Assessment of the Genetic Diversity of the Breeding Lines and a Genome Wide Association Study of Three Horticultural Traits Using Worldwide Cucumber (Cucumis spp.) Germplasm Collection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials
2.2. Phenotypic Evaluation and Correlation Analysis
2.3. Genomic DNA Extraction and GBS
2.4. Reference-Based SNP Calling and Construction of the SNP Set
2.5. Population Structure Analysis
2.6. Phylogenetic and the Principal Coordinate Analyses
2.7. Genome-wide Association Study (GWAS) and Candidate Gene Identification
3. Results
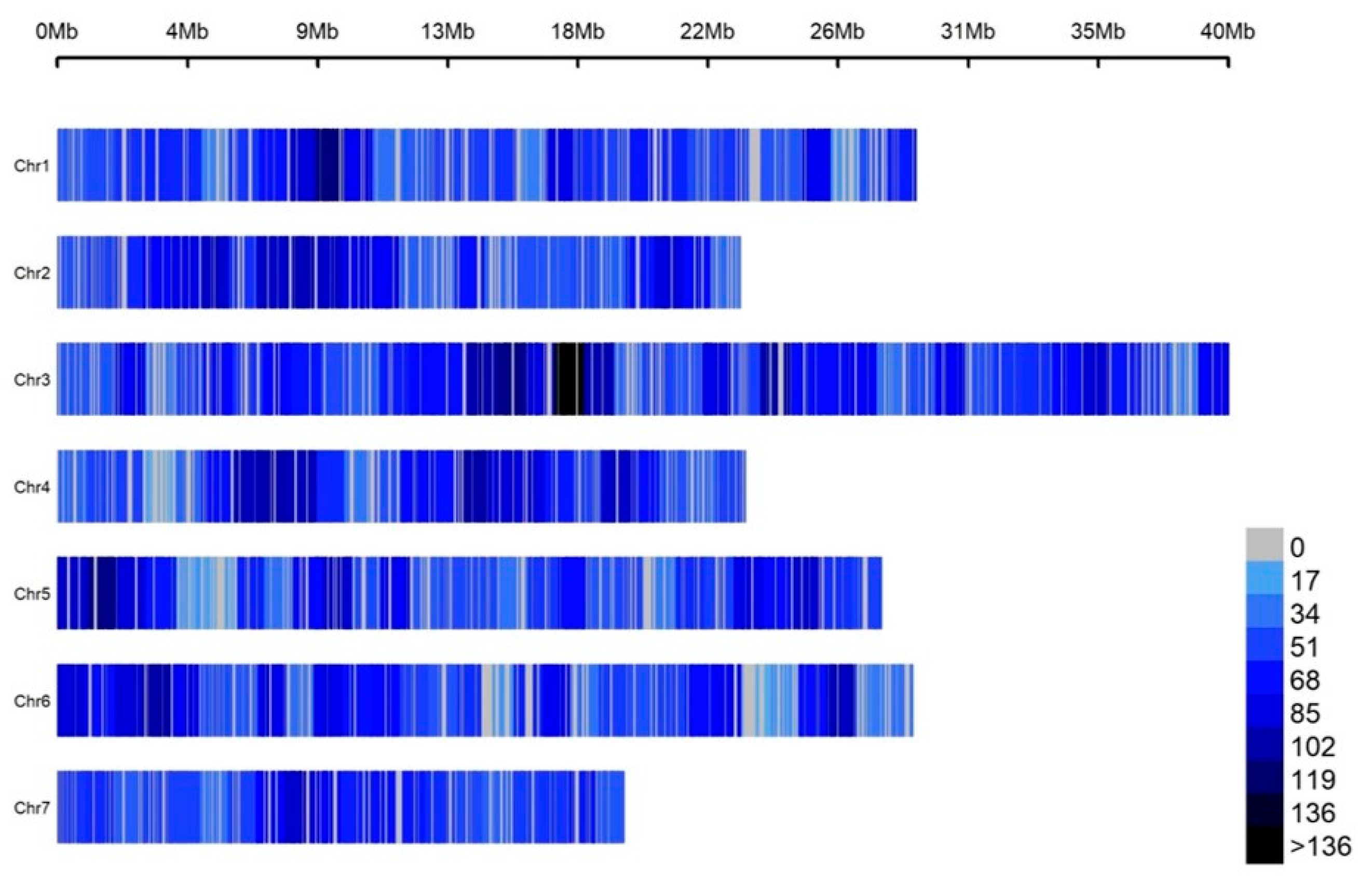
3.1. Genotypes and Genetic Variation of the Cucumber Germplasm Collection
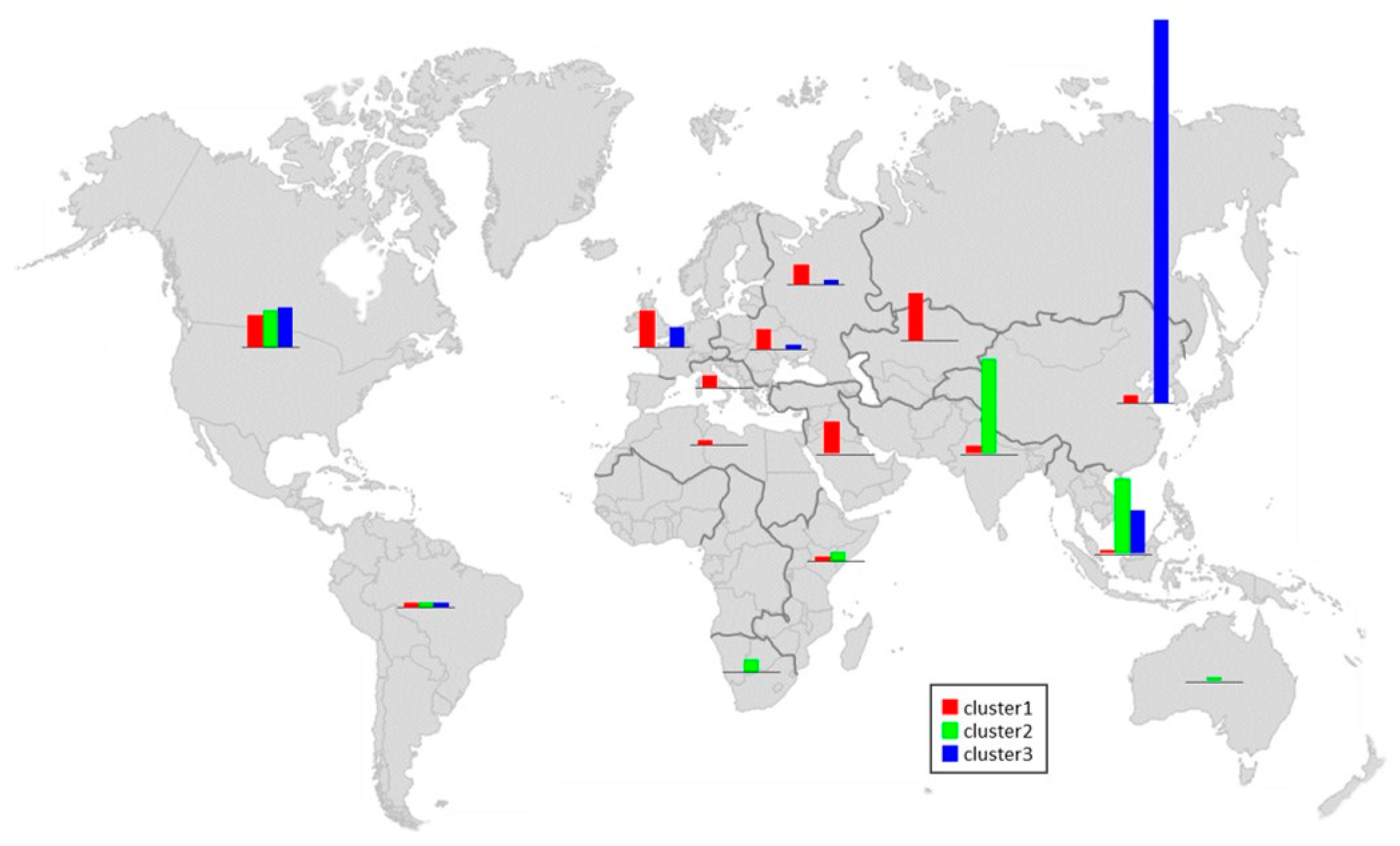
3.2. Population Structure and Genetic Diversity of the Cucumber Germplasm Collection
3.3. Genetic Relatedness among the Population
3.4. Evaluation of Powdery Mildew (PM) Resistance and Horticultural Traits
3.5. GWAS and Effective SNPs Influencing Horticultural Traits of Cucumber
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Che, G.; Zhang, X. Molecular basis of cucumber fruit domestication. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2019, 47, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, N.; Gan, Z.; Nie, J.; Liu, H.; Wang, Z.; Sui, X. Comprehensive Characterization of Fruit Volatiles and Nutritional Quality of Three Cucumber (Cucumis Sativus L.) Genotypes from Different Geographic Groups after Bagging Treatment. Foods 2020, 9, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sebastian, P.; Schaefer, H.; Telford, I.R.H.; Renner, S.S. Cucumber (Cucumis sativus) and melon (C. melo) have numerous wild relatives in Asia and Australia, and the sister species of melon is from Australia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 14269–14273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, L.; Koo, D.H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Luan, F.; Havey, M.J.; Jiang, J.; Weng, Y. Chromosome rearrangements during domestication of cucumber as revealed by high-density genetic mapping and draft genome assembly. Plant J. 2012, 71, 895–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, K.; Ma, Z.; Chen, J.; Weng, Y. Molecular mapping reveals structural rearrangements and quantitative trait loci underlying traits with local adaptation in semi-wild Xishuangbanna Cucumber (Cucumis sativus L. var. xishuangbannanesis Qi et Yuan). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2015, 128, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaut, B.S.; Seymour, D.K.; Liu, Q.; Zhou, Y. Demography and its effects on genomic variation in crop domestication. Nat. Plants 2018, 4, 512–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osipowski, P.; Pawełkowicz, M.; Wojcieszek, M.; Skarzyńska, A.; Przybecki, Z.; Pląder, W. A high-quality cucumber genome assembly enhances computational comparative genomics. Mol. Genet. Genomics 2020, 295, 177–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qi, J.; Liu, X.; Shen, D.; Miao, H.; Xie, B.; Li, X.; Zeng, P.; Wang, S.; Shang, Y.; Gu, X.; et al. A genomic variation map provides insights into the genetic basis of cucumber domestication and diversity. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 1510–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Bao, K.; Reddy, U.K.; Bai, Y.; Hammar, S.A.; Jiao, C.; Wehner, T.C.; Ramírez-Madera, A.O.; Weng, Y.; Grumet, R.; et al. The USDA cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) collection: Genetic diversity, population structure, genome-wide association studies, and core collection development. Hortic. Res. 2018, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renner, S.S. A valid name for the Xishuangbanna gourd, a cucumber with carotene-rich fruits. PhytoKeys 2017, 94, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, S.; Li, R.; Zhang, Z.; Li, L.; Gu, X.; Fan, W.; Lucas, W.J.; Wang, X.; Xie, B.; Ni, P.; et al. The genome of the cucumber, Cucumis sativus L. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 1275–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Q.; Li, H.; Huang, W.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, S.; Ruan, J.; Huang, S.; Zhang, Z. A chromosome-scale genome assembly of cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). Gigascience 2019, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cavagnaro, P.F.; Senalik, D.A.; Yang, L.; Simon, P.W.; Harkins, T.T.; Kodira, C.D.; Huang, S.; Weng, Y. Genome-wide characterization of simple sequence repeats in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). BMC Genom. 2010, 11, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rubinstein, M.; Katzenellenbogen, M.; Eshed, R.; Rozen, A.; Katzir, N.; Colle, M.; Yang, L.; Grumet, R.; Weng, Y.; Sherman, A.; et al. Ultrahigh-Density Linkage Map for Cultivated Cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) Using a Single-Nucleotide Polymorphism Genotyping Array. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, P.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, L.; Chen, L.; Zhou, S. Mining candidate genes associated with powdery mildew resistance in cucumber via super-BSA by specific length amplified fragment (SLAF) sequencing. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; VandenLangenberg, K.; Wen, C.; Wehner, T.C.; Weng, Y. QTL mapping of downy and powdery mildew resistances in PI 197088 cucumber with genotyping-by-sequencing in RIL population. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2018, 131, 597–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Yu, G.; Wang, X.; Meng, X.; Lv, C. Genetics and Resistance Mechanism of the Cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) Against Powdery Mildew. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakata, Y.; Kubo, N.; Morishita, M.; Kitadani, E.; Sugiyama, M.; Hirai, M. QTL analysis of powdery mildew resistance in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2006, 112, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukino, N.; Yoshioka, Y.; Sugiyama, M.; Sakata, Y.; Matsumoto, S. Identification and validation of powdery mildew (Podosphaera xanthii)-resistant loci in recombinant inbred lines of cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). Mol. Breed. 2013, 32, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Li, Y.; Pandey, S.; Yandell, B.S.; Pathak, M.; Weng, Y. QTL mapping of powdery mildew resistance in WI 2757 cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2013, 126, 2149–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, J.; He, H.; Peng, J.; Yang, X.; Bie, B.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Y.; Si, L.; Pan, J.S.; Cai, R. Identification and fine mapping of pm 5.1: A recessive gene for powdery mildew resistance in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). Mol. Breed. 2015, 35, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshioka, Y.; Sakata, Y.; Sugiyama, M.; Fukino, N. Identification of quantitative trait loci for downy mildew resistance in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). Euphytica 2014, 198, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.N.; Miao, H.; Lu, H.W.; Cui, J.Y.; Tian, G.L.; Wehner, T.C.; Gu, X.F.; Zhang, S.P. Molecular mapping and candidate gene analysis for resistance to powdery mildew in Cucumis sativus Stem. Genet. Mol. Res. 2017, 16, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Yu, T.; Xu, R.; Shi, Y.; Lin, X.; Xu, Q.; Qi, X.; Weng, Y.; Chen, X. Fine mapping of a dominantly inherited powdery mildew resistance major-effect QTL, pm 1.1, in cucumber identifies a 41.1 kb region containing two tandemly arrayed cysteine-rich receptor-like protein kinase genes. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2016, 129, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Tan, J.; Wu, Z.; VandenLangenberg, K.; Wehner, T.C.; Wen, C.; Zheng, X.; Owens, K.; Thornton, A.; Bang, H.H.; et al. STAYGREEN, STAY HEALTHY: A loss-of-susceptibility mutation in the STAYGREEN gene provides durable, broad-spectrum disease resistances for over 50 years of US cucumber production. New Phytol. 2019, 221, 415–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sheng, Y.; Pan, Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, L.; Weng, Y. Quantitative trait loci for fruit size and flowering time-related traits under domestication and diversifying selection in cucumber (Cucumis sativus). Plant Breed. 2020, 139, 176–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Gao, M.; Liang, X.; Xu, M.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, J.; Gao, Y.; Qu, S.; et al. Quantitative Trait Loci for Seed Size Variation in Cucurbits—A Review. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Bo, K.; Gu, X.; Pan, J.; Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Wen, C.; Ren, Z.; Ren, H.; Chen, X.; et al. Molecularly tagged genes and quantitative trait loci in cucumber with recommendations for QTL nomenclature. Hortic. Res. 2020, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Wen, C.; Weng, Y. Fine mapping of the pleiotropic locus B for black spine and orange mature fruit color in cucumber identifies a 50 Kb region containing a R2R3-MYB transcription factor. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2013, 126, 2187–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Win, K.T.; Kim, Y.C.; Lee, S. Two types of mutations in the HEUKCHEEM gene functioning in cucumber spine color development can be used as signatures for cucumber domestication. Planta 2019, 250, 1491–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce, L.K.; Wehner, T.C. Review of Genes and Linkage Groups in Cucumber. HortScience 1990, 25, 605–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walters, S.A.; Shetty, N.V.; Wehner, T.C. Segregation and Linkage of Several Genes in Cucumber. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 2001, 126, 442–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, K.; Lee, H.Y.; Ro, N.Y.; Hur, O.S.; Lee, J.H.; Kwon, J.K.; Kang, B.C. QTL mapping and GWAS reveal candidate genes controlling capsaicinoid content in Capsicum. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2018, 16, 1546–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, H.-Y.; Ro, N.-Y.; Patil, A.; Lee, J.-H.; Kwon, J.-K.; Kang, B.-C. Uncovering Candidate Genes Controlling Major Fruit-Related Traits in Pepper via Genotype-by-Sequencing Based QTL Mapping and Genome-Wide Association Study. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and accurate long-read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Depristo, M.A.; Banks, E.; Poplin, R.; Garimella, K.V.; Maguire, J.R.; Hartl, C.; Philippakis, A.A.; Del Angel, G.; Rivas, M.A.; Hanna, M.; et al. A framework for variation discovery and genotyping using next-generation DNA sequencing data. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 491–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubisz, M.J.; Falush, D.; Stephens, M.; Pritchard, J.K. Inferring weak population structure with the assistance of sample group information. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2009, 9, 1322–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pritchard, J.K.; Stephens, M.; Donnelly, P. Inference of Population Structure Using Multilocus Genotype Data. Genetics 2000, 155, 945–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evanno, G.; Regnaut, S.; Goudet, J. Detecting the number of clusters of individuals using the software Structure: A simulation study. Mol. Ecol. 2005, 14, 2611–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perrier, X.; Jacquemoud-Collet, J.P. DARwin Software. Available online: http://darwin.cirad.fr/darwin (accessed on 6 November 2020).
- Stacklies, W.; Redestig, H.; Scholz, M.; Walther, D.; Selbig, J. pcaMethods—A bioconductor package providing PCA methods for incomplete data. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 1164–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipka, A.E.; Tian, F.; Wang, Q.; Peiffer, J.; Li, M.; Bradbury, P.J.; Gore, M.A.; Buckler, E.S.; Zhang, Z. GAPIT: Genome association and prediction integrated tool. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 2397–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bonferroni, C.E. Teoria statistica delle classi e calcolo delle probabilita. Pubbl. R Ist. Sup. Sci. Econ. Commer. Fir. 1936, 8, 3–62. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.P.; Liu, M.M.; Miao, H.; Zhang, S.Q.; Yang, Y.H.; Xie, B.Y.; Gu, X.F. QTL mapping of resistance genes to powdery mildew in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). Sci. Agric. Sin. 2011, 44, 3584–3593. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, L.S.P.; Shinozaki, K.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. Role of cytokinin responsive two-component system in ABA and osmotic stress signalings. Plant Signal. Behav. 2010, 5, 148–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baumann, K.; Perez-Rodriguez, M.; Bradley, D.; Venail, J.; Bailey, P.; Jin, H.; Koes, R.; Roberts, K.; Martin, C. Control of cell and petal morphogenesis by R2R3 MYB transcription factors. Development 2007, 134, 1691–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oshima, Y.; Shikata, M.; Koyama, T.; Ohtsubo, N.; Mitsuda, N.; Ohme-Takagi, M. MIXTA-Like Transcription Factors and WAX INDUCER1/SHINE1 Coordinately Regulate Cuticle Development in Arabidopsis and Torenia fournieri. Plant Cell 2013, 25, 1609–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Malbert, B.; Burger, M.; Lopez-Obando, M.; Baudry, K.; Launay-Avon, A.; Härtel, B.; Verbitskiy, D.; Jörg, A.; Berthomé, R.; Lurin, C.; et al. The Analysis of the Editing Defects in the dyw2 Mutant Provides New Clues for the Prediction of RNA Targets of Arabidopsis E+-Class PPR Proteins. Plants 2020, 9, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okuda, K.; Chateigner-Boutin, A.L.; Nakamura, T.; Delannoy, E.; Sugita, M.; Myouga, F.; Motohashi, R.; Shinozaki, K.; Small, I.; Shikanai, T. Pentatricopeptide Repeat Proteins with the DYW Motif Have Distinct Molecular Functions in RNA Editing and RNA Cleavage in Arabidopsis Chloroplasts. Plant Cell 2009, 21, 146–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]




| Traits | Gene ID | Protein Name | CHR | Start (bp) | End (bp) | Strand | Related SNPs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM | Csa5G453160 | Short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase | 5 | 16,045,687 | 16,048,001 | + | s5_16047445 |
| Csa5G471070 | Anaphase-promoting complex subunit | 5 | 16,621,524 | 16,631,782 | − | s5_16623037 | |
| SDc | Csa1G006300 | Response regulator 6 | 1 | 1,180,448 | 1,182,094 | + | s1_1181919 |
| Csa3G824850 | MYB transcription factor | 3 | 32,580,286 | 32,581,685 | + | s3_32581537 | |
| SPc | Csa2G368270 | Pentatricopeptide repeat-containing protein | 2 | 17,761,336 | 17,763,934 | + | s2_17762942, s2_17762964 |
| Csa3G236570 | Zinc-containing alcohol dehydrogenase quinone oxidoreductase | 3 | 15,235,551 | 15,240,040 | − | s3_15236835 | |
| Csa5G175680 | Pentatricopeptide repeat-containing protein | 5 | 7,309,092 | 7,311,316 | + | s5_7311032 | |
| Csa6G448170 | Thaumatin-like protein | 6 | 21,137,853 | 21,139,047 | + | s6_21138663, s6_21138684 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, H.-Y.; Kim, J.-G.; Kang, B.-C.; Song, K. Assessment of the Genetic Diversity of the Breeding Lines and a Genome Wide Association Study of Three Horticultural Traits Using Worldwide Cucumber (Cucumis spp.) Germplasm Collection. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1736. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10111736
Lee H-Y, Kim J-G, Kang B-C, Song K. Assessment of the Genetic Diversity of the Breeding Lines and a Genome Wide Association Study of Three Horticultural Traits Using Worldwide Cucumber (Cucumis spp.) Germplasm Collection. Agronomy. 2020; 10(11):1736. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10111736
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Hea-Young, Jeong-Gu Kim, Byoung-Cheorl Kang, and Kihwan Song. 2020. "Assessment of the Genetic Diversity of the Breeding Lines and a Genome Wide Association Study of Three Horticultural Traits Using Worldwide Cucumber (Cucumis spp.) Germplasm Collection" Agronomy 10, no. 11: 1736. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10111736
APA StyleLee, H.-Y., Kim, J.-G., Kang, B.-C., & Song, K. (2020). Assessment of the Genetic Diversity of the Breeding Lines and a Genome Wide Association Study of Three Horticultural Traits Using Worldwide Cucumber (Cucumis spp.) Germplasm Collection. Agronomy, 10(11), 1736. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10111736




