Estimation of Sensible and Latent Heat Fluxes Using Surface Renewal Method: Case Study of a Tea Plantation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site and Climate
2.2. Footprint Analysis
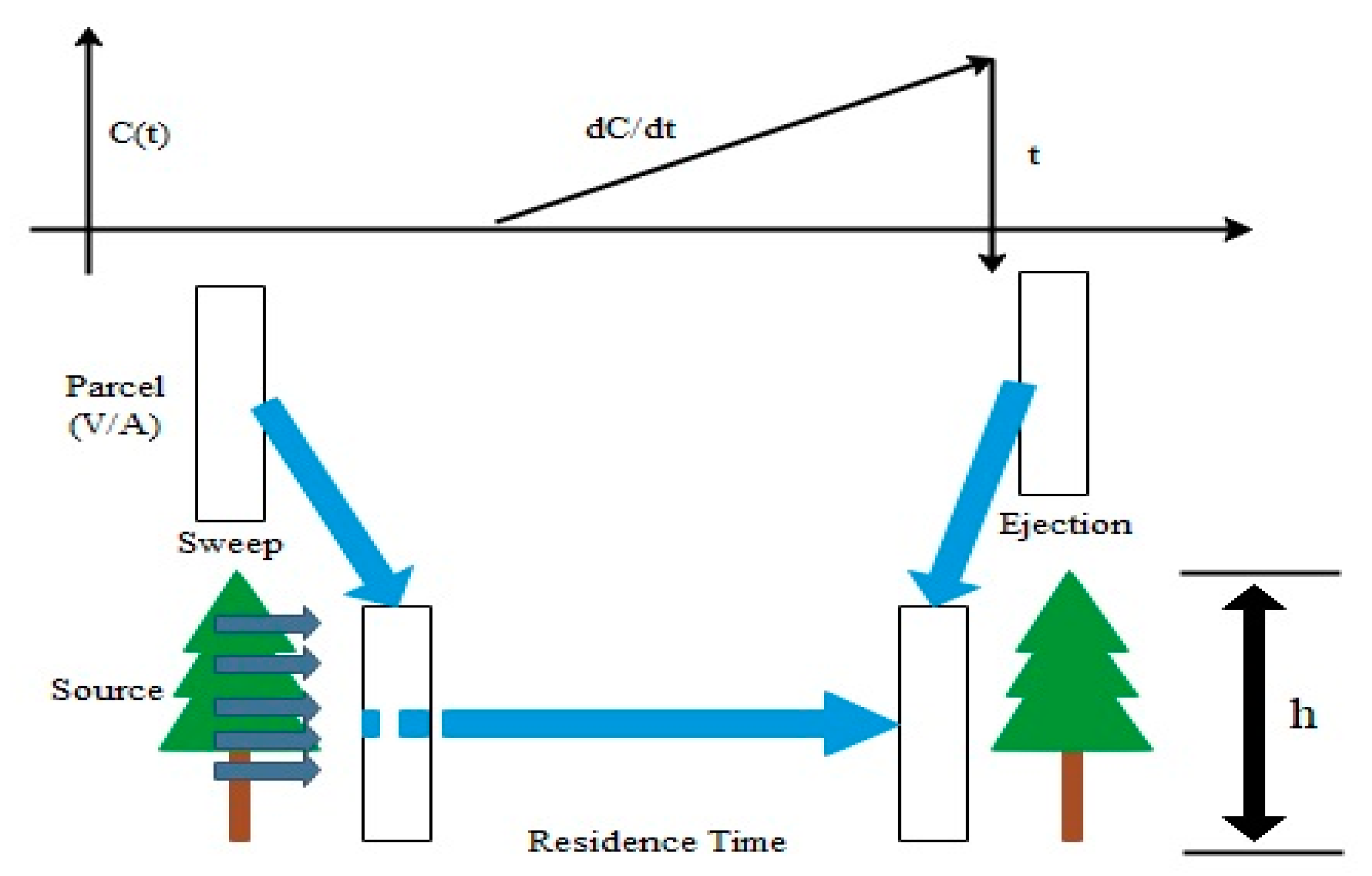
2.3. Surface Renewal (SR) Method
3. Results and Discussion
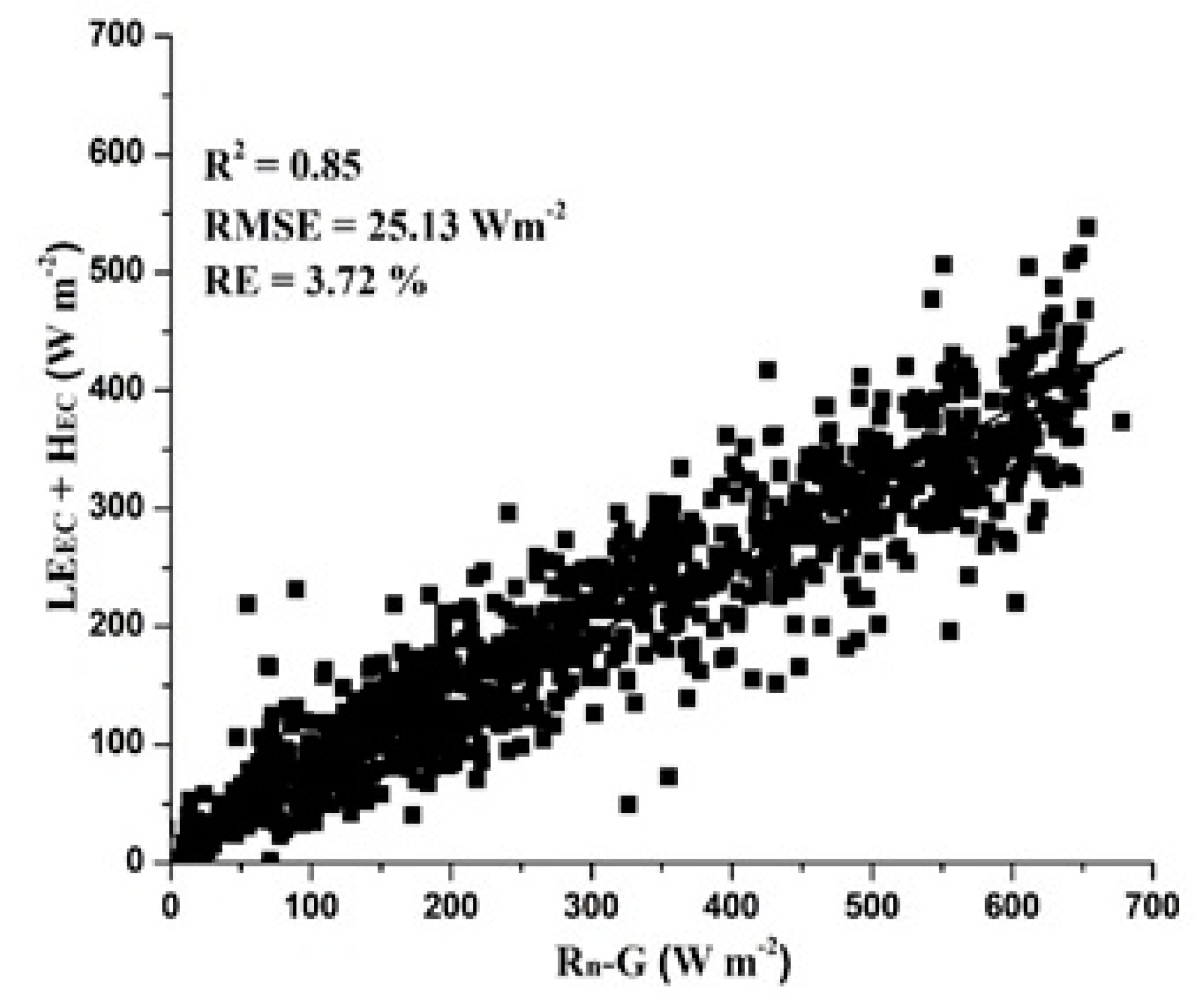
3.1. Energy Balance Closure
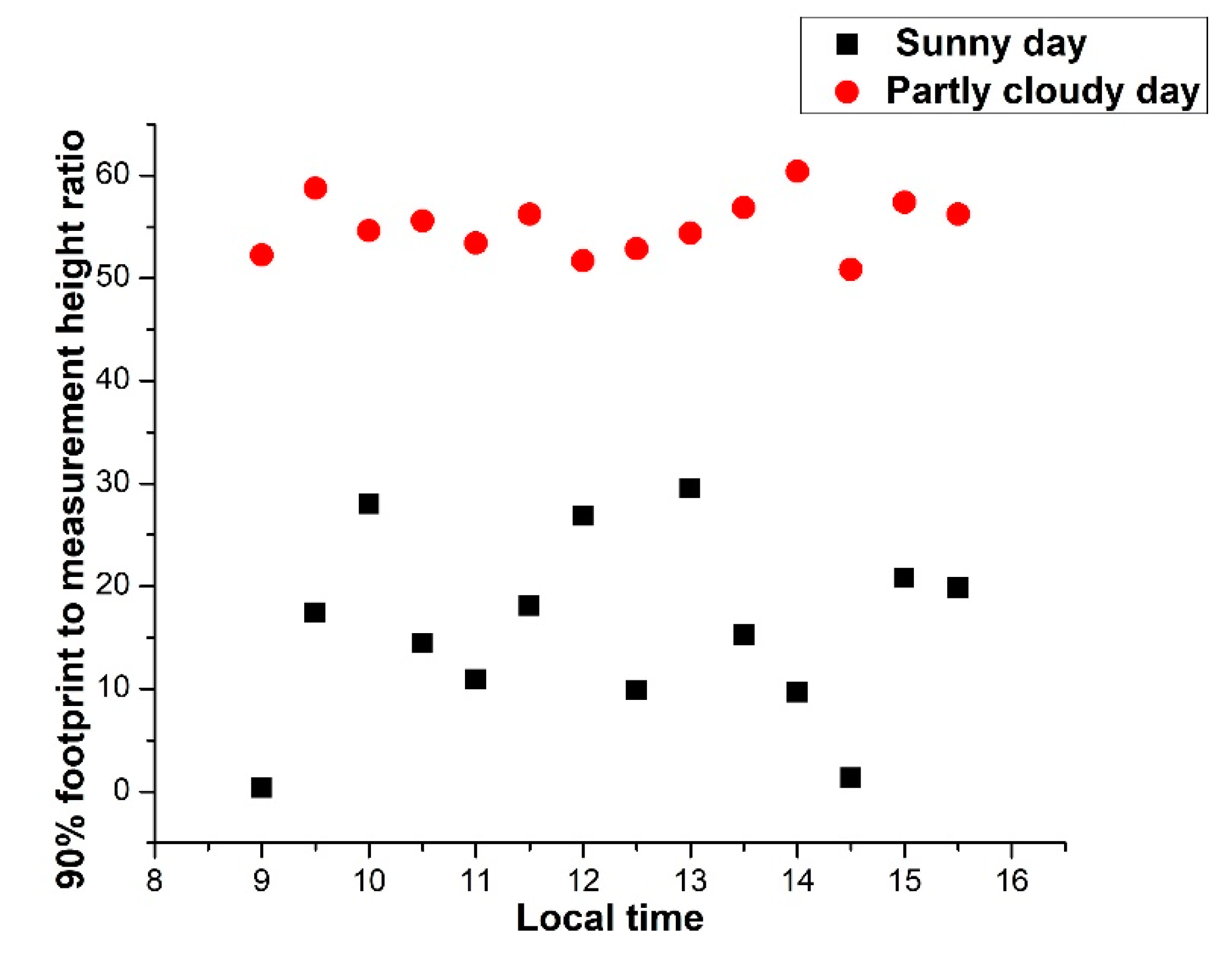
3.2. The Footprint of EC Flux Measurements
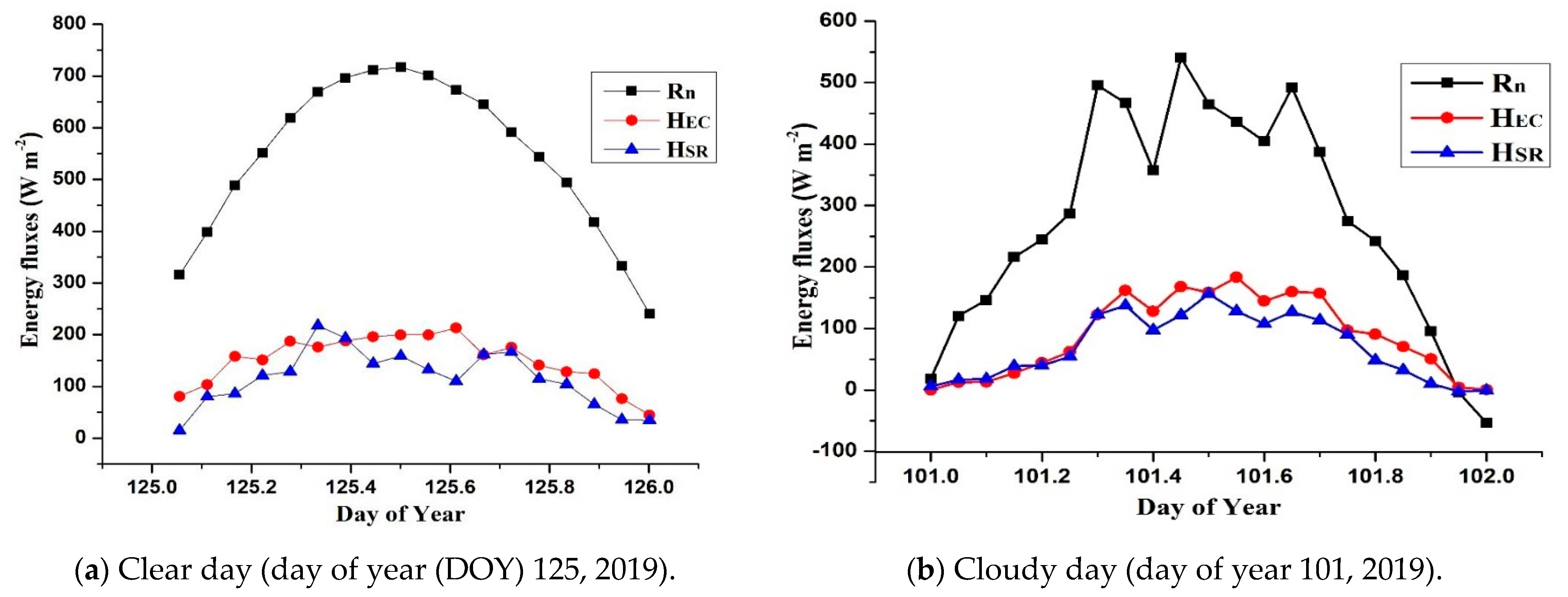
3.3. Sensible Heat Flux
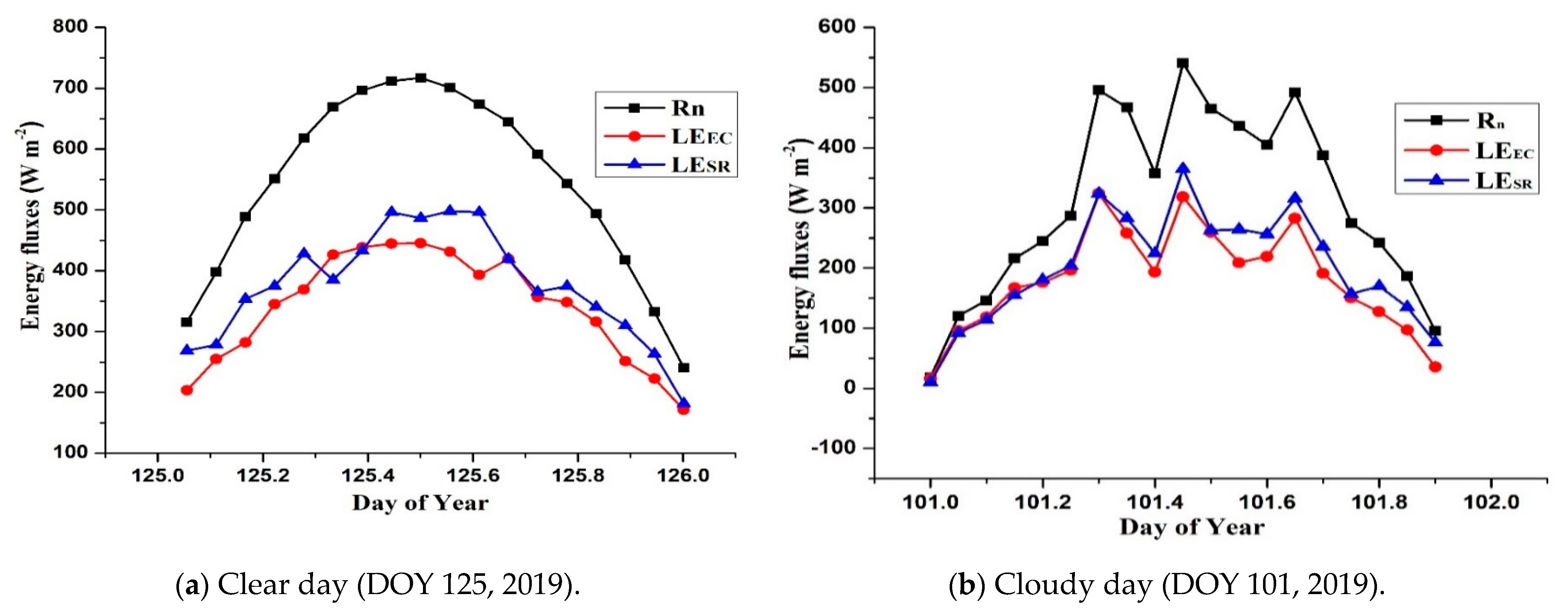
3.4. Latent Heat Flux
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Allen, R.; Pereira, L.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. Crop Evapotranspiration-Guidelines for Computing Crop Water Requirements-FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper 56; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 1998; Volume 300. [Google Scholar]
- Buttar, N.A.; Yongguang, H.; Shabbir, A.; Lakhiar, I.A.; Ullah, I.; Ali, A.; Aleem, M.; Yasin, M.A. Estimation of evapotranspiration using Bowen ratio method. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2018, 51, 807–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drexler, J.Z.; Anderson, F.E.; Snyder, R.L. Evapotranspiration rates and crop coefficients for a restored marsh in the Sacramento–San Joaquin Delta, California, USA. Hydrol. Process. 2008, 22, 725–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niaghi, A.R.; Jia, X.; Scherer, T.; Steele, D. Measurement of unirrigated turfgrass evapotranspiration rate in the red river valley. Vadose Zone J. 2019, 18, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castellvi, F. Combining surface renewal analysis and similarity theory: A new approach for estimating sensible heat flux. Water Resour. Res. 2004, 40, W052011–W0520120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Savage, M.J. Estimation of evaporation using a dual-beam surface layer scintillometer and component energy balance measurements. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2009, 149, 501–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drexler, J.Z.; Snyder, R.L.; Spano, D.; Paw, K.T. A review of models and micrometeorological methods used to estimate wetland evapotranspiration. Hydrol. Process. 2004, 18, 2071–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atta, V. Effect of coherent structures on structure functions of temperature in the atmospheric boundary layer. Arch. Mech. Stosow. 1977, 29, 161–171. [Google Scholar]
- Snyder, R.L.; Duce, P.; Paw, K.T.U. Surface renewal analysis for sensible heat flux density using structure functions. Agric. For. Meteorol. 1997, 86, 259–271. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Buttar, N.A.; Tanny, J.; Snyder, R.L.; Savage, M.J.; Lakhiar, I.A. Surface Renewal Application for Estimating Evapotranspiration: A Review. Adv. Meteorol. 2018, 2018, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mengistu, M.G.; Savage, M.J. Surface renewal method for estimating sensible heat flux. Water SA 2010, 36, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paw, K.T.; Snyder, R.L.; Spano, D.; Su, H.B. Surface Renewal Estimates of Scalar Exchange. CA Water Plan Update 2009, 4, 1–65. [Google Scholar]
- Buttar, N.A.; Hu, Y.; Tanny, J.; Akram, M.W.; Shabbir, A. Fetch Effect on Flux-Variance Estimations of Sensible and Latent Heat Fluxes of Camellia sinensis. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ullah, I.; Buttar, N.A.; Hu, Y.; Aleem, M. Height effect of air temperature measurement on sensible heat flux estimation using flux variance method. Pak. J. Agric. Sci. 2019, 56, 793–800. [Google Scholar]
- Castellví, F. A method for estimating the sensible heat flux in the inertial sub-layer from high-frequency air temperature and averaged gradient measurements. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2013, 180, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabbir, A.; Mao, H.; Ullah, I.; Buttar, N.A.; Ajmal, M.; Lakhiar, I.A. Effects of drip irrigation emitter density with various irrigation levels on physiological parameters, root, yield, and quality of cherry tomato. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekhmandarov, Y.; Pirkner, M.; Achiman, O.; Tanny, J. Application of the surface renewal technique in two types of screenhouses: Sensible heat flux estimates and turbulence characteristics. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2015, 203, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poblete-Echeverría, C.; Sepúlveda-Reyes, D.; Ortega-Farías, S. Effect of height and time lag on the estimation of sensible heat flux over a drip-irrigated vineyard using the surface renewal (SR) method across distinct phenological stages. Agric. Water Manag. 2014, 141, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyngaard, J.C.; Coté, O.R. Cospectral similarity in the atmospheric surface layer. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1972, 98, 590–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yongguang, H.; Chen, Z.; Pengfei, L.; Amoah, A.E.; Pingping, L. Sprinkler irrigation system for tea frost protection and the application effect. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2016, 9, 17–23. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell Scientific Inc. Eddy Covariance System Doperator’s Manual, CA27 and KH20; Campbell Scientific Inc.: Logan, UT, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Tanny, J.; Haijun, L.; Cohen, S. Airflow characteristics, energy balance and eddy covariance measurements in a banana screenhouse. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2006, 139, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, E.K.; Pearman, G.I.; Leuning, R. Correction of flux measurements for density effects due to heat and water vapour transfer. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1980, 106, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, C.J. Frequency response corrections for eddy correlation systems. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 1986, 37, 17–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kljun, N.P.; Calanca, M.W.; Rotach, S.; Schmid, H.P. A simple two-dimensional parameterisation for Flux Footprint Prediction (FFP). Geosci. Model. Dev. 2015, 8, 3695–3713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gash, J.H.C. A note on estimating the effect of a limited fetch on micrometeorological evaporation measurements. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 1986, 35, 409–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savage, M.J.; Everson, C.S.; Metelerkamp, B.R. Evaporation Measurement Above Vegetated Surfaces Using Micrometeorological Techniques; Water Research Commission: Pretoria, South Africa, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh, C.I.; Lai, M.C.; Hsia, Y.J.; Chang, T.J. Estimation of sensible heat, water vapor, and CO2 fluxes using the flux-variance method. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2008, 52, 521–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savage, M.J.; Everson, C.S.; Odhiambo, G.O.; Mengistu, M.G.; Jarmain, C. Theory and Practice of Evaporation Measurement, with Spatial Focus on SLS as an Operational Tool for the Estimation of Spatially-Averaged Evaporation; Report No. 1335/1/04; Water Research Commission: Pretoria, South Africa, 2004; p. 204. [Google Scholar]
- Deardorff, J.W. Observed characteristics of the outer layer. In Short Course on the Planetary Boundary Layer; American Meteorological Society: Boulder, CO, USA, 1978; p. 101. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Liu, Y.; Tanaka, H.; Hiyama, T. A Comparison of Flux Variance and Surface Renewal Methods with Eddy Covariance. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2010, 3, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albertson, J.D.; Parlange, M.B.; Katul, G.G.; Chu, C.R.; Stricker, H.; Tyler, S. Sensible Heat Flux from Arid Regions: A Simple Flux-Variance Method. Water Resour. Res. 1995, 31, 969–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Snyder, R.L.; Spano, D.; Pawu, K.T. Surface renewal analysis for sensible and latent heat flux density. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 1996, 77, 249–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tha, P.U.K.; Jie, Q.; Hong-Bing, S.; Tomonori, W.; Yves, B. Surface renewal analysis: A new method to obtain scalar fluxes. Agric. For. Meteorol. 1995, 74, 119–137. [Google Scholar]
- Spano, D.; Snyder, R.L.; Duce, P.; Paw, K.T. Estimating sensible and latent heat flux densities from grapevine canopies using surface renewal. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2000, 104, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anandakumar, K. Sensible heat flux over a wheat canopy: Optical scintillometer measurements and surface renewal analysis estimations. Agric. For. Meteorol. 1999, 96, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellví, F.; Snyder, R.L.; Baldocchi, D.D. Surface energy-balance closure over rangeland grass using the eddy covariance method and surface renewal analysis. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2008, 148, 1147–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubinet, M.; Vesala, T.; Papale, D.; Kb, D.P.D.F.; William, J.M.; Loescher, H.W.; Luo, H.; Rebmann, C.; Kolle, O.; Heinesch, B.; et al. Eddy Covariance: A Practical Guide to Measurement and Data Analysis; Springer Science & Business Media: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, K.; Goldstein, A.; Falge, E.; Aubinet, M.; Baldocchi, D.; Berbigier, P.; Bernhofer, C.; Ceulemans, R.; Dolman, H.; Field, C.; et al. Energy balance closure at FLUXNET sites. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2002, 113, 223–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allen, R.G. Using the FAO-56 dual crop coefficient method over an irrigated region as part of an evapotranspiration intercomparison study. J. Hydrol. 2000, 229, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


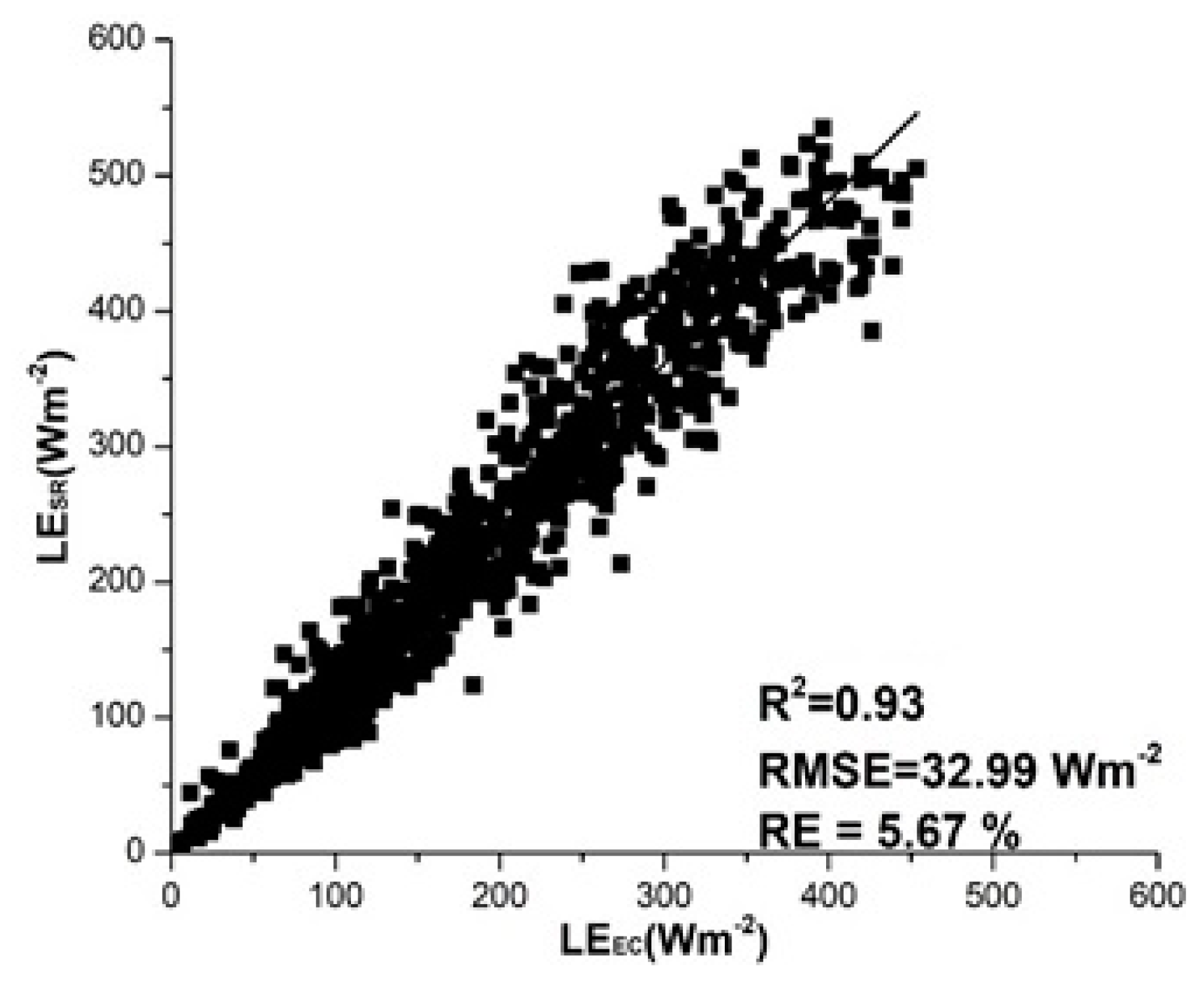
| Fluxes | z (m) | Time-Lag (s) | Slope (α) | R2 | RMSE (W·m−2) | RE (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HSR vs. HEC | 1.8 | 0.5 | 0.68 | 0.80 | 27.87 | 9.02 |
| LESR vs. LEEC | 1.8 | 0.5 | 1.21 | 0.93 | 32.99 | 5.67 |
| (Rn − G) vs. (LE + H) | 2.3 | 0.5 | 0.64 | 0.85 | 25.13 | 3.72 |
| Observations | Notation | Unit | Installation Height (m) | Instruments |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3D wind velocity, sonic temperature | u, v, w, Ts | m·s−1 °C | 2.3 | CSAT3, Sonic anemometer, Camp-bell Scientific, Logan, Utah, USA |
| H2O and CO2 concentrations | - | µmol·m−3 | 2.3 | EC150, Campbell Scientific, Logan, Utah, USA |
| Soil temperature | Tsoil | °C | 0.02–0.06 (Depth) | TCAV-L, Campbell Scientific, Logan, Utah, USA |
| Air temperature for SR analysis | Ta | °C | 1.8 | Fine-wire thermocouple, COCO-002, Omega, Eng., UK |
| Relative humidity | RH | % | 2.1 | HC2S3-L, Campbell Scientific, Logan, Utah, USA |
| Soil heat flux | G | W·m−2 | 0.08 | HFP01, Hukse flux plate sensor |
| Net radiation | Rn | W·m−2 | 2.3 | CNR4-L, KIPP and ZENON |
| Liquid precipitation | - | mm | 2.1 | TE525MM, Campbell Scientific Inc., Logan, Utah, USA |
| Soil water content | ϴv | m3·m−3 | 0.04 (Depth) | CS655, Campbell Scientific Inc., Logan, Utah, USA |
| Datalogger | CR3000 | Campbell Scientific Inc., Logan, Utah, USA. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Buttar, N.A.; Hu, Y.; Lakhiar, I.A.; Javed, Q.; Shabbir, A. Estimation of Sensible and Latent Heat Fluxes Using Surface Renewal Method: Case Study of a Tea Plantation. Agronomy 2021, 11, 179. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11010179
Wang J, Buttar NA, Hu Y, Lakhiar IA, Javed Q, Shabbir A. Estimation of Sensible and Latent Heat Fluxes Using Surface Renewal Method: Case Study of a Tea Plantation. Agronomy. 2021; 11(1):179. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11010179
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jizhang, Noman Ali Buttar, Yongguang Hu, Imran Ali Lakhiar, Qaiser Javed, and Abdul Shabbir. 2021. "Estimation of Sensible and Latent Heat Fluxes Using Surface Renewal Method: Case Study of a Tea Plantation" Agronomy 11, no. 1: 179. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11010179
APA StyleWang, J., Buttar, N. A., Hu, Y., Lakhiar, I. A., Javed, Q., & Shabbir, A. (2021). Estimation of Sensible and Latent Heat Fluxes Using Surface Renewal Method: Case Study of a Tea Plantation. Agronomy, 11(1), 179. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11010179








