Laboratory and Greenhouse Evaluation of Melia volkensii Extracts for Potency against African Sweet Potato Weevil, Cylas puncticollis, and Fall Armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection and Processing of Plant Materials
2.2. Preparation of Treatments
2.3. Rearing of Insects
2.4. Antifeedant Bioassay against C. puncticollis and S. exigua in the Laboratory
2.5. Efficacy of M. volkensii Extracts against C. puncticollis and S. frugiperda in Greenhouse Conditions
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Laboratory Evaluation of Antifeedant Activity of M. volkensii Crude Extracts against C. puncticollis and S. exigua
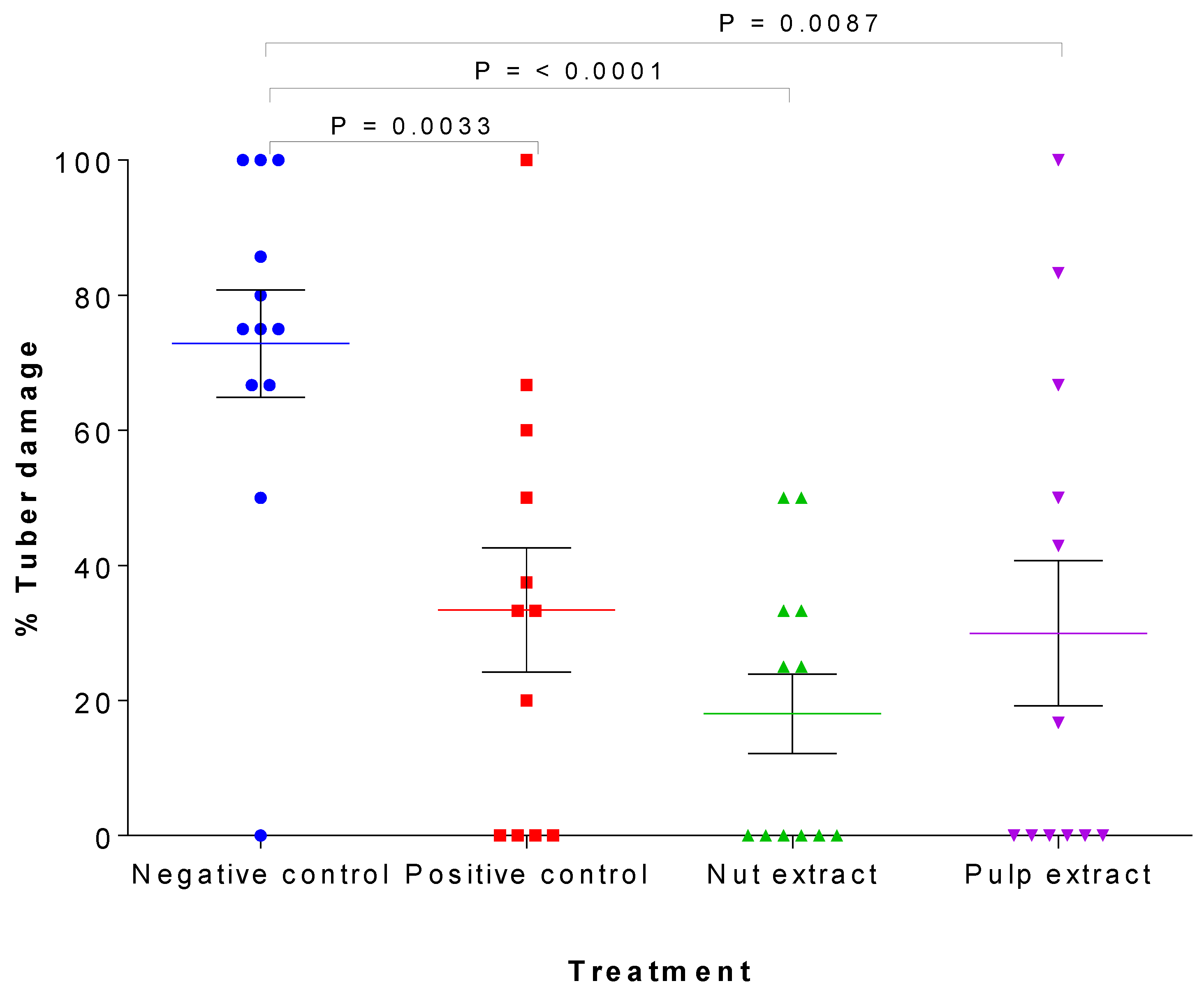
3.2. Antifeedant Activity of M. volkensii Crude Extracts against C. puncticollis in Greenhouse Conditions
3.3. Antifeedant Activity of M. volkensii Crude Extracts against Spodoptera frugiperda under Greenhouse Conditions
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Céspedes, C.L.; Calderón, J.S.; Lina, L.; Aranda, E. Growth inhibitory effects on fall armyworm Spodoptera frugiperda of some limonoids isolated from Cedrela spp. (Meliaceae). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 1903–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wycliffe, W. Toxicological Studies of Fruit Powder and Extracted Cake of Melia volkensii Guerke (Family: Meliaceae) on Maasai Goats in Kenya. Int. J. Pharm. Chem. 2017, 3, 82–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cantrell, C.L.; Rajab, M.S.; Franzblau, S.G.; Fischer, N.H. Antimycobacterial triterpenes from Melia volkensii. J. Nat. Prod. 1999, 62, 546–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamau, R.W.; Juma, B.F.; Baraza, L.D. Antimicrobial compounds from root, stem bark and seeds of Melia volkensii. Nat. Prod. Res. 2016, 30, 1984–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, S.-F.; Rembold, H.; Mwangi, R.W.; Isman, M.B.; Arnason, J.T.; Towers, G.H. Other Meliaceous Plants Containing Ingredients for Integrated Pest. Management and Further Purposes; VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Mulanda, E.S.; Chuhila, Y.; Awori, R.M.; Adero, M.O.; Amugune, N.O.; Akunda, E.; Kinyamario, J.I. Morphological and RAPD-marker characterization of Melia volkensii (Grke) in vitro plants regenerated via direct and indirect somatic embryogenesis. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2015, 14, 1261–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mitchell, P.L.; Thielen, J.B.; Stell, F.M.; Fescemyer, H.W. Activity of Melia volkensii (Meliaceae) extract against southern green stink bug (Hemiptera: Heteroptera: Pentatomidae). J. Agric. Urban. Entomol. 2005, 21, 131–141. [Google Scholar]
- Wilps, H.; Nasseh, O.; Rembold, H.; Krall, S. The effect of Melia volkensii extracts on mortality and fitness of adult Schistocerca gregaria (Forskal) (Orth., Cyrtacanthacrinae). J. Appl. Entomol. 1993, 116, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaoko, V.; Nji Tizi Taning, C.; Backx, S.; Mulatya, J.; Van den Abeele, J.; Magomere, T.; Olubayo, F.; Mangelinckx, S.; Werbrouck, S.P.O.; Smagghe, G. The phytochemical composition of Melia volkensii and its potential for insect pest management. Plants 2020, 9, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brookes, D.R.; James, P.; Walter, G.H.; Furlong, M.J. Origins, Divergence, and Contrasting Invasion History of the Sweet Potato Weevil Pests Cylas formicarius (Coleoptera: Brentidae) and Euscepes batatae (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) in the Asia-Pacific. J. Econ. Entomol. 2019, 112, 2931–2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irungu, L.W.; Mwangi, R.W. Effects of a biologically actuve fraction from Melia volkensii on Culex quinquefasciatus. Insect Sci. Its Appl. 1996, 16, 159–162. [Google Scholar]
- Rukarwa, R.J.; Prentice, K.; Ormachea, M.; Kreuze, J.F.; Tovar, J.; Mukasa, S.B.; Ssemakula, G.; Mwanga, R.O.M.; Ghislain, M. Evaluation of bioassays for testing Bt sweetpotato events against sweetpotato weevils. Afr. Crop. Sci. J. 2013, 21, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nderitu, J.; Sila, M.; Nyamasyo, G. Effectiveness of Entomopathogenic nematodes against sweet potato weevil (Cylas puncticollis Boheman) under semi-arid conditions in Kenya. J. Entomol. 2009, 6, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alghali, A.; Munde, W. Evaluation of sweet potato clones for resistance to Cylas puncticollis in Sierra leone. Tropicultura 2001, 19, 5–9. [Google Scholar]
- Leng, P.H.; Reddy, G.V.P. Bioactivity of selected eco-friendly pesticides against Cylas formicarius (Coleoptera: Brentidae). Florida Entomol. 2012, 95, 1040–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, R.Y.; Sylva, C.D.; Mello, C.L.; Snook, K.A. Biological and Microbial Control Reduced Emergence of Cylas formicarius elegantulus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) from Sweet Potato Roots by Heterorhabditis indica. J. Econ. Entomol. 2020, 113, 1129–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reddy, G.V.P.; Zhao, Z.; Humber, R.A. Laboratory and field efficacy of entomopathogenic fungi for the management of the sweetpotato weevil, Cylas formicarius (Coleoptera: Brentidae). J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2014, 122, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Braun, A.R.; Van De Fliert, E. Evaluation of the impact of sweetpotato weevil (Cylas formicarius) and of the effectiveness of cylas sex pheromone traps at the farm level in indonesia. Int. J. Pest. Manag. 1999, 45, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehisianya, C.N.; Ukeh, D.A.; Isah, M.D.; Lale, N.E.S.; Umeozor, O.C. Field Efficacy of Neem Seed Oil and Diazinon in the Management of Sweetpotato Weevil, Cylas puncticollis (Boh.) in South-eastern Nigeria. J. Plant Stud. 2013, 2, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kyereko, W.; Hongbo, Z.; Amoanimaa-Dede, H.; Meiwei, G.; Yeboah, A. The Major Sweet Potato Weevils; Management and Control: A Review. Entomol. Ornithol. Herpetol. Curr. Res. 2019, 8, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Phambala, K.; Tembo, Y.; Kasambala, T.; Kabambe, V.H.; Stevenson, P.C.; Belmain, S.R. Bioactivity of common pesticidal plants on fall Armyworm Larvae (Spodoptera frugiperda). Plants 2020, 9, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deshmukh, S.; Pavithra, H.B.; Kalleshwaraswamy, C.M.; Shivanna, B.K.; Maruthi, M.S.; Mota-Sanchez, D. Field Efficacy of Insecticides for Management of Invasive Fall Armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda (JE Smith) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) on Maize in India. Florida Entomol. 2020, 103, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sena, D.G.; Pinto, F.A.C.; Queiroz, D.M.; Viana, P.A. Fall armyworm damaged maize plant identification using digital images. Biosyst. Eng. 2003, 85, 449–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magrini, F.E.; Specht, A.; Gaio, J.; Girelli, C.P.; Migues, I.; Heinzen, H.; Saldaña, J.; Sartori, V.C.; Cesio, V. Antifeedant activity and effects of fruits and seeds extracts of Cabralea canjerana canjerana (Vell.) Mart. (Meliaceae) on the immature stages of the fall armyworm Spodoptera frugiperda (JE Smith) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 65, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prentice, K.; Christiaens, O.; Wamalwa, L.; Ghislain, M.; Gheysen, G.; Smagghe, G. Insecticidal activity of orally delivered dsRNA in field-collected African sweetpotato weevils Cylas puncticollis (Coleoptera, Brentidae) from Uganda and Kenya. IOBC/WPRS Bull. 2018, 131, 85–89. [Google Scholar]
- Christiaens, O.; Tardajos, M.G.; Reyna, Z.L.M.; Dash, M.; Dubruel, P.; Smagghe, G. Increased RNAi efficacy in Spodoptera exigua via the formulation of dsRNA with guanylated polymers. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, Y.; Isman, M.B. Generalization of a habituated feeding deterrent response to unrelated antifeedants following prolonged exposure in a generalist herbivore, Trichoplusia ni. J. Chem. Ecol. 2004, 30, 1349–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liyun, R.; Ganghui, Z.; Bimei, C.; Longfei, H.; Yongmei, L.; Baoshan, C. Evaluation of ten botanical insecticides against the sweet potato Weevil, Cylas formicarius (Fabricius, 1798) (Coleoptera: Brentidae). Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2020, 16, 1531–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nta, A.I.; Oku, E.E. Effects of Dennettia tripetalla (Backer), Xylopia aethiopica (Dunal) and Aframomum melegueta Schum Oils against the African Sweet Potato Weevil, Cylas puncticollis (Boheman). Asian J. Res. Zool. 2019, 2, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, X.; Xu, W.; Blanco, M.H.; Williams, W.P. Evaluation of fall armyworm resistance in maize germplasm lines using visual leaf injury rating and predator survey. Insect Sci. 2014, 21, 541–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourenço, A.M.; Haddi, K.; Ribeiro, B.M.; Corrêia, R.F.T.; Tomé, H.V.V.; Santos-Amaya, O.; Pereira, E.J.G.; Guedes, R.N.C.; Santos, G.R.; Oliveira, E.E.; et al. Essential oil of Siparuna guianensis as an alternative tool for improved lepidopteran control and resistance management practices. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caballero-Gallardo, K.; Pino-Benitez, N.; Pajaro-Castro, N.; Stashenko, E.; Olivero-Verbel, J. Plants cultivated in Choco, Colombia, as source of repellents against Tribolium castaneum (Herbst). J. Asia. Pac. Entomol. 2014, 17, 753–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charleston, D.S.; Kfir, R.; Dicke, M.; Vet, L.E.M. Impact of botanical pesticides derived from Melia azedarach and Azadirachta indica on the biology of two parasitoid species of the diamondback moth. Biol. Control. 2005, 33, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras-Cornejo, H.A.; del-Val, E.; Macías-Rodríguez, L.; Alarcón, A.; González-Esquivel, C.E.; Larsen, J. Trichoderma atroviride, a maize root associated fungus, increases the parasitism rate of the fall armyworm Spodoptera frugiperda by its natural enemy Campoletis sonorensis. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 122, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, R.C. Antifeedants in tropical pest management. Int. J. Trop. Insect Sci. 1987, 8, 731–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Q.G.; Luo, X.D. Meliaceous limonoids: Chemistry and biological activities. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 7437–7522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas-Méndez, L.Y.; Sanabria-Flórez, P.L.; Saavedra-Reyes, L.M.; Merchan-Arenas, D.R.; Kouznetsov, V.V. Bioactivity of semisynthetic eugenol derivatives against Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) larvae infesting maize in Colombia. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 26, 1613–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva-Aguayo, G.; Rodríguez-Maciel, J.C.; Lagunes-Tejeda, A.; Llanderal-Cázares, C.; Alatorre-Rosas, R.; Shelton, A.M.; Blanco, C.A. Bioactivity of boldo (Peumus boldus Molina) (Laurales: Monimiaceae) on Spodoptera frugiperda (J.E. Smith) and Helicoverpa zea (Boddie) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Southwest. Entomol. 2010, 35, 215–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, G.; Rodríguez, J.C.; Blanco, C.A.; Lagunes, A. Bioactivity of a water extract of boldus (Peumus boldus molina) against Spodoptera frugiperda (J.E. Smith) and Helicoverpa zea Boddie (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Chil. J. Agric. Res. 2013, 73, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paredes-Sánchez, F.A.; Rivera, G.; Bocanegra-García, V.; Martínez-Padrón, H.Y.; Berrones-Morales, M.; Niño-García, N.; Herrera-Mayorga, V. Advances in Control Strategies against Spodoptera frugiperda. A Review. Molecules 2021, 26, 5587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nta, A.I.; Okweche, S.I.; Umoetok, S.B. Efficacy of Three Plant Powders in the Control of Cylas puncticollis (Boheman) (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) on Sweet Potato during Storage. Afr. Entomol. 2018, 26, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, Y.; Isman, M.B. Comparative growth inhibitory and antifeedant effects of plant extracts and pure allelochemicals on four phytophagous insect species. J. Appl. Entomol. 2004, 128, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jaoko, V.; Taning, C.N.T.; Backx, S.; Motti, P.; Mulatya, J.; Vandenabeele, J.; Magomere, T.; Olubayo, F.; Mangelinckx, S.; Werbrouck, S.P.O.; et al. Laboratory and Greenhouse Evaluation of Melia volkensii Extracts for Potency against African Sweet Potato Weevil, Cylas puncticollis, and Fall Armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1994. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11101994
Jaoko V, Taning CNT, Backx S, Motti P, Mulatya J, Vandenabeele J, Magomere T, Olubayo F, Mangelinckx S, Werbrouck SPO, et al. Laboratory and Greenhouse Evaluation of Melia volkensii Extracts for Potency against African Sweet Potato Weevil, Cylas puncticollis, and Fall Armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda. Agronomy. 2021; 11(10):1994. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11101994
Chicago/Turabian StyleJaoko, Victor, Clauvis Nji Tizi Taning, Simon Backx, Pierfrancesco Motti, Jackson Mulatya, Jan Vandenabeele, Titus Magomere, Florence Olubayo, Sven Mangelinckx, Stefaan P. O. Werbrouck, and et al. 2021. "Laboratory and Greenhouse Evaluation of Melia volkensii Extracts for Potency against African Sweet Potato Weevil, Cylas puncticollis, and Fall Armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda" Agronomy 11, no. 10: 1994. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11101994
APA StyleJaoko, V., Taning, C. N. T., Backx, S., Motti, P., Mulatya, J., Vandenabeele, J., Magomere, T., Olubayo, F., Mangelinckx, S., Werbrouck, S. P. O., & Smagghe, G. (2021). Laboratory and Greenhouse Evaluation of Melia volkensii Extracts for Potency against African Sweet Potato Weevil, Cylas puncticollis, and Fall Armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda. Agronomy, 11(10), 1994. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11101994







