Polybenzoxazine/Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxane (POSS) Nanocomposites
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Preparation of PBZs Containing POSS Nanocomposites
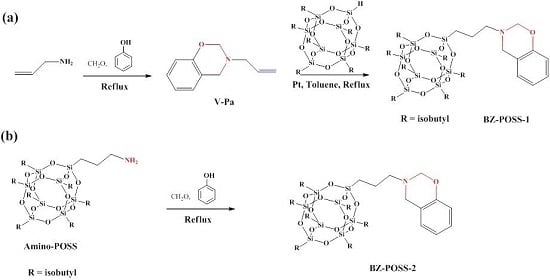
2.1. Monobenzoxazine-Functionalized POSS (BZ-POSS)
2.2. Multibenzoxazine-Functionalized POSS
2.3. Other Functionalized POSS Derivatives in PBZ
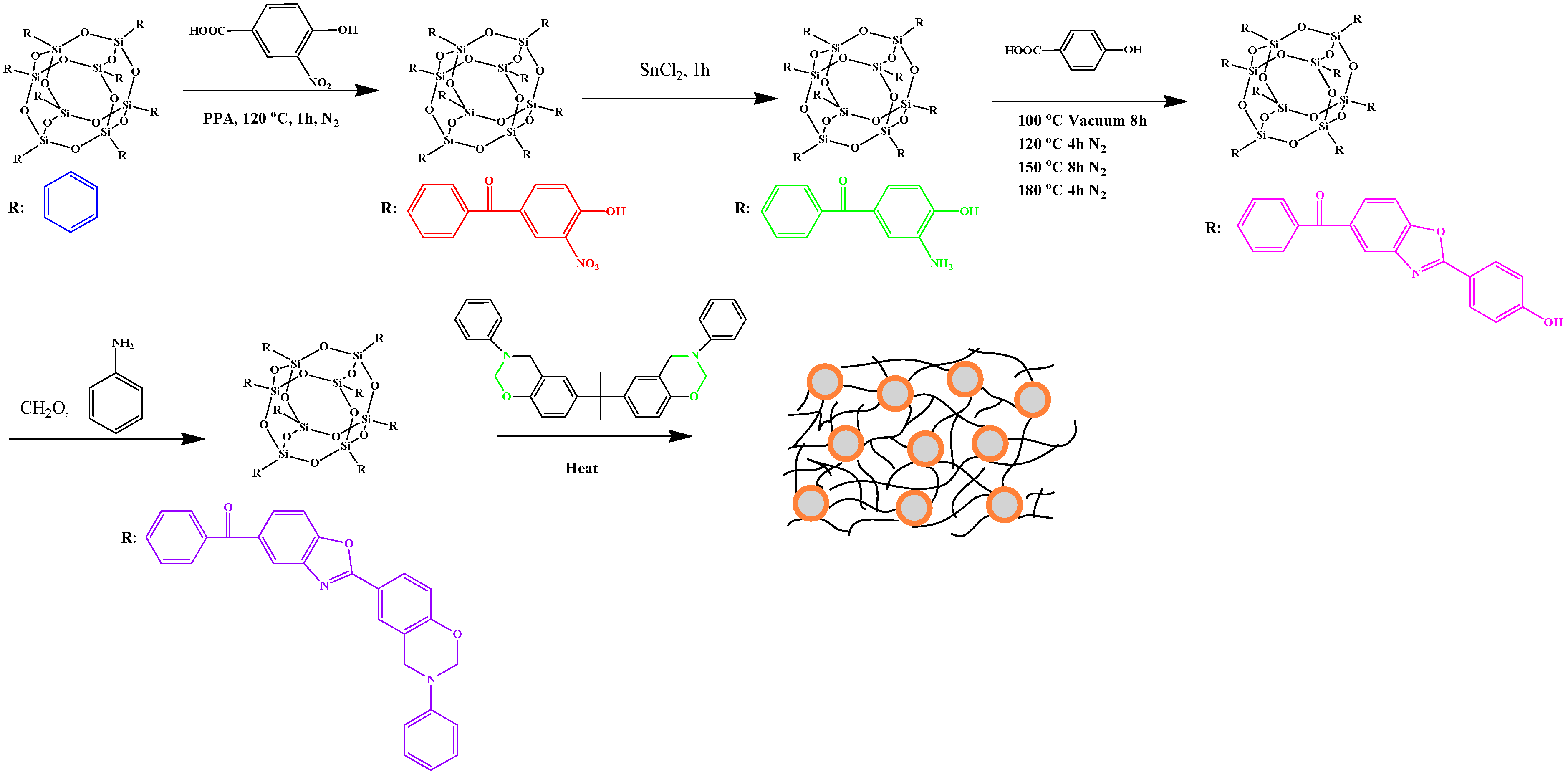
2.4. Hydrogen-Bonding Interactions from Heteronucleobase-Functionalized BZ and POSS
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Laobutee, A.; Chirachanchai, S.; Ishida, H. Asymmetric mono-oxazine: An inevitable product from Mannich reaction of benzoxazine dimers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 9947–9955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, N.N.; Kiskan, B.; Yagci, Y. Polybenzoxazines-new high performance thermosetting resins: synthesis and properties. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2007, 32, 1344–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsutomu, T.; Takehiro, K.; Tarek, A. High performance polybenzoxazines as a novel type of phenolic resin. Polymer. J. 2008, 40, 1121–1131. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.J.; Brunovska, Z.; Ishida, H. Synthesis and thermal characterization of polybenzoxazines based on acetylene-functional monomers. Polymer 1999, 40, 6565–6573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, S.W.; Liu, W.C. Synthesis and characterization of a cured epoxy resin with a benzoxazine monomer containing allyl groups. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 117, 3121–3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudoh, R.; Sudo, A.; Endo, T. A Highly reactive benzoxazine monomer, 1-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1,3-benzoxazine: activation of benzoxazine by neighboring group participation of hydroxyl group. Macromolecules 2010, 43, 1185–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, S.W.; Wu, Y.C.; Wang, C.F.; Jeong, K.W. Preparing low-surface energy polymer materials by minimizing intermolecular hydrogen bonding interactions. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 20666–20673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernykh, A.; Liu, L.P.; Ishida, H. Synthesis and properties of a new crosslinkable polymer containing benzoxazine moiety in the main chain. Polymer 2006, 47, 7664–7669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, H.K.; Chu, Y.L.; Chang, F.C.; Zhu, C.Y.; Kuo, S.W. A cross-linkable triphenylamine derivative as a hole injection/transporting material in organic light-emitting diodes. Polym. Chem. 2015, 6, 6227–6237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, G. Synthesis and properties of thermosetting resin based on urushiol. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 2768–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslan, M.; Kiskan, B.; Yagci, Y. Combing elemental sulfur with polybenzoxazines via vulcanization. Macromolecules 2016, 49, 767–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohashi, S.; Kilbane, J.; Heyl, T.; Ishida, H. Synthesis and characterization of cyanate ester functional benzoxazine and its polymer. Macromolecules 2015, 48, 8412–8417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, G.M.; Hsiao, C.H.; Loo, F.; Dai, L.Z.; Kuo, S.W. Multifunctional polybenzoxazine nanocomposites containing photoresponsive azobenzene units, catalytic carboxylic acid groups, and pyrene units capable of dispersing carbon nanotubes. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 45201–45212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, Z.; Ishida, H. An anomalous trade-off effect on the properties of smart ortho-functional benzoxazines. Polym. Chem. 2015, 6, 2541–2550. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, G.M.; Hsu, K.C.; Kuo, S.W. Bifunctional polybenzoxazine nanocomposites containing photo-crosslinkable coumarin units and pyrene units capable of dispersing single-walled carbon nanotubes. Polym. Chem. 2015, 6, 2423–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xia, Y.; Xu, W.; Ran, Q.; Gu, Y. The curing procedure for a benzoxazine‑cyanate‑epoxy system and the properties of the terpolymer. Polym. Chem. 2012, 3, 1629–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudo, A.; Kudo, R.; Nakayama, H.; Arima, K.; Endo, T. Selective formation of poly(N,O-acetal) by polymerization of 1,3-benzoxazine and its main chain rearrangement. Macromolecules 2008, 41, 9030–9034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.F.; Chang, F.C.; Kuo, S.W. Surfaces properties of polybenzoxazines. In Handbook of benzoxazine resins; Ishida, H., Agag, T., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; p. 579. [Google Scholar]
- Demir, D.K.; Kiskan, B.; Latthe, S.S.; Demirel, L.A.; Yagci, Y. Thermally curable fluorinated main chain benzoxazine polyethers via Ullmann coupling. Polym. Chem. 2013, 4, 2106–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, G.M.; Lin, R.C.; Tu, F.C.; Hong, L.J.; Jeong, U.K.; Wang, F.C.; Kuo, S.W. Thermal property of an aggregation-induced emission fluorophore that forms metal–ligand complexes with Zn(ClO4)2 of salicylaldehyde azine-functionalized polybenzoxazine. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 65635–65645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, H.; Low, H.Y. A study on the volumetric expansion of benzoxazine-based phenolic resin. Macromolecules 1999, 30, 1099–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vengatesan, M.R.; Devarau, S.; Dinkaran, K.; Alagar, M. SBA-15 filled polybenzoxazine nanocomposites for low-k dielectric applications. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 7559–7566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holly, F.; Cope, C.A. Condensation products of aldehydes and ketones with o-aminobenzyl alcohol and o-hydroxybenzylamine. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1944, 66, 1875–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, H.; Allen, J.D. Mechanical characterization of copolymers based on benzoxazine and epoxy. Polymer 1996, 37, 4487–4495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, X.; Ishida, H. Phenolic materials via ring-opening polymerization: Synthesis and characterization of bisphenol-A based benzoxazines and their polymers. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 1994, 32, 1121–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassapoglu, F.; Cianga, I.; Yagci, Y.; Takeichi, T.J. Photoinitiated cationic polymerization of monofunctional benzoxazine. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2003, 41, 3320–3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Liu, J.; Ishida, H. High performance crosslinked polyimide based on main-chain type polybenzoxazine. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 62550–62556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.R.; Mohamed, M.G.; Jia, Y.W.; Yu, R.J.; Kuo, S.W. Multivalent photo-crosslinkable coumarin-containing polybenzoxazines exhibiting enhanced thermal and hydrophobic surface properties. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 10683–10696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagci, Y.; Kiskan, B.; Ghosh, N.N. Recent advancement on polybenzoxazine-a newly developed high performance thermoset. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2008, 47, 5565–5576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Gu, Y. Study on the volumetric expansion of benzoxazine curing with different catalysts. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2002, 84, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.F.; Su, Y.C.; Kuo, S.W.; Huang, C.F.; Sheen, C.Y.; Chang, F.C. Low-surface-free-energy materials based on polybenzoxazines. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 2248–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.L.; Hung, J.Y.; Yu, R.K.; Chyi, M.L.; Tzong, M.L.; Guey, S.L. Novel near-infrared and multi-colored electrochromic polybenzoxazines with electroactive triarylamine moieties. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 7796–7803. [Google Scholar]
- Ishida, H.; Allen, D. Physical and mechanical characterization of near-zero shrinkage polybenzoxazines. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 1996, 34, 1019–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Jianlong, W.; Chong, F.; Yahui, S.; Kaixi, L. Synthesis of polybenzoxazine based nitrogen-rich porous carbons for carbon dioxide capture. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 6534–6544. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, C.S.; Wang, C.F.; Lin, H.C.; Chou, H.Y.; Chang, F.C. Fabrication of patterned superhydrophobic polybenzoxazine hybrid surfaces. Langmuir 2009, 25, 3359–3362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, W.C.; Kuo, S.W. Reversible surface properties o polybenzoxazine/silica nanocomposites thin films. J. Nanomater. 2013, 2013, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.F.; Wang, Y.T.; Tung, P.H.; Kuo, S.W.; Lin, C.H.; Sheen, Y.C.; Chang, F.C. Stable superhydrophobic polybenzoxazine surfaces over a wide pH range. Langmuir 2006, 22, 8289–8292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.F.; Chen, H.Y.; Kuo, S.W.; Lai, Y.S.; Yang, P.F. Rapid, low temperature microwave synthesis of durable, superhydrophobic carbon nanotube‑polybenzoxazine nanocomposites. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 9764–9769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.F.; Chiou, S.H.; Ko, F.H.; Chou, C.T.; Lin, H.C.; Huang, C.F.; Chang, F.C. Fabrication of biomimetic super-amphiphobic surfaces through plasma modification of benzoxazine films. Macromol. Rapid. Commun. 2006, 27, 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.F.; Chiou, F.H.; Ko, F.H.; Chen, J.K.; Chou, C.T.; Huang, C.F.; Kuo, S.W.; Chang, F.C. Polybenzoxazine as a mold-release agent for nanoimprint lithography. Langmuir 2007, 23, 5868–5871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, W.C.; Li, J.G.; Kuo, S.W. From flexible to mesoporous polybenzoxazine resins templated by poly (ethylene oxide-b-ε-caprolactone) copolymer through reaction induced microphase separation mechanism. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 6485–6498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velez-Herrara, P.; Doyama, K.; Abe, H.; Ishida, H. Synthesis and characterization of highly fluorinated polymer with the benzoxazine moiety in the main chain. Macromolecules 2008, 41, 9704–9714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, G.M.; Su, W.C.; Lin, Y.C.; Wang, C.F.; Chen, J.K.; Jeong, U.K.; Kuo, S.W. Azopyridine-functionalized benzoxazine with Zn(ClO4)2 form high-performance polybenzoxazine stabilized through metal–ligand coordination. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 50373–50385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohashi, S.; Pandey, V.; R.Arza, C.; Frimowicz, P.; Ishida, H. Simple and low energy consuming synthesis of cyanate ester functional naphthoxazines and their properties. Polym. Chem. 2016, 7, 2245–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Zhuang, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, X.; Yang, G.; Han, Z. Preparation and properties of novel low dielectric constant benzoxazole-based polybenzoxazine. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2012, 50, 5115–5123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.W.; Kuo, S.W. Nanocomposites of polybenzoxazine and exfoliated montmorillonite using a polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane surfactant and click chemistry. J. Polym. Res. 2013, 20, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunovska, Z.; Lyon, R.; Ishida, H. Thermal properties of phthalonitrile functional polybenzoxazines. Thermochim. Acta. 2000, 357, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.C.; Lin, Y.C.; Wang, P.I.; Liaw, D.J.; Kuo, S.W. Polybenzoxazine/single-walled carbon nanotube nanocomposites stabilized through noncovalent bonding interactions. 2014, 55, 2044–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.W.; Huang, K.W.; Kuo, S.W. Heteronucleobase-functionalized benzoxazine: synthesis, thermal properties, and self-assembled structure formed through multiple hydrogen bonding interactions. Polym. Chem. 2012, 3, 1546–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiskan, B.; Ghosh, N.N.; Yagci, Y. Polybenzoxazine-based composites as high-performance materials. Polym. Int. 2011, 60, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oie, H.; Sudo, A.; Endo, T. Synthesis of networked polymers by crosslinking reactions of polybenzoxazine bearing allyl group in the side chain. J. Polym. Sci. Part. A Polym. Chem. 2013, 51, 2035–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.K.; Huang, C.F.; Kuo, S.W.; Lin, H.C.; Yei, D.R.; Chang, F.C. Effect of an organically modified nanoclay on low-surface-energy materials of polybenzoxazine. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2008, 29, 1216–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.F.; Kuo, S.W.; Lin, C.H.; Chen, H.G.; Liao, C.S.; Hung, P.R. Benzoxazine as a reactive noncovalent dispersant for carbon nanotubes. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 36012–36016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.M.; Kuo, S.W.; Huang, H.J.; Wang, Y.X.; Chen, Y.T. Preparation of VB-a/POSS hybrid monomer and its polymerization of polybenzoxazine/POSS hybrid nanocomposites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 111, 628–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, K.D.; Kiskan, B.; Yagci, Y. Thermally curable acetylene-containing main-chain benzoxazine polymers via sonogashira coupling reaction. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 1801–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xu, R.; Yu, D. A novel poly-benzoxazinyl functionalized polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane and its nanocomposite with polybenzoxazine. Eur. Polym. J. 2007, 43, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.M.; Knight, P.T.; Chung, T.; Mather, P.T. Polycaprolactone−POSS chemical/physical double networks. Macromolecules 2008, 41, 4730–4748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, S.W. Building Blocks Precisely from Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxane Nanoparticles. ACS Cent. Sci. 2016, 2, 62–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, S.W.; Chang, F.C. POSS related polymer nanocomposites. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2011, 36, 1649–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordes, D.B.; Lickiss, P.D.; Rataboul, F. Recent developments in the chemistry of cubic polyhedral oligosilsesquioxanes. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 2081–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomasz, P.; Anna, K.; Bozena, Z.; Marek, J.P. Structure, dynamics, and host−guest interactions in POSS functionalized cross-linked nanoporous hybrid organic−inorganic polymers. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 26575–26587. [Google Scholar]
- Shea, K.J.; Loy, D.A. Bridged polysilsesquioxanes. Molecular-engineered hybrid organic−inorganic materials. Chem. Mater. 2001, 13, 3306–3319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, S.H.; Haddad, T.S.; Tomczak, S.J. Development in nanoscience: Polyherdral oligomeric silsesquioxane (POSS)-polymers. Cur Opi. Sol. Sta. Mater. Sci. 2004, 8, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, B.; Thoms, T.P.S.; Murfee, H.J.; Lebrun, M.L. Highly dendritic macromolecules with core polyhedral silsesquioxane functionalities. Inorg. Chem. 1997, 36, 6146–6147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strachota, A.; Kroutilova, I.; Kovaro, J.; Matejka, L. Epoxy networks reinforced with Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxanes (POSS) thermomechanical properties. Macromolecules 2004, 37, 9457–9464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leu, C.M.; Chang, Y.T.; Wei, K.H. Synthesis and dielectric properties of polyimide-tethered Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxane (POSS) nanocomposites via POSS-diamine. Macromolecules 2003, 36, 9122–9127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, D.W. Thermal rearrangement of branched-chain methylpolysiloxanes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1946, 68, 356–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebunoluwa, A.; Biswajit, S.; Paschalis, A. Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxane (POSS)-containing polymer nanocomposites. Nanomaterials 2012, 2, 445–475. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, M.J.; Gorzkowski, E.; McAlliste, K. Dielectric properties of polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane (POSS)-based nanocomposites at 77k. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2001, 18, 082006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Wang, L.; Ni, H.; Pittman, C.U., Jr. Polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane (POSS) polymers and copolymers: A Review. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. 2001, 11, 123–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Mather, P.T. POSS polymers: Physical properties and biomaterials applications. Polym. Rev. 2009, 49, 25–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baney, R.H.; Itoh, M.; Sakakibara, A.; Suzuki, T. Silsesquioxanes. Chem. Rev. 1995, 95, 1409–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcolli, C.; Calzaferri, G. Review monosubstituted octasilasesquioxanes. Appl. Organometal. Chem. 1999, 13, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shockey, E.G.; Bolf, A.G.; Jones, P.F.; Schwab, J.J.; Chaffee, K.P.; Haddad, T.S.; Lichtenhan, J.D. Functionalized polyhedral oligosilsesquioxanes (POSS) macromers: new graftable POSS hydride, POSS a-Olefin POSS epoxy, and POSS chlorosilane macromers and POSS-siloxane triblocks. Appl. Organometal. Chem. 1999, 13, 311–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchida, A.; Bolln, C.; Sernetz, F.G.; Frey, H.; Mulhaupt, R. Ethene and propene copolymers containing silsesquioxane side groups. Macromolecules 1997, 30, 2818–2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feher, F.J.; Newman, D.A.; Walzer, J.F. Silsesquioxanes as models for silica surfaces. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997, 3, 900–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feher, F.J.; Weller, K.J. Polyhedral aluminosilsesquioxanes as models for aluminosilicates: unique synthesis of anionic aluminum/silicon/oxygen frameworks. Organometallics 1990, 9, 2638–2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenn, Y.C.; Lu, C.H.; Huang, F.C.; Kuo, S.W. Synthesis and characterization of amorphous octakis-functionalized polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxanes for polymer nanocomposites. Polymer 2008, 49, 4017–4024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Laine, R.M. Hydrosilylation of allyl alcohol with [HSiMe2OSiO1.5]8: octa(3-hydroxypropyldimethylsiloxy) octasilsesquioxane and its octamethacrylate derivative as potential precursors to hybrid nanocomposites. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 6979–6988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, S.W.; Lin, H.C.; Huang, W.J.; Huang, C.F.; Chang, F.C. Hydrogen bonding interactions and miscibility between phenolic resin and octa (acetoxystyryl) polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane (AS-POSS) nanocomposites. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2006, 44, 673–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellinger, A.; Laine, R.M. Silsesquioxanes as synthetic platforms. Thermally curable and photocurable inorganic/organic hybrids. Macromolecules 1996, 29, 2327–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, R.S.; Lu, C.H.; Kuo, S.W.; Chang, F.C. Hydrogen bond-mediated self-assembly of polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane-based supramolecules. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 12855–12862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, M.C.; Liu, Y.L. Preparation, morphology, and ultra-low dielectric constants of benzoxazine-based polymers/polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane (POSS) nanocomposites. Polymer 2015, 51, 5567–5575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.; Oh, W.; Hwang, Y.T.; Park, Y.H.; Yoon, J.; Ree, M. Ultralow-k nanoporous organosilicate dielectric films imprinted with dendritic spheres. Nat. Mater. 2005, 4, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiou, C.W.; Lin, Y.C.; Wang, L.; Maeda, R.; Hayakawa, T.; Kuo, S.W. Hydrogen bond interactions mediate hierarchical self-assembly of POSS-containing block copolymers lended with phenolic resin. Macromolecules 2014, 47, 8709–8721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.Y.; Kuo, S.W.; Lee, J.S.; Chang, F.C. Preparations, thermal properties, and Tg increase mechanism of inorganic/organic hybrid polymers based on Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxanes. Macromolecules 2002, 35, 8788–8790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, S.W.; Lee, H.F.; Huang, W.J.; Jeong, K.U.; Chang, F.C. Solid state and solution self-assembly of helical polypeptides tethered to Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxanes. Macromolecules 2009, 42, 1619–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.W.; Tsai, L.W.; Kuo, S.W. Influence of octakis-functionalized polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxanes on the physical properties of their polymer nanocomposites. Polymer 2009, 50, 4876–4887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.Y.; Knight, P.T.; Mather, P.T. Tailored drug release from biodegradable stent coatings based on hybrid polyurethanes. J. Control. Release 2009, 137, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.L. Developments of highly proton-conductive sulfonated polymers for proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Polym. Chem. 2012, 3, 1373–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Harcup, J.; Yee, A.F.; Zhu, Q.; Laine, R.M. Organic/inorganic hybrid composites from cubic silsesquioxanes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 11420–11430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.C.; Choi, J.; Tamaki, R.; Laine, R.M. Synthesis of amino-containing oligophenylsilsesquioxanes. Polymer 2006, 46, 4514–4524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Striolo, A.; McCabe, C.; Cummings, P.T. Organic-inorganic telechelic molecules: Solution properties from simulations. J. Chem. Phys. 2006, 125, 104904–104911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Xu, R.W.; Yu, D.S. A novel and facile method for the synthesis of octa(aminophenyl)silsesquioxane and its nanocomposites with bismaleimide-diamine resin. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 103, 1004–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pescarmona, P.P.; Waal, J.C.; Maxwell, I.E.; Maschmeyer, T. A New, efficient route to titanium-Silsesquioxane oxidation catalysts developed by using high-speed experimentation techniques. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2001, 40, 740–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pescarmona, P.P.; Maschmeyer, T. Oligomeric silsesquioxanes: synthesis, characterization and selected applications. Aust. J. Chem. 2001, 54, 583–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.Y.; Yang, B.H.; Gao, X.Y.; Li, C.; Guang, S.Y. Synthesis and characterization of organic–inorganic hybrid polymers with a well-defined structure from diamines and epoxy-functionalized polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxanes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 101, 3730–3735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gravel, M.C.; Zhang, C.; Dinderman, M.; Laine, R.M. Octa(3-chloroammoniumpropyl) octasilsesquioxane. Appl. Organometal. Chem. 1999, 13, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, W.; Wenjie, D.; Yixian, W.; Riwei, Y.; Dingsheng, Y. Synthesis and characterizations of a latent polyhedral oligomeric silsequioxane-containing catalyst and its application in polybenzoxazine resin. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 126, 150–155. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q.; Xu, R.; Zhang, J.; Yu, D. Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxane (POSS) nanoscale reinforcement of thermosetting resin from benzoxazine and bisoxazoline. Macromol. Rapid. Commun. 2005, 26, 1878–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiou, C.W.; Lin, Y.C.; Wang, L.; Hirano, C.; Suzuki, Y.; Hayakawa, T.; Kuo, S.W. Strong screening effect of Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxanes (POSS) nanoparticles on hydrogen onded polymer blends. Polymers 2014, 6, 926–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.F.; Kuo, S.W.; Lin, F.J.; Huang, W.J.; Wang, C.F.; Chen, W.Y.; Chang, F.C. Influence of PMMA-chain-end tethered polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxanes on the miscibility and specific interaction with phenolic blends. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.H.; Wang, J.H.; Chang, F.C.; Kuo, S.W. Star block copolymers through nitroxide-mediated radical polymerization from Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxane (POSS) core. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2010, 211, 1339–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, M.G.; Hsu, K.C.; Hong, J.L.; Kuo, S.W. Unexpected fluorescence from maleimide-containing polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxanes: nanoparticle and sequence distribution analyses of polystyrene-based alternating copolymers. Polym. Chem. 2016, 7, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.J.; Kuo, S.W.; Su, Y.C.; Chen, J.K.; Tu, C.W.; Chang, F.C. Syntheses, thermal properties, and phase morphologies of novel benzoxazines functionalized with polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane (POSS) nanocomposites. Polymer 2004, 45, 6321–6331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.J.; Kuo, S.W.; Huang, C.F.; Chang, F.C. Synthesis and characterization of polybenzoxazine networks nanocomposites containing multifunctional polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane (POSS). Polymer 2006, 4, 4378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.J.; Huang, J.M.; Kuo, S.W.; Chen, J.K.; Chang, F.C. Synthesis and characterizations of a vinyl-terminated benzoxazine monomer and its blending with polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane (POSS). Polymer 2005, 46, 2320–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.C.; Kuo, S.W. Synthesis and characterization of polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane (POSS) with multifunctional benzoxazine groups through click chemistry. Polymer 2010, 51, 3948–3955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Zhuang, Q.; Liu, X.; Yang, G.; Cai, R.; Han, Z. A new benzoxazine containing benzoxazole-functionalized Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxane and the corresponding polybenzoxazine nanocomposites. Macromolecules 2013, 46, 2696–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.W.; Kuo, S.W. High-performance polybenzoxazine nanocomposites containing multifunctional POSS cores presenting vinyl-terminated benzoxazine groups. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2010, 211, 2301–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Periyasamy, T.; Asrafali, S.P.; Muthusamy, S. New benzoxazines containing polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane from eugenol, guaiacol and vanillin. New. J. Chem. 2015, 39, 1691–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.S.; Ariraman, M.; Alagar, M. Design of lamellar structured POSS/BPZ polybenzoxazine nanocomposites as a novel class of ultra-low-k dielectric materials. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 19127–19136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haung, K.W.; Kuo, S.W. High-performance nanocomposites derived from allyl-terminated benzoxazine and octakis (propylglycidyl ether) polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane. Polym. Comp. 2011, 32, 1086–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zheng, S. Inorganic–organic nanocomposites of polybenzoxazine with octa(propylglycidyl ether) polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane. J. Polym. Sci. Part. A Polym. Chem. 2006, 44, 1168–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvi, M.; Devaraju, S.; Vengatesan, M.R.; Go, J.S.; Kumar, M.; Alagar, M. The effect of UV radiation on polybenzoxazine/epoxy/OG-POSS nanocomposites. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 8238–8244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.S.; Alagar, M. Dielectric and thermal behaviors of POSS reinforced polyurethane based polybenzoxazine nanocomposites. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 33008–33015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.H.; Huang, K.W.; Chiou, C.W.; Kuo, S.W. Complementary multiple hydrogen bonding interactions induce the self-assembly of supramolecular structures from heteronucleobase-functionalized benzoxazine and Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxane nanoparticles. Macromolecules 2012, 45, 9020–9028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, H.K.; Hsieh, C.C.; Mohamed, G.M.; Zhu, C.Y.; Kuo, S.W. Ternary polybenzoxazine/POSS/SWCNT hybrid nanocomposites stabilized through supramolecular interactions. Soft Matter 2016, 12, 1847–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





















© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mohamed, M.G.; Kuo, S.-W. Polybenzoxazine/Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxane (POSS) Nanocomposites. Polymers 2016, 8, 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8060225
Mohamed MG, Kuo S-W. Polybenzoxazine/Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxane (POSS) Nanocomposites. Polymers. 2016; 8(6):225. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8060225
Chicago/Turabian StyleMohamed, Mohamed Gamal, and Shiao-Wei Kuo. 2016. "Polybenzoxazine/Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxane (POSS) Nanocomposites" Polymers 8, no. 6: 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8060225
APA StyleMohamed, M. G., & Kuo, S.-W. (2016). Polybenzoxazine/Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxane (POSS) Nanocomposites. Polymers, 8(6), 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8060225