Abstract
Improvement of nitrogen use efficiency (NUE) via active optical sensors has gained attention in recent decades, with the focus of optimizing nitrogen (N) input while simultaneously sustaining crop yields. To the authors’ knowledge, a comprehensive review of the literature on how optical sensors have impacted winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) NUE and grain yield has not yet been performed. This work reviewed and documented the extent to which the use of optical sensors has impacted winter wheat NUE and yield. Two N management approaches were evaluated; optical sensor and conventional methods. The study included 26 peer-reviewed articles with data on NUE and grain yield. In articles without NUE values but in which grain N was included, the difference method was employed to compute NUE based on grain N uptake. Using optical sensors resulted in an average NUE of 42% (±2.8% standard error). This approach improved NUE by approximately 10.4% (±2.3%) when compared to the conventional method. Grain yield was similar for both approaches of N management. Optical sensors could save as much as 53 (±16) kg N ha−1. This gain alone may not be adequate for increased adoption, and further refinement of the optical sensor robustness, possibly by including weather variables alongside sound agronomic management practices, may be necessary.
1. Introduction
Fertilizer nitrogen (N) is an integral part of the modern crop production system. This is particularly true in cereal crop production where these systems rely heavily on external N inputs. This has led to a significant portion of N used in cereal crops to be applied from inorganic fertilizer sources. As producers aim to increase crop yields through the application of more N, there has also been a growing call from environmentalists and other scientists to improve its recovery efficiency in the grain [1]. This is because of the increasing concern over the environmental fate of excess N that is not recovered in the grain [2]. World cereal nitrogen use efficiency (NUE), computed as [3], averages 33% [4]. This indicates that nearly 67% of fertilizer N applied for cereal crop production may not be recovered in the grain. This has led to an intensive research effort to find the best approaches to improve NUE and make crop production more environmentally friendly [1,4,5].
Despite the fact that split application, in-season estimated N, crop rotation, and other sound agronomic management practices have been found to improve NUE to varying degrees [4,5,6,7], many producers still apply the entire N amount preplant based solely on either yield goals or soil test recommendations. Cui et al. [7] further reported that some producers in China apply, on average, 325 kg N ha−1 without any substantial yield difference from the one achieved with 128 kg N ha−1 applied using the midseason approach evaluated for the region. This could lead to a substantial build-up of N in the soil with the potential of being lost to the environment [8]. The amount of N applied determined based on yield goal or an average yield of the last 3 to 5 years plus 20% [9] was found not to be an effective means of estimating crop N requirements [10]. The authors evaluated data from three long-term experiments and reported that yield goal, on average, explained approximately 5.1% of the variability in winter wheat grain yield. However, Raun et al. [11] proposed combining both predicted yield level and crop response or response index [12,13] to arrive at an accurate N recommendation. This may be achieved by adopting optical sensor-based technology that accurately predicts yield potential and N requirements midseason. Raun et al. [5] reported an improvement in NUE by 15% through the use of in-season optical sensor-based N estimates compared to conventional methods. Optical sensors could, therefore, be more precise in determining crop N needs and save as much as 32.5 kg N ha−1 when compared to conventional methods [14]. This could result in the saving of excess N which would otherwise play no major role in yield improvement [15]. Worldwide, it has been reported that a 1% improvement in NUE could save up to 489,892 Mg of fertilizer N [4]. Considering the suggested vital role in NUE improvement [16], active optical sensors may play a major role in N optimization. Additionally, optical sensors may offer an added benefit of attaining grain yield which exceeds that obtained with conventional methods. For instance, Morris et al. [13] found that applying 90 kg N ha−1 preplant followed by the midseason sensor-based recommended rate of 60 kg N ha−1 resulted in 0.5 Mg ha−1 more grain yield than the 5.2 Mg ha−1 obtained by sole application of 90 kg N ha−1, and this difference was significant. This is an illustration that optical sensors do not only improve NUE but also grain yield. However, some studies have reported little to no added yield benefit and profitability of optical sensors relative to conventional methods of N management [17,18,19].
Conventional methods of N management entail applying a predetermined amount of N preplant or in-season [20,21]. In some cases, the amount is split into equal or varying amounts and applied preplant and midseason [22,23]. Because this approach does not consider N supplied from the soil during the crop growing season, a considerable amount of residual N may be found in the soil [24]. In addition, spatial and temporal variations may not be considered and, thus, a recommendation suitable for a specific site is made for the entire region [24].
Optical sensors, on the other hand, emit and record reflectance of radiation within the visible and near infrared regions of the electromagnetic spectrum [25]. This has been shown to have a good relationship with crop biomass and crop N status with r2 as high as over 80% [26]. One commonly used index, called normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI), is derived from reflectance values recorded by the sensor in the visible and near infrared regions with specific wavelengths varying for each sensor. How NDVI is used to make N recommendation may vary depending on the sensor used [5,27]. For instance, with the GreenSeekerTM (Trimble Inc., Sunnyvale, California, USA), the NDVI values are divided by growing degree days (GDD) to obtain midseason estimated yield, and this is related to the final winter wheat grain yield [5]. When this is combined with the response index , the prediction of yield potential and recommendation for N are made. As such, crop canopy sensing provides a mechanism to estimate crop N needs based on real time assessment of crop N status.
Even though active optical sensors have previously been the subject of review studies, this work has not exhaustively addressed the extent to which NUE is improved by making use of active optical sensors such as GreenSeekerTM. Furthermore, having a clear basis for comparison of sensors to other N management approaches may improve our understanding of the contribution of optical sensors to NUE and grain yield improvement. This can best be achieved by extensively reviewing the literature to document the extent to which active optical reflectance sensors have contributed to enhanced grain NUE and yield for winter wheat. Specifically, limiting the review to winter wheat crops may lead to a deeper understanding of the crop-specific impact of active optical sensor technology on grain NUE and yield than when multiple crops are considered simultaneously. Generally, wheat is a very important crop that occupies more than a quarter of the global land production area (780 million ha) under cereal crops [28]. This possibly means it consumes a significant portion of the 61.2 million Mg of N applied in 2015 [29]. It is, therefore, vital that a review is undertaken regarding the use of optical sensors in winter wheat and document potential evidence that advances in N management technology are contributing to NUE and grain yield improvement.
Therefore, the objective of this work was to investigate the impact of active optical sensors on winter wheat grain NUE and yield through an extensive review of published research articles.
2. Materials and Methods
In this study, 26 published research articles were reviewed. These articles were divided into two groups. The first group had 15 articles that were used to make a direct comparison between optical sensor and conventional methods of N management (Table 1). The second group had 11 articles that were generated from studies that only used conventional methods of N management (Table 2). The research articles were searched using a combination of keywords, such as active optical sensor for winter wheat, in-season nutrient management, winter wheat grain protein, winter wheat NUE, GreenSeeker, and NUE for winter wheat. The searches were performed in Google Scholar, Web of Science, Science Direct, Scopus, United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) National Agricultural Library (https://pubag.nal.usda.gov/), and ACCESS Digital Library (https://dl.sciencesocieties.org/). The articles considered in this study reported NUE, grain N uptake, and/or documented grain protein concentration at different N rates. This study focused explicitly on grain NUE for winter wheat. In each paper, the current study collected data pertaining to NUE, N rates, and grain yield.

Table 1.
Peer-reviewed research articles used to compute NUE and grain yield at selected N rates using active optical sensors and conventional methods of N management.

Table 2.
Peer-reviewed research publications used to compute NUE and grain yield at selected rates that some producers are expected to apply using conventional methods of N management.
From the first group of articles, two N rates were selected from each study to document yield and NUE (Table 1). Firstly, the sensor recommended N rate where an initial dose of at least 34 kg N ha−1 was applied preplant. This was to ensure that delaying N application until midseason was not a factor affecting grain yield maximization using the optical sensor approach of N management [5,40]. In addition, the sensor-based N recommended rate was then applied midseason. Nonetheless, if a sensor-based study did not apply preplant N, then a midseason N rate was selected. Secondly, an N rate based on conventional methods of N management that applied at least 90 kg N ha−1 was selected. The choice of at least 90 kg N ha−1 was based on the average N rate for wheat in the U.S. in 2017 [41]. This second N rate was either applied preplant or split and applied equally or unequally at preplant and midseason.
The second group of articles reviewed (Table 2) only used the second N rate discussed under the first group of articles (conventional method) but with a slightly different criterion for selection, as highlighted below.
For all the articles considered in this study, grain NUE was computed using the difference method shown in Equation (1). This index and other indices were adequately discussed by Rao et al. [3] and Syers et al. [53]. If NUE provided in a given study was obtained based on grain N uptake, the values provided were used as presented by the authors.
In articles where NUE values were not provided but grain N or crude protein was reported, NUE was computed accordingly using Equation (1). Crude protein values were converted to percent grain N using Equation (2) [54].
Percent grain N was then multiplied by grain yield to obtain grain N (kg ha−1) using Equation (3) [4]. The grain N values obtained were subsequently used in Equation (1) to compute NUE. If no grain N was provided in a study, we multiplied grain yield by 2.13% N to obtain grain N. The 2.13% grain N was obtained from work done by Batal et al. [55].
For the second group of articles, additional data for N rates, grain yield, and NUE were collected from peer-reviewed studies that used conventional methods of N management (Table 2). Although not in all cases, an attempt was made to find N rates that might be considered non-limiting for winter wheat production. This also helped to account for large quantities of N applied in some regions of the world [29]. It is worth noting that these were studies conducted independently of those summarized in Table 1 and that makes direct comparison more difficult. However, this offers insight into what grain yield and NUE might be expected when more N is applied using the conventional method.
Countries were also grouped into regions, that is, the U.S. and Asia (China and India) using data generated from Table 1. These two regions were considered because they had more data points that can be analyzed statistically.
This review included two types of active optical sensors (Table 1), that is, GreenSeekerTM (Trimble, Sunnyvale, California, USA) and Crop Circle ACS-430 active crop canopy sensor (Holland Scientific, Lincoln, NE, USA). Details of how GreenSeekerTM and Crop Circle arrive at a recommendation for N were extensively elaborated by Raun et al. [5] and Stamatiadis et al. [27], respectively.
Applied statistical analyses for all the data collected were accomplished using R statistical package (R Foundation, Vienna, Austria) [56]. A paired t-test was used to compare average NUE and grain yield under active optical sensors and conventional methods of N management. Unpaired t-test was also used, for instance, in situations such as comparing grain yield and NUE for different regions that may not have the same number of observations. The accuracy of means and difference between mean estimates were assessed using standard error and coefficient of variations (%). Standard error is shown as a plus or minus (±) standard error value in Table 1, Table 2 and Table 3 and in-text values specified within the manuscript. Data visualization was done using ggplot2 within the tidyverse package [57].

Table 3.
Evaluation of the differences in grain yield, nitrogen use efficiency (NUE) and nitrogen (N) rate that occurred between active optical sensors and conventional methods of N management as well as regional differences using paired t-test (unpaired t-test for regional differences).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Nitrogen Use Efficiency and N Management Approach
Results from this review of existing literature indicate that the use of active optical sensors for N management improved NUE. Nitrogen use efficiency achieved when N was recommended using an optical sensor was 10.4% (±3.8%) higher than the 31.6% (±2.6%) NUE for the conventional N management approach (Table 1). Paired t-tests showed that the observed difference of 10.4% NUE was significant (PR (|T| > |t|) < 0.01; Table 3). However, NUE for active optical sensor N management varied widely, from 2.5% to 76.0%. The variation in NUE for active optical sensors could be due to differences in associated algorithms. This could also be due to differences in crop N response from year to year or location to location [58]. Similar variability in NUE (−1.4–71%) was observed for the conventional N management approach. This suggests that even though optical sensors resulted in an improved NUE of 42.0% (±2.8%), further enhancement is still possible.
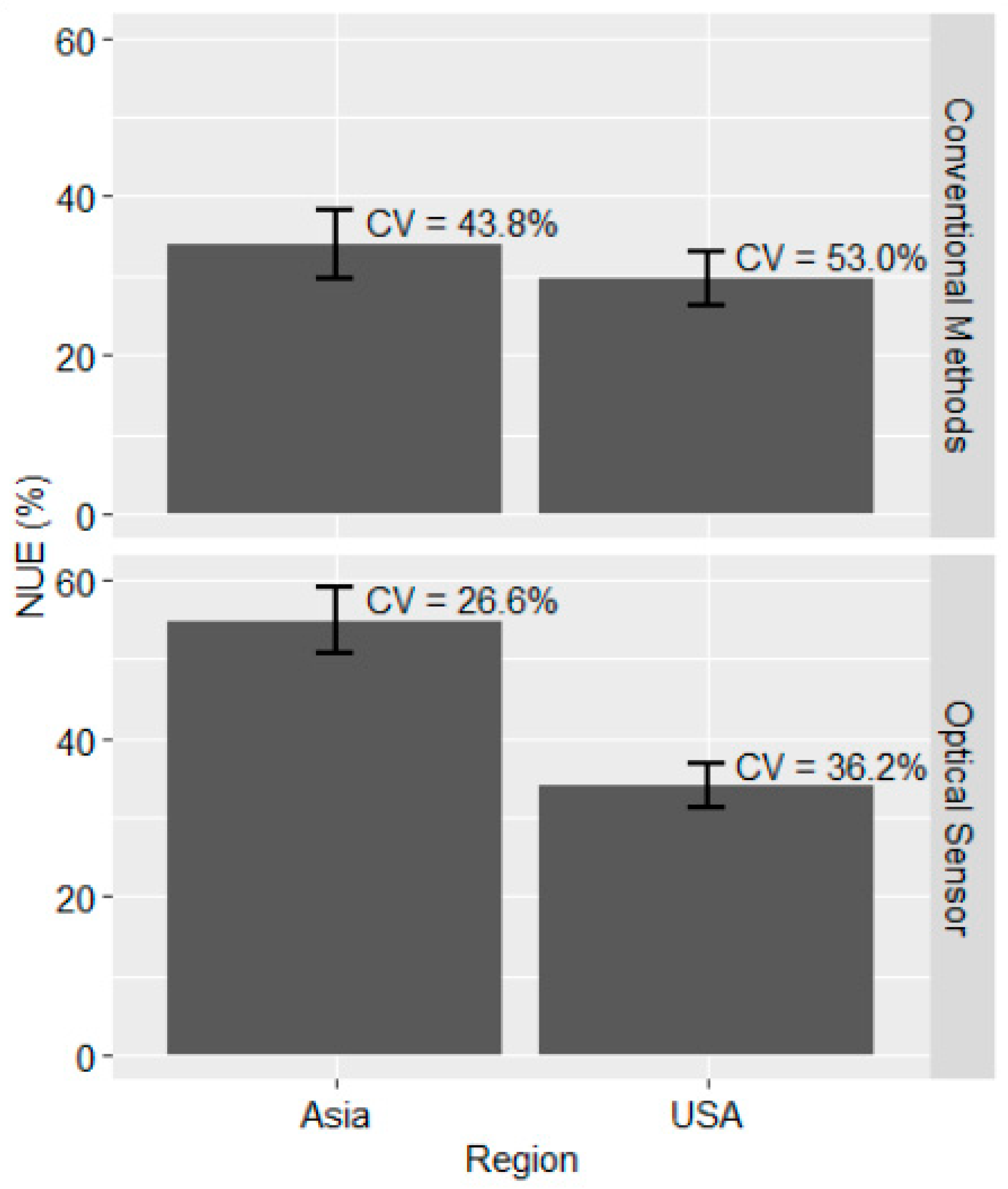
Regionally, Asia had the highest NUE of approximately 54.8% (±4.2%) when using optical sensors (Trimble Inc., Sunnyvale, California, USA), and this was significantly different from the 34.0% (±2.7%) NUE for the U.S. (PR(|T| > |t|) < 0.01; Figure 1; Table 3). There was no difference between NUE for the two regions when conventional methods were used (PR (|T| > |t|) = 0.45). Asia had a slightly higher NUE of approximately 33.9% (±4.3%) when compared to 29.7% for the U.S. under conventional methods (Figure 1). These results suggest that NUE varied between regions and that optical sensors within each region tended to have a higher NUE over conventional methods. It is unclear as to why Asia had a higher NUE when using optical sensors than the U.S. but temporal and spatial variability could be one of the reasons for the differences observed. Although details have been highlighted under yield section, it is worth noting that wheat grain yield in Asia via optical sensor N management exceeded that of the U.S. by 82%. This may indicate that wheat response to applied N in that region is high, and that when a correct recommendation is made using optical sensors, a significant portion of it is recovered in the grain. Indeed, soil organic carbon (SOC) within the two regions are markedly different, with Asia having an average SOC of 2.9 g kg−1 (±0.4 g kg−1) and the U.S. an average of 9.3 g kg−1 (±0.8 g kg−1). This could have affected the mineralization rate and how crops responded to added N. It is possible that the U.S. had potentially more N released to the soil from mineralization of soil organic matter than in Asia, leading to the lower NUE with optical sensors.
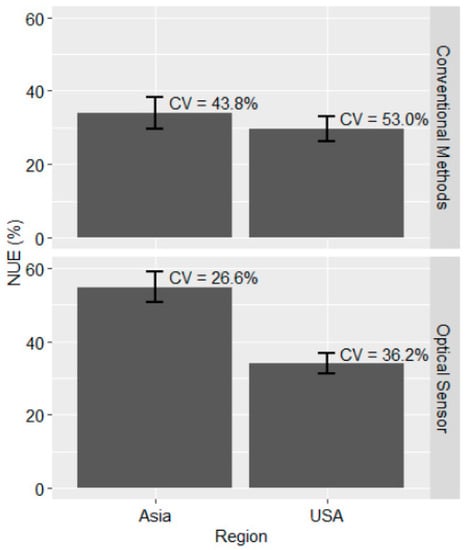
Figure 1.
NUE for optical sensor and conventional methods of N management for the U.S. and Asia. The error bar indicates standard error, while CV represents coefficient of variation.
This review also found active optical sensors to recommend on average 52.9 kg ha−1 (±10.0 kg ha−1) less N compared to conventional methods (Table 1). This in part explains why NUE was higher with active optical sensors. The 10.4% (±2.3%) higher NUE attained with active optical sensors over the conventional methods of N management was slightly lower than the 15% NUE reported by Raun et al. [5]. Because optical sensors allow for the application of N in-season, producers are best placed to make decisions that also integrate other variables vital for determining how much N to apply. Thomason et al. [59] also reported that optical sensors use 7% less fertilizer N in comparison to conventional methods of N management. Butchee et al. [15] reported that optical sensors can use 22.6 kg N ha−1 less N when compared to the conventional method.
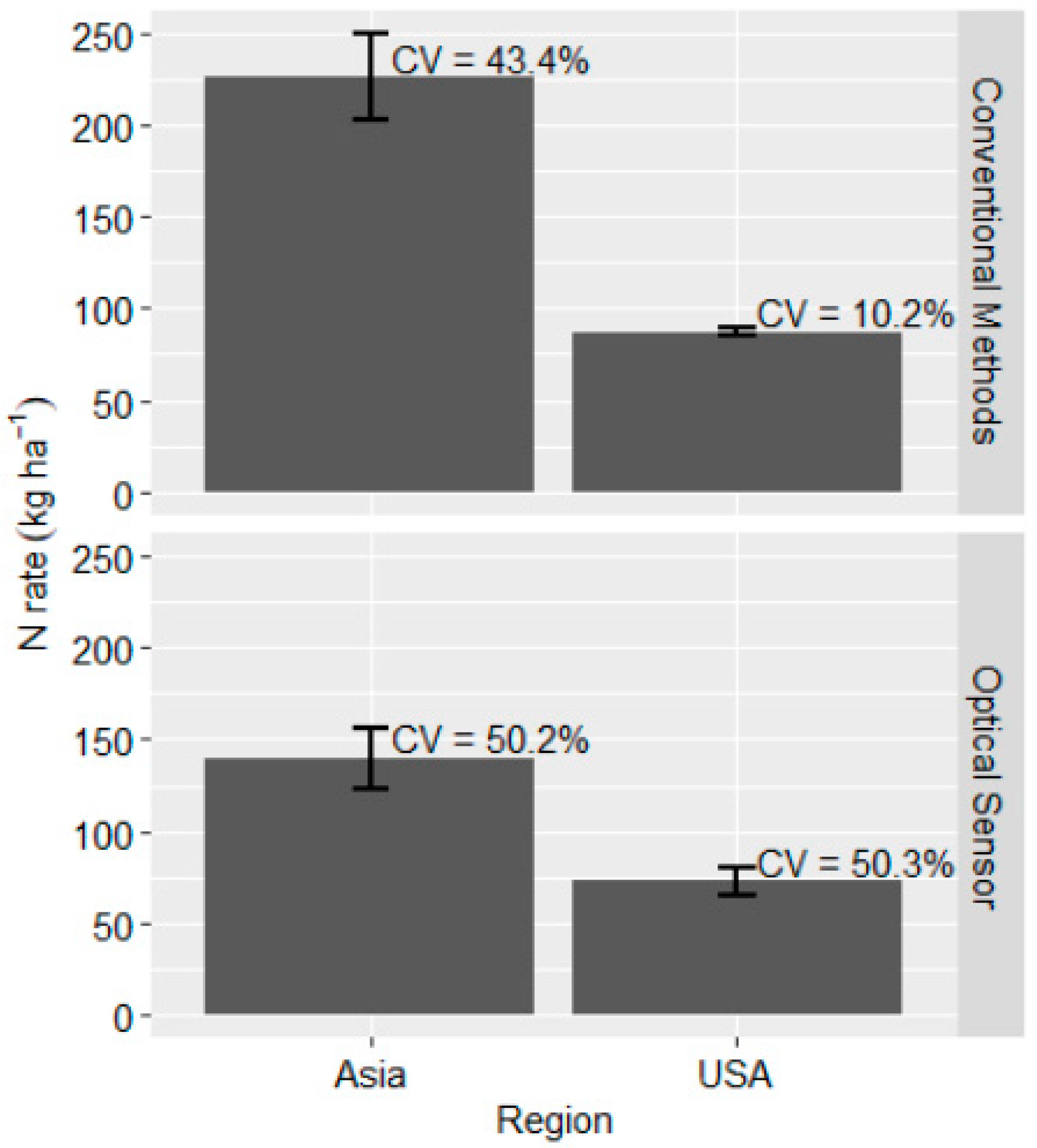
On a regional basis, Asia recommended 67 kg ha−1 (±18.3 kg ha−1) more N than the 73 kg N ha−1 (±8.0 kg ha−1) applied in the U.S. using the optical sensor-based approach (Figure 2). This was a significant difference in N usage between the two regions (PR (|T| > |t|) < 0.01; Table 3). Asia applied, on average, 226 kg N ha−1 (±23.1 kg N ha−1) when using conventional methods of N management and was much higher than the 87 kg N ha−1 (±1.9 kg N ha−1) applied in the U.S. (PR (|T| > |t|) < 0.01; Table 3; Figure 2). This would, in theory, be expected to produce a much lower NUE, but because of the low SOC in the region where studies were conducted, it appears that crops were able to utilize applied N and maintain NUE within the global average of 33% [4]. Results for the U.S. suggest that if sensor algorithms recommend rates that are similar to conventional methods, then NUE may not differ by much, since the 4% difference between the two approaches was small (PR(|T| > |t|) = 0.33; Figure 1).
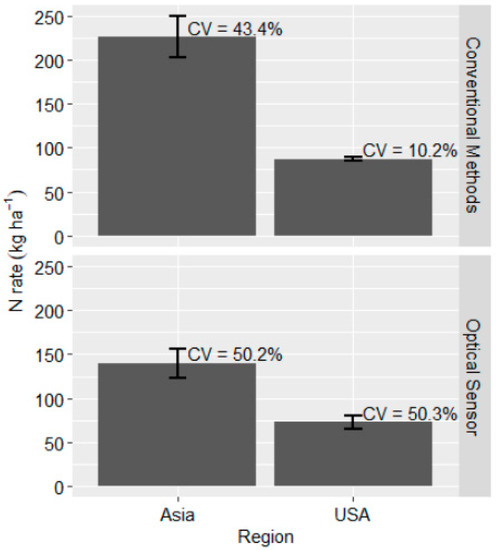
Figure 2.
The quantity of nitrogen applied to winter wheat when using optical sensor and conventional methods of N management for USA and Asia. The error bar indicates standard error, while CV represents that stand coefficient of variation.
In a review of world NUE, Omara et al. [29] found NUE for developed nations to be approximately 41%. This is consistent with an average NUE of 42.0% (±2.8%) for optical sensors reported in this study. It is also apparent that active optical sensors are mostly used in developed and emerging economies such as the U.S. and China. In that review, Omara et al. [29] noted that the improvement in NUE has mainly been attributed to crop genetic advancement over the years. Nevertheless, evidence from this review seems to indicate that active optical sensors could also be contributing to the observed NUE improvement. Regardless of the approach to N management, NUE averaged 36.8% (±2.0%), a figure which is slightly above the 33% reported by Raun and Johnson [4]. The lower NUE associated with conventional methods of N management could be due to several variables that may interact with each other to influence NUE, including the application of N in quantities that exceed crop requirements, precipitation, and temperature.
Active optical sensors could, therefore, reduce the ad libitum application of N in economies such as China and India [29,60], with consequential improvement in NUE.
Summary of studies documented in Table 2 suggests that about 77 kg N ha−1 (±15.5) above the active optical sensor recommended rate might be applied when producers apply N at rates that might be considered non-limiting for winter wheat production. Yet this was accompanied by 17.0% (±4.4%) decrease in NUE (Table 1 and Table 2). When we averaged NUE values in Table 1 and Table 2 for both methods, we found an overall NUE of approximately 34.3% (±1.8%), a value consistent with 33% reported by Raun and Johnson [4]. Applying a large amount of N might have contributed to this decline in NUE. Li et al. [16] showed that applying 372 kg N ha−1 produced an NUE of 13.1% compared to 61.3% achieved with optical sensor technology that applied 67 kg N ha−1. This is why the use of an approach that improves NUE is important to reduce the impact of agriculture on the environment.
Despite the fact that optical sensors tend to perform better than the conventional methods in terms of NUE, the 42.0% (±2.8%) NUE suggests that further improvement is still possible, since most of the applied N was not recovered in the grain. This is particularly relevant because some past reviews suggested that the benefits of the sensors may be overstated [17]. A better NUE is expected when N is applied midseason, as is the case with optical sensors in this review, or split applied using a conventional method of N management [17]. While split application improves N uptake [20,22,31,61], the fact that a predetermined amount is applied regardless of the changes in soil N contents from mineralization of soil organic matter during the growing season [62] makes it susceptible to over application of N, particularly in years with low crop response to additional N [5]. The savings in fertilizer N resulting from the use of optical sensors could prove vital in reducing the effect of excess N application, such as emission of heat-trapping nitrous oxide (N2O) [63] and eutrophication of water bodies [64]. The benefit could extend to the reduction in energy consumption from 47.1% using conventional methods to between 26.8% and 40.0% using optical sensors.
3.2. Grain Yield and N Management Approach
Using a paired t-test evaluating the two N management approaches, no significant difference in winter wheat grain yield was found (PR (|T| > |t|) = 0.86, Table 3). The average yield generated as a result of making an N application decision based on optical sensor midseason was 0.18% lower than the 4.9 Mg ha−1 (±0.3 Mg ha−1) average grain yield obtained by applying N via the conventional methods of N management (Table 1). This result suggests that producers could get similar grain yields using both approaches. Nonetheless, the grain yield achieved using the two approaches varied widely, possibly due to location and year effects.
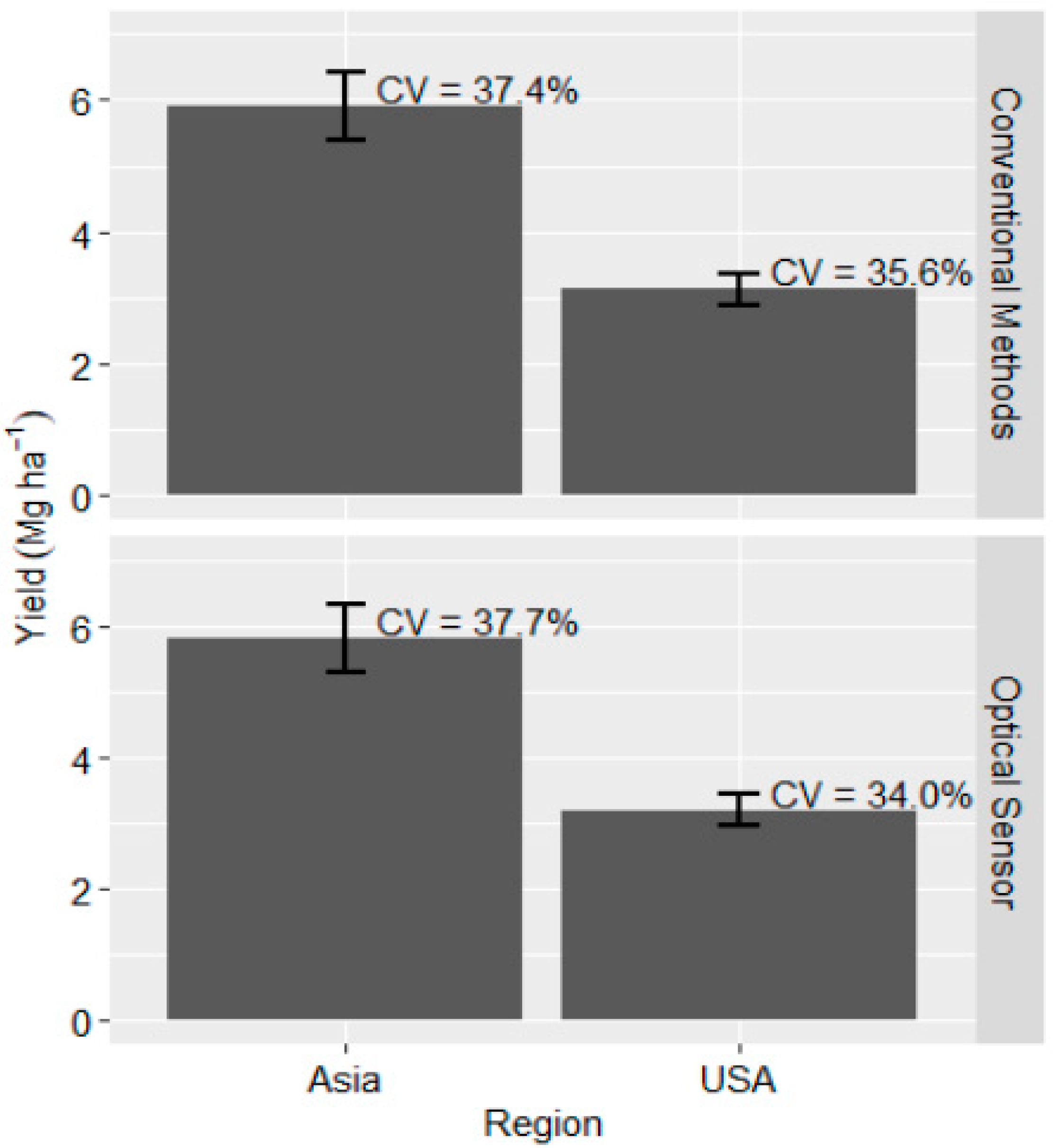
Regionally, grain yield differed between Asia and U.S. when using both optical sensors and conventional methods to make recommendation for N (PR (|T| > |t|) < 0.01; Table 3). Grain yield in the U.S. based on in-season spectral reflectance measurements was 2.6 Mg ha−1 (±0.6 Mg ha−1) less than the 5.8 Mg ha−1 (±0.5 Mg ha−1) grain yield recorded in Asia using the same approach (Figure 3). Similarly, conventional methods resulted in a grain yield difference of 2.8 Mg ha−1 (±0.6 Mg ha−1) with Asia having the highest grain yield of 5.9 Mg ha−1 (±0.5 Mg ha−1) (Figure 3). Within each region, yield appeared to be similar for the two N management approaches and yet conventional methods applied more N than the optical sensors. In particular, Asia applied 226 kg N ha−1 (±23.1 kg N ha−1) while using the conventional methods and this was above optical sensor recommended rate by 86 kg N ha−1 (Figure 2). This result is an indication that in Asia, particularly in China and India, producers may be over-applying N for no major grain yield gain and this has been reported in several studies [7,29,65].
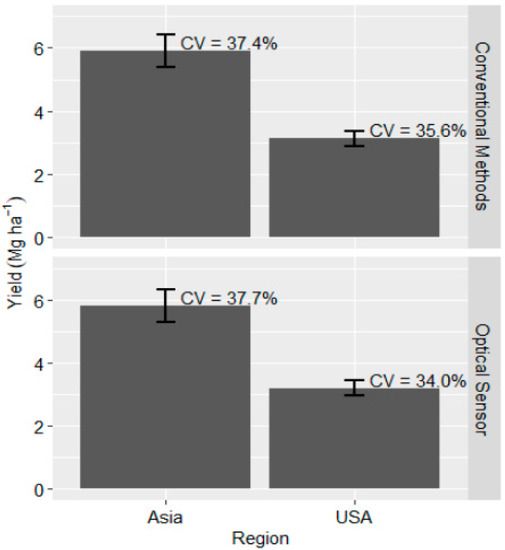
Figure 3.
Winter wheat rain yield for optical sensor and conventional methods of N management for the U.S. and Asia.
Results summarized in Table 2 also demonstrated that applying large quantities of N may not always result in a grain yield that exceeds yield obtained with optical sensors. At an average of 186 kg N ha−1 (±12.9 kg N ha−1), mean grain yield was 30.4% lower than yield achieved with an active optical sensor and conventional methods of N management (Table 1 and Table 2). Applying N beyond crop requirements could increase grain N and protein [66,67], but also has the potential to lead to lodging, a factor that reduces grain yield [68]. Additionally, this could also lead to an increase in N loss via leaching and other pathways [69]. Spatial and temporal variability could have also contributed to the observed grain yield difference.
The similarity in yield between active optical sensor and conventional methods of N management has previously been reported [5,31,70]. Attaining a drastic yield increase with optical sensors over conventional methods of N management may not be easy, since in some areas the yield levels are close to the maximum yield [71]. However, optical sensor N management achieved the same yield levels, with a lower amount of fertilizer N applied [15]. In fact, work done by Stamatiadis et al. [27] showed that optical sensors may in some case produce grain yield that exceeds conventional methods by as much as 1 Mg ha−1. This is because the precision nutrient management approach is able to accurately predict in-season yield potential and crop response for a more accurate N estimate [72]. Variable-rate application of N using the optical sensor provides room to further enhance the accuracy of N application [73]. Due to the precision of estimates for yield potential and N requirement, approximately 83% of the total variations in winter wheat grain yield are explainable using the in-season estimated yield and response index, which are all derived from spectral reflectance measurements [74]. Making a determination and application of N midseason without preplant N could improve NUE, but may also lead to a decline in yield relative to where the same amount of N is applied preplant. Raun et al. [5] showed that failure to apply N preplant could reduce grain yield by as much as 457 kg ha−1 while maintaining a 17% higher NUE over a treatment where N was applied preplant followed by midseason recommended rate. One possible explanation for this is that weather variables such as precipitation could have led to early-season leaching and/or denitrification losses of preplant applied N before significant plant uptake [75].
The wide variability in optimum N from year to year and location to location is an important factor that makes it vital to reevaluate the conventional methods of N management [58]. Moreover, the precision with which we estimate crop N requirement has increasingly become more and more cumbersome due to increasing entropy or randomness, indicating the need to include more environmental variables in algorithms of the future [76]. The current active optical sensors have demonstrated relevance in improving winter wheat NUE, as well as in sustaining yield at levels achieved with conventional methods and yet there remains an opportunity for improvement to achieve higher NUE levels while simultaneously maintaining or increasing grain yield. This could mean integration of more factors such as soil water content at 0–5 cm soil depth in the yield prediction algorithms [77]. A possibility that the active optical sensors could be customized to reduce the cost for poor resource farmers, particularly in developing countries, is perhaps one good development that might expand the frontier for increased use of active sensors [78].
3.3. Profitability of Optical Sensors and Opportunities for Improvement
The profitability of the sensor-based technology primarily drives its adoption among producers. There has been a mixed report on the economics of the sensor technology. For example, Biermacher et al. [33] reported that the conventional method resulted in a US$351 ha−1 net return that was above gains realized with optical sensors by at least US$8 ha−1. Roberts et al. [79] added that optical sensors are likely to bring, on average, US$ 18.74 ha−1 less return to producers when compared to the conventional method, particularly when anhydrous ammonia is the source of N. Colaço and Bramley [17] suggested that optical sensors returned about US$ 30 ha−1 in profitability, but that this is shrouded with a lot of uncertainty that may lead to loss of income. To demonstrate the level of uncertainty, Colaço and Bramley [17] stated that there was a 37% likelihood that a producer might make an economic loss from using optical sensor technology. It is this kind of uncertainty that is probably responsible for the low adoption rate of precision agriculture technology. Therefore, reducing the uncertainty in this technology may prove pivotal in increasing the number of adopters reported by one study to be about 13% [80]. With further refinement, the cost of the technology is also anticipated to reduce in the future and possibly increase adoption [81].
Furthermore, many studies evaluated the optical sensor technology as an approach for N management [77,82,83,84], but few of the published studies have used it to estimate and apply N for winter wheat midseason [17]. This is partly because the algorithm is site- or region-specific and requires validation for each region. This presents a challenge, as determination of profitability is being made on just a few studies.
A good return is likely to be realized if a technology such as the sensor-based approach can improve wheat grain yield, and this may, in turn, increase its adoption among producers around the world [85]. One potential option is to make the sensor more robust with the capability to deliver N management that takes into account temporal and spatial variability. Currently, the algorithm uses a single independent variable, in particular in-season estimated yield (INSEY), to predict yield in-season [74,86] and through a series of steps, the amount of N required by crops is estimated [5,74]. The accuracy of the algorithm may ultimately be improved by including more predictors such as in-season rainfall and temperature currently available via various networks, most notably the Oklahoma Mesonet (mesonet.org) that reports live weather statistics (rainfall, ambient temperature, wind speed, soil moisture, soil temperature, and solar radiation) using 120 automated stations covering 77 counties in Oklahoma, U.S.
Using optical sensors to determine the time and rate of N application [5] together with the right N source and placement method [87], as well as crop genetic manipulation [88], could also be a viable option to make the crop sensor more robust for yield as well as NUE gains.
Without some of these variables, the sensors may not be able to adequately capture temporal and spatial variability. For instance, water stress at the time of sensing may lead to an underestimation of yield potential and, thus, a lower amount of N is recommended [61]. This affects the final grain yield that a producer is able to obtain. Soils with a high proportion of sand, such as sandy loam, may dry out faster upon receiving rainfall [5]. This may also affect the temporal and spatial performance of the sensor technology. As a result, some of these variables need to be evaluated with a particular interest of obtaining a linear or non-linear model that can be used directly or indirectly to estimate the quantity of N to apply.
4. Conclusions
This review found that N management using active optical sensors had a higher NUE for winter wheat when compared to conventional methods. On average, active optical sensors had an NUE of 42.0% (±2.8%), higher than that of conventional methods by 10.4% (±3.8%). For the regions considered, Asia had the highest NUE of 54.8% (±4.2%) but applied 67 kg ha−1 (±18.3 kg ha−1) more N than the U.S. when optical sensor was the N management approach selected. Winter wheat grain yield based on the two approaches for N management was not highly significant, but the trend was consistent. Grain yield differed by region, with Asia having the highest grain yield for both N management approaches. Although we cannot explicitly state the reasons for this, the studies reviewed indicated that Asia had a lower soil organic matter content than the U.S., and this might have led to high response to applied N in Asia. The major contribution of active optical sensors is aligned to the saving of approximately 53 kg N ha−1 (±16 kg N ha−1). The sensor-based approach for N management has assisted in applying N more precisely, and that has increased NUE. In addition, the anticipated reduction in the cost of the technology following further refinement could spur widespread adoption and use. However, the challenge in fertilizer management is still evident when considering that 58% of total N applied in cereal production remains unrecovered in the grain. Adoption of sensor-based approaches may not completely address this challenge. Improving N availability for crop uptake in soils with poor N retention can be achieved by implementing management practices such as cover cropping during the off-season, a crop rotation system involving non-legumes and legumes, and an appropriate tillage system.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.A. and P.O.; methodology, L.A.; writing—original draft preparation, L.A., and P.O.; writing—review & editing, P.O., E.N., F.B.O. and W.R.R.; visualization, L.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The APC was funded by the Oklahoma Agricultural Experiment Station.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Cassman, K.G.; Dobermann, A.; Walters, D.T. Agroecosystems, nitrogen-use efficiency, and nitrogen management. AMBIO 2002, 31, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Chen, D. Nitrogen fertilizer use in China–Contributions to food production, impacts on the environment and best management strategies. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2002, 63, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, A.; Smith, J.; Parr, J.; Papendick, R. Considerations in estimating nitrogen recovery efficiency by the difference and isotopic dilution methods. Fert. Res. 1992, 33, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raun, W.R.; Johnson, G.V.J.A.j. Improving nitrogen use efficiency for cereal production. Agron. J. 1999, 91, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raun, W.R.; Solie, J.B.; Johnson, G.V.; Stone, M.L.; Mullen, R.W.; Freeman, K.W.; Thomason, W.E.; Lukina, E.V. Improving nitrogen use efficiency in cereal grain production with optical sensing and variable rate application. Agron. J. 2002, 94, 815–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Lam, S.K.; Chen, D.; Wang, J.; Tang, Q.; Yan, X. Can knowledge-based N management produce more staple grain with lower greenhouse gas emission and reactive nitrogen pollution? A meta-analysis. GCB Bioenerg. 2017, 23, 1917–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Zhang, F.; Chen, X.; Miao, Y.; Li, J.; Shi, L.; Xu, J.; Ye, Y.; Liu, C.; Yang, Z. On-farm evaluation of an in-season nitrogen management strategy based on soil Nmin test. Field Crop. Res. 2008, 105, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omara, P.; Aula, L.; Raun, W.R. Nitrogen uptake efficiency and total soil nitrogen accumulation in long-term beef manure and inorganic fertilizer application. Int. J. Agron. 2019, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahnke, W.; Swenson, L.; Goos, R.J.; Leholm, A. Choosing a Crop Yield Goal; North Dakota State University: Fargo, ND, USA, 1988; SF–822. [Google Scholar]
- Raun, W.; Figueiredo, B.; Dhillon, J.; Fornah, A.; Bushong, J.; Zhang, H.; Taylor, R. Can yield goals be predicted? Agron. J. 2017, 109, 2389–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raun, W.R.; Solie, J.B.; Stone, M.L. Independence of yield potential and crop nitrogen response. Precis. Agric. 2011, 12, 508–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, G.; Raun, W. Nitrogen response index as a guide to fertilizer management. J. Plant Nutr. 2003, 26, 249–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, K.B.; Martin, K.; Freeman, K.; Teal, R.; Girma, K.; Arnall, D.; Hodgen, P.; Mosali, J.; Raun, W.; Solie, J. Mid-season recovery from nitrogen stress in winter wheat. J. Plant Nutr. 2006, 29, 727–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godwin, R.; Wood, G.; Taylor, J.; Knight, S.; Welsh, J. Precision farming of cereal crops: A review of a six year experiment to develop management guidelines. Biosyst. Eng. 2003, 84, 375–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butchee, K.S.; May, J.; Arnall, B. Sensor based nitrogen management reduced nitrogen and maintained yield. Crop Manag. 2011, 10, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Miao, Y.; Zhang, F.; Cui, Z.; Li, R.; Chen, X.; Zhang, H.; Schroder, J.; Raun, W.; Jia, L. In-season optical sensing improves nitrogen-use efficiency for winter wheat. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2009, 73, 1566–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colaço, A.F.; Bramley, R.G. Do crop sensors promote improved nitrogen management in grain crops? Field Crop. Res. 2018, 218, 126–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zillmann, E.; Graeff, S.; Link, J.; Batchelor, W.D.; Claupein, W. Assessment of cereal nitrogen requirements derived by optical on-the-go sensors on heterogeneous soils. Agron. J 2006, 98, 682–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyer, C.N.; Brorsen, B.W.; Solie, J.B.; Raun, W.R. Profitability of variable rate nitrogen application in wheat production. Precis. Agric. 2011, 12, 473–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcoz, M.M.; Hons, F.M.; Haby, V.A.J.A.J. Nitrogen fertilization timing effect on wheat production, nitrogen uptake efficiency, and residual soil nitrogen. Agron. J. 1993, 85, 1198–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, B.D.; Petrie, S. Irrigated hard winter wheat response to fall, spring, and late season applied nitrogen. Field Crop. Res. 2006, 96, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, J.; Eickhoff, E.; Aula, L.; Omara, P.; Weymeyer, G.; Nambi, E.; Oyebiyi, F.; Carpenter, T.; Raun, W. Nitrogen management impact on winter wheat grain yield and estimated plant nitrogen loss. Agron. J. 2019, 112, 564–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowers, K.E.; Pan, W.L.; Miller, B.C.; Smith, J.L. Nitrogen use efficiency of split nitrogen applications in soft white winter wheat. Agron. J. 1994, 86, 942–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.N.; Peterson, W.; Easter, K.W. Do farmers overuse nitrogen fertilizer to the detriment of the environment? Resour. Econ. 1997, 9, 323–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdle, K.; Mistele, B.; Schmidhalter, U. Comparison of active and passive spectral sensors in discriminating biomass parameters and nitrogen status in wheat cultivars. Field Crop. Res. 2011, 124, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flowers, M.; Weisz, R.; Heiniger, R. Quantitative approaches for using color infrared photography for assessing in-season nitrogen status in winter wheat. Agron. J. 2003, 95, 1189–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatiadis, S.; Schepers, J.; Evangelou, E.; Tsadilas, C.; Glampedakis, A.; Glampedakis, M.; Dercas, N.; Spyropoulos, N.; Dalezios, N.; Eskridge, K. Variable-rate nitrogen fertilization of winter wheat under high spatial resolution. Precis. Agric. 2018, 19, 570–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aula, L.; Dhillon, J.S.; Omara, P.; Wehmeyer, G.B.; Freeman, K.W.; Raun, W.R. World Sulfur Use Efficiency for Cereal Crops. Agron. J. 2019, 111, 2485–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omara, P.; Aula, L.; Oyebiyi, F.; Raun, W.R. Environment World cereal nitrogen use efficiency trends: Review and current knowledge. Agrosyst. Geosci. Environ. 2019, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgen, P.; Raun, W.; Johnson, G.; Teal, R.; Freeman, K.; Brixey, K.; Martin, K.; Solie, J.; Stone, M. Relationship between response indices measured in-season and at harvest in winter wheat. J. Plant Nutr. 2005, 28, 221–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tubaña, B.; Arnall, D.; Holtz, S.; Solie, J.; Girma, K.; Raun, W. Effect of treating field spatial variability in winter wheat at different resolutions. J. Plant Nutr. 2008, 31, 1975–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.; Miao, Y.; Feng, G.; Gao, X.; Liu, B.; Liu, Y.; Li, F.; Khosla, R.; Mulla, D.J.; Zhang, F. Improving nitrogen use efficiency with minimal environmental risks using an active canopy sensor in a wheat-maize cropping system. Field Crop. Res. 2017, 214, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biermacher, J.T.; Epplin, F.M.; Brorsen, B.W.; Solie, J.B.; Raun, W.R. Economic feasibility of site-specific optical sensing for managing nitrogen fertilizer for growing wheat. Precis. Agric. 2009, 10, 213–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Monasterio, I.; Raun, W. Reduced nitrogen and improved farm income for irrigated spring wheat in the Yaqui Valley, Mexico, using sensor based nitrogen management. J. Agric. Sci. Camb. 2007, 145, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijay-Singh; Sharma, R.; Jaspreet-Kaur; Jat, M.L.; Martin, K.L.; Yadvinder-Singh; Varinderpal-Singh; Chandna, P.; Choudhary, O.P.; Gupta, R.K.; et al. Assessment of the nitrogen management strategy using an optical sensor for irrigated wheat. Agron. Sust. Dev. 2011, 31, 589–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulochna; Alam, M.P.; Ali, N.; Singh, S. Nitrogen Management by Using Optical Sensor in Wheat in Jharkhand. Curr. J. Appl. Sci. Tech. 2018, 31, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.; Miao, Y.; Li, F.; Gao, X.; Liu, B.; Lu, D.; Chen, X. Developing a new Crop Circle active canopy sensor-based precision nitrogen management strategy for winter wheat in North China Plain. Precis. Agric. 2017, 18, 2–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijay-Singh; Varinderpal-Singh; Yadvinder-Singh; Thind, H.; Kumar, A.; Choudhary, O.; Gupta, R.; Vashistha, M. Site-specific fertilizer nitrogen management using optical sensor in irrigated wheat in the Northwestern India. Agric. Res. 2017, 6, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranney, R. An organic carbon-organic matter conversion equation for Pennsylvania surface soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1969, 33, 809–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solari, F.; Shanahan, J.F.; Ferguson, R.B.; Adamchuk, V.I. An active sensor algorithm for corn nitrogen recommendations based on a chlorophyll meter algorithm. Agron. J. 2010, 102, 1090–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Department of Agriculture-Economic Research Service (USDA). Fertilizer Use and Price. Available online: https://www.ers.usda.gov/data-products/fertilizer-use-and-price.aspx (accessed on 8 April 2019).
- Zhu, X.; Guo, W.; Ding, J.; Li, C.; Feng, C.; Peng, Y. Enhancing nitrogen use efficiency by combinations of nitrogen application amount and time in wheat. J. Plant Nutr. 2011, 34, 1747–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, P.; Zhou, Y.; Coventry, D.R.; McDonald, G.K. Use of nitrogen fertilizer in a targeted way to improve grain yield, quality, and nitrogen use efficiency. Agron. J. 2015, 107, 903–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teal, R.K.; Freeman, K.; Girma, K.; Arnall, D.; Lawles, J.; Martin, K.; Mullen, R.; Raun, W. Effect of tillage and anhydrous ammonia application on nitrogen use efficiency of hard red winter wheat. J. Sustain. Agric. 2007, 30, 51–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomason, W.; Raun, W.; Johnson, G. Winter wheat fertilizer nitrogen use efficiency in grain and forage production systems. J. Plant Nutr. 2000, 23, 1505–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Q.; He, P.; Zhang, X.; Yang, L.; Xiong, G. Optimizing fertilizer nitrogen for winter wheat production in Yangtze River region in China. J. Plant Nutr. 2015, 38, 1639–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanampiu, F.K.; Raun, W.R.; Johnson, G.V. Effect of nitrogen rate on plant nitrogen loss in winter wheat varieties. J. Plant Nutr. 1997, 20, 389–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mohammed, Y.A.; Kelly, J.; Chim, B.K.; Rutto, E.; Waldschmidt, K.; Mullock, J.; Torres, G.; Desta, K.G.; Raun, W. Nitrogen fertilizer management for improved grain quality and yield in winter wheat in Oklahoma. J. Plant Nutr. 2013, 36, 749–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montemurro, F.; Convertini, G.; Ferri, D. Nitrogen application in winter wheat grown in Mediterranean conditions: Effects on nitrogen uptake, utilization efficiency, and soil nitrogen deficit. J. Plant Nutr. 2007, 30, 1681–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lees, H.; Raun, W.; Johnson, G. Increased plant nitrogen loss with increasing nitrogen applied in winter wheat observed with 15nitrogen. J. Plant Nutr. 2000, 23, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Si, L. Effects of topdressing with nitrogen fertilizer on wheat yield, and nitrogen uptake and utilization efficiency on the Loess Plateau. Acta Agric. Scand. Sect. Soil Plant Sci. 2015, 65, 681–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girma, K.; Freeman, K.W.; Teal, R.; Arnall, D.B.; Tubana, B.; Holtz, S.; Raun, W.R.; Science, S. Analysis of yield variability in winter wheat due to temporal variability, and nitrogen and phosphorus fertilization. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2007, 53, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syers, J.; Johnston, A.; Curtin, D. Efficiency of soil and fertilizer phosphorus use. FAO Fertil. Plant Nutr. Bull. 2008, 18, 108. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, C.; Matros, A.; Mock, H.-P.; Mühling, K.-H. Protein composition and baking quality of wheat flour as affected by split nitrogen application. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batal, A.; Dale, N.; Persia, M.J.I. TX: Informa Ingredient analysis table: 2012 edition. Feedstuffs Ref. Issue Buy. Guide 2011, 83, 16–17. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing (R-4.0.1); R Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wickham, H.; Averick, M.; Bryan, J.; Chang, W.; McGowan, L.D.A.; François, R.; Grolemund, G.; Hayes, A.; Henry, L.; Hester, J.; et al. Welcome to the Tidyverse. J. Open Source Softw. 2019, 4, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhital, S.; Raun, W. Variability in optimum nitrogen rates for maize. Agron. J. 2016, 108, 2165–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomason, W.; Phillips, S.; Davis, P.; Warren, J.; Alley, M.; Reiter, M. Variable nitrogen rate determination from plant spectral reflectance in soft red winter wheat. Precis. Agric. 2011, 12, 666–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, X.-T.; Xing, G.-X.; Chen, X.-P.; Zhang, S.-L.; Zhang, L.-J.; Liu, X.-J.; Cui, Z.-L.; Yin, B.; Christie, P.; Zhu, Z.-L.; et al. Reducing environmental risk by improving N management in intensive Chinese agricultural systems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 3041–3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Bellido, L.; López-Bellido, R.J.; Redondo, R. Nitrogen efficiency in wheat under rainfed Mediterranean conditions as affected by split nitrogen application. Field Crop. Res. 2005, 94, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.; Liu, W.; Li, S.; Zhang, P.; Wang, C.; Lu, H.; Wang, L.; Xie, Y.; Ma, D.; Kang, G. Determining the optimal N input to improve grain yield and quality in winter wheat with reduced apparent N loss in the North China Plain. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuejun, L.; Fusuo, Z. Nitrogen fertilizer induced greenhouse gas emissions in China. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2011, 3, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conley, D.J.; Paerl, H.W.; Howarth, R.W.; Boesch, D.F.; Seitzinger, S.P.; Havens, K.E.; Lancelot, C.; Likens, G.E. Controlling eutrophication: Nitrogen and phosphorus. Science 2009, 323, 1014–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, Y.; Stewart, B.A.; Zhang, F. Long-term experiments for sustainable nutrient management in China. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2011, 31, 397–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raun, W.R.; Johnson, G.V. Soil-plant buffering of inorganic nitrogen in continuous winter wheat. Agron. J. 1995, 87, 827–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, P.; Rohde, C. Tillage, soil depth, and precipitation effects on wheat response to nitrogen. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1991, 55, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bundy, L.G.; Andraski, T.W. Diagnostic tests for site-specific nitrogen recommendations for winter wheat. Agron. J. 2004, 96, 608–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Tian, Z.; Zhang, N.; Li, X. Nitrate pollution of groundwater in northern China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 1996, 59, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diacono, M.; Rubino, P.; Montemurro, F. Precision nitrogen management of wheat. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2013, 33, 219–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samborski, S.M.; Gozdowski, D.; Stępień, M.; Walsh, O.S.; Leszczyńska, E. On-farm evaluation of an active optical sensor performance for variable nitrogen application in winter wheat. Eur. J. Agron. 2016, 74, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raun, W.; Solie, J.; Stone, M.; Martin, K.; Freeman, K.; Mullen, R.; Zhang, H.; Schepers, J.; Johnson, G. Optical sensor-based algorithm for crop nitrogen fertilization. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant. Anal. 2005, 36, 2759–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quebrajo, L.; Pérez-Ruiz, M.; Rodriguez-Lizana, A.; Agüera, J. An approach to precise nitrogen management using hand-held crop sensor measurements and winter wheat yield mapping in a mediterranean environment. Sensors 2015, 15, 5504–5517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raun, W.R.; Solie, J.B.; Johnson, G.V.; Stone, M.L.; Lukina, E.V.; Thomason, W.E.; Schepers, J.S. In-season prediction of potential grain yield in winter wheat using canopy reflectance. Agron. J. 2001, 93, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, U.; Haider, K. Denitrification-and Nitrate Leaching-Losses in an Intensively Cropped Watershed. Z. Pflanzenernähr. Bodenkd. 1992, 155, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raun, W.R.; Dhillon, J.; Aula, L.; Eickhoff, E.; Weymeyer, G.; Figueirdeo, B.; Lynch, T.; Omara, P.; Nambi, E.; Oyebiyi, F. Unpredictable nature of environment on nitrogen supply and demand. Agron. J. 2019, 111, 2786–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, O.S.; Klatt, A.; Solie, J.; Godsey, C.; Raun, W. Use of soil moisture data for refined GreenSeeker sensor based nitrogen recommendations in winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Precis. Agric. 2013, 14, 343–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crain, J.; Ortiz-Monasterio, I.; Raun, B. Evaluation of a reduced cost active NDVI sensor for crop nutrient management. J. Sens 2012, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, D.C.; Brorsen, B.W.; Solie, J.B.; Raun, W.R. The effect of parameter uncertainty on whole-field nitrogen recommendations from nitrogen-rich strips and ramped strips in winter wheat. Agric. Syst. 2011, 104, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llewellyn, R.; Ouzman, J. Adoption of Precision Agriculture-Related Practices: Status, Opportunities and the Role of Farm Advisers; Report for Grains Research and Development Corporation; CSIRO: Canberra, Australia, December 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, M.; Wagner, P. Prerequisites for the adoption of new technologies–the example of precision agriculture. Poljoprivredna Tehnika(Agricultural Engineering) 2015, 2007, 9–14. [Google Scholar]
- Bushong, J.T.; Mullock, J.L.; Miller, E.C.; Raun, W.R.; Klatt, A.R.; Arnall, D.B. Development of an in-season estimate of yield potential utilizing optical crop sensors and soil moisture data for winter wheat. Precis. Agric. 2016, 17, 451–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukina, E.; Freeman, K.; Wynn, K.; Thomason, W.; Mullen, R.; Stone, M.; Solie, J.; Klatt, A.; Johnson, G.; Elliott, R. Nitrogen fertilization optimization algorithm based on in-season estimates of yield and plant nitrogen uptake. J. Plant Nutr. 2001, 24, 885–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiratsuchi, L.; Ferguson, R.; Shanahan, J.; Adamchuk, V.; Rundquist, D.; Marx, D.; Slater, G. Water and nitrogen effects on active canopy sensor vegetation indices. Agron. J. 2011, 103, 1815–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Mauzerall, D.L.; Davidson, E.A.; Kanter, D.R.; Cai, R. The economic and environmental consequences of implementing nitrogen-efficient technologies and management practices in agriculture. J. Environ. Qual. 2015, 44, 312–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A.M.; Ibrahim, S. Wheat grain yield and nitrogen uptake prediction using atLeaf and GreenSeeker portable optical sensors at jointing growth stage. Inform. Process. Agric 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, L.K.; Bali, S.K. A review of methods to improve nitrogen use efficiency in agriculture. Sustainability 2018, 10, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guttieri, M.J.; Frels, K.; Regassa, T.; Waters, B.M.; Baenziger, P.S. Variation for nitrogen use efficiency traits in current and historical great plains hard winter wheat. Euphytica 2017, 213, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).