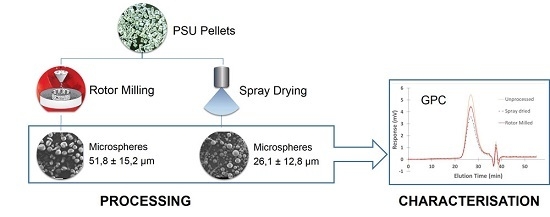
Processing of Polysulfone to Free Flowing Powder by Mechanical Milling and Spray Drying Techniques for Use in Selective Laser Sintering
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2 Solubility Determination
2.3. Viscosity Determination
2.4. Spray Drying
2.5. Mechanical Milling
2.5.1. Ball Milling
2.5.2. Rotor Milling
2.6. GPC Measurements
2.7. DSC Measurements
2.8. Particle Size Distribution (PSD)
2.9. XRD Measurements
3. Results
3.1 Solubility Determination
3.2. Viscosity Determination
3.3. Morphology
3.4. Particle Size Distribution (PSD)
3.5. GPC Measurements
3.6. DSC Measurements
3.7. XRD Measurements
4. Discussion
4.1. Morphology
4.2. Physicochemical Properties
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AM | Additive Manufacturing |
| DIPS | Diffusion Induced Phase Separation |
| DMF | N,N-Dimethylformamide |
| EPS | Evaporation Induced Phase Separation |
| HDT | Heat Deflection Temperature |
| HSP | Hansen Solubility Parameter |
| PSD | Particle Size Distribution |
| SD | Spray Drying |
| SLS | Selective Laser Sintering |
| TIPS | Thermal Induced Phase Separation |
References
- Hopkinson, N.; Hague, R.; Dickens, P. Rapid Manufacturing: An Industrial Revolution for the Digital Age; John Wiley and Sons Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Kruth, J.-P.; Leu, M.C.; Nakagawa, T. Progress in additive manufacturing and rapid prototyping. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 1998, 47, 525–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wohlers Associates. Wohlers Reports, (2009) 250. Available online: http://www.wohlersassociates.com/books-reports.html (accessed on 25 June 2015).
- Goodridge, R.D.; Tuck, C.J.; Hague, R.J.M. Laser sintering of polyamides and other polymers. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2012, 57, 229–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, R.S.; Bourell, D.L.; Beaman, J.J.; Campbell, M.I. SLS materials development method for rapid manufacturing. In Proceedings of SFF Symposium, Austin, Texas, TX, USA, 1–3 August 2005.
- Gibson, I.; Shi, D. Material properties and fabrication parameters in selective laser sintering processnull. Rapid Prototyp. J. 1997, 3, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, C.; Spontak, R.J.; Koch, C.C.; Saw, C.K.; Balik, C.M. Structural changes in poly(ethylene terephthalate) induced by mechanical milling. Polymer 2000, 41, 7147–7157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonna, S.; Lyons, J. Processing and properties of cryogenically milled post-consumer mixed plastic waste. Polym. Test. 2005, 24, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Shaw, W.J.D. Properties of a mechanically processed polymeric material. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1994, 52, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castricum, H.L.; Yang, H.; Bakker, H.; van Deursen, J.H. A Study of milling of pure polymers and a structural transformation of polyethylene. Mater. Sci. Forum 1996, 235–238, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Font, J.; Muntasell, J. Effect of ball milling on semicrystalline bisphenol A polycarbonate. Mater. Res. Bull. 2000, 35, 681–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, T. Mechanical alloying of polytetrafluoroethylene with polyethylene. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 1994, 13, 623–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, C.R.; Koleng, J.J.; McGinity, J.W. Production of spherical pellets by a hot-melt extrusion and spheronization process. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 242, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuyama, H. Formation of polypropylene particles via thermally induced phase separation. Polymer (Guildf) 2000, 41, 8673–8679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van De Witte, P.; Dijkstra, P.J.; Van Den Berg, J.W.A.; Feijen, J. Phase separation processes in polymer solutions in relation to membrane formation. J. Memb. Sci. 1996, 117, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arya, R.K. Drying induced phase separation in multicomponent polymeric coatings–Simulation study. Int. J. Sci. Technol. Res. 2012, 1, 48–52. [Google Scholar]
- Nandiyanto, A.B.D.; Okuyama, K. Progress in developing spray-drying methods for the production of controlled morphology particles: From the nanometer to submicrometer size ranges. Adv. Powder Technol. 2011, 22, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Berkland, C.; Kevin Kim, K.; Pack, D.W. Fabrication of PLG microspheres with precisely controlled and monodisperse size distributions. J. Control. Release 2001, 73, 59–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobry, D.; Settell, D.; Baumann, J.; Ray, R.; Graham, L.; Beyerinck, R. A model-based methodology for spray-drying process development. J. Pharm. Innov. 2009, 4, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solvay, Udel Polysulfone Design Guide, Solvay, n.d. Available online: http://www.solvayplastics.com/sites/solvayplastics/EN/Solvay Plastics Literature/DPG_Udel_Design_Guide_EN.pdf (accessed on 25 June 2015).
- Naim, R.; Ismail, A.F.; Saidi, H.; Saion, E. Development of sulfonated polysulfone membranes as a material for Proton Exchange Membrane (PEM). In Proceedings of the Regional Symppsium on Membrane Science Technology, Puteri Pan Pacific Hotel, Johor Bharu, Malaysia, 21–25 April 2004.
- Sata, T.; Tsujimoto, M.; Yamaguchi, T.; Matsusaki, K. Change of anion exchange membranes in an aqueous sodium hydroxide solution at high temperature. J. Memb. Sci. 1996, 112, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mys, N.; van de Sande, R.; Verberckmoes, A.; Cardon, L. Processing of polysulfone to free flowing powder for part manufacturing through selective laser sintering. Reg. Conf. Polym. Process. Soc. 2015. (In Press) [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, C.M. Hansen Solubiliy Parameters: A User′s Handbook, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Mys, N.; Haverans, T.; Verberckmoes, A.; Cardon, L. Production of syndiotactic polystyrene powder for part manufacturing through SLS. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Polymers and Molds Innovations, University of Minho, Guimarães, Porgutal, 12 September 2014.
- Arpagaus, C.; Schafroth, N.; Meuri, M. Laboratory Scale Spray Drying of Inhalable Drugs: A Review; Best@Buchi: New Castle, DE, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, A.P.; Shay, J.S.; Spontak, R.J.; Balik, C.M.; Ade, H.; Smith, S.D. High-energy mechanical milling of poly(methyl methacrylate), polyisoprene and poly(ethlene-alt-propylene). Polymer 2000, 41, 6271–6283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangwar, J.; Gupta, B.K.; Tripathi, S.K.; Srivastava, A.K. Phase dependent thermal and spectroscopic responses of Al2O3 nanostructures with different morphogenesis. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 13313–13344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchi, GEA Niro. Scale-up from the Buchi Mini Spray Dryer B-290 to the Niro Mobil Minor, Inf. Bull. 52, 2008. Available online: http://static1.buchi.com/sites/default/files/downloads/B-290_Scale-up_B-290_Niro_MOBILE_MINOR_en_01.pdf (accessed on 25 June 2015).
- Vehring, R.; Foss, W.R.; Lechuga-Ballesteros, D. Particle formation in spray drying. J. Aerosol Sci. 2007, 38, 728–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroda, S.; Terauchi, K.; Nogami, K.; Mita, I. Degradation of aromatic polymers—I. Rates of crosslinking and chain scission during thermal degradation of several soluble aromatic polymers. Eur. Polym. J. 1989, 25, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnár, G.; Botvay, A.; Pöppl, L.; Torkos, K.; Borossay, J.; Máthé, Á.; Török, T. Thermal degradation of chemically modified polysulfones. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2005, 89, 410–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroda, S.; Nagura, A.; Horie, K.; Mita, I. Degradation of aromatic polymers—III. Crosslinking and chain scission during photodegradation of polysulphones. Eur. Polym. J. 1989, 25, 621–627. [Google Scholar]
- Beyler, C.L.; Hirschler, M.M. Thermal decomposition of polymers, SFPE Handb. Fire Prot. Eng. 2002, 2, 110–131. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.-L.; Jones, W.H.; Monnat, F.; Wudl, F.; Houk, K.N. Mechanisms of thermal decompositions of polysulfones: A DFT and CBS-QB3 study. Macromolecules 2005, 38, 10279–10285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Solvents | δt (MPa1/2) | δd (MPa1/2) | δp (MPa1/2) | δh (MPa1/2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polysulfone | 23.6 | 19.8 | 11.2 | 6.2 |
| Chloroform | 18.9 | 17.8 | 3.1 | 5.7 |
| N,N-Dimethylformamide | 24.9 | 17.4 | 13.7 | 11.3 |
| N,N-Dimethylacetamide | 22.8 | 16.8 | 11.5 | 10.2 |
| Tetrahydrofuran | 19.5 | 16.8 | 5.7 | 8.0 |
| Processing method | Mw 1 | Mn 2 | Polydispersity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Virgin/unprocessed | 60,318 ± 283 | 29,804.5 ± 146 | 2.02 ± 4 |
| Rotor milling | 60,293 ± 217 | 30,297.5 ± 1,272 | 1.99 ± 0.11 |
| Spray drying | 61,662 ± 110 | 30,803.5 ± 1,769 | 2.01 ± 0.09 |
| Ball milling | n.a..3 | n.a..3 | n.a..3 |
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mys, N.; Van De Sande, R.; Verberckmoes, A.; Cardon, L. Processing of Polysulfone to Free Flowing Powder by Mechanical Milling and Spray Drying Techniques for Use in Selective Laser Sintering. Polymers 2016, 8, 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8040150
Mys N, Van De Sande R, Verberckmoes A, Cardon L. Processing of Polysulfone to Free Flowing Powder by Mechanical Milling and Spray Drying Techniques for Use in Selective Laser Sintering. Polymers. 2016; 8(4):150. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8040150
Chicago/Turabian StyleMys, Nicolas, Ruben Van De Sande, An Verberckmoes, and Ludwig Cardon. 2016. "Processing of Polysulfone to Free Flowing Powder by Mechanical Milling and Spray Drying Techniques for Use in Selective Laser Sintering" Polymers 8, no. 4: 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8040150
APA StyleMys, N., Van De Sande, R., Verberckmoes, A., & Cardon, L. (2016). Processing of Polysulfone to Free Flowing Powder by Mechanical Milling and Spray Drying Techniques for Use in Selective Laser Sintering. Polymers, 8(4), 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8040150