Towards Sustainable Dairy Production in Argentina: Evaluating Nutrient and CO2 Release from Raw and Processed Farm Waste
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Dairy Farm Description
2.2. Soil and Amendments Characterization
2.3. Soil Incubations
2.3.1. Microcosms Preparation
2.3.2. C Mineralization from Microcosms
2.3.3. N and P Mineralization from Microcosms
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
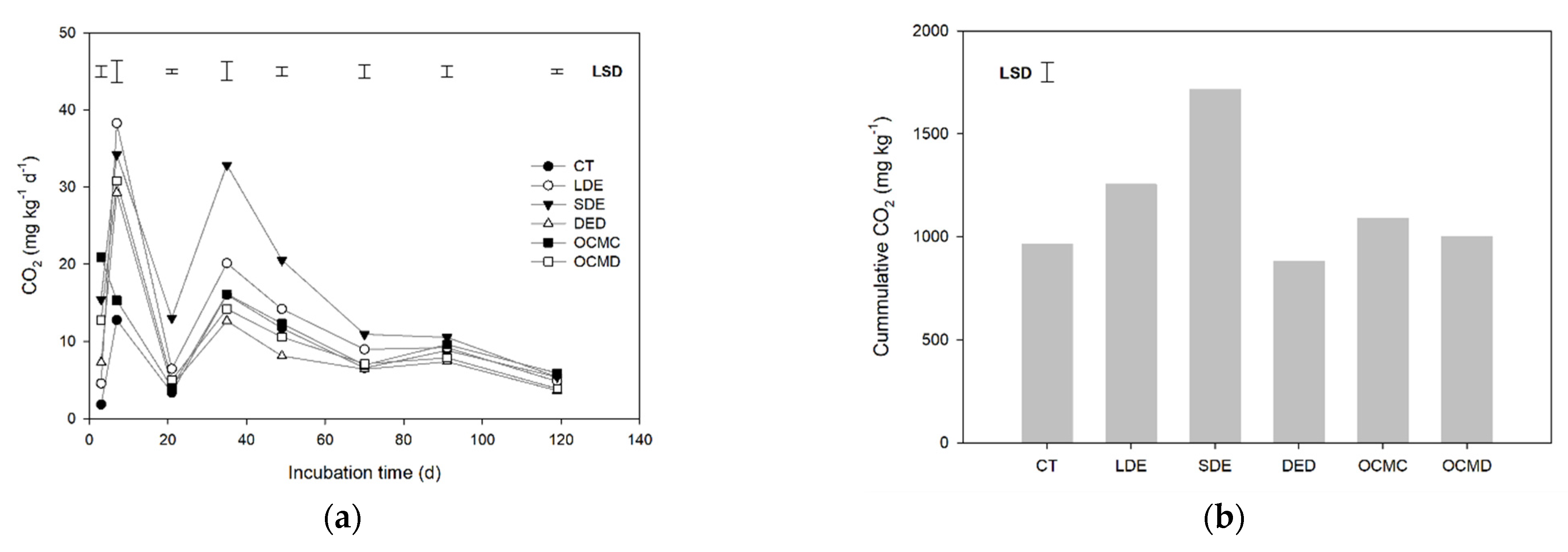
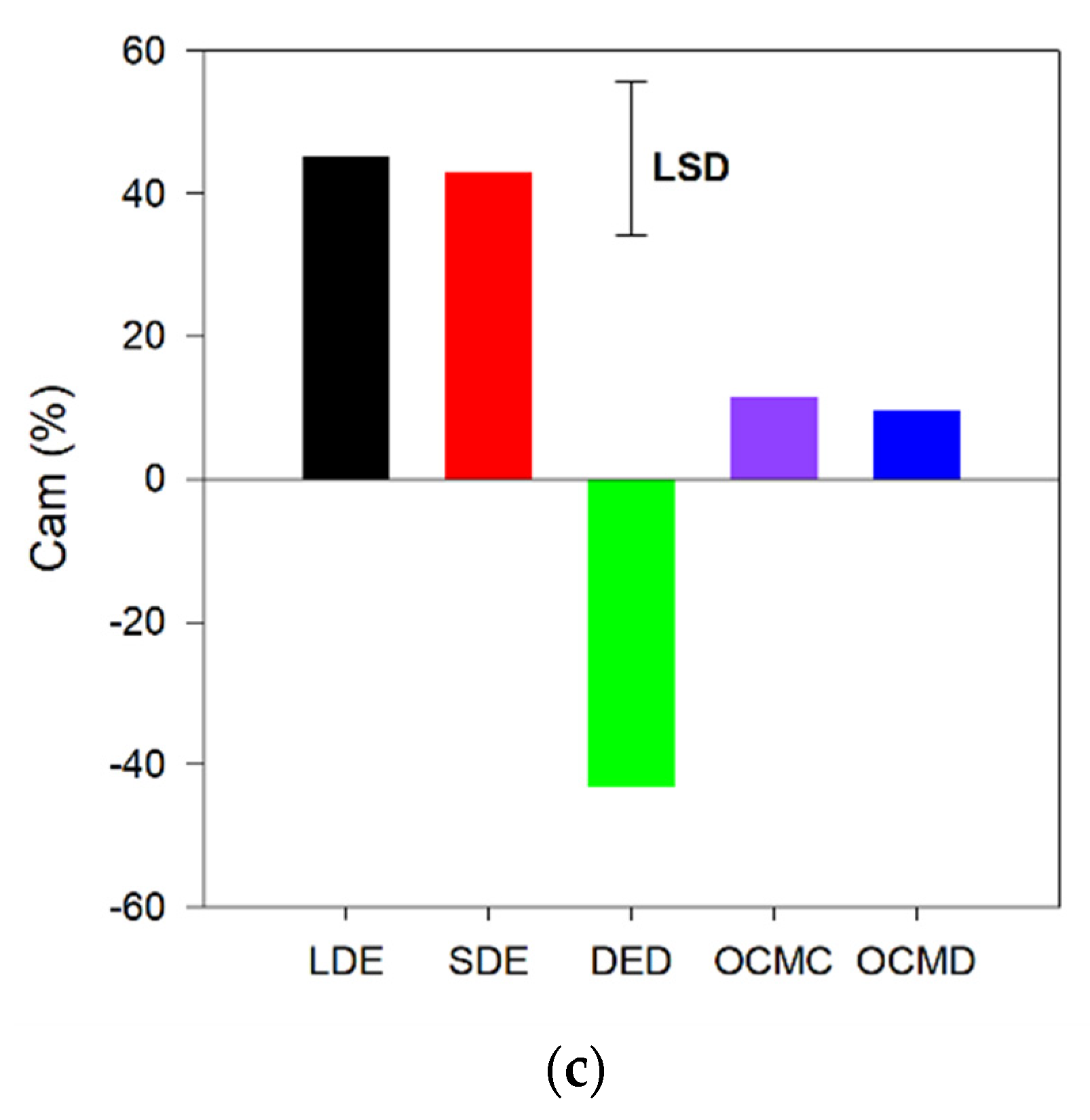
3.1. C Mineralization
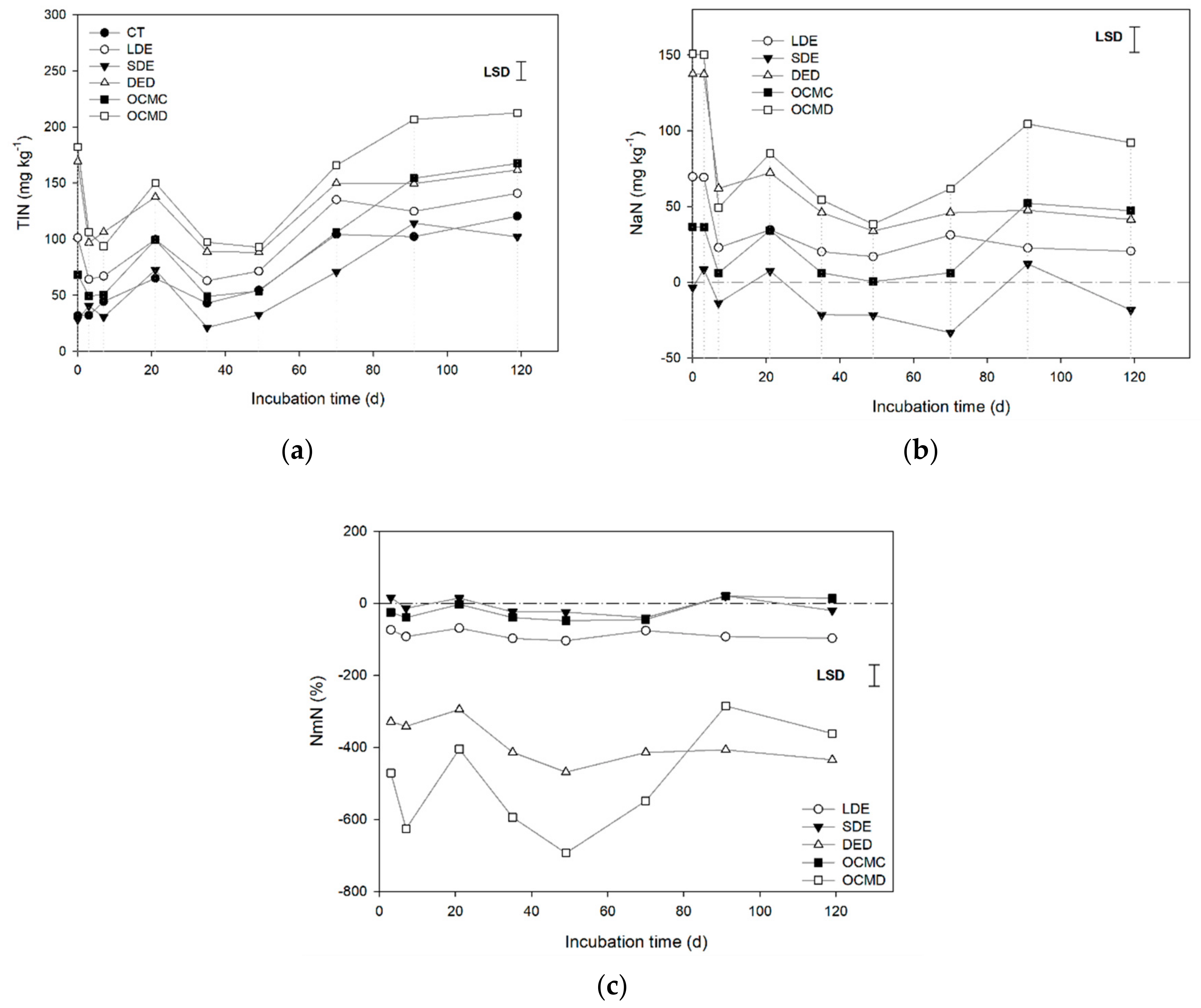
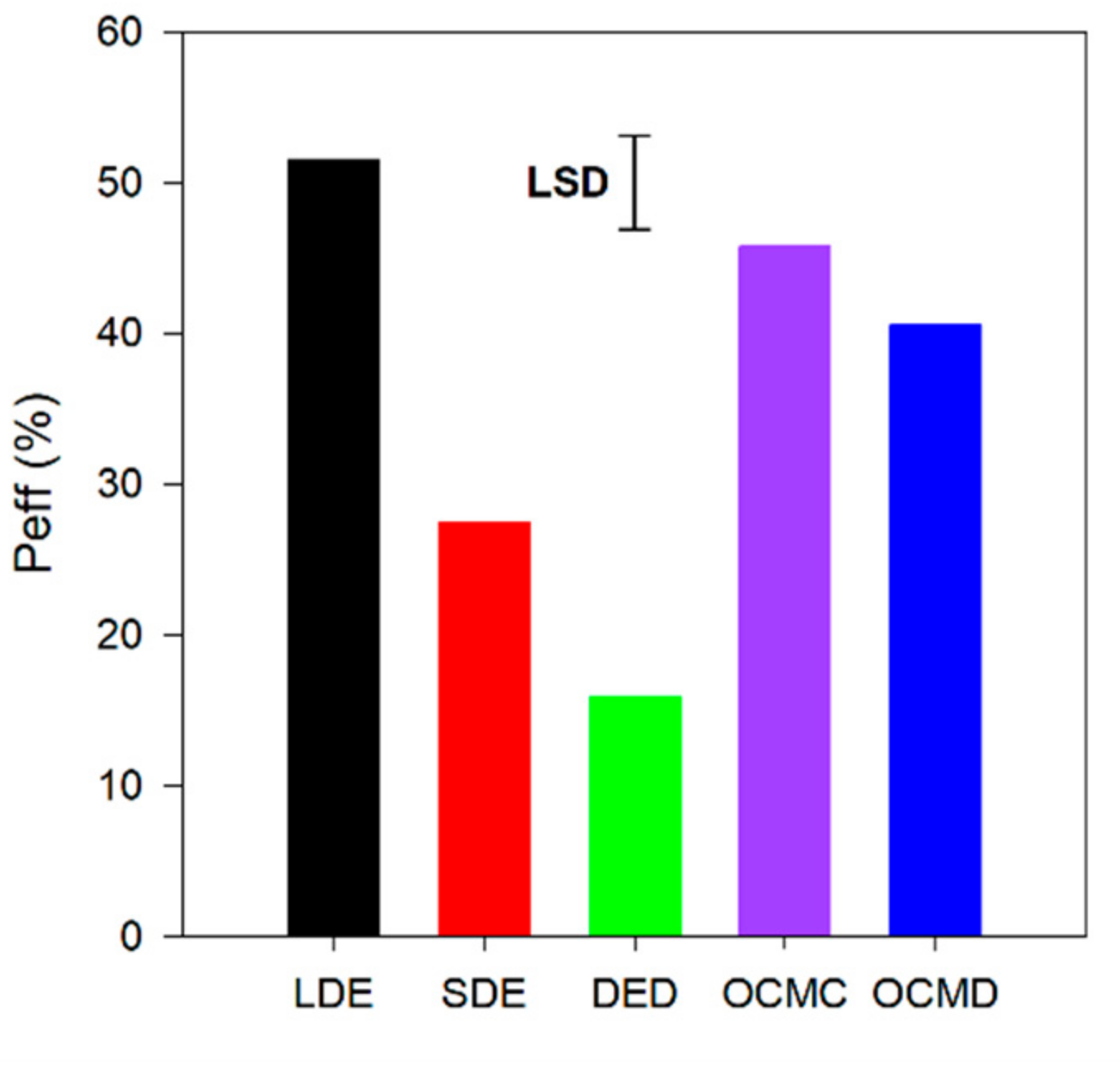
3.2. N Mineralization
3.3. P Mineralization
4. Discussion
4.1. Amendment Characterization and Its Implications
4.2. C Mineralization
4.3. N Mineralization
4.4. P Mineralization
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Herrero, M.A.; Palhares, J.C.P.; Salazar, F.J.; Charlón, V.; Tieri, M.P.; Pereyra, A.M. Dairy Manure Management Perceptions and Needs in South American Countries. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2018, 2, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USDA-FAS. Dairy and Products Annual. Argentina; U.S. Department of Agriculture Foreign Agricultural Service: Washington, DC, USA, 2021. Available online: https://apps.fas.usda.gov/newgainapi/api/Report/DownloadReportByFileName?fileName=Dairy%20and%20Products%20Annual_Buenos%20Aires_Argentina_10-15-2020 (accessed on 8 September 2021).
- OCLA. Informacion de la Produccion Primaria. 2021. Available online: https://www.ocla.org.ar/contents/news/details/18219202-lecheria-argentina-datos-clave-202021 (accessed on 18 November 2021).
- Lazzarini, B.; Baudracco, J.; Tuñon, G.; Gastaldi, L.; Lyons, N.; Quattrochi, H.; Lopez-Villalobos, N. Review: Milk production from dairy cows in Argentina: Current state and perspectives for the future. Appl. Anim. Sci. 2019, 35, 426–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diacono, M.; Montemurro, F. Long-term effects of organic amendments on soil fertility. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2010, 30, 401–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iocoli, G.A.; Zabaloy, M.C.; Pasdevicelli, G.; Gómez, M.A. Use of biogas digestates obtained by anaerobic digestion and co-digestion as fertilizers: Characterization, soil biological activity and growth dynamic of Lactuca sativa L. Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 647, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerardi, M.H. The Microbiology of Anaerobic Digesters; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Insam, H.; Gómez-Brandón, M.; Ascher, J. Manure-based biogas fermentation residues–Friend or foe of soil fertility? Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 84, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möller, K.; Müller, T. Effects of anaerobic digestion on digestate nutrient availability and crop growth: A review. Eng. Life Sci. 2012, 12, 242–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkoa, R. Agricultural benefits and environmental risks of soil fertilization with anaerobic digestates: A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2014, 34, 473–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhogal, A.; Nicholson, F.A.; Rollett, A.; Taylor, M.; Litterick, A.; Whittingham, M.J.; Williams, J.R. Improvements in the Quality of Agricultural Soils Following Organic Material Additions Depend on Both the Quantity and Quality of the Materials Applied. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2018, 2, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iocoli, G.A.; Pieroni, O.I.; Gómez, M.A.; Alvarez, M.B.; Galantini, J.A. Rapid characterisation of agro-industrial effluents for environmental fate by UV–visible and infrared spectroscopy from fractions obtained by centrifugation. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2017, 97, 756–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, F.J.; Cole, M.A. Cycles of Soils: Carbon, Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Sulfur and Micronutrients, 2nd ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, M.R.; Bilkis, S.; Hoque, T.S.; Uddin, S.; Jahiruddin, M.; Rahman, M.M.; Siddique, A.B.; Hossain, M.A.; Marfo, T.D.; Danish, S.; et al. Mineralization of Farm Manures and Slurries under Aerobic and Anaerobic Conditions for Subsequent Release of Phosphorus and Sulphur in Soil. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cambardella, C.A.; Richard, T.L.; Russell, A. Compost mineralization in soil as a function of composting process conditions. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2003, 39, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Achat, D.L.; Bakker, M.R.; Zeller, B.; Pellerin, S.; Bienaimé, S.; Morel, C. Long-term organic phosphorus mineralization in Spodosols under forests and its relation to carbon and nitrogen mineralization. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2010, 42, 1479–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spohn, M.; Kuzyakov, Y. Phosphorus mineralization can be driven by microbial need for carbon. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 61, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bünemann, E.K. Assessment of gross and net mineralization rates of soil organic phosphorus–A review. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 89, 82–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suñer, L.G.; Galantini, J.A. Dinámica de las formas del P en suelos de la región sudoeste Pampeana: Estudio de la incubación con fertilizante fosfatado. Cienc. Del Suelo 2013, 31, 33–44. Available online: http://www.scielo.org.ar/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1850-20672013000100004&lng=en&nrm=iso (accessed on 18 November 2021).
- United States Department of Agriculture. Soil Survey Division, Soil survey manual. Soil Conservation Service U.S. Department of Agriculture Handbook No.18.; US Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1993.
- Rodriguez, D.; Schulz, G.; Moretti, L. Carta de Suelos de la Republica Argentina. Partido de Villarino, Provincia de Buenos Aires; INTA Ediciones: Hurlingham, Buenos Aires, Argentina, 2018; Available online: https://inta.gob.ar/sites/default/files/inta-carta_de_suelos_villarino.pdf (accessed on 18 November 2021).
- Walkley, A.; Black, I.A. An Examination Of The Degtjareff Method For Determining Soil Organic Matter, And A Proposed Modification Of The Chromic Acid Titration Method. Soil Sci. 1934, 37, 29–38. Available online: https://journals.lww.com/soilsci/Fulltext/1934/01000/AN_EXAMINATION_OF_THE_DEGTJAREFF_METHOD_FOR.3.aspx (accessed on 18 November 2021). [CrossRef]
- Eaton, A.D.; Clesceri, L.S.; Greenberg, A.E.; Franson, M.A.H. American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association, and Water Environment Federation, Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 20th ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Bray, R.H.; Kurtz, L.T. Determination of Total Organic and Available Forms of Phosphorus in Soils. Soil Sci. 1945, 59, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommers, L.E.; Nelson, D.W. Determination of Total Phosphorus in Soils: A Rapid Perchloric Acid Digestion Procedure. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1972, 36, 902–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orden, L.; Ferreiro, N.; Satti, P.; Navas-Gracia, L.M.; Chico-Santamarta, L.; Rodríguez, R.A. Effects of Onion Residue, Bovine Manure Compost and Compost Tea on Soils and on the Agroecological Production of Onions. Agriculture 2021, 11, 962. Available online: https://www.mdpi.com/2077-0472/11/10/962 (accessed on 18 November 2021). [CrossRef]
- Zibilske, L.M. Carbon Mineralization1. In Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 2—Microbiological and Biochemical Properties; Bottomley, P.S., Angle, J.S., Weaver, R.W., Eds.; Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 1994; pp. 835–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigatti, M.; di Girolamo, G.; Chincarini, R.; Ciavatta, C.; Barbanti, L. Potential nitrogen mineralization, plant utilization efficiency and soil CO2 emissions following the addition of anaerobic digested slurries. Biomass Bioenergy 2011, 35, 4619–4629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Littell, R.C.; Stroup, W.W.; Freund, R.J. SAS for Lineal Models; Wiley InterScienc: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- Longhurst, R.D.; Rajendram, G.; Miller, B.R.; Dexter, M. Nutrient content of liquid and solid effluents on NZ dairy cow farms. In Science and Policy: Nutrient Management Challenges for the Next Generation; Currie, L.D., Hedley, M.D., Eds.; Fertilizer and Lime Research Centre, Massey University 9: Palmerston North, New Zealand, 2017; Volume 30. [Google Scholar]
- Morvan, T.; Nicolardot, B.; Péan, L. Biochemical composition and kinetics of C and N mineralization of animal wastes: A typological approach. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2006, 42, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, K.; Jensen, L.S. Biochemical characteristics of solid fractions from animal slurry separation and their effects on C and N mineralisation in soil. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2011, 47, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernal, M.P.; Alburquerque, J.A.; Moral, R. Composting of animal manures and chemical criteria for compost maturity assessment. A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 5444–5453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.L.; Xiao, J.; Liu, D.Y.; Ye, G.P.; Luo, J.F.; Houlbrooke, D.; Laurenson, S.; Yan, J.; Chen, L.J.; Tian, J.P.; et al. Effect of application of dairy manure, effluent and inorganic fertilizer on nitrogen leaching in clayey fluvo-aquic soil: A lysimeter study. Sci. Total. Environ. 2017, 592, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernai, M.P.; Paredes, C.; Sánchez-Monedero, M.A.; Cegarra, J. Maturity and stability parameters of composts prepared with a wide range of organic wastes. Bioresour. Technol. 1998, 63, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, M.V.; Carballo, M.T.; Calvo, L.F. Fertilization of maize with compost from cattle manure supplemented with additional mineral nutrients. Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 1432–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tambone, F.; Genevini, P.; D’Imporzano, G.; Adani, F. Assessing amendment properties of digestate by studying the organic matter composition and the degree of biological stability during the anaerobic digestion of the organic fraction of MSW. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 3140–3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tambone, F.; Scaglia, B.; D’Imporzano, G.; Schievano, A.; Orzi, V.; Salati, S.; Adani, F. Assessing amendment and fertilizing properties of digestates from anaerobic digestion through a comparative study with digested sludge and compost. Chemosphere 2010, 81, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pognani, M.; D’Imporzano, G.; Scaglia, B.; Adani, F. Substituting energy crops with organic fraction of municipal solid waste for biogas production at farm level: A full-scale plant study. Process. Biochem. 2009, 44, 817–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchmann, H.; Lundvall, A. Relationship between N immobilization and volatile fatty acids in soil after application of pig and cattle slurry. Biol. Fertil. Soils 1993, 15, 161–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risberg, K.; Cederlund, H.; Pell, M.; Arthurson, V.; Schnürer, A. Comparative characterization of digestate versus pig slurry and cow manure–Chemical composition and effects on soil microbial activity. Waste Manag. 2017, 61, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavalli, D.; Corti, M.; Baronchelli, D.; Bechini, L.; Gallina, P.M. CO2 emissions and mineral nitrogen dynamics following application to soil of undigested liquid cattle manure and digestates. Geoderma 2017, 308, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latifah, O.; Ahmed, O.H.; Majid, N.M.A. Soil pH Buffering Capacity and Nitrogen Availability Following Compost Application in a Tropical Acid Soil. Compost. Sci. Util. 2018, 26, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odlare, M.; Arthurson, V.; Pell, M.; Svensson, K.; Nehrenheim, E.; Abubaker, J. Land application of organic waste–Effects on the soil ecosystem. Appl. Energy 2011, 88, 2210–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tambone, F.; Genevini, P.; Adani, F. The Effects of Short-Term Compost Application On Soil Chemical Properties and on Nutritional Status of Maize Plant. Compost. Sci. Util. 2007, 15, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Béghin-Tanneau, R.; Guérin, F.; Guiresse, M.; Kleiber, D.; Scheiner, J.D. Carbon sequestration in soil amended with anaerobic digested matter. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 192, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Changa, C.M.; Watson, M.E.; Dick, W.A.; Chen, Y.; Hoitink, H.A.J. Maturity indices for composted dairy and pig manures. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2004, 36, 767–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alburquerque, J.A.; de la Fuente, C.; Bernal, M.P. Chemical properties of anaerobic digestates affecting C and N dynamics in amended soils. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2012, 160, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcato, C.-E.; Mohtar, R.; Revel, J.-C.; Pouech, P.; Hafidi, M.; Guiresse, M. Impact of anaerobic digestion on organic matter quality in pig slurry. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2009, 63, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Busby, R.R.; Torbert, H.A.; Gebhart, D.L. Carbon and nitrogen mineralization of non-composted and composted municipal solid waste in sandy soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2007, 39, 1277–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemens, J.; Huschka, A. The effect of biological oxygen demand of cattle slurry and soil moisture on nitrous oxide emissions. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosystems 2001, 59, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dendooven, L.; Bonhomme, E.; Merckx, R.; Vlassak, K. Injection of pig slurry and its effects on dynamics of nitrogen and carbon in a loamy soil unter laboratory conditions. Biol. Fertil. Soils 1998, 27, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drury, C.F.; Voroney, R.P.; Beauchamp, E.G. Availability of NH4+-N to microorganisms and the soil internal N cycle. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1991, 23, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merrick, M.J.; Edwards, R.A. Nitrogen control in bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1995, 59, 604–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernal, M.P.; Roig, A. Nitrogen transformations in calcareous soils amended with pig slurry under aerobic incubation. J. Agric. Sci. 2009, 120, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cayuela, M.L.; Sinicco, T.; Mondini, C. Mineralization dynamics and biochemical properties during initial decomposition of plant and animal residues in soil. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2009, 41, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, T.; Moral, R.; Perez-Espinosa, A.; Moreno-Caselles, J.; Perez-Murcia, M.D.; García, C. Nitrogen mineralisation potential in calcareous soils amended with sewage sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2002, 83, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leconte, M.C.; Mazzarino, M.J.; Satti, P.; Crego, M.P. Nitrogen and phosphorus release from poultry manure composts: The role of carbonaceous bulking agents and compost particle sizes. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2011, 47, 897–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Fuente, C.; Alburquerque, J.A.; Clemente, R.; Bernal, M.P. Soil C and N mineralisation and agricultural value of the products of an anaerobic digestion system. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2013, 49, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gioacchini, P.; Manici, L.M.; Ramieri, N.A.; Marzadori, C.; Ciavatta, C. Nitrogen dynamics and microbial response in soil amended with either olive pulp or its by-products after biogas production. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2007, 43, 621–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amlinger, F.; Götz, B.; Dreher, P.; Geszti, J.; Weissteiner, C. Nitrogen in biowaste and yard waste compost: Dynamics of mobilisation and availability—A review. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2003, 39, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzarino, M.; Satti, P.; Moyano, S.; Laos, F. Biosolids compost: Screening effect on soil nitrogen immobilization. Cienc. Del Suelo 2004, 22, 19–26. [Google Scholar]
- Eghball, B.; Wienhold, B.J.; Gilley, J.E.; Eigenberg, R.A. Mineralization of manure nutrients. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2002, 57, 470–473. [Google Scholar]
- Oehl, F.; Oberson, A.; Probst, M.; Fliessbach, A.; Roth, H.-R.; Frossard, E. Kinetics of microbial phosphorus uptake in cultivated soils. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2001, 34, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preusch, P.L.; Adler, P.R.; Sikora, L.J.; Tworkoski, T.J. Nitrogen and Phosphorus Availability in Composted and Uncomposted Poultry Litter. J. Environ. Qual. 2002, 31, 2051–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, S.; Sposito, G. On the mechanism of specific phosphate adsorption by hydroxylated mineral surfaces: A review. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1985, 16, 801–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanyal, S.K.; De Datta, S.K. Chemistry of Phosphorus Transformations in Soil. In Advances in Soil Science: Volume 16; Stewart, B.A., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1991; pp. 1–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Zhang, Y.; Dijkstra, F.A.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Lu, Y.; Shi, J.; Yang, L. Effects of amendments on phosphorous status in soils with different phosphorous levels. Catena 2019, 172, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bünemann, E.K.; Bossio, D.A.; Smithson, P.C.; Frossard, E.; Oberson, A. Microbial community composition and substrate use in a highly weathered soil as affected by crop rotation and P fertilization. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2004, 36, 889–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Liu, X. Organic and inorganic phosphorus uptake by bacteria in a plug-flow microcosm. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2013, 7, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maguire, R.O.; Sims, J.T.; Dentel, S.K.; Coale, F.J.; Mah, J.T. Relationships between biosolids treatment process and soil phosphorus availability. J. Environ. Qual. 2001, 30, 1023–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dodd, R.J.; Sharpley, A.N. Recognizing the role of soil organic phosphorus in soil fertility and water quality. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2015, 105, 282–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Chemical Property | Units | Soil | LDE 1 | SDE | DED | OCMC | OCMD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | g kg−1 | 14.10 | 218.25 | 241.86 | 170.46 | 213.67 | 314.89 |
| TKN | g kg−1 | 1.40 | 26.34 | 10.69 | 66.31 | 15.13 | 66.56 |
| NO3 | 0.03 | 0.16 | 0.01 | 0.71 | 2.88 | 1.07 | |
| NH4 | 0.01 | 9.07 | 0.28 | 47.33 | 0.08 | 52.64 | |
| TIN | 0.04 | 9.23 | 0.29 | 48.04 | 2.96 | 53.71 | |
| TN | 1.43 | 26.50 | 10.71 | 67.02 | 18.01 | 67.64 | |
| No | - | 17.27 | 10.42 | 18.98 | 15.05 | 13.92 | |
| P | g kg−1 | 0.42 | 6.17 | 2.87 | 5.29 | 12.72 | 8.68 |
| Pe | 0.01 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| pH | 7.20 | 7.35 | 7.90 | 7.22 | 8.61 | 7.60 | |
| EC | dS m−1 | 0.10 | 10.27 | 3.40 | 12.07 | 3.03 | 12.80 |
| VS | % | - | 1.93 | 26.31 | 1.03 | 50.83 | 3.52 |
| TS | % | - | 41.05 | 41.66 | 29.69 | 33.56 | 61.52 |
| Chemical Property | Units | LDE 1 | SDE | DED | OCMC | OCMD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | mg kg−1 | 641.1 | 1750.4 | 198.9 | 1092.7 | 366.1 |
| TKN | mg kg−1 | 77.4 | 77.4 | 77.4 | 77.4 | 77.4 |
| NO3 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 0.8 | 14.7 | 1.2 | |
| NH4 | 26.7 | 2 | 55.2 | 0.4 | 61.2 | |
| TIN | 27.1 | 2.1 | 56.1 | 15.1 | 62.4 | |
| TN | 77.9 | 77.5 | 78.2 | 92.1 | 78.6 | |
| No | 50.7 | 75.4 | 22.1 | 77 | 16.2 | |
| P | mg kg−1 | 18.1 | 20.8 | 6.2 | 65 | 10.1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Iocoli, G.A.; Orden, L.; López, F.M.; Gómez, M.A.; Villamil, M.B.; Zabaloy, M.C. Towards Sustainable Dairy Production in Argentina: Evaluating Nutrient and CO2 Release from Raw and Processed Farm Waste. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2595. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11122595
Iocoli GA, Orden L, López FM, Gómez MA, Villamil MB, Zabaloy MC. Towards Sustainable Dairy Production in Argentina: Evaluating Nutrient and CO2 Release from Raw and Processed Farm Waste. Agronomy. 2021; 11(12):2595. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11122595
Chicago/Turabian StyleIocoli, Gastón A., Luciano Orden, Fernando M. López, Marisa A. Gómez, María B. Villamil, and María C. Zabaloy. 2021. "Towards Sustainable Dairy Production in Argentina: Evaluating Nutrient and CO2 Release from Raw and Processed Farm Waste" Agronomy 11, no. 12: 2595. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11122595
APA StyleIocoli, G. A., Orden, L., López, F. M., Gómez, M. A., Villamil, M. B., & Zabaloy, M. C. (2021). Towards Sustainable Dairy Production in Argentina: Evaluating Nutrient and CO2 Release from Raw and Processed Farm Waste. Agronomy, 11(12), 2595. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11122595








