Nanoindentation Investigation of Temperature Effects on the Mechanical Properties of Nafion® 117
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Experiments
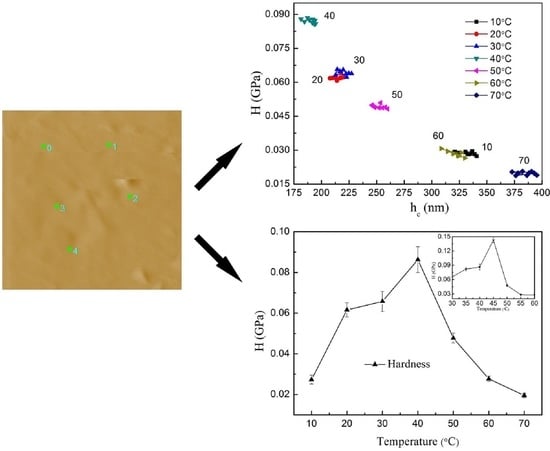
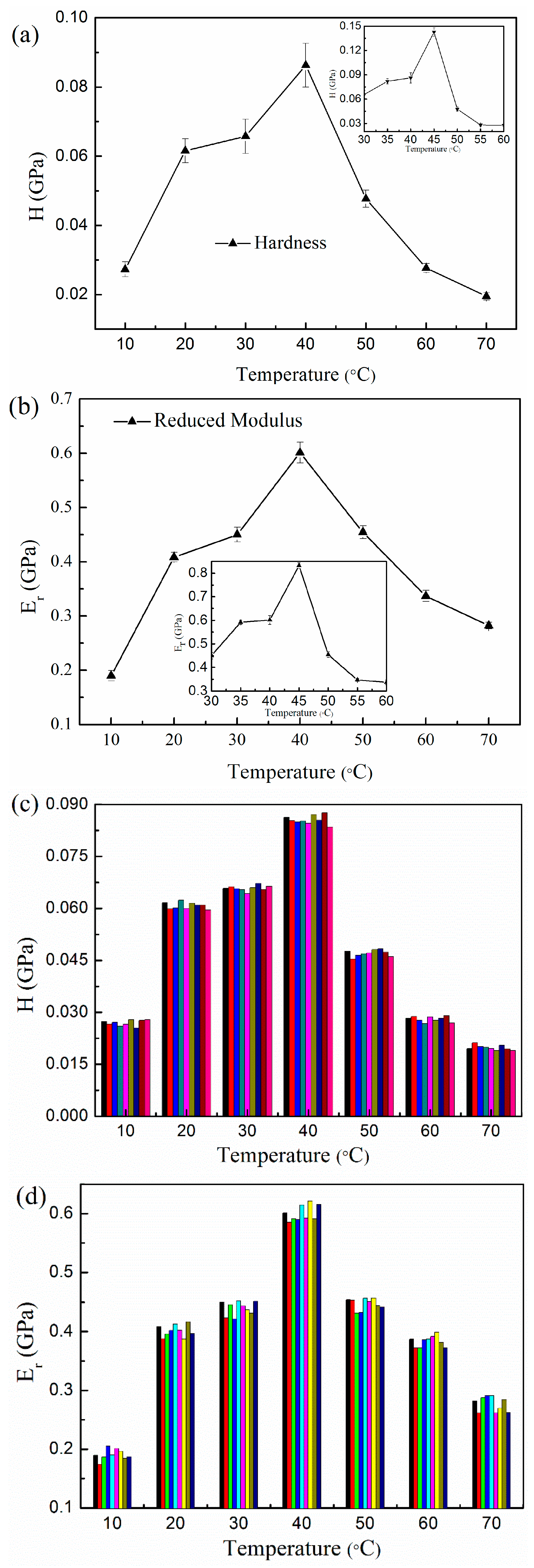
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Borup, R.; Meyers, J.; Pivovar, B.; Kim, Y.S.; Mukundan, R.; Garland, N.; Myers, D.; Wilson, M.; Garzon, F.; Wood, D.; et al. Scientific aspects of polymer electrolyte fuel cell durability and degradation. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 3904–3951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauritz, K.A.; Moore, R.B. State of understanding of Nafion. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 4535–4585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khattra, N.S.; Santare, M.H.; Karlsson, A.M.; Schmiedel, T.; Busby, F.C. Effect of water transport on swelling and stresses in PFSA membranes. Fuel Cells 2015, 15, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesan, S.V.; Lim, C.; Holdcroft, S.; Kjeang, E. Progression in the morphology of fuel cell membranes upon conjoint chemical and mechanical degradation. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2016, 163, F637–F643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alavijeh, A.S.; Goulet, M.A.; Khorasany, R.M.H.; Ghataurah, J.; Lim, C.; Lauritzen, M.; Kjeang, E.; Wang, G.G.; Rajapakse, R.K.N.D. Decay in mechanical properties of catalyst coated membranes subjected to combined chemical and mechanical membrane degradation. Fuel Cells 2015, 15, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, K.A.; Shin, J.W.; Eastman, S.A.; Rowe, B.W.; Kim, S.; Kusoglu, A.; Yager, K.G.; Stafford, G.R. In situ method for measuring the mechanical properties of Nafion thin films during hydration cycles. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2015, 7, 17874–17883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Karlsson, A.M.; Santare, M.H.; Gilbert, M.; Cleghorn, S.; Johnson, W.B. An experimental investigation of humidity and temperature effects on the mechanical properties of perfluorosulfonic acid membrane. Mater. Sci. Eng. A Struct. 2006, 425, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Kusoglu, A.; Karlsson, A.M.; Santare, M.H.; Cleghorn, S.; Johnson, W.B. Mechanical properties of a reinforced composite polymer electrolyte membrane and its simulated performance in PEM fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2008, 175, 817–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorasany, R.M.H.; Alavijeh, A.S.; Kjeang, E.; Wang, G.G.; Rajapakse, R.K.N.D. Mechanical degradation of fuel cell membranes under fatigue fracture tests. J. Power Sources 2015, 214, 1208–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, F.; Denneler, S.; Willert-Porada, M. Influence of temperature and humidity on the mechanical properties of Nafion® 117 polymer electrolyte membrane. J. Polym. Sci. Polym. Phys. 2005, 43, 786–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusoglu, A.; Savagatrup, S.; Clark, K.T.; Weber, A.Z. Role of mechanical factors in controlling the structure-function relationship of PFSA ionomers. Macromolecules 2012, 45, 7467–7476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Lugo, M.; Santare, M.H.; Karlsson, A.M.; Busby, F.C.; Walsh, P. An experimental investigation of strain rate, temperature and humidity effects on the mechanical behavior of a perfluorosulfonic acid membrane. J. Power Sources 2012, 214, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khattra, N.S.; Lu, Z.; Karlsson, A.M.; Santare, M.H.; Busby, F.C.; Schmiedel, T. Time-dependent mechanical response of a composite PFSA membrane. J. Power Sources 2013, 228, 256–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khattra, N.S.; Karlsson, A.M.; Santare, M.H.; Walsh, P.; Busby, F.C. Effect of time-dependent material properties on the mechanical behavior of PFSA membranes subjected to humidity cycling. J. Power Sources 2012, 214, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casciola, M.; Capitani, D.; Comite, A.; Donnadio, A.; Frittella, V.; Pica, M.; Sganappa, M.; Varzi, A. Nafion–zirconium phosphate nanocomposite membranes with high filler loadings: Conductivity and mechanical properties. Fuel Cells 2008, 8, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casciola, M.; Capitani, D.; Donnadio, A.; Frittella, V.; Pica, M.; Sganappa, M. Preparation, proton conductivity and mechanical properties of Nafion 117-Zirconium Phosphate Sulphophenylphosphonate composite membranes. Fuel Cells 2009, 9, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colinart, T.; Perrin, J.C.; Moyne, C. Application of a micro/macro-homogenization procedure to the investigation of the mechanical behavior of ionomer membranes for fuel cells. J. Polym. Sci. Polym. Phys. 2014, 52, 1496–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solasi, R.; Zou, Y.; Huang, X.; Reifsnider, K.; Condit, D. On mechanical behavior and in-plane modeling of constrained PEM fuel cell membranes subjected to hydration and temperature cycles. J. Power Sources 2007, 167, 366–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theiler, A.; Karpenko-Jereb, L. Modelling of the mechanical durability of constrained Nafion membrane under humidity cycling. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2015, 40, 9773–9782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, W.C.; Pharr, G.M. An improved technique for mining hardness and elastic modulus using load and displacement sensing indentation experiments. J. Mater. Res. 1992, 7, 1564–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díez-Pascual, A.M.; Gómez-Fatou, M.A.; Ania, F.; Flores, A. Nanoindentation in polymer nanocomposites. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2015, 67, 1–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.C.; Jones, D.C.; Tandon, G.P.; Putthanarat, S.; Schoeppner, G.A. High temperature nanoindentation of PMR-15 polyimide. Exp. Mech. 2010, 50, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Leng, J. Shape memory properties of electrospun Nafion nanofibers. Fibers Polym. 2014, 15, 534–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, W.; Cheng, Y.T.; Grummon, D.S. Recovery of microindents in a nickel–titanium shape-memory alloy: A “self-healing” effect. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2002, 80, 3310–3312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shastry, V.V.; Ramamurty, U. Simultaneous measurement of mechanical and electrical contact resistances during nanoindentation of NiTi shape memory alloys. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 5119–5129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.C.; Fulcher, J.T.; Tandon, G.P.; Foster, D.C.; Baur, J.W. Microscale thermomechanical characterization of environmentally conditioned shape memory polymers. Polym. Test. 2011, 30, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Sun, Q.P.; Zhao, Y.P.; Yu, T.X. Depth dependence of nanohardness in a CuAlNi single crystal shape memory alloy. Int. J. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2002, 3, 535–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, A.; Yan, W.; Sun, Q.P. Depth dependency of indentation hardness during solid-state phase transition of shape memory alloys. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 99, 021901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soejima, Y.; Motomura, S.; Mitsuhara, M.; Inamura, T.; Nishida, M. In situ scanning electron microscopy study of the thermoelastic martensitic transformation in Ti–Ni shape memory alloy. Acta Mater. 2016, 103, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulcher, J.T.; Lu, Y.C.; Tandon, G.P.; Foster, D.C. Thermomechanical characterization of shape memory polymers using high temperature nanoindentation. Polym. Test. 2010, 29, 544–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kranenburg, J.M.; Tweedie, C.A.; Vliet, K.J.V.; Schubert, U.S. Challenges and progress in high-throughput screening of polymer mechanical properties by indentation. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 3551–3561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.T.; Cheng, C.M. Relationships between initial unloading slope, contact depth, and mechanical properties for conical indentation in linear viscoelastic solids. J. Mater. Res. 2005, 20, 1046–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.T.; Cheng, C.M. Relationships between initial unloading slope, contact depth, and mechanical properties for spherical indentation in linear viscoelastic solids. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2005, 409, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagn, A.H.W.; Tang, B. Viscoelastic effects during unloading in depth-sensing indentation. J. Mater. Res. 2002, 17, 2604–2610. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Ngan, A.H.W. Nanomechanical characterization of soft materials. In Nanomechanical Analysis of High Performance Materials; Tiwari, A., Ed.; Springer Netherlands: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 153–172. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.T.; Ni, W.; Cheng, C.M. Determining the instantaneous modulus of viscoelastic solids using instrumented indentation measurements. J. Mater. Res. 2005, 20, 3061–3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyen, M.L. Sensitivity of polymer nanoindentation creep measurements to experimental variables. Acta Mater. 2007, 55, 3633–3639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Temperature (°C) | 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 | 70 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Depth at peak load, (nm) | 520.5 ± 11.6 | 328.0 ± 9.4 | 342.2 ± 9.4 | 294.2 ± 6.4 | 346.2 ± 8 | 416.5 ± 6.4 | 479.0 ± 9.4 |
| Remnant depth, (nm) | 176.4 ± 9.5 | 85.5 ± 5.1 | 97.4 ± 6.9 | 109.0 ± 4.5 | 162.5 ± 3.7 | 220.0 ± 5.7 | 267.5 ± 12 |
| Depth recovery ratio, | 66.1% | 73.9% | 71.5% | 62.9% | 53.1% | 47.2% | 44% |
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xia, R.; Zhou, H.; Wu, R.; Wu, W.-P. Nanoindentation Investigation of Temperature Effects on the Mechanical Properties of Nafion® 117. Polymers 2016, 8, 344. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8090344
Xia R, Zhou H, Wu R, Wu W-P. Nanoindentation Investigation of Temperature Effects on the Mechanical Properties of Nafion® 117. Polymers. 2016; 8(9):344. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8090344
Chicago/Turabian StyleXia, Re, Hongjian Zhou, Runni Wu, and Wen-Ping Wu. 2016. "Nanoindentation Investigation of Temperature Effects on the Mechanical Properties of Nafion® 117" Polymers 8, no. 9: 344. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8090344
APA StyleXia, R., Zhou, H., Wu, R., & Wu, W.-P. (2016). Nanoindentation Investigation of Temperature Effects on the Mechanical Properties of Nafion® 117. Polymers, 8(9), 344. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8090344