Abstract
The aim of this study was to evaluate the ability of three hemp cultivars to accumulate heavy metals under sewage sludge (SS) and phosphogypsum (PG) application. The field study was carried out from 2014 to 2016 on Luvisol (loamy sand) in Poland. The experiment scheme included five treatments—T0: the control without fertilization, T1: 170 kg N (nitrogen) ha−1 from sewage sludge, T2: 170 kg N ha−1 from sewage sludge and 100 kg ha−1 of phosphogypsum, T3: 170 kg N ha−1 from sewage sludge and 500 kg ha−1 of phosphogypsum, and T4: 170 kg N ha−1 from sewage sludge and 1000 kg ha−1 of phosphogypsum. It was found that the application of municipal sewage sludge enriched the soil with the bioavailable forms of heavy metals to the greatest extent and contributed to the highest increase in their contents in vegetative and generative organs of hemp plants. These parameters showed a phosphogypsum dose-dependent decline, which could hinder the phytoextraction process. The greatest extractions of heavy metal(loid)s (HMs) from the soil treated with SS and PG were achieved by the Tygra variety, which had the highest bioconcentration factor (BCF) and biomass yield.
1. Introduction
Heavy metal(loid)s (HMs) (i.e., elements with an atomic density greater than 4–6 g cm−3) (with the exception of As, B, and Se) include both biologically essential (e.g., Fe, Co, Cu, Cr, Mn, Ni, and Zn) as well as non-essential (Cd, Pb, Hg, and As) elements. Both groups are toxic to plants at excessive concentrations. Moreover, unlike organic contaminants, they generally do not undergo microbial or chemical degradation, thus bioaccumulating and remaining a potential threat to living organisms throughout all levels of the food chain for many years after entering the soil [1,2,3,4]. Hence, the presence of these potentially toxic compounds restricts the utilization of byproducts such as sewage sludge (SS) or phosphogypsum (PG) for agricultural purposes in many countries [5,6,7].
Sewage sludge is a heterogeneous byproduct of sewage treatment processes consisting primarily of a mixture of organic and inorganic compounds, including assumably hazardous elements such as heavy metals. In the European Union, more than 10 million tons of SS dry matter (10 to 15 kg per person) are generated annually. In the future, this is expected to increase to 15 million tons. The main route for their recovery is land application, which is in accordance with circular economy policies [5,8,9,10,11,12].
Phosphogypsum is a waste byproduct composed mainly of calcium sulfate dihydrate (>90% gypsum) from the processing of phosphate rock by the “wet acid method” of fertilizer production, according to the reaction [13,14,15]:
Ca5(PO4)3F + 5H2SO4 + 10H2O → 5CaSO4 ·2H2O + 3H3PO4 + HF.
During this process, 2%–12% of trace elements from phosphate rock is transferred to PG, except for Pb, Sr, Ce, and Y, which are characterized by higher values of this indicator (27%–66%). Worldwide, 100 to 280 Mt of PG (i.e., 4 to 5 tons per ton of phosphoric acid) are produced each year. However, barely 15% of PG is reused as agricultural fertilizer, soil stabilizer, and in the cement industry. The rest (85%) is stored in the vicinity of factories, posing a potential threat to the environment [13,14,15,16].
Most research has focused only on the impact of SS application on HM transformations [6,8,9,10], and its co-application with phosphogypsum has not been studied.
One effective strategy for the utilization of metal-rich byproducts such as SS and PG may be their land application and the biological removal of HMs via plants [6,17,18,19]. Since the polluted biomass could pose a potential risk to the environment, it has to be stored, disposed of, or recycled in a sustainable way [17]. The majority of phytoextraction studies have been conducted on pot and laboratory experiments, while very few studies have attempted to evaluate the natural hyperaccumulators of high-biomass crops like industrial hemp for phytoextraction under field conditions [19,20].
Industrial hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) is an annual dioecious herb that was rediscovered in the 1990s as an important raw material for bio-based products in a sustainable bioeconomy [21]. Hemp can be grown for its biomass, which in turn is used for biogas, cellulosic bioethanol, and lignocellulosic co-firing of coal burners, as well as for seeds, wooden core, fibers, oil, cannabinoids, etc. Ca. sativa L. that contains excessive amounts of heavy metals is recommended for energy use (combustion and recyclation of ash). Hemp fibers with metal contents that are slightly exceeding acceptable limits have industrial application (e.g., the production of composite materials or paper) [22]. Hemp plants are tolerant to contaminants and yield high biomass. Furthermore, they have a short life cycle of 180 days and the ability to accumulate HMs, affected by the genotype, along with the stabilization of the contaminated area [1,7,18,19,23,24,25]. Ca. sativa L. as a phytoextractor presents an innovative and cost-effective solution to decontaminate polluted environments with the simultaneous procurement of bioproducts, hence enabling the boosting of the economy [26]. It should be noted that there is limited knowledge on different hemp varieties’ uptake and translocation of heavy metals in vegetative and generative organs [18,25,27].
The aim of this study was to evaluate the ability of three hemp cultivars to accumulate heavy metals under sewage sludge and phosphogypsum application.
2. Materials and Methods
A field study was carried out in 2014–2016 in a randomized design with three replicates at the Poświętne experimental field of the Mazovian Agricultural Advisory Centre in Poland (52°38′07.5” N 20°22′51.3” E). The soil of the experiment was classified as Luvisol (loamy sand), characterized by a neutral reaction, very high availability of phosphorus, and medium availability of potassium and magnesium. Heavy metal concentrations in the soil did not exceed the permissible limits recommended for agricultural use (i.e., 2 mg kg−1, 50 mg kg−1, 35 mg kg−1, 60 mg kg−1, 120 mg kg−1, and 75 mg kg−1 for cadmium, copper, nickel, lead, zinc, and chromium, respectively) [28].
We selected three hemp cultivars with high biomass production and good climate adaptability which are registered in the Community Catalogue of Varieties cultivars [29] as the test plants (i.e., Białobrzeskie, Tygra, and Beniko).
The experiment scheme included five treatments—T0: the control without fertilization, T1: 170 kg N ha−1 from sewage sludge, T2: 170 kg N ha−1 from sewage sludge and 100 kg ha−1 of phosphogypsum, T3: 170 kg N ha−1 from sewage sludge and 500 kg ha−1 of phosphogypsum, and T4: 170 kg N ha−1 from sewage sludge and 1000 kg ha−1 of phosphogypsum. Prior to sowing hemp seeds (60 kg ha−1), the soil was treated with sewage sludge and phosphogypsum.
The sewage sludge used in the experiment, meeting the permissible standards on the content of heavy metals [28], was collected from the municipal wastewater treatment plant in Płońsk. The phosphogypsum was obtained from Grupa Azoty Zakłady Chemiczne “Police” S.A. The sludge’s organic carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorous contents were 342.8 g kg−1, 40.01 g kg−1, and 9.4 g kg−1, respectively. The phosphogypsum contained 940 g CaSO4 2H2O kg−1, 8.0 g P kg−1, and 5.8 g SiO2 kg−1. The annual rainfall was 381.0 mm, 286.9 mm, and 448.2 mm in 2014, 2015, and 2016, respectively. The mean monthly temperatures in January and July were −3.3 °C and 21.0 °C, 1.0 °C and 19.3 °C, −3.2 °C and 19.2 °C, respectively.
The plants were harvested in autumn (in October) from the entire surface of each plot. The plant material was dried, the vegetative and generative organs were separated, and the material was weighed. Each year, the plant samples were analyzed for the concentration of trace elements (Cd, Co, Cu, Cr, Fe, Mn, Ni, Zn, and Pb) by atomic absorption spectrometry (AAS) after digestion in concentrated nitric acid [30]. Moreover, bioavailable forms of heavy metals were determined in the soil samples collected at the end of each growing season in 2014, 2015, and 2016, according to the Rinkis test (the extractant: 1 M HCl) [31]. HM contents in plant organs that were below detection limits (i.e., Pb and Co) were not included in the figures.
The results are presented in the manuscript as means for the 3 years of studies (i.e., for the period 2014–2016) [17]. Statistica PL 13.3 (TIBCO Software Inc., Tulsa, OK, USA) was used to conduct ANOVA analysis, and Tukey’s mean separation was used to determine the statistical significance at p < 0.05. The heavy metal balance was calculated as a difference between the amount of HM added with the byproducts (SS and PG) and removed with the hemp yield [17]. The bioconcentration factor (BCF) was expressed as the ratio of the metal content in straw/inflorescences to its concentration in a bioavailable form in the soil [32].
3. Results and Discussion
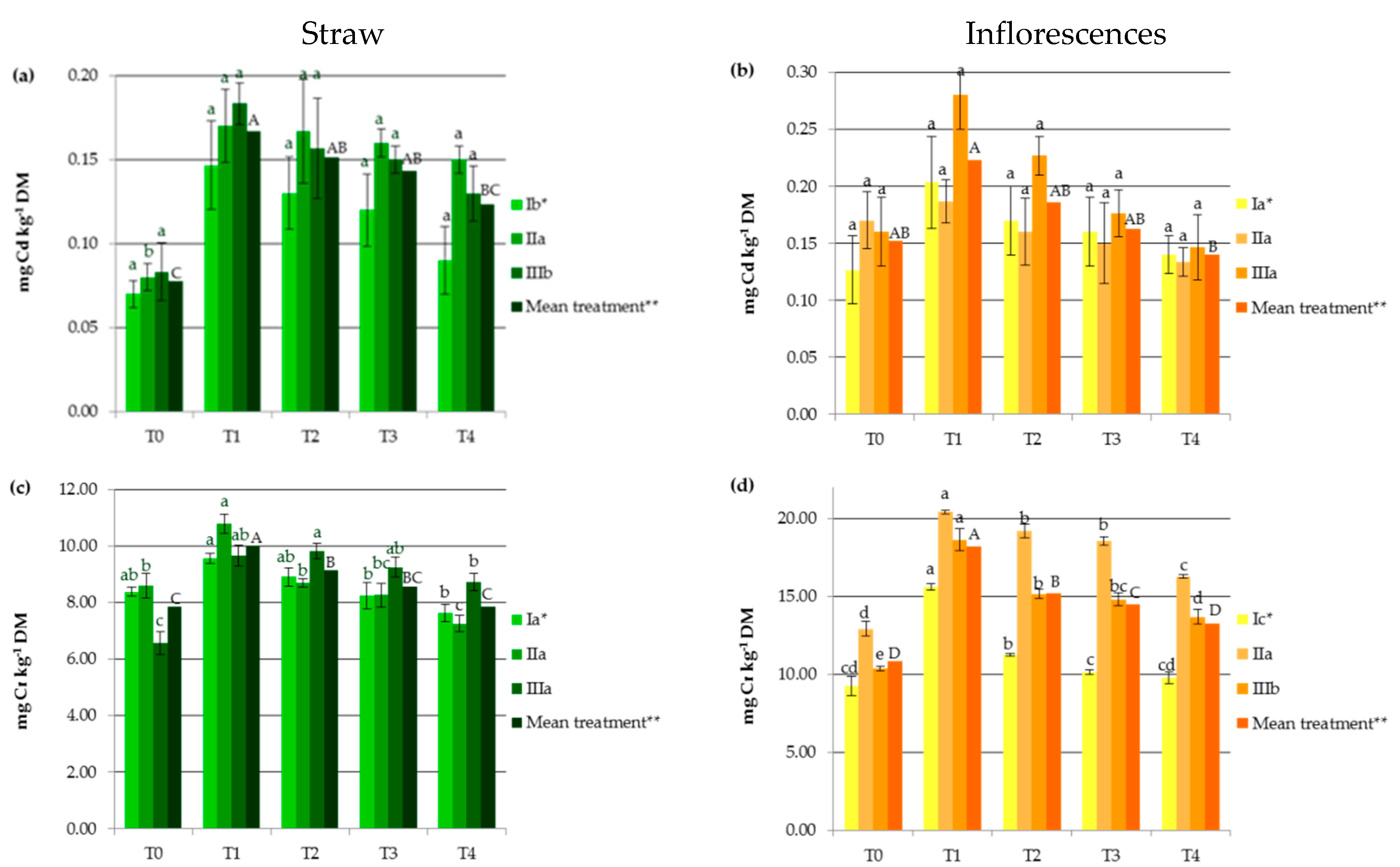
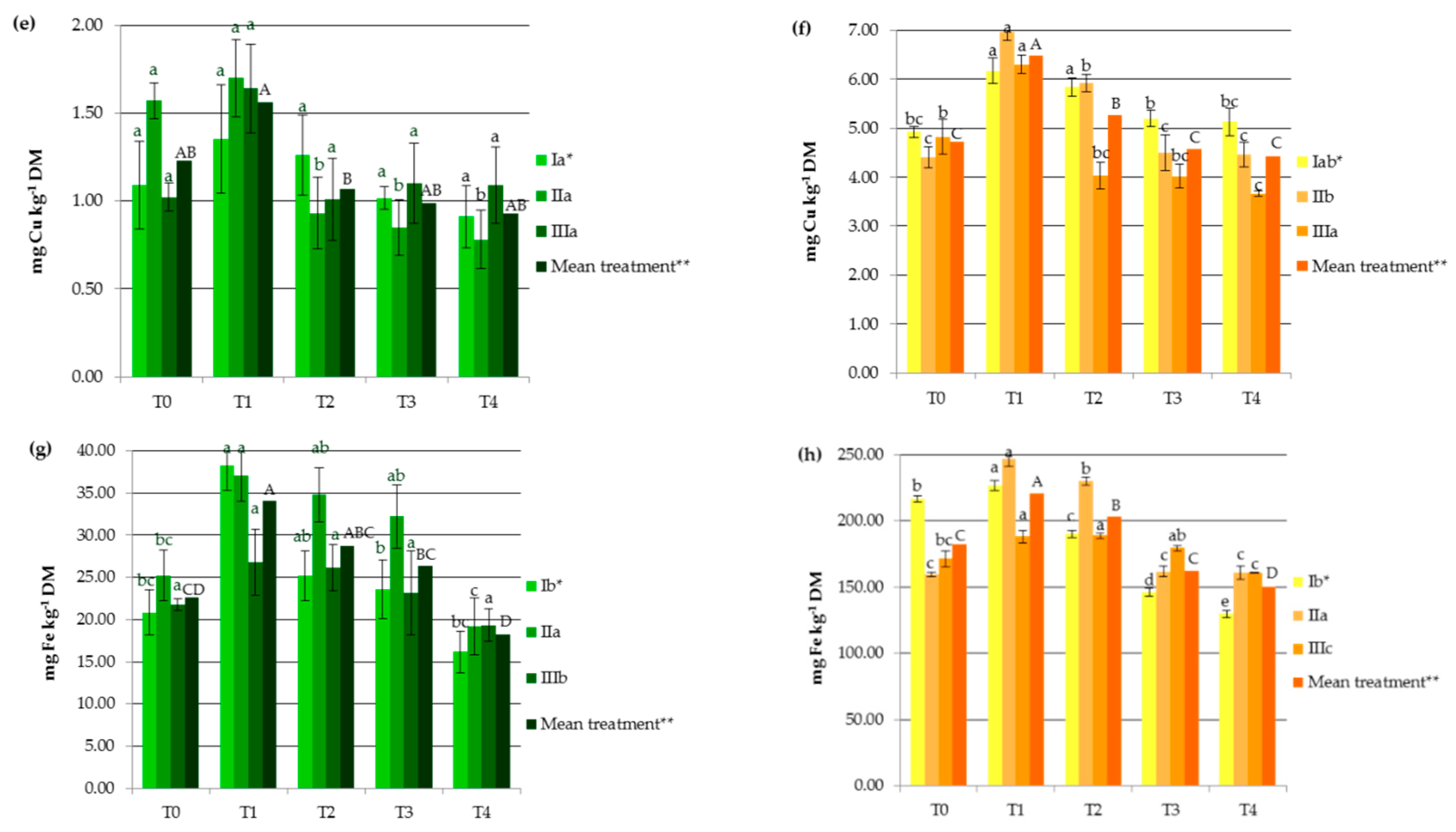
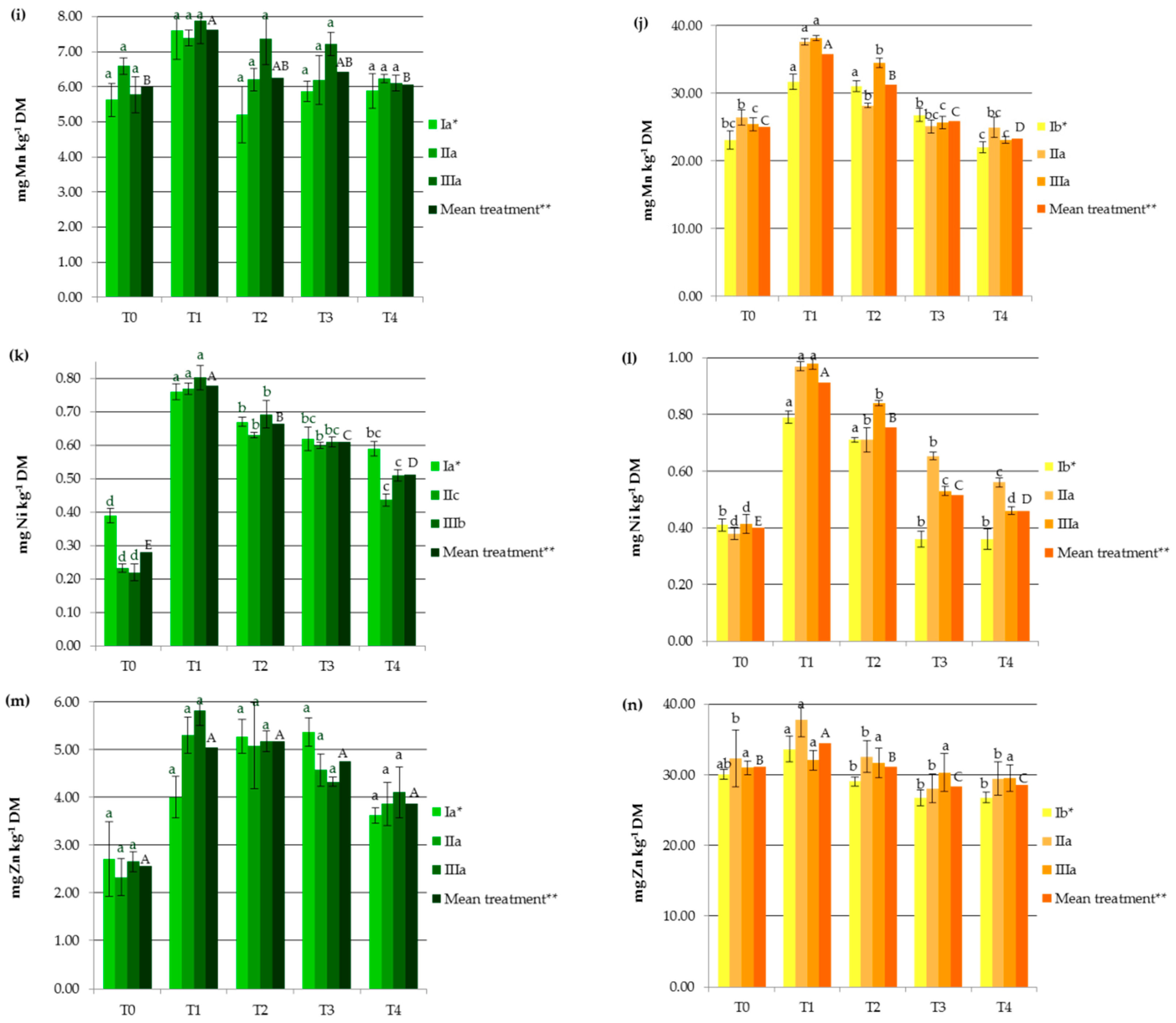
Industrial hemp absorbs a wide range of heavy metals in vegetative and generative parts, in different concentrations (Figure 1), making it suitable to be considered in soil remediation processes. Other studies carried out on Ca. sativa L. have also provided evidence supporting its use as a hyperaccumulator for different toxic trace metals, which pose a great risk to ecological systems [1,23,24,25,27]. In the present study, HM accumulation by hemp was the highest for Fe followed by Mn, Zn, Cr, Cu, Ni, and then Cd (Figure 1). It should be noted that the observed values were lower than those reported for the hemp plants used as a phytoextractor on contaminated soils [19,33,34].
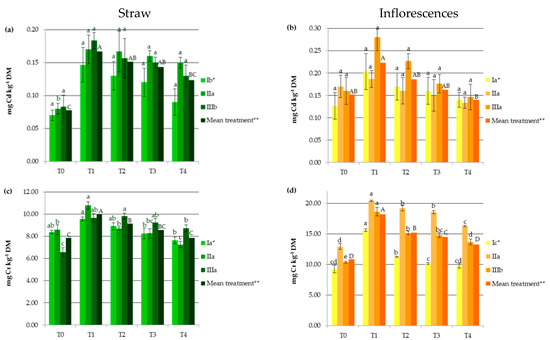
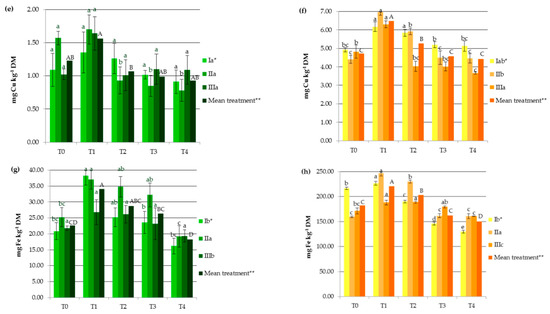
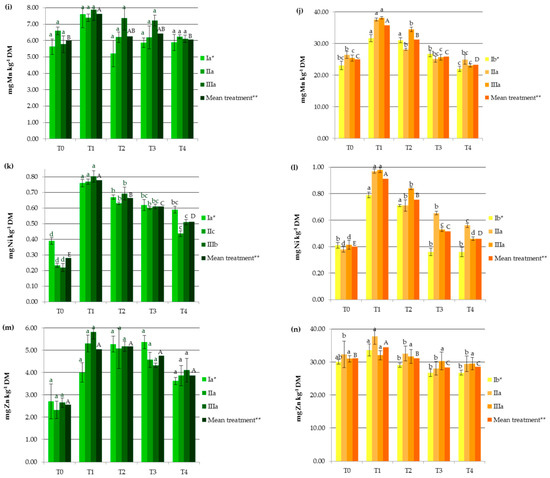
Figure 1.
Impact of soil amendments on contents of heavy metals in hemp straw: (a) Cd, (c) Cr, (e) Cu, (g) Fe, (i) Mn, (k) Ni, (m) Zn, and inflorescences (b) Cd, (d) Cr, (f) Cu, (h) Fe, (j) Mn, (l) Ni, (n) Zn. T0: the control without fertilization, T1: 170 kg N ha−1 from sewage sludge, T2: 170 kg N ha−1 from sewage sludge and 100 kg ha−1 of phosphogypsum, T3: 170 kg N ha−1 from sewage sludge and 500 kg ha−1 of phosphogypsum, T4: 170 kg N ha−1 from sewage sludge and 1000 kg ha−1 of phosphogypsum, I: cv. Białobrzeskie, II: cv. Tygra, III: cv. Beniko. * means of varieties regardless of treatments; ** means of treatments regardless of cultivars. Bars with the same letter are not significantly different (capital letters indicate differences among the means of treatments regardless of cultivars).
Changes in heavy metal contents in hemp depended on the amendment used (SS and PG) and the cultivar (Figure 1). Sewage sludge application contributed to significant increases in HM contents in both vegetative parts except Zn and Cu (by 27.11% for Mn and 176.87% for Ni) and generative organs except Cd (by 11.95% for Zn and by 127.68% for Ni), when compared to the values obtained in the T0 treatment (Figure 1). This was similar to the earlier findings, in which concentrations of HMs were elevated in plants fertilized with sewage sludge [7,8,9,10,11,12].
Increasing the rate of PG application resulted in the depletion of plant concentrations of heavy metals to levels similar to or lower than those recorded in the control treatments. Seemingly, the application of this byproduct induced the immobilization of HMs, mainly due to the interaction of heavy metals with the surface sites of Fe, Al, and Si oxides found in PG and the formation of surface metal complexes [2,33]. Additionally, in the presence of sulfate and phosphate added with PG, the enhanced sorption of some polyvalent cations on metal oxides may have occurred. This is attributed to the increase in the negative charge brought to the surfaces by these ligands, which promoted electrostatic interactions, the formation of ternary A- or B-type complexes, or a mixture of ternary complexes and electrostatics [35]. The reduction in HM concentrations in hemp was undoubtedly also favored by the soil pH, that was greater than 6 in the experimental treatments at which the adsorption of most heavy metals decreased due to the precipitation reaction as well as the antagonistic interactions between the trace elements and/or calcium [36]. Moreover, PG, being a source of additional nutrients (e.g., Ca, S, and P), affected the increase in hemp yield and may have caused a dilution effect. The negative correlation between hemp yield and its HM contents (from r = −0.684 for Cr to r = −0.947 for Zn) seems to confirm this hypothesis. The effect of the cultivar on the heavy metal contents was more important for generative than for vegetative parts (Figure 1). The Tygra cultivar accumulated more Fe, Zn, Cr, and Ni in inflorescences than the two other varieties. Many authors have confirmed the existence of significant genotype differences among varieties in the heavy metal uptake and distribution [27,34].
The bioconcentration factor (BCF), representing the ability of the plant to absorb heavy metal from the soil and translocate it to aboveground tissues [18,19,25,32], was higher in generative than in vegetative organs (Table 1). Angelova et al. [27] have also shown that HMs are particularly stored in hemp inflorescences. The bioaccumulation factors of Cd and Cr in straw and inflorescences were high (>1), indicating that these elements were easily taken up by the hemp. Copper and zinc were accumulated to such an extent only in generative organs, whereas the BCFs for these elements in vegetative parts reached an average level. The translocation of Mn and Ni was also average (BCF 0.1–1.0). Hemp’s ability to absorb Fe from the soil and transport it to the aboveground tissues was very small and ranged from 0.01 in the straw to 0.19 in the inflorescences. This was consistent with the results of previous studies, which demonstrated that Ca. sativa L. meets the criterion of a phytoextractor related to the HM transfer from root to shoot [18,34]. According to Antonkiewicz et al. [17], the total amount of HMs accumulated by high-biomass energy plants could be even greater than that of hyperaccumulators. The bioconcentration factor in most cases showed a PG dose-dependent decline—a fact undoubtedly connected with the phytostabilization processes occurring in PG treatments [18]. It should be noted that the amount of HM uptake by the plants mainly depended on the biomass production in the agroecosystems. Significant positive correlations between HM uptake and hemp yield were found (r = 0.843 for Mn, r = 0.857 for Cd, r = 0.567 for Cu, r = 0.879 for Cr, r = 0.729 for Fe, r = 0.891 for Zn, r = 0.819 for Ni). Other authors reported that the phytoextraction efficiency of plants is determined by two key features, that is, the capacity to take up and store elements within the aboveground biomass and biomass production [6,19,20]. The lowest balances of HM in the case of the Tygra variety (Table 1) characterized by the highest yield and BCF seems to confirm this hypothesis.

Table 1.
Impact of soil amendments on bioconcentration factors and balances of heavy metals.
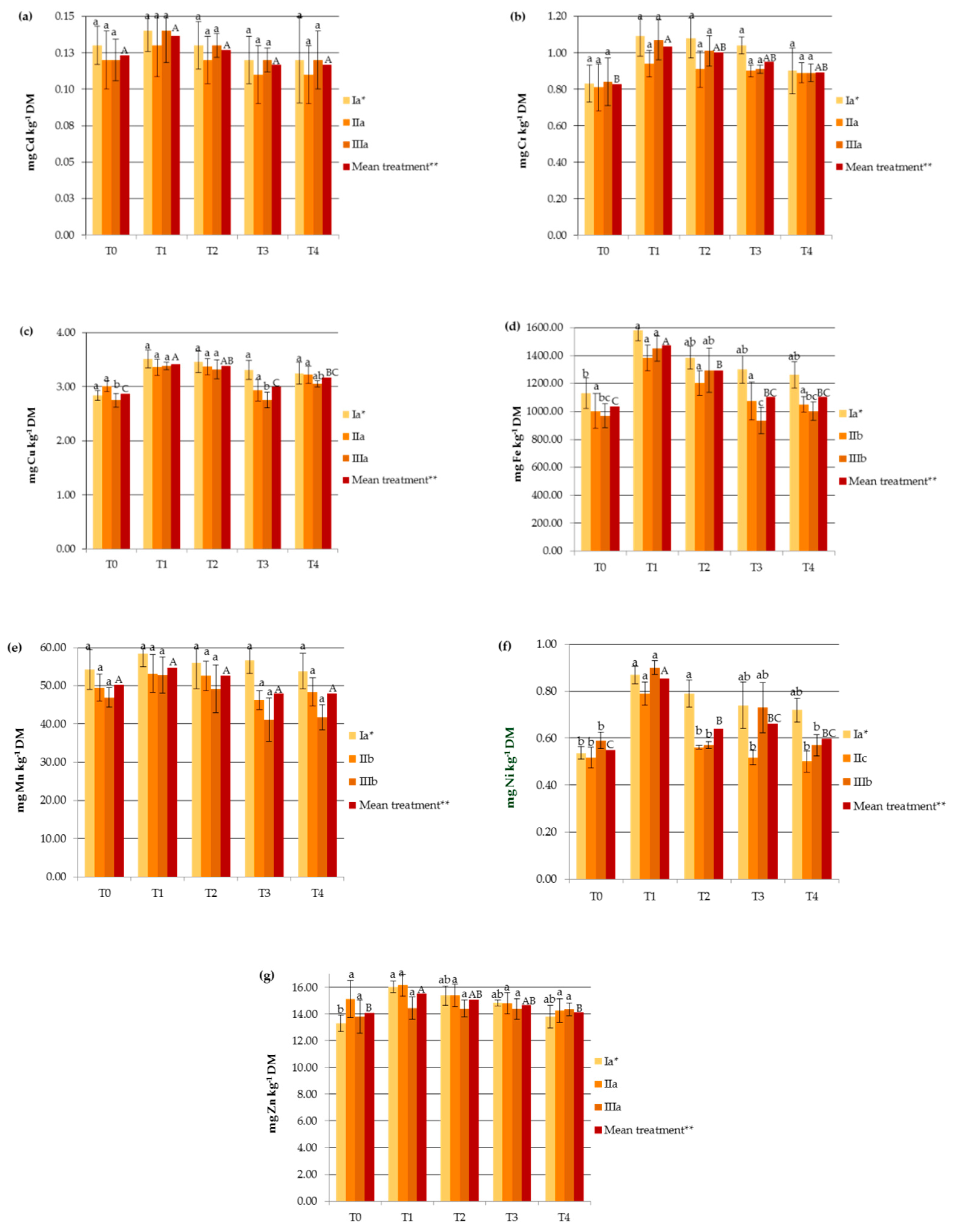
The amount of HMs accumulated in hemp organs increased linearly with the concentrations of available HMs in the soil (r = 0.363 for Mn, r = 0.707 for Cd, r = 0.640 for Cu, r = 0.498 for Cr, r = 0.524 for Fe, r = 0.589 for Zn, r = 0.703 for Ni). It should be underlined that soil metal contents after the application of SS and PG remained in the range typical for unpolluted soils. The highest significant increase in heavy metal concentrations in the soil after SS application was for Ni and Fe, while the effect on Mn and Zn was less pronounced (Figure 2). It is worth mentioning that SS provided more HMs (except for Cd) to the agroecosystem than PG.
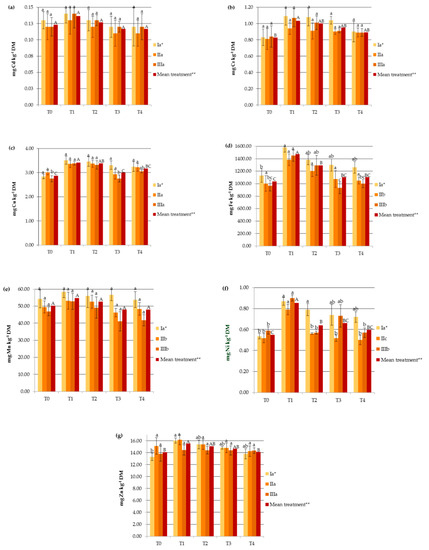
Figure 2.
Impact of soil amendments on the contents of available heavy metals in the soil: (a) Cd, (b) Cr, (c) Cu, (d) Fe, (e) Mn, (f) Ni, (g) Zn. T0: the control without fertilization, T1: 170 kg N ha−1 from sewage sludge, T2: 170 kg N ha−1 from sewage sludge and 100 kg ha−1 of phosphogypsum, T3: 170 kg N ha−1 from sewage sludge and 500 kg ha−1 of phosphogypsum, T4: 170 kg N ha−1 from sewage sludge and 1000 kg ha−1 of phosphogypsum, I: cv. Białobrzeskie, II: cv. Tygra, III: cv. Beniko. * means of varieties regardless of treatments; ** means of treatments regardless of cultivars. Bars with the same letter are not significantly different (capital letters indicate differences among the means of treatments regardless of cultivars).
The amendment with phosphogypsum contributed to a decrease in the contents of available HMs in the soil, which was mirrored in the hemp plants as described above. Heavy metal immobilization differed significantly in the case of Cu, Fe, Zn, and Ni (Figure 2). Previous studies have also demonstrated the immobilization of HMs in the soil through PG amendment [33].
4. Conclusions
The results of the current study indicate that HM contents in hemp were the highest for Fe followed by Mn, Zn, Cr, Cu, Ni, and then Cd, and correlated with the bioavailability of these metals in the soil. Cadmium and chromium were accumulated the most (BCF > 1), whereas iron was absorbed and transported to the aboveground hemp tissues to the smallest extent (BCF ranged from 0.01 in the straw to 0.19 in the inflorescences). The uptaken elements were stored particularly in plant inflorescences. The greatest extractions of HMs from the soil treated with SS and PG were achieved by the Tygra variety, which had the highest BCF and biomass yield, with the latter being more significant.
The application of municipal sewage sludge enriched the soil with the bioavailable forms of heavy metals to the greatest extent and contributed to the highest increase in their contents in the vegetative (by 27.11% for Mn and 176.87% for Ni) and generative organs of hemp plants (by 11.95% for Zn and 127.68% for Ni). These parameters showed a phosphogypsum dose-dependent decline, which could hinder the phytoextraction process. Further study is recommended in order to identify factors influencing this phenomenon, especially in soils polluted with HMs to a greater degree than in the conducted experiment.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.Z. and S.R.; methodology, D.Z. and S.R.; investigation, D.Z. and S.R.; formal analysis, D.Z., S.R., M.S., B.R. and W.S.; writing—original draft preparation, review, and editing, D.Z., S.R. and M.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the European Social Fund, POKL.04.03.00-00-042/12-00.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Ahmad, R.; Tehsin, Z.; Tanvir, S.; Saeed, M.; Asad, A.; Shahzad, M.; Bilal, M.; Shah, M.M.; Khan, S.A. Phytoremediation potential of hemp (Cannabis sativa L.): Identification and characterization of heavy metals responsive genes. Clean Soil Air Water 2016, 44, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Lamb, D.; Paneerselvam, P.; Choppala, G.; Bolan, N.; Chung, J.W. Role of organic amendments on enhanced bioremediation of heavy metal(loid) contaminated soils. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 185, 549–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardhan, K.H.; Kumar, P.S.; Panda, R.C. A review on heavy metal pollution, toxicity and remedial measures: Current trends and future perspectives. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 290, 111197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vareda, J.P.; Valente, A.J.M.; Durãesa, L. Assessment of heavy metal pollution from anthropogenic activities and remediation strategies: A review. J. Environ. Manage. 2019, 246, 101–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collivignarelli, M.C.; Abbà, A.; Frattarola, A.; Miino, M.C.; Padovani, S.; Katsoyiannis, I.; Torretta, V. Legislation for the reuse of biosolids on agricultural land in Europe: Overview. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nissim, W.G.; Cincinelli, A.; Martellini, T.; Alvisi, L.; Palm, E.; Mancuso, S.; Azzarello, E. Phytoremediation of sewage sludge contaminated by trace elements and organic compounds. Environ. Res. 2018, 164, 356–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seleiman, M.F.; Santanen, A.; Stoddard, F.L.; Mäkelä, P. Feedstock quality and growth of bioenergy crops fertilized with sewage sludge. Chemosphere 2012, 89, 1211–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laidlaw, W.S.; Arndt, S.K.; Huynh, T.T.; Gregory, D.; Baker, A.J.M. Phytoextraction of heavy metals by willows growing in biosolids under field conditions. J. Environ. Qual. 2012, 41, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narasimha, M.; Prasad, V.; De Campos Favas, P.J.; Vithanage, M.; Mohan, S.V. (Eds.) Industrial and Municipal Sludge: Emerging Concerns and Scope for Resource, 1st ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann, Elsevier Science: Oxford, UK, 2019; p. 856. [Google Scholar]
- Skowrońska, M.; Bielińska, E.J.; Szymański, K.; Futa, B.; Antonkiewicz, J.; Kolodziej, B. An integrated assessment of the long-term impact of municipal sewage sludge on the chemical and biological properties of soil. Catena 2020, 189, 104484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urra, J.; Alkorta, I.; Garbisu, C. Potential benefits and risks for soil health derived from the use of organic amendments in agriculture. Agronomy 2019, 9, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.-H.; Zhu, G.-Y.; Li, H.L.; Han, X.-M.; Li, J.-M.; Ma, Y.B. Accumulation and bioavailability of heavy metals in a soil-wheat/maize system with long-term sewage sludge amendments. J. Integr. Agric. 2018, 17, 1861–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernysh, Y.; Balintova, M.; Plyatsuk, L.; Holub, M.; Demcak, S. The influence of phosphogypsum addition on phosphorus release in biochemical treatment of sewage sludge. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Layr, K.; Hartlieb, P. Market analysis for urban mining of phosphogypsum. Berg Huettenmaenn Mon. 2019, 164, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadaoui, E.; Ghazel, N.; Romdhane, C.B.; Massoudi, N. Phosphogypsum: Potential uses and problems—A review. J. Environ. Sci. 2017, 74, 558–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hentati, O.; Abrantes, N.; Caetano, A.L.; Bouguerra, S.; Gonçalves, F.; Römbke, J.; Pereira, R. Phosphogypsum as a soil fertilizer: Ecotoxicity of amended soil and elutriates to bacteria, invertebrates, algae and plants. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 294, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonkiewicz, J.; Kołodziej, B.; Bielińska, E.J. Phytoextraction of heavy metals from municipal sewage sludge by Rosa multiflora and Sida hermaphrodita. Int. J. Phytoremediat. 2017, 19, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauddh, K.; Singh, B.; Korstad, J. (Eds.) Phytoremediation Potential of Bioenergy Plants; Springer: Singapore, 2017; p. 472. [Google Scholar]
- Chandra, R.; Kumar, V. Phytoextraction of heavy metals by potential native plants and their microscopic observation of root growing on stabilized distillery sludge as a prospective tool for in situ phytoremediation of industrial waste. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 2605–2619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaverková, M.D.; Zloch, J.; Adamcová, D.; Radziemska, M.; Vyhnánek, T.; Elbl, J.; Trojan, V.; Winkler, J.; Dorđević, B.; Elbl, J.; et al. Landfill Leachate Effects on Germination and Seedling Growth of Hemp Cultivars (Cannabis sativa L.). Waste Biomass Valor. 2019, 10, 369–376. [Google Scholar]
- Adesina, I.; Bhowmik, A.; Sharma, H.; Shahbazi, A. A review on the current state of knowledge of growing conditions, agronomic soil health practices and utilities of hemp in the United States. Agriculture 2020, 10, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griga, M.; Bjelková, M. Flax (Linum usitatissimum L.) and hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) as fibre crops for phytoextraction of heavy metals. Biological, agro-technological and economical point of view. In Plant-Based Remediation Process; Gupta, D.K., Ed.; Springer: Heidelberg/Berlin, Germany, 2013; pp. 199–237. [Google Scholar]
- Galić, M.; Perčin, A.; Zgorelec, Ž.; Kisić, I. Evaluation of heavy metals accumulation potential of hemp (Cannabis sativa L.). J. Cent. Eur 2019, 20, 711. [Google Scholar]
- Girdhar, M.; Sharma, N.R.; Rehman, H.; Kumar, A.; Mohan, A. Comparative assessment for hyperaccumulatory and phytoremediation capability of three wild weeds. Biotech 2014, 4, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Praspaliauskas, M.; Žaltauskaitė, J.; Pedišius, N.; Striūgas, N. Comprehensive evaluation of sewage sludge and sewage sludge char soil amendment impact on the industrial hemp growth performance and heavy metal accumulation. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 150, 112396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bioremediation and Bioeconomy; Prasad, M.N.V., Ed.; Elsevier: Waltham, MA, USA, 2016; p. 730. [Google Scholar]
- Angelova, V.; Ivanova, R.; Delibaltova, V.; Ivanov, K. Bio-accumulation and distribution of heavy metals in fibre crops (flax, cotton and hemp). Ind. Crops Prod. 2004, 19, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regulation of the Minister of the Natural Environment on Municipal Sewage Sludge Dated 6 February 2015. J. Laws Pol. 2015, 257.
- European Council. Official Journal of the European Union 56; C 378; Publications Office of the EU: Brussels, Belgium, 2014; pp. 1–44.
- Jones, J.B., Jr.; Case, V.V. Sampling, Handling, and Analyzing Plant Tissue Samples, SSSA Book Series 3. In Soil Testing and Plant Analysis, 3rd ed.; Westerman, R.L., Ed.; Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Rinkis, G.Y. Methods of Accelerated Colorimetric Analysis of Trace Elements in Biological Objects; Academy of Sciences of Latvian SSR: Riga, Latvia, 1963. (in Russian) [Google Scholar]
- De Souza, S.C.R.; De Andrade, S.A.L.; De Souza, L.A.; Schiavinato, M.A. Lead tolerance and phytoremediation potential of Brazilian leguminous tree species at the seedling stage. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 110, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, E.; Abd El-Kader, N. Heavy metal immobilization in contaminated soils using phosphogypsum and rice straw compost. Land Degrad. Dev. 2015, 26, 819–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrová, Š.; Benešová, D.; Soudek, P.; Vanĕk, T. Enhancement of metal(loid)s phytoextraction by Cannabis sativa L. J. Food Agric. Environ. 2012, 10, 631–641. [Google Scholar]
- Caporale, A.G.; Violante, A. Chemical processes affecting the mobility of heavy metals and metalloids in soil environments. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2016, 2, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fageria, V.D. Nutrient interactions in crop plants. J. Plant Nutr. 2001, 24, 1269–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).