Unique Halloysite Nanotubes–Polyvinyl Alcohol–Polyvinylpyrrolidone Composite Complemented with Physico–Chemical Characterization
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Procedures of Composite
2.3. Characterization Techniques
3. Results and discussion
3.1. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
3.2. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
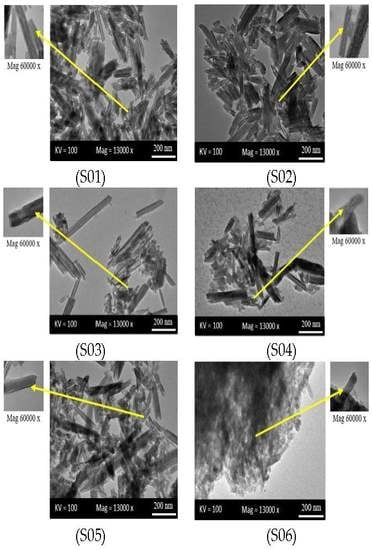
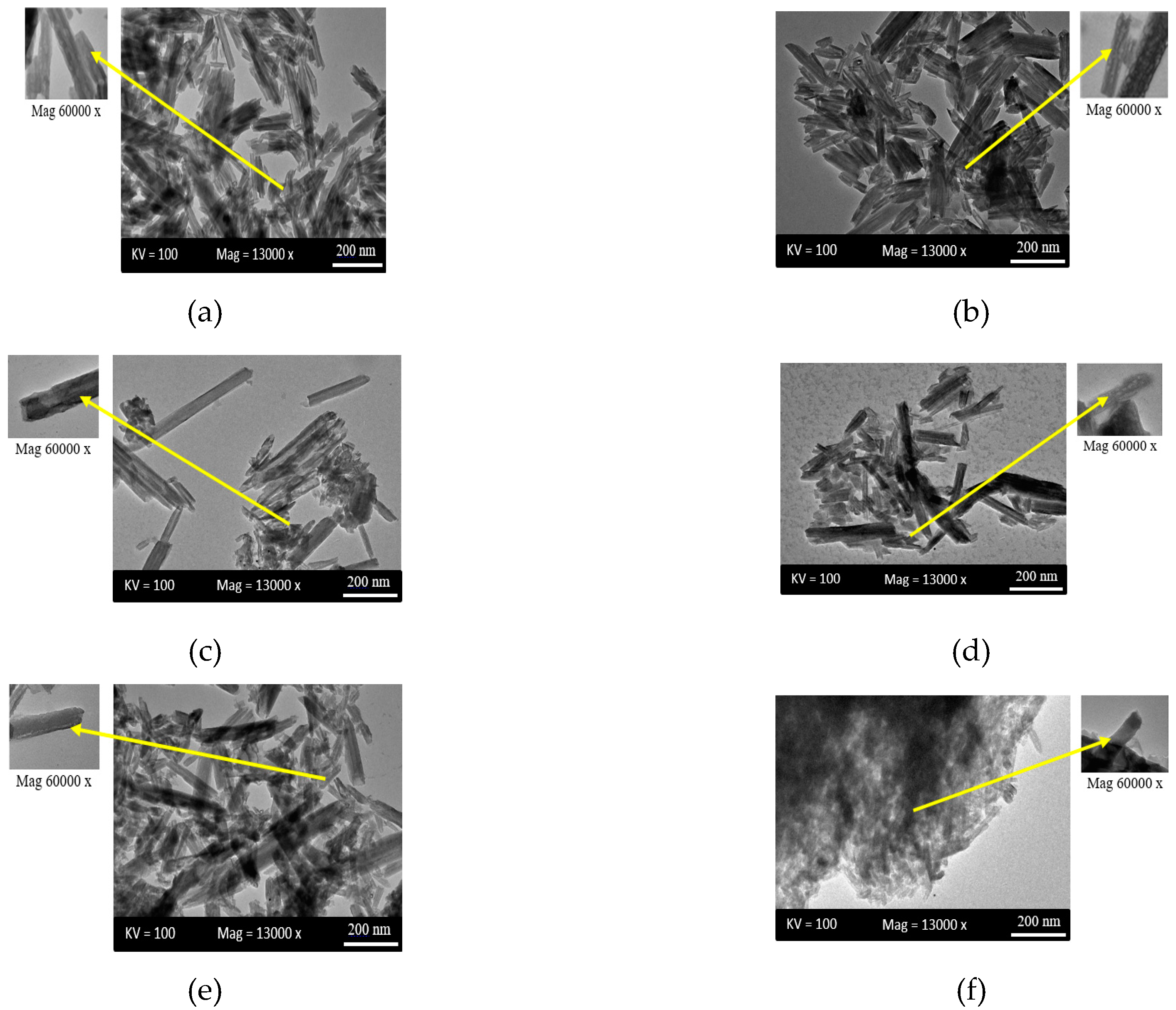
3.3. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
3.4. Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy (FESEM)
3.5. Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET)
3.6. Size Distribution
3.7. Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM)
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cavallaro, G.; Lazzara, G.; Konnova, S.; Fakhrullin, R.; Lvov, Y. Composite films of natural clay nanotubes with cellulose and chitosan. Green Mater. 2014, 2, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, P.; Tan, D.; Annabi-Bergaya, F. Properties and applications of halloysite nanotubes: Recent research advances and future prospects. Appl. Clay Sci. 2015, 112, 75–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaaz, T.S.; Sulong, A.B.; Kadhum, A.A.H.; Al-Amiery, A.A.; Nassir, M.H.; Jaaz, A.H. The Impact of Halloysite on the Thermo-Mechanical Properties of Polymer Composites. Molecules 2017, 22, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaaz, T.S.; Sulong, A.B.; Kadhum, A.A.H. Effect of HNTs Addition in the Injection Moulded Thermoplastic Polyurethane Matrix on the Mechanical and Thermal Properties. Sains Malays. 2016, 45, 1235–1242. [Google Scholar]
- Sulong, A.B.; Gaaz, T.S.; Sahari, J. Mechanical and Physical Properties of Injection Molded Halloysite Nanotubes–Thermoplastic Polyurethane Nanocomposites. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2015, 195, 2748–2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamble, R.; Ghag, M.; Gaikawad, S.; Panda, B.K. Halloysite Nanotubes and Applications: A Review. J. Adv. Sci. Res. 2012, 3, 25–29. [Google Scholar]
- Gaaz, T.S.; Sulong, A.B.; Kadhum, A.A.H.; Ba-Abbad, M.; Al-Amiery, A.A. Enhancement of physical and chemical properties of halloysite nanotubes using sulfuric acid. Wulfenia 2015, 22, 264–284. [Google Scholar]
- Cavallaro, G.; Donato, D.I.; Lazzara, G.; Milioto, S. Films of halloysite nanotubes sandwiched between two layers of biopolymer: from the morphology to the dielectric, thermal, transparency, and wettability properties. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 20491–20498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallaro, G.; Lazzara, G.; Milioto, S. Dispersions of nanoclays of different shapes into aqueous and solid biopolymeric matrices. Extended physicochemical study. Langmuir 2010, 27, 1158–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonifacio, M.A.; Gentile, P.; Ferreira, A.M.; Cometa, S.; De Giglio, E. Insight into halloysite nanotubes-loaded gellan gum hydrogels for soft tissue engineering applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 163, 280–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joussein, E.; Petit, S.; Churchman, J.; Theng, B.; Righi, D.; Delvaux, B. Halloysite clay minerals—A review. Clay Miner. 2005, 40, 383–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, K.; Netravali, A.N. Halloysite nanotube reinforced biodegradable nanocomposites using noncrosslinked and malonic acid crosslinked polyvinyl alcohol. Polym. Compos. 2013, 34, 799–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lun, H.; Ouyang, J.; Yang, H. Enhancing dispersion of halloysite nanotubes via chemical modification. Phys. Chem. Miner. 2014, 41, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zeng, J.; Lv, D.; Gao, J.; Zhang, J.; Bai, S.; Li, R.; Hong, M.; Wu, J. Halloysite nanotube-based electrospun ceramic nanofibre mat: A novel support for zeolite membranes. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2016, 3, 160552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, M.; Guo, B.; Jia, D. Newly emerging applications of halloysite nanotubes: A review. Polym. Int. 2010, 59, 574–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Liu, Q.; Yang, J.; Zhang, J.; Frost, R.L.; Du, X. Infrared spectroscopic study of halloysite–potassium acetate intercalation complex. J. Mol. Struct. 2011, 990, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foo, C.T.; Mahmood, C.S.; Salleh, M.A.M. The study of aluminum loss and consequent phase transformation in heat-treated acid-leached kaolin. Mater. Charact. 2011, 62, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belver, C.; Bañares Muñoz, M.A.; Vicente, M.A. Chemical activation of a kaolinite under acid and alkaline conditions. Chem. Mater. 2002, 14, 2033–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ouyang, J.; Yang, H. Metal oxide nanoparticles deposited onto carbon-coated halloysite nanotubes. Appl. Clay Sci. 2014, 95, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, K. Biobased and Biodegradable Polymer Nanocomposites. Ph.D. Thesis, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY, USA, August 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Cavallaro, G.; Lazzara, G.; Milioto, S. Sustainable nanocomposites based on halloysite nanotubes and pectin/polyethylene glycol blend. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2013, 98, 2529–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belsky, A.; Maiella, P.; Brill, T. Spectroscopy of hydrothermal reactions 13. Kinetics and mechanisms of decarboxylation of acetic acid derivatives at 100–260 °C under 275 bar. J. Phys. Chem. A 1999, 103, 4253–4260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollak, P.; Vouillamoz, R. Fine chemicals. Wiley Online Library: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solaro, R.; Corti, A.; Chiellini, E. Biodegradation of poly (vinyl alcohol) with different molecular weights and degree of hydrolysis. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2000, 11, 873–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiellini, E.; Corti, A.; D’Antone, S.; Solaro, R. Biodegradation of poly (vinyl alcohol) based materials. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2003, 28, 963–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.Y.; Guo, B.; Liu, M.; Liao, R.; Rabie, A.B.M.; Jia, D. Poly(vinyl alcohol)/halloysite nanotubes bionanocomposite films: Properties and in vitro osteoblasts and fibroblasts response. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2010, 93, 1574–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Ng, K.M.; Chan, C.-M.; Sun, G.; Wu, J. High-impact polystyrene/halloysite nanocomposites prepared by emulsion polymerization using sodium dodecyl sulfate as surfactant. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 358, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jian, S.; Ming, S.X. Crosslinked PVA–PS thin-film composite membrane for reverse osmosis. Desalination 1987, 62, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumdar, S.; Adhikari, B. Polyvinyl alcohol: A taste sensing material. Sens. Actuators B 2006, 114, 747–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoo, W.; Ismail, H.; Ariffin, A. Tensile, swelling, and oxidative degradation properties of crosslinked polyvinyl alcohol/chitosan/halloysite nanotube composites. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2013, 62, 390–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaaz, T.S.; Sulong, A.B.; Akhtar, M.N.; Kadhum, A.A.H.; Mohamad, A.B.; Al-Amiery, A.A. Properties and applications of polyvinyl alcohol, halloysite nanotubes and their nanocomposites. Molecules 2015, 20, 22833–22847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seabra, A.B.; De Oliveira, M.G. Poly (vinyl alcohol) and poly (vinyl pyrrolidone) blended films for local nitric oxide release. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 3773–3782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernal, A.; Kuritka, I.; Saha, P. Poly (vinyl alcohol)–poly (vinyl pyrrolidone) blends: Preparation and characterization for a prospective medical application. In Proceedings of the 13th WSEAS International Conference on Mathematical and Computational Methods in Science and Engineering, Sicily, Italy, 3–5 November 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Lewandowska, K. The miscibility of poly (vinyl alcohol)/poly (N-vinylpyrrolidone) blends investigated in dilute solutions and solids. Eur. polym. J. 2005, 41, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T. Surfactant Assisted Dispersion of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes in Polyvinylpyrrolidone Solutions. Master’s Thesis, The University of Western Ontario, Ontario, ON, Canada, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Rajeswari, N.; Selvasekarapandian, S.; Karthikeyan, S.; Sanjeeviraja, C.; Iwai, Y.; Kawamura, J. Structural, vibrational, thermal, and electrical properties of PVA/PVP biodegradable polymer blend electrolyte with CH3COONH4. Ionics 2013, 19, 1105–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, U.M.; Kumar, S.V.; Nagiah, N.; Sivagnanam, U.T. Fabrication of polyvinyl alcohol–polyvinylpyrrolidone blend scaffolds via electrospinning for tissue engineering applications. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2014, 63, 476–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, D.; Mollick, M.M.R.; Bhowmick, B.; Maity, D.; Bain, M.K.; Rana, D.; Mukhopadhyay, A.; Dana, K.; Chattopadhyay, D. Effect of poly (vinyl pyrrolidone) on the morphology and physical properties of poly (vinyl alcohol)/sodium montmorillonite nanocomposite films. Prog. Nat. Sci. 2013, 23, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Song, R.; Zhang, W.; Qi, C.; Zhang, S.; Li, J. Development of Eco-friendly Soy Protein Isolate Films with High Mechanical Properties through HNTs, PVA, and PTGE Synergism Effect. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaaz, T.S.; Sulong, A.B.; Kadhum, A.A.H.; Nassir, M.H.; Al-Amiery, A.A. Impact of sulfuric acid treatment of halloysite on physico-chemic property modification. Materials 2016, 9, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasbakhsh, P.; Ismail, H.; Fauzi, M.A.; Bakar, A.A. EPDM/modified halloysite nanocomposites. Appl. Clay Sci. 2010, 48, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordeepong, S.; Bhongsuwan, D.; Pungrassami, T.; Bhongsuwan, T. Characterization of halloysite from Thung Yai District, Nakhon Si Thammarat Province, in Southern Thailand. Sonklanakarin J. Sci. Technol. 2011, 33, 599. [Google Scholar]
- Abdullayev, E.; Lvov, Y. Halloysite clay nanotubes for controlled release of protective agents. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2011, 11, 10007–10026. [Google Scholar]
- Swapna, V.; Suresh, K.; Saranya, V.; Rahana, M.; Stephen, R. Thermal properties of poly (vinyl alcohol)(PVA)/halloysite nanotubes reinforced nanocomposites. Int. J. Plast. Technol. 2015, 19, 124–136. [Google Scholar]
- Gaaz, T.S.; Sulong, A.B.; Kadhum, A.A.H.; Nassir, M.H.; Al-Amiery, A.A. Surface Improvement of Halloysite Nanotubes. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemifard, S.A.; Ismail, A.F.; Matsuura, T. Mixed matrix membrane incorporated with large pore size halloysite nanotubes (HNT) as filler for gas separation: Experimental. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 359, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Jia, Z.; Jia, D.; Zhou, C. Recent advance in research on halloysite nanotubes–polymer nanocomposite. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 39, 1498–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasbakhsh, P.; How, H.K.; Piao, C.S. Modification of halloysite nanotubes with glycidyl methacrylate. Proceedings of Australian Clay Minerals Society Conference, Selangor, Malaysia, 20 Feburary 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Jiang, G.; Ding, Y.; Wang, Y.; Sun, X.; Wang, X.; Chen, W. Photocatalytic activity of heterostructures based on TiO2 and halloysite nanotubes. ACS Appl. Mater. & Int. 2011, 3, 4154–4158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ouyang, J.; Yang, H. Halloysite nanotubes as hydrogen storage materials. Phys. Chem. Miner. 2014, 41, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kırımlıoğlu, G.Y.; Yazan, Y.; Erol, K.; Ünel, Ç.Ç. Gamma-aminobutyric acid loaded halloysite nanotubes and in vitro-in vivo evaluation for brain delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 495, 816–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Guo, B.; Du, M.; Jia, D. Drying induced aggregation of halloysite nanotubes in polyvinyl alcohol/halloysite nanotubes solution and its effect on properties of composite film. Appl. Phys. A 2007, 88, 391–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullayev, E.; Joshi, A.; Wei, W.; Zhao, Y.; Lvov, Y. Enlargement of halloysite clay nanotube lumen by selective etching of aluminum oxide. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 7216–7226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, C.Y.; Lai, J.Y. Polyvinyl alcohol plasma deposited nylon 4 membrane for hemodialysis. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1993, 27, 983–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Zhou, C. Chitin–natural clay nanotubes hybrid hydrogel. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 58, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akar, S.T.; San, E.; Akar, T. Chitosan–alunite composite: an effective dye remover with high sorption, regeneration and application potential. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 143, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, X.; Liu, J.; Zhang, H. Improving the antifouling property of polyethersulfone ultrafiltration membrane by incorporation of dextran grafted halloysite nanotubes. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 237, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azmi, S.; Razak, S.I.A.; Abdul Kadir, M.R.; Iqbal, N.; Hassan, R.; Nayan, N.H.M.; Wahab, A.H.A.; Shaharuddin, S. Reinforcement of poly (vinyl alcohol) hydrogel with halloysite nanotubes as potential biomedical materials. Soft Mater. 2017, 15, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Chen, D. Study on the nonisothermal crystallization behavior of poly (vinyl alcohol)/attapulgite nanocomposites by DSC analysis. J. Polym. Sci. B 2006, 44, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Chemical Compositions | O:SiO2 | Al:Al2O3 | Si:SiO2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Weight% | 61.19 | 18.11 | 20.11 |
| Chemical Formula | Surface Area | Pore Volume | Density |
|---|---|---|---|
| Al2Si2O5(OH)4·nH2O | 60 m2/g | ~1.25 mL/g | 2540 kg/m3 |
| Materials | Typical Data | Value | Sources |
|---|---|---|---|
| SDS (C12H25NaO4S) | Molecular weight (g/gmol) | 288.4 | BioShop Canada Inc., Burlington, ON, Canada |
| Melting point (°C) | 204–20 | ||
| pH | 9.5 | ||
| Density (g/cm3) | 1.106 | ||
| PVA (C2H4O)n | Molecular weight (g/gmol) | 89–98 | Sigma Aldrich, St. Louis, MI, USA |
| pH | 5–7 | ||
| Viscosity (cpc) | 11.6–15.4 | ||
| Density (g/cm3) | 1.269 | ||
| Melting point (°C) | 200 | ||
| PVP (C6H9NO)n | Molecular weight (g/gmol) | 40 | Sigma Aldrich, St. Louis, MI, USA |
| pH | 3–7 | ||
| Viscosity | 350–600 | ||
| Density (g/cm3) | 1.2 | ||
| Melting point (°C) | 150–180 | ||
| MA (C3H4O4) | Molecular weight (g/gmol) | 104.06 | Sigma Aldrich, St. Louis, MI, USA |
| Purity (%) | 98.5–101.5 |
| Sample Name | Composition by Weight (g) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neat HNTs | Treated HNTs | PVA | PVP | MA | |
| S01 | 1.0 g | - | - | - | - |
| S02 | - | 1.0 g | - | - | - |
| S03 | 1.0 g | - | 0.10 g | 0.10 g | - |
| S04 | - | 1.0 g | 0.10 g | 0.10 g | |
| S05 | 1.0 g | - | 0.10 g | 0.10 g | 0.10 g |
| S06 | - | 1.0 g | 0.10 g | 0.10 g | 0.10 g |
| Sample | S01 | S02 | S03 | S04 | S05 | S06 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OH/O–H–Structure | O–H inner | 3695.3 | 3694.8 | 3695.2 | 3695.4 | 3695.5 | 3695.9 |
| OH–inner | 3624.3 | 3620.4 | 3627.1 | 5624.5 | 3626.7 | 3620.7 | |
| O–H intramolecular | - | - | - | 3430.2 | - | - | |
| C–H stretching and bending | - | - | 2924.2 | - | - | ||
| 2356.6 | - | - | 2357.3 | - | - | ||
| - | 2104.1 | - | 2108.1 | 2114.8 | |||
| - | - | - | - | 2011.5 | |||
| [O–H]: deformation of [COOH] group | 1650.5 | 1641.1 | 1652.5 | 1650.9 | 1650.9 | 1641.4 | |
| (C=O) mono disodium MA | - | - | - | 1444.2 | 1442.2 | ||
| Si–OH | 1120.0 | - | 1121.2 | 1121.1 | - | ||
| Si–O–Si | 1033.3 | 1037.2 | 1030.6 | 1037.4 | 1031.5 | 1038.6 | |
| Al–OH | 911.8 | 912.5 | 910.6 | 912.2 | 910.6 | 911.8 | |
| Al–O–OH | 750.8 | - | 751.0 | 750.9 | - | ||
| - | 796.4 | - | 795.3 | - | 795.5 | ||
| - | 689.6 | - | 690.2 | - | 691.6 | ||
| Sample | S01 | S02 | S03 | S04 | S05 | S06 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BET surface area (m2/g) | 59.1 | 40.1 | 44.4 | 83.8 | 58.2 | 121.1 |
| Total pore volume (cm3/g) | 0.26 | 0.21 | 0.22 | 0.30 | 0.27 | 0.31 |
| Micropore volume (cm3/g) | 0.001 | 0.0001 | 0.0006 | 0.004 | 0.003 | 0.006 |
| Mesopore volume (cm3/g) | 68.0 | 41.3 | 54.4 | 83.7 | 61.1 | 105.3 |
| Mesopore surface area (m2/g) | 0.28 | 0.23 | 0.24 | 0.31 | 0.27 | 0.32 |
| Average pore size (nm) | 167.4 | 304.6 | 176.9 | 136.8 | 156.7 | 121.9 |
| Sample | S01 | S02 | S03 | S04 | S05 | S06 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Roughness (Sq) (nm) | 41.4 | 24.6 | 0.4 | 4.2 | 10.5 | 25.0 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gaaz, T.S.; Kadhum, A.A.H.; Michael, P.K.A.; Al-Amiery, A.A.; Sulong, A.B.; Nassir, M.H.; Jaaz, A.H. Unique Halloysite Nanotubes–Polyvinyl Alcohol–Polyvinylpyrrolidone Composite Complemented with Physico–Chemical Characterization. Polymers 2017, 9, 207. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9060207
Gaaz TS, Kadhum AAH, Michael PKA, Al-Amiery AA, Sulong AB, Nassir MH, Jaaz AH. Unique Halloysite Nanotubes–Polyvinyl Alcohol–Polyvinylpyrrolidone Composite Complemented with Physico–Chemical Characterization. Polymers. 2017; 9(6):207. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9060207
Chicago/Turabian StyleGaaz, Tayser Sumer, Abdul Amir H. Kadhum, Patina Kiah Anak Michael, Ahmed A. Al-Amiery, Abu Bakar Sulong, Mohamed H. Nassir, and Ahed Hameed Jaaz. 2017. "Unique Halloysite Nanotubes–Polyvinyl Alcohol–Polyvinylpyrrolidone Composite Complemented with Physico–Chemical Characterization" Polymers 9, no. 6: 207. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9060207
APA StyleGaaz, T. S., Kadhum, A. A. H., Michael, P. K. A., Al-Amiery, A. A., Sulong, A. B., Nassir, M. H., & Jaaz, A. H. (2017). Unique Halloysite Nanotubes–Polyvinyl Alcohol–Polyvinylpyrrolidone Composite Complemented with Physico–Chemical Characterization. Polymers, 9(6), 207. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9060207