The Influence of Various Forms of Nitrogen Fertilization and Meteorological Factors on Nitrogen Compounds in Soil under Laboratory Conditions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site and Experimental Design
2.2. Analytical Methods
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Breitburg, D.L.; Levin, L.A.; Oschlies, A.; Grégoire, M.; Chavez, F.P.; Conley, D.J.; Garçon, V.; Gilbert, D.; Gutiérrez, D.; Isensee, K.; et al. Declining oxygen in the global ocean and coastal waters. Science 2018, 359, eaam7240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pinay, G.; Bernal, S.; Abbott, B.W.; Lupon, A.; Martí, E.; Sabater, F.; Krause, S. Riparian Corridors: A New Conceptual Framework for Assessing Nitrogen Buffering Across Biomes. Front. Environ. Sci. 2018, 6, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutkowska, A.; Fotyma, M. Calibration of soil test for mineral nitrogen in Poland. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2009, 40, 987–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oenema, O.; Bleeker, A.; Braathen, N.A.; Budňáková, M.; Bull, K.; Čermák, P.; Geupel, M.; Hicks, K.B.; Hoft, R.; Kozlova, N. Nitrogen in current European policies. In The European Nitrogen Assessment; Sutton, M., Howard, C., Erisman, J., Billen, G., Bleeker, A., Grennfelt, P., Grinsven, H., Grizzetti, B., Eds.; Cambridge University Press (CUP): Cambridge, UK, 2011; pp. 62–81. ISBN 978-1107006126. [Google Scholar]
- Cameira, M.D.R.; Mota, M. Nitrogen Related Diffuse Pollution from Horticulture Production—Mitigation Practices and Assessment Strategies. Horticulturae 2017, 3, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buckley, C.; Carney, P. The potential to reduce the risk of diffuse pollution from agriculture while improving economic performance at farm level. Environ. Sci. Policy 2013, 25, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Riemann, B.; Carstensen, J.; Dahl, K.; Fossing, H.; Hansen, J.W.; Jakobsen, H.H.; Josefson, A.B.; Krause-Jensen, D.; Markager, S.; Stæhr, P.A.; et al. Recovery of Danish coastal ecosystems after reductions in nutrient loading: A holistic approach. Estuaries Coast 2016, 39, 82–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tripolskaja, L.; Verbylienė, I. The effect of different forms of nitrogen fertilizers on nitrogen leaching. Zemdirbyste 2014, 101, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, R.; Zhang, X.-X.; Guo, X.; Wang, D.; Chu, H. Bacterial diversity in soils subjected to long-term chemical fertilization can be more stably maintained with the addition of livestock manure than wheat straw. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 88, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treder, W.; Klamkowski, K.; Kowalczyk, W.; Sas, D.; Wójcik, K. Possibilities of using image analysis to estimate the nitrogen nutrition status of apple trees. Zemdirbyste 2016, 103, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Muller, C.; Cai, Z. Temperature sensitivity of gross N transformation rates in an alpine meadow on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. J. Soils Sediments 2016, 17, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zheng, Q.; Noll, L.; Hu, Y.; Wanek, W. Environmental effects on soil microbial nitrogen use efficiency are controlled by allocation of organic nitrogen to microbial growth and regulate gross N mineralization. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 135, 304–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagemann, N.; Harter, J.; Behrens, S. Elucidating the Impacts of Biochar Applications on Nitrogen Cycling Microbial Communities. In Biochar Application: Essential Soil Microbial Ecology; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 163–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nearing, M.; Jetten, V.; Baffaut, C.; Cerdan, O.; Couturier, A.; Hernandez, M.; Le Bissonnais, Y.; Nichols, M.; Nunes, J.; Renschler, C.; et al. Modeling response of soil erosion and runoff to changes in precipitation and cover. Catena 2005, 61, 131–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangarajan, R.; Bolan, N.S.; Naidu, R.; Surapaneni, A. Effects of temperature and amendments on nitrogen mineralization in selected Australian soils. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 22, 8843–8854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suter, H.C.; Pengthamkeerati, P.; Walker, C.; Chen, D. Influence of temperature and soil type on inhibition of urea hydrolysis by N-(n-butyl) thiophosphoric triamide in wheat and pasture soils in south-eastern Australia. Soil Res. 2011, 49, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, K.S.; Andresen, L.C.; Beier, C.; Jonasson, S.; Albert, K.R.; Ambus, P.; Arndal, M.F.; Carter, M.S.; Christensen, S.; Holmstrup, M.; et al. Reduced N cycling in response to elevated CO2, warming, and drought in a Danish heathland: Synthesizing results of the CLIMAITE project after two years of treatments. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2010, 17, 1884–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Li, Y.; Xiao, J.; Xu, Z.; Cheng, X.; Liu, Q. Enhanced root exudation stimulates soil nitrogen transformations in a subalpine coniferous forest under experimental warming. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2013, 19, 2158–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beier, C.; Emmett, B.A.; Peñuelas, J.; Schmidt, I.K.; Tietema, A.; Estiarte, M.; Gundersen, P.; Lorens, L.; Riis-Nielsen, T.; Sowerby, A.; et al. Carbon and nitrogen cycles in European ecosystems respond differently to global warming. Sci. Total. Environ. 2008, 407, 692–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auyeung, D.S.N.; Suseela, V.; Dukes, J.S. Warming and drought reduce temperature sensitivity of nitrogen transformations. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2012, 19, 662–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, C.A.; Fillery, I.R.P.; Bootsma, N.; McInnes, K.J. Effect of temperature and nitrogen source on nitrification in a sandy soil. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2002, 33, 1975–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripolskaja, L.; Verbylienė, I. The influence of climate variability on the infiltration of atmospheric precipitation in east Lithuania Haplic Luvisol. Žemės Ūkio Mokslai 2016, 23, 28–35. (In Lithuanian) [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Yu, G.; Luo, C.; Zhou, P. Groundwater Nitrogen Pollution and Assessment of Its Health Risks: A Case Study of a Typical Village in Rural-Urban Continuum, China. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.-J.; Gao, J.-E.; Li, X.-H.; Zhang, S.-L. Nitrate Accumulation and Leaching in Surface and Ground Water Based on Simulated Rainfall Experiments. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0136274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haberle, J.; Kusá, H.; Svoboda, P.; Klír, J. The changes of soil mineral nitrogen observed on farms between autumn and spring and modelled with a simple leaching equation. Soil Water Res. 2009, 4, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gallucci, A.D.; Natera, M.; Moreira, L.A.; Nardi, K.T.; Altarugio, L.M.; Mira, A.B.; Almeida, R.F.; Otto, R. Nitrogen-Enriched Vinasse as a Means of Supplying Nitrogen to Sugarcane Fields: Testing the Effectiveness of N Source and Application Rate. Sugar Tech 2018, 21, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, G.; Cheng, W.; Guo, S.; Zhang, H.; Shi, W. Do high nitrogen use efficiency rice cultivars reduce nitrogen losses from paddy fields? Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2015, 209, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- WRB. World reference base for soil resources. In World Soil Resources Reports No. 106; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2014; pp. 112–113. [Google Scholar]
- Hill, T.; Levicki, P. Statistics Methods and Applications, 1st ed.; StatSoft, Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 2005; 800p, ISBN 978-1884233593. [Google Scholar]
- Raudonius, S. Application of statistics in plant and crop research: Important issues. Zemdirbyste 2017, 104, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spohn, M.; Novák, T.J.; Incze, J.; Giani, L. Dynamics of soil carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus in calcareous soils after land-use abandonment—A chronosequence study. Plant Soil 2016, 401, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, Y.H.; Wang, Y.L.; Niu, L.; Xu, X.; Tian, Y.Q. Interactive effects of soil temperature and moisture on soil N mineralization in a Stipa krylovii grassland in Inner Mongolia, China. J. Arid. Land 2014, 6, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guntinas, M.E.; Leirós, M.C.; Trasarcepeda, C.; Gil-Sotres, F. Effects of moisture and temperature on net soil nitrogen mineralization: A laboratory study. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2012, 48, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortoletto-Santos, R.; Ribeiro, C.; Polito, W.L. Controlled release of nitrogen-source fertilizers by natural-oil-based poly(urethane) coatings: The kinetic aspects of urea release. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 133, 43790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faber, B. Nitrogen changes in the soil, and it changes fast. University of California, Science-Based Solutions for Ventura County’s Communities, Farms and Environment. 2016. Available online: http://ceventura.ucdavis.edu/?blogpost=21818&blogasset=19305 (accessed on 25 August 2020).
- MAcLean, A.A.; McRes, K.B. Rate of hydrolysis and nitrification of urea and implications of its use in potato production. Can. J. Soil Sci. 1987, 672, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochette, P.; Angers, D.A.; Chantigny, M.H.; Gasser, M.-O.; Macdonald, J.D.; Pelster, D.E.; Bertrand, N. Ammonia Volatilisation and Nitrogen Retention: How Deep to Incorporate Urea? J. Environ. Qual. 2013, 42, 1635–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abalos, D.; De Deyn, G.B.; Kuyper, T.W.; Van Groenigen, J.W. Plant species identity surpasses species richness as a key driver of N2O emissions from grassland. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2013, 20, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conant, R.T.; Ryan, M.G.; Ågren, G.I.; Birge, H.E.; Davidson, E.A.; Eliasson, P.E.; Evans, S.E.; Frey, S.D.; Giardina, C.P.; Hopkins, F.M.; et al. Temperature and soil organic matter decomposition rates—Synthesis of current knowledge and a way forward. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2011, 17, 3392–3404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cenkseven, S.; Kizildag, N.; Koçak, B.; Sagliker, H.A.; Darici, C. Soil Organic Matter Mineralization under Different Temperatures and Moisture Conditions in Kõzõldağ Plateau, Turkey. Sains Malays. 2017, 46, 763–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, R.; Zavaschi, E.; Souza-Netto, G.J.M.D.; Machado, B.D.A.; Mira, A.B.D. Ammonia volatilization from nitrogen fertilizers applied to sugarcane straw. Rev. Ciênc. Agron. 2017, 48, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.W.; Yang, X.Y.; Hu, F.J.; Xu, C.Y.; Zhang, J.; Lin, Y.Q. Adsorption properties of rare earth soils on Ammonium Nitrogen. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Water Resource and Environment (WRE 2018), Kaohsiung City, Taiwan, 17–21 July 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaly, A.E.; Ramakrishnan, V.V. Nitrogen Sources and Cycling in the Ecosystem and its Role in Air, Water and Soil Pollution: A Critical Review. J. Pollut. Eff. Control 2015, 3, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holcomb, J.C.; Sullivan, D.M.; Horneck, D.A.; Clough, G.H. Effect of Irrigation Rate on Ammonia Volatilization. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2011, 75, 2341–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Lv, J.; Dawuda, M.M.; Xie, J.; Yu, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Tang, C.; Wang, C.; Gan, Y. Appropriate Ammonium-Nitrate Ratio Improves Nutrient Accumulation and Fruit Quality in Pepper (Capsicum annuum L.). Agronomy 2019, 9, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shaviv, A.; Hagin, J. Interaction of ammonium and nitrate nutrition with potassium in wheat. Fertil. Res. 1988, 17, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandeler, E.; Eder, G.; Sobotik, M. Microbial biomass, N mineralization, and the activities of various enzymes in relation to nitrate leaching and root distribution in a slurry-amended grassland. Biol. Fertil. Soils 1994, 18, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripolskaja, L.; Bagdanavičienė, Z.; Romanovskaja, D. Changes in mineral nitrogen and microbiological activity of soil during decomposition of organic fertilizers in the autumn-winter season. Žemės ūkio Mokslai 2002, 2, 3–12. (In Lithuanian) [Google Scholar]
- Cookson, W.R.; Cornforth, I.S.; Rowarth, J.S. Winter soil temperature (2–15 °C) effects on nitrogen transformations in clover green manure amended or unamended soils; a laboratory and field study. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2002, 34, 1401–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Yang, A.; Wang, Z.; Roelcke, M.; Chen, X.; Zhang, F.; Pasda, G.; Zerulla, W.; Wissemeier, A.H.; Liu, X. Effect of a new urease inhibitor on ammonia volatilization and nitrogen utilization in wheat in north and northwest China. Field Crop. Res. 2015, 175, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, B.; Lam, S.K.; Mosier, A.; Luo, Y.; Chen, D. Ammonia volatilization from synthetic fertilizers and its mitigation strategies: A global synthesis. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 232, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardinier, A.; Ketterings, Q.; Verbeten, B.; Hunter, M. Urea fertilizer. Fact Sheet 80. Agronomy Fact Sheet Series. Cornell University Cooperative Extension. 2013. Available online: http://nmsp.cals.cornell.edu/publications/fact-sheets/factsheet80.pdf (accessed on 10 September 2020).
- Sommer, S.G.; Hutchings, N. Ammonia emission from field applied manure and its reduction—Invited paper. Eur. J. Agron. 2001, 15, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

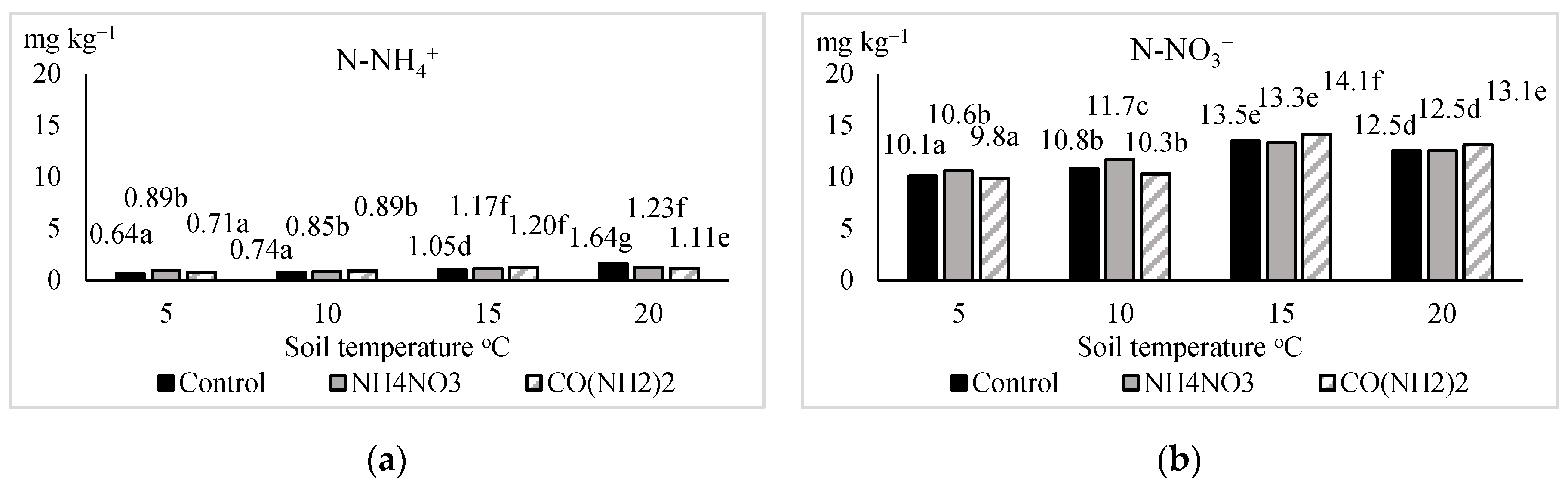

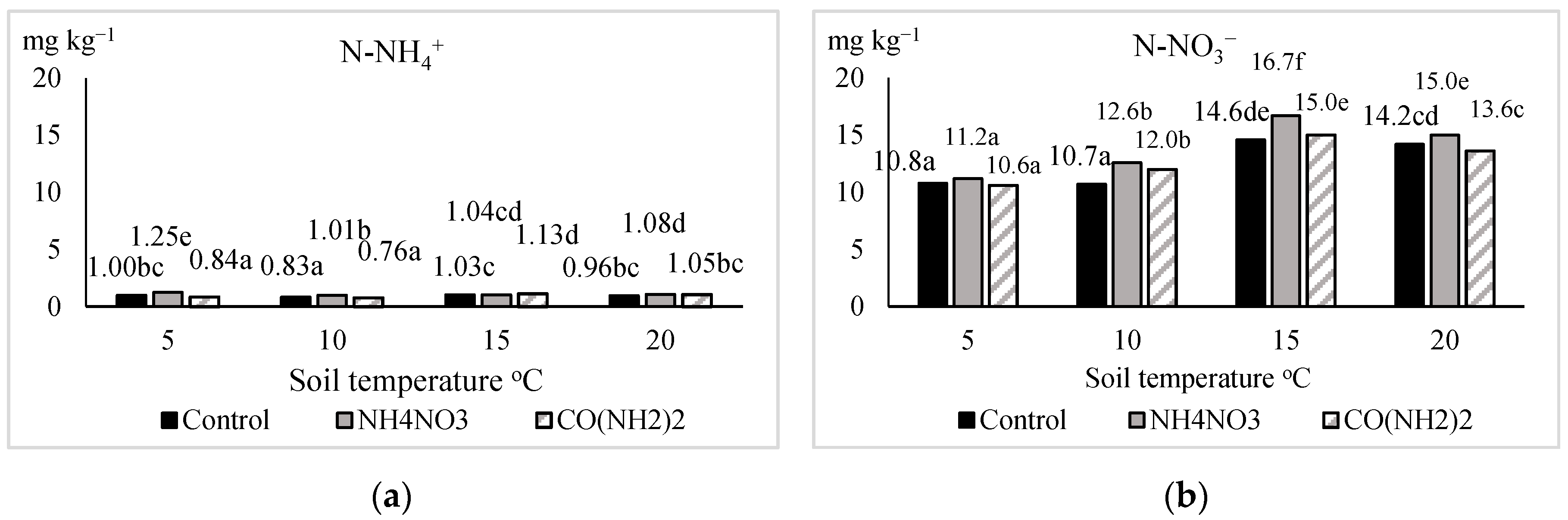
| Fertilizer (Factor A) | Temperature (°C) in the 0–15 cm Soil Layer (Factor B) | Temperature (°C) in the 0–15 cm Soil Layer (Factor B) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | |
| Simulated precipitation at 10 mm | ||||||||
| Control | 12.0a | 13.6b | 17.3c | 20.9d | 10.7a | 11.5b | 14.6de | 14.1d |
| NH4NO3 | 46.0i | 48.7lj | 54.5k | 54.4k | 11.5b | 12.6c | 14.5de | 13.7d |
| CO(NH2)2 | 25.2e | 31.2f | 39.9h | 37.4g | 10.5a | 11.2ab | 15.3e | 14.2de |
| Simulated precipitation at 20 mm | ||||||||
| Control | 12.0a | 15.4bc | 17.0c | 13.8ab | 11.8ab | 11.5a | 15.7ef | 15.2de |
| NH4NO3 | 46.8g | 52.4h | 56.9i | 58.2i | 12.4b | 13.6c | 17.7g | 16.0ef |
| CO(NH2)2 | 27.1d | 34.1e | 42.4f | 46.2g | 11.4a | 12.7b | 16.1f | 14.7d |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dromantienė, R.; Pranckietienė, I.; Jodaugienė, D.; Paulauskienė, A. The Influence of Various Forms of Nitrogen Fertilization and Meteorological Factors on Nitrogen Compounds in Soil under Laboratory Conditions. Agronomy 2020, 10, 2011. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10122011
Dromantienė R, Pranckietienė I, Jodaugienė D, Paulauskienė A. The Influence of Various Forms of Nitrogen Fertilization and Meteorological Factors on Nitrogen Compounds in Soil under Laboratory Conditions. Agronomy. 2020; 10(12):2011. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10122011
Chicago/Turabian StyleDromantienė, Rūta, Irena Pranckietienė, Darija Jodaugienė, and Aurelija Paulauskienė. 2020. "The Influence of Various Forms of Nitrogen Fertilization and Meteorological Factors on Nitrogen Compounds in Soil under Laboratory Conditions" Agronomy 10, no. 12: 2011. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10122011
APA StyleDromantienė, R., Pranckietienė, I., Jodaugienė, D., & Paulauskienė, A. (2020). The Influence of Various Forms of Nitrogen Fertilization and Meteorological Factors on Nitrogen Compounds in Soil under Laboratory Conditions. Agronomy, 10(12), 2011. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10122011





