Climate-Smart Agriculture on Small-Scale Farms: A Systematic Literature Review
Abstract
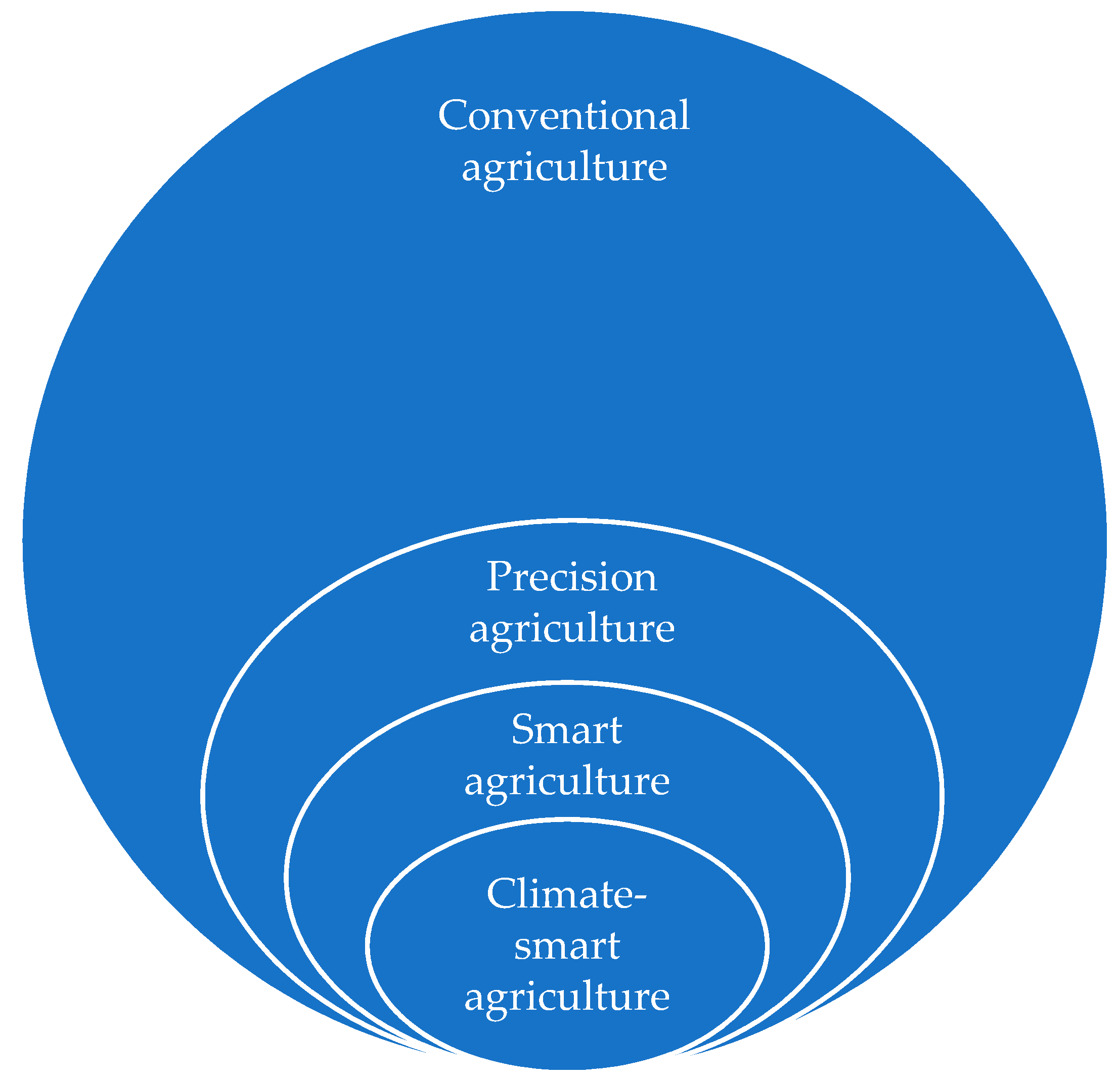
1. Introduction
- higher agricultural productivity and income in a sustainable way;
- higher (adapted and built) resilience to climate change;
- efforts towards GHG reduction.
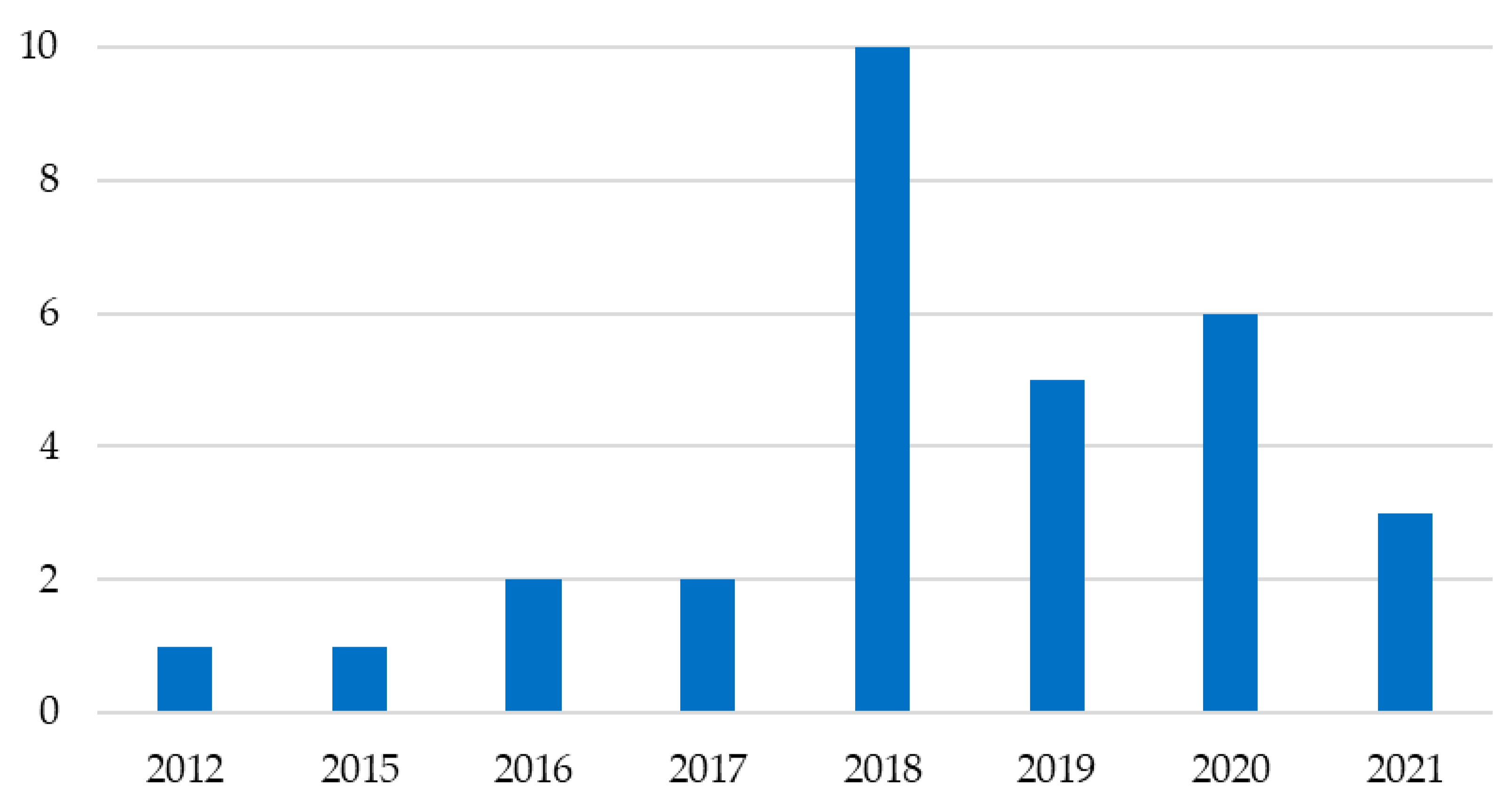
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Productivity/Technology Related CSA
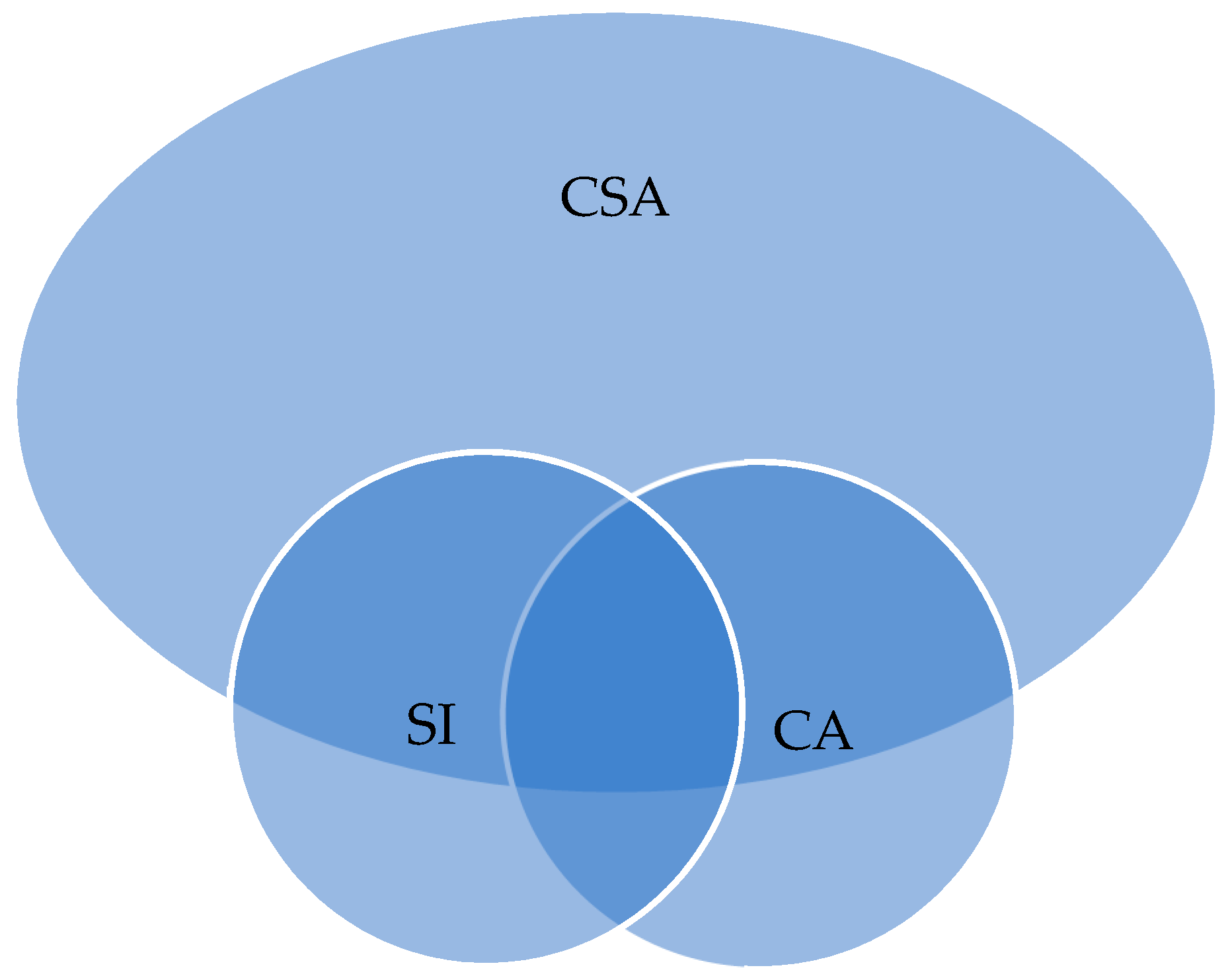
3.2. Combining Economic and Environmental CSA
3.3. Influencing Factors of CSA Adoption
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division. World Population Prospects 2019: Highlights; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2019.
- Ayaz, M.; Ammad-Uddin, M.; Sharif, Z.; Mansour, A.; Aggoune, E.-H.M. Internet-of-Things (IoT)-based smart agriculture: Toward making the fields talk. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 129551–129583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Global Warming of 1.5 °C. An IPCC Special Report on the Impacts of Global Warming of 1.5 °C Above Pre-Industrial Levels and Related Global Greenhouse Gas Emission Pathways, in the Context of Strengthening the Global Response to the Threat of Climate Change, Sustainable Development, and Efforts to Eradicate Poverty; Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. “Climate-Smart” Agriculture. Policies, Practices and Financing for Food Security, Adaptation and Mitigation; Food and Agriculture Organisation of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. Climate-Smart Agriculture Sourcebook; Food and Agriculture Organisation of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2013.
- Siedenburg, J.; Martin, A.; McGuire, S. The power of “farmer friendly” financial incentives to deliver climate smart agriculture: A critical data gap. J. Integr. Environ. Sci. 2012, 9, 201–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrieu, N.; Howland, F.; Acosta-Alba, I.; Le Coq, J.-F.; Osorio-Garcia, A.M.; Martinez-Baron, D.; Gamba-Trimiño, C.; Loboguerrero, A.M.; Chia, E. Co-designing Climate-Smart Farming Systems with Local Stakeholders: A Methodological Framework for Achieving Large-Scale Change. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2019, 3, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, A.; McNamara, K.E.; Dargusch, P. Climate-smart agriculture: Perspectives and framings. Clim. Policy 2018, 18, 526–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, B.M.; Thornton, P.; Zougmoré, R.; van Asten, P.; Lipper, L. Sustainable intensification: What is its role in climate smart agriculture? Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2014, 8, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipper, L.; Thornton, P.; Campbell, B.M.; Baedeker, T.; Braimoh, A.; Bwalya, M.; Caron, P.; Cattaneo, A.; Garrity, D.; Henry, K.; et al. Climate-smart agriculture for food security. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2014, 4, 1068–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Parliament, Directorate-General for Internal Policies. Precision Agriculture: An Opportunity for EU Farmers—Potential Support with the CAP 2014–2020; European Parliament: Brussels, Belgium, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budaev, D.; Lada, A.; Simonova, E.; Skobelev, P.; Travin, V.; Yalovenko, O.; Voschuk, G.; Zhilyaev, A. Conceptual design of smart farming solution for precise agriculture. Int. J. Des. Nat. Ecodyn. 2018, 13, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzetto, F.; Gallo, R.; Sacco, P. Reflections and Methodological Proposals to Treat the Concept of “Information Precision” in Smart Agriculture Practices. Sensors 2020, 20, 2847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regan, Á. ‘Smart farming’ in Ireland: A risk perception study with key governance actors. NJAS Wagening. J. Life Sci. 2019, 90–91, 100292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatri-Chhetri, A.; Pant, A.; Aggarwal, P.K.; Vasireddy, V.V.; Yadav, A. Stakeholders prioritization of climate-smart agriculture interventions: Evaluation of a framework. Agric. Syst. 2019, 174, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charania, I.; Li, X. Smart farming: Agriculture’s shift from a labor intensive to technology native industry. Internet Things 2020, 9, 100142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, E.; Costa, N.; Pereira, A. A Systematic Review of IoT Solutions for Smart Farming. Sensors 2020, 20, 4231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, T.B.; Blok, V.; Coninx, I. Barriers to the adoption and diffusion of technological innovations for climate-smart agriculture in Europe: Evidence from the Netherlands, France, Switzerland and Italy. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdanski, A. Integrated food–energy systems for climate-smart agriculture. Agric. Food Secur. 2012, 1, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. The State of Food and Agriculture 2020. Overcoming Water Challenges in Agriculture; Food and Agriculture Organisation of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng’ombe, J.N.; Tembo, M.C.; Masasi, B. “Are They Aware, and Why?” Bayesian Analysis of Predictors of Smallholder Farmers’ Awareness of Climate Change and Its Risks to Agriculture. Agronomy 2020, 10, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abegunde, V.O.; Sibanda, M.; Obi, A. Mainstreaming Climate-Smart Agriculture in Small-Scale Farming Systems: A Holistic Nonparametric Applicability Assessment in South Africa. Agriculture 2020, 10, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sain, G.; Loboguerrero, A.M.; Corner-Dolloff, C.; Lizarazo, M.; Nowak, A.; Martínez-Barón, D.; Andrieu, N. Costs and benefits of climate-smart agriculture: The case of the Dry Corridor in Guatemala. Agric. Syst. 2017, 151, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akrofi-Atitianti, F.; Ifejika Speranza, C.; Bockel, L.; Asare, R. Assessing Climate Smart Agriculture and Its Determinants of Practice in Ghana: A Case of the Cocoa Production System. Land 2018, 7, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caffaro, F.; Cavallo, E. The Effects of Individual Variables, Farming System Characteristics and Perceived Barriers on Actual Use of Smart Farming Technologies: Evidence from the Piedmont Region, Northwestern Italy. Agriculture 2019, 9, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrieu, N.; Sogoba, B.; Zougmore, R.; Howland, F.; Samake, O.; Bonilla-Findji, O.; Lizarazo, M.; Nowak, A.; Dembele, C.; Corner-Dolloff, C. Prioritizing investments for climate-smart agriculture: Lessons learned from Mali. Agric. Syst. 2017, 154, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, S. Drought Impact and Adaptation Strategies in the Mid-Hill Farming System of Western Nepal. Environments 2018, 5, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, M.A.; Ali, A.; Ashfaq, M.; Hassan, S.; Culas, R.; Ma, C. Impact of Climate Smart Agriculture (CSA) Practices on Cotton Production and Livelihood of Farmers in Punjab, Pakistan. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abegunde, V.O.; Sibanda, M.; Obi, A. Determinants of the Adoption of Climate-Smart Agricultural Practices by Small-Scale Farming Households in King Cetshwayo District Municipality, South Africa. Sustainability 2020, 12, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emerick, K.; de Janvry, A.; Sadoulet, E.; Dar, M. Identifying Early Adopters, Enhancing Learning, and the Diffusion of Agricultural Technology; Public Documents; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Dedehayir, O.; Ortt, R.J.; Riverola, C.; Miralles, F. Innovators and early adopters in the diffusion of innovations: A literature review. Digit. Disruptive Innov. 2020, 36, 85–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frattini, F.; Bianchi, M.; De Massis, A.; Sikimic, U. The role of early adopters in the diffusion of new products: Differences between platform and nonplatform innovations. J. Prod. Innov. Manag. 2013, 31, 466–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinesh, D.; Aggarwal, P.; Khatri-Chhetri, A.; Rodríguez, A.M.L.; Mungai, C.; Sebastian, L.; Zougmore, R. The rise in Climate-Smart Agriculture strategies, policies, partnerships and investments across the globe. Agric. Dev. 2017, 30, 4–9. [Google Scholar]
- Chandra, A.; McNamara, K.E.; Dargusch, P. The relevance of political ecology perspectives for smallholder Climate-Smart Agriculture: A review. J. Political Ecol. 2017, 24, 821–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mzyece, A.; Ng’ombe, J.N. Does Crop Diversification Involve a Trade-Off Between Technical Efficiency and Income Stability for Rural Farmers? Evidence from Zambia. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doshi, J.; Patel, T.; Bharti, S.K. Smart Farming using IoT, a solution for optimally monitoring farming conditions. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2019, 160, 746–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pivoto, D.; Waquil, P.D.; Talamini, E.; Finocchio, C.P.S.; Dalla Corte, V.F.; de Vargas Mores, G. Scientific development of smart farming technologies and their application in Brazil. Inf. Process. Agric. 2018, 5, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, S.; Muller, A. Payments for environmental services to promote “climate-smart agriculture”? Potential and challenges. Agric. Econ. 2016, 47, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, F.J.; Blanco, M.; Ponce, R.D.; Vásquez-Lavín, F.; Roco, L. Implications of climate change for semi-arid dualistic agriculture: A case study in Central Chile. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2018, 19, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mango, N.; Makate, C.; Tamene, L.; Mponela, P.; Ndengu, G. Adoption of small-scale irrigation farming as a climate-smart agriculture practice and its influence on household income in the Chinyanja Triangle, Southern Africa. Land 2018, 7, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, U.; Gebremedhin, Z.; Brychkova, G.; Spillane, C. Smallholder farmers and climate smart agriculture: Technology and labor-productivity constraints amongst women smallholders in Malawi. Gender Technol. Dev. 2016, 20, 117–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellin, J.; Fisher, E. Climate-smart agriculture and non-agricultural livelihood transformation. Climate 2019, 7, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branca, G.; Arslan, A.; Paolantonio, A.; Grewer, U.; Cattaneo, A.; Cavatassi, R.; Lipper, L.; Hillier, J.; Vetter, S. Assessing the economic and mitigation benefits of climate-smart agriculture and its implications for political economy: A case study in Southern Africa. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 285, 125161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyasimi, M.; Kimeli, P.; Sayula, G.; Radeny, M.; Kinyangi, J.; Mungai, C. Adoption and Dissemination Pathways for Climate-Smart Agriculture Technologies and Practices for Climate-Resilient Livelihoods in Lushoto, Northeast Tanzania. Climate 2017, 5, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prestele, R.; Verburg, P.H. The overlooked spatial dimension of climate-smart agriculture. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2019, 26, 1045–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FAO. Conservation Agriculture; Food and Agriculture Organisation of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2015.
- Giller, K.E.; Andersson, J.A.; Corbeels, M.; Kirkegaard, J.; Mortensen, D.; Erenstein, O.; Vanlauwe, B. Beyond conservation agriculture. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, D.; Orr, A. Is rainfed agriculture really a pathway from poverty? Agric. Syst. 2014, 123, 84–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Baron, D.; Orjuela, G.; Renzoni, G.; Rodríguez, A.M.L.; Prager, S.D. Small-scale farmers in a 1.5 C future: The importance of local social dynamics as an enabling factor for implementation and scaling of climate-smart agriculture. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2018, 31, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makate, C.; Makate, M.; Mango, N. Farm household typology and adoption of climate-smart agriculture practices in smallholder farming systems of southern Africa. Afr. J. Sci. Technol. Innov. Dev. 2018, 10, 421–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abegunde, V.O.; Sibanda, M.; Obi, A. The dynamics of climate change adaptation in Sub-Saharan Africa: A review of climate-smart agriculture among small-scale farmers. Climate 2019, 7, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setshedi, K.; Modirwa, S. Socio-economic characteristics influencing small-scale farmers’ level of knowledge on climate-smart agriculture in mahikeng local municipality, North West province, South Africa. S. Afr. J. Agric. Ext. 2020, 48, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutenje, M.J.; Farnworth, C.R.; Stirling, C.; Thierfelder, C.; Mupangwa, W.; Nyagumbo, I. A cost-benefit analysis of climate-smart agriculture options in Southern Africa: Balancing gender and technology. Ecol. Econ. 2019, 163, 126–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zougmoré, R.B.; Partey, S.T.; Ouédraogo, M.; Torquebiau, E.; Campbell, B.M. Facing climate variability in sub-Saharan Africa: Analysis of climate-smart agriculture opportunities to manage climate-related risks. Cah. Agric. 2018, 27, 34001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zougmoré, R.; Partey, S.; Ouédraogo, M.; Omitoyin, B.; Thomas, T.; Ayantunde, A.; Ericksen, P.; Said, M.; Jalloh, A. Toward climate-smart agriculture in West Africa: A review of climate change impacts, adaptation strategies and policy developments for the livestock, fishery and crop production sectors. Agric. Food Secur. 2016, 5, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilarova, T.; Bavorova, M.; Kandakov, A. Do farmer, household and farm characteristics influence the adoption of sustainable practices? The evidence from the Republic of Moldova. Int. J. Agric. Sustain. 2018, 16, 367–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslan, A.; McCarthy, N.; Lipper, L.; Asfaw, S.; Cattaneo, A.; Kokwe, M. Climate smart agriculture? Assessing the adaptation implications in Zambia. J. Agric. Econ. 2015, 66, 753–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKune, S.; Poulsen, L.; Russo, S.; Devereux, T.; Faas, S.; McOmber, C.; Ryley, T. Reaching the end goal: Do interventions to improve climate information services lead to greater food security? Clim. Risk Manag. 2018, 22, 22–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.K.; Desiere, S.; D’Haese, M.; Kumar, L. Impact of climate-smart agriculture adoption on the food security of coastal farmers in Bangladesh. Food Secur. 2018, 10, 1073–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Ridaura, S.; Frelat, R.; van Wijk, M.T.; Valbuena, D.; Krupnik, T.J.; Jat, M. Climate smart agriculture, farm household typologies and food security: An ex-ante assessment from Eastern India. Agric. Syst. 2018, 159, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruales, J.H.; Serino, M.N.V.; Ratilla, T.C.; Cuizon, J.G.; Enerlan, W.C. Investment appraisal of selected climate smart agricultural (CSA) practices among small scale coconut farmers in Leyte, Philippines. Sci. Pap. Ser. Manag. Econ. Eng. Agric. Rural Dev. 2020, 20, 499–506. [Google Scholar]
- Alexander, S. What climate-smart agriculture means to members of the Global Alliance for climate-smart agriculture. Future Food J. Food Agric. Soc. 2019, 7, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Totin, E.; Segnon, A.C.; Schut, M.; Affognon, H.; Zougmoré, R.B.; Rosenstock, T.; Thornton, P.K. Institutional Perspectives of Climate-Smart Agriculture: A Systematic Literature Review. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerssa, G.; Feyssa, D.; Kim, D.-G.; Eichler-Löbermann, B. Challenges of Smallholder Farming in Ethiopia and Opportunities by Adopting Climate-Smart Agriculture. Agriculture 2021, 11, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acevedo, M.; Pixley, K.; Zinyengere, N.; Meng, S.S.; Tufan, H.; Cichy, K.; Bizikova, L.; Isaacs, K.; Ghezzi-Kopel, K.; Porciello, J. A scoping review of adoption of climate-resilient crops by small-scale producers in low- and middle-income countries. Nat. Plants 2020, 6, 1231–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makate, C. Effective scaling of climate smart agriculture innovations in African smallholder agriculture: A review of approaches, policy and institutional strategy needs. Environ. Sci. Policy 2019, 96, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsige, M.; Synnevåg, G.; Aune, J.B. Gendered constraints for adopting climate-smart agriculture amongst smallholder Ethiopian women farmers. Sci. Afr. 2020, 7, e00250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzad, M.F.; Abdulai, A. The heterogeneous effects of adoption of climate-smart agriculture on household welfare in Pakistan. Appl. Econ. 2021, 53, 1013–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; You, L.; Wielgosz, B.; Ringler, C. Estimating the potential for expanding smallholder irrigation in Sub-Saharan Africa. Agric. Water Manag. 2014, 131, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| The 3 Highest Accepted CSA Practices | The 3 Lowest Accepted CSA Practices | |
|---|---|---|
| Technicality | use of organic manure (545), planting of cover crops (533), crop rotation (529) | soil conservation (423), agroforestry (430), conservation agriculture (432) |
| Economics of use | use of organic manure (542), mulching (541), crop rotation (515) | planting of drought- and heat-tolerant crops (430), agroforestry (436), diet improvement for animals (447) |
| Environmental friendliness | use of organic manure (524), crop rotation (504), soil conservation (503) | efficient manure management (436), use of wetlands (445), crop diversification (462) |
| Major CSA Practices | Adopting Factors/Constraints | Potential Solutions | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water management, including irrigation | awareness, experience/skills, information, high costs-access to finance, labor-intensity | education, extension services, farmer friendly incentives, microfinancing, sorjan method | [6,23,40,41,52,54,55,56,57,60,65,66] |
| improved, more tolerant varieties | awareness, experience/skills, information, input accessibility | education, extension services, secured inputs, knowledge sharing | [23,41,43,51,52,54,56,62,66] |
| conservation agriculture | awareness, experience/skills, information, high costs-access to finance | education, extension services, policy incentives, farmer friendly incentives, microfinancing | [22,43,51,52,56,58,59] |
| integrated/mixed farming (e.g., crops-livestock) | awareness, experience/skills, information, | education, extension services, knowledge sharing | [44,52,56,61] |
| agroforestry | awareness, experience/skills, information, | education, extension services, policy incentives | [23,27,52,55,56,65] |
| crop rotation and diversification | experience/skills, information | education, extension services, knowledge sharing | [22,23,27,29,44,51,52,54,58,62] |
| climate information services | poor Internet, awareness and climate change perception | access to weather forecasts, knowledge sharing | [29,53,55,56,62,69] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mizik, T. Climate-Smart Agriculture on Small-Scale Farms: A Systematic Literature Review. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1096. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11061096
Mizik T. Climate-Smart Agriculture on Small-Scale Farms: A Systematic Literature Review. Agronomy. 2021; 11(6):1096. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11061096
Chicago/Turabian StyleMizik, Tamás. 2021. "Climate-Smart Agriculture on Small-Scale Farms: A Systematic Literature Review" Agronomy 11, no. 6: 1096. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11061096
APA StyleMizik, T. (2021). Climate-Smart Agriculture on Small-Scale Farms: A Systematic Literature Review. Agronomy, 11(6), 1096. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11061096






