Genetic Composition of Korean Ginseng Germplasm by Collection Area and Resource Type
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials
2.2. DNA Extraction
2.3. SSR Genotyping
2.4. Genetic Diversity Analysis
2.5. Population Structure Analysis
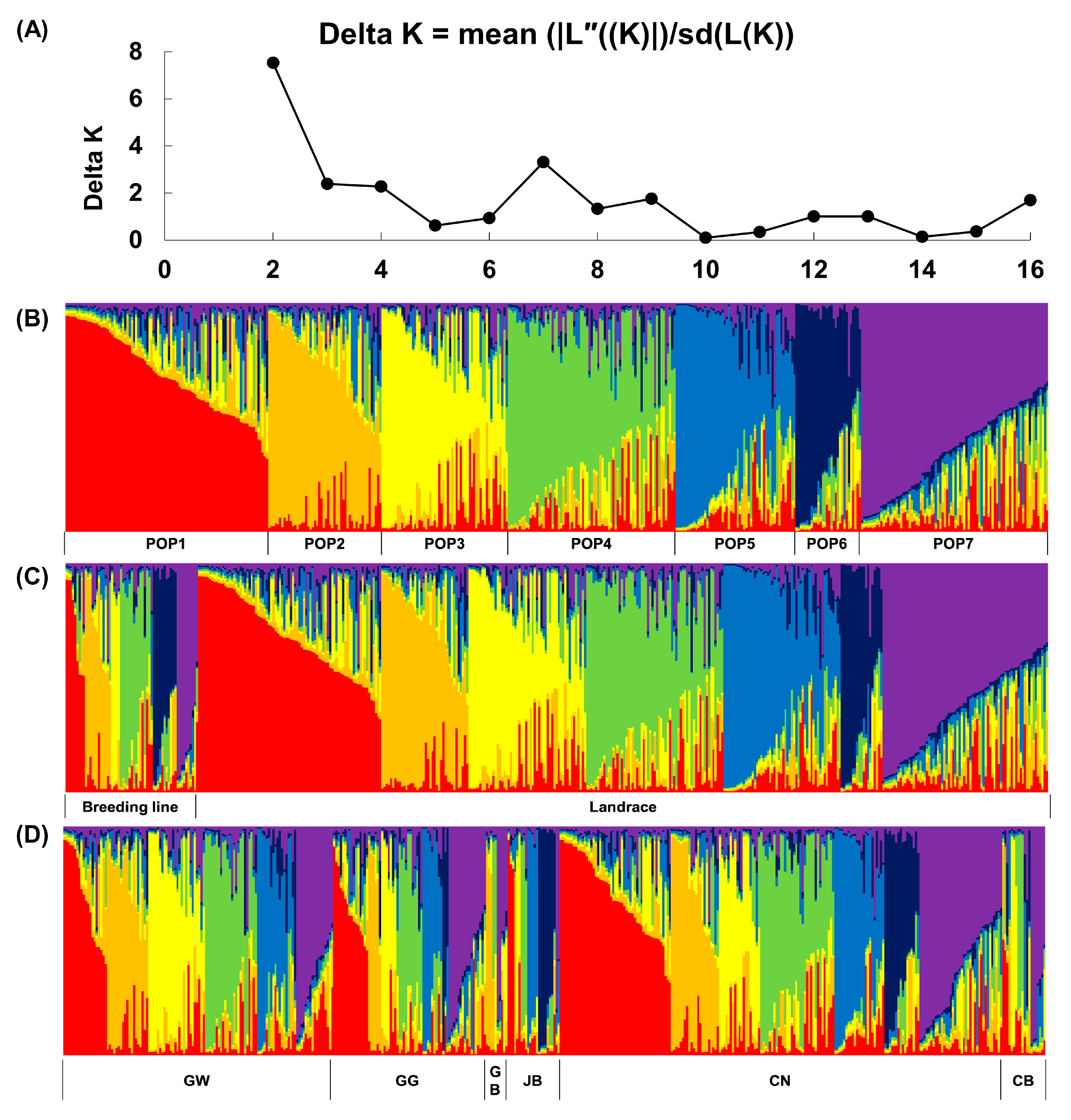
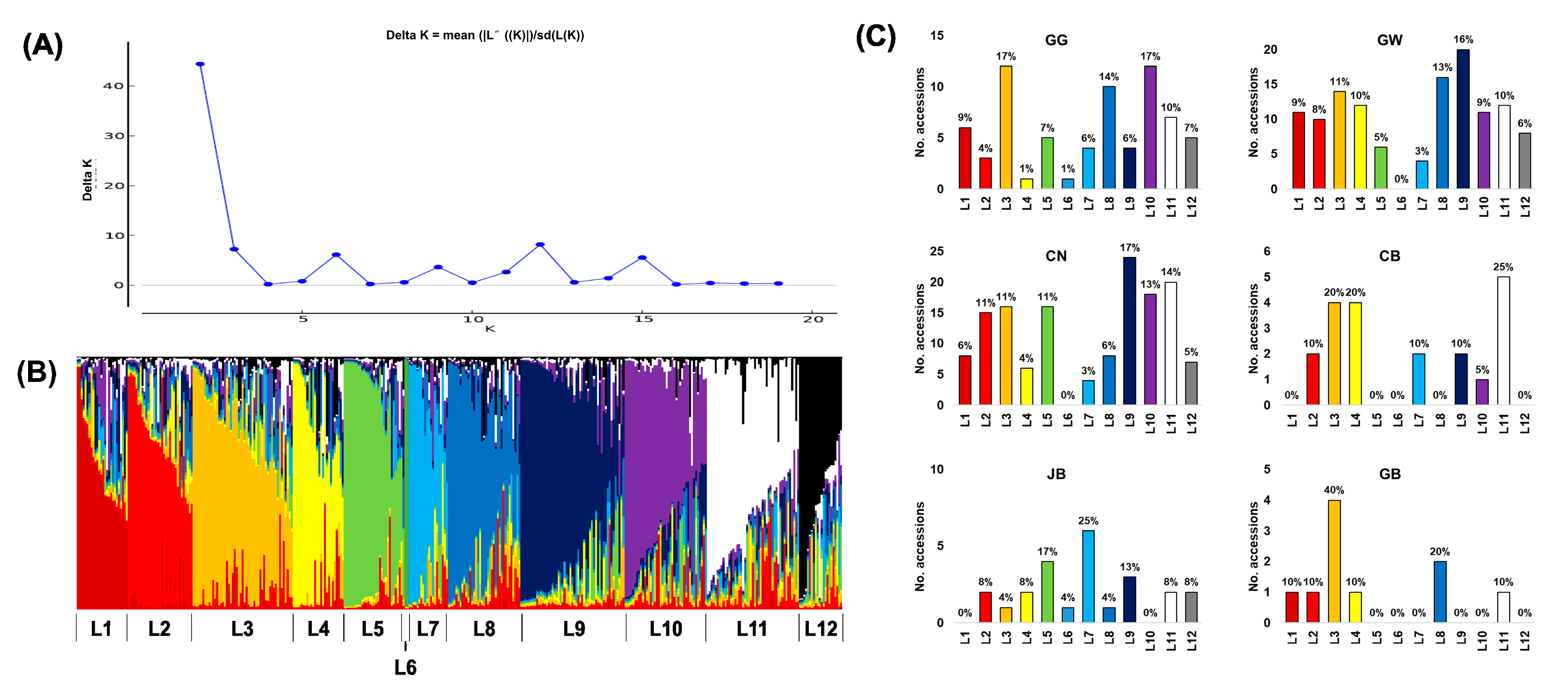
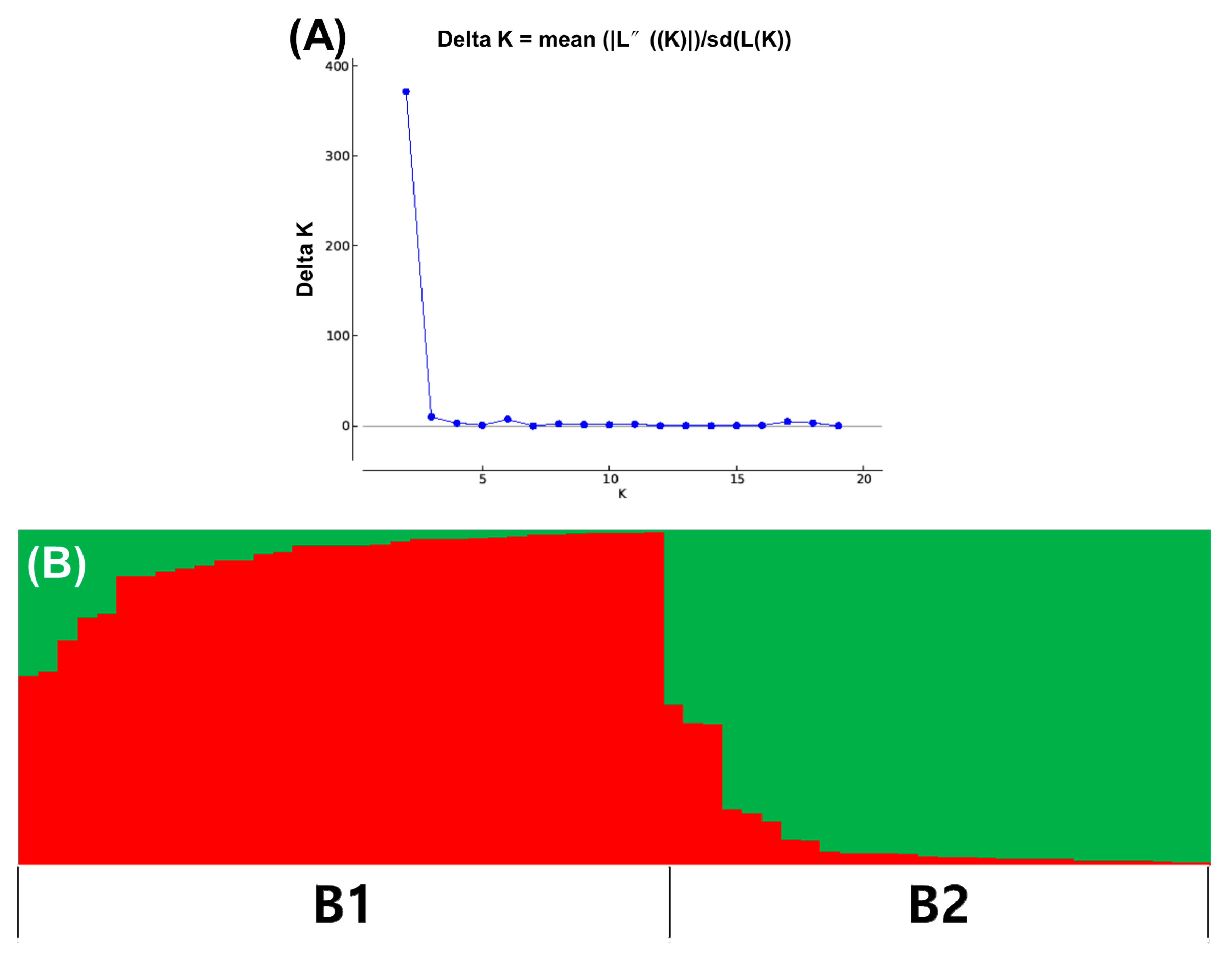
3. Results
3.1. Distribution of Collection Areas in Korean Ginseng Accessions
3.2. Profiling of SSR Markers in Korean Ginseng Accessions
3.3. Population Structure of Korean Ginseng Accessions
3.4. Genetic Diversity and Population Differentiation of Korean Ginseng Accessions
4. Discussion
4.1. Distribution of Korean Ginseng Accessions
4.2. Genetic Differentiation of Korean Ginseng Accessions
4.3. Increasing the Genetic Diversity of the NAC’s Ginseng Germplasm
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Louwaars, N.P. Plant breeding and diversity: A troubled relationship? Euphytica 2018, 214, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van de Wouw, M.; Kik, C.; Hintum, T.; Treuren, R.; Visser, B. Genetic erosion in crops: Concept, research results and challenges. Plant. Genet. Resour. 2010, 8, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hammer, K.; Teklu, Y. Plant Genetic Resources: Selected Issues from Genetic Erosion to Genetic Engineering. J. Agr. Rural Dev. Trop. 2008, 109, 15–59. [Google Scholar]
- Tanksley, S.D.; McCouch, S.R. Seed Banks and Molecular Maps: Unlocking Genetic Potential from the Wild. Science 1997, 277, 1063–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simmonds, N.W. Genetic Resources in Plants—Their Exploration and Conservation; Frankel, O.H., Bennett, E., Eds.; Blackwell Scientific Publications: Oxfordshire, UK, 1970; p. 554. [Google Scholar]
- Upadhyaya, H.; Gowda, C.; Sastry, D.V.S.S.R. Plant genetic resources management: Collection, characterization, conservation and utilization. J. SAT Agric. Res. 2008, 6, 16. [Google Scholar]
- Migdadi, H.; Fayad, M.; Ajloni, M.; Syouf, M.; Brake, M.; Abulila, K.; Tahebsum, Z. The Second Report on the State of the World’s Plant Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture; Commission on Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2010.
- Engelmann, F. 17—Germplasm collection, storage, and conservation. In Plant Biotechnology and Agriculture; Altman, A., Hasegawa, P.M., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2012; pp. 255–267. [Google Scholar]
- NAC Hompage. Available online: https://genebank.rda.go.kr. (accessed on 10 September 2020).
- Van Dan, N.; Ramchiary, N.; Choi, S.R.; Uhm, T.S.; Yang, T.-J.; Ahn, I.-O.; Lim, Y.P. Development and characterization of new microsatellite markers in Panax ginseng (C.A. Meyer) from BAC end sequences. Conserv. Genet. 2010, 11, 1223–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, K.-H.; Kim, Y.-C.; Lee, J.-W.; Cho, I.-H.; Hong, C.-E.; Hyun, D.-Y.H.; Kim, J.-U. Major Achievement and Prospect of Ginseng Breeding in Korea. Kor. J. Breed. Sci. 2020, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, W.; Jang, Y.; Kim, N.-H.; Waminal, N.E.; Kim, Y.C.; Lee, J.W.; Yang, T.-J. Genetic diversity among cultivated and wild Panax ginseng populations revealed by high-resolution microsatellite markers. J. Ginseng Res. 2020, 44, 637–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginseng, K.A.O. Korean Ginseng; Ministry for Food, Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries (MlFAFF) and Korea Association of Ginseng, Ed.; Korea Association of Ginseng: Seoul, Korea, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Proctor, J.T.A.; Lee, J.C.; Lee, S.-S. Ginseng Production in Korea. HortScience 1990, 25, 746–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yeo, I. A study on the origins of ‘Korean Ginseng’. Kor. J. Med. Hist. 2004, 13, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuravlev, Y.; Reunova, G.D.; Kats, I.L.; Muzarok, T.I.; Bondar, A.A. Molecular variation of wild Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer (Araliaceae) by AFLP markers. Chin. Med. 2010, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuravlev, Y.; Koren, O.D.; Reunova, G.I.; Muzarok, T.; Gorpenchenko, T.L.; Kats, I.; Khrolenko, Y. Panax ginseng natural populations: Their past, current state and perspectives. Acta Pharmacologica Sinica 2008, 29, 1127–1136. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shin, B.-K.; Kwon, S.W.; Park, J.H. Chemical diversity of ginseng saponins from Panax ginseng. J. Ginseng Res. 2015, 39, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, S.; Li, J.; Yang, X.-L.; Cheng, Z.; Zhang, W.-J. Genetic diversity and differentiation of cultivated ginseng (Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer) populations in North-east China revealed by inter-simple sequence repeat (ISSR) markers. Genet. Resour. Crop. Evol. 2011, 58, 815–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.-R.; Shi, F.-X.; Li, Y.-L.; Jiang, P.; Jiao, L.; Liu, B.; Li, L.-F. Genome-Wide Variation Patterns Uncover the Origin and Selection in Cultivated Ginseng (Panax ginseng Meyer). Genome Biol. Evol. 2017, 9, 2159–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Choi, K.T. Botanical characteristics, pharmacological effects and medicinal components of Korean Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer. Acta Phamacologica Sinica 2008, 29, 1109–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cho, C.-W.; Kim, Y.-C.; Rhee, Y.K.; Lee, Y.-C.; Kim, K.-T.; Hong, H.-D. Chemical composition characteristics of Korean straight ginseng products. J. Ethn. Foods 2014, 1, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bang, K.-H.; Jo, I.-H.; Chung, J.-W.; Kim, Y.-C.; Lee, J.-W.; Seo, A.Y.; Park, J.-H.; Kim, O.; Hyun, D.-Y.; Kim, D.-H.; et al. Analysis of Genetic Polymorphism of Korean Ginseng Cultivars and Foreign Accessions using SSR Markers. Kor. J. Med. Crop. Sci. 2011, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, D.; Li, Y.-G.; Xu, H.; Sun, S.-Q.; Wang, Z.-T. Differentiation of the root of Cultivated Ginseng, Mountain Cultivated Ginseng and Mountain Wild Ginseng using FT-IR and two-dimensional correlation IR spectroscopy. J. Mol. Struct. 2008, 883–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, H.; Seo, S.M.; Woo, S.Y.; Lee, D.-S. Forest cultivated ginseng in Korea: All cure medicinal plants. J. Med. Plants Res. 2011, 5, 5331–5336. [Google Scholar]
- Ellstrand, N.C.; Elam, D.R. Population Genetic Consequences of Small Population Size: Implications for Plant Conservation. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 1993, 24, 217–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furlan, E.; Stoklosa, J.; Griffiths, J.; Gust, N.; Ellis, R.; Huggins, R.M.; Weeks, A.R. Small population size and extremely low levels of genetic diversity in island populations of the platypus, Ornithorhynchus anatinus. Ecol. Evol. 2012, 2, 844–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramanatha Rao, V.; Hodgkin, T. Genetic diversity and conservation and utilization of plant genetic resources. Plant Cell Tissue Org. Cult. 2002, 68, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.J.; Lee, J.-R.; Sebastin, R.; Cho, G.-T.; Hyun, D.Y. Molecular Genetic Diversity and Population Structure of Ginseng Germplasm in RDA-Genebank: Implications for Breeding and Conservation. Agronomy 2020, 10, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, N.-H.; Choi, H.-I.; Ahn, I.-O.; Yang, T.-J. EST-SSR Marker Sets for Practical Authentication of All Nine Registered Ginseng Cultivars in Korea. J. Ginseng Res. 2012, 36, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Choi, H.-I.; Kim, N.-H.; Kim, J.H.; Choi, B.S.; Ahn, I.-O.; Lee, J.-S.; Yang, T.-J. Development of Reproducible EST-derived SSR Markers and Assessment of Genetic Diversity in Panax ginseng Cultivars and Related Species. J. Ginseng Res. 2011, 35, 399–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kamvar, Z.N.; Tabima, J.F.; Grünwald, N.J. Poppr: An R package for genetic analysis of populations with clonal, partially clonal, and/or sexual reproduction. PeerJ 2014, 2, e281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peakall, R.; Smouse, P.E. GenAlEx 6.5: Genetic analysis in Excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research—An update. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 2537–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pritchard, J.K.; Stephens, M.; Donnelly, P. Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 2000, 155, 945–959. [Google Scholar]
- Earl, D.A.; von Holdt, B.M. STRUCTURE HARVESTER: A website and program for visualizing STRUCTURE output and implementing the Evanno method. Conserv Genet. Resour 2012, 4, 359–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genebank Management System (GMS). Available online: http://genebank.rda.go.kr (accessed on 10 September 2020).
- FAO. Genebank Standards for Plant. Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2013.
- Sung, M.-H. Ginseng Industry changes and policy tasks. In Ginseng Industry Changes and Policy Tasks; Korea Rural Economic Institute: Jeollanam-do, Korea, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- The Korean Society of Wild Ginseng. A study on the Development Suggestions in Mountain Ginseng (Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer) Industry; Forest Service: Daejeon, Korea, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Agriculture Food and Rural Affairs. Ginseng Annual Report; Ministry of Agriculture Food and Rural Affairs: Sejong-si, Korea, 2019.
- Berthaud, J.; Pressoir, G.; Ramírez-Corona, F.; Bellon, M. Farmers Management of Maize Landrace Diversity. A Case Study in Oaxaca and beyond. In Proceedings of the 7th International Symposium on The Biosafety of Genetically Modified Organisms, Beijing, China, 10–16 October 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Park, H. The history of ginseng cultivation in the orient. Acta Horticiltirae 2003, 620, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahrajabian, M.H.; Sun, W.; Cheng, Q. A review of Ginseng species in different regions as a multipurpose herb in traditional Chinese medicine, modern herbology and pharmacological science. J. Med. Plant. Res. 2019, 13, 213–226. [Google Scholar]
- Ellstrand, N.C. Gene Flow by Pollen: Implications for Plant Conservation Genetics. Oikos 1992, 63, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouborg, N.J.; Pertoldi, C.; Loeschcke, V.; Bijlsma, R.; Hedrick, P.W. Conservation genetics in transition to conservation genomics. Trends Genet. 2010, 26, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.R.; Choi, J.E.; Lee, B.Y.; Yu, J.N.; Lim, C.E. Genetic diversity and structure of an endangered medicinal herb: Implications for conservation. AoB PLANTS 2018, 10, ply021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karron, J.D. A comparison of levels of genetic polymorphism and self-compatibility in geographically restricted and widespread plant congeners. Evol. Ecol. 1987, 1, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karron, J.D. Patterns of genetic variation and breeding systems in rare plant species. In Genetics and Conservation of Rare Plants; Falk, D.A., Holsinger, K.E., Eds.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1991; pp. 87–98. [Google Scholar]
- Cole, C. Genetic Variation in Rare and Common Plants. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2003, 34, 213–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horticulture Business Division. 2017 Ginseng Data Sheet; Ministry of Agriculture Food and Rural Affairs: Sejong-si, Korea, 2018.
- NIHHS. Distribution Status of Panax ginseng in China and Comparative Analysis on the Characteristics of Korean and China ginseng; RDA: Wansan-gu, Korea, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Korean Seeds and Variety Service. Available online: www.seed.go.kr (accessed on 10 September 2020).
- Lee, S.-S.; Lee, J.-H.; Ahn, I.-O. Characteristics of new cultivars in Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer. In Proceedings of the Ginseng Society Conference, Daejeon, Korea, 23 May 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Westberg, E.; Ohali, S.; Shevelevich, A.; Fine, P.; Barazani, O. Environmental effects on molecular and phenotypic variation in populations of Eruca sativa across a steep climatic gradient. Ecol. Evol. 2013, 3, 2471–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simberloff, D. The Contribution of Population and Community Biology to Conservation Science. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 1988, 19, 473–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soule, M.E. Thresholds for survival: Maintaining fitness and evolutionary potential. In Conservation Biology: An Evolutionary-Ecological Perspective; Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Ahn, I.-O.; Lee, S.-S.; Lee, J.-H.; Lee, B.-S.; In, J.-G.; Yang, D.-C. Characteristics of Plantlets Redifferentiated from F1 Hybrid between Panax ginseng and Panax quinquefolius. J. Plant. Biotech. 2006, 33, 45–48. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.J.; Silva, J.; Zhang, D.; Shi, J.; Joo, S.C.; Jang, M.G.; Kwon, W.S.; Yang, D.C. Development of interspecies hybrids to increase ginseng biomass and ginsenoside yield. Plant. Cell Rep. 2016, 35, 779–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.Y.; Adhikari, P.B.; Ahn, C.H.; Kim, D.H.; Chang Kim, Y.; Han, J.Y.; Kondeti, S.; Choi, Y.E. High frequency somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration of interspecific ginseng hybrid between Panax ginseng and Panax quinquefolius. J. Ginseng Res. 2019, 43, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, K.T.; Ahn, S.D.; Park, K.J. Biological effects of ethyl methane sulphonate treatment on ginseng seeds. J. Ginseng Res. 1981, 5, 163–169. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.S.; Kim, S.Y.; Jeong, I.Y.; Kim, J.B.; Lee, G.J.; Kang, S.Y.; Kim, W. Improvement of ginsenoside production by Panax ginseng adventitious roots induced by γ-irradiation. Biologia Plantarum 2009, 53, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung Woo, L.; Jo, I.-H.; Kim, J.-U.; Hong, C.E.; Bang, K.-H.; Park, Y.-D. Determination of mutagenic sensitivity to gamma rays in ginseng (Panax ginseng) dehiscent seeds, roots, and somatic embryos. Hortic. Environ. Biotech. 2019, 60, 721–731. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.-Y.; Bae, T.-W.; Boo, K.-H.; Sun, H.-J.; Song, I.-J.; Pham, C.-H.; Ganesan, M.; Yang, D.-H.; Kang, H.-G.; Ko, S.-M.; et al. Ginsenoside Production and Morphological Characterization of Wild Ginseng (Panax ginseng Meyer) Mutant Lines Induced by γ-irradiation ((60)Co) of Adventitious Roots. J. Ginseng Res. 2011, 35, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

| No. Acc | Total Alleles | Na 1 | Ng | H | Ho | GD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Landraces | 390 | 223 | 6.76 ± 5.72 | 16.83 ± 23.14 | 0.92 ± 0.43 | 0.88 ± 0.27 | 0.52 ± 0.16 |
| Breeding lines | 61 | 148 | 4.49 ± 3.97 | 6.18 ± 7.02 | 0.93 ± 0.43 | 0.88 ± 0.30 | 0.52 ± 0.16 |
| Total | 451 | 226 | 6.85 ± 5.82 | 17.79 ± 24.60 | 0.92 ± 0.43 | 0.88 ± 0.27 | 0.52 ± 0.16 |
| Source | df 1 | SS | MS | Est. Var. | % | PhiPT | Nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Collection area of total ginseng accessions | |||||||
| Among Pops. | 5 | 236.102 | 47.220 | 0.487 | 3% | 0.028 | 17.213 |
| Within Pops | 445 | 7466.739 | 16.779 | 16.779 | 97% | (p < 0.001) | |
| Total | 450 | 7702.840 | 17.267 | 100% | |||
| STRUCTURE of total ginseng accessions | |||||||
| Among Pops | 6 | 305.185 | 50.864 | 0.54 | 3% | 0.031 | 15.431 |
| Within Pops | 444 | 7397.655 | 16.661 | 16.661 | 97% | (p < 0.001) | |
| Total | 450 | 7702.84 | 17.201 | 100% | |||
| STRUCTURE of ginseng landraces | |||||||
| Among Pops | 11 | 385.070 | 35.006 | 0.578 | 3% | 0.034 | 14.322 |
| Within Pops | 378 | 6255.419 | 16.549 | 16.549 | 97% | (p < 0.001) | |
| Total | 389 | 6640.490 | 17.126 | 100% | |||
| STRUCTURE of ginseng breeding lines | |||||||
| Among Pops | 1 | 19.859 | 19.859 | 0.178 | 1% | 0.012 | 40.761 |
| Within Pops | 59 | 854.239 | 14.479 | 14.479 | 99% | (p < 0.028) | |
| Total | 60 | 874.098 | 14.656 | 100% | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, K.J.; Sebastin, R.; Kim, S.-H.; Yoo, E.; Lee, S.; Cho, G.-T.; Kang, M.; Hyun, D.Y. Genetic Composition of Korean Ginseng Germplasm by Collection Area and Resource Type. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1643. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10111643
Lee KJ, Sebastin R, Kim S-H, Yoo E, Lee S, Cho G-T, Kang M, Hyun DY. Genetic Composition of Korean Ginseng Germplasm by Collection Area and Resource Type. Agronomy. 2020; 10(11):1643. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10111643
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Kyung Jun, Raveendar Sebastin, Seong-Hoon Kim, Eunae Yoo, Sookyeong Lee, Gyu-Taek Cho, Manjung Kang, and Do Yoon Hyun. 2020. "Genetic Composition of Korean Ginseng Germplasm by Collection Area and Resource Type" Agronomy 10, no. 11: 1643. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10111643
APA StyleLee, K. J., Sebastin, R., Kim, S.-H., Yoo, E., Lee, S., Cho, G.-T., Kang, M., & Hyun, D. Y. (2020). Genetic Composition of Korean Ginseng Germplasm by Collection Area and Resource Type. Agronomy, 10(11), 1643. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10111643






