Quantification of Biologically Fixed Nitrogen by White Lupin (Lupins albus L.) and Its Subsequent Uptake by Winter Wheat Using the 15N Isotope Dilution Method
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description
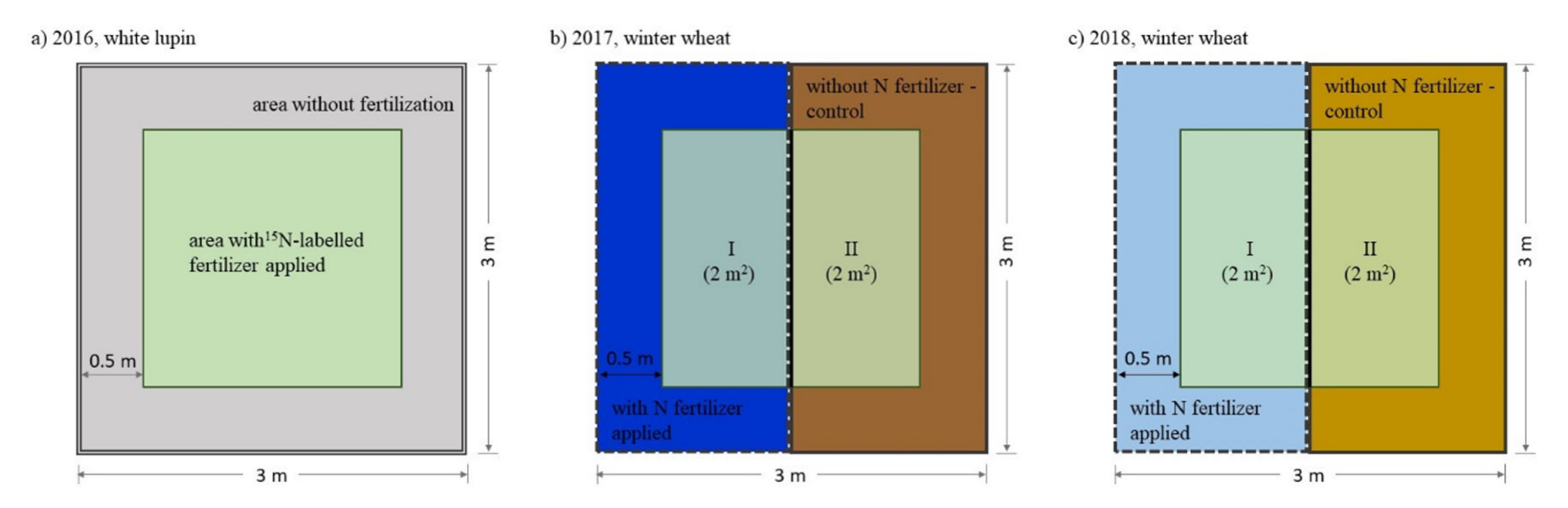
2.2. Experiment Design and Agronomic Management
2.3. Chemical and Isotopic Analysis
2.4. Calculations
- (1)
- %N derived from atmosphere
- (2)
- Amount of N fixed by white lupin from atmosphere (kg ha−1)
- (3)
- % N derived from fertilizer
- (4)
- Amount of N derived from fertilizer (kg ha−1)
- (5)
- % N derived from soil
- (6)
- Coefficient of N-utilization (N-use efficiency) from fertilizer
- (7)
- % N in the winter wheat from white lupin residue
- (8)
- % N derived from residue
- (9)
- Amount of N derived from residue (kg ha−1) = (% NdfR in wheat × TN in winter wheat/N in residues kg ha−1) × 100
- (10)
- Coefficient of nitrogen utilization by winter wheat from crop residue of white lupin (%) =
- (11)
- Total amount of 15N in biomass of lupin and winter wheat (kg ha−1)
- (12)
- % of 15N uptake = (15N kg ha−1 in plant/15N kg ha−1 in fertilizer) × 100.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Preissel, S.; Reckling, M.; Schläfke, N.; Zander, P. Magnitude and farm-economic value of grain pre-crop benefits in Europe. A review. Field Crops Res. 2015, 175, 64–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Księżak, J.; Staniak, M.; Bojarszczuk, J. The regional differentiation of legumes cropping area in Poland between 2001 and 2007. Pol. J. Agron. 2009, 1, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sujak, A.; Kotlarz, A.; Strobel, W. Compositional and nutritional evaluation of several lupin seeds. Food Chem. 2006, 98, 711–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annicchiarico, P.; Harzic, N.; Carroni, A.M. Adaptation, diversity, and exploitation of global white lupin (Lupinus albus L.) landrace genetic resources. Field Crops Res. 2010, 119, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, M.M.; Stoddard, F.L.; Anniechiarico, P.; Prias, J.; Martinez-Villaluenga, C.; Sussmann, D.; Duranti, M.; Seger, A.; Zander, P.K.; Pueyo, J.J. The future of lupine as a protein crop in Europe. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, R.J.; Martin, J.R.J.; Goh, K.M. Nitrogen fixation, accumulation of soil nitrogen and nitrogen balance for some field-grown legumes crops. Field Crops Res. 1993, 35, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, J.; McNeill, A.M.; Unkovick, M.J.; Fettell, N.A.; Heenan, D.P. Nat nitrogen balances for cool-season grain legume crops and contributions to wheat nitrogen uptake. A review. Aust. J. Exp. Agric. 2001, 41, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemecek, T.; von Richthofen, J.S.; Dubois, G.; Casta, P.; Charles, R.; Pahl, H. Environmental impacts of introducing grain legumes into European crop rotations. Eur. J. Agron. 2008, 28, 380–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, J.; Buegger, F.; Jensen, F.S.; Schloter, M.; Heβ, J. Estimating N rhizodeposition of grain legumes using a 15N in situ stem labelling method. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2003, 35, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wichern, F.; Eberhardt, E.; Mayer, J.; Joergensen, R.G.; Müller, M. Nitrogen rhizodeposition in agriculture crops: Methods, estimates and future prospects. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2008, 40, 30–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fustec, J.; Lesuffleur, F.; Mahieu, S.; Cliquet, J.B. Nitrogen rhizodeposition of legumes. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2010, 30, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Unkovich, M.J.; Pate, J.S. An appraisal of recent field measurements of symbiotic N2 fixation by annual legumes. Field Crops Res. 2003, 65, 211–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peoples, M.B.; Brockwell, J.; Herridge, D.F.; Rochester, I.J.; Alves, J.R.; Urgulaga, S.; Boddey, R.M.; Dakora, F.D.; Battarai, S.; Maskey, S.L.; et al. The contribution of nitrogen-fixing crop legumes to the productivity of agricultural systems. Symbiosis 2009, 48, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carranca, C.; Torres, M.O.; Madeira, M. Underestimated role of legume roots for soil N fertility. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2015, 35, 1095–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guidelines on Nitrogen Management in Agricultural Systems; IAEA-TCS-29; IAEA: Vienna, Austria, 2008; pp. 62, 134, 150, 182. ISSN 1018-5518.
- Stevenson, F.C.; Walley, F.L.; van Kessel, C. Direct vs. indirect nitrogen-15 approaches to estimate nitrogen contributions from crop residues. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1998, 62, 1327–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hood, R.C.N.; N’goran, K.; Aigner, M.; Hardarson, G. A comparison of direct and indirect 15N isotope techniques for estimating crop N uptake from organic residues. Plant Soil. 1999, 208, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkegaard, J.A.; Christen, O.; Krupinsky, J.; Layzell, D.B. Break crop benefits in temperate wheat production. Field Crops Res. 2008, 107, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkins, C.A.; Smith, P.M. Regulation of pod set and seed development in lupin. In Proceedings of the Regulation of Pod Set and Seed Development in Lupin, Laugarvatn, Iceland, 1 January 2004; pp. 275–278. [Google Scholar]
- Faluyi, M.A.; Zhou, X.M.; Zhang, F.; Leibovitch, S.; Migner, P.; Smith, D.L. Seed quality of sweet white lupin (Lupinus albus) and management practice in eastern Canada. Eur. J. Agron. 2000, 13, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herridge, D.F.; Peoples, M.B.; Bodday, R. Global inputs of biological nitrogen fixation in agricultural systems. Plant Soil. 2008, 311, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pampana, S.; Masoni, A.; Mariotti, M.; Ercoli, L.; Arduini, I. Nitrogen fixation of grain legumes differs in response to nitrogen fertilisation. Experimental Agric. 2018, 54, 66–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montemurro, F. Different nitrogen fertilization sources, soil tillage, and crop rotations in winter wheat: Effect on yield, quality, and nitrogen utilization. J. Plant Nut. 2009, 32, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimizadeh, M.; Kashani, A.; Zare–Feizabadi, A.; Koocheki, A.R.; Nassiri–Mahallati, M. Nitrogen use efficiency of wheat as affected by preceding crop, application rate of nitrogen and crop residues. Aust. J. Crop Sci. 2010, 4, 363–368. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, K.; Goh, K.M. Management practices of antecedent leguminous and non-leguminous crop residues in relation to winter wheat yields, nitrogen uptake, soil nitrogen mineralization and simple nitrogen balance. Eur. J. Agron. 2002, 16, 295–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutkowska, A.; Pikuła, D. Efficacy of 15N—Nitrogen in fertilization of pea mixtures with wheat, barley, and oats. Plant Soil Environ. 2016, 62, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Babulicová, M. The influence of fertilization and crop rotation on the winter wheat production. Plant Soil Environ. 2014, 60, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Faligowska, A.; Szymańska, G.; Panasiewicz, K.; Szukała, J.; Koziara, W.; Ratajczak, K. The long-term effect of legumes as forecrops on the productivity of rotation (winter rape-winter wheat-winter wheat) with nitrogen fertilization. Plant Soil Environ. 2019, 65, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panasiewicz, K.; Faligowska, A.; Szymańska, G.; Szukała, J.; Ratajczak, K.; Sulewska, H. The effect of various tillage systems on productivity of narrow-leaved lupin-winter wheat-winter triticale-winter barley rotation. Agronomy 2020, 10, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Porporato, A.; D’Odorico, P.; Laio, F.; Rodriguez-Iturbe, I. Hydrologic controls on soil carbon and nitrogen cycles. I. Modeling scheme. Adv. Water Res. 2003, 26, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, G.P.; Groffman, P.M. Nitrogen transformations. In Microbiology and Biochemistry Soil, 3rd ed.; Paul, E.A., Ed.; Academic Press: Burlington, VT, USA, 2007; pp. 341–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, D.; Coyle, M.; Skiba, U.; Sutton, M.A.; Cape, J.N.; Reis, S.; Sheppard, L.J.; Jenkins, A.; Grizzetti, B.; Galloway, J.N.; et al. The global nitrogen cycle in the twenty-first century. Phil. Trans. R Soc. B 2013, 368, 20130164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anglade, J.; Billen, G.; Garnier, J. Relationships for estimating N2 fixation in legumes: Incidence for N balance of legume-based cropping systems in Europe. Ecosphere 2015, 6, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Year /Month | Mean Monthly Air Temperature (°C) | x | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D | ||
| 2016 | −1.9 | 3.4 | 3.7 | 8.6 | 15.4 | 18.3 | 18.8 | 17.5 | 16.5 | 8.0 | 2.9 | 1.7 | 9.4 |
| 2017 | −2.2 | 0.4 | 6.2 | 7.3 | 13.7 | 17.4 | 18.0 | 18.9 | 13.3 | 10.6 | 5.1 | 2.6 | 9.3 |
| 2018 | 1.8 | −3.0 | 0.6 | 12.9 | 16.8 | 18.5 | 20.1 | 21.4 | 15.8 | 11.0 | 5.1 | 2.5 | 10.3 |
| 1951–2015 | −1.2 | −0.2 | 3.5 | 8.8 | 14.3 | 17.5 | 19.3 | 18.6 | 13.9 | 9.1 | 3.9 | 0.2 | 15.6 |
| Monthly Rainfall Sum (mm) | ∑ | ||||||||||||
| 2016 | 31.6 | 36.8 | 49.0 | 37.4 | 43.0 | 83.6 | 149 | 40.6 | 5.6 | 105 | 47.8 | 42.6 | 672 |
| 2017 | 17.7 | 18.4 | 45.4 | 40.6 | 56.8 | 68.2 | 168 | 82.0 | 45.6 | 91.8 | 50.0 | 33.8 | 720 |
| 2018 | 44.6 | 5.0 | 22.6 | 36.2 | 17.4 | 25.4 | 70.5 | 11.6 | 44.2 | 24.8 | 11.4 | 46.2 | 360 |
| 1951–2015 | 31.5 | 27.7 | 31.7 | 31.0 | 50.5 | 59.4 | 77.2 | 55.4 | 45.2 | 34.1 | 35.6 | 38.9 | 518 |
| Crop Rotation (Harvest Year) | ||
|---|---|---|
| 2016 | 2017 | 2018 |
| white lupin + spring winter (reference plant) | winter wheat | winter wheat |
| Specification | Seeds/ Grain | Crop Residues | Sum/Mean Weighted * |
|---|---|---|---|
| White lupin | |||
| Yield (t ha−1) | 3.92 | 4.30 | 8.22 |
| Total nitrogen content (%) | 5.34 | 0.79 | 2.95 * |
| Total nitrogen content in biomass (kg ha−1) | 209.3 | 33.9 | 243.2 |
| Atomic-enrichment percentage (at% 15Nexcess) | 1.071 | 0.972 | 1.058 * |
| Nitrogen fixed from atmosphere (kg ha−1) | 93.7 (44.8%) ** | 17.5 (51.7%) ** | 111.2 |
| Nitrogen uptake from (15NH4)2SO4 (kg ha−1) | 11.3 (5.42%) ** | 1.7 (5.01%) ** | 13.0 |
| Nitrogen uptake from the soil (kg ha−1) | 104.2 (49.8%) ** | 15.2 (43.3%) ** | 119.4 |
| Spring wheat (reference plant) | |||
| Yield (t ha−1) | 1.24 | 2.93 | 4.17 |
| Total nitrogen content (%) | 2.30 | 0.65 | 1.14 * |
| Atomic-enrichment percentage (at% 15Nexcess) | 1.940 | 2.014 | 1.956 * |
| Specification | Nitrogen Dose kg ha−1 | Grain | Crop Residues | Sum/Mean Weighted * |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yield (t ha−1) | 0 | 4.31 b | 7.58 b | 11.89 b |
| 100 | 6.31 a | 8.42 a | 14.73 a | |
| Effect of fertilization 100 kg ha−1 N | +2.0 | + 0.8 | +2.8 | |
| Total nitrogen content (%) | 0 | 1.47 b | 0.19 a | 0.65 b, * |
| 100 | 1.89 a | 0.18 a | 0.90 a, * | |
| Nitrogen in winter wheat biomass (kg ha−1) | 0 | 63.3 b | 14.4 a | 77.7 b |
| 100 | 117.4 a | 15.1 a | 132.5 a | |
| Coefficient of nitrogen utilization (%) | 54.1 | 0.7 | 54.8 | |
| Atomic-enrichment percentage (at% 15Nexcess) | 0 | 0.256 a | 0.232 a | 2.240 a, * |
| 100 | 0.149 a | 0.193 a | 0.171 a, * | |
| Nitrogen content in winter wheat derived from white lupin residues (%) | 0 | 26.3 b | 23.8 b | 25.0 b, * |
| 100 | 15.3 a | 19.8 a | 17.6 a, * | |
| Nitrogen in winter wheat derived from white lupin residues (kg ha−1) | 0 | 16.6 b | 3.4 b | 20.0 b |
| 100 | 18.0 a | 3.0 a | 21.0 a | |
| Coefficient of nitrogen utilization by winter wheat from white lupin residues (%) | 0 | 48.9 b | 10.1 b | 59.0 b |
| 100 | 53.1 a | 8.8 a | 61.9 a | |
| Specification | Nitrogen Dose kg ha−1 | Grain | Crop Residues | Sum/Mean Weighted * |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yield (t ha−1) | 0 | 3.10 b | 7.46 b | 10.56 b |
| 100 | 4.20 a | 8.20 a | 12.40 a | |
| Effect of fertilization 100 kg ha−1 N | +1.10 | +0.74 | +1.84 | |
| Total nitrogen content (%) | 0 | 1.71 b | 0.54 b | 0.88 b, * |
| 100 | 1.97 a | 0.78 a | 1.18 a, * | |
| Nitrogen in winter wheat biomass (kg ha−1) | 0 | 53.0 b | 40.2 b | 93.2 b |
| 100 | 82.7 a | 63.9 a | 146.6 a | |
| Coefficient of nitrogen utilization (%) | 29.7 | 23.7 | 53.4 | |
| Atomic-enrichment percentage (at% 15Nexcess) | 0 | 0.080 a | 0.065 a | 0.068 a, * |
| 100 | 0.069 a | 0.052 a | 0.065 a, * | |
| Nitrogen in winter wheat derived from crop residues of white lupin (%) | 0 | 8.23 b | 6.88 b | 6.99 b, * |
| 100 | 7.09 a | 5.34 a | 6.22 a, * | |
| Nitrogen in winter wheat derived from crop residues of white lupin (kg ha−1) | 0 | 4.36 b | 2.76 b | 7.12 b |
| 100 | 5.86 a | 3.41 a | 9.27 a | |
| Coefficient of nitrogen utilization by winter wheat from crop residues of white lupin (%) | 0 | 12.9 b | 8.1 b | 21.0 b |
| 100 | 17.2 a | 10.0 a | 27.2 a | |
| 33.9 kg ha−1 of nitrogen introduced in crop residues of white lupin | ||||
| Specification | Nitrogen Dose kg ha−1 | Grain | Crop Residues | Sum |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total nitrogen uptake by winter wheat in the second and third years of rotation (kg ha−1) | 0 | 20.96 b | 6.18 b | 27.14 b |
| 100 | 23.86 a | 6.40 a | 30.26 a | |
| Coefficient of nitrogen utilization derived by winter wheat from white lupin residues (%) | 0 | 61.8 b | 18.2 b | 80.0 b |
| 100 | 70.3 a | 18.8 a | 89.1 a | |
| Change in nitrogen utilization rate as a result of nitrogen fertilization | +8.5 | +0.6 | +9.1 | |
| Specification | Nitrogen Dose kg ha−1 | Seeds/GRAIN | Crop Residues | Sum | Percentage Share in Relation to the Initial Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amount of isotope 15N in the biomass of white lupin harvested in 2016 (kg ha−1) | 2.241 | 0.329 | 2.570 | 43.4 | |
| Amount of 15N isotope in winter wheat harvested in 2017 (kg ha−1) | 0 | 0.162 b | 0.033 b | 0.195 b | 3.29 |
| 100 | 0.174 a | 0.029 a | 0.203 a | 3.42 | |
| Amount of 15N isotope in winter wheat harvested in 2018 (kg ha−1) | 0 | 0.042 b | 0.026 b | 0.068 b | 1.14 |
| 100 | 0.057 a | 0.033 a | 0.090 a | 1.52 | |
| Sum for dose N: 0 kg ha−1/100 kg ha−1 | 47.83/48.34 | ||||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kalembasa, S.; Szukała, J.; Faligowska, A.; Kalembasa, D.; Symanowicz, B.; Becher, M.; Gebus-Czupyt, B. Quantification of Biologically Fixed Nitrogen by White Lupin (Lupins albus L.) and Its Subsequent Uptake by Winter Wheat Using the 15N Isotope Dilution Method. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1392. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10091392
Kalembasa S, Szukała J, Faligowska A, Kalembasa D, Symanowicz B, Becher M, Gebus-Czupyt B. Quantification of Biologically Fixed Nitrogen by White Lupin (Lupins albus L.) and Its Subsequent Uptake by Winter Wheat Using the 15N Isotope Dilution Method. Agronomy. 2020; 10(9):1392. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10091392
Chicago/Turabian StyleKalembasa, Stanisław, Jerzy Szukała, Agnieszka Faligowska, Dorota Kalembasa, Barbara Symanowicz, Marcin Becher, and Beata Gebus-Czupyt. 2020. "Quantification of Biologically Fixed Nitrogen by White Lupin (Lupins albus L.) and Its Subsequent Uptake by Winter Wheat Using the 15N Isotope Dilution Method" Agronomy 10, no. 9: 1392. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10091392
APA StyleKalembasa, S., Szukała, J., Faligowska, A., Kalembasa, D., Symanowicz, B., Becher, M., & Gebus-Czupyt, B. (2020). Quantification of Biologically Fixed Nitrogen by White Lupin (Lupins albus L.) and Its Subsequent Uptake by Winter Wheat Using the 15N Isotope Dilution Method. Agronomy, 10(9), 1392. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10091392






