Smartphone Applications Targeting Precision Agriculture Practices—A Systematic Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Role of ICT, Smartphones and Mobile Applications in Agriculture
“[…] it may be safely stated that modern large scale farming technology […] controlled by state of the art information and communication technology has the potential for substantial reductions of the production costs for agricultural commodities.”
1.2. Mobile Ecosystems
1.3. Smartphone Embedded Sensors/Modems and Their Functionalities
1.4. Smartphone Applications for Agriculture
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Data Sources
2.2. Groups of Agricultural Applications
- Crop operations:
- (a)
- Crop protection and diagnosis:
- Pest and diseases detection and diagnosis;
- Weeds identification and treatment;
- Soil and plant diagnosis.
- (b)
- Crop nutrition and fertilization:
- Crop nutrition monitoring;
- Spraying management;
- Fertilization application.
- (c)
- Crop irrigation:
- Crop hydric status and irrigation decision;
- Support irrigation.
- (d)
- Crop growth and canopy management:
- Track canopy growth;
- Calculate LAI (Leaf Area Index).
- (e)
- Crop harvest:
- Estimation of productivity;
- Indicators of quality.
- Farm management:
- (a)
- Field mapping and soil information:
- Field location and area calculation;
- Identification of sample collection points;
- Soils agricultural indicators: colour, pH, NPK (N—nitrogen, P—phosphorus and K—potassium), carbon content, etc.
- (b)
- Machinery management:
- Machinery costs estimator;
- Real-time field trajectories monitoring;
- Machinery monitoring: activities, productivity, efficient use, stability, etc.
- (c)
- Control of farm activities:
- Manage field tasks;
- Manage farm workers’ activities.
- Information system:
- ●
- Agricultural tips and knowledge;
- ●
- Market information;
- ●
- Relevant news;
- ●
- Chat with experts;
- ●
- Climate.
2.3. Filtering Criteria
- Applications not relevant to agriculture;
- Applications for non-plant-based agriculture (e.g., livestock, aquaculture, poultry farming, etc.);
- Applications that communicate with a remote terminal only to monitor sensors (e.g., weather stations);
- Web-based applications that cannot be installed on mobile devices (e.g., applications that run in the web browser);
- Applications that do not provide the English language.
- Applications found on Google Play and/or App Store rated less than 3.5 stars (if available in both stores, must be less than 3.5 in both) on the date of this review (May 2020);
- Paid applications found on Google Play and/or App Store.
2.4. Information Displayed
- Type of application (crop protection and diagnosis; crop nutrition and fertilization; crop irrigation; crop growth and canopy management; crop harvest; field mapping and soil information; machinery management; control of farm activities; information system);
- Processing type (without processing; local processing; cloud processing);
- Operating platform (Android; iOS; Windows 10 Mobile) and source from which the application was found (scientific database; Google Play; App Store);
- Download availability;
- Languages in which it is available;
- Need for the Internet connection;
- Use of internal sensors;
- Need for external sensors;
- Possibility to save and reuse data (export and import data);
- Interface (little cared; simple; elaborated) and ease of use.
3. Results
3.1. Crop Operation
3.1.1. Crop Protection and Diagnosis
3.1.2. Crop Nutrition and Fertilization
3.1.3. Crop Irrigation
3.1.4. Crop Growth and Canopy Management
3.1.5. Crop Harvest
3.2. Farm Management
3.2.1. Field Mapping and Soil Information
3.2.2. Machinery Management
3.2.3. Control of Farm Activities
3.3. Information System
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions and Final Remarks
5.1. Research Challenges
5.2. Limitations in Application Development
5.3. Future Trends
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| ALS | Ambient Light Sensor |
| ARS | Agricultural Research Service |
| AWS | Automated Weather Stations |
| CD | Coverage Density |
| CSV | Comma-Separated Values |
| DL | Deep Learning |
| DRS | Diameter Relative Span |
| EVI | Enhanced Vegetation Index |
| GIS | Geographic Information System |
| GNSS | Global Navigation Satellite System |
| GPS | Global Positioning System |
| ICT | Information and Communications Technologies |
| IT | Information Technology |
| LAI | Leaf Area Index |
| MCT | Mobile Communication Technologies |
| ML | Machine Learning |
| NARO | National Agricultural Research Organization |
| NDVI | Normalized Difference Vegetation Index |
| NFC | Near Field Communication |
| NGB | Near-infrared, Green, Blue |
| NIR | Near-infrared |
| NRG | Near-infrared, Red, Green |
| pCAPS | portable Classification Application for Plants and Soil |
| PET | Potential Evapotranspiration |
| PGC | Percentage of Green Cover |
| RZSWD | Root Zone Soil Water Deficits |
| SHP | Shapefile |
| SS | Scoring System |
| USDA | United States Department of Agriculture |
| VMD | Volumetric Median Diameter |
| WLAN | wireless Local Area Networking |
| WSN | Wireless sensor network |
| XML | Extensible Markup Language |
References
- Da Cruz, S.M.S.; Vieira, A.C.D.M.; Marques, M.M. Technological Management of Small Crops Through Mobile Apps and Precision Agriculture. In Proceedings of the Annual Conference on Brazilian Symposium on Information Systems: Information Systems: A Computer Socio-Technical Perspective (SBSI 2015), Goiania, Brazil, 26–29 May 2015; Volume 1, pp. 379–386. [Google Scholar]
- Kasey, P. Gartner Top 10 Strategic Technology Trends for 2018. Available online: https://www.gartner.com/smarterwithgartner/gartner-top-10-strategic-technology-trends-for-2018 (accessed on 4 November 2019).
- Statista. Number of Mobile App Downloads Worldwide in 2016, 2017 and 2021, by Store. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/276602/annual-number-of-mobile-app-downloads-by-store/ (accessed on 30 October 2019).
- Rita, I.G. A InfluêNcia das AplicaçõEs Móveis na Percepção da Imagem de Marcas Comerciai—A Perspectiva dos Consumidores. Master’s Thesis, Universidade Europeia—Laureate International Universities, Lisbon, Portugal, June 2016. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/10400.26/14350 (accessed on 4 November 2019).
- Patel, H.; Patel, D. Survey of android apps for agriculture sector. Int. J. Inf. Sci. Tech. 2016, 6, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuharić, D.; Bubalo, A.; Galić, A. Mobile applications in agriculture. In Proceedings of the 10th International Scientific/Professional Conference, Agriculture in Nature and Environment Protection, Vukovar, Croatia, 5–7 June 2017; pp. 237–242. [Google Scholar]
- Arroqui, M.; Mateos, C.; Machado, C.; Zunino, A. RESTful Web Services improve the efficiency of data transfer of a whole-farm simulator accessed by Android smartphones. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2012, 87, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brugger, F. Mobile Applications in Agriculture; Syngenta Foundation: Basel, Switzerland, 2011; pp. 1–38. [Google Scholar]
- Mittal, S.; Gandhi, S.; Tripathi, G. Socio-Economic Impact of Mobile Phones on Indian Agriculture; Working Paper, No. 246; Indian Council for Research on International Economic Relations (ICRIER): New Delhi, India, 2010; Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/10419/176264 (accessed on 6 November 2019).
- Csótó, M. Mobile devices in agriculture: Attracting new audiences or serving the tech-savvy? J. Agric. Inform. 2015, 6, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuhlmann, F.; Berg, E. The Farm as an Enterprise—The European Perspective. In Proceedings of the 13th International Farm Management Congress, Wageningen, The Netherlands, 7–12 July 2002; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Maréchal, N. What Do We Mean by Mobile Ecosystems? Available online: https://rankingdigitalrights.org/2016/09/15/what-are-mobile-ecosystems/ (accessed on 23 January 2020).
- Statista. Number of Apps Available in Leading App Stores as of 3rd Quarter 2019. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/276623/number-of-apps-available-in-leading-app-stores/ (accessed on 23 January 2020).
- Statista. Distribution of Free and Paid Apps in the Apple App Store and Google Play as of December 2019. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/263797/number-of-applications-for-mobile-phones/ (accessed on 23 January 2020).
- Google Developers. Connectivity Overview. Available online: https://developer.android.com/guide/topics/connectivity (accessed on 7 November 2019).
- Google Developers. Sensors Overview. Available online: https://developer.android.com/guide/topics/sensors/sensors_overview (accessed on 7 November 2019).
- Karetsos, S.; Costopoulou, C.; Sideridis, A. Developing a smartphone app for m-government in agriculture. J. Agric. Inform. 2014, 5, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morais, R.; Silva, N.; Mendes, J.; Adão, T.; Pádua, L.; López-Riquelme, J.A.; Pavón-Pulido, N.; Sousa, J.J.; Peres, E. mySense: A comprehensive data management environment to improve precision agriculture practices. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 162, 882–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bambini, M.D.; Luchiari-Júnior, A.; Romani, L.A.S. Mercado de aplicativos móveis (apps) para uso na agricultura. In Proceedings of the Simpósio Nacional de Instrumentação Agropecuária (SIAGRO 2014), São Carlos, Brazil, 18–20 November 2014; pp. 711–714. [Google Scholar]
- Pongnumkul, S.; Chaovalit, P.; Surasvadi, N. Applications of smartphone-based sensors in agriculture: A systematic review of research. J. Sens. 2015, 2015, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Plantix. The Smart Crop Assistant on Your Smartphone. Available online: https://plantix.net/ (accessed on 7 October 2019).
- International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics. Mobile App to Help Farmers Overcome Crop Damage. Available online: http://www.icrisat.org/mobile-app-to-help-farmers-overcome-crop-damage/ (accessed on 25 May 2020).
- BioLeaf. Foliar Analysis™. Available online: http://bioleaf.icmc.usp.br/ (accessed on 7 October 2019).
- Machado, B.B.; Orue, J.P.; Arruda, M.S.; Santos, C.V.; Sarath, D.S.; Goncalves, W.N.; Silva, G.G.; Pistori, H.; Roel, A.R.; Rodrigues, J.F., Jr. BioLeaf: A professional mobile application to measure foliar damage caused by insect herbivory. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2016, 129, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reddy, S.; Pawar, A.; Rasane, S.; Kadam, S. A Survey on Crop Disease Detection and Prevention using Android Application. Int. J. Innov. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2015, 2, 621–626. [Google Scholar]
- ADAMA. ADAMA Bullseye. Available online: https://www.adama.com/us/en/adama-bullseye (accessed on 25 May 2020).
- Macmillan, C. PMapp: A Mobile App for Assessing Powdery Mildew. Available online: http://www.vineyardteam.org/files/resources/PMapp.pdf (accessed on 9 October 2019).
- Scott, E.S.; Powell, S.; Evans, K.; Barry, K.; Petrovic, T.; Kravchuk, O.; Zanker, T.; Evans, K.J. Digital tools to facilitate assessing powdery mildew on grape bunches. In Proceedings of the 21st Australasian Plant Pathology Society Biennial Conference: Science Protecting Plant Health, Brisbane, Australia, 26–28 September 2017; p. 142. [Google Scholar]
- Petrellis, N. A smart phone image processing application for plant disease diagnosis. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Modern Circuits and Systems Technologies (MOCAST 2017), Thessaloniki, Greece, 4–6 May 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Petrellis, N. Plant Disease Diagnosis for Smart Phone Applications with Extensible Set of Diseases. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- ImScope. Application for Android and An Experimental Tool Oriented to Visualization and Recording of Indicators of Plant Health. Available online: https://www.idoneos.com/procesamiento_de_imagenes/imscope/imscope_(english).html (accessed on 9 October 2019).
- Buinickaitė, A. Crop Problem Identification—Quick and Easy. Available online: https://blog.farmis.lt/crop-problem-identification-quick-and-easy-3be14752fd8c (accessed on 25 May 2020).
- Machado, B.B.; Spadon, G.; Arruda, M.S.; Goncalves, W.N.; Carvalho, A.C.; Rodrigues-Jr, J.F. A smartphone application to measure the quality of pest control spraying machines via image analysis. In Proceedings of the 33rd Annual ACM Symposium on Applied Computing (SAC’18), Pau, France, 9–13 April 2018; pp. 956–963. [Google Scholar]
- Hefty, D.; Hefty, B. Ag PhD Crop Nutrient Deficiencies App Now Available! Available online: http://www.agphd.com/resources/ag-phd-mobile-apps/ag-phd-crop-nutrient-deficiencies/ (accessed on 12 November 2019).
- Yara International ASA. Farmer’s Toolbox TankmixIT. Available online: https://www.yara.co.uk/crop-nutrition/farmers-toolbox/tankmixit/ (accessed on 12 November 2019).
- TeeJet Technologies. SpraySelect. Available online: https://www.teejet.com/tools/index.aspx (accessed on 25 May 2020).
- Ferguson, J.C.; Chechetto, R.G.; O’Donnell, C.C.; Fritz, B.K.; Hoffmann, W.C.; Coleman, C.E.; Chauhan, B.S.; Adkins, S.W.; Kruger, G.R.; Hewitt, A.J. Assessing a novel smartphone application—SnapCard, compared to five imaging systems to quantify droplet deposition on artificial collectors. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2016, 128, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bueno-Delgado, M.V.; Molina-Martínez, J.M.; Correoso-Campillo, R.; Pavón-Mariño, P. Ecofert: An Android application for the optimization of fertilizer cost in fertigation. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2016, 121, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vellidis, G.; Liakos, V.; Andreis, J.H.; Perry, C.D.; Porter, W.M.; Barnes, E.M.; Morgan, K.T.; Fraisse, C.; Migliaccio, K.W. Development and assessment of a smartphone application for irrigation scheduling in cotton. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2016, 127, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skewes, M.; Petrie, P.R.; Liu, S.; Whitty, M. Smartphone tools for measuring vine water status. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Sensing Plant Water Status—Methods and Applications in Horticultural Science (SPWS 2016), Potsdam, Germany, 5–7 October 2016; pp. 53–58. [Google Scholar]
- Petrie, P.R.; Wang, Y.; Liu, S.; Lam, S.; Whitty, M.A.; Skewes, M.A. The accuracy and utility of a low cost thermal camera and smartphone-based system to assess grapevine water status. Biosyst. Eng. 2019, 179, 126–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Society for Enology and Viticulture. A Thermal Camera-Based Smartphone Application to Measure Vine Water Status. Available online: http://www.asev.org/abstract/thermal-camera-based-smartphone-application-measure-vine-water-status (accessed on 16 October 2019).
- Hernández-Hernández, J.L.; Ruiz-Hernández, J.; García-Mateos, G.; González-Esquiva, J.M.; Ruiz-Canales, A.; Molina-Martínez, J.M. A new portable application for automatic segmentation of plants in agriculture. Agric. Water. Manag. 2017, 183, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Mateos, G.; Hernández-Hernández, J.L.; Escarabajal-Henarejos, D.; Jaén-Terrones, S.; Molina-Martínez, J.M. Study and comparison of color models for automatic image analysis in irrigation management applications. Agric. Water. Manag. 2015, 151, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Júnior, W.M.; Valeriano, T.T.B.; De Souza Rolim, G. EVAPO: A smartphone application to estimate potential evapotranspiration using cloud gridded meteorological data from NASA-POWER system. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 156, 187–192. [Google Scholar]
- Fuentes, S.; De Bei, R.; Pozo, C.; Tyerman, S. Development of a smartphone application to characterise temporal and spatial canopy architecture and leaf area index for grapevines. Wine Vitic. J. 2012, 6, 56–60. [Google Scholar]
- Fuentes, S.; Poblete-Echeverría, C.; Ortega-Farias, S.; Tyerman, S.; De Bei, R. Automated estimation of leaf area index from grapevine canopies using cover photography, video and computational analysis methods. Aust. J. Grape Wine Res. 2014, 20, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bei, R.; Fuentes, S.; Gilliham, M.; Tyerman, S.; Edwards, E.; Bianchini, N.; Smith, J.; Collins, C. VitiCanopy: A free computer App to estimate canopy vigor and porosity for grapevine. Sensors 2016, 16, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Easlon, H.M.; Bloom, A.J. Easy Leaf Area: Automated digital image analysis for rapid and accurate measurement of leaf area. Appl. Plant Sci. 2014, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easlon, H.M. Easy-Leaf-Area. Available online: https://github.com/heaslon/Easy-Leaf-Area (accessed on 20 December 2019).
- Easlon, H.M. Canopy Cover Free (Version 1.0.3—2016). Available online: https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.heaslon.canopycover (accessed on 15 October 2019).
- Patrignani, A.; Ochsner, T.E. Canopeo: A powerful new tool for measuring fractional green canopy cover. Agron. J. 2015, 107, 2312–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Canopeo. Rapid and Accurate Green Canopy Cover Measurement Tool. Available online: http://www.canopeoapp.com/ (accessed on 15 October 2019).
- Booth, D.T.; Cox, S.E.; Berryman, R.D. Point sampling digital imagery with “SamplePoint”. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2006, 123, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Systat Software. SigmaScan Pro—Analyze Images Automatically. Available online: https://systatsoftware.com/products/sigmascan/ (accessed on 20 December 2019).
- Confalonieri, R.; Foi, M.; Casa, R.; Aquaro, S.; Tona, E.; Peterle, M.; Boldini, A.; De Carli, G.; Ferrari, A.; Finotto, G.; et al. Development of an app for estimating leaf area index using a smartphone. Trueness and precision determination and comparison with other indirect methods. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2013, 96, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Confalonieri, R.; Francone, C.; Foi, M. The PocketLAI smartphone app: An alternative method for leaf area index estimation. In Proceedings of the 7th International Congress on Environmental Modelling and Software (iEMSs 2014), San Diego, CA, USA, 15–19 June 2014; pp. 288–293. [Google Scholar]
- Orlando, F.; Movedi, E.; Coduto, D.; Parisi, S.; Brancadoro, L.; Pagani, V.; Guarneri, T.; Confalonieri, R. Estimating leaf area index (LAI) in vineyards using the PocketLAI smart-app. Sensors 2016, 16, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sinergise. Sentinel-2 NDVI Maps—Sentinel App for Android. Available online: http://www.sentinel-hub.com/explore/industries-and-showcases/sentinel-2-ndvi-maps (accessed on 15 October 2019).
- OneSoil. Make Reliable Agricultural Decisions with AI. Available online: https://onesoil.ai/en/ (accessed on 12 November 2019).
- Bauer, J.; Siegmann, B.; Jarmer, T.; Aschenbruck, N. Smart fLAIr: A smartphone application for fast LAI retrieval using ambient light sensors. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Sensors Applications Symposium (SAS 2016), Catania, Italy, 20–22 April 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Huning, L.; Bauer, J.; Aschenbruck, N. A Privacy Preserving Mobile Crowdsensing Architecture for a Smart Farming Application. In Proceedings of the First ACM Workshop on Mobile Crowdsensing Systems and Applications (CrowdSenSys’17), Delft, The Netherlands, 5 November 2017; pp. 62–67. [Google Scholar]
- Aquino, A.; Millan, B.; Gaston, D.; Diago, M.P.; Tardaguila, J. vitisFlower®: Development and testing of a novel Android-smartphone application for assessing the number of grapevine flowers per inflorescence using artificial vision techniques. Sensors 2015, 15, 21204–21218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aquino, A.; Barrio, I.; Diago, M.P.; Millan, B.; Tardaguila, J. vitisBerry: An Android-smartphone application to early evaluate the number of grapevine berries by means of image analysis. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2018, 148, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Koirala, A.; Walsh, K.; Anderson, N.; Verma, B. In Field Fruit Sizing Using A Smart Phone Application. Sensors 2018, 18, 3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carvalho, P. As Apps NA Agricultura—Agri Precision. Abolsamia, 105, March and April 2017. p. 98. Available online: https://issuu.com/abolsamia/docs/abolsamia_105/98 (accessed on 17 October 2019).
- Buinickaitė, A. 2,5M Farmers Are Already Measuring Their Fields for Free. Available online: https://blog.farmis.lt/2-5m-farmers-are-already-measuring-their-fields-for-free-4908bc0ee0a0 (accessed on 25 May 2020).
- Randytė, A. Why Measuring and Tracking the Field Is So Important? Available online: https://blog.farmis.lt/why-measuring-and-tracking-the-field-is-so-important-4b949bca2acb (accessed on 25 May 2020).
- Farmis. Soil Sampler (Version 1.0.10—2018). Available online: https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.noframe.farmissoilsamples (accessed on 17 October 2019).
- Delgado, J.A.; Kowalski, K.; Tebbe, C. The first Nitrogen Index app for mobile devices: Using portable technology for smart agricultural management. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2013, 91, 121–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, J.A.; Gagliardi, P.M.; Rau, E.J.; Fry, R.; Figueroa, U.; Gross, C.; Cueto-Wong, J.; Shaffer, M.J.; Kowalski, K.; Neer, D.; et al. Nitrogen Index 4.4, User Manual. 2011. Available online: https://vtechworks.lib.vt.edu/bitstream/handle/10919/69932/4975_Nitrogen_Index_4_4_User_Manual_final.pdf (accessed on 17 October 2019).
- Agri Info Design. AgriBus-NAVI: GPS Guidance System to Mount on Agricultural Machinery. Available online: https://agri-info-design.com/en/agribus-navi/ (accessed on 22 October 2019).
- Hamada, Y.; Matsuo, Y.; Yamashita, T. Agricultural Vehicle Navigation System. Jpn. Agric. Res. Q. 2009, 43, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamamoto, S.; Matsuo, Y.; Hamada, Y.; Yukimoto, O. Farm Operation-Supporting Program, Operation Navigator for Agricultural Vehicle and Farm Operation-Supporting Method. Japanese Patent JP4572417B2, 4 November 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Buinickaitė, A. Are Large Investments Necessary to Obtain the Benefits of Precision Farming? Available online: https://blog.farmis.lt/how-field-navigator-can-help-a-farmer-94aaadf11ae6 (accessed on 25 May 2020).
- Lantzos, T.; Koykoyris, G.; Salampasis, M. FarmManager: An Android application for the management of small farms. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Information and Communication Technologies in Agriculture, Food and Environment (HAICTA 2013), Corfu Island, Greece, 19–22 September 2013; pp. 587–592. [Google Scholar]
- Agroop. Agroop Cooperation—Crop Monitoring. Available online: https://www.agroop.net/en/whatwedo#cooperation (accessed on 13 November 2019).
- AgriApp Technologies. AgriApp—Connecting Farmers. Available online: http://agriapp.co.in/ (accessed on 24 October 2019).
- Zargar, H. AgriApp: An App for Farmers to Help Them Improve Crop Output. Available online: https://www.livemint.com/Technology/btn0QkaCI3rBtdotyiQdfL/AgriApp-An-app-for-farmers-to-help-them-improve-crop-output.html (accessed on 25 May 2020).
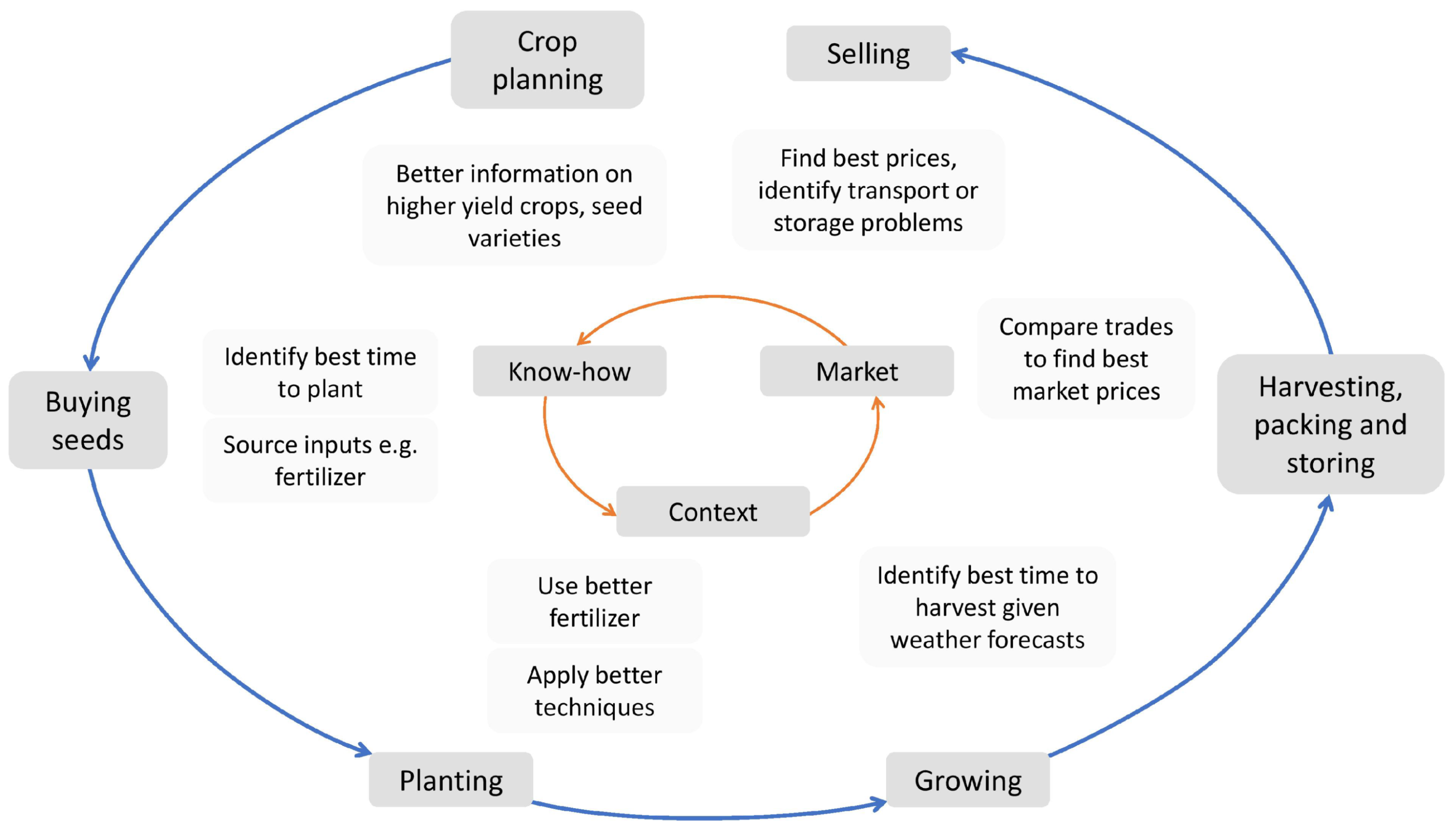






































| Stage | Typical Information Needed |
|---|---|
| Know-how | What are the new crop options? |
| Are there higher value crops that I can grow? | |
| Contextual information | When/how much should I sow? |
| When should I harvest taking climate/soil into account? | |
| What are the best practices for my crop/soil? | |
| Market information | What are the products prices? |
| What are the market needs? |
| Smartphone Sensors and Modems | General Function | Application in Agricultural Practices |
|---|---|---|
| Motion sensors | ||
| Accelerometer | Measure rotational velocity along the Roll, Pitch, and Yaw axes | Motion detection (shake, tilt, etc.) to assist in the agricultural machine’s navigation |
| Gyroscope | Measure orientation and angular velocity | Rotation detection (spin, turn, etc.) to assist in the agricultural machine’s navigation |
| Magnetometer | Measure direction, strength, or relative change of a magnetic field | Create a compass to assist in the agricultural machine’s navigation |
| Image sensors | ||
| Camera | Record images and videos | Image processing for objects characterization and counting |
| Environment sensors | ||
| Temperature | Measure the ambient temperature | Measure the ambient temperature in the field to be used, for example, by growth, climate and pest models |
| Relative Humidity | Measure the ambient relative humidity | Measure the ambient relative humidity in the field to be used, for example, by growth, climate and pest models |
| Pressure | Measure the ambient pressure | Measure the ambient pressure in the field to calculate altitude, for example |
| Light | Measure ambient illuminance in lux | Measure ambient illuminance in the field to correct image colors, for example |
| Position sensors | ||
| Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) | Provide geolocation and time information | Geolocation of samples taken in the field and agricultural machines navigation |
| Connectivity modems | ||
| Cellular network | Allow connection to a cellular network | Communicate with a remote server to send data and/or receive information resulting from its processing |
| WiFi | Create wireless local area networking (WLAN) of devices | Communicate with devices that may be scattered across the field and communicate with a remote server to send data and/or receive information resulting from its processing |
| Bluetooth | Exchange data between fixed and mobile devices over short distances | Communicate with devices that may be scattered across the field |
| Near Field Communication (NFC) | Enable wireless information exchange between nearby devices | Read information of tags distributed across fields |
| Work | Name | Type | Processing Type | Platform (Source) | Available for Download | Languages | Need Internet | Use Internal Sensors | Need External Sensors | Import or Export Data | Interface and Ease of Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [21,22] | Plantix | CPD | Cloud | Android (GP) | Yes | EN, PT, FR, ES, *1 | Yes | Camera | No | No | Elaborated Easy to use |
| [23,24] | BioLeaf | CPD | Local | Android (SDB) | Yes | EN, PT, RU, ES | No | Camera | No | Yes | Simple Easy to use |
| [25] | E-agree | CPD | Cloud | Android (SDB) | No | EN, MR | Yes | Camera | No | No | Little cared Easy to use |
| [26] | ADAMA Bullseye | CPD | No | Android, iOS (AS) | Yes | EN | No | No | No | No | Elaborated Easy to use |
| [27,28] | PMapp | CPD | No | Android (SDB) | Yes | EN | No | No | No | Yes | Little cared Easy to use |
| [29,30] | Plant Disease | CPD | Local | Win10Mob (SDB) | No | EN, EL | No | Camera, GNSS | No | No | Elaborated Easy to use |
| [31] | ImScope | CPD | Local | Android (GP) | Yes | EN, ES | No | Camera | No | No | Little cared Easy to use |
| [32] | Agrobase | CPD | No | Android, iOS (AS) | Yes | EN, PT, FR, ZH, AR, NL, BG, FI, # | No | No | No | No | Simple Easy to use |
| [33] | DropLeaf | CNF | Local | Android (SDB) | Yes | EN, PT, ES, RU | No | Camera | No | No | Simple Easy to use |
| [34] | Crop Nutrient Deficiencies | CNF | No | Android, iOS (GP) | Yes | EN | Yes | No | No | No | Elaborated Easy to use |
| [35] | Yara TankmixIT | CNF | No | Android, iOS (GP) | Yes | EN, PT, IT, DE, DA, ES, FR, # | Yes | No | No | Yes | Little cared Easy to use |
| [36] | SpraySelect | CNF | No | Android, iOS (GP) | Yes | EN | Yes | No | No | No | Elaborated Easy to use |
| [37] | SnapCard | CNF | Local | Android, iOS (SDB) | Yes | EN | No | Camera | No | Yes | Simple Easy to use |
| [38] | EcoFert | CNF | No | Android (SDB) | No | EN, ES, FR, DE | Yes | No | No | Yes | Little cared Easy to use |
| [39] | Smartirrigation Cotton | CNF | No | Android, iOS (SDB) | Yes | EN | Yes | GNSS | No | Yes | Elaborated Easy to use |
| [40,41,42] | Grapevine Water Stress | CI | Local | Android (SDB) | No | EN | No | No | FLIR One | —– | Simple Easy to use |
| [43] | pCAPS | CI | Local | Android (SDB) | No | EN | No | Camera, GNSS | No | Yes | Little cared Easy to use |
| [45] | EVAPO | CI | No | Android (SDB) | Yes | EN | Yes | GNSS | No | Yes | Simple Easy to use |
| [46,47,48] | VitiCanopy | CGCM | Local | Android, iOS (SDB) | Yes | EN | No | Camera, GNSS | No | Yes | Simple Easy to use |
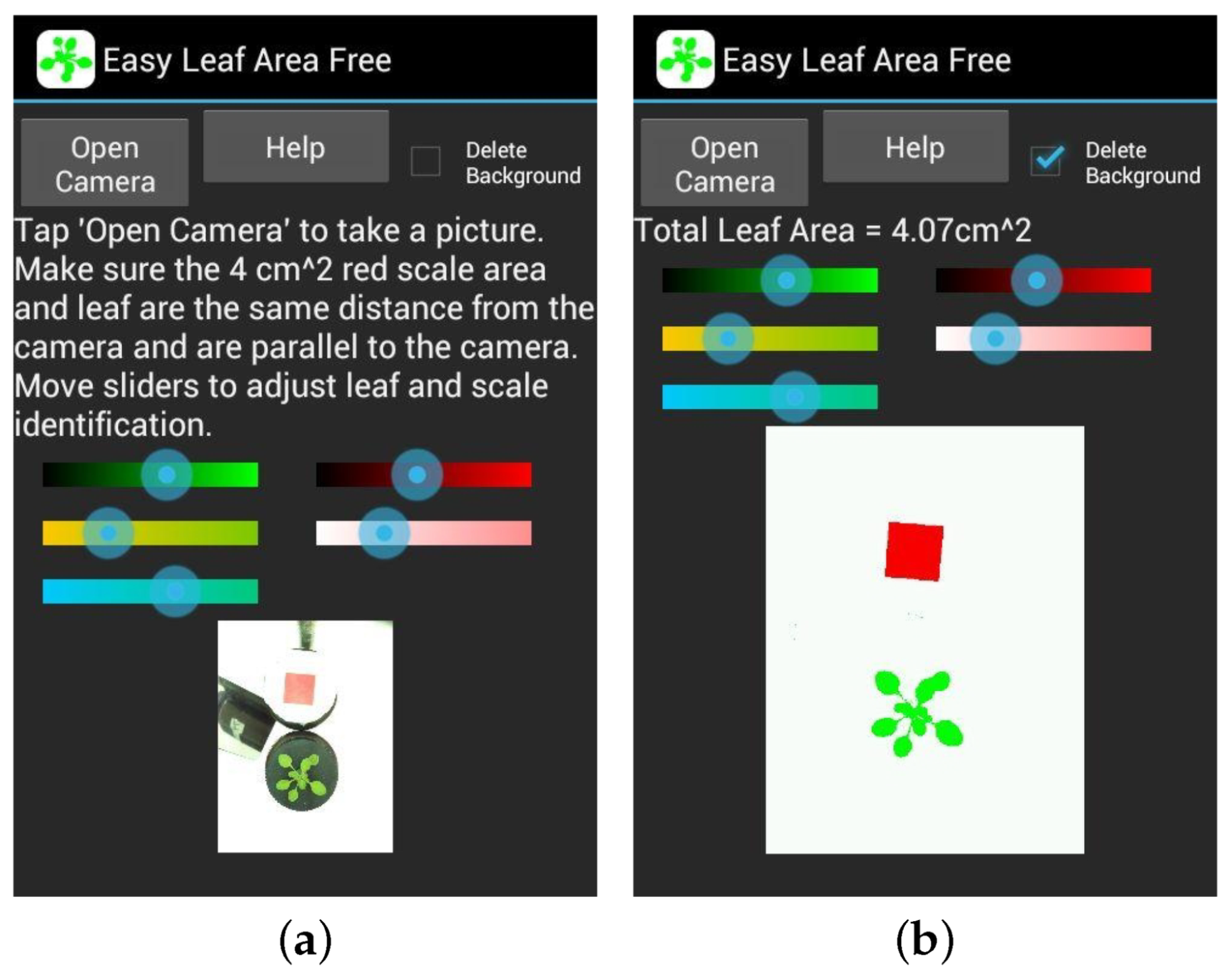
| [49] | Easy Leaf Area | CGCM | Local | Android (SDB) | Yes | EN | No | Camera | No | No | Little cared Easy to use |
| [51] | Canopy Cover Free | CGCM | Local | Android (GP) | Yes | EN | No | Camera, GNSS | No | Yes | Little cared Easy to use |
| [52,53] | Canopeo | CGCM | Local | Android, iOS (SDB) | Yes | EN | No | Camera, GNSS | No | Yes | Simple Easy to use |
| [56,57,58] | PocketLAI | CGCM | Local | Android (SDB) | No | EN | No | Camera, GNSS, Accelerometer | No | Yes | Simple Easy to use |
| [59] | Sentinel-2 NDVI Maps | CGCM | No | Android (GP) | Yes | EN | Yes | No | No | No | Simple Easy to use |
| [60] | OneSoil Scouting | CGCM | No | Android, iOS (AS) | Yes | EN, PT, FR, ES, IT, DE, RU | Yes | No | No | No | Elaborated Easy to use |
| [61,62] | Smart fLAIr | CGCM | No | Android (SDB) | Yes | EN | No | Ambient Light, GNSS | No | Yes | Little cared Easy to use |
| [63] | vitisFlower | CH | Local | Android (SDB) | Yes | EN, ES | No | Camera | No | Yes | Simple Easy to use |
| [64] | vitisBerry | CH | Local | Android (SDB) | No | EN, ES | No | Camera | No | Yes | Simple Easy to use |
| [65] | FruitSize | CH | Local | Android (SDB) | Yes | EN | No | Camera, GNSS | No | Yes | Little cared Easy to use |
| [66] | Agri Precision | FMSI | No | Android (GP) | Yes | EN, PT, IT, ES, FR | No | GNSS | No | Yes | Little cared Easy to use |
| [67,68] | GPS Fields Area Measure | FMSI | No | Android, iOS (AS) | Yes | EN, PT, FR, ES, ZH, AR, CS, NL, # | No | GNSS | No | Yes | Simple Easy to use |
| [69] | Soil Sampler | FMSI | No | Android (GP) | Yes | EN, PT, FR, ZH, AR, *2 | Yes | GNSS | No | Yes | Simple Easy to use |
| [70] | Nitrogen Index | FMSI | No | Android (SDB) | Yes | EN, ES | No | No | No | Yes | Little cared Easy to use |
| [72] | AgriBus-NAVI | MM | No | Android (GP) | Yes | EN, PT, ES, # | Yes | GNSS | No | No | Simple Easy to use |
| [75] | Field Navigator | MM | No | Android (GP) | Yes | EN, PT, FR, ZH, *3 | Yes | GNSS | No | No | Simple Easy to use |
| [76] | FarmManager | CFA | No | Android (SDB) | No | EN, EL | Yes | No | No | —– | Little cared Easy to use |
| [77] | Agroop Cooperation | CFA | No | Android, iOS (AS) | Yes | EN, PT | Yes | No | Stoock device | No | Elaborated Easy to use |
| [78,79] | AgriApp | IS | No | Android (GP) | Yes | EN | Yes | No | No | No | Elaborated Easy to use |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mendes, J.; Pinho, T.M.; Neves dos Santos, F.; Sousa, J.J.; Peres, E.; Boaventura-Cunha, J.; Cunha, M.; Morais, R. Smartphone Applications Targeting Precision Agriculture Practices—A Systematic Review. Agronomy 2020, 10, 855. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10060855
Mendes J, Pinho TM, Neves dos Santos F, Sousa JJ, Peres E, Boaventura-Cunha J, Cunha M, Morais R. Smartphone Applications Targeting Precision Agriculture Practices—A Systematic Review. Agronomy. 2020; 10(6):855. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10060855
Chicago/Turabian StyleMendes, Jorge, Tatiana M. Pinho, Filipe Neves dos Santos, Joaquim J. Sousa, Emanuel Peres, José Boaventura-Cunha, Mário Cunha, and Raul Morais. 2020. "Smartphone Applications Targeting Precision Agriculture Practices—A Systematic Review" Agronomy 10, no. 6: 855. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10060855
APA StyleMendes, J., Pinho, T. M., Neves dos Santos, F., Sousa, J. J., Peres, E., Boaventura-Cunha, J., Cunha, M., & Morais, R. (2020). Smartphone Applications Targeting Precision Agriculture Practices—A Systematic Review. Agronomy, 10(6), 855. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10060855










