Genotype-by-Environment Interaction Effects under Heat Stress in Tropical Maize
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Field Trials across Locations under Heat Stress
2.3. Characterization of Locations and Weather Parameters
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Heat Stress at Different Testing Locations
3.2. Performance of Hybrids across Locations
3.3. Contribution of Environmental Factor in G × E Interaction Effects
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO. GIEWS—Crop Prospects and Food Situation; No. 4; FAO: Rome, Italy, December 2018; ISBN 9789251311653.
- Shiferaw, B.; Prasanna, B.M.; Hellin, J.; Bänziger, M. Crops that feed the world 6. Past successes and future challenges to the role played by maize in global food security. Food Secur. 2011, 3, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Westcott, B. Some methods of analysing genotype-environment interaction. Heredity 1986, 56, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vargas, M.; Glaz, B.; Alvarado, G.; Pietragalla, J.; Morgounov, A.; Zelenskiy, Y.; Crossa, J. Analysis and interpretation of interactions in agricultural research. Agron. J. 2015, 107, 748–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, Q.; Buyanovsky, G. Climate effects on corn yield in Missouri. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2003, 42, 1626–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W. Mega-environment Analysis and Test Location Evaluation Based on Unbalanced Multiyear Data. Crop Sci. 2015, 55, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinayan, M.T.; Zaidi, P.H.; Seetharam, K.; Alam, M.A.; Ahmed, S.; Koirala, K.B.; Arshad, M.; Kuchanur, P.; Patil, A.; Mandal, S.S. Environmental variables contributing to differential performance of tropical maize hybrids across heat stress environments in South Asia. Aust. J. Crop Sci. 2019, 13, 828–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siebert, S.; Ewert, F.; Eyshi Rezaei, E.; Kage, H.; Graß, R. Impact of heat stress on crop yield—On the importance of considering canopy temperature. Environ. Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 044012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carter, E.K.; Melkonian, J.; Riha, S.J.; Shaw, S.B. Separating heat stress from moisture stress: Analyzing yield response to high temperature in irrigated maize. Environ. Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 094012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troy, T.J.; Kipgen, C.; Pal, I. The impact of climate extremes and irrigation on US crop yields. Environ. Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 054013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pinto, R.S.; Reynolds, M.P. Common genetic basis for canopy temperature depression under heat and drought stress associated with optimized root distribution in bread wheat. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2015, 128, 575–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rattalino Edreira, J.I.; Budakli Carpici, E.; Sammarro, D.; Otegui, M.E. Heat stress effects around flowering on kernel set of temperate and tropical maize hybrids. Field Crop. Res. 2011, 123, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicchino, M.; Rattalino Edreira, J.I.; Otegui, M.E. Heat stress during late vegetative growth of maize: Effects on phenology and assessment of optimum temperature. Crop Sci. 2010, 50, 1431–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobell, D.B.; Baldos, U.L.C.; Hertel, T.W. Climate adaptation as mitigation: The case of agricultural investments. Environ. Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 015012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizhsky, L.; Liang, H.; Shuman, J.; Shulaev, V.; Davletova, S.; Mittler, R. When defense pathways collide. The response of arabidopsis to a combination of drought and heat stress. Plant Physiol. 2004, 134, 1683–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rizhsky, L.; Liang, H.; Mittler, R. The combined effect of drought stress and heat shock on gene expression in tobacco. Plant Physiol. 2002, 130, 1143–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barnabás, B.; Jäger, K.; Fehér, A. The effect of drought and heat stress on reproductive processes in cereals. Plant Cell Environ. 2008, 31, 11–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cairns, J.E.; Crossa, J.; Zaidi, P.H.; Grudloyma, P.; Sanchez, C.; Luis Araus, J.; Thaitad, S.; Makumbi, D.; Magorokosho, C.; Bänziger, M.; et al. Identification of drought, heat, and combined drought and heat tolerant donors in maize. Crop Sci. 2013, 53, 1335–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cairns, J.E.; Sonder, K.; Zaidi, P.H.; Verhulst, N.; Mahuku, G.; Babu, R.; Nair, S.K.; Das, B.; Govaerts, B.; Vinayan, M.T.; et al. Maize Production in a Changing Climate. Impacts, Adaptation, and Mitigation Strategies. In Advances in Agronomy; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2012; Volume 114, pp. 1–58. [Google Scholar]
- Burke, M.; Lobell, D. Climate change and food security: Adapting agriculture to a warmer world. Clim. Chang. Food Secur. Adapt. Agric. Warmer World 2010, 37, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rowhani, P.; Lobell, D.B.; Linderman, M.; Ramankutty, N. Climate variability and crop production in Tanzania. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2011, 151, 449–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.; Diallo, A.O.; Islam, T.M.T.; Deutsch, J. Progress from Selection in Eight Tropical Maize Populations Using International Testing. Crop Sci. 1986, 26, 879–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmeades, G.O.; Bolaños, J.; Chapman, S.C.; Lafitte, H.R.; Bänziger, M. Selection Improves Drought Tolerance in Tropical Maize Populations. Crop Sci. 1999, 39, 1315–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monneveux, P.; Sánchez, C.; Beck, D.; Edmeades, G.O. Drought tolerance improvement in tropical maize source populations: Evidence of progress. Crop Sci. 2006, 39, 1315–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.B. Relative Humidity or Vapor Pressure Deficit. Ecology 1936, 17, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, G.C.C. Genotypic Stability Analysis and Its Application to Potato Regional Trials. Crop Sci. 1971, 11, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angela, P.; Mateo, V.; Gregorio, A.; Francisco, R.; Marco, L.; Jose, C.; Juan, B. GEA-R (Genotype × Environment Analysis with R for Windows) Version 4.0; CIMMYT: El-Batan, Mexico, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Torres Flores, J.L.; Mendoza García, B.; Prasanna, B.M.; Alvarado, G.; San Vicente, F.M.; Crossa, J. Grain yield and stability of white early maize hybrids in the highland valleys of Mexico. Crop Sci. 2017, 57, 3002–3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Denis, J.B. Two Way Analysis Using Covariates. Statistics 1988, 19, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Eeuwijk, F.; Kang, M.; Denis, J. Incorporating Additional Information on Genotypes and Environments in Models for Two-way Genotype by Environment Tables. In Genotype-by-Environment Interaction; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1996; pp. 15–50. [Google Scholar]
- Vargas, M.; Crossa, J.; Van Eeuwijk, F.A.; Ramírez, M.E.; Sayre, K. Using partial least squares regression, factorial regression, and AMMI models for interpreting genotype × environment interaction. Crop Sci. 1999, 39, 955–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatfield, J.L.; Prueger, J.H. Temperature extremes: Effect on plant growth and development. Weather Clim. Extrem. 2015, 10, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharon, M.G.; Adam, M.S.; David, B.L. Global crop exposure to critical high temperatures in the reproductive period: Historical trends and future projections. Environ. Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 024041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.A.; Seetharam, K.; Zaidi, P.H.; Dinesh, A.; Vinayan, M.T.; Nath, U.K. Dissecting heat stress tolerance in tropical maize (Zea mays L.). Field Crop. Res. 2017, 204, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero, M.P.; Johnson, R.R. High Temperature Stress and Pollen Viability of Maize. Crop Sci. 1980, 20, 796–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupuis, I.; Dumas, C. Influence of temperature stress on in vitro fertilization and heat shock protein synthesis in maize (Zea mays L.) reproductive tissues. Plant Physiol. 1990, 94, 665–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Windhausen, V.S.; Atlin, G.N.; Hickey, J.M.; Crossa, J.; Jannink, J.-L.; Sorrells, M.E.; Raman, B.; Cairns, J.E.; Tarekegne, A.; Semagn, K.; et al. Effectiveness of Genomic Prediction of Maize Hybrid Performance in Different Breeding Populations and Environments. G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 2012, 2, 1427–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Monneveux, P.; Sanchez, C. Tiessen, Future progress in drought tolerance in maize needs new secondary traits and cross combinations. J. Agric. Sci. 2008, 146, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ben-Asher, J.; Garcia, A.; Flitcroft, I.; Hoogenboom, G. Effect of atmospheric water vapor on photosynthesis, transpiration and canopy conductance: A case study in corn. Plant Soil Environ. 2013, 59, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siebert, S.; Webber, H.; Zhao, G.; Ewert, F. Heat stress is overestimated in climate impact studies for irrigated agriculture. Environ. Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 054023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinta Romay, M.; Malvar, R.A.; Campo, L.; Alvarez, A.; Moreno-González, J.; Ordás, A.; Revilla, P. Climatic and genotypic effects for grain yield in maize under stress conditions. Crop Sci. 2010, 50, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lobell, D.B.; Bänziger, M.; Magorokosho, C.; Vivek, B. Nonlinear heat effects on African maize as evidenced by historical yield trials. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2011, 1, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyshi Rezaei, E.; Webber, H.; Gaiser, T.; Naab, J.; Ewert, F. Heat stress in cereals: Mechanisms and modelling. Eur. J. Agron. 2015, 64, 98–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commuri, P.D.; Jones, R.J. High temperatures during endosperm cell Division in maize. Crop Sci. 2001, 41, 1122–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasanna, B.; Vivek, B.; Sadananda, A.; Jeffers, D.; Zaidi, P.; Boeber, C.; Erenstein, O.; Babu, R.; Nair, S.K.; Gerard, B.; et al. Maize for Food, Feed, Nutrition Environment Security. In Proceedings of the 12th Asian Maize Conference and Expert Consultation on Maize for Food, Feed, Nutrition and Environmental Security, Bangkok, Thailand, 30 October–1 November 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Fonseca, A.E.; Westgate, M.E. Relationship between desiccation and viability of maize pollen. Field Crop. Res. 2005, 94, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.S. Genotype-environment interaction: Progress and prospects. In Quantitative Genetics, Genomics and Plant Breeding; CABI Publishing: Wallingford, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Bänziger, M.; Setimela, P.S.; Hodson, D.; Vivek, B. Breeding for improved abiotic stress tolerance in maize adapted to southern Africa. Agric. Water Manag. 2006, 80, 212–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, S.S.; Gcadclmann, J.L. Influence of water stress on grain yield response to recurrent selection in maize. Crop Sci. 1989, 29, 558–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Year | Environment | Country | Latitude and Longitude | Planting Date | Grain Yield (t/ha) | Repeatability | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2015 | E1 | Bgudi * | India | 16.73 N;76.79 E | 12/28/2014 | 5.47 | 0.92 |
| E2 | Hyderabad * | India | 17.51 N;78.27 E | 3/19/2015 | 5.76 | 0.96 | |
| E3 | Rampur * | Nepal | 27.84 N;83.90 E | 3/6/2015 | 6.18 | 0.95 | |
| E12 | Hoshiarpur * | India | 31.52 N;75.90 E | 3/27/2015 | 2.73 | 0.95 | |
| E15 | Jessore * | Bangladesh | 23.17 N;89.18 E | 4/4/2015 | 10.56 | 0.89 | |
| E16 | Julandhar * | India | 28.63 N;77.21 E | 3/17/2015 | 5.57 | 0.92 | |
| E25 | Sahiwal * | Pakistan | 30.66 N;73.10 E | 3/25/2015 | 7.13 | 0.70 | |
| E27 | Bejjanki † | India | 18.25 N;79.01 E | 3/18/2015 | 3.01 | 0.10 | |
| 2016 | E1 | Bgudi | India | 16.73 N;76.79 E | 1/25/2016 | 3.66 | 0.74 |
| E2 | Hyderabad * | India | 17.51 N;78.27 E | 3/15/2016 | 1.43 | 0.75 | |
| E3 | Rampur * | Nepal | 27.84 N;83.90 E | 2/23/2016 | 6.27 | 0.60 | |
| E4 | Sabor | India | 22.35 N;87.05 E | 2/7/2016 | 6.65 | 0.86 | |
| E5 | Savar * | Bangladesh | 24.83 N;89.37 E | 3/29/2016 | 6.63 | 0.67 | |
| E6 | Barisal * | Bangladesh | 22.70 N;90.37 E | 3/8/2016 | 6.45 | 0.83 | |
| E7 | Barisal1 | Bangladesh | 22.70 N;90.37 E | 3/14/2016 | 6.45 | 0.83 | |
| E9 | Faisalabad * | Pakistan | 31.41 N;73.08 E | 3/30/2016 | 2.49 | 0.73 | |
| E12 | Hoshiarpur | India | 31.52 N;75.90 E | 3/18/2016 | 5.96 | 0.58 | |
| E13 | Ishurwadi * | Bangladesh | 24.12 N;89.06 E | 3/12/2016 | 5.6 | 0.67 | |
| E16 | Julandhar | India | 28.63 N;77.21 E | 3/18/2016 | 3.42 | 0.81 | |
| E18 | Lahore | Pakistan | 31.52 N;74.35 E | 3/16/2016 | 2.24 | 0.81 | |
| E19 | Lalmonirhat | Bangladesh | 23.70 N;90.41 E | 3/16/2016 | 5.42 | 0.86 | |
| E24 | Raichur * | India | 16.22 N;77.38 E | 3/18/2016 | 3.85 | 0.88 | |
| E26 | Aurangabad | India | 19.69 N;75.08 E | 1/23/2016 | 6.55 | 0.54 | |
| E27 | Bejjanki † | India | 18.25 N;79.01 E | 3/17/2016 | 0.98 | 0.15 | |
| 2017 | E1 | Bgudi * | India | 16.73 N;76.79 E | 3/14/2017 | 4.79 | 0.61 |
| E2 | Hyderabad * | India | 17.51 N;78.27 E | 3/13/2017 | 6.31 | 0.82 | |
| E4 | Sabor | India | 22.35 N;87.05 E | 3/20/2017 | 4.71 | 0.57 | |
| E5 | Savar | Bangladesh | 23.70 N;90.41 E | 4/2/2017 | 6.47 | 0.92 | |
| E8 | Bogra | Bangladesh | 24.83 N;89.37 E | 4/11/2017 | 6.57 | 0.77 | |
| E10 | Gazipur * | Bangladesh | 24.09 N;90.41 E | 3/28/2017 | 5.00 | 0.60 | |
| E17 | Kustia * | Bangladesh | 23.89 N;89.10 E | 4/30/2017 | 6.68 | 0.57 | |
| E20 | Lucknow1 * | India | 26.84 N;80.94 E | 3/6/2017 | 7.29 | 0.72 | |
| E21 | Lucknow2 * | India | 26.84 N;80.94 E | 3/31/2017 | 3.75 | 0.60 | |
| E22 | Maltan | Pakistan | 30.20 N;71.45 E | 3/20/2017 | 1.03 | 0.77 | |
| E23 | Nepalgunj | Nepal | 28.05 N;81.61 E | 3/21/2017 | 1.72 | 0.61 | |
| Parameters | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Range | Across | Range | Across | Range | Across | |
| Grand Mean (t/ha) | 2.73–10.56 | 6.19 | 1.43–6.65 | 4.78 | 1.03–7.29 | 4.94 |
| LSD | 0.39–1.43 | 0.51 | 0.5–1.57 | 0.51 | 0.43–1.45 | 0.58 |
| Heritability | 0.7–0.96 | 0.41 | 0.54–0.88 | 0.85 | 0.57–0.92 | 0.70 |
| Genotype Variance | 0.34–1.77 | 0.11 | 0.22–1.90 | 0.37 | 0.19–3.79 | 0.27 |
| Genotype × Location Variance | 0.92 | 0.64 | 0.81 | |||
| Location Variance | 5.43 | 3.10 | 4.15 | |||
| Replications | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Number of Environments | 7 | 15 | 11 | |||
| Genotypic significance | 1.11 × 10−10–0.01 | 0.05 | 3.10 × 10−7–0.06 | 8.30 × 10−21 | 1.87 × 10−9–0.03 | 2.63 × 10−7 |
| Genotype × Location significance | 2.01 × 10−26 | 1.97 × 10−23 | 1.13 × 10−19 | |||
| Location significance | 1.71 × 10−11 | 3.35 × 10−9 | 1.42 × 10−7 | |||
| Year | Name | Low Yielding | Moderate Yielding | High Yielding |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| <3 t/ha | 3–6 t/ha | >6 t/ha | ||
| 2015 | ZH141592 | 3.49 | 5.65 ± 0.62 | 8.23 ± 1.95 |
| CAH1516 | 2.51 | 6.49 ± 1.18 | 8.45 ± 2.93 | |
| VH112887 | 2.71 | 5.93 ± 1.27 | 8.49 ± 2.64 | |
| † CAH153 | 2.05 | 5.36 ± 0.76 | 8.90 ± 2.98 | |
| 2016 | CAH1432 | 1.61 ± 0.58 | 5.05 ± 1.16 | 6.54 ± 0.61 |
| † CAH1719 | 1.39 ± 0.56 | 4.96 ± 1.54 | 7.35 ± 0.67 | |
| ZH15440 | 1.66 ± 0.84 | 5.05 ± 1.30 | 7.30 ± 0.90 | |
| † CAH1715 | 1.78 ± 0.16 | 5.06 ± 1.82 | 7.34 ± 0.39 | |
| † CAH153 | 1.49 ± 0.65 | 4.95 ± 1.87 | 7.40 ± 0.43 | |
| 2017 | ZH15400 | 1.10 ± 0.00 | 4.32 ± 1.32 | 7.79 ± 0.91 |
| † ZH15333 | 0.94 ± 0.38 | 4.72 ± 0.87 | 7.21 ± 0.59 | |
| † CAH1714 | 1.60 ± 0.30 | 5.24 ± 1.36 | 7.56 ± 0.39 |
| Source of Variation | Year | Df | Sum of Squares | % Variation Explained | Pr (>F) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genotype × environment | 2015 | 84 | 208.24 | 16.83 | 0.0000 |
| 2016 | 170 | 350.81 | 11.53 | 0.0000 | |
| 2017 | 116 | 234.51 | 33.2 | 0.0001 | |
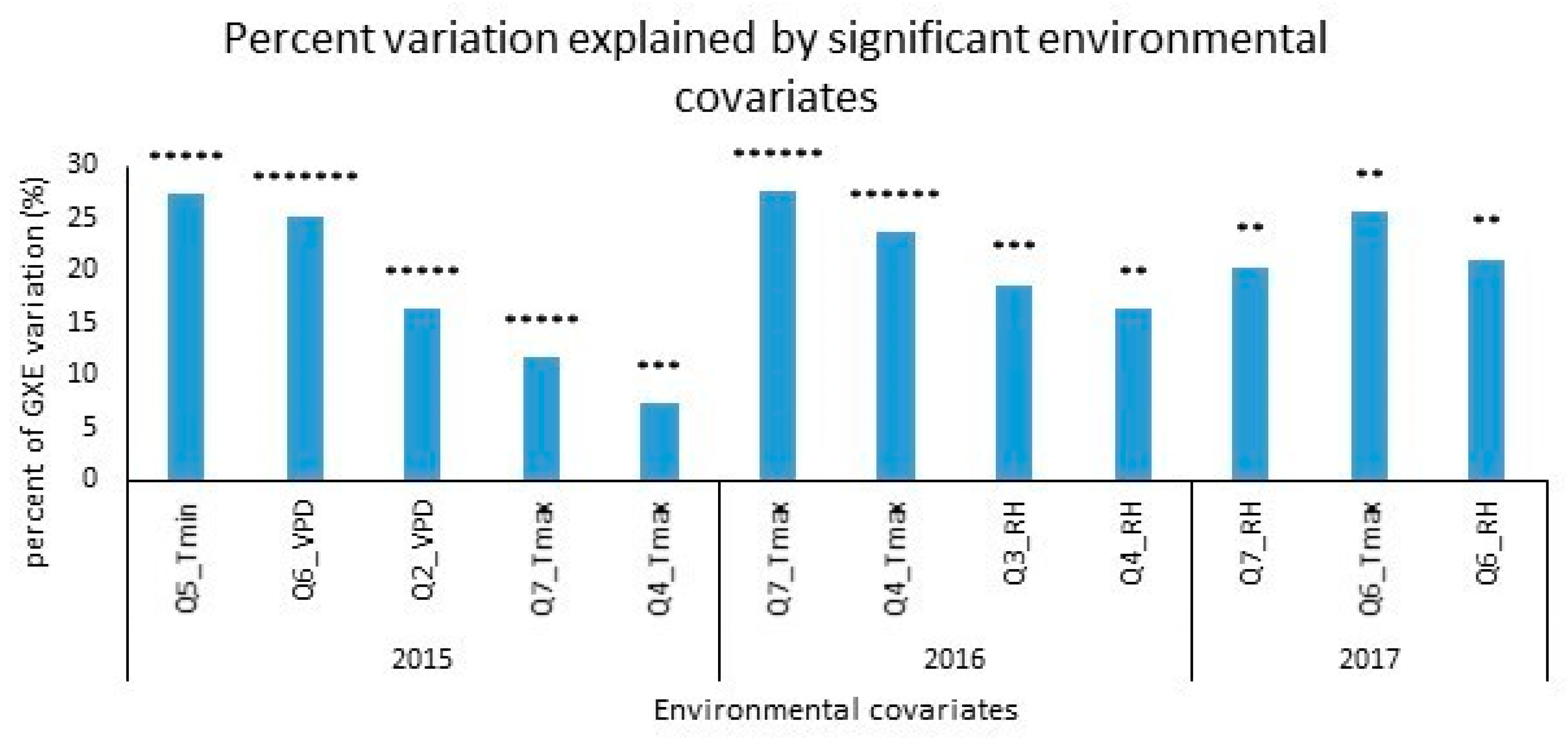
| Genotype × Q5_Tmin | 2015 | 14 | 56.87 | 27.31 | 0.0000 |
| Genotype × Q6_VPD | 14 | 52.35 | 25.14 | 0.0000 | |
| Genotype × Q2_VPD | 14 | 34.02 | 16.34 | 0.0000 | |
| Genotype × Q7_Tmax | 14 | 24.34 | 11.69 | 0.0000 | |
| Genotype × Q4_Tmax | 14 | 15.17 | 7.284 | 0.00232 | |
| Genotype × Q7_Tmax | 2016 | 34 | 96.41 | 27.48 | 0.00000 |
| Genotype × Q4_Tmax | 34 | 82.80 | 23.60 | 0.00000 | |
| Genotype × Q3_RH | 34 | 65.52 | 18.68 | 0.00033 | |
| Genotype × Q4_RH | 34 | 57.23 | 16.31 | 0.00234 | |
| Genotype × Q7_RH | 2017 | 29 | 47.85 | 20.40 | 0.03407 |
| Genotype × Q6_Tmax | 29 | 59.90 | 25.54 | 0.00337 | |
| Genotype × Q6_RH | 29 | 49.44 | 21.08 | 0.02552 | |
| Residuals | 2015 | 147 | 61.58 | ||
| 2016 | 119 | 93.98 | |||
| 2017 | 125 | 127.21 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Madhumal Thayil, V.; Zaidi, P.H.; Seetharam, K.; Rani Das, R.; Viswanadh, S.; Ahmed, S.; Miah, M.A.; Koirala, K.B.; Tripathi, M.P.; Arshad, M.; et al. Genotype-by-Environment Interaction Effects under Heat Stress in Tropical Maize. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1998. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10121998
Madhumal Thayil V, Zaidi PH, Seetharam K, Rani Das R, Viswanadh S, Ahmed S, Miah MA, Koirala KB, Tripathi MP, Arshad M, et al. Genotype-by-Environment Interaction Effects under Heat Stress in Tropical Maize. Agronomy. 2020; 10(12):1998. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10121998
Chicago/Turabian StyleMadhumal Thayil, Vinayan, Pervez H. Zaidi, Kaliyamoorthy Seetharam, Reshmi Rani Das, Sudarsanam Viswanadh, Salahuddin Ahmed, Mohammad Alamgir Miah, Kesab B. Koirala, Mahendra Prasad Tripathi, Mohammad Arshad, and et al. 2020. "Genotype-by-Environment Interaction Effects under Heat Stress in Tropical Maize" Agronomy 10, no. 12: 1998. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10121998
APA StyleMadhumal Thayil, V., Zaidi, P. H., Seetharam, K., Rani Das, R., Viswanadh, S., Ahmed, S., Miah, M. A., Koirala, K. B., Tripathi, M. P., Arshad, M., Pandey, K., Chaurasia, R., Kuchanur, P. H., Patil, A., & Mandal, S. S. (2020). Genotype-by-Environment Interaction Effects under Heat Stress in Tropical Maize. Agronomy, 10(12), 1998. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10121998





