Simultaneous Determination of Carotenoids and Chlorophylls by the HPLC-UV-VIS Method in Soybean Seeds
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Standards, Solvents, and Reagents
2.2. Instrumentation and Chromatographic Conditions
2.3. Preparation of Standard Solutions
2.4. Analytical Method Validation
2.5. Method Sensitivity, LOD, and LOQ
2.6. Linearity and Range
2.7. Recovery
2.8. Precision
2.9. Method Application to Soybean and Other Legume Samples
2.10. Analytical Evaluation and Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optimization of Chromatographic Conditions
3.2. Choosing Extractant Volume and Seed Flour Sample Weight
3.3. Method Validation
3.4. Method Application for Determining Carotenoids and Chlorophylls in Soybean Seeds
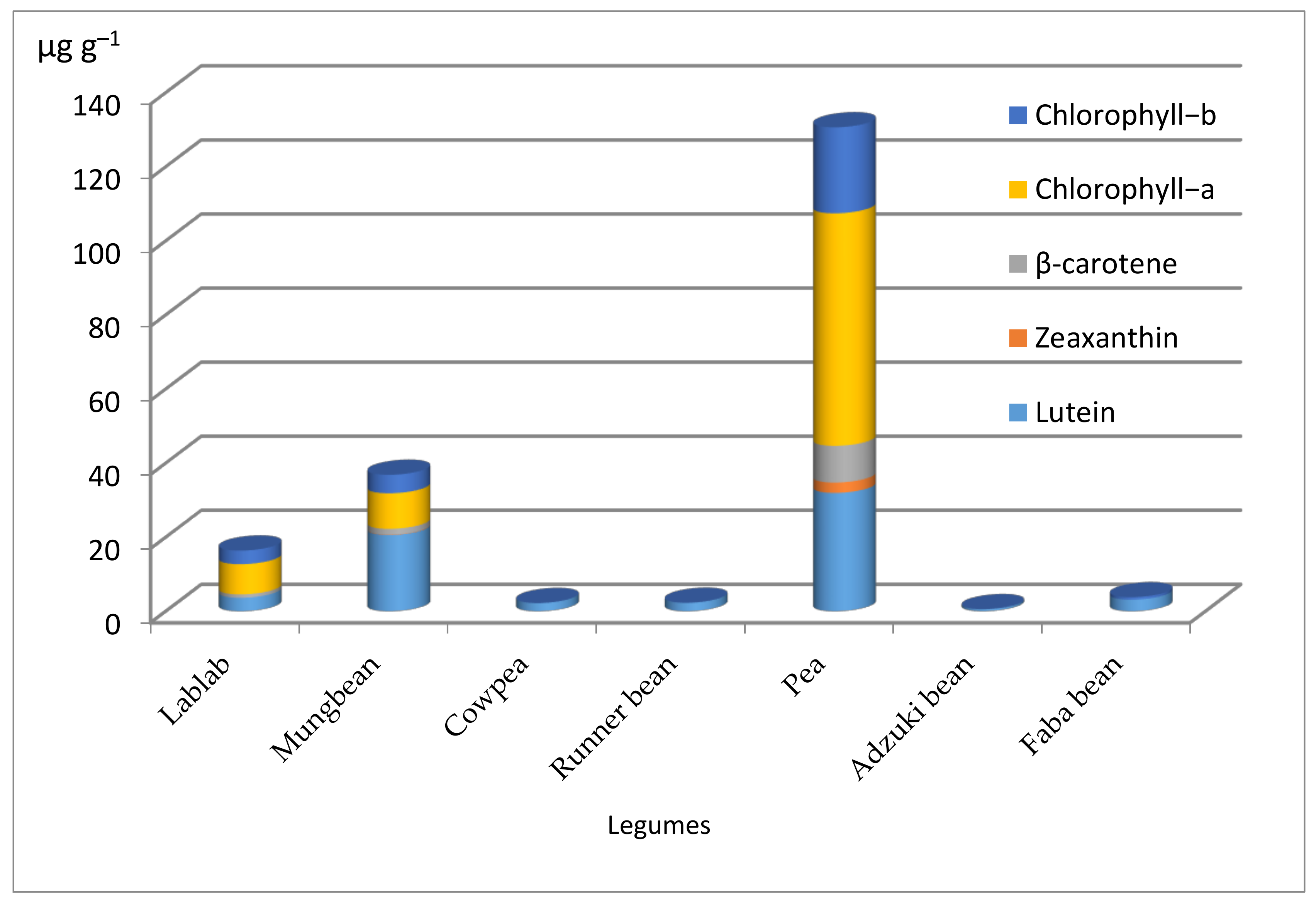
3.5. Quantification of Carotenoids and Chlorophylls in Other Legumes
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rodriguez-Concepcion, M.; Avalos, J.; Bonet, M.L.; Boronat, A.; Gomez-gomez, L.; Hornero-Mendez, D.; Limon, M.C.; Meléndez-martínez, A.J.; Olmedilla-alonso, B.; Palou, A.; et al. A global perspective on carotenoids: Metabolism, biotechnology, and benefits for nutrition and health. Prog. Lipid Res. 2018, 70, 62–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sachindra, N.M.; Sato, E.; Maeda, H.; Hosokawa, M.; Niwano, Y.; Kohno, M.; Miyashita, K. Radical scavenging and singlet oxygen quenching activity of marine carotenoid fucoxanthin and its metabolites. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 8516–8522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elvira-Torales, L.I.; García-Alonso, J.; Periago-Castón, M.J. Nutritional importance of carotenoids and their effect on liver health: A review. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hrvolová, B.; Martínez-huélamo, M.; Colmán-martínez, M.; Hurtado-barroso, S.; Lamuela-raventós, R.M. Development of an advanced HPLC—MS/MS method for the determination of carotenoids and fat-soluble vitamins in human plasma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiPietro, N.; DiTomo, P.; Pandolf, A. Carotenoids in cardiovascular disease prevention. JSM Atheroscler. 2016, 1, 1002. [Google Scholar]
- Saini, R.K.; Keum, Y. Carotenoid extraction methods: A review of recent developments. Food Chem. 2018, 240, 90–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mel´endez-Mart´ınez, A.J. An overview of carotenoids, apocarotenoids, and vitamin A in agro-food, nutrition, health, and disease. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2019, 63, 1801045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landrum, J.T.; Bone, R.A. Lutein, zeaxanthin, and the macular pigment. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2001, 385, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Deng, Z.; Tang, Y.; Chen, P.; Liu, R.; Ramdath, D.D.; Liu, Q.; Hernandez, M.; Tsao, R. Fatty acid, carotenoid and tocopherol compositions of 20 Canadian lentil cultivars and synergistic contribution to antioxidant activities. Food Chem. 2014, 161, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eggersdorfer, M.; Wyss, A. Carotenoids in human nutrition and health. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2018, 652, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatnagar-Panwar, M.; Bhatnagar-Mathur, P.; Bhaaskarla, V.V.A.; Dumbala, S.R.; Sharma, K.K. Rapid, accurate and routine HPLC method for large-scale screening of pro-vitamin A carotenoids in oilseeds. J. Plant Biochem. Biotechnol. 2013, 24, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granado, F.; Olmedilla, B.; Gil-Martinez, E.; Blanco, I. A fast, reliable and low-cost saponification protocol for analysis of carotenoids in vegetables. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2001, 14, 479–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slavin, M.; Yu, L.L. A single extraction and HPLC procedure for simultaneous analysis of phytosterols, tocopherols and lutein in soybeans. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 2789–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferruzzi, M.G.; Blakeslee, J. Digestion, absorption, and cancer preventative activity of dietary chlorophyll derivatives. Nutr. Res. 2007, 27, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.P.; Tai, C.Y.; Chen, B.H. Improved liquid chromatographic method for determination of carotenoids in Taiwanese mango (Mangifera indica L.). J. Chromatogr. A 2004, 1054, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feltl, L.; Pacakova, V.; Stulik, K.; Volka, K. Reliability of carotenoid analyses: A review. Curr. Anal. Chem. 2005, 1, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inbaraj, B.S.; Chien, J.T.; Chen, B.H. Improved high performance liquid chromatographic method for determination of carotenoids in the microalga Chlorella pyrenoidosa. J. Chromatogr. A 2006, 1102, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puspitasari-nienaber, N.L.; Ferruzzi, M.G.; Schwartz, S.J. Simultaneous detection of tocopherols, carotenoids, and chlorophylls in vegetable oils by direct injection C30 RP-HPLC with coulometric electrochemical array detection. JAOCS 2002, 79, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, J.; Palou, A. Chromatographic determination of carotenoids in foods. J. Chromatogr. A 2000, 881, 543–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangels, A.R.; Holde, J.M.; Beecrep, G.R.; Forman, M.R.; Lanz, E. Carotenoid content of fruits and vegetables: An evaluation of analytic data. J Am Diet Assoc 1993, 93, 284–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferruzzi, M.G.; Nguyen, M.L.; Sander, L.C.; Rock, C.L.; Schwartz, S.J. Analysis of lycopene geometrical isomers in biological microsamples by liquid chromatography with coulometric array detection. J. Chromatogr. B 2001, 760, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capello, C.; Fischer, U.; Hungerbu, K. What is a green solvent? A comprehensive framework for the environmental assessment of solvents. Green Chem. 2007, 9, 927–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xie, J.J.; Yu, H.J.; Lv, J.; Zhang, F.J.; Wang, L.X.; Wang, C.; Tang, N.C.; Zhang, C.Y.; Dawuda, M.M.; et al. Reverse-phase high performance liquid chromatography for the quantification and optimization for extracting ten kinds of carotenoids in pepper ( Capsicum annuum L.) leaves. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 8475–8488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ICH (International Conference on Harmonization). ICH Harmonised Tripartite Guideline, Validation of Analytical Procedures: Text and Methodology; ICH Q2; ICH: Geneva, Switzerland, 2005; pp. 4–12. [Google Scholar]
- Al-amri, K.A.; Mohsin, K.; Alanazi, F.K. Development and validation of a UPLC method for quantification of antiviral agent, Acyclovir in lipid-based formulations. Arab. J. Chem. 2014, 12, 1707–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gedawy, A.; Al-salami, H.; Dass, C.R. Development and validation of a new analytical HPLC method for simultaneous determination of the antidiabetic drugs, metformin and gliclazide. J. Food Drug Anal. 2018, 27, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzman, I.; Yousef, G.G.; Brown, A.F. Simultaneous extraction and quantitation of carotenoids, chlorophylls, and tocopherols in Brassica vegetables. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 7238–7244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeb, A.; Ullah, F. Reversed phase HPLC-DAD profiling of carotenoids, chlorophylls and phenolic compounds in Adiantum capillus-veneris leaves. Front. Chem. 2017, 5, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SAS Institute Inc. Base SAS® 9.3 Procedures Guide: Statistical Procedures; SAS Institute Inc: Cary, NC, USA, 2011; 528p. [Google Scholar]
- Edelenbos, M.; Christensen, L.P.; Grevsen, K. HPLC determination of chlorophyll and carotenoid pigments in processed green pea cultivars (Pisum sativum L.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 4768–4774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandul-rojas, B.; Cepero, M.R.; Mínguez-mosquera, M.I. Use of chlorophyll and carotenoid pigment composition to determine authenticity of virgin olive oil. JAOCS 2000, 77, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanamaru, K.; Wang, S.; Abe, J.; Yamada, T.; Kitamura, K. Identification and characterization of wild soybean (Glycine soja Sieb. et Zecc.) strains with high lutein content. Breed. Sci. 2006, 56, 231–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanamaru, K.; Wang, S.; Yamada, T.; Abe, J.; Kitamura, K. Genetic analysis and biochemical characterization of the high lutein trait of wild soybean (Glycine soja Sieb. et Zucc.). Breed. Sci. 2008, 58, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes-Pinto, M.M.; Ferreira, A.N.C.S.S.; Caris-Veyrat, C.; Pinho, P.G. De Carotenoid, chlorophyll, and chlorophyll-derived compounds in grapes and port wines. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 10034–10041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monma, M.; Ito, M.; Saito, M.; Chikuni, K. Carotenoid components in soybean seeds varying with seed color and maturation stage. Biosci. Biotech. Biochem 1994, 58, 926–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stinco, C.M.; Benítez-gonzález, A.M.; Hernanz, D.; Vicario, I.M.; Meléndez-martínez, A.J. Development and validation of a rapid resolution liquid chromatography method for the screening of dietary plant isoprenoids: Carotenoids, tocopherols and chlorophylls. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1370, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraser, P.D.; Pinto, M.E.S.; Holloway, D.E.; Bramley, P.M. Application of high-performance liquid chromatography with photodiode array detection to the metabolic profiling of plant isoprenoids. Plant J. 2000, 24, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dincel, D.; Tekkeli, S.E.K.; Önal, C.; Önal, A.; Sagirli, O. Liquid chromatographic analysis of carotenoids in foods. J. Chil. Chem. Soc. 2019, 64, 4492–4495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamffer, Z.K.; Bindon, K.A.; Oberholster, A. Optimization of a method for the extraction and quantification of carotenoids and chlorophylls during ripening in grape berries (Vitis vinifera cv. Merlot). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 6578–6586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, J.; Fraser, P.D.; Bramley, P.M. Identification and quantification of carotenoids, tocopherols and chlorophylls in commonly consumed fruits and vegetables. Phytochemistry 2003, 62, 939–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seguin, P.; Tremblay, G.; Pageau, D.; Liu, W.; Turcotte, P. Soybean lutein concentration: Impact of crop management and genotypes. Crop Sci. 2011, 51, 1151–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Kanamaru, K.; Li, W.; Abe, J.; Yamada, T.; Kitamura, K. Simultaneous accumulation of high contents of α -tocopherol and lutein is possible in seeds of soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merr.). Breed. Sci. 2007, 57, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sengul, U. Comparing determination methods of detection and quantification limits for aflatoxin analysis in hazelnut. J. Food Drug Anal. 2016, 24, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magnusson, B.; Örnemark, U. (Eds.) Eurachem Guide: The Fitness for Purpose of Analytical Methods—A Laboratory Guide to Method Validation and Related Topics, 2nd ed.; Eurachem: Teddington, UK, 2014; pp. 7–39. [Google Scholar]
- Karnjanawipagul, P.; Nittayanuntawech, W.; Rojsanga, P.; Suntornsuk, L. Analysis of beta-carotene in carrot by spectrophotometry. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 37, 8–16. [Google Scholar]
- Zeb, A. A simple, sensitive HPLC-DAD method for simultaneous determination of carotenoids, chlorophylls and α-tocopherol in leafy vegetables. Food Meas. 2017, 11, 979–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petry, F.C.; Mercadante, A.Z. New method for carotenoid extraction and analysis by HPLC-DAD-MS/MS in freeze-dried citrus and mango pulps. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2018, 29, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.T.; Chen, B.H. Separation of lycopene and its cis isomers by liquid chromatography. Chromatographia 2001, 54, 613–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulistyowati, E.; Martono, S.; Riyanto, S.; Lukitaningsih, E. Development and validation for free aglycones daidzein and genistein in soybeans (Glycine max (L.) Merr.) using RP HPLC method. Int. J. Appl. Pharm. 2019, 11, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, H.; Gorain, B.; Karmakar, S.; Pal, T.K. Development and validation of RP-HPLC method: Scope of application in the determination of oil solubility of paclitaxel. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2013, 52, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kan, L.; Nie, S.; Hu, J.; Wang, S.; Bai, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Jiang, J.; Zeng, Q.; Song, K. Comparative study on the chemical composition, anthocyanins, tocopherols and carotenoids of selected legumes. Food Chem. 2018, 260, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashokkumar, K.; Diapari, M.; Jha, A.B.; Tar’an, B.; Arganosa, G.; Warkentin, T.D. Genetic diversity of nutritionally important carotenoids in 94 pea and 121 chickpea accessions. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2015, 43, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tee, E.; Ah-Heng, G.; Swan-Choo, K. Carotenoid composition and content of legumes, tubers and starchy roots by HPLC. Mal. J. Nutr. 1995, 1, 63–74. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-marín, B.; Míguez, F.; Méndez-fernández, L.; Agut, A.; Becerril, J.M.; García-Plazaola, J.I.; Kranner, I.; Colville, L. Seed carotenoid and tocochromanol composition of wild fabaceae species is shaped by phylogeny and ecological factors. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Analyte | Rt. | LOD | LOQ | Conc.Range | Linear Regression | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lutein | 10.40 | 0.0096 | 0.0290 | 0.05–10.00 | Y = 111.14x + 0.93 | 0.9999 |
| Zeaxanthin | 11.91 | 0.0065 | 0.0198 | 0.05–5.00 | Y = 125.56x + 4.40 | 0.9998 |
| β-carotene | 28.58 | 0.0175 | 0.0529 | 0.10–10.00 | Y = 30.99x + 3.37 | 0.9993 |
| α-carotene | 25.87 | 0.0063 | 0.0192 | 0.05–10.00 | Y = 131.65x + 7.44 | 0.9997 |
| β-cryptoxanthin | 19.28 | 0.0051 | 0.0155 | 0.05–20.00 | Y = 91.02x + 10.96 | 0.9997 |
| Chlorophyll-a | 13.42 | 0.0300 | 0.0909 | 0.10–30.00 | Y = 24.14x − 0.42 | 0.9999 |
| Chlorophyll-b | 9.82 | 0.0081 | 0.0247 | 0.05–10.00 | Y = 77.43x + 0.09 | 0.9999 |
| Analyte | Concentration Added (μg mL−1) | Concentration Found (μg mL−1) | Recovery (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lutein | 0.00 | 2.00 | - |
| 1.25 | 2.40 | 95.28 | |
| 2.50 | 2.88 | 105.43 | |
| 5.00 | 3.57 | 94.27 | |
| Zeaxanthin | 0.00 | 0.03 | - |
| 0.10 | 0.06 | 106.58 | |
| 0.50 | 0.20 | 102.04 | |
| 1.00 | 0.35 | 97.19 | |
| β–carotene | 0.00 | 0.19 | - |
| 2.50 | 0.91 | 86.99 | |
| 5.00 | 1.62 | 86.02 | |
| 7.50 | 2.27 | 83.12 | |
| Chlorophyll–a | 0.00 | 6.01 | - |
| 2.50 | 6.74 | 88.51 | |
| 5.00 | 7.61 | 96.55 | |
| 10.00 | 9.02 | 90.34 | |
| Chlorophyll–b | 0.00 | 2.10 | - |
| 1.00 | 2.40 | 89.62 | |
| 5.00 | 3.60 | 88.06 | |
| 10.00 | 5.40 | 97.02 |
| Analyte | Precision, RSD (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| System Precision | Method Precision | |||||
| Repeatability | Intermediate | |||||
| Intra-Sample (n = 1; i = 6) | Mix-Standard (i = 6) | Day-1 (n = 6) | Day-2 (n = 6) | Day-3 (n = 6) | (n = 6; k = 3) | |
| Lutein | 0.32 | 0.23 | 2.19 | 2.44 | 2.39 | 3.33 |
| Zeaxanthin | 0.81 | 0.26 | 3.46 | 2.65 | 2.38 | 4.20 |
| β-carotene | 0.77 | 0.15 | 1.25 | 1.30 | 1.71 | 2.80 |
| Chlorophyll-a | 0.56 | 0.74 | 2.38 | 2.31 | 2.24 | 3.44 |
| Chlorophyll-b | 0.57 | 0.22 | 2.03 | 2.04 | 2.74 | 3.60 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gebregziabher, B.S.; Zhang, S.; Qi, J.; Azam, M.; Ghosh, S.; Feng, Y.; Huai, Y.; Li, J.; Li, B.; Sun, J. Simultaneous Determination of Carotenoids and Chlorophylls by the HPLC-UV-VIS Method in Soybean Seeds. Agronomy 2021, 11, 758. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11040758
Gebregziabher BS, Zhang S, Qi J, Azam M, Ghosh S, Feng Y, Huai Y, Li J, Li B, Sun J. Simultaneous Determination of Carotenoids and Chlorophylls by the HPLC-UV-VIS Method in Soybean Seeds. Agronomy. 2021; 11(4):758. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11040758
Chicago/Turabian StyleGebregziabher, Berhane Sibhatu, Shengrui Zhang, Jie Qi, Muhammad Azam, Suprio Ghosh, Yue Feng, Yuanyuan Huai, Jing Li, Bin Li, and Junming Sun. 2021. "Simultaneous Determination of Carotenoids and Chlorophylls by the HPLC-UV-VIS Method in Soybean Seeds" Agronomy 11, no. 4: 758. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11040758
APA StyleGebregziabher, B. S., Zhang, S., Qi, J., Azam, M., Ghosh, S., Feng, Y., Huai, Y., Li, J., Li, B., & Sun, J. (2021). Simultaneous Determination of Carotenoids and Chlorophylls by the HPLC-UV-VIS Method in Soybean Seeds. Agronomy, 11(4), 758. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11040758










