Substitution of Mineral Fertilizer with Organic Fertilizer in Maize Systems: A Meta-Analysis of Reduced Nitrogen and Carbon Emissions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Evaluated Variables and Data Treatment
2.3. Meta-Analysis
2.4. Net Global Warming Potential
3. Results
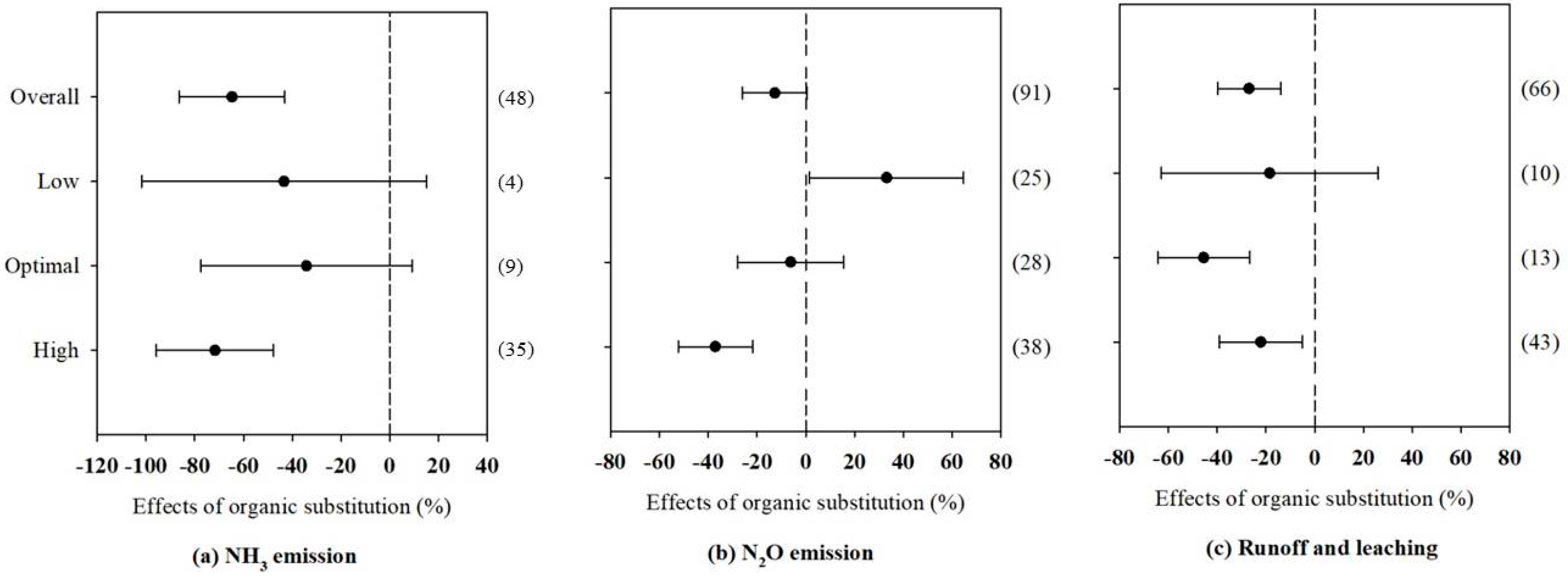
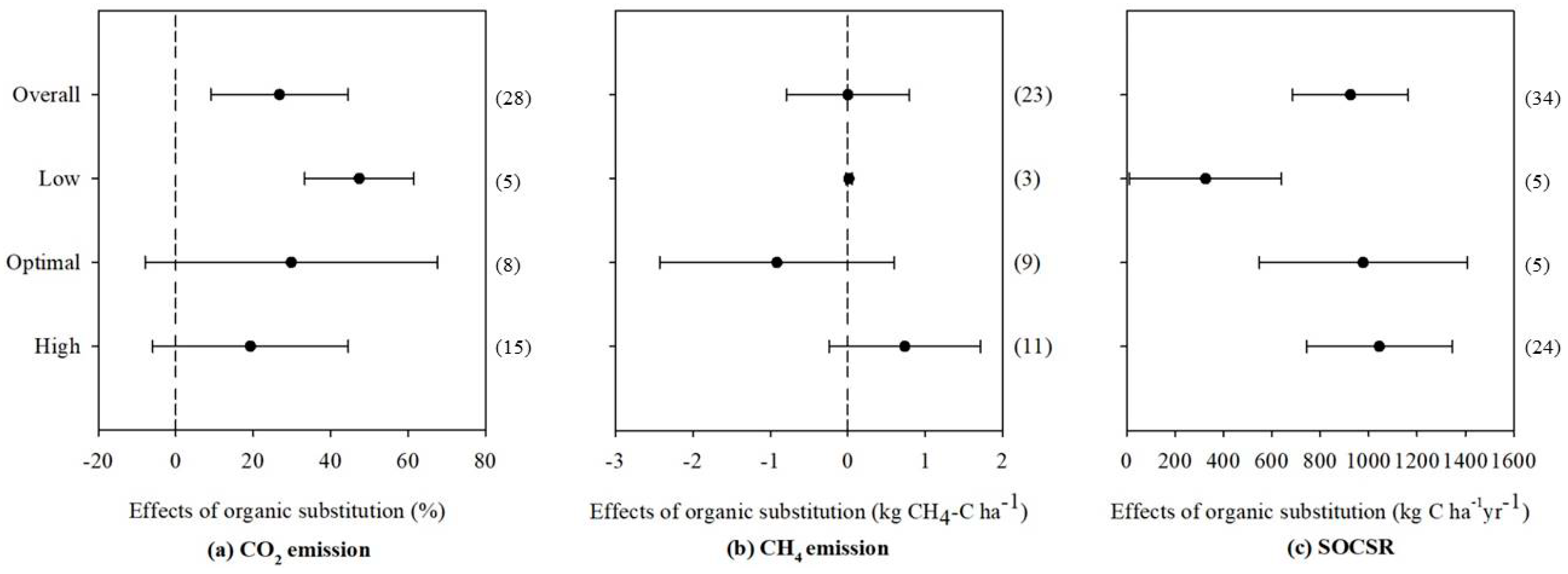
3.1. Effects of Organic Fertilizer Substitution on N and C Emissions by Fertilization Rate
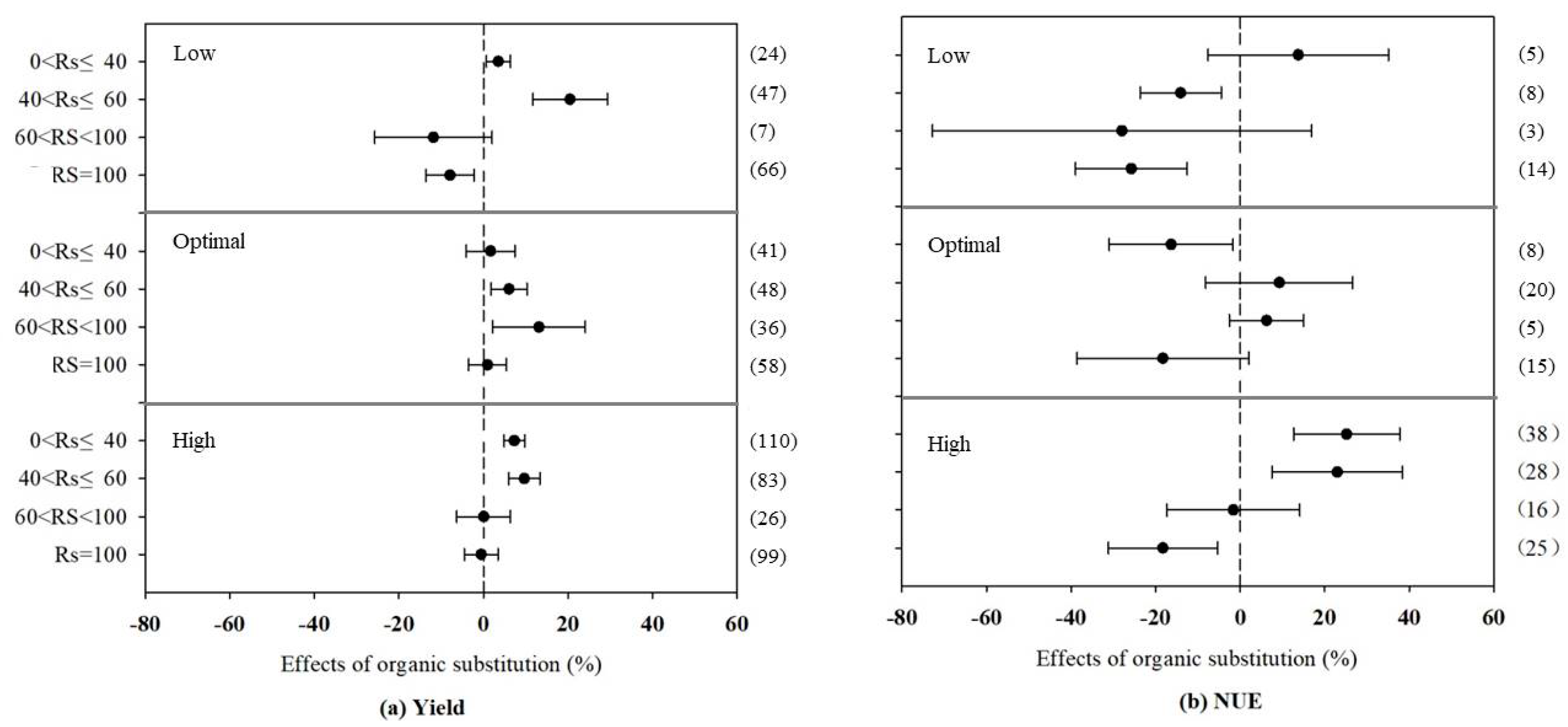
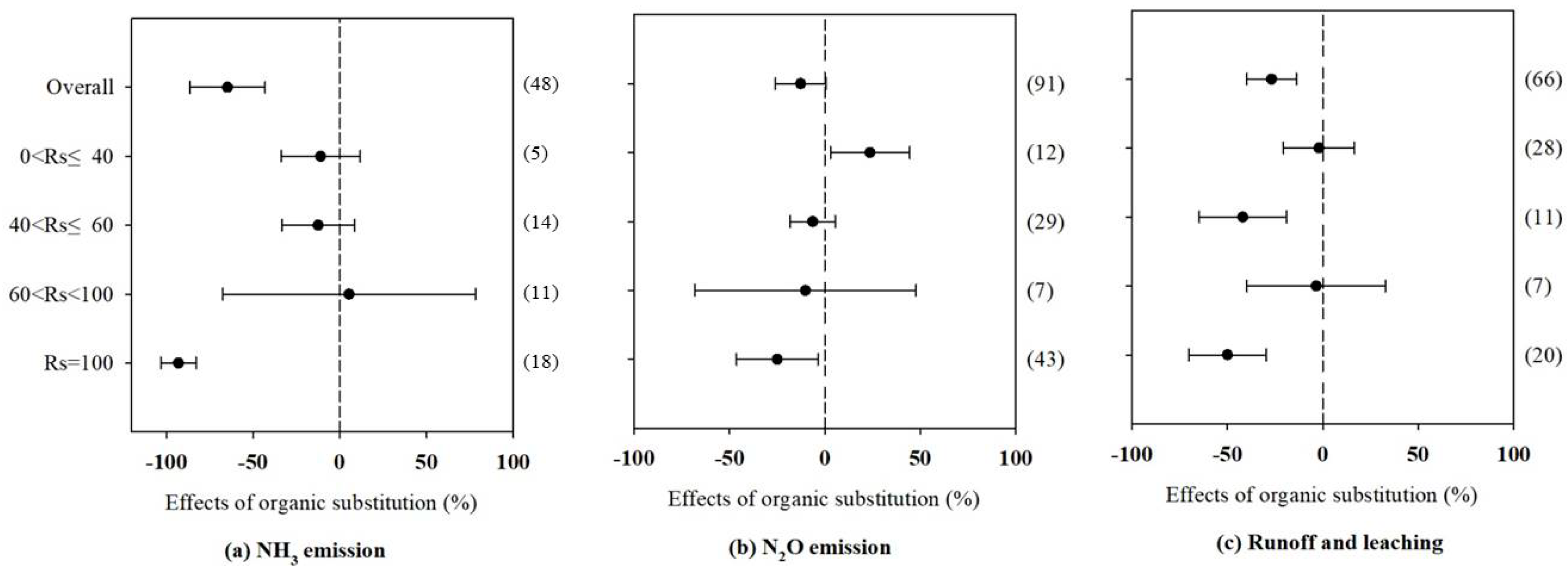
3.2. Effects of Organic Fertilizer Substitution on N and C Emissions at Different Substitution Rates
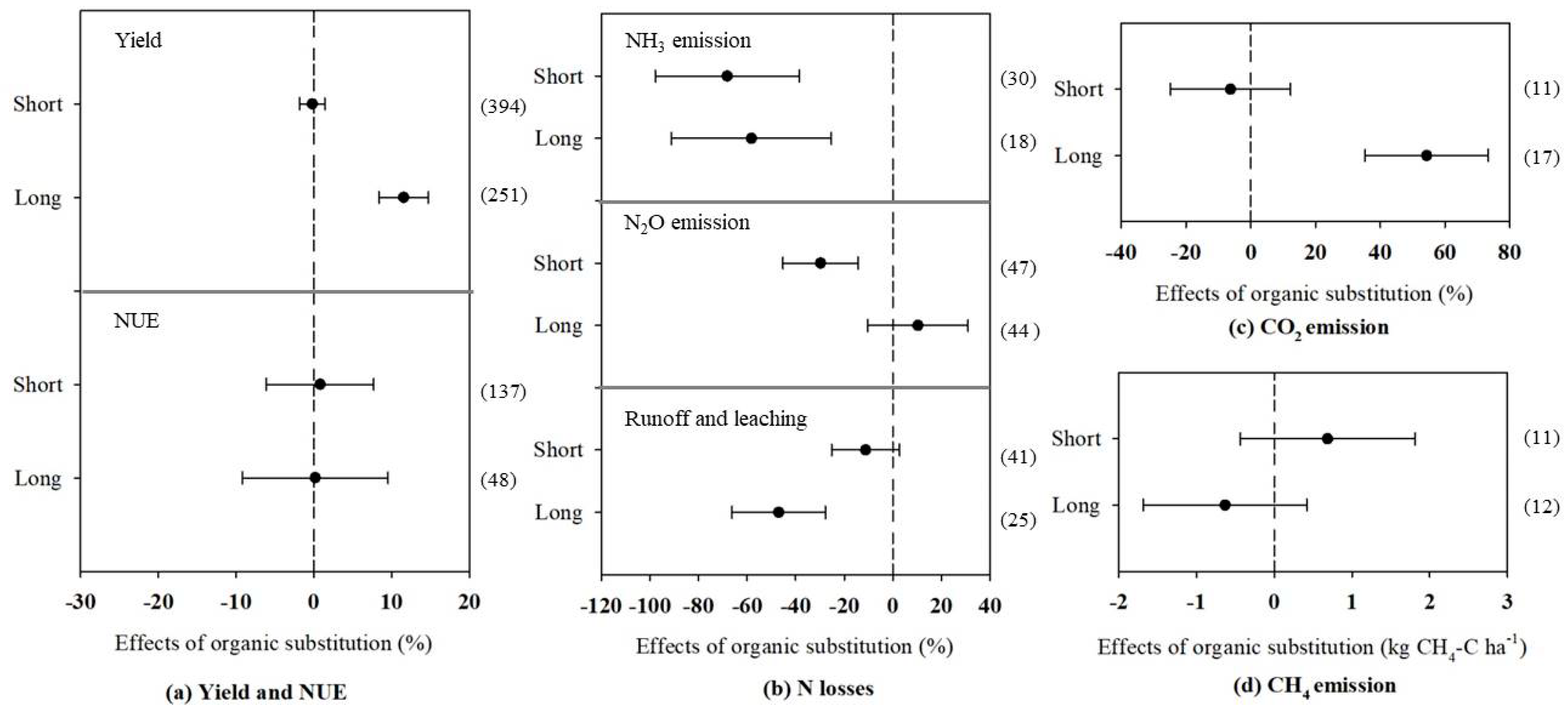
3.3. Effects of Organic Fertilizer Substitution on N and C Emissions by Treatment Duration
3.4. Effects of Organic Fertilizer Substitution on GWP and NGWP
4. Discussion
4.1. Maize Productivity and Soil Conditions
4.2. N and C emissions
4.3. SOCSR
4.4. Fertilization and Substitution Rates
4.5. Limitations of This Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, X.; Davidson, E.A.; Mauzerall, D.L.; Searchinger, T.D.; Dumas, P.; Shen, Y. Managing Nitrogen for Sustainable Development. Nature 2015, 528, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Z.L.; Yue, S.C.; Wang, G.L.; Meng, Q.F.; Wu, L.; Yang, Z.P.; Zhang, Q.; Li, S.Q.; Zhang, F.S.; Chen, X.P. Closing the Yield Gap could Reduce Projected Greenhouse Gas Emissions: A Case Study of Maize Production in China. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2013, 19, 2467–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Z.L.; Zhang, H.Y.; Chen, X.P.; Zhang, C.C.; Ma, W.Q.; Huang, C.D.; Zhang, W.F.; Mi, G.H.; Miao, Y.X.; Li, X.L.; et al. Pursuing Sustainable Productivity with Millions of Smallholder Farmers. Nature 2018, 555, 363–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.H.; Liu, X.J.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, J.L.; Han, W.X.; Zhang, W.F.; Christie, P.; Goulding, K.W.T.; Vitousek, P.M.; Zhang, F.S. Significant Acidification in Major Chinese Croplands. Science 2010, 327, 1008–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, M.A.; Howard, C.M.; Erisman, J.W.; Billen, G.; Bleeker, A.; Grennfelt, P.; Van Grinsven, H.; Grizzetti, B. The European Nitrogen Assessment: Sources, Effects and Policy Perspectives; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, B.J.; Ju, X.T.; Chang, J.; Ge, Y.; Vitousek, P.M. Integrated Reactive Nitrogen Budgets and Future Trends in China. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oenema, O.; Oudendag, D.; Velthof, G.L. Nutrient Losses from Manure Management in the European Union. Livest. Sci. 2007, 112, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Z.H.; Ma, L.; Jin, S.Q.; Ma, W.Q.; Velthof, G.L.; Oenema, O.; Liu, L.; Chadwick, D.; Zhang, F.S. Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Potassium Flows through the Manure Management Chain in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 13409–13418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadwick, D.; Jia, W.; Tong, Y.A.; Yu, G.H.; Shen, Q.R.; Chen, Q. Improving Manure Nutrient Management Towards Sustainable Agricultural Intensification in China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2015, 209, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chee-Sanford, J.C.; Mackie, R.I.; Koike, S.; Krapac, I.G.; Lin, Y.F.; Yannarell, A.C.; Maxwell, S.; Aminov, R.I. Fate and Transport of Antibiotic Residues and Antibiotic Resistance Genes Following Land Application of Manure Waste. J. Environ. Qual. 2009, 38, 1086–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobo, S.; Dominguez-Ramos, A.; Irabien, A. Minimization of Resource Consumption and Carbon Footprint of a Circular Organic Waste Valorization System. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 3493–3501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maillard, E.; Angers, D.A. Animal Manure Application and Soil Organic Carbon Stocks: A Meta-Analysis. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2014, 20, 666–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oldfield, E.E.; Bradford, M.A.; Wood, S.A. Global Meta-Analysis of the Relationship Between Soil Organic Matter and Crop Yields. Soil 2019, 5, 15–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingo-Olivé, F.; Bosch-Serra, À.D.; Yagüe, M.R.; Poch, R.M.; Boixadera, J. Long Term Application of Dairy Cattle Manure and Pig Slurry to Winter Cereals Improves Soil Quality. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2016, 104, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chivenge, P.; Vanlauwe, B.; Six, J. Does The Combined Application of Organic and Mineral Nutrient Sources Influence Maize Productivity? A Meta Analysis. Plant Soil 2011, 342, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Lam, S.K.; Yan, X.; Chen, D. How Does Recycling of Livestock Manure in Agroecosystems Affect Crop Productivity, Reactive Nitrogen Losses, and Soil Carbon Balance? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 7450–7457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Fang, Q.; Zhang, T.; Ma, W.; Velthof, G.L.; Hou, Y.; Oenema, O.; Zhang, F. Benefits and Trade-offs of Replacing Synthetic Fertilizers by Animal Manures in Crop Production in China: A Meta-Analysis. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hijbeek, R.; Ittersum, M.K.V.; Berge, H.F.M.T.; Gort, G.; Spiegel, H.; Whitmore, A.P. Do Organic Inputs Matter—A Meta-Analysis of Additional Yield Effects for Arable Crops in Europe. Plant Soil 2017, 411, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sileshi, G.W.; Jama, B.; Vanlauwe, B.; Negassa, W.; Harawa, R.; Kiwia, A.; Kimani, D. Nutrient Use Efficiency and Crop Yield Response to the Combined Application of Cattle Manure and Inorganic Fertilizer in Sub-Saharan Africa. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2019, 113, 181–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tovihoudji, P.G.; Akponikpè, P.B.I.; Adjogboto, A.; Djenontin, J.A.; Agbossou, E.K.; Bielders, C.L. Combining Hill-Placed Manure and Mineral Fertilizer Enhances Maize Productivity and Profitability in Northern Benin. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2018, 110, 375–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jjagwe, J.; Chelimo, K.; Karungi, J.; Komakech, A.J.; Lederer, J. Comparative Performance of Organic Fertilizers in Maize (Zea mays L.) Growth, Yield, and Economic Results. Agronomy 2020, 10, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.Q. Fertilizer Recommendations for Three Major Cereal Crops based on Regional Fertilizer Formula and Site Specific Adjustment in China. Ph.D. Thesis, China Agricultural University, Beijing, China, 1 May 2014. (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Efthimiadou, A.; Bilalis, D.; Karkanis, A.; Froudwilliams, B. Combined Organic/Inorganic Fertilization Enhance Soil Quality and Increased Yield, Photosynthesis and Sustainability of Sweet Maize Crop. Aust. J. Crop. Sci. 2010, 4, 722–729. [Google Scholar]
- Diez, J.A.; Hernaiz, P.; Munoz, M.J.; La Torre, A.D.; Vallejo, A. Impact of Pig Slurry on Soil Properties, Water Salinization, Nitrate Leaching and Crop Yield in a Four-Year Experiment in Central Spain. Soil Use Manag. 2004, 20, 444–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedges, L.V.; Gurevitch, J.; Curtis, P.S. The Meta-Analysis of Response Ratios in Experimental Ecology. Ecology 1999, 80, 1150–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Liu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, T.; Lin, Z.; Liu, G.; Wang, X.; Ma, J.; Wang, H.; Jin, H.; et al. Biochar Application as a Tool to Decrease Soil Nitrogen Losses (NH3 Volatilization, N2O Emissions, and N Leaching) from Croplands: Options and Mitigation Strength in a Global Perspective. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, H.; Yin, Y.; Zheng, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Xue, Y.; Stefanovski, D.; Cui, Z.; Dou, Z. Newer and Select Maize, Wheat, and Rce Varieties can Help Mitigate N Footprint While Producing More Grain. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracken, M.B. Effective Care of the Newborn Infant; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Feral, J.P. IPCC, 2014—Climate Change 2014. Synthesis Report; Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Paustian, K.; Ravindranath, N.H.; Amstel, A.V. Agriculture, forestry and other land use. In 2006 IPCC Guidelines for National Greenhouse Gas Inventories; International Panel on Climate Change: Hayama, Japan, 2006; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- Petersen, J. Nitrogen Fertilizer Replacement Value of Sewage Sludge, Composted Household Waste and Farmyard Manure. J. Agric. Sci. 2003, 140, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagliari, P.H.; Laboski, C.A.M. Investigation of the Inorganic and Organic Phosphorus Forms in Animal Manure. J. Environ. Qual. 2012, 41, 901–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.T.; Wang, W.L.; Tang, J.H.; Liu, F.; Liu, H.E.; Liu, S.L.; Han, Y.L.; Zheng, J. Effect of Animal Manure Organic Fertilizer and Nitrogen Combined Application on Maize Soil Physical & Chemical Properties. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 38, 34–39, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, L.; Liu, H.; Zhang, J.; Huang, J.; Wang, B. Long-Term Application of Organic Manure and Mineral Fertilizer on N2O and CO2 Emissions in a Red Soil from Cultivated Maize-Wheat Rotation in China. Agric. Sci. China 2011, 10, 1748–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C. Effects of Long-Term Fertilization on Crop Productivity and Soil Fertility as well as Its Mechanisms under Upland Red Soil in Subtropical China. Ph.D. Thesis, Nanjing Agricultural University, Nanjing, China, 1 October 2009. (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Guan, J.X.; Wang, Z.Y.; Wang, B.R.; Liu, S.J. Effects of Organic Fertilizer on Red Soil Upland Maize Yield and Soil Properties. Hunan Agric. Sci. 2016, 52–54, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Gao, H.; Lal, R.; Zhu, P.; Peng, C.; Deng, A.; Zheng, C.; Song, Z.; Zhang, W. Nitrous Oxide Emission, Global Warming Potential, and Denitrifier Abundances as Affected by Long-Term Fertilization on Mollisols of Northeastern China. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2019, 65, 1831–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, A.; Zhang, W.; Xu, M.; Wang, B.; Wen, S.; Shah, S.A.A. Soil Fertility and Crop Yield after Manure Addition to Acidic Soils in South China. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2018, 111, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franke, A.C.; Schulz, S.; Oyewole, B.D.; Diels, J.; Tobe, O.K. The Role of Cattle Manure in Enhancing on-farm Productivity, Macro- and Micro-nutrient Uptake, and Profitability of Maize in the Guinea Savanna. Exp. Agric. 2008, 44, 313–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Guo, S.; Pan, J.; Zhai, L.; Khoshnevisan, B.; Wu, S.; Wang, H.; Yang, B.; Liu, H.; Lei, B. The Reactive Nitrogen Loss and GHG Emissions from a Maize System after a Long-Term Livestock Manure Incorporation in the North China Plain. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 720, 137558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Wang, F.; Liu, R.L.; Li, Y.H.; Zhao, T.C.; Chen, C. Effects of Long-Term Fertilization on Yield and Nitrogen Utilization of Spring Maize in Irrigation Silting Soils. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2017, 31, 248–261, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liang, B. Effect of Long-Term Combined Application of Manure and Inorganic Fertilizers on Soil Nitrogen Availability and Its Mechanism. Ph.D. Thesis, Northwest A&F University, Yanglin, China, 1 April 2012. (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Lou, Y.; Wang, J.; Liang, W. Impacts of 22-Year Organic and Inorganic N Managements on Soil Organic C Fractions in a Maize Field, Northeast China. Catena 2011, 87, 386–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Z.; Gao, H.J.; Peng, C.; Li, Q.; Zhu, P. Effects of Combined Application of Organic Manure and Chemical Fertilizer on Maize Yield and Nitrogen Utilization under Equal Nitrogen Rates. J. Maize Sci. 2012, 20, 123–127, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.R.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.L.; Zhang, W.A.; Jiang, T.M. Effects of Long-Term Fertilization on Soil Organic Carbon Balance and Maize Yield in Yellow Soil. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2016, 53, 1275–1285, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yan, Z.; Qin, J.; Ma, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L. The Potential of Residues of Furfural and Biogas as Calcareous Soil Amendments for Corn Seed Production. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 23, 6217–6226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; Zou, J.; Liu, S. Optimizing Net Greenhouse Gas Balance of a Bioenergy Cropping System in Southeast China with Urease and Nitrification Inhibitors. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 83, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crill, P.M.; Martikainen, P.J.; Nykanen, H.; Silvola, J. Temperature and N Fertilization Effects on Methane Oxidation in a Drained Peatland Soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1994, 26, 1331–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.F.; Dou, Z.X.; He, P.; Ju, X.T.; Powlson, D.; Chadwick, D.; Norse, D.; Lu, Y.L.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, L.; et al. New Technologies Reduce Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Nitrogenous Fertilizer in China. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 8375–8380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Xu, F.; Ge, X.; Li, Y. Improving the Sustainability of Organic Waste Management Practices in the Food-Energy-Water Nexus: A Comparative Review of Anaerobic Digestion and Composting. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 2018, 89, 151–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.P.; Cui, Z.L.; Fan, M.S.; Vitousek, P.; Zhao, M.; Ma, W.Q.; Wang, Z.L.; Zhang, W.J.; Yan, X.Y.; Yang, J.C.; et al. Producing More Grain with Lower Environmental Costs. Nature 2014, 514, 486–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Ju, X.; Powlson, D.; Oenema, O.; Smith, P. Nitrogen Surplus Benchmarks for Controlling N Pollution in the Main Cropping Systems of China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 6678–6687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Parameter | Overall | Full Substitution | Partial Substitution |
|---|---|---|---|
| NH3 (kg N ha−1) | −14.6 | −31.6 | −4.13 |
| N2O (kg N ha−1) | −0.06 | −0.05 | −0.05 |
| Leaching/runoff (kg N ha−1) | −5.63 | −13.5 | −2.15 |
| CH4 (kg C ha−1) | 0.00 | 0.52 | −0.47 |
| SOCSR (kg C ha−1 yr−1) | 925 | 817 | 968 |
| GWP (kg CO2 eq ha−1) | −116 | −203 | −67.2 |
| NGWP (kg CO2 eq ha−1) | −3507 | −3200 | −3617 |
| Soil Property | Control | Mineral Fertilizer | Organic Fertilizer | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | n | Mean | SD | n | Mean | SD | n | |
| SOC (g kg−1) [20,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46] | 9.69 | 2.16 | 22 | 10.37 | 2.87 | 30 | 13.28 | 4.38 | 30 |
| TN (g kg−1) [34,35,37,38,39,41,42,44,46] | 1.09 | 0.15 | 14 | 1.10 | 0.26 | 19 | 1.29 | 0.36 | 19 |
| pH [34,35,37,38,39,41,44,46] | 7.68 | 1.12 | 13 | 6.47 | 1.66 | 18 | 6.77 | 1.27 | 18 |
| BD (g cm−3) [36,41,46] | 1.35 | 0.09 | 8 | 1.32 | 0.10 | 11 | 1.26 | 0.05 | 11 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, Z.; Ying, H.; Guo, X.; Zhuang, M.; Cui, Z.; Zhang, F. Substitution of Mineral Fertilizer with Organic Fertilizer in Maize Systems: A Meta-Analysis of Reduced Nitrogen and Carbon Emissions. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1149. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10081149
Wei Z, Ying H, Guo X, Zhuang M, Cui Z, Zhang F. Substitution of Mineral Fertilizer with Organic Fertilizer in Maize Systems: A Meta-Analysis of Reduced Nitrogen and Carbon Emissions. Agronomy. 2020; 10(8):1149. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10081149
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Zhibiao, Hao Ying, Xiaowei Guo, Minghao Zhuang, Zhenling Cui, and Fusuo Zhang. 2020. "Substitution of Mineral Fertilizer with Organic Fertilizer in Maize Systems: A Meta-Analysis of Reduced Nitrogen and Carbon Emissions" Agronomy 10, no. 8: 1149. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10081149
APA StyleWei, Z., Ying, H., Guo, X., Zhuang, M., Cui, Z., & Zhang, F. (2020). Substitution of Mineral Fertilizer with Organic Fertilizer in Maize Systems: A Meta-Analysis of Reduced Nitrogen and Carbon Emissions. Agronomy, 10(8), 1149. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10081149







