Risk of Secondary Soil Salinization under Mixed Irrigation Using Brackish Water and Reclaimed Water
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Tested Soil
2.2. Experimental Device and Scheme
2.3. Measured Indexes and Methods
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
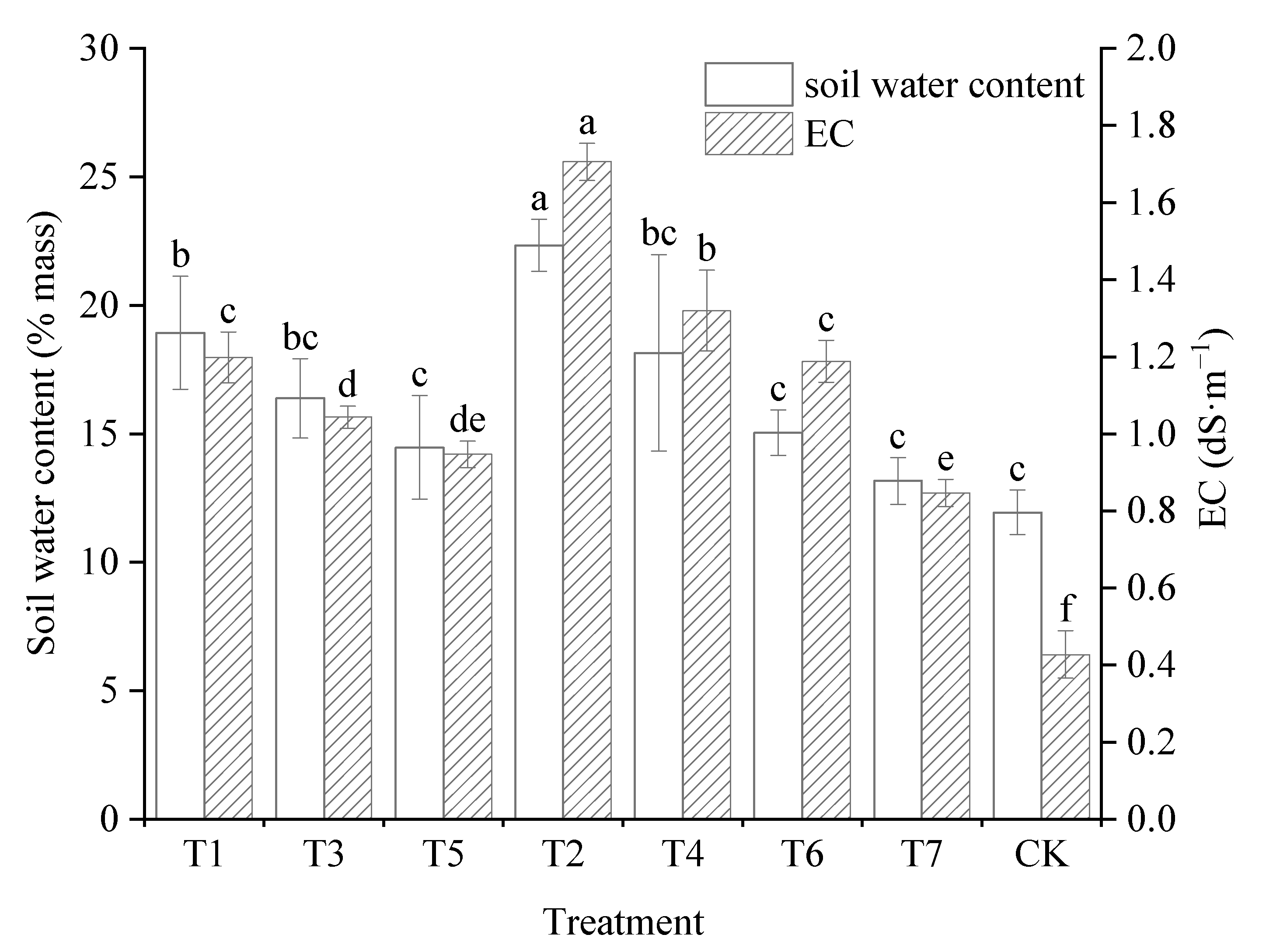
3.1. Effects of Mixed Irrigation on Soil Water and Salt
3.2. Effects of Mixed Irrigation on Soil pH
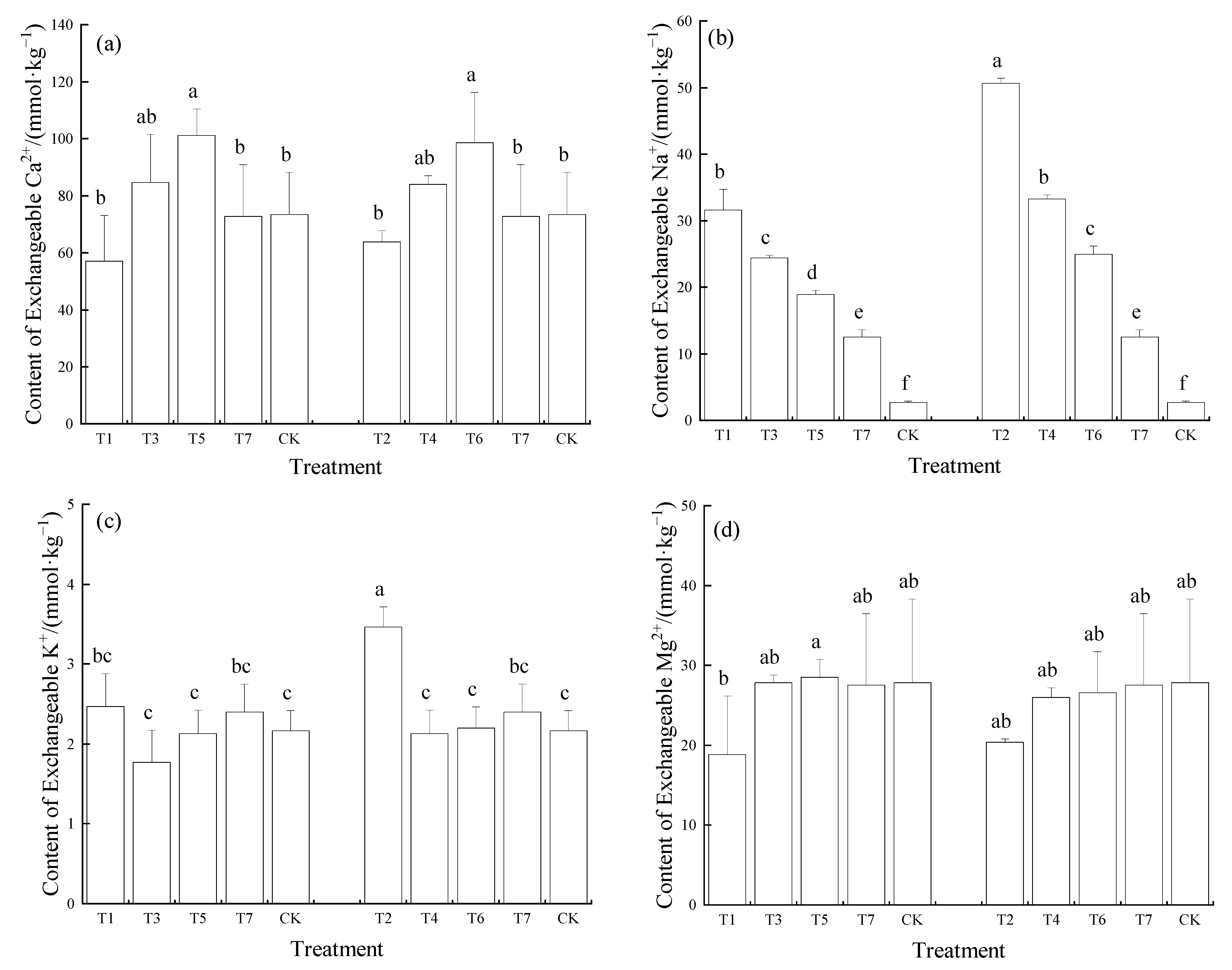
3.3. Effects of Mixed Irrigation on Soil Exchangeable Ions
3.4. Effects of Mixed Irrigation on the Soil Exchangeable K/Na Ratio
3.5. Effects of Mixed Irrigation on the Soil ESP and SAR
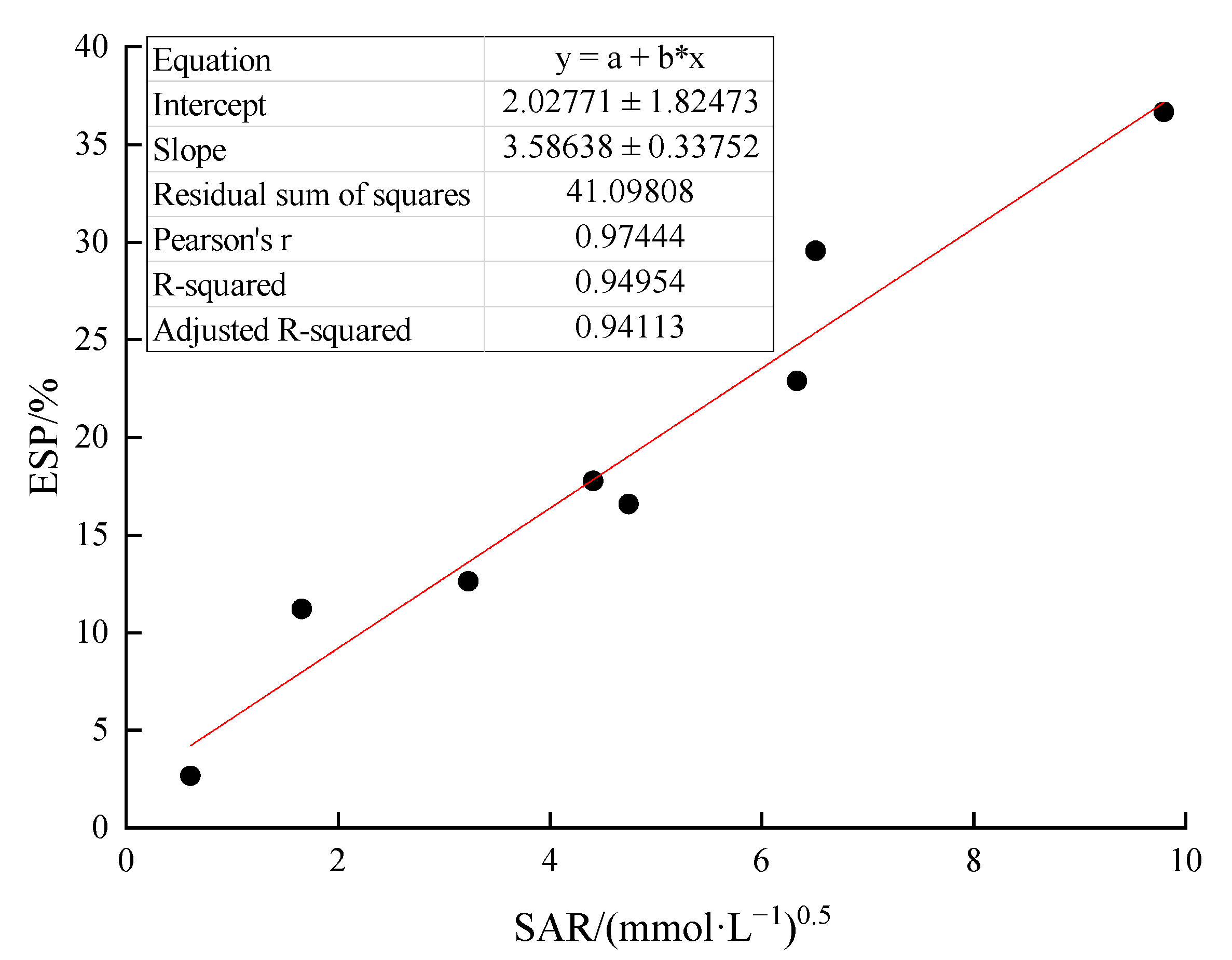
3.6. Correlation between ESP and SAR
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Diluted Irrigation Water on Soil Water and Salinity
4.2. Effects of Mixed Irrigation on Exchangeable Ion Content in Soil
4.3. Effects of Mixed Irrigation on the Soil ESP and SAR
4.4. Effects of Mixed Irrigation on Biomass of Crop
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shahbaz, M.; Ashraf, M. Improving Salinity Tolerance in Cereals. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2013, 32, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Blumwald, E. Developing salt-tolerant crop plants: Challenges and opportunities. Trends Plant Sci. 2005, 10, 615–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamil, A.; Riaz, S.; Ashraf, M.; Foolad, M.R. Gene Expression Profiling of Plants under Salt Stress. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2011, 30, 435–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Feng, S.; Huo, Z.; Ji, Q. Effects of deficit irrigation with saline water on soil water-salt distribution and water use efficiency of maize for seed production in arid Northwest China. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 212, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastava, P.; Kumar, R. Soil salinity: A serious environmental issue and plant growth promoting bacteria as one of the tools for its alleviation. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2015, 22, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, W.; Wang, Z.; Jin, M.; Ferre, T.P.A.; Wang, J.; Huang, J.; Wang, X. Effect of Sodium Chloride and Manganese in Irrigation Water on Cotton Growth. Agron. J. 2018, 110, 900–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Jin, M.; Kuo, Y.M.; Di, Z.; Xian, Y.; Yuan, J. Compartment Model for Estimating Element Content in a Water–Soil–Cotton System. Agron. J. 2016, 108, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Dou, Y.; Hou, Y. The Influences of Different Nitrogen and Salt Levels Interactions on Fluorescence Characteristics, Yield and Quality of Processed Tomato Under Drip Irrigation. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2020, 53, 990–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Ge, A.-H.; Toth, T.; An, F.; Guo, L.; Nie, Z.; Liu, J.; Yang, F.; Wang, Z. Soil bacterial microbiota predetermines rice yield in reclaiming saline-sodic soils leached with brackish ice. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Zheng, C.; Li, K.; Dang, H.; Cao, C.; Rahma, A.E.; Zhang, J.; Feng, D. Responses of Soil Water-salt Variation and Cotton Growth to Drip Irrigation with Saline Water in the Low Plain Near the Bohai Sea. Irrig. Drain. 2020, 69, 448–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustan, A.; Cohen, S.; Malach, Y.D.; Zimmermann, P.; Golan, R.; Sagi, M.; Pasternak, D. Effects of timing and duration of brackish irrigation water on fruit yield and quality of late summer melons. Agric. Water Manag. 2005, 74, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Wang, S.; Kong, X.; Liu, X.; Sun, H. Modeling and assessing feasibility of long-term brackish water irrigation in vertically homogeneous and heterogeneous cultivated lowland in the North China Plain. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 211, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Jin, M.; Ferré, T.P.A.; Liu, Y.; Xian, Y.; Shan, T.; Ping, X. Spatial distribution of soil moisture, soil salinity, and root density beneath a cotton field under mulched drip irrigation with brackish and fresh water. Field Crop. Res. 2018, 215, 207–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jin, M.; Zhou, N.; Huang, J.; Jiang, S.; Telesphore, H. Evaluation of evapotranspiration and deep percolation under mulched drip irrigation in an oasis of Tarim basin, China. J. Hydrol. 2016, 538, 677–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tahtouh, J.; Mohtar, R.; Assi, A.; Schwab, P.; Jantrania, A.; Deng, Y.; Munster, C. Impact of brackish groundwater and treated wastewater on soil chemical and mineralogical properties. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 647, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucci, G.; Lacolla, G.; Boari, F.; Mastro, M.A.; Cantore, V. Effect of water salinity and irrigation regime on maize (Zea mays L.) cultivated on clay loam soil and irrigated by furrow in Southern Italy. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 222, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Li, Y.; Guo, L.; Guan, B.; Liao, Y.; Wang, J. Effect of brackish water irrigation on water and salt movement in repellent soils. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2011, 27, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petousi, I.; Daskalakis, G.; Fountoulakis, M.S.; Lydakis, D.; Fletcher, L.; Stentiford, E.I.; Manios, T. Effects of treated wastewater irrigation on the establishment of young grapevines. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 658, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrero, F.; Camposeo, S.; Pace, B.; Cefola, M.; Vivaldi, G.A. Use of reclaimed wastewater on fruit quality of nectarine in Southern Italy. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 203, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Li, P.; Qi, X.; Cui, B.; Chang, D.; Ma, H. Effects of Different Levels of Irrigation with Reclaimed Water on Soil Enzyme Activity and Distribution of Thermotolerant Coliforms. Environ. Sci. 2018, 39, 4366–4374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Qi, X.; Li, P.; Li, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Xiao, Y. Impact of reclaimed water irrigation and nitrogen fertilization on soil bacterial community structure. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2017, 37, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesser, L.E.; Mora, A.; Moreau, C.; Mahlknecht, J.; Hernández-Antonio, A.; Ramírez, A.I.; Barrios-Pina, H. Survey of 218 organic contaminants in groundwater derived from the world‘s largest untreated wastewater irrigation system: Mezquital Valley, Mexico. Chemosphere 2018, 198, 510–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, S.; Zhang, X.; Liang, P. Influence of drip irrigation by reclaimed water on the dynamic change of the nitrogen element in soil and tomato yield and quality. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 139, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perulli, G.D.; Gaggia, F.; Sorrenti, G.; Donati, I.; Boini, A.; Bresilla, K.; Manfrini, L.; Baffoni, L.; Di Gioia, D.; Grappadelli, L.C.; et al. Treated wastewater as irrigation source: A microbiological and chemical evaluation in apple and nectarine trees. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 244, 106403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liu, H.; Pang, J.; Li, S.; Cui, Y.; Sun, J. Effects of Water and Nitrogen Interaction on Growth and Nutrient Accumulation of Potted Tomatoes. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2019, 50, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Li, K.; Ma, J.; Zheng, C. Utilization status and development potential of shallow salt groundwater in the Hebei Lowland Plain. Anhui Agric. Sci. Bull. 2007, 13, 66–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, K.; Zheng, C.; Cao, C.; Sun, C.; Dang, H.; Feng, D.; Sun, J. Cotton Responses to Saline Water Irrigation in the Low Plain around the Bohai Sea in China. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2018, 144, 04018027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S. Soil Agrochemical Analysis, 3rd ed.; China Agricultural Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; School, l.; Bi, D.; Wei, J.; Yuan, G. Processes of Leonardite Altering Cation and Anion Composition of Soil Solution in Salt-affected Soil in the Yellow River Delta. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2018, 55, 1367–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Wang, Y.; Ren, S.; Wei, C.; He, X.; Xu, Z. Soil Moisture and Saline Distribution Characteristics and Maize Stem Water Uptake under Alternate Irrigation between Saline Water and Groundwater. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2020, 51, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Liu, S.; Yan, K.; Tian, L.; Li, P.; Li, X.; He, X. Effect of Drip Irrigation with Brackish Water on the Soil Chemical Properties for a Typical Desert Plant (Haloxylon Ammodendron) in the Manas River Basin. Irrig. Drain. 2020, 69, 460–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strawn, D.G.; Bohn, H.L.; O’Connor, G.A. Soil Chemistry, 4th ed.; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: Oxford, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lucas, R.W.; Klaminder, J.; Futter, M.N.; Bishop, K.H.; Egnell, G.; Laudon, H.; Högberg, P. A meta-analysis of the effects of nitrogen additions on base cations: Implications for plants, soils, and streams. For. Ecol. Manag. 2016, 262, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.G.; Cao, J.; Li, F.M. Influence of Salinity, Sodicity and Organic Matter on Some Physical Properties of Salt -affected Soils. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 2004, 35, 64–72. [Google Scholar]



| Treatment | CK | T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 | T5 | T6 | T7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mixed solution | FW | 3 g/L of BW | 5 g/L of BW | 1:1 of BW (3 g/L) to RW | 1:1 of BW (5 g/L) to RW | 1:2 of BW (3 g/L) to RW | 1:2 of BW (5 g/L) to RW | RW |
| Water Source | EC (dS·m−1) | SAR | Ion Content (mmol·L−1) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Na+ | K+ | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | Cl− | HCO3− | SO42− | CO32− | |||
| Freshwater | 0.321 | 0.34 | 0.43 | 0.04 | 0.98 | 0.63 | 0.85 | 1.97 | 1.08 | - |
| Reclaimed Water | 2.120 | 5.82 | 13.48 | 0.36 | 2.28 | 3.08 | 8.86 | 4.56 | 5.28 | - |
| Brackish Water (3 g/L) | 6.100 | 43.30 | 57.83 | 0.05 | 1.08 | 0.71 | 54.19 | 2.33 | 0.96 | - |
| Brackish Water (5 g/L) | 9.432 | 67.19 | 86.96 | 0.07 | 0.93 | 0.75 | 90.89 | 2.28 | 1.14 | - |
| Treatment | CK | T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 | T5 | T6 | T7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soil salt content (g·kg 1) | 0.48 ± 0.04 f | 1.34 ± 0.06 b | 1.87 ± 0.10 a | 1.08 ± 0.10 c | 1.40 ± 0.12 b | 0.89 ± 0.05 d | 1.17 ± 0.10 c | 0.72 ± 0.02 c |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, C.; Cui, B.; Zeleke, K.T.; Hu, C.; Wu, H.; Cui, E.; Huang, P.; Gao, F. Risk of Secondary Soil Salinization under Mixed Irrigation Using Brackish Water and Reclaimed Water. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2039. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11102039
Liu C, Cui B, Zeleke KT, Hu C, Wu H, Cui E, Huang P, Gao F. Risk of Secondary Soil Salinization under Mixed Irrigation Using Brackish Water and Reclaimed Water. Agronomy. 2021; 11(10):2039. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11102039
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Chuncheng, Bingjian Cui, Ketema Tilahun Zeleke, Chao Hu, Haiqing Wu, Erping Cui, Pengfei Huang, and Feng Gao. 2021. "Risk of Secondary Soil Salinization under Mixed Irrigation Using Brackish Water and Reclaimed Water" Agronomy 11, no. 10: 2039. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11102039
APA StyleLiu, C., Cui, B., Zeleke, K. T., Hu, C., Wu, H., Cui, E., Huang, P., & Gao, F. (2021). Risk of Secondary Soil Salinization under Mixed Irrigation Using Brackish Water and Reclaimed Water. Agronomy, 11(10), 2039. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11102039







