Evaluation of Sugarcane Agroindustrial Wastes as Substrate in Soilless Cultivation of Tomato (S. lycopersicum Linnaeus): Effect of Substrate Composition on Yield Production
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials
2.2. Characterization
2.3. Substrate Preparation
2.4. Nutritive Solution Management
2.5. Plant Height, Number of Leaves, Substrate pH, and Fruit Yield Evaluation
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of Substrate Components
3.2. Characterization of Soilless Substrates and Phenological Development of Tomato in Different Substrates
3.3. Harvest Stage
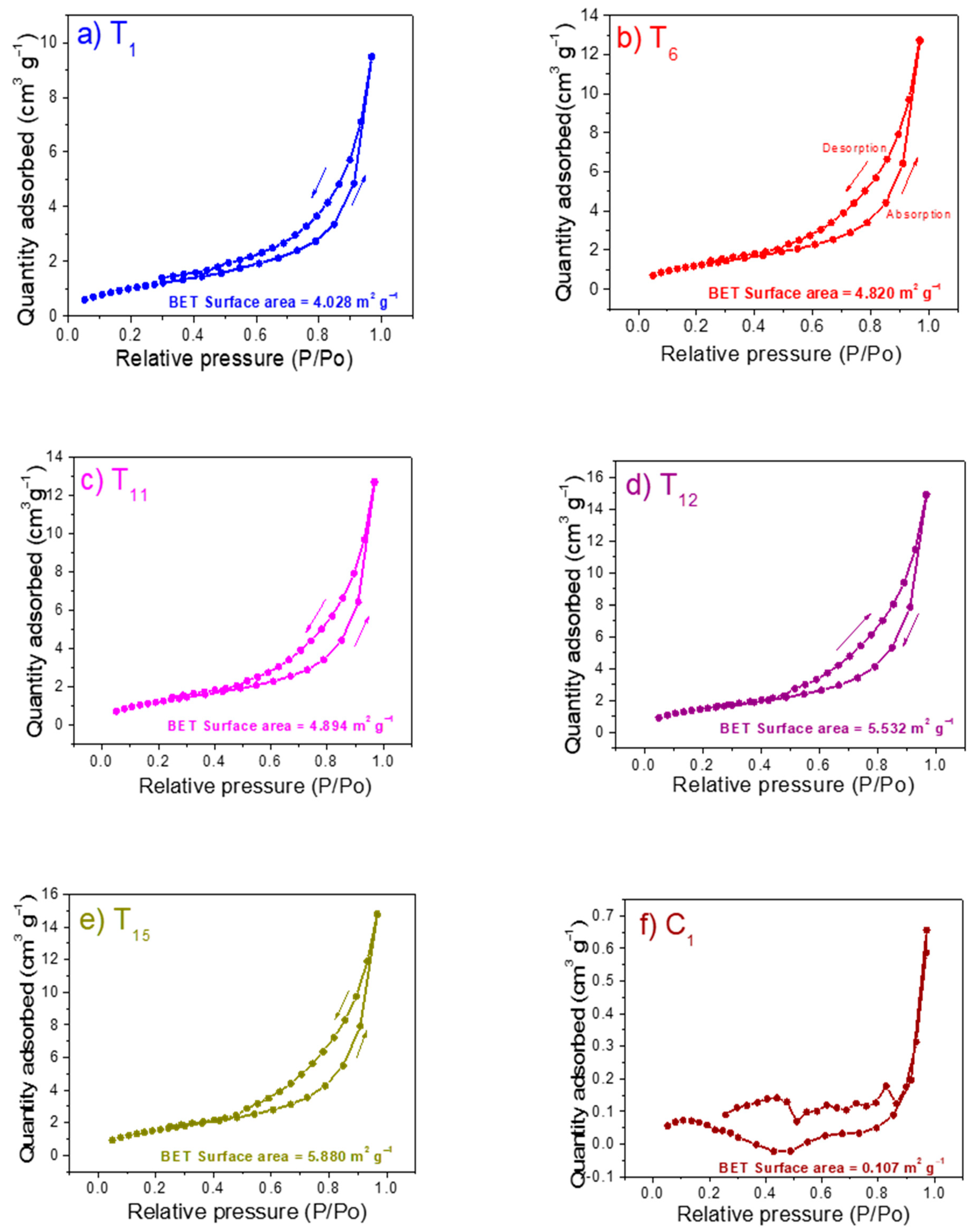
3.4. BET Surface Area Analysis of Samples
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Farfan, J.; Lohrmann, A.; Breyer, C. Integration of greenhouse agriculture to the energy infrastructure as an alimentary solution. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 110, 368–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orduño Torres, M.A.; Kallas, Z.; Ornelas Herrera, S.I. Farmers’ environmental perceptions and preferences regarding climate change adaptation and mitigation actions; towards a sustainable agricultural system in México. Land Use Policy 2020, 99, 105031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López Feldman, A.J.; Hernández Cortés, D. Cambio climático y agricultura: Una revisión de la literatura con énfasis en América Latina. Trimest. Econímico 2016, 83, 459–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elliott, J.; Deryng, D.; Müller, C.; Frieler, K.; Konzmann, M.; Gerten, D.; Glotter, M.; Flörke, M.; Wada, Y.; Best, N.; et al. Constraints and potentials of future irrigation water availability on agricultural production under climate change. PNAS 2014, 111, 3239–3244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bertoni, D.; Cavicchioli, D.; Donzelli, F.; Ferrazzi, G.; Frisio, D.G.; Pretolani, R.; Ricci, E.C.; Ventura, V. Recent contributions of agricultural economics research in the field of sustainable development. Agriculture 2018, 8, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cárdenas-Elizalde, M.R.; Cortés-Cáceres, F.A.; Escobar-Latapí, A.; Nahmad-Sittón, S.; Scott-Andretta, J.; Teruel-Belismelis, G.A. Informe de Evaluación de la Política de Desarrollo Social 2018; CONEVAL: Ciudad de México, Mexico, 2018; pp. 1–60. Available online: https://www.coneval.org.mx/Evaluacion/IEPSM/IEPSM/Documents/RESUMEN_EJECUTIVO_IEPDS2018.pdf (accessed on 18 January 2021).
- Mubiru, D.N.; Namakula, J.; Lwasa, J.; Otim, G.A.; Kashagama, J.; Nakafeero, M.; Nanyeenya, W.; Coyne, M.S. Conservation farming and changing climate: More beneficial than conventional methods for degraded ugandan soils. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Torres Pineda, I.; Lee, Y.D.; Kim, Y.S.; Lee, S.M.; Park, K.S. Review of inventory data in life cycle assessment applied in production of fresh tomato in greenhouse. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 282, 124395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maham, S.G.; Rahimi, A.; Subramanian, S.; Smith, D.L. The environmental impacts of organic greenhouse tomato production based on the nitrogen-fixing plant (Azolla). J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 245, 118679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margenot, A.J.; Griffin, D.E.; Alves, B.S.Q.; Rippner, D.A.; Li, C.; Parikh, S.J. Substitution of peat moss with softwood biochar for soil-free marigold growth. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2018, 112, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saavedra, T.M.; Figueroa, G.A.; Cauih, J.G.D. Origin and evolution of tomato production Lycopersicon esculentum in México. Cienc. Rural 2017, 47, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soto Mora, C. La agricultura comercial de los distritos de riego en México y su impacto en el desarrollo agrícola. Investig. Geográficas 2003, 50, 173–195. [Google Scholar]
- Schröder, J.J. An evaluation of whole-farm nitrogen balances and related indices for efficient nitrogen use. Eur. J Agron. 2003, 20, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, M.K.; Varun; Chaudhary, S.; Kumar, S.; Samar. Life cycle assessment of sugar industry: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2011, 15, 3445–3453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santamaria, P.; Campanile, G.; Parente, A.; Elia, A. Subirrigation vs. drip-irrigation: Effects on yield and quality of soilless grown cherry tomato. J. Hortic. Sci. Biotech. 2003, 78, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horinouchi, H.; Muslim, A.; Suzuki, T.; Hyakumachi, M. Fusarium equiseti GF191 as an effective biocontrol agent against Fusarium crown and root rot of tomato in rock wool systems. J. Crop Prot. 2007, 26, 1514–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clematis, F.; Minuto, A.; Gullino, M.L.; Garibaldi, A. Suppressiveness to fusarium oxysporum f. sp. radicis lycopersici in re-used perlite and perlite–peat substrates in soilless tomatoes. Biol. Control 2009, 48, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronga, D.; Zaccardelli, M.; Lovelli, S.; Perrone, D.; Francia, E.; Milc, J.; Ulrici, A.; Pecchioni, N. Biomass production and dry matter partitioning of processing tomato under organic vs conventional cropping systems in a Mediterranean environment. Sci. Hortic. 2017, 224, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tringovska, I.; Yankova, V.; Markova, D.; Mihov, M. Effect of companion plants on tomato greenhouse production. Sci. Hortic. 2015, 186, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlile, W.R.; Cattivello, C.; Zaccheo, P. Organic growing media: Constituents and properties. Vadose Zone J. 2015, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, R.; Qin, W.; Jiang, C.; Kang, L.; Nendel, C.; Chen, Q. Sweet corn significantly increases nitrogen retention and reduces nitrogen leaching as summer catch crop in protected vegetable production systems. Soil Tillage Res. 2018, 180, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Hu, J.; Wang, X.; Choi, S.; Zhang, T.-A.; Tsang, Y.F.; Gao, M.-T. An integrated strategy for the utilization of rice straw: Production of plant growth promoter followed by ethanol fermentation. Process Saf. Environ. 2019, 129, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronga, D.; Gallingani, T.; Zaccardelli, M.; Perrone, D.; Francia, E.; Milc, J.; Pecchioni, N. Carbon footprint and energetic analysis of tomato production in the organic vs the conventional cropping systems in Southern Italy. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 220, 836–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wakelyn, P.J.; Chaudhry, M.R. 11—Organic cotton: Production practices and post-harvest considerations. In Sustainable Textiles; Blackburn, R.S., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2009; pp. 231–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruda, N.; Schnitzler, W.H. Suitability of wood fiber substrates for production of vegetable transplants II.: The effect of wood fiber substrates and their volume weights on the growth of tomato transplants. Sci. Hortic. 2004, 100, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lévesque, V.; Jeanne, T.; Dorais, M.; Ziadi, N.; Hogue, R.; Antoun, H. Biochars improve tomato and sweet pepper performance and shift bacterial composition in a peat-based growing medium. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2020, 153, 103579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Könönen, M.; Jauhiainen, J.; Straková, P.; Heinonsalo, J.; Laiho, R.; Kusin, K.; Limin, S.; Vasander, H. Deforested and drained tropical peatland sites show poorer peat substrate quality and lower microbial biomass and activity than unmanaged swamp forest. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 123, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez, E.; Nelson, B.; Muñoz-Escobar, C. Efectos de la extracción de turba sobre la composición y estructura de una turbera de Sphagnum explotada y abandonada hace 20 años, Chile. An. Inst. Patagon. 2011, 40, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miguel, E. Manuales de Desarrollo Sostenible: 2. Conservación y Restauración de Turberas; Fundación Santander Central Hispano: Madrid, Spain, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Pratap-Singh, D.; Bahadur-Singh, H.; Prabha, R. Microbial inoculants in sustainable agricultural productivity. In Functional Applications; Springer: New Delhi, India, 2016; Volume 2, p. 301. [Google Scholar]
- Zaller, J.G. Vermicompost as a substitute for peat in potting media: Effects on germination, biomass allocation, yields and fruit quality of three tomato varieties. Sci. Hortic. 2007, 112, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughn, S.F.; Kenar, J.A.; Thompson, A.R.; Peterson, S.C. Comparison of biochar’s derived from wood pellets and pelletized wheat straw as replacements for peat in potting substrates. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2013, 51, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraska, T.; Kleinschmidt, B.; Weinand, J.; Pude, R. Cascading use of Miscanthus as growing substrate in soilless cultivation of vegetables (tomatoes, cucumbers) and subsequent direct combustion. Sci. Hortic. 2018, 235, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughn, S.F.; Deppe, N.A.; Palmquist, D.E.; Berhow, M.A. Extracted sweet corn tassels as a renewable alternative to peat in greenhouse substrates. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2011, 33, 514–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceglie, F.G.; Bustamante, M.A.; Ben Amara, M.; Tittarelli, F. The challenge of peat substitution in organic seedling production: Optimization of growing media formulation through mixture design and response surface analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0128600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez, M.L.; Gascó, G.; Plaza, C.; Paz-Ferreiro, J.; Méndez, A. Hydrochars from biosolids and urban wastes as substitute materials for peat. Land Degrad. Dev. 2017, 28, 2268–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, D.W.; Brian, E.J.; Michael, C.B.; Jake, F.B. The landscape performance of annual bedding plants grown in pine tree substrate. HortTechnology 2009, 19, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramos Del Carmen, M. Evaluación de un Proceso de Biorremediación de Lodos Urbanos y Agroindustriales. Ph.D. Thesis, Benemérita Universidad Autónoma de Puebla, Puebla, Mexico, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Parameswaran, B. Sugarcane bagasse. In Biotechnology for Agro-Industrial Residues Utilisation: Utilisation of Agro-Residues; Singh nee’ Nigam, P., Pandey, A., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Candido, R.G.; Gonçalves, A.R. Evaluation of two different applications for cellulose isolated from sugarcane bagasse in a biorefinery concept. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2019, 142, 111616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantas, G.A.; Legey, L.F.L.; Mazzone, A. Energy from sugarcane bagasse in Brazil: An assessment of the productivity and cost of different technological routes. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 21, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, P.S.; de Oliveira, S., Jr. Exergy analysis of pretreatment processes of bioethanol production based on sugarcane bagasse. Energy 2014, 76, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanwar, D.A.; Aggarwal, A. Sugarcane bagasse: A novel substrate for mass multiplication of Funneliformis mosseae with onion as host. J. Cent. Eur Agric. 2013, 14, 1502–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirel, B.; Scherer, P. Trace element requirements of agricultural biogas digesters during biological conversion of renewable biomass to methane. Biomass Bioenerg. 2011, 35, 992–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janke, L.; Leite, A.; Nikolausz, M.; Schmidt, T.; Liebetrau, J.; Nelles, M.; Stinner, W. Biogas production from sugarcane waste: Assessment on kinetic challenges for process designing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 20685–20703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leite, A.F.; Janke, L.; Harms, H.; Zang, J.W.; Fonseca-Zang, W.A.; Stinner, W.; Nikolausz, M. Assessment of the variations in characteristics and methane potential of major waste products from the Brazilian bioethanol industry along an operating season. Energ. Fuel. 2015, 29, 4022–4029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López González, L.M.; Pereda Reyes, I.; Dewulf, J.; Budde, J.; Heiermann, M.; Vervaeren, H. Effect of liquid hot water pre-treatment on sugarcane press mud methane yield. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 169, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Torres, R.; Rios-Leal, E.; Martinez-Toledo, Á.; Ramos-Morales, F.R.; Cruz-Sánchez, J.S.; Cuevas-Díaz, M.d.C. Uso de cachaza y bagazo de caña de azúcar en la remoción de hidrocarburos en suelo contaminado. Rev. Int. Contam. Ambient. 2011, 27, 31–39. [Google Scholar]
- Seleiman, M.F.; Kheir, A.M.S. Saline soil properties, quality and productivity of wheat grown with bagasse ash and thiourea in different climatic zones. Chemosphere 2018, 193, 538–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bento, L.R.; Castro, A.J.R.; Moreira, A.B.; Ferreira, O.P.; Bisinoti, M.C.; Melo, C.A. Release of nutrients and organic carbon in different soil types from hydrochar obtained using sugarcane bagasse and vinasse. Geoderma 2019, 334, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, H.; Dang, L.; Khabbaz, H.; Fatahi, B.; Terzaghi, S. Remediation of expansive soils using agricultural waste bagasse ash. Procedia Eng. 2016, 143, 1368–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lyra, G.P.; dos Santos, V.; De Santis, B.C.; Rivaben, R.R.; Fischer, C.; Pallone, E.M.d.J.A.; Rossignolo, J.A. Reuse of sugarcane bagasse ash to produce a lightweight aggregate using microwave oven sintering. Const. Build. Mater. 2019, 222, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.L.; Sairam, V.; Muruganandam, L.; Srinivasan, K. An overview of the influences of mechanical and chemical processing on sugarcane bagasse ash characterization as a supplementary cementitious material. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 245, 118854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Olivares, F.; Elizabeth Medina-Alvarado, R.; Burneo-Valdivieso, X.E.; Rodrigo Zúñiga-Suárez, A. Short sugarcane bagasse fibers cementitious composites for building construction. Const. Build. Mater. 2020, 247, 118451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis, 21st ed.; AOAC International: Rockville, MD, USA, 2019; Available online: https://www.aoac.org/aoac_prod_imis/AOAC/Publications/Official_Methods_of_Analysis/AOAC_Member/Pubs/OMA/AOAC_Official_Methods_of_Analysis.aspx (accessed on 19 January 2021).
- Gonçalves, A.R.; Moriya, R.Y.; Oliveira, L.R.M.; Saad, M.B.W. Xylanase recycling for the economical biobleaching of sugarcane bagasse and straw pulps. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2008, 43, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grunert, O.; Hernandez-Sanabria, E.; Vilchez-Vargas, R.; Jauregui, R.; Pieper, D.H.; Perneel, M.; Van Labeke, M.-C.; Reheul, D.; Boon, N. Mineral and organic growing media have distinct community structure, stability and functionality in soilless culture systems. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 18837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gruda, N. Current and future perspective of growing media in Europe. Acta Hortic. 2012, 960, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flogeac, K.; Guillon, E.; Aplincourt, M.; Marceau, E.; Stievano, L.; Beaunier, P.; Frapart, Y.-M. Characterization of soil particles by X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2005, 25, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, L.; Wei, X.; Chang, G.; Huang, X.; Han, D. Structure and saccharification of sugarcane bagasse pretreated with acid coupled alkaline. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Mechanical Engineering and Material Science (ISMEMS 2017), Suzhou, China, 17–19 November 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kamath, S.R.; Proctor, A. Silica gel from rice hull ash: Preparation and characterization. Cereal Chem. 1998, 75, 484–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, J. Sugarcane press mud modification of expansive soil stabilized at optimum lime content: Strength, mineralogy and microstructural investigation. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2020, 12, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munasir; Triwikantoro; Zainuri, M.; Darminto. Syntheis of SiO2 containing quartz and cristobalite phases from silica sands. Mater. Sci-Poland. 2015, 33, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bar-Tal, A.; Saha, U.K.; Raviv, M.; Tuller, M. Chapter 7—Inorganic and synthetic organic components of soilless culture and potting mixtures. In Soilless Culture, 2nd ed.; Raviv, M., Lieth, J.H., Bar-Tal, A., Eds.; Elsevier: Boston, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 259–301. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Negi, Y.S.; Choudhary, V.; Bhardwaj, N. Characterization of cellulose nanocrystals produced by acid-hydrolysis from sugarcane bagasse as agro-waste. J. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2014, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong Sak Hoi, L.; Martincigh, B.S. Sugar cane plant fibres: Separation and characterisation. Ind. Crop Prod. 2013, 47, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledo-Jaldin, H.P.; Sánchez-Mendieta, V.; Blanco-Flores, A.; López-Téllez, G.; Vilchis-Nestor, A.R.; Martín-Hernández, O. Low-cost sugarcane bagasse and peanut shell magnetic-composites applied in the removal of carbofuran and iprodione pesticides. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 7872–7885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, I.; Chow, W.S. Tailoring chemical, physical, and morphological properties of sugarcane bagasse cellulose nanocrystals via phosphorylation method. J. Nat. Fibers. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharachorloo, M.; Ghasemi Afshar, P.; Honarvar, M.; Eshratabadi, P.; Bazyar, B. Advances in environmental biology investigation of the physico-chemical properties of press mud: A sugar industry waste. Adv. Environ. Biol. 2014, 8, 1053–1058. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Marel, H.W.; Beutelspacher, H. Atlas of Infrared Spectroscopy of Clay Minerals and their Admixtures; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Castaldelli, V.; Akasaki, J.; Melges, J.L.P.; Tashima, M.; Soriano, L.; Borrachero, M.; Monzo, J.; Payá, J. Use of Slag/Sugar Cane Bagasse Ash (SCBA) blends in the production of alkali-activated materials. Materials 2013, 6, 3108–3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, N.; Tripathi, S.; Balomajumder, C. Characterization of pressmud: A sugar industry waste. Fuel 2011, 90, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, D.; Morelli, M. Effect of calcination temperature on the pozzolanic activity of Brazilian Sugar Cane Bagasse Ash (SCBA). Mater. Res. 2014, 17, 974–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maldonado-García, M.A.; Hernández-Toledo, U.I.; Montes-García, P.; Valdez-Tamez, P.L. The influence of untreated sugarcane bagasse ash on the microstructural and mechanical properties of mortars. Mater. Construcción 2018, 68, e148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abebe, B.; Murthy, H.C.A.; Zereffa, E. Summary on adsorption and photocatalysis for pollutant remediation: Mini review. J. Encap. Adsorp. Sci. 2018, 08, 225–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Asaduzzaman, M.; Saifullah, M.; Mollick, A.K.M.; Hossain, M.; Halim, G.M.A.; Asao, T. Influence of soilless culture substrate on improvement of yield and produce quality of horticultural crops. In Soilless Culture-Use of Substrates for the Production of Quality Horticultural Crop; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2015; pp. 1–32. [Google Scholar]
- Ming, D.; Allen, E. Use of natural zeolites in agronomy, horticulture and environmental soil remediation. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2001, 45, 619–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albino, V.S.; Peixoto, J.R.; Caetano Junior, V.; Vilela, M.S. Rootstock performance for cherry tomato production under organic, greenhouse production system. Hortic. Bras. 2018, 36, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgognone, D.; Colla, G.; Rouphael, Y.; Cardarelli, M.; Rea, E.; Schwarz, D. Effect of nitrogen form and nutrient solution pH on growth and mineral composition of self-grafted and grafted tomatoes. Sci. Hortic. 2013, 149, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyśko, J.; Kaniszewski, S.; Kowalczyk, W. The effect of nutrient solution PH on phosphorus availability in soilless culture of tomato. J. Elem. 2008, 13, 189–198. [Google Scholar]
- Dyśko, J.; Kowalczyk, W.; Kaniszewski, S. The influence of pH of nutrient solution on yield and nutritional status of tomato plants grown in soilless culture system. Veg. Crops Res. Bull. 2009, 70, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Tang, X.; Wang, Z.; Peng, X. Pore characterization of different types of coal from coal and gas outburst disaster sites using low temperature nitrogen adsorption approach. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2017, 27, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Sun, X. Effects of rhamnolipid and initial compost particle size on the two-stage composting of green waste. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 163, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Sun, X. Improving green waste composting by addition of sugarcane bagasse and exhausted grape marc. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 218, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bustamante, M.A.; Said-Pullicino, D.; Agulló, E.; Andreu, J.; Paredes, C.; Moral, R. Application of winery and distillery waste composts to a Jumilla (SE Spain) vineyard: Effects on the characteristics of a calcareous sandy-loam soil. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2011, 140, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Verma, D.; Singh, B.L.; Kumar, U.; Shweta. Composting of sugar-cane waste by-products through treatment with microorganisms and subsequent vermicomposting. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 6707–6711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, D.L.; Matos, A.T.d.; Melo, E.d.C. Resistance to forced airflow through layers of composting organic material. J. Waste Manag. 2015, 36, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanwar, A.; Aggarwal, A.; Yadav, A.; Parkash, V. Screening and selection of efficient host and sugarcane bagasse as substrate for mass multiplication of Funneliformis mosseae. Biol. Agric. Hortic. J. 2013, 29, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meunchang, S.; Panichsakpatana, S.; Weaver, R.W. Co-composting of filter cake and bagasse; by-products from a sugar mill. Bioresour. Technol. 2005, 96, 437–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webber, C.; White, P., Jr.; Spaunhorst, D.; Petrie, E. Impact of sugarcane bagasse ash as an amendment on the physical properties, nutrient content and seedling growth of a certified organic greenhouse growing media. J. Agric. Sci. 2017, 9, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Webber, C.; White, P.; Petrie, E.; Shrefler, J.; Taylor, M. Sugarcane bagasse ash as a seedling growth media component. J. Agric. Sci. 2015, 8, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cifuentes, R.; de León, R.; Porres, C.; Rolz, C. Windrow composting of waste sugar cane and press mud mixtures. Sugar Tech 2013, 15, 406–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh-e-In, M.; Yeasmin, S.; Paul, B.; Ahsan, M.; Rahman, M.; Roy, S. Chemical studies on press mud: A sugar industries waste in Bangladesh. Sugar Tech. 2012, 14, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negim, O.; Mustafa, A.; Fouad, H. Effect of pressmud, as an organic fertilizer, on some soil properties, growth of tomato plant and infestation of tuta absluta under saline irrigation water. J. Soil Sci. Agric. Eng. 2016, 7, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Samuel, J.D.; Marta Camps, A.; Peter, A.B.; Jason, J.W. Closing the loop: Use of biochar produced from tomato crop green waste as a substrate for soilless, hydroponic tomato production. HortScience 2015, 50, 1572–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almanza-Merchán, P.J.; Arévalo, Y.A.; Cely, R.G.E.; Pinzón, E.H.; Serrano, C.P.A. Fruit growth characterization of the tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) hybrid Ichiban’grown under cover. Agron. Colomb. 2016, 34, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López González, L.M.; Pereda Reyes, I.; Pedraza Garciga, J.; Barrera, E.L.; Romero Romero, O. Energetic, economic and environmental assessment for the anaerobic digestion of pretreated and codigested press mud. J. Waste Manag. 2020, 102, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendieta, O.; Castro, L.; Rodríguez, J.; Escalante, H. Synergistic effect of sugarcane scum as an accelerant co-substrate on anaerobic co-digestion with agricultural crop residues from non-centrifugal cane sugar agribusiness sector. Bioresour. Techn. 2020, 303, 122957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, N.; Ruiz, R.Y.; Cifuentes, B.; Cobo, M. Controlling sugarcane press-mud fermentation to increase bioethanol steam reforming for hydrogen production. J. Waste Manag. 2019, 98, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karwal, M.; Kaushik, A. Co-composting and vermicomposting of coal fly-ash with press mud: Changes in nutrients, micro-nutrients and enzyme activities. J. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 18, 100708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.Y.; Haque, M.M.; Molla, A.H.; Rahman, M.M.; Alam, M.Z. Antioxidant compounds and minerals in tomatoes by Trichoderma-enriched biofertilizer and their relationship with the soil environments. J. Integr. Agr. 2017, 16, 691–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Determination | Ash | Sugarcane Bagasse | Filter Press Mud | Sphagnum Peat Moss |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moisture (%) | 3.68 ± 0.36 | 8.34 ± 0.15 | 6.38 ± 0.64 | 3.85 ± 0.33 |
| Ash (%) | - | 3.98 ± 0.22 | 39.88 ± 2.23 | 5.96 ± 0.34 |
| Ether Extract (%) | 7.03 ± 0.23 | <0.10 | <0.10 | <0.10 |
| Crude Protein (%) | 1.16 ± 0.09 | 1.3 ± 0.19 | 6.94 ± 0.40 | 6.8 ± 0.9 |
| Crude fiber (%) | 27.08 ± 0.6 | 38.90 ± 1.11 | 15.15 ± 0.90 | 36.84 ± 1.5 |
| pH | 6.8 ± 0.36 | 5.8 ± 0.11 | 7.7 ± 0.10 | 4.7 ± 0.20 |
| Apparent density (g cm−3) | 0.26 ± 0.06 | 0.1 ± 0.03 | 0.34 ± 0.02 | 0.34 ± 0.02 |
| σ (Ω cm−1) | 2.12 × 10−3 ± 1 × 10−4 | 2.33 × 10−4 ± 3 × 10−5 | 3.57 × 10−6 ± 3.1 × 10−7 | 5.88 × 10−4 ± 5 × 10−5 |
| Element | Sugarcane Bagasse | Filter Press Mud | Sugarcane Bagasse Ash | Commercial Sphagnum Peat Moss |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Atomic %) | ||||
| C | 54.78 | - | - | 82.36 |
| O | 44.24 | 79.24 | 62.37 | 16.89 |
| Mg | 0.02 | 0.75 | 1.19 | 0.05 |
| Al | 0.11 | 2.16 | 2.56 | 0.06 |
| Si | 0.51 | 7.17 | 23.59 | 0.33 |
| P | 0.02 | 2.16 | 1.46 | - |
| S | 0.03 | 0.32 | 0.63 | - |
| Cl | 0.02 | 0.16 | 0.32 | - |
| K | 0.14 | 1.21 | 4.51 | - |
| Ca | 0.06 | 5.64 | 1.92 | 0.31 |
| Fe | 0.04 | 0.7 | 0.83 | - |
| Cu | 0.04 | 0.14 | 0.21 | - |
| Na | - | 0.28 | 0.35 | - |
| Substrate | FPM (%) | SCB (%) | SCBA (%) | SPM(%) | Plant Height (cm) | Leaf Number | Substrate pH | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20 DAT | 74 DAT | 130 DAT | 20 DAT | 74 DAT | 130 DAT | 20 DAT | 74 DAT | 130 DAT | |||||
| T1 | 60 | 36 | 4 | - | 21.5 ± 2.55 a | 44.75 ± 2.90 bcde | 66.10 ± 8.20 fghi | 21.00 ± 2.00 a | 34.00 ± 4.36 bc | 95.5 ± 2.82 efgh | 5.50 ± 0.50 bc | 5.33 ± 0.29 defg | 5.33 ± 0.29 ijk |
| T2 | 60 | 28 | 12 | - | 25.90 ± 1.98 a | 31.30 ± 0.00 bc | 44.40 ± 0.00 f | 19.00 ± 1.41 a | 21.00 ± 0.00 b | 104.00 ± 0.00 e | - | - | 4.83 ± 0.29 hijk |
| T3 | 60 | 20 | 20 | - | 25.60 ± 2.69 a | 25.70±0.00b | - | 16.67 ± 5.51 a | - | - | - | - | 5.00 ± 0.00 hijk |
| T4 | 60 | 12 | 28 | - | 24.30 ± 0.00 a | - | - | 21.00 ± 0.00 a | - | - | - | - | 3.33 ± 0.58 hi |
| T5 | 60 | 4 | 36 | - | 25.50 ± 0.00 a | - | - | 16.00 ± 0.00 a | - | - | - | - | 3.67 ± 1.15 hij |
| T6 | 70 | 27 | 3 | - | 24.60 ± 3.91 a | 56.43 ± 6.71 cde | 79.00 ± 2.26 ghij | 31.50 ± 0.71 b | 48.00 ± 2.82 cd | 244.00 ± 12.72 fghi | 6.17 ± 1.04 c | 6.67 ± 0.29 g | 6.00 ± 0.50 k |
| T7 | 70 | 21 | 9 | - | 25.90 ± 2.69 a | 48.80 ± 5.09 bcde | 72.35 ± 11.24 fghij | 16.00 ± 0.0 a | 28.67 ± 8.08 bc | 197.00 ± 0.00 efgh | 5.83 ± 1.04 bc | 4.83 ± 1.61 defg | 5.17 ± 1.25 ijk |
| T8 | 70 | 15 | 15 | - | 28.10 ± 0.43 a | 40.10 ± 1.13 bcd | 51.15 ± 5.30 fg | 25.50 ± 4.92 ab | 34.00 ± 7.07 bc | 110.00 ± 9.90 ef | 3.00 ± 0.00 a | 3.50 ± 0.71 de | 4.50 ± 0.50 hijk |
| T9 | 70 | 9 | 21 | - | 28.45 ± 0.35 a | 54.80 ± 0.00cde | 69.45 ± 14.35 fghi | 22.00 ± 2.83 ab | 45.00 ± 0.00 cd | 210.00 ± 0.00 efghi | 3.00 ± 0.00 a | 4.00 ± 1.41 def | 3.83 ± 1.44 hij |
| T10 | 70 | 3 | 27 | - | 26.23 ± 2.39 a | 42.30 ± 0.85 abcd | 65.6 ± 1.13 fgh | 19.50 ± 3.53 a | 32.50 ± 2.12 bc | 148.50 ± 21.92 efg | 3.00 ± 0.00 a | 3.50 ± 0.71 de | 3.00 ± 0.00 h |
| T11 | 80 | 18 | 2 | - | 21.40 ± 3.83 a | 56.05 ± 6.43 cde | 76.50 ± 7.88 ghij | 24.00 ± 0.00 ab | 44.67 ± 2.08 cd | 230.00 ± 1.41 efghi | 5.83 ± 0.29 bc | 6.00 ± 0.87 efg | 5.50 ± 1.00 jk |
| T12 | 80 | 14 | 6 | - | 24.53 ± 0.76 a | 61.96±1.98 e | 84.6±4.10 hij | 21.00±0.00 a | 42.50 ±2.12 cd | 277.00 ± 9.16 ghi | 5.17 ± 0.29 bc | 4.00 ± 1.00 def | 5.33 ± 0.29 ijk |
| T13 | 80 | 10 | 10 | - | 20.80 ± 3.15 a | 62.00 ± 0.00 e | 90.2 ± 0.00 hij | 15.50 ± 4.94 a | 35.50 ± 12.02 bcd | 201.00 ± 0.00 efghi | 5.00 ± 0.00 defg | 5.00 ± 0.00 hijk | |
| T14 | 80 | 6 | 14 | - | 28.46 ± 2.55 a | 49.03 ± 6.47 bcde | 77.25 ± 7.99 ghij | 21.67 ± 1.52 ab | 31.00 ± 4.36 bc | 154.00 ± 39.60 efgh | 4.00 ± 1.00 ab | 3.33 ± 0.58 d | 3.33 ± 0.58 hi |
| T15 | 80 | 2 | 18 | - | 29.17 ± 3.09 a | 57.80 ± 8.42 cde | 99.80 ± 7.92 j | 24.50 ± 0.71 ab | 43.67 ± 8.14 cd | 289.67 ± 14.29 hi | 3.00 ± 0.00 a | 3.00 ± 0.00 d | 3.00 ± 0.00 h |
| C1 | - | - | - | 100 | 26.85 ± 4.03 a | 59.95 ± 8.13 de | 95.45 ± 11.24 ij | 24.50 ± 0.70 ab | 56.00 ± 8.48 d | 335.00 ± 7.07 i | 5.83 ± 0.29 bc | 6.50 ± 0.50 fg | 5.33 ± 0.29 ijk |
| Substrate | Fruit Yield | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fresh Fruit Weight (g) | Dehydrated Fruit Weight (g) | Polar Diameter (mm) | Equatorial Diameter (mm) | Crop Yield (%) | |
| T1 | 42.50 ± 2.12 ab | 3.00 ± 0.14 c | 51.49 ± 0.71 gh | 41.00 ± 0.00 ef | 2.25 |
| T6 | 55.00 ± 3.46 b | 9.63 ± 0.57 d | 65.17 ± 3.21 i | 53.91 ± 4.24 f | 42.60 |
| T11 | 47.20 ± 3.53 ab | 6.48 ± 0.50 c | 64.28 ± 3.21 hi | 46.63 ± 2.08 ef | 39.23 |
| T12 | 42.50 ± 3.53 ab | 3.99 ± 0.20 c | 46.17 ± 3.21 g | 41.00 ± 5.66 ef | 30.31 |
| T15 | 43.00 ± 0.00 a | 3.71 ± 0.26 c | 54.17 ± 0.00 gh | 43.98 ± 4.24 e | 35.16 |
| C1 | 41.00 ± 1.15 a | 3.33 ± 0.25 c | 45.24 ± 3.51 g | 37.29 ± 2.09 ef | 26.94 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Orta-Guzmán, V.N.; Lois-Correa, J.A.; Domínguez-Crespo, M.A.; Pineda-Pineda, J.; Torres-Huerta, A.M.; Rodríguez-Salazar, A.E.; Licona-Aguilar, Á.I. Evaluation of Sugarcane Agroindustrial Wastes as Substrate in Soilless Cultivation of Tomato (S. lycopersicum Linnaeus): Effect of Substrate Composition on Yield Production. Agronomy 2021, 11, 206. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11020206
Orta-Guzmán VN, Lois-Correa JA, Domínguez-Crespo MA, Pineda-Pineda J, Torres-Huerta AM, Rodríguez-Salazar AE, Licona-Aguilar ÁI. Evaluation of Sugarcane Agroindustrial Wastes as Substrate in Soilless Cultivation of Tomato (S. lycopersicum Linnaeus): Effect of Substrate Composition on Yield Production. Agronomy. 2021; 11(2):206. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11020206
Chicago/Turabian StyleOrta-Guzmán, Vanessa Natalie, Jorge Aurelio Lois-Correa, Miguel Antonio Domínguez-Crespo, Joel Pineda-Pineda, Aidé Minerva Torres-Huerta, Adela Eugenia Rodríguez-Salazar, and Ángeles Iveth Licona-Aguilar. 2021. "Evaluation of Sugarcane Agroindustrial Wastes as Substrate in Soilless Cultivation of Tomato (S. lycopersicum Linnaeus): Effect of Substrate Composition on Yield Production" Agronomy 11, no. 2: 206. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11020206
APA StyleOrta-Guzmán, V. N., Lois-Correa, J. A., Domínguez-Crespo, M. A., Pineda-Pineda, J., Torres-Huerta, A. M., Rodríguez-Salazar, A. E., & Licona-Aguilar, Á. I. (2021). Evaluation of Sugarcane Agroindustrial Wastes as Substrate in Soilless Cultivation of Tomato (S. lycopersicum Linnaeus): Effect of Substrate Composition on Yield Production. Agronomy, 11(2), 206. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11020206





