Prediction of Rice Yield in East China Based on Climate and Agronomic Traits Data Using Artificial Neural Networks and Partial Least Squares Regression
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection
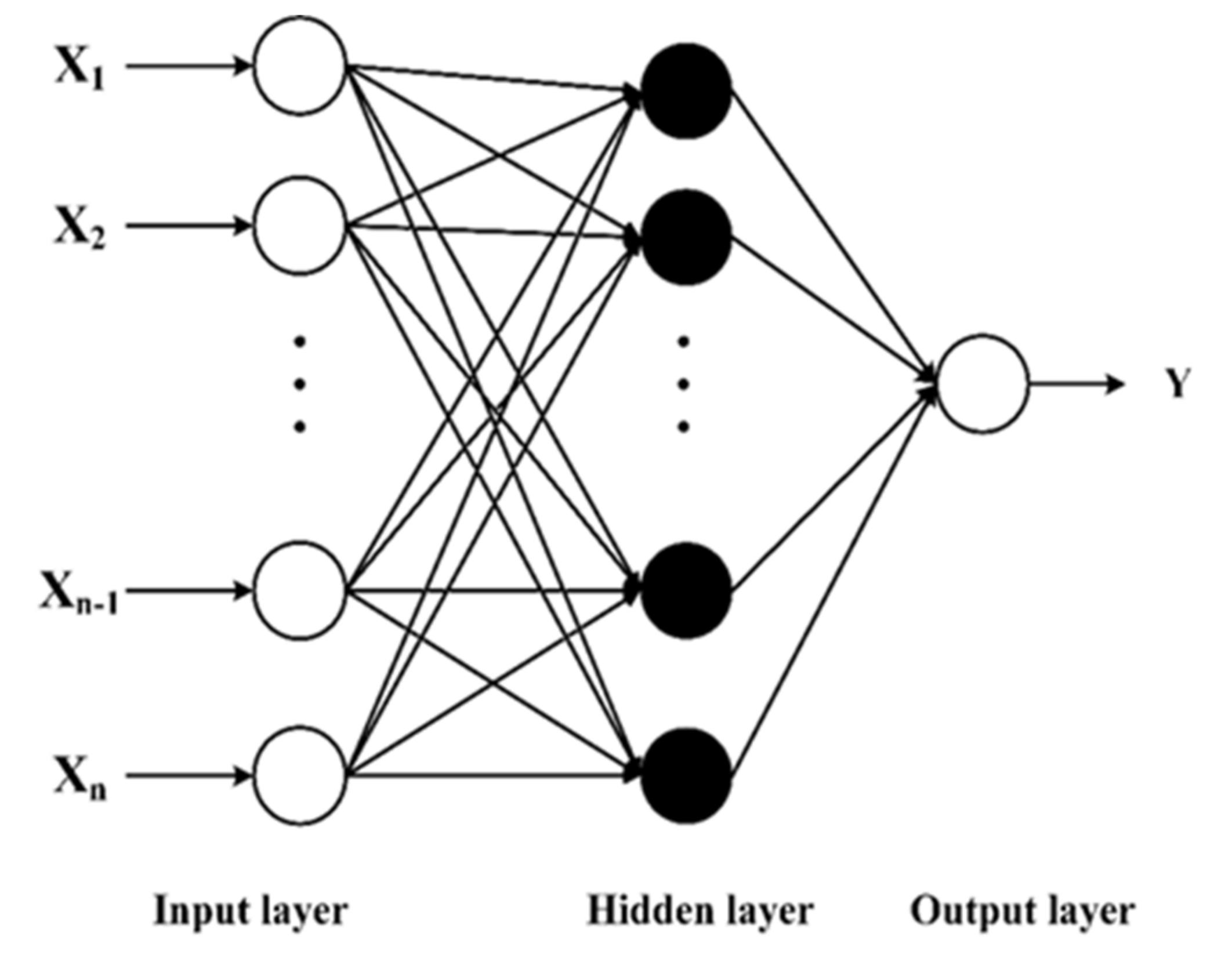
2.2. Feed-Forward Backpropagation Neural Network (FFBN)
2.3. Partial Least Squares Regression (PLSR)
2.4. Model Evaluations
3. Results and Discussion
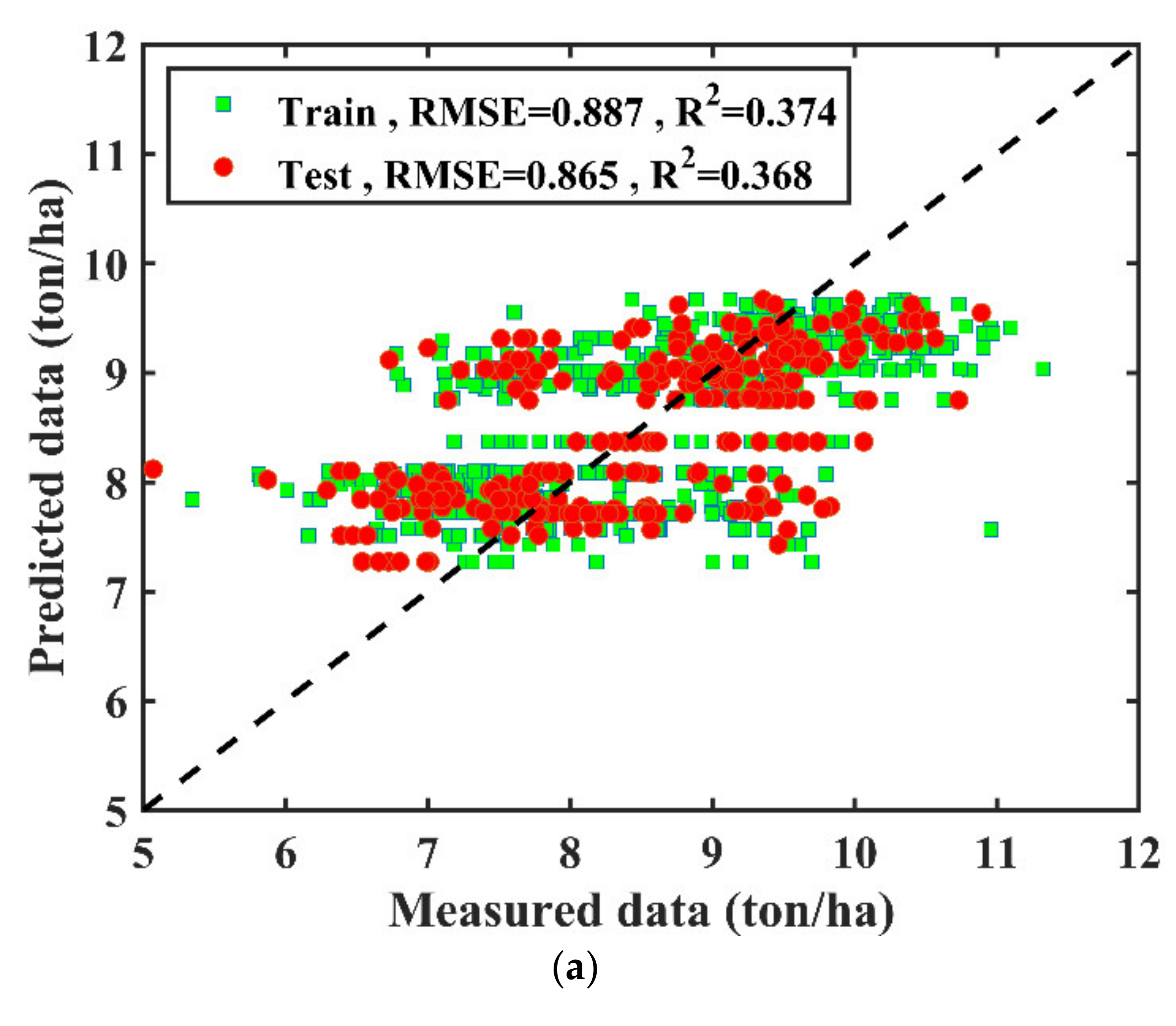
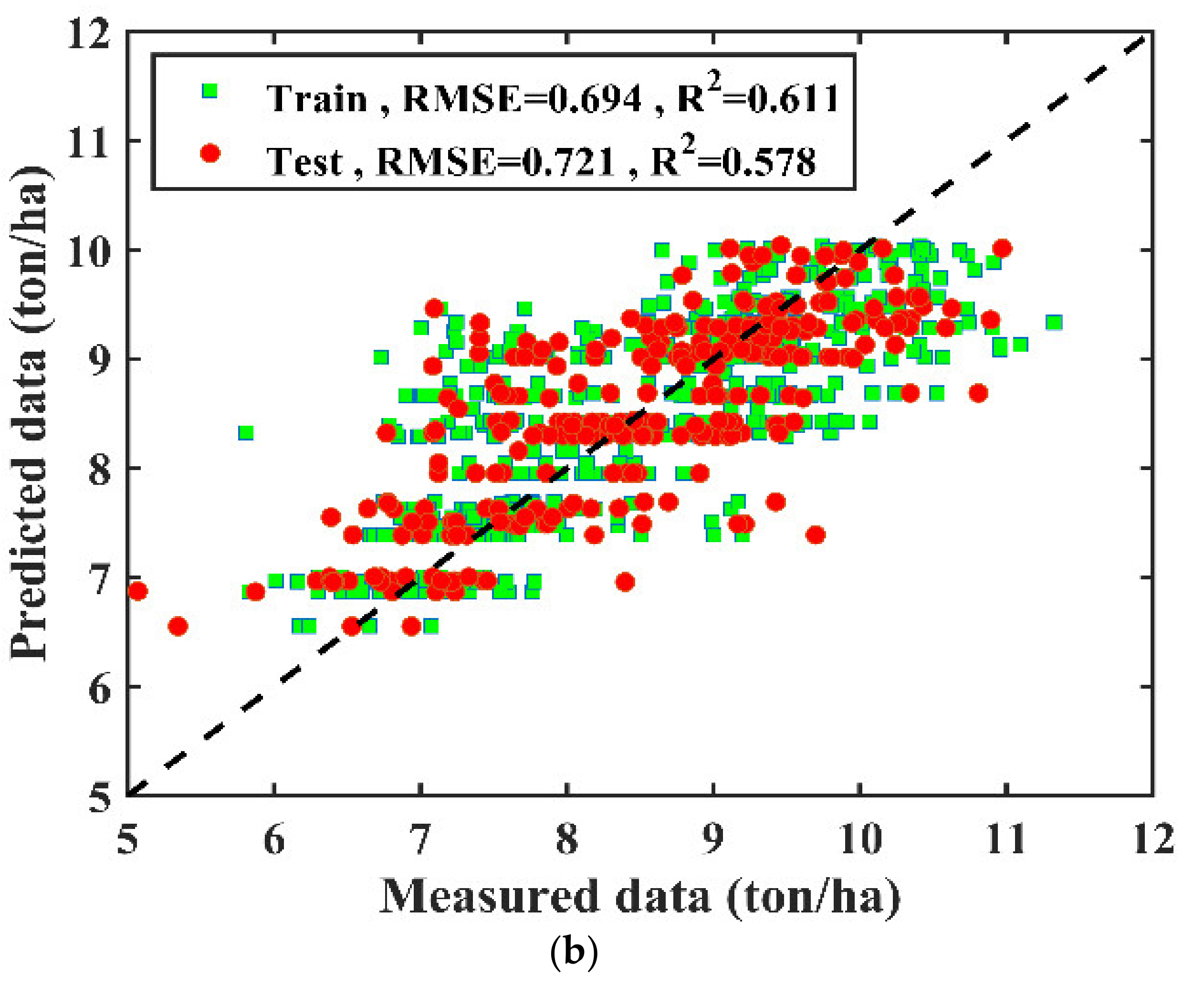
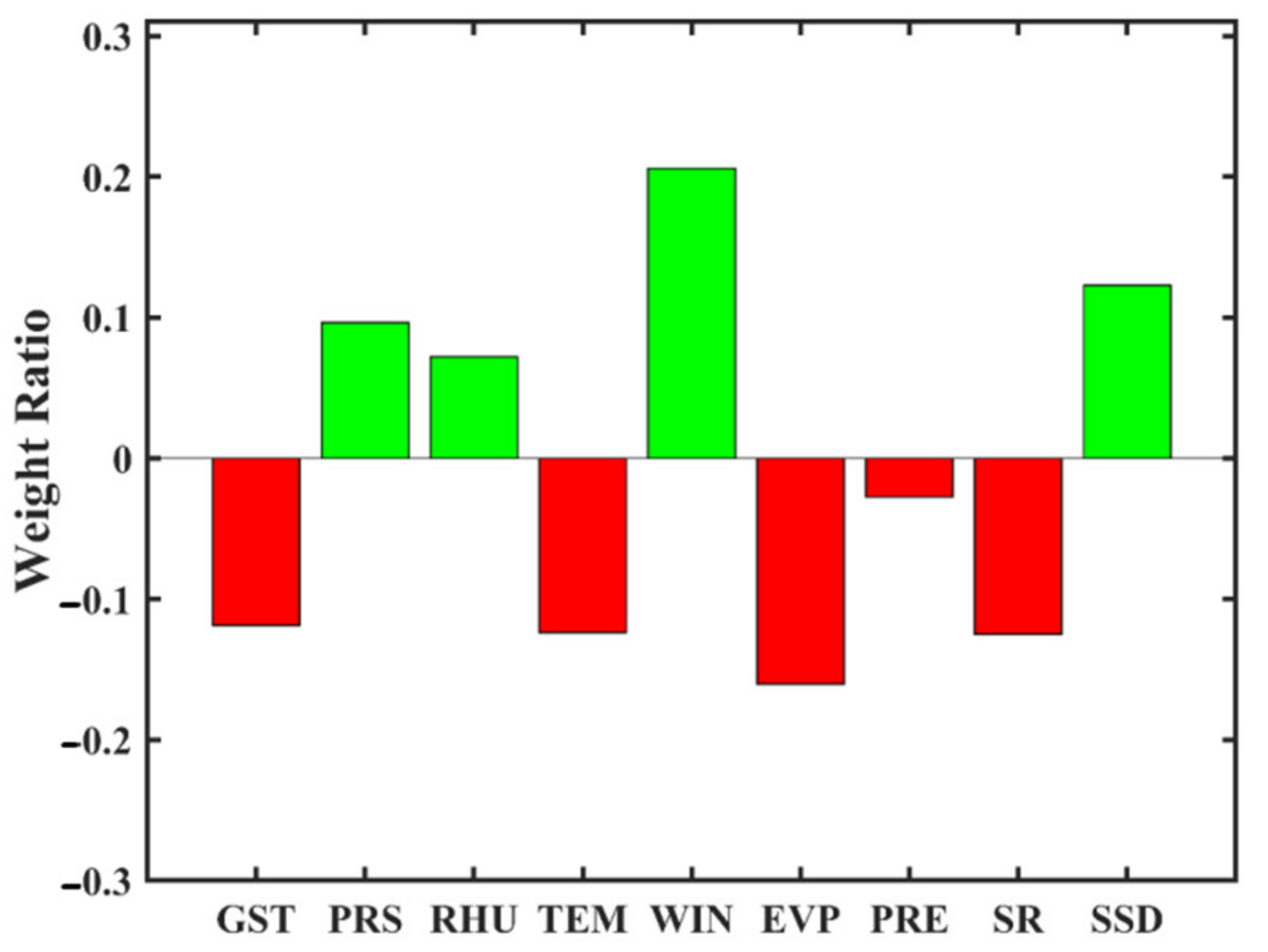
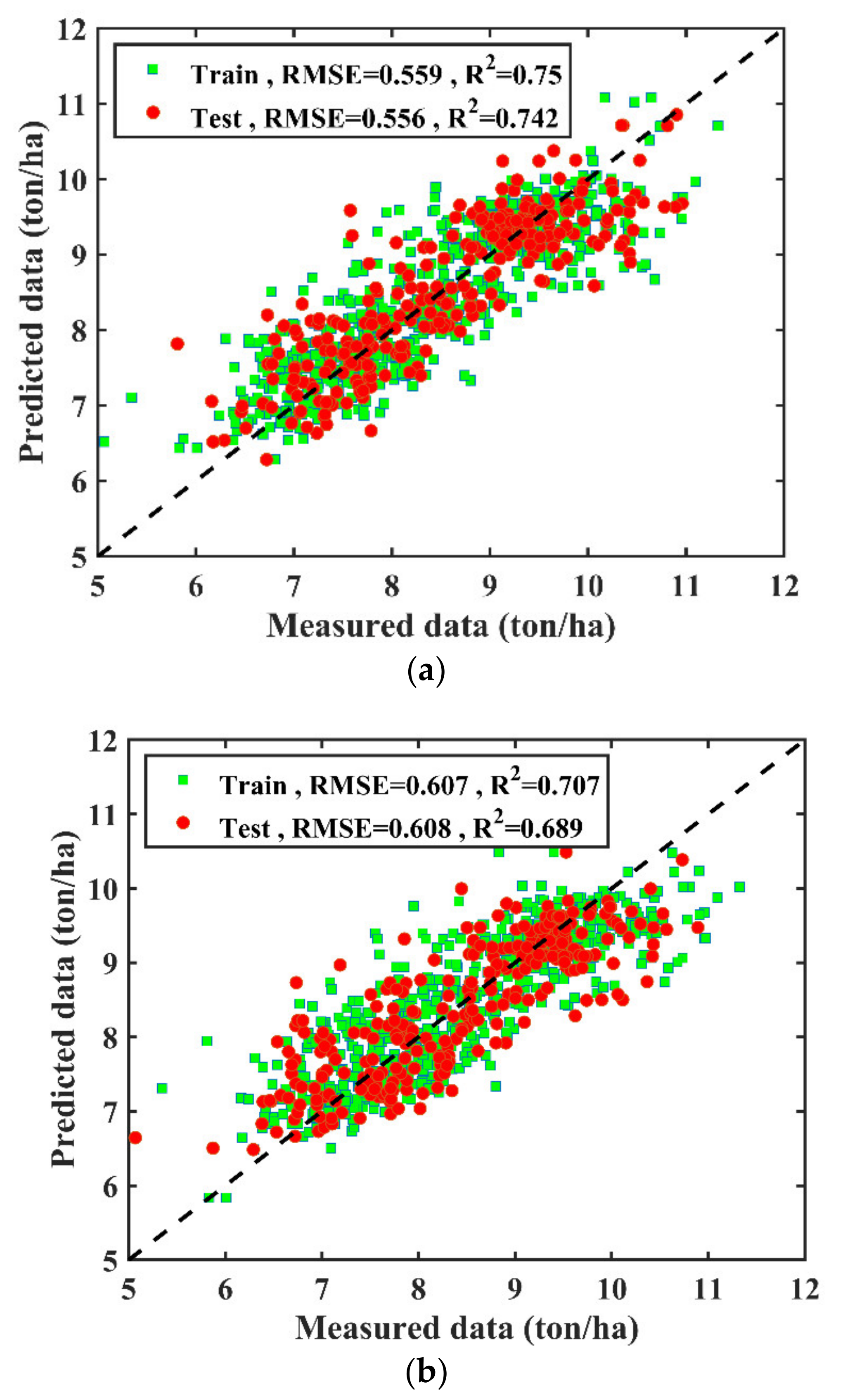
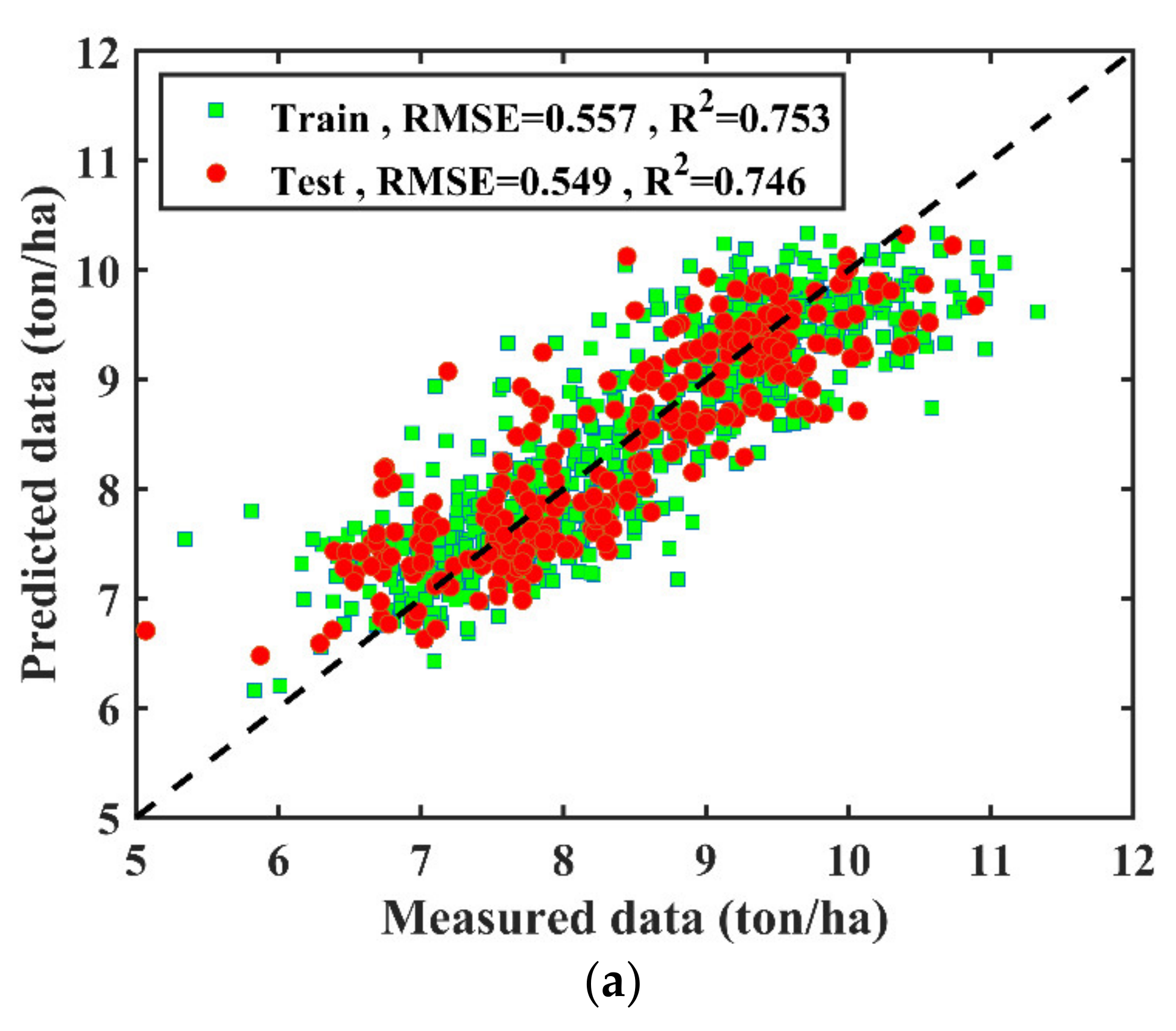
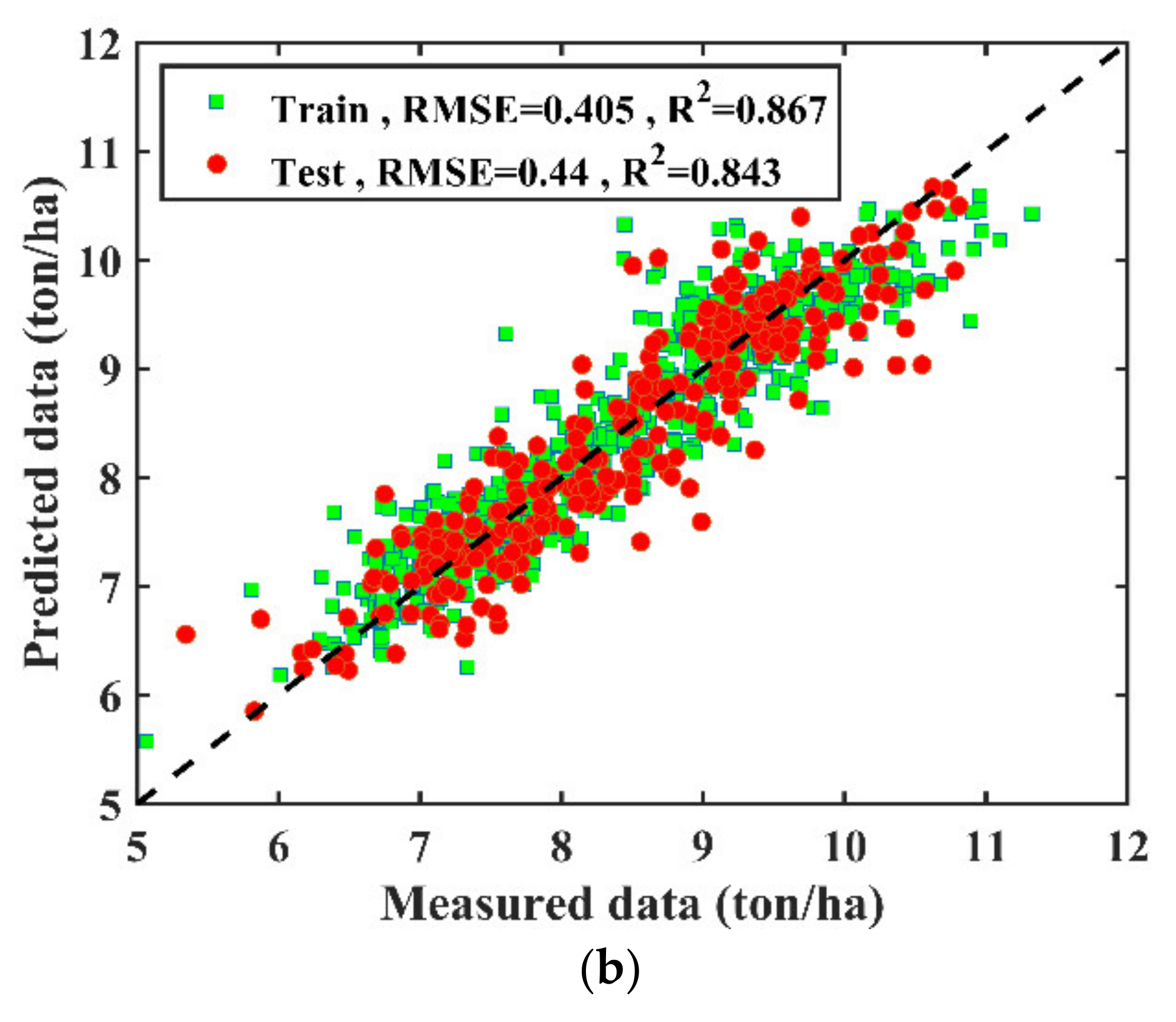
3.1. Climate Data Based Modeling
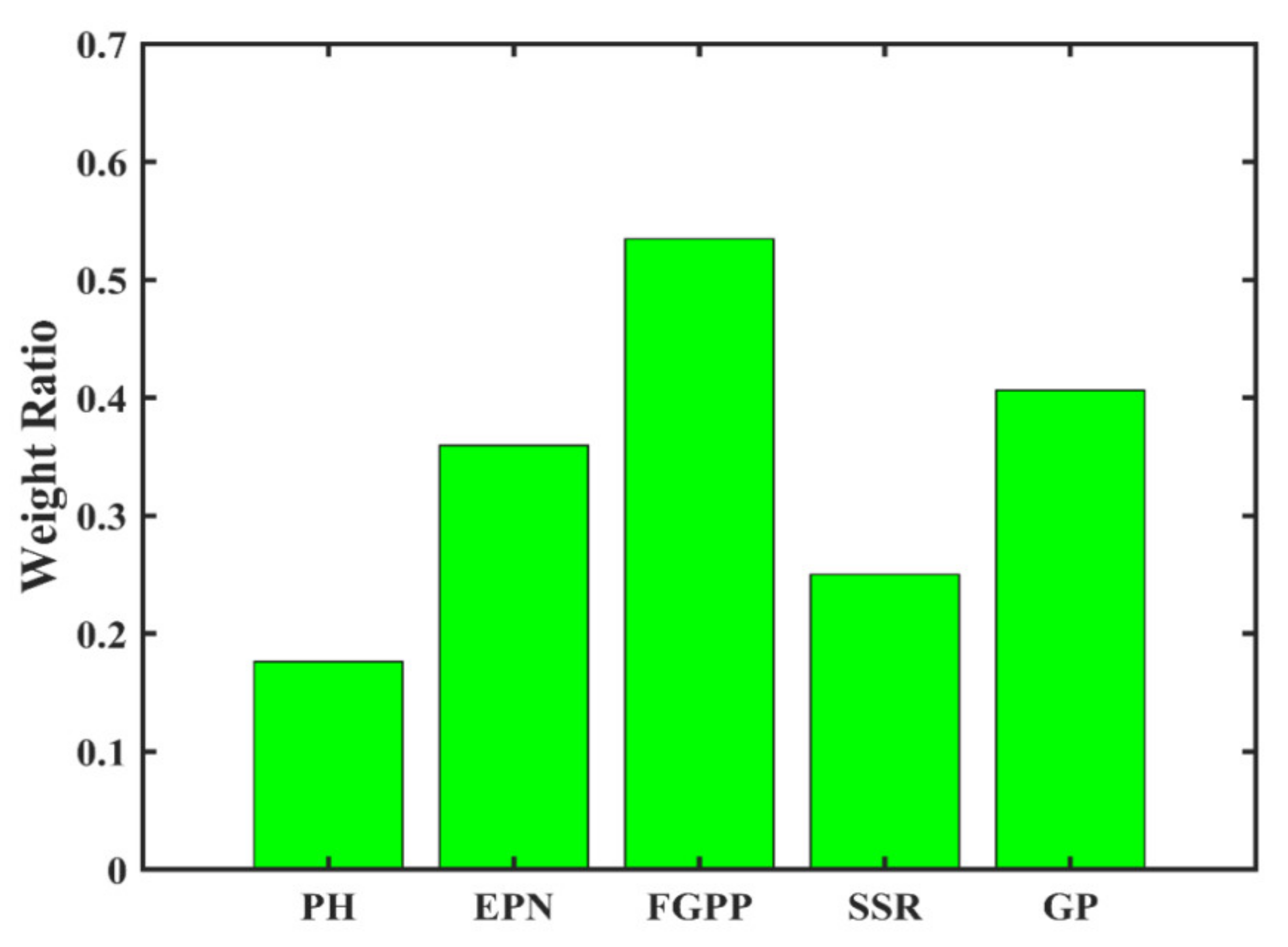
3.2. Agronomic Trait-Based Modeling
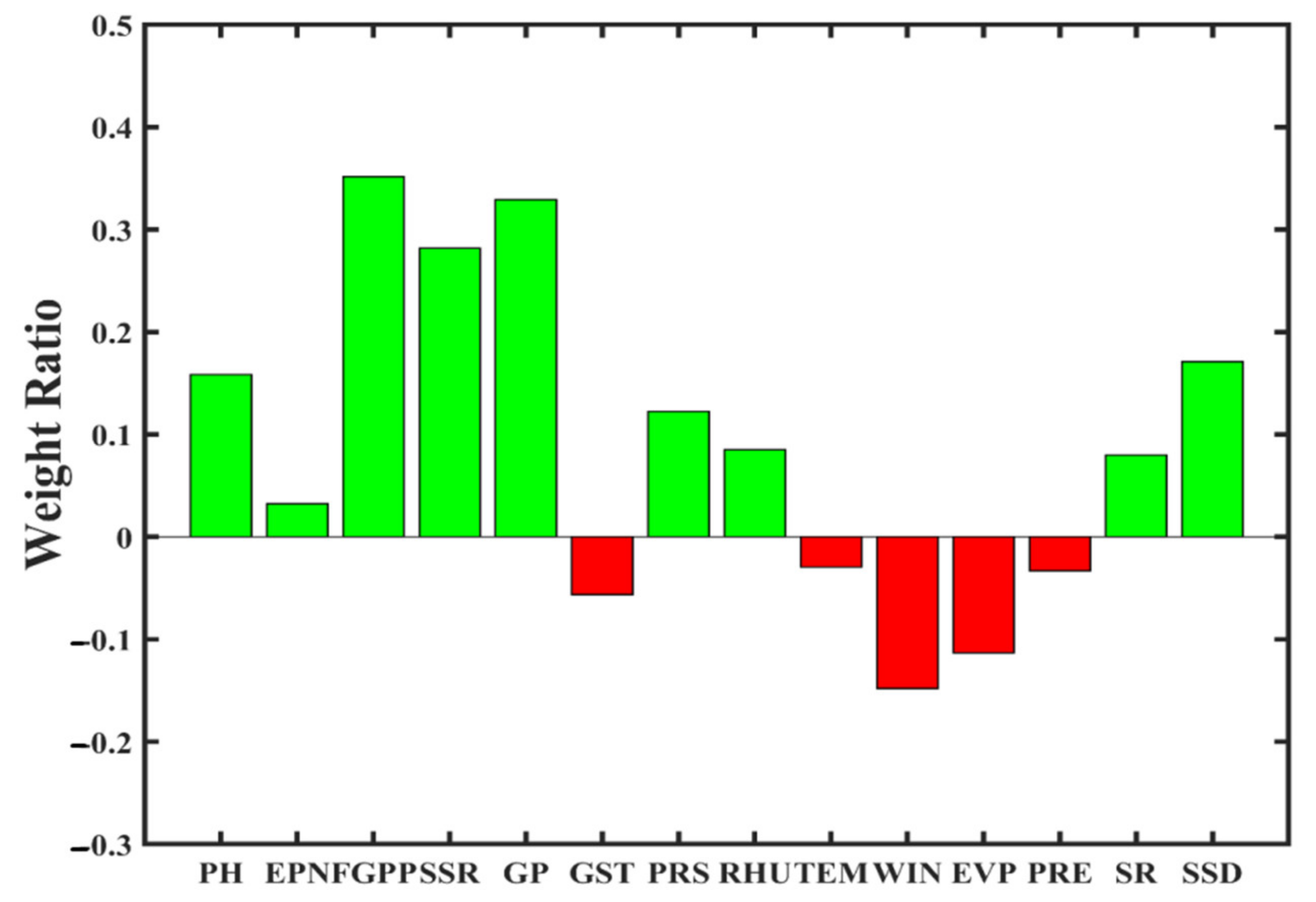
3.3. Climate and Agronomic Traits Data Fused Modelling
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO. Global Climate Changes and Rice Food Security; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Center, A.R. CGIAR Research Program 3.3: GRiSP-A Global Rice Science Partnership. 2010. Available online: https://cgspace.cgiar.org/handle/10947/5312 (accessed on 3 February 2021).
- Cheng, S.H.; Zhuang, J.Y.; Fan, Y.Y.; Du, J.H.; Cao, L.Y. Progress in research and development on hybrid rice: A super-domesticate in China. Ann. Bot. 2007, 100, 959–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, N.-T.; Chen, C.F.; Chen, C.R.; Guo, H.Y.; Cheng, Y.S.; Chen, S.L.; Lin, H.S.; Chen, S.H. Machine learning approaches for rice crop yield predictions using time-series satellite data in Taiwan. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2020, 41, 7868–7888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.A.; Uddin, M.N.; Hossain, M.A.; Jang, Y.M. Predicting rice yield for Bangladesh by exploiting weather conditions. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Information and Communication Technology Convergence (ICTC), Jeju Island, Korea, 18–20 October 2017; pp. 589–594. [Google Scholar]
- Abdipour, M.; Younessi-Hmazekhanlu, M.; Ramazani, S.H.R. Artificial neural networks and multiple linear regression as potential methods for modeling seed yield of safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.). Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 127, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emamgholizadeh, S.; Parsaeian, M.; Baradaran, M. Seed yield prediction of sesame using artificial neural network. Eur. J. Agron. 2015, 68, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantazi, X.E.; Moshou, D.; Alexandridis, T.; Whetton, R.L.; Mouazen, A.M. Wheat yield prediction using machine learning and advanced sensing techniques. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2016, 121, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.J.; Hwang, C.S.; Vlek, P.L.G. Comparison of adaptive techniques to predict crop yield response under varying soil and land management conditions. Agric. Syst. 2005, 85, 59–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabrowska-Zielinska, K.; Kogan, F.; Ciolkosz, A.; Gruszczynska, M.; Kowalik, W. Modelling of crop growth conditions and crop yield in Poland using AVHRR-based indices. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2002, 23, 1109–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Liang, S.; Hoogenboom, G.; Teasdale, J.; Cavigelli, M. Corn-yield estimation through assimilation of remotely sensed data into the CSM-CERES-Maize model. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 3011–3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bala, S.K.; Islam, A.S. Correlation between potato yield and MODIS-derived vegetation indices. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 30, 2491–2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mkhabela, M.S.; Bullock, P.; Raj, S.; Wang, S.; Yang, Y. Crop yield forecasting on the Canadian Prairies using MODIS NDVI data. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2011, 151, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, N.T.; Chen, C.F.; Chen, C.R.; Minh, V.Q.; Trung, N.H. A comparative analysis of multitemporal MODIS EVI and NDVI data for large-scale rice yield estimation. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2014, 197, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boser, B.E.; Guyon, I.M.; Vapnik, V.N. A training algorithm for optimal margin classifiers. In Proceedings of the Fifth Annual Workshop on Computational Learning Theory, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 27–29 July 1992; pp. 144–152. [Google Scholar]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liakos, K.G.; Busato, P.; Moshou, D.; Pearson, S.; Bochtis, D. Machine learning in agriculture: A review. Sensors 2018, 18, 2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mountrakis, G.; Im, J.; Ogole, C. Support vector machines in remote sensing: A review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2011, 66, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, C.; Tang, D.; Zhou, J.; Wang, H.; Shaviv, A. Prediction of nitrate release from polymer-coated fertilizers using an artificial neural network model. Biosyst. Eng. 2008, 99, 478–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kung, H.-Y.; Kuo, T.-H.; Chen, C.-H.; Tsai, P.-Y. Accuracy analysis mechanism for agriculture data using the ensemble neural network method. Sustainability 2016, 8, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wei, S.; Jiao, W.; Qi, G.; Liu, Y. Modelling of adsorption in rotating packed bed using artificial neural networks (ANN). Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2016, 114, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.-W.; Liang, F.-N.; Liu, Y.-Z. Artificial neural network modeling of biosorption process using agricultural wastes in a rotating packed bed. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2018, 140, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, B.T.; Nguyen, M.D.; Bui, K.-T.T.; Prakash, I.; Chapi, K.; Bui, D.T. A novel artificial intelligence approach based on Multi-layer Perceptron Neural Network and Biogeography-based Optimization for predicting coefficient of consolidation of soil. Catena 2019, 173, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Su, Y.; Tao, W. Mass transfer performance of CO2 capture in rotating packed bed: Dimensionless modeling and intelligent prediction. Appl. Energy 2014, 136, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Freitas, E.C.S.; de Paiva, H.N.; Neves, J.C.L.; Marcatti, G.E.; Leite, H.G. Modeling of eucalyptus productivity with artificial neural networks. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilardelli, C.; Stella, T.; Frasso, N.; Cappelli, G.; Bregaglio, S.; Chiodini, M.E.; Scaglia, B.; Confalonieri, R. WOFOST-GTC: A new model for the simulation of winter rapeseed production and oil quality. Field Crops Res. 2016, 197, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niazian, M.; Sadat-Noori, S.A.; Abdipour, M. Modeling the seed yield of Ajowan (Trachyspermum ammi L.) using artificial neural network and multiple linear regression models. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 117, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meshram, S.G.; Singh, V.P.; Kisi, O.; Karimi, V.; Meshram, C. Application of artificial neural networks, support vector machine and multiple model-ann to sediment yield prediction. Water Resour. Manag. 2020, 34, 4561–4575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdi, H. Partial least squares regression and projection on latent structure regression (PLS Regression). Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Comput. Stat. 2010, 2, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, A.K.; Bhan, M.; Agrawal, K.K. Districtwise wheat and rice yield predictions using meteorological variables in eastern Madhya Pradesh. J. Agrometeorol. 2017, 19, 366–368. [Google Scholar]
- Dhekale, B.S.; Nageswararao, M.M.; Nair, A.; Mohanty, U.C.; Swain, D.K.; Singh, K.K.; Arunbabu, T. Prediction of kharif rice yield at Kharagpur using disaggregated extended range rainfall forecasts. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2018, 133, 1075–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakhee; Singh, A.; Kumar, A. Weather based fuzzy regression models for prediction of rice yield. J. Agrometeorol. 2018, 20, 297–301. [Google Scholar]
- Biswas, R.; Bhattacharyya, B. Rice yield prediction in lower Gangetic Plain of India through multivariate approach and multiple regression analysis. J. Agrometeorol. 2019, 21, 101–103. [Google Scholar]
- Das, B.; Nair, B.; Reddy, V.; Venkatesh, P. Evaluation of multiple linear, neural network and penalised regression models for prediction of rice yield based on weather parameters for west coast of India. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2018, 62, 1809–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lee, J.; Sang, W.G.; Shin, P.; Cho, H.; Seo, M.C. Rice yield prediction in South Korea by using random forest. Korean J. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2019, 21, 75–84. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Fu, Y.; Hao, F.; Zhang, X.; Wu, W.; Jin, X.; Robin Bryant, C.; Senthilnath, J. Integrated phenology and climate in rice yields prediction using machine learning methods. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variables | Synonym | Min | Max | Mean | Std | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agronomic Traits | Plant height (cm) | PH | 75.10 | 143.5 | 106.9 | 14.43 |
| Effective panicle number (ten thousands/hm2) | EPN | 160.5 | 441.0 | 276.2 | 49.67 | |
| Filled grains per panicle (grains) | FGPP | 73.90 | 273.70 | 143.60 | 43.21 | |
| Seed set rate (%) | SSR | 0.66 | 0.95 | 0.84 | 0.05 | |
| Growth period (day) | GP | 105.1 | 179.5 | 133.1 | 15.22 | |
| ClimateData | Ground surface temperature (°C) | GST | 17.25 | 23.53 | 20.18 | 1.54 |
| Pressure of the station (hPa) | PRS | 983.3 | 1015.5 | 999.4 | 9.31 | |
| Relative humidity (%) | RHU | 69.32 | 81.35 | 75.56 | 2.87 | |
| Temperature (°C) | TEM | 15.24 | 20.40 | 17.71 | 1.40 | |
| Wind speed (m/s) | WIN | 1.37 | 3.30 | 2.15 | 0.45 | |
| Evaporation (mm) | EVP | 1.63 | 3.60 | 2.53 | 0.38 | |
| Precipitation (mm) | PRE | 2.47 | 6.86 | 4.45 | 1.06 | |
| Solar radiation (MJ/m2) | SR | 9.83 | 22.03 | 13.71 | 2.26 | |
| Sunshine duration (hour) | SSD | 4.04 | 6.20 | 4.84 | 0.49 | |
| Rice Yield | Rice yield (ton/ha) | YIELD | 5.07 | 11.30 | 8.48 | 1.11 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, Y.; Xiang, H.; Li, Z.; Ma, F.; Du, C. Prediction of Rice Yield in East China Based on Climate and Agronomic Traits Data Using Artificial Neural Networks and Partial Least Squares Regression. Agronomy 2021, 11, 282. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11020282
Guo Y, Xiang H, Li Z, Ma F, Du C. Prediction of Rice Yield in East China Based on Climate and Agronomic Traits Data Using Artificial Neural Networks and Partial Least Squares Regression. Agronomy. 2021; 11(2):282. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11020282
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Yuming, Haitao Xiang, Zhenwang Li, Fei Ma, and Changwen Du. 2021. "Prediction of Rice Yield in East China Based on Climate and Agronomic Traits Data Using Artificial Neural Networks and Partial Least Squares Regression" Agronomy 11, no. 2: 282. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11020282
APA StyleGuo, Y., Xiang, H., Li, Z., Ma, F., & Du, C. (2021). Prediction of Rice Yield in East China Based on Climate and Agronomic Traits Data Using Artificial Neural Networks and Partial Least Squares Regression. Agronomy, 11(2), 282. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11020282







