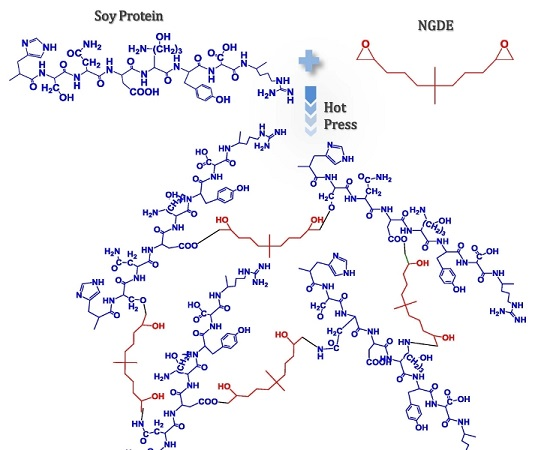
A New Flexible Soy-Based Adhesive Enhanced with Neopentyl Glycol Diglycidyl Ether: Properties and Application
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Soybean Meal-Based Adhesive
2.3. Preparation of the Plywood Sample
2.4. Solids Content Measurement
2.5. Dynamic Viscoelastic Measurement
2.6. Water Resistance Measurement
2.7. Insolubles Measurement
2.8. Cracks Observation of Cured Adhesive
2.9. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy
2.10. Thermogravimetric (TG) Measurement
2.11. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Dynamic Viscoelastic, Solids Content and Insolubles Left Measurement
3.2. FTIR Spectroscopic Analysis
3.3. TGA Analysis
3.4. SEM Analysis
3.5. Crack Observation of Cured Adhesive
3.6. Tensile Shear Strength Measurement
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pizzi, A.; Mittal, K.L. Wood Adhesives; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Sellers, T.J. Wood adhesive innovations and applications in north america. For. Prod. J. 2001, 51, 12–22. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, D.-B.; Li, G.-Y.; Qin, T.-F.; Chu, F.-X. Synthesis and structure characterization of phenol-urea-formaldehyde resins in the presence of magnesium oxide as catalyst. Polymers 2014, 6, 2221–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Luo, J.L.; Yuan, C.; Zhang, W.; Li, J.Z.; Gao, Q.; Chen, H. An eco-friendly wood adhesive from soy protein and lignin: Performance properties. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 100849–100855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzi, A. Advanced Wood Adhesives Technology; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Wool, R.; Sun, X.S. Bio-Based Polymers and Composites; Academic Press: Burlington, MA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Jahanshahi, S.; Pizzi, A.; Abdulkhani, A.; Shakeri, A. Analysis and testing of bisphenol a—Free bio-based tannin epoxy-acrylic adhesives. Polymers 2016, 8, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Li, X.; Wang, W. Soy flour adhesive modified with urea, citric acid and boric acid. Pigment Resin Technol. 2010, 39, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordqvist, P.; Khabbaz, F.; Malmström, E. Comparing bond strength and water resistance of alkali-modified soy protein isolate and wheat gluten adhesives. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2010, 30, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Chen, N.; Bian, L.; Fan, M. Development and mechanism characterization of high performance soy-based bio-adhesives. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2012, 34, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero, P.; De la Caba, K. Thermal and mechanical properties of soy protein films processed at different pH by compression. J. Food Eng. 2010, 100, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Li, C.; Li, X.; Luo, J.; Gao, Q.; Li, J. A new soybean meal-based bioadhesive enhanced with 5,5-dimethyl hydantoin polyepoxide for the improved water resistance of plywood. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 62957–62965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaith, B.S.; Jindal, R.; Bhatia, J.K. Morphological and thermal evaluation of soy protein concentrate on graft copolymerization with ethylmethacrylate. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2011, 120, 2183–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, I.; Bhalla, T.; Deepika, N.; Gautam, N. Study of the biodegradation behavior of soy protein-grafted polyethylene by the soil burial method. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 111, 2460–2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzi, A. Recent developments in eco-efficient bio-based adhesives for wood bonding: Opportunities and issues. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2006, 20, 829–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, C.S.; Wang, G.Y.; Wu, D.; Zhu, J.; Liu, X.Q. Synthesis of a bio-based polyamidoamine-epichlorohydrin resin and its application for soy-based adhesives. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2013, 44, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Qin, Z.; Li, C.; Zhang, S.; Li, J. Preparation of wood adhesives based on soybean meal modified with pegda as a crosslinker and viscosity reducer. BioResources 2013, 8, 5380–5391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, G.Y.; Sun, X.S. Soy protein adhesive blends with synthetic latex on wood veneer. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2011, 88, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, H.; Du, G.; Wu, Z.; Xi, X.; Dong, Z. Cross-linked soy-based wood adhesives for plywood. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2014, 50, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Shi, S.Q.; Zhang, S.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Ding, W.; Liang, K.; Wang, J. Soybean meal-based adhesive enhanced by muf resin. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 125, 3676–3681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral-Labat, G.; Pizzi, A.; Goncalves, A.; Celzard, A.; Rigolet, S.; Rocha, G. Environment-friendly soy flour-based resins without formaldehyde. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 108, 624–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Luo, J.; Li, X.; Yi, Z.; Gao, Q.; Li, J. Soybean meal-based wood adhesive enhanced by ethylene glycol diglycidyl ether and diethylenetriamine. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2015, 74, 613–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrusciel, J.J.; Lesniak, E. Modification of epoxy resins with functional silanes, polysiloxanes, silsesquioxanes, silica and silicates. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2015, 41, 67–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Luo, J.; Gao, Q.; Li, J. Effects of heat treatment on wet shear strength of plywood bonded with soybean meal-based adhesive. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2015, 63, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frihart, C.R.; Birkeland, M.J. Soy properties and soy wood adhesives. In Soy-Based Chemicals and Materials; Brentin, R., Ed.; ACS Symposium Series; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2014; pp. 167–192. [Google Scholar]
- Frihart, C.R.; Birkeland, M. Soy products for wood bonding. In Proceedings of the 59th International Convention of Society of Wood Science and Technology, Curitiba, Brazil, 6–10 March 2016.
- Rubinstein, M.; Colby, R. Polymers Physics; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Nishinari, K.; Fang, Y.; Guo, S.; Phillips, G. Soy proteins: A review on composition, aggregation and emulsification. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 39, 301–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tranter, G.E. Protein structure analysis by CD, FTIR, and Raman spectroscopies. In Reference Module in Chemistry, Molecular Sciences and Chemical Engineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hering, J.A.; Haris, P.I. FTIR spectroscopy for analysis of protein secondary structure. In Biological and Biomedical Infrared Spectroscopy; IOS Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 129–167. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, V.; Giacomelli, C.; Soldi, V. Thermal stability of films formed by soy protein isolate-sodium dodecyl sulfate. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2005, 87, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Gao, Q. Investigating the use of peanut meal: A potential new resource for wood adhesives. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 80136–80141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, G.; Woell, S.; Argos, P. Protein thermal stability, hydrogen bonds, and ion pairs. J. Mol. Biol. 1997, 269, 631–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bikerman, J.J. The Science of Adhesive Joints; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Dillard, D. Advances in Structural Adhesive Bonding; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]





| Sample | Adhesive Formulation | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soybean meal flour (g) | Deionized water (g) | Sodium dodecyl sulfate (g) | NGDE (g) | PAE solution (g) | ||
| 0 | SM adhesive | 28 | 72 | – | – | – |
| 1 | SM/SDS adhesive | 28 | 72 | 1 | – | – |
| 2 | SM/SDS/NGDE-2 adhesive | 28 | 72 | 1 | 2 | – |
| 3 | SM/SDS/NGDE-4 adhesive | 28 | 72 | 1 | 4 | – |
| 4 | SM/SDS/NGDE-6 adhesive | 28 | 72 | 1 | 6 | – |
| 5 | SM/SDS/NGDE-8 adhesive | 28 | 72 | 1 | 8 | – |
| 6 | SM/PAE adhesive | 28 | 22 | – | – | 50 |
| 7 | MUF resin | Molar ratio of F/(U+M):1.1; M additon is 8% for the resultant resin | ||||
| Adhesive Sample | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adheisve spread (g/m2) | 260 | 249 | 234 | 220 | 212 | 205 | 208 | 160 |
| Adhesive Sample | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial viscosity (mPa·s) | 35,310 | 138,800 | 20,530 | 19,230 | 13,090 | 8583 | 44,840 | 300 |
| Solids content (%) | 27.0 | 28.1 | 29.9 | 31.7 | 33.0 | 34.2 | 33.7 | 54.2 |
| Insolubles left (%) | 76.3 | 77.5 | 81.7 | 84.3 | 85.8 | 84.7 | 84.4 | 86.1 |
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, J.; Luo, J.; Zhang, J.; Bai, Y.; Gao, Q.; Li, J.; Li, L. A New Flexible Soy-Based Adhesive Enhanced with Neopentyl Glycol Diglycidyl Ether: Properties and Application. Polymers 2016, 8, 346. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8090346
Luo J, Luo J, Zhang J, Bai Y, Gao Q, Li J, Li L. A New Flexible Soy-Based Adhesive Enhanced with Neopentyl Glycol Diglycidyl Ether: Properties and Application. Polymers. 2016; 8(9):346. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8090346
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Jing, Jianlin Luo, Jizhi Zhang, Yuanyuan Bai, Qiang Gao, Jianzhang Li, and Li Li. 2016. "A New Flexible Soy-Based Adhesive Enhanced with Neopentyl Glycol Diglycidyl Ether: Properties and Application" Polymers 8, no. 9: 346. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8090346
APA StyleLuo, J., Luo, J., Zhang, J., Bai, Y., Gao, Q., Li, J., & Li, L. (2016). A New Flexible Soy-Based Adhesive Enhanced with Neopentyl Glycol Diglycidyl Ether: Properties and Application. Polymers, 8(9), 346. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8090346