced endothelialization of synthetic vascular graft materials. Colloids Surf. B 2015, 134, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koobatian, M.T.; Row, S.; Smith, R.J., Jr.; Koenigsknecht, C.; Andreadis, S.T.; Swartz, D.D. Successful endothelialization and remodeling of a cell-free small-diameter arterial graft in a large animal model. Biomaterials 2016, 76, 344–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Gao, C.; Mao, Z.; Zhou, J.; Shen, J.; Hu, X.; Han, C. Collagen/chitosan porous scaffolds with improved biostability for skin tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 4833–4841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rho, K.S.; Jeong, L.; Lee, G.; Seo, B.; Park, Y.J.; Hong, S.D.; Roh, S.; Cho, J.J.; Park, W.H.; Min, B.M. Electrospinning of collagen nanofibers: Effects on the behavior of normal human keratinocytes and early-stage wound healing. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 1452–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandika, P.; Ko, S.C.; Oh, G.W.; Heo, S.Y.; Nguyen, V.T.; Jeon, Y.J.; Lee, B.; Jang, C.H.; Kim, G.; Park, W.S.; et al. Fish collagen/alginate/chitooligosaccharides integrated scaffold for skin tissue regeneration application. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 81, 504–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, H.; Chen, M.M.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.Y.; Huang, Y.Q.; Wang, J.H.; Chen, J.D.; Zhang, Q.Q. Fish collagen-based scaffold containing PLGA microspheres for controlled growth factor delivery in skin tissue engineering. Colloids Surf. B 2015, 136, 1098–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soft Tissue Fillers (Dermal Fillers). Available online: http://www.fda.gov/MedicalDevices/ProductsandMedicalProcedures/CosmeticDevices/WrinkleFillers/default.htm (accessed on 15 January 2016).
- Koulikovska, M.; Rafat, M.; Petrovski, G.; Veréb, Z.; Akhtar, S.; Fagerholm, P.; Lagali, N. Enhanced regeneration of corneal tissue via a bioengineered collagen construct implanted by a nondisruptive surgical technique. Tissue Eng. Part. A 2015, 2, 1116–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Redmond, S.L.; Teh, B.M.; Yan, S.; Wang, Y.; Atlas, M.D.; Dilley, R.J.; Zheng, M.; Marano, R.J. Tympanic membrane repair using silk fibroin and acellular collagen scaffolds. Laryngoscope 2013, 123, 1976–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Redmond, S.L.; Papadimitriou, J.M.; Teh, B.M.; Yan, S.; Wang, Y.; Atlas, M.D.; Marano, R.J.; Zheng, M.; Dilley, R.J. The biocompatibility of silk fibroin and acellular collagen scaffolds for tissue engineering in the ear. Biomed. Mater. 2014, 9, 015015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dong, C.; Lv, Y. Application of Collagen Scaffold in Tissue Engineering: Recent Advances and New Perspectives. Polymers 2016, 8, 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8020042
Dong C, Lv Y. Application of Collagen Scaffold in Tissue Engineering: Recent Advances and New Perspectives. Polymers. 2016; 8(2):42. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8020042
Chicago/Turabian StyleDong, Chanjuan, and Yonggang Lv. 2016. "Application of Collagen Scaffold in Tissue Engineering: Recent Advances and New Perspectives" Polymers 8, no. 2: 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8020042
APA StyleDong, C., & Lv, Y. (2016). Application of Collagen Scaffold in Tissue Engineering: Recent Advances and New Perspectives. Polymers, 8(2), 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8020042