Light-Up of Rhodamine Hydrazide to Generate Emissive Initiator for Polymerization and to Afford Photochromic Polypeptide Metal Complex
Abstract
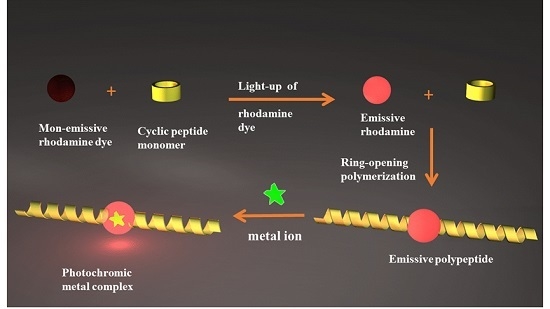
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
Ring-Opening of R-C by the Cyclic Peptide Monomer of PLG–NCA
3. Characterizations of R–PLGx
4. Emissive Properties of R–PLG13 and R–PLG23
5. Metal Chelation
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviated Terminology
| ROP | ring-opening polymerization |
| PLG–NCA | γ-propargyl-l-glutamate N-carboxyanhydride |
| R-C | rhodamine 6G hydrazide |
| AIE | aggregation-induced emission |
| Rh–C | N-phenyl-rhodaminelactam |
| UV | ultraviolet |
| ESIPT | excited-state intramolecular proton transfer |
| DMF | N,N-dimethyl formamide |
| THF | tetrahydrofuran |
| FTIR | Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy |
| NMR | nuclear magnetic resonance |
| MW | molecular weight |
| CD | circular dichroism |
| DLS | dynamic light scattering |
References
- Chan, W.C.W.; Maxwell, D.J.; Gao, X.; Bailey, R.E.; Han, M.; Nie, S. Luminescent quantum dots for multiplexed biological detection and imaging. Anal. Biotechnol. 2002, 13, 40–46. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.N.; Lee, M.H.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, J.S.; Yoon, J. A new trend in rhodamine-based chemosensors: Application of spirolactam ring-opening to sensing ions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 1465–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beija, M.; Afonso, C.A.M.; Martinho, J.M.G. Synthesis and applications of rhodamine derivatives as fluorescent probes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 2410–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutierrez, M.C.; Hortiguela, M.J.; Ferrer, M.L.; del Monte, F. Highly fluorescent rhodamine B nanoparticles entrapped in hybrid glasses. Langmuir 2007, 23, 2175–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stracke, F.; Heupel, M.; Thiel, E. Singlet molecular oxygen photosensitized by rhodamine dyes: correlation with photophysical properties of the sensitizers. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 1999, 126, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Ma, H. Spectroscopic probes with changeable π-conjugated systems. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 8732–8744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Feng, W.; Li, F. Luminescent Chemodosimeters for Bioimaging. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 192–270. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Seidlits, S.K.; Adams, M.M.; Lynch, V.M.; Schmidt, C.E.; Anslyn, E.V.; Shear, J.B. A highly selective low-background fluorescent imaging agent for nitric oxide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 13114–13116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bera, K.; Das, A.K.; Nag, M.; Basak, S. Development of a rhodamine–rhodanine-based fluorescent mercury sensor and its use to monitor real-time uptake and distribution of inorganic mercury in live zebrafish larvae. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 2740–2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonov, L.; Gergov, G.; Petrov, V.; Kubista, M.; Nygren, J. UV–Vis spectroscopic and chemometric study on the aggregation of ionic dyes in water. Talanta 1999, 49, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdes-Aguilera, O.; Neckers, D.C. Aggregation phenomena in xanthene dyes. Acc. Chem. Res. 1989, 22, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraggi, M.; Peretz, P.; Rosenthal, I.; Weinraub, D. Solution properties of dye lasers, rhodamine B in alcohols. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1984, 103, 310–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bujdak, J.; Iyi, N. Molecular aggregation of rhodamine dyes in dispersions of layered silicates: Influence of dye molecular structure and silicate properties. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 2180–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasai, R.; Iyi, N.; Fujita, T.; Arbeloa, F.L.; Martinez, V.M.; Takagi, K.; Itoh, H. Luminescence properties of rhodamine 6G intercalated in surfactant/clay hybrid thin solid films. Langmuir 2004, 20, 4715–4719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dare-Doyen, S.; Doizi, D.; Guilbaud, P.; Djedaini-Pilard, F.; Perly, B.; Millie, P. Dimerization of xanthene dyes in water: experimental studies and molecular dynamic simulations. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 13803–13812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamino, S.; Horio, Y.; Komeda, S.; Minoura, K.; Ichikawa, H.; Horigome, J.; Tatsumi, A.; Kaji, S.; Yamaguchi, T.; Usami, Y.; et al. A new class of rhodamine luminophores: Design, syntheses and aggregation-induced emission enhancement. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 9013–9015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Y.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Tang, B.Z. Aggregation-induced emission: Phenomenon, mechanism and applications. Chem. Commun. 2009, 29, 4332–4353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, D.; Li, K.; Liu, B.; Tang, B.Z. Bioprobes dased on AIE fluorogens. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 2441–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Tang, B.Z. Tetraphenylethene: A versatile AIE building block for the construction of efficient luminescent materials for organic light-emitting diodes. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 23726–23740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, D.; Zhu, D.; Tang, B.Z. Fluorescent bio/chemosensor based on silole and tetraphenylethene luminogens with aggregation-induced emission feature. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 1858–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Tang, B.Z. Aggregation-induced emission. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 5361–5388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, R.; Leung, N.L.C.; Tang, B.Z. AIE macromolecules: syntheses, structures and functionalities. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 4494–4562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Zhao, E.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Tang, B.Z. AIE luminogens: Emission brightened by aggregation. Mater Today 2015, 18, 365–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knauer, K.H.; Gleiter, R. Photochromie von rhodaminderivaten. Angew. Chem. 1977, 89, 116–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willwohl, H.; Wolfrum, J.; Gleiter, R. Kinetics and mechanism of the photochromism of N-phenyl-rhodaminelacta. Laser Chem. 1989, 10, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fölling, J.; Belov, V.; Kunetsyk, R.; Medda, R.; Schönle, A.; Egner, A.; Eggeling, C.; Bossi, M.; Hell, S.E.W.; Eggeling, C.; et al. Photochromic rhodamines provide nanoscopy with optical sectioning. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 6266–6270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belov, V.N.; Bossi, M.L.; Fölling, J.; Boyarskiy, V.P.; Hell, S.W. Rhodamine Spiroamides for multicolor single-molecule switching fluorescent nanoscopy. Chem. Eur. J. 2009, 15, 10762–10776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Dai, Y.; Marriott, G. Optical control of calcium affinity in a spiroamido-rhodamine based calcium chelator. Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 2018–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schäfer, C.G.; Gallei, M.; Zahn, J.; Engelhardt, J.; Hellmann, G.P.; Rehahn, M. Reversible light-, thermo-, and mechano-responsive elastomeric polymer opal films. Chem. Mater. 2013, 25, 2309–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Xiang, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Hu, R.; Tong, A.; Tang, B.Z. Reversible photochromic system based on rhodamine B salicylaldehyde hydrazone metal complex. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 1643–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Dong, Y.; Mi, B.; Tang, Y.; Häussler, M.; Tong, H.; Dong, Y.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Ren, Y.; Sung, H.H.Y.; et al. Structural control of the photoluminescence of silole regioisomers and their utility as sensitive regiodiscriminating chemosensors and efficient electroluminescent Materials. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 10061–10066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Law, C.C.W.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Dong, Y.; Lo, S.M.F.; Williams, I.D.; Zhu, D.; Tang, B.Z. Synthesis, Light Emission, Nanoaggregation, and Restricted Intramolecular Rotation of 1,1-Substituted 2,3,4,5-Tetraphenylsiloles. Chem. Mater. 2003, 15, 1535–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Kim, S.; Yang, Y.K.; Bae, S.; Tae, J. Fluorescent and colorimetric detection of acid vapors by using solid-supported rhodamine hydrazides. Tetrahedron Lett. 2009, 50, 2010–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, J.; Warren, N.J.; Ames, S.P. Synthesis of rhodamine 6G-based compounds for the ATRP synthesis of fluorescently labelled biocompatible polymers. Biomaterials 2011, 12, 2225–2234. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.C.; Kuo, S.W. Hierarchical self-assembly and secondary structures of linear polypeptides graft onto POSS in the side chain through click chemistry. Polym. Chem. 2012, 3, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Hu, M.; Zhan, P.; Peng, X. Energy transfer cassettes based on organic fluorophores: Construction and applications in ratiometric sensing. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Othman, A.B.; Lee, J.W.; Wu, J.S.; Kim, J.S.; Abidi, R.; Thuery, P.; Strub, J.M.; Dorsselaer, A.V.; Vicens, J. Calix[4]arene- based, Hg2+-induced intramolecular fluorescence resonance energy transfer chemosensor. J. Org. Chem. 2007, 72, 7634–7640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, L.; Lin, W.; Xie, Y.; Chen, B.; Zhu, S. Single fluorescent probe responds to H2O2, NO, and H2O2/NO with three different sets of fluorescence signals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 134, 1305–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Xiao, Y.; Qian, X. A ratiometric fluorescent probe based on FRET for imaging Hg2+ ions in living cells. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 8025–8029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Xiao, Y.; Qian, X. Highly efficient energy transfer in the light harvesting system composed of three kinds of boron−dipyrromethene derivatives. Org. Lett. 2008, 10, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majumdar, P.; Zhao, J. 2-(2-Hydroxyphenyl)-benzothiazole (HBT)-rhodamine dyad: acid switchable absorption and fluorescence of excited-state intramolecular proton transfer (ESIPT). J. Phys. Chem. B 2015, 119, 2384–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Lu, H.; Lin, Y.; Cheng, J. Water-soluble polypeptides with elongated, charged side chains adopt ultrastable helical conformations. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 6641–6644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.C.; Kuo, S.W. Hierarchical self-assembly structures of POSS-containing polypeptide block copolymers synthesized using a combination of ATRP, ROP and click chemistry. Polym. Chem. 2012, 3, 882–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.P.; Caughey, W.S. Protein secondary structures in water from second-derivative amide I infrared spectra. Biochemistry 1990, 29, 3303–3308. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, J.; Deming, T.J. Methylated mono- and di(ethylene glycol)-functionalized β-sheet forming polypeptides. Biomacromolecules 2001, 2, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadopoulous, P.; Floudas, G.; Klok, H.A.; Schnell, I.; Pakula, T. Self-assembly and dynamics of poly(γ-benzyl-l-glutamate) peptides. Biomacromolecules 2004, 5, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
















| Sample | MW (Dalton/mol) | Secondary structure (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mn,NMR a | Mn,mass b | Mw,mass b | a-Helix | b-Sheet | Turn | Random coil | |
| R–PLG13 | 1837 a | 2147 b | 2323 b | 36.3 c(13.6) d | 52.4 c(38.6) d | 11.3 c(22.5) d | -(25.4) d |
| R–PLG23 | 3871 a | 3815 b | 4396 b | 83.7 c(49.5) d | 13.4 c(28.3) d | 2.9 c(16.6) d | -(5.5) d |
| Sample | ΦF (%) of R–PLG in DMF/ether a with volumetric ratio of x/y = | ΦF (%) of R–PLG in DMF with concentration of | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10/0 | 9/1 | 7/3 | 5/5 | 4/6 | 3/7 | 2/8 | 10−4 M | 10−3 M | 10−2 M | |
| R–PLG23 | 1.1 | 1.4 | 1.9 | 3.1 | 4.2 | 5.0 | 6.1 | 1.1 | 13.8 | 62.5 |
| R–PLG13 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 1.1 | 1.4 | 1.6 | 1.7 | 1.9 | 0.8 | 2.7 | 46.7 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, J.-Y.; Huang, W.-C.; Huang, P.-Y.; Song, C.-Y.; Hong, J.-L. Light-Up of Rhodamine Hydrazide to Generate Emissive Initiator for Polymerization and to Afford Photochromic Polypeptide Metal Complex. Polymers 2017, 9, 419. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9090419
Gao J-Y, Huang W-C, Huang P-Y, Song C-Y, Hong J-L. Light-Up of Rhodamine Hydrazide to Generate Emissive Initiator for Polymerization and to Afford Photochromic Polypeptide Metal Complex. Polymers. 2017; 9(9):419. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9090419
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Jhen-Yan, Wen-Chih Huang, Pei-Yi Huang, Cheng-Yu Song, and Jin-Long Hong. 2017. "Light-Up of Rhodamine Hydrazide to Generate Emissive Initiator for Polymerization and to Afford Photochromic Polypeptide Metal Complex" Polymers 9, no. 9: 419. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9090419
APA StyleGao, J.-Y., Huang, W.-C., Huang, P.-Y., Song, C.-Y., & Hong, J.-L. (2017). Light-Up of Rhodamine Hydrazide to Generate Emissive Initiator for Polymerization and to Afford Photochromic Polypeptide Metal Complex. Polymers, 9(9), 419. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9090419