Lead (Pb)-Induced Oxidative Stress Alters the Morphological and Physio-Biochemical Properties of Rice (Oryza sativa L.)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials, Growth Conditions, and Lead Application
2.2. Sampling and Phenotypic Evaluation under Lead Treatment
2.3. Chlorophyll Content Determination and Panicle Length Measurement
2.4. Estimation of Electrolyte Leakage
2.5. Proline Measurement Assay
2.6. Enzymatic Antioxidant Assay, Protein, DAB Staining, and Soluble Sugar Contents
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
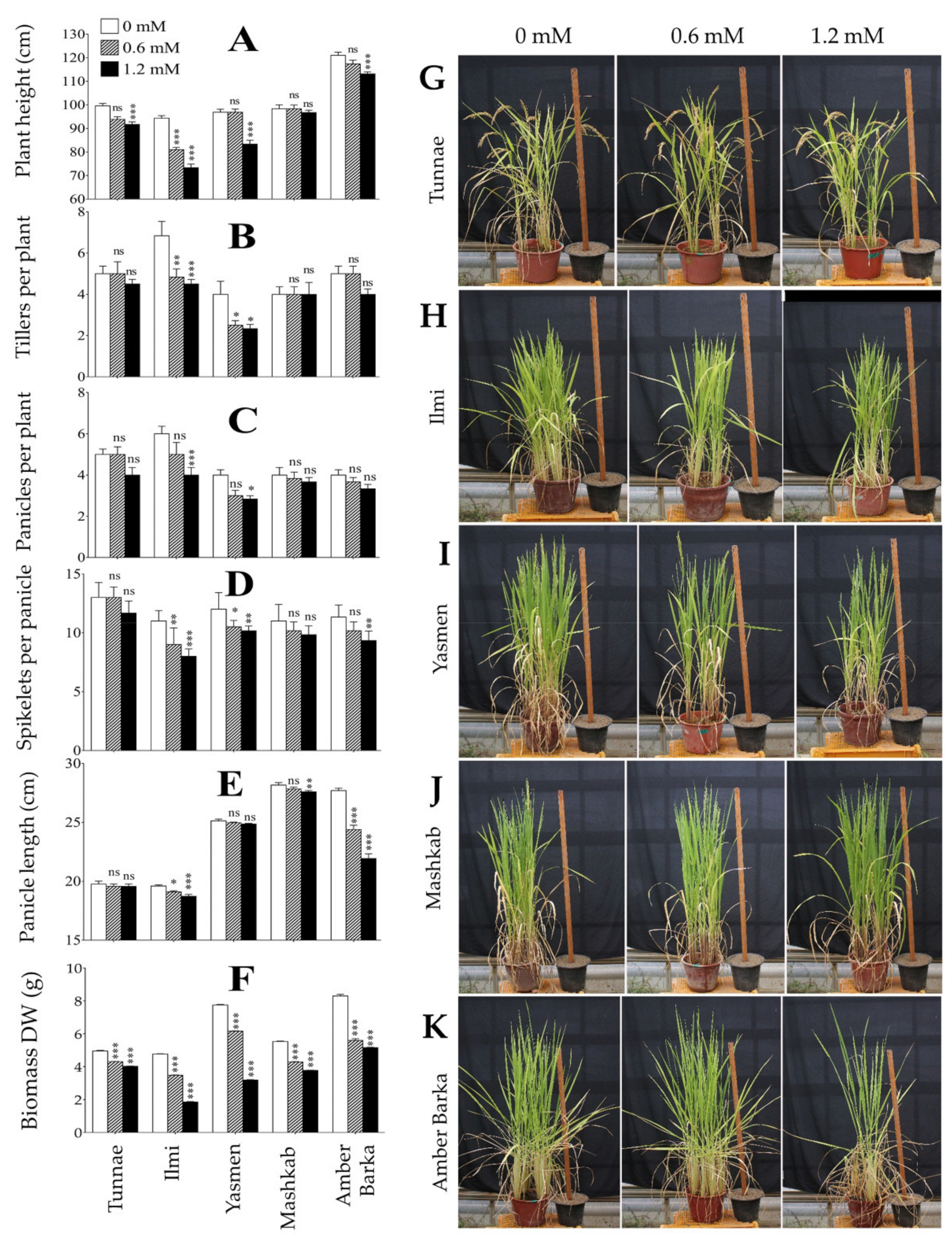
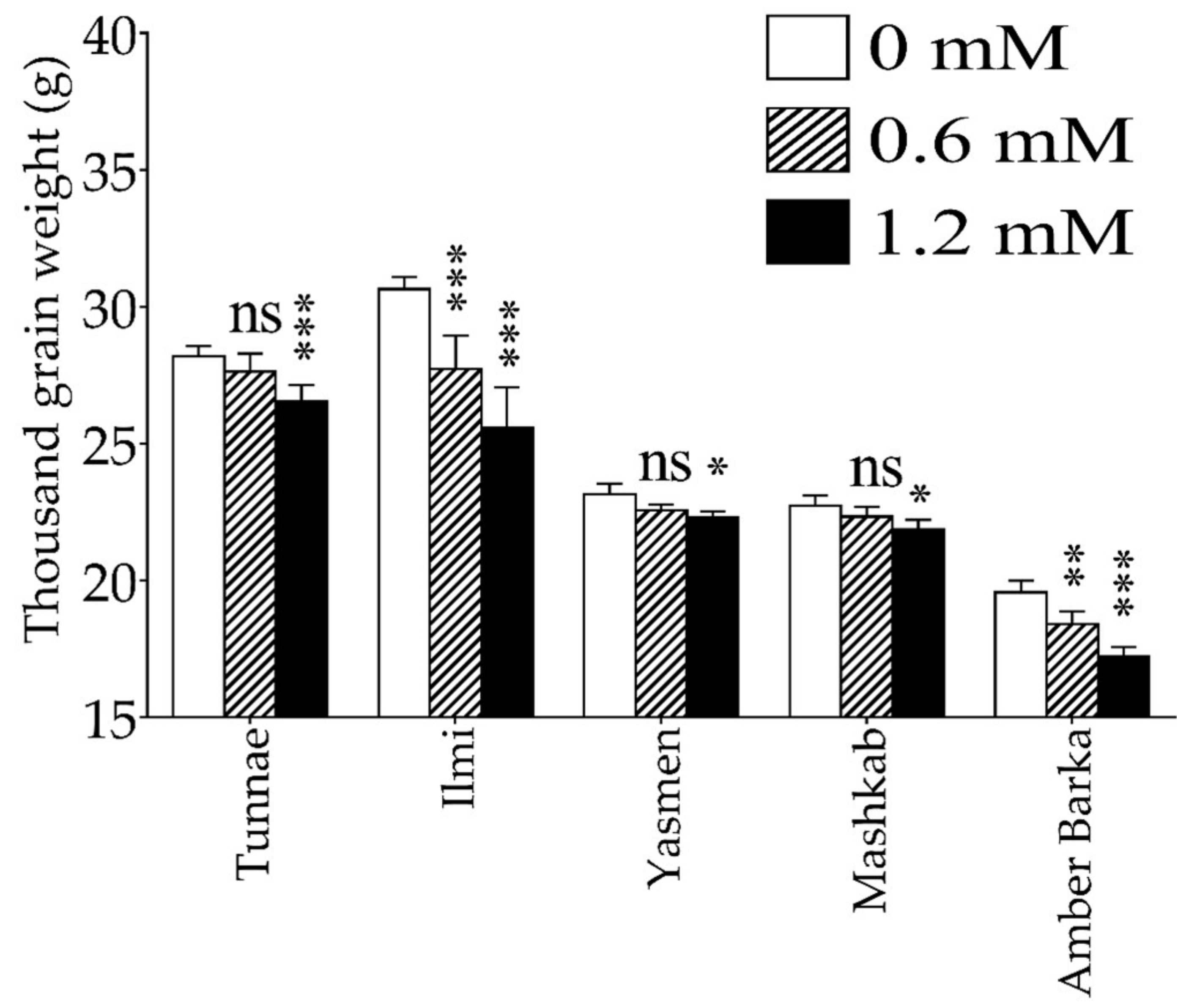
3.1. Lead-Induced Oxidative Stress Inhibited Plant Growth, and Reduced Rice Productivity and Biomass
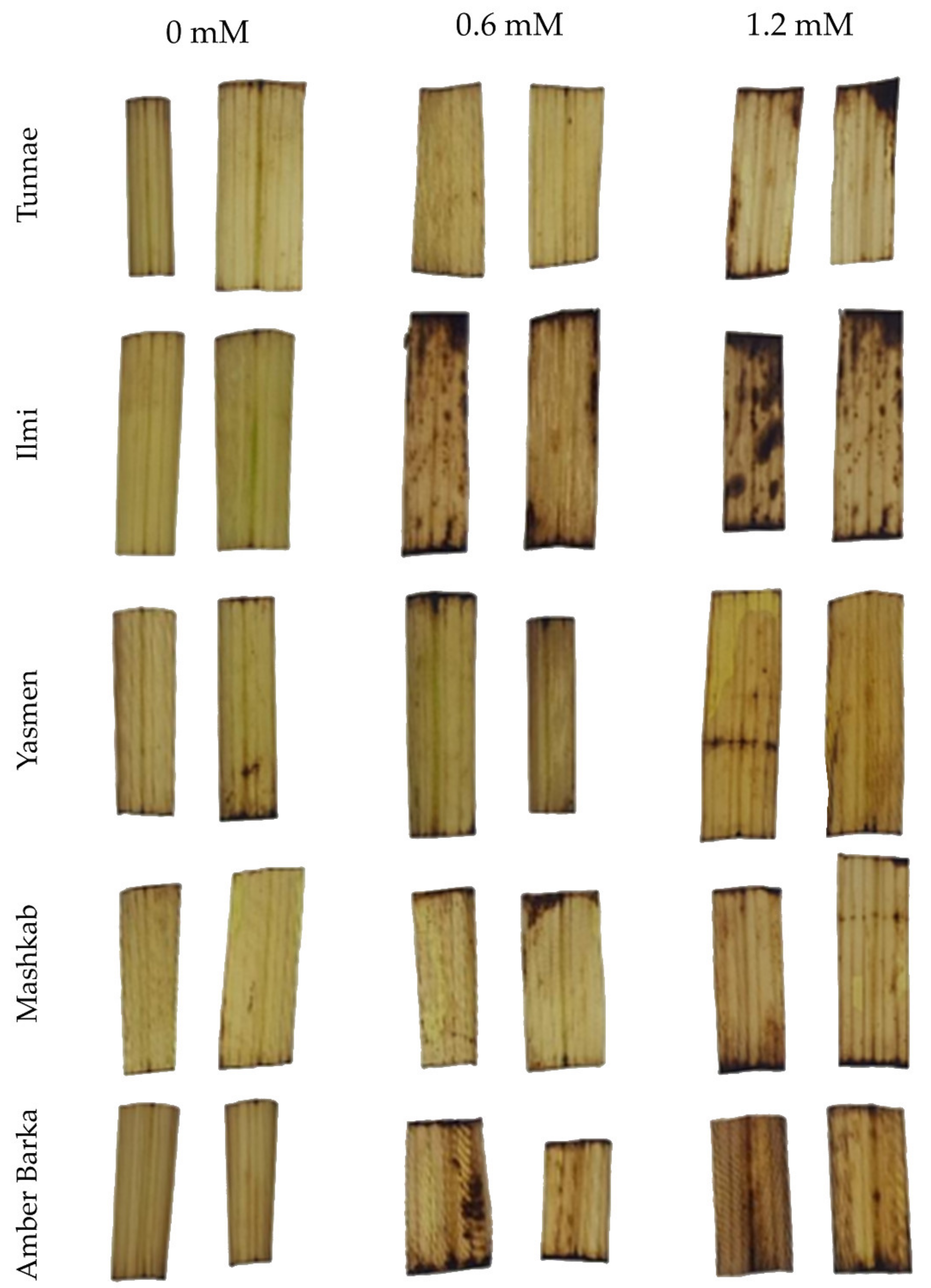
3.2. Lead-Induced Oxidative Stress Triggered Hydrogen Peroxide Accumulation and Activated Antioxidant Enzymes
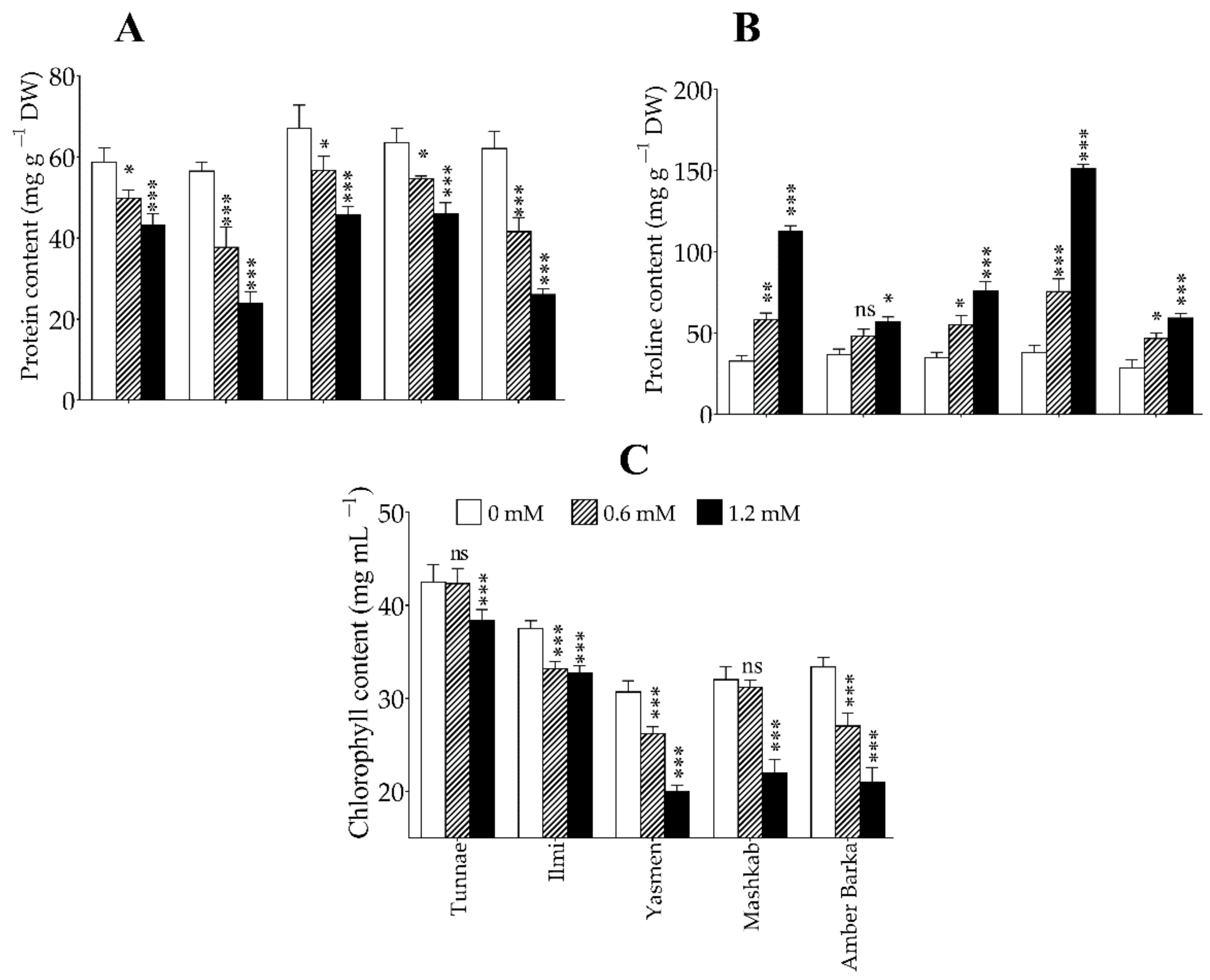
3.3. Application of Lead Reduced Protein and Chlorophyll Accumulation, and Increased Proline Content
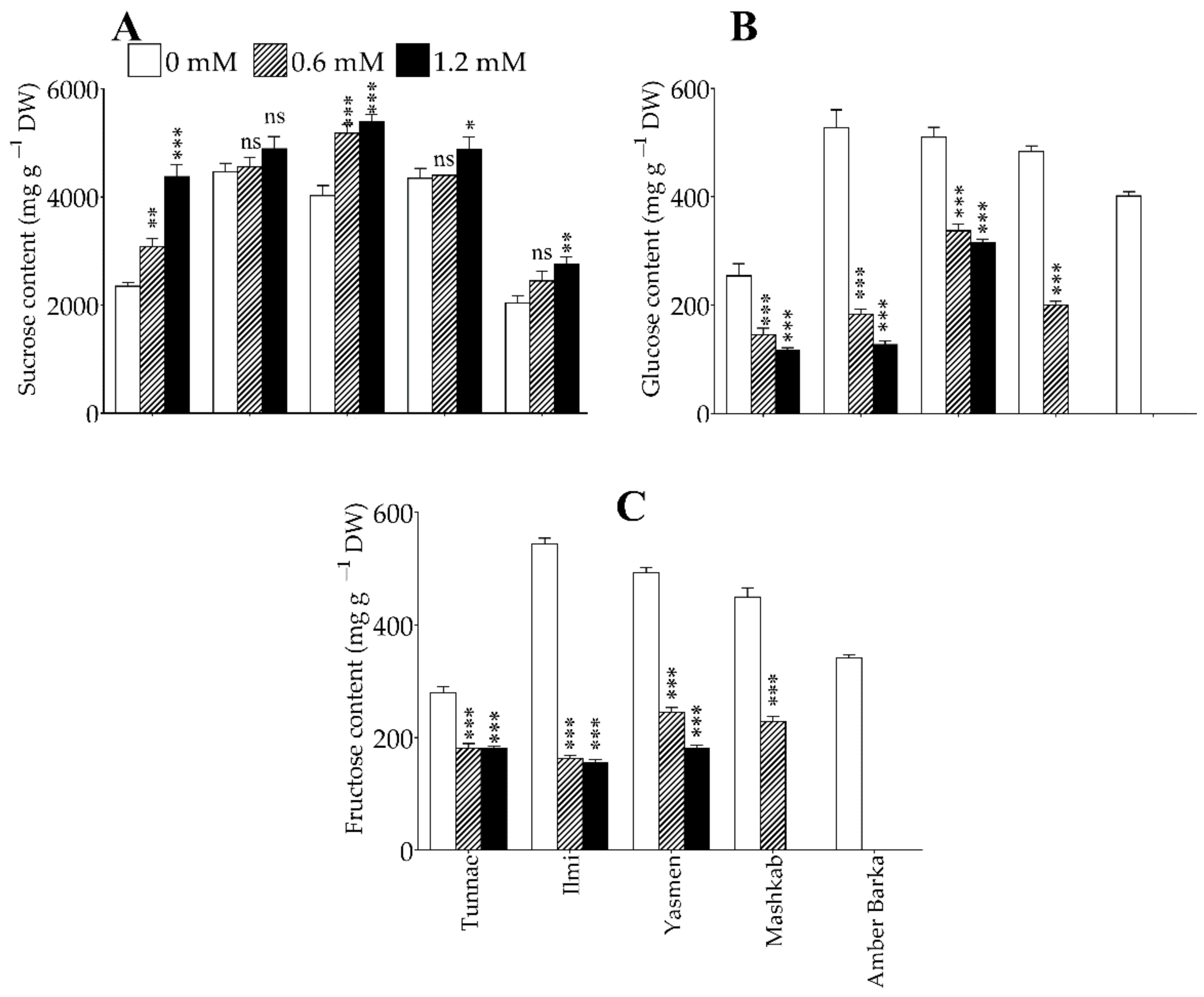
3.4. Lead Application Differentially Affected Soluble Sugar Levels in Rice
4. Discussion
4.1. Exogenous Application of Lead Inhibits Plant Growth and Reduces Productivity of Rice
4.2. Lead-Mediated Oxidative Stress Alters the Physiological and Biochemical Properties of Rice
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anjum, S.A.; Ashraf, U.; Khan, I.; Tanveer, M.; Ali, M.; Hussain, I.; Wang, L.C. Chromium and aluminum phytotoxicity in maize: Morpho—Physiological responses and metal uptake. CLEAN Soil Air Water 2016, 44, 1075–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.M.; Zhang, C.; Qiu, B.L.; Ashraf, U.; Azad, R.; Wu, J.H.; Ali, S. Biotransfer of Cd along a soil-plant- mealybug-ladybird food chain: A comparison with host plants. Chemosphere 2017, 168, 699–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.Z.; Shi, G.X.; Xu, Q.S.; Wang, X.; Yuan, Q.H.; Du, K.H. Effects of Pb2+ on the active oxygen-scavenging enzyme activities and ultrastructure in Potamogeton crispus leaves. Russ. J. Plant Physiol. 2007, 54, 414–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Gou, X.; Wang, G.; Zhang, Q.; Su, Q.; Xiao, G. Heavy metal contamination and source in arid agricultural soil in central Gansu Province, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2008, 20, 607–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimm, N.B.; Foster, D.; Groffman, P.; Grove, J.M.; Hopkinson, C.S.; Nadelhoffer, K.J.; Pataki, D.E.; Peters, D.P.C. The changing landscape: Ecosystem responses to urbanization and pollution across climatic and societal gradients. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2008, 6, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gaya, U.; Ikechukwu, S. Heavy metal contamination of selected spices obtained from Nigeria. J. Appl. Sci. Environ. Manag. 2016, 20, 681–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Islam, E.; Yang, X.; Li, T.Q.; Liu, D.; Jin, X.F.; Meng, F.H. Effect of Pb toxicity on root morphology, physiology and ultrastructure in the two ecotypes of Elsholtzia argyi. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 147, 806–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzu, G.; Sobanska, S.; Aliouane, Y.; Pradere, P.; Dumat, C.J.E.P. Study of lead phytoavailability for atmospheric industrial micronic and sub-micronic particles in relation with lead speciation. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 1178–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dogan, M.; Saygideger, S.D.; Colak, U. Effect of Lead Toxicity on Aquatic Macrophyte Elodea canadensis Michx. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2009, 83, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, D.K.; Nicoloso, F.T.; Schetinger, M.R.C.; Rossato, L.V.; Pereira, L.B.; Castro, G.Y.; Srivastava, S.; Tripathi, R.D. Antioxidant defense mechanism in hydroponically grown Zea mays seedlings under moderate lead stress. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 172, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maestri, E.; Marmiroli, M.; Visioli, G.; Marmiroli, N. Metal tolerance and hyperaccumulation: Costs and trade-offs between traits and environment. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2010, 68, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, U.; Kanu, A.S.; Mo, Z.W.; Hussain, S.; Anjum, S.A.; Khan, I.; Abbas, R.N.; Tang, X.R. Lead toxicity in rice: Effects, mechanisms, and mitigation strategies-a mini review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. R 2015, 22, 18318–18332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, S.; Dubey, R.S. Lead toxicity induces lipid peroxidation and alters the activities of antioxidant enzymes in growing rice plants. Plant Sci. 2003, 164, 645–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemens, S. Evolution and function of phytochelatin synthases. J. Plant Physiol. 2006, 163, 319–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittler, R.J. Oxidative stress, antioxidants and stress tolerance. Trends Plant Sci. 2002, 7, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, B.; Xu, X.; Gill, R.A.; Yang, S.; Ali, S.; Tahir, M.; Zhou, W.J. Promotive role of 5-aminolevulinic acid on mineral nutrients and antioxidative defense system under lead toxicity in Brassica napus. Ind. Crops Prod. 2014, 52, 617–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.; Choudhuri, M.J. Amelioration of lead and mercury effects on germination and rice seedling growth by antioxidants. Biol. Plant. 1998, 41, 469–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.S.; Liu, D.H. Pb-induced cellular defense system in the root meristematic cells of Allium sativum L. BMC Plant Biol. 2010, 10, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheng, W.D.; Zhang, G.P.; Yao, H.G.; Wu, W.; Xu, M. Genotypic and environmental variation in cadmium, chromium, arsenic, nickel, and lead concentrations in rice grains. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2006, 7, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davis, J.M.; Elias, R.W.; Grant, L.D. Current Issues in Human Lead-Exposure and Regulation of Lead. Neurotoxicology 1993, 14, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, L.; Bian, X.; Zhang, W. Source attributions of heavy metals in rice plant along highway in Eastern China. J. Environ. Sci. 2011, 23, 1158–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.G.; Ma, X.M.; Wang, M.X.; Sun, X.W. Genotypic differences among rice cultivars in lead accumulation and translocation and the relation with grain Pb levels. Ecotox. Environ. Safe 2013, 90, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, F.M.; Zhao, N.C.; Xu, H.M.; Li, Y.; Zhang, W.F.; Zhu, Z.W.; Chen, M.X. Cadmium and lead contamination in japonica rice grains and its variation among the different locations in southeast China. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 359, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, C.; Dube, B.K.; Sinha, P.; Srivastava, P. Detrimental effects of lead phytotoxicity on growth, yield, and metabolism of rice. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2004, 35, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourrut, B.; Shahid, M.; Dumat, C.; Winterton, P.; Pinelli, E. Lead Uptake, Toxicity, and Detoxification in Plants. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. Vol. 2011, 213, 113–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rolly, N.K.; Imran, Q.M.; Shahid, M.; Imran, M.; Khan, M.; Lee, S.-U.; Hussain, A.; Lee, I.-J.; Yun, B.-W.J. Drought-induced AtbZIP62 transcription factor regulates drought stress response in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 156, 384–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashraf, U.; Hussain, S.; Anjum, S.A.; Abbas, F.; Tanveer, M.; Noor, M.A.; Tang, X.J. Alterations in growth, oxidative damage, and metal uptake of five aromatic rice cultivars under lead toxicity. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 115, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ubaidillah, M.; Faperta, M.; Kim, K.-M. Identification of phytohormone changes and its related genes under abiotic stresses in transgenic rice. Biocell 2019, 43, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badro, H.; Furtado, A.; Henry, R. Relationships between Iraqi Rice Varieties at the Nuclear and Plastid Genome Levels. Plants 2019, 8, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, J.-W.; Kabange, N.R.; Phyo, Z.; Park, S.-Y.; Lee, S.-M.; Lee, J.-Y.; Shin, D.; Cho, J.H.; Park, D.-S.; Ko, J.-M.; et al. Combined Linkage Mapping and Genome-Wide Association Study Identified QTLs Associated with Grain Shape and Weight in Rice (Oryza Sativa L.). Agronomy 2020, 10, 1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Asaf, S.; Khan, A.L.; Adhikari, A.; Jan, R.; Ali, S.; Imran, M.; Kim, K.M.; Lee, I.J. Halotolerant Rhizobacterial Strains Mitigate the Adverse Effects of NaCl Stress in Soybean Seedlings. Biomed. Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 9530963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khan, M.; Imran, Q.M.; Shahid, M.; Mun, B.G.; Lee, S.U.; Khan, M.A.; Hussain, A.; Lee, I.J.; Yun, B.W. Nitric oxide- induced AtAO3 differentially regulates plant defense and drought tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bates, L.S.; Waldren, R.P.; Teare, I. Rapid determination of free proline for water-stress studies. Plant Soil 1973, 39, 205–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.R.; Ullah, I.; Waqas, M.; Park, G.S.; Khan, A.L.; Hong, S.J.; Ullah, R.; Jung, B.K.; Park, C.E.; Ur-Rehman, S.; et al. Host plant growth promotion and cadmium detoxification in Solanum nigrum, mediated by endophytic fungi. Ecotox. Environ. Safe 2017, 136, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirhindi, G.; Mir, M.A.; Abd-Allah, E.F.; Ahmad, P.; Gucel, S. Jasmonic Acid Modulates the Physio-Biochemical Attributes, Antioxidant Enzyme Activity, and Gene Expression in Glycine max under Nickel Toxicity. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chance, B.; Maehly, A. Assay of catalases and peroxidases. Methods Enzymol. 1955, 2, 764–775. [Google Scholar]
- De Sousa, A.; AbdElgawad, H.; Asard, H.; Pinto, A.; Soares, C.; Branco-Neves, S.; Braga, T.; Azenha, M.; Selim, S.; Al Jaouni, S. Metalaxyl effects on antioxidant defenses in leaves and roots of Solanum Nigrum L. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jambunathan, N. Determination and detection of reactive oxygen species (ROS), lipid peroxidation, and electrolyte leakage in plants. In Plant Stress Tolerance; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 291–297. [Google Scholar]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yemm, E.W.; Willis, A.J. The estimation of carbohydrates in plant extracts by anthrone. Biochem. J. 1954, 57, 508–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alloway, B.J. Heavy Metals in Soils: Trace Metals and Metalloids in Soils and their Bioavailability; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; Volume 22. [Google Scholar]
- Bunzl, K.; Schmidt, W.; Sansoni, B.J. Kinetics of ion exchange in soil organic matter. IV. Adsorption and desorption of Pb2+, Cu2+, Cd2+, Zn2+ and Ca2+ by peat. J. Soil Sci. 1976, 27, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerndorff, H.; Schnitzer, M.J. Sorption of metals on humic acid. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1980, 44, 1701–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, L.; Clement, C.; Hopper, M.J. Lead uptake from solution by perennial ryegrass and its transport from roots to shoots. Plant Soil 1973, 38, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yang, X.; He, Z.; Jilani, G.; Sun, C.; Chen, S.J. Fractionation of lead in paddy soils and its bioavailability to rice plants. Geoderma 2007, 141, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koeppe, D.E.J. The uptake, distribution, and effect of cadmium and lead in plants. Sci. Total Environ. 1977, 7, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourrut, B.; Shahid, M.; Dumat, C.; Winterton, P.; Pinelli, E. Lead uptake, toxicity, and detoxification in plants. In Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; Volume 213, pp. 113–136. [Google Scholar]
- Ashraf, U.; Kanu, A.S.; Deng, Q.; Mo, Z.; Pan, S.; Tian, H.; Tang, X.J. Lead (Pb) toxicity; physio-biochemical mechanisms, grain yield, quality, and Pb distribution proportions in scented rice. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoon, J.; Cao, X.; Zhou, Q.; Ma, L.Q. Accumulation of Pb, Cu, and Zn in native plants growing on a contaminated Florida site. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 368, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rout, G.R.; Samantaray, S.; Das, P. Differential lead tolerance of rice and black gram genotypes in hydroponic culture. Rost Vyroba 2001, 47, 541–548. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, S.; Parihar, P.; Singh, R.; Singh, V.P.; Prasad, S.M. Heavy metal tolerance in plants: Role of transcriptomics, proteomics, metabolomics, and ionomics. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 6, 1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Al Azzawi, T.N.I.; Khan, M.; Hussain, A.; Shahid, M.; Imran, Q.M.; Mun, B.-G.; Lee, S.-U.; Yun, B.-W.J. Evaluation of Iraqi Rice Cultivars for Their Tolerance to Drought Stress. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibra, M. Effects of mercury on some growth parameters of rice (Oryza Sativa L.). Soil Environ. 2008, 27, 23–28. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Branicky, R.; Noë, A.; Hekimi, S.J. Superoxide dismutases: Dual roles in controlling ROS damage and regulating ROS signaling. J. Cell Biol. 2018, 217, 1915–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, P.; Jha, A.B.; Dubey, R.S.; Pessarakli, M.J. Reactive oxygen species, oxidative damage, and antioxidative defense mechanism in plants under stressful conditions. J. Bot. 2012, 2012, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beckman, J.S.; Koppenol, W.H. Nitric oxide, superoxide, and peroxynitrite: The good, the bad, and ugly. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 1996, 271, C1424–C1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamada, M.; Morishita, H.; Urano, K.; Shiozaki, N.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K.; Shinozaki, K.; Yoshiba, Y. Effects of free proline accumulation in petunias under drought stress. J. Exp. Bot. 2005, 56, 1975–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.T.; Chen, L.-M.; Lin, C.C.; Kao, C.H. Regulation of proline accumulation in detached rice leaves exposed to excess copper. Plant Sci. 2001, 160, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Serrano, M.; Romero-Puertas, M.C.; Pazmino, D.M.; Testillano, P.S.; Risueño, M.C.; Luis, A.; Sandalio, L.M. Cellular response of pea plants to cadmium toxicity: Cross talk between reactive oxygen species, nitric oxide, and calcium. Plant Physiol. 2009, 150, 229–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Devi, R.; Munjral, N.; Gupta, A.K.; Kaur, N. Effect of exogenous lead on growth and carbon metabolism of pea (Pisum Sativum L.) seedlings. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plant. 2013, 19, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, S.; Dubey, R.S.; Tripathi, R.D.; Chakrabarty, D.; Trivedi, P.K. Omics and biotechnology of arsenic stress and detoxification in plants: Current updates and prospective. Environ. Int. 2015, 74, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khan, M.; Rolly, N.K.; Al Azzawi, T.N.I.; Imran, M.; Mun, B.-G.; Lee, I.-J.; Yun, B.-W. Lead (Pb)-Induced Oxidative Stress Alters the Morphological and Physio-Biochemical Properties of Rice (Oryza sativa L.). Agronomy 2021, 11, 409. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11030409
Khan M, Rolly NK, Al Azzawi TNI, Imran M, Mun B-G, Lee I-J, Yun B-W. Lead (Pb)-Induced Oxidative Stress Alters the Morphological and Physio-Biochemical Properties of Rice (Oryza sativa L.). Agronomy. 2021; 11(3):409. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11030409
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhan, Murtaza, Nkulu Kabange Rolly, Tiba Nazar Ibrahim Al Azzawi, Muhammad Imran, Bong-Gyu Mun, In-Jung Lee, and Byung-Wook Yun. 2021. "Lead (Pb)-Induced Oxidative Stress Alters the Morphological and Physio-Biochemical Properties of Rice (Oryza sativa L.)" Agronomy 11, no. 3: 409. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11030409
APA StyleKhan, M., Rolly, N. K., Al Azzawi, T. N. I., Imran, M., Mun, B.-G., Lee, I.-J., & Yun, B.-W. (2021). Lead (Pb)-Induced Oxidative Stress Alters the Morphological and Physio-Biochemical Properties of Rice (Oryza sativa L.). Agronomy, 11(3), 409. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11030409










