Temperature-Associated Effects on Flavonol Content in Field-Grown Phaseolus vulgaris L. Zolfino del Pratomagno
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Germplasm, Open-Field Experimental Locations, and Treatments
2.3. Polyphenol Extraction and Measurement
2.4. Seed Color Intensity
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effects of Genotype, Location (Temperature), Irrigation and Fertilizer Treatment on Polyphenol and Flavonol Expression
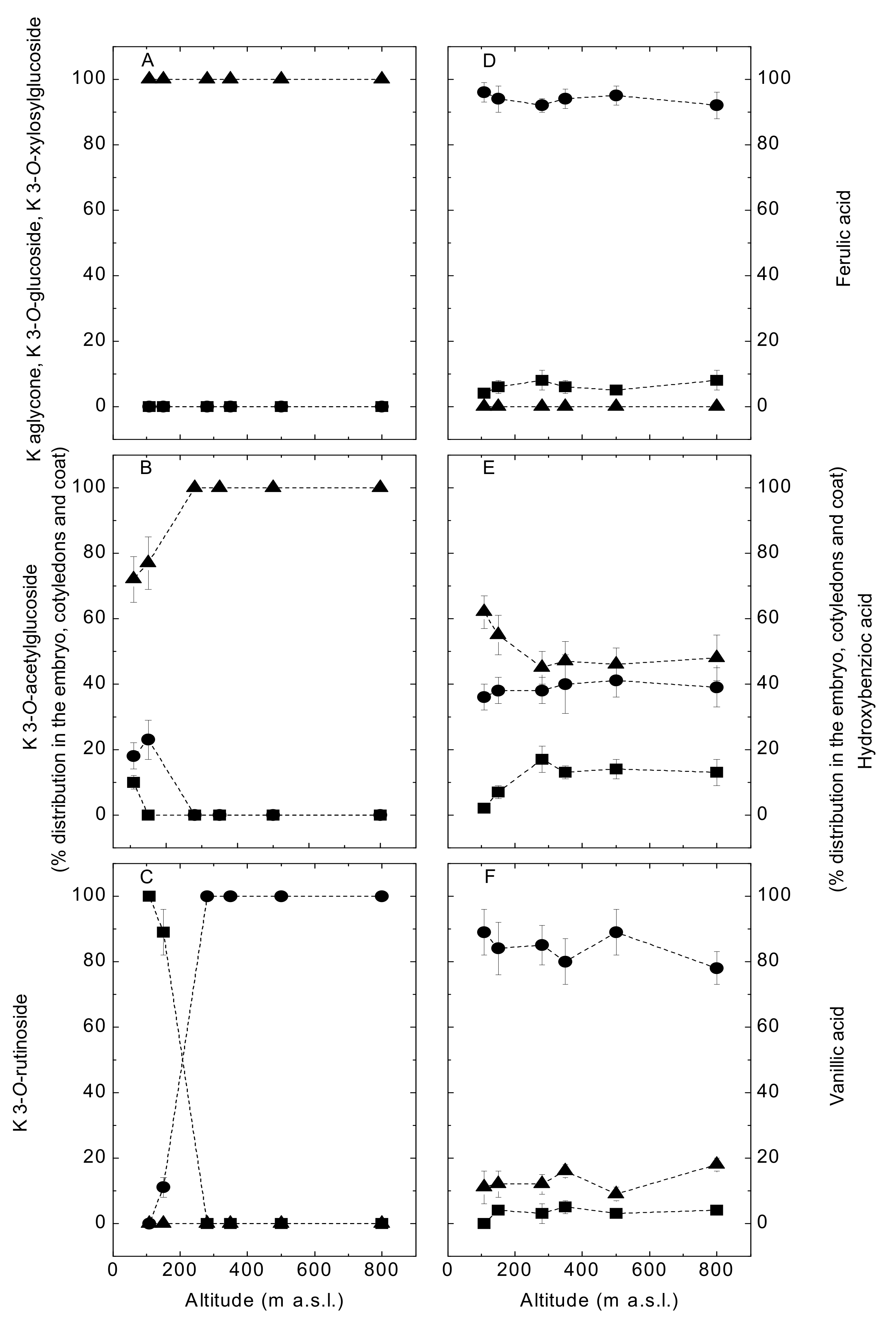
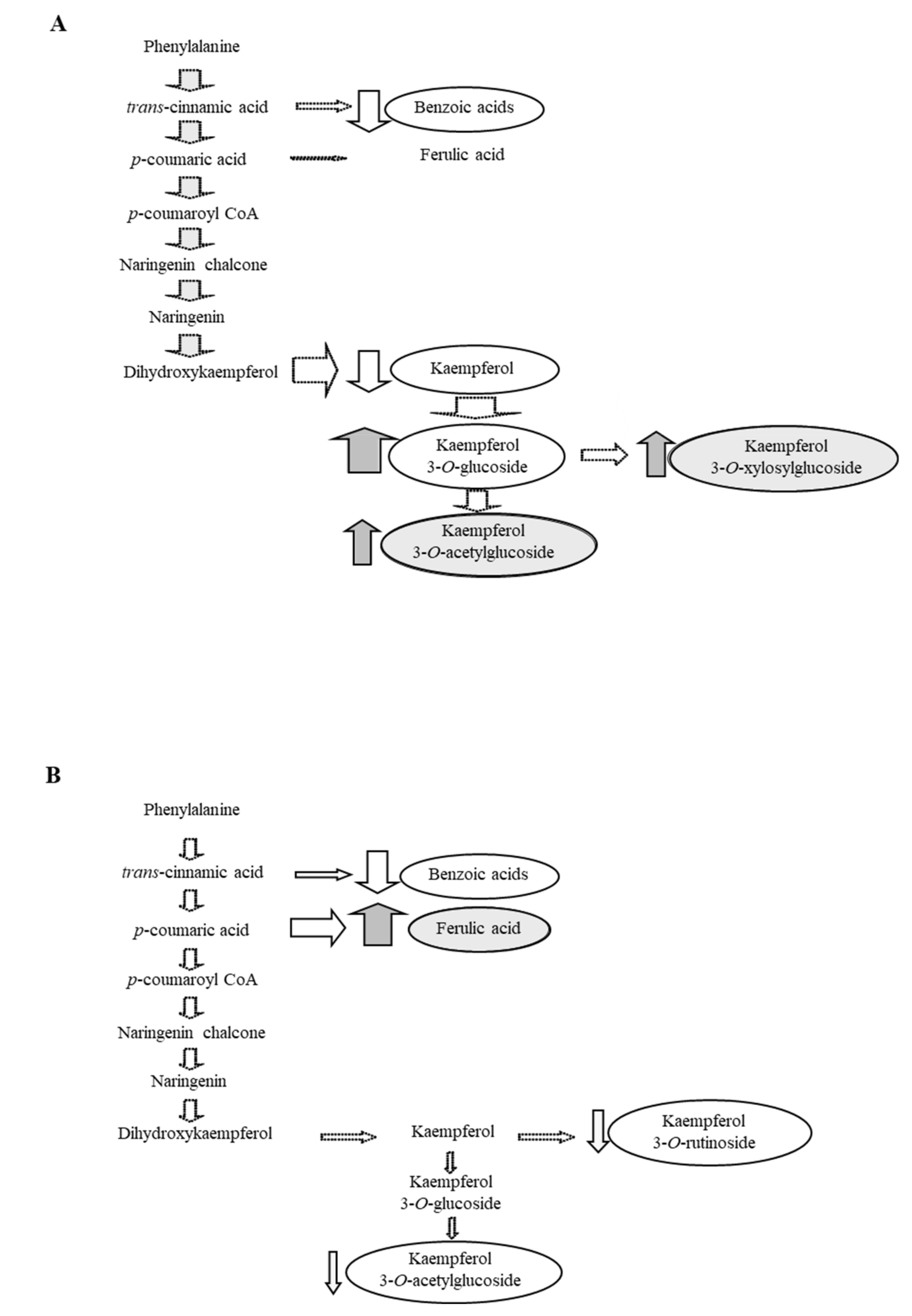
3.2. Effects of Altitude (Temperature) on Flavonol Constituent Expression and Distribution within the Ecoptype “Zolfino del Pratomagno”
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chávez-Mendosa, C.; Sánchez, E. Bioactive compounds from Mexican varieties of the common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris): Implications for Health. Molecules 2017, 22, 1360–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, Q.Q.; Gan, R.Y.; Ge, Y.Y.; Zhang, D.; Corke, H. Polyphenols in common beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.): Chemistry, Analysis, and Factors affecting composition. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2018, 17, 1518–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Díaz-Batalla, L.; Widholm, J.M.; Fahey, G.C., Jr.; Castaňno-Tostado, E.; Peredes-López, O. Chemical components with health implications in wild and cultivated Mexican common beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 2045–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinelli, G.; Bonetti, A.; Marotti, I.; Minelli, M.; Catizone, P.; Mazzanti, A. Contents of flavonoids in the Italian bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) ecotypes. Food Chem. 2006, 99, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranilla, L.; Genovese, M.I.; Lajolo, F.M. Polyphenols and antioxidant capacity of seed coat and cotyledon from Brazilian and Peruvian Bean cultivars (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosi, S.; Bregola, V.; Dinelli, G.; Trebbi, G.; Truzzi, F.; Marotti, I. The nutraceutical value of grain legumes: Characterisation of bioactives and antinutritionals related to diabesity management. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 2863–2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera-De la Fuente, M.; González-Morales, S.; Juárez-Maldonado, A.; Leija-Martínez, P.; Benavides-Mendoza, A. Plant nutrition and agronomic management to obtain crops with better nutritional and nutraceutical quality. In Therapeutic Foods: Handbook of Food Bioengineering; Holban, A.M., Grumezescu, A.M., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2018; pp. 99–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazai, P.; Noulas, C.; Khah, E.; Vlachostergios, D. Yield and seed quality parameters of common bean cultivars grown under water and heat stress field conditions. AIMS Agric. Food 2019, 4, 285–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, M.D.; Acosta-Gallegos, J.A.; Reynoso-Camacho, R.; Pérez-Ramírez, I.F. Common bean seeds from plants subjected to severe drought, restricted- and full-irrigation regimes show differential phytochemical fingerprint. Food Chem. 2019, 294, 368–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusvuran, S.; Dasgan, H.Y. Effects of drought stress on physiological and biochemical changes in Phaseolus vulgaris L. Legume Res. 2017, 40, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soureshjani, H.K.; Nezami, A.; Kafi, M.; Tadayon, M. Responses of two common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) genotypes to deficit irrigation. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 213, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvi, G. I Legume da Granella. Ministero Delle Politiche Agricole Alimentari e Forestali. 2016. Available online: www.politicheagricole.it/flex/cm/pages/ServeAttachment.php/L/IT/D/9%2Fa%2F7%2FD (accessed on 19 February 2020).
- Xu, B.J.; Chang, S.K. A comparative study on phenolic profiles and antioxidant activities of legumes as affected by extraction solvents. J. Food Sci. 2007, 72, S159–S166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singleton, V.L.; Rossi, J.A. Colorimetry of Total Phenolics with Phosphomolybdic-Phosphotungstic Acid Reagents. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 1965, 16, 144–158. [Google Scholar]
- Mattila, P.; Kampulainen, J. Determination of free and total phenolic acids in plant-derived foods by HPLC with Diode-Array detection. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 3660–3667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romani, A.; Vignolini, P.; Galardi, C.; Mulinacci, N.; Benedettelli, S.; Heimler, D. Germplasm characterization of Zolfino landraces (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) by flavonoid content. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 3838–3842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sako, Y.; Regnier, E.E.; Daoust, T.; Fujimura, K.; Harrison, S.K.; Miller, B.; McDonald, M.B. Computer image analysis and classification of giant ragweed seeds. Weed Sci. 2001, 49, 738–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinelli, G.; Aloisio, I.; Bonetti, A.; Marotti, I.; Cifuentes, A. Compositional changes induced by UV-B radiation treatment of common bean and soybean seedlings monitored by capillary electrophoresis with diode array detection. J. Sep. Sci. 2007, 30, 604–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darkwa, K.; Ambachew, D.; Mohammed, H.; Asfaw, A.; Blair, M.W. Evaluation of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) genotypes for drought stress adaptation in Ethiopia. Crop J. 2016, 4, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, L.; Wen, K.S.; Ruan, X.; Zhao, Y.X.; Wei, F.; Wang, Q. Response of plant secondary metabolites to environmental factors. Molecules 2018, 23, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soil Survey Division Staff. Examination and Description of Soil Profiles. In Soil Survey Manual, US Department of Agriculture Handbook 18; Soil Survey Division Staff, Ed.; US Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 2017; pp. 83–230. [Google Scholar]
- Chávez-Mendoza, C.; Hernández-Figueroa, K.I.; Sánchez, E. Antioxidant capacity and phytonutrient content in the seed coat and cotyledon of common beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) from Various Regions in Mexico. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jimoh, M.O.; Afolayan, A.J.; Lewu, F.B. Antioxidant and phytochemical activities of Amaranthus caudatus L. harvested from different soils at various growth stages. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozovaya, V.V.; Lygin, A.V.; Ulanov, A.V.; Nelson, R.L.; Daydé, J.; Widholm, J.M. Effect of temperature and soil moisture status during seed development on soybean seed isoflavone concentration and composition. Crop Sci. 2010, 45, 1934–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kashyap, D.; Sharma, A.; Tuli, H.S.; Sak, K.; Punia, S.; Mukherjee, T.K. Kaempferol –A dietary anticancer molecule with multiple mechanisms of action: Recent trends and advancements. J. Funct. Foods 2010, 30, 203–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaakola, L.; Hohtola, A. Effect of latitude on flavonoid biosynthesis on plants. Plant Cell Environ. 2010, 33, 1239–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albert, A.; Sareedenchai, V.; Heller, W.; Seidlitz, H.K.; Zidorn, C. Temperature is the key to altitudinal variation of phenolics in Arnica montana L. c.v. ARBO. Oecologia 2009, 160, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, S.; Zietz, M.; Schreiner, M.; Rohn, S.; Kroh, L.W.; Krumbein, A. Genotypic and climatic influences on the concentration and composition of flavonoids in kale (Brassica oleracea var. sabellica). Food Chem. 2010, 119, 1293–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballizany, W.L.; Hofmann, R.W.; Jahufer, M.Z.Z.; Barrett, B.A. Genotype × environment analysis of flavonoid accumulation and morphology in white clover under contrasting field conditions. Field Crops Res. 2012, 28, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitura, K.; Arntfield, S.D. Characteristics of flavonol glycosides in bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) seed coats. Food Chem. 2019, 272, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiesinger, J.A.; Glahn, R.P.; Cichy, K.A.; Kolba, N.; Hart, J.J.; Tako, E. An in vivo (Gallus gallus) feeding trial demonstrating the enhanced iron bioavailability properties of the fast cooking Manteca Yellow Bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Nutrients 2019, 11, 1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, J.; Dixon, R.A. The ‘ins’ and ‘outs’ of flavonoid transport. Trends Plant Sci. 2009, 15, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Principle Factors | Polyphenols (mg g−1) | Flavonols (µg g−1) | Yield (t ha−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Year 1 | 3.79 * | 409.0 * | 2.00 ns |
| Year 2 | 3.49 * | 349.7 * | 1.90 ns |
| Genotype Zolfino | 1.18 ** | 353.9 * | 1.77 ** |
| Genotype Verdone | 6.10 ** | 404.8 * | 2.13 ** |
| Pisa (17.5 to 21.9 °C ) | 3.45 ** | 354.8 * | 2.28 * |
| Bologna (21.4 to 24.8 °C) | 3.84 ** | 403.9 * | 1.63 * |
| No Irrigation (ca 50% FC) | 3.72 * | 416.2 ** | 1.58 ** |
| Full Irrigation | 3.56 * | 342.2 ** | 2.33 ** |
| No Fertilizer | 3.72 ns | 409.8 ** | 1.61 ** |
| Fertilizer | 3.56 ns | 348.9 ** | 2.29 ** |
| Location × Genotype | Pisa Zolfino | Bologna Zolfino | Pisa Verdone | Bologna Verdone |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yield (t ha−1) | ||||
| All Treatments | 1.83 ± 0.63 | 1.71 ± 0.87 | 2.72 ± 0.85 | 1.55 ± 0.81 |
| Non-Irrigated | 1.55 ± 0.51 | 1.22 ± 0.38 | 2.43 ± 0.65 | 1.10 ± 0.40 |
| Irrigated | 2.09 ± 0.66 | 2.20 ± 0.97 | 3.08 ± 0.94 | 1.97 ± 0.87 |
| Flavonols (µg g−1) | ||||
| All Treatments | 388.5 ± 84.5 | 319.3 ± 61.0 | 321.0 ± 68.9 | 488.9 ± 136.0 |
| Non-Irrigated | 434.3 ± 85.0 | 350.9 ± 49.0 | 342.5 ± 76.0 | 545.0 ± 118.0 |
| Irrigated | 351.6 ± 72.0 | 287.6 ± 49.0 | 299.0 ± 55.8 | 431.2 ± 132.0 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marotti, I.; Whittaker, A.; Benvenuti, S.; Benedettelli, S.; Ghiselli, L.; Dinelli, G.; Bosi, S. Temperature-Associated Effects on Flavonol Content in Field-Grown Phaseolus vulgaris L. Zolfino del Pratomagno. Agronomy 2020, 10, 682. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10050682
Marotti I, Whittaker A, Benvenuti S, Benedettelli S, Ghiselli L, Dinelli G, Bosi S. Temperature-Associated Effects on Flavonol Content in Field-Grown Phaseolus vulgaris L. Zolfino del Pratomagno. Agronomy. 2020; 10(5):682. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10050682
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarotti, Ilaria, Anne Whittaker, Stefano Benvenuti, Stefano Benedettelli, Lisetta Ghiselli, Giovanni Dinelli, and Sara Bosi. 2020. "Temperature-Associated Effects on Flavonol Content in Field-Grown Phaseolus vulgaris L. Zolfino del Pratomagno" Agronomy 10, no. 5: 682. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10050682
APA StyleMarotti, I., Whittaker, A., Benvenuti, S., Benedettelli, S., Ghiselli, L., Dinelli, G., & Bosi, S. (2020). Temperature-Associated Effects on Flavonol Content in Field-Grown Phaseolus vulgaris L. Zolfino del Pratomagno. Agronomy, 10(5), 682. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10050682






