Institutionalizing Quality Declared Seed in Uganda
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Framework and Methodology
2.1. Theoretical Framework
2.2. Methodology
3. Seed Sector in Uganda as of 2012
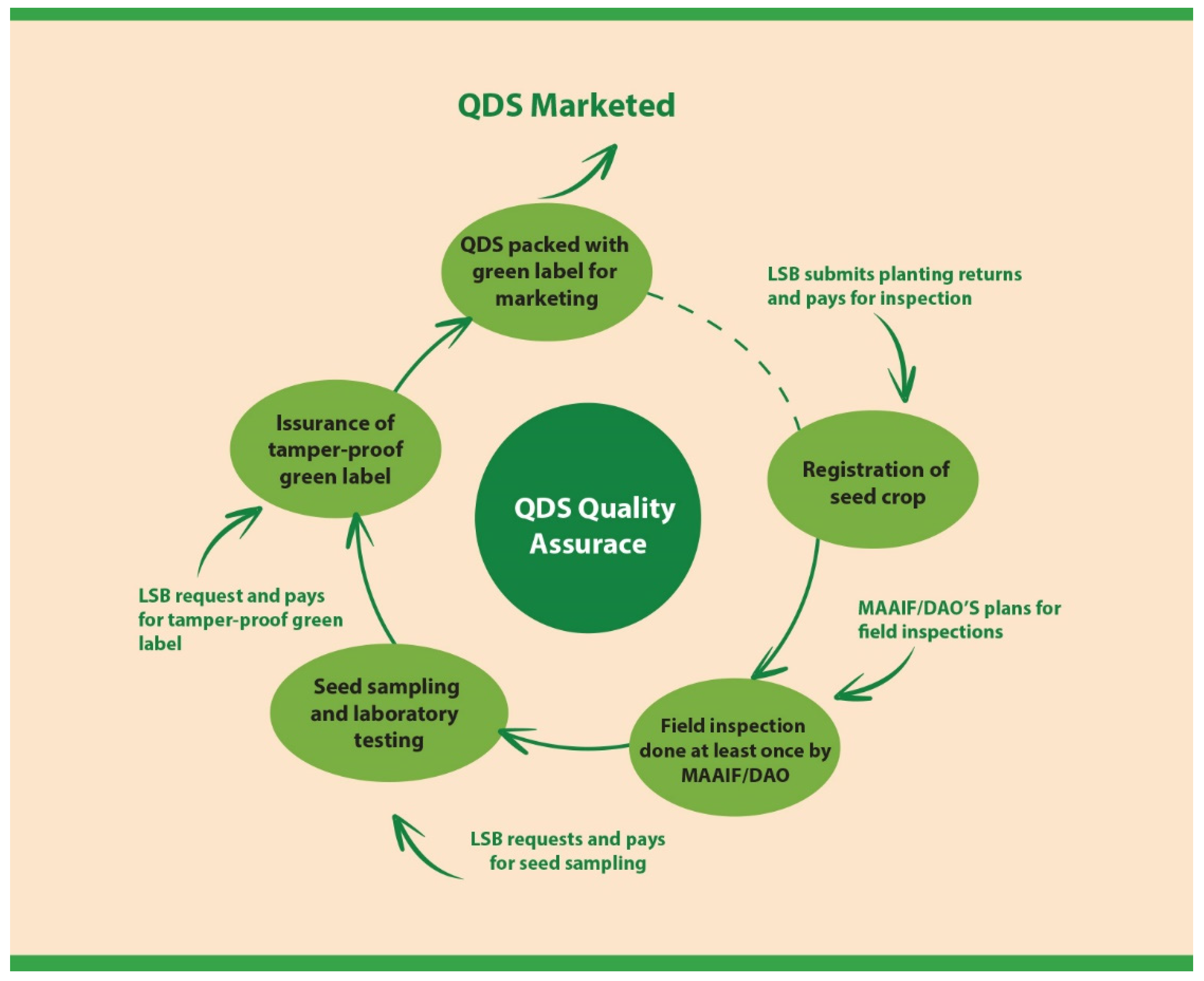
4. Quality Declared Seed and Local Seed Businesses
4.1. Quality Declared Seed Production and Supply System
4.2. Local Seed Businesses
5. Strategies towards Institutionalizing the Quality Declared Seed Class
- Generate evidence to demonstrate that local seed business model (farmer groups) can produce and market quality seed;
- Engage stakeholder towards an inclusive seed policy; and
- Develop a separate QDS regulatory framework.
5.1. Local Seed Businesses Producing and Marketing Quality Seed
5.2. Stakeholder Engagement towards Inclusive Seed Policy
5.2.1. National Processes
5.2.2. Zonal and District Level Processes
5.3. QDS Regulatory Framework
6. Achieved Level of Institutionalization of the QDS Class
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hoogendoorn, J.C.; Audet-Bélanger, G.; Böber, C.; Donnet, M.L.; Lweya, K.B.; Malik, R.K.; Gildemacher, P.R. Maize seed systems in different agro-ecosystems; what works and what does not work for smallholder farmers. Food Secur. 2018, 10, 1089–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kansiime, M.K.; Mastenbroek, A. Enhancing resilience of farmer seed system to climate-induced stresses: Insights from a case study in West Nile region, Uganda. J. Rural Stud. 2016, 47, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Louwaars, N.P.; de Boef, W.S. Integrated Seed Sector Development in Africa: A Conceptual Framework for Creating Coherence Between Practices, Programs, and Policies. J. Crop Improv. 2012, 26, 39–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuire, S.; Sperling, L. Seed systems smallholder farmers use. Food Secur. 2016, 8, 179–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sperling, L.; Mcguire, S. Understanding and Strengthening Informal Seed Markets. Exp. Agric. 2010, 46, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tripp, R. Strategies for Seed System Development in Sub-Saharan Africa: A study of Kenya, Malawi, Zambia, and Zimbabwe. J. SAT Agric. Res. 2006, 2, 1–50. [Google Scholar]
- Sperling, L.; Gallagher, P.; McGuire, S.; March, J.; Templer, N. Informal Seed Traders: The Backbone of Seed Business and African Smallholder Seed Supply. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spielman, D.J.; Kennedy, A. Towards better metrics and policymaking for seed system development: Insights from Asia’s seed industry. Agric. Syst. 2016, 147, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barriga, A.; Fiala, N. The supply chain for seed in Uganda: Where does it go wrong? World Dev. 2020, 130, 104928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kankwamba, H.; Mangisoni, J.; Simtowe, F.; Mausch, K.; Siambi, M. Improving Legume Seed Demand Systems in Central Malawi: What do farmers’ seed expenditures say about their preferences? In Proceedings of the International Association of Agricultural Economics Triennial Conference, Foz do Iguacu, Brazil, 18–24 August 2012; pp. 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Maredia, M.K.; Shupp, R.; Opoku, E.; Mishili, F.; Reyes, B.; Kusolwa, P.; Kusi, F.; Kudra, A. Farmer perception and valuation of seed quality: Evidence from bean and cowpea seed auctions in Tanzania and Ghana. Agric. Econ. 2019, 50, 495–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperling, L.; Boettiger, S. Impacts of Selling Seed in Small Packs: Evidence from Legume Sales; AgPartnerXChange: Basel, Switzerland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Simtowe, F.; Marenya, P.; Amondo, E.; Worku, M.; Rahut, D.B.; Erenstein, O. Heterogeneous seed access and information exposure: Implications for the adoption of drought-tolerant maize varieties in Uganda. Agric. Food Econ. 2019, 7, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mulesa, T.H.; Dalle, S.P.; Makate, C.; Haug, R.; Westengen, O.T. Pluralistic Seed System Development: A Path to Seed Security? Agronomy 2021, 11, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastenbroek, A.; Ntare, B.R. Uganda Early Generation Seed Study: Unlocking Pathways for Sustainable Provision of EGS for Food Crops in Uganda; Wageningen UR Uganda: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lipper, L.; Anderson, L.; Dalton, T.J. Seed Trade in Rural Markets: Implications for Crop Diversity and Agricultural Development; FAO and Earthscan: London, UK, 2010; ISBN 9781844076847. [Google Scholar]
- Bishaw, Z.; van Gastel, A.J.G. ICARDA’s Seed-Delivery Approach in Less Favorable Areas Through Village-Based Seed Enterprises: Conceptual and Organizational Issues. J. New Seeds 2008, 9, 68–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Boef, W.S.; Dempewolf, H.; Byakweli, J.M.; Engels, J.M.M. Integrating genetic resource conservation and sustainable development into strategies to increase the robustness of seed systems. J. Sustain. Agric. 2010, 34, 504–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, S. Farmer seed enterprises: A sustainable approach to seed delivery? Agric. Hum. Values 2004, 21, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- FAO. Quality Declared Seed Ystem; FAO Plant Production and Protection Paper; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Government of Uganda Seed and Plant (QDS) Regulations; Ministry of Agriculture, Animal Industry and Fisheries: Entebbe, Uganda, 2020.
- Molenaar, J.W.; Gorter, J.; Heilbron, L.; Simons, L.; Vorley, B.; Blackmore, E.; Dallinger, J. Sustainable Sector Transformation How to Drive Sustainability Performance in Smallholder-Dominated Agricultural Sectors? White Paper; Aidenvironment–NewForesight–IIED: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; ISBN 978-1-78431-160-5. [Google Scholar]
- WCDI Seed Alert. Methodology Brief; Wageningen Centre for Development Innovation: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Louwaars, N.P.; de Boef, W.S.; Edeme, J. Integrated Seed Sector Development in Africa: A Basis for Seed Policy and Law. J. Crop Improv. 2013, 27, 186–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borman, G.; Hassena, M.; Verhoosel, K.; Molenaar, J.W. Guiding Sector Transformation: The Case of Integrated Seed Sector Development in Ethiopia; Wageningen Centre for Development Innovation: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Brouwer, H.; Woodhill, J.; Hemmati, M.; Verhoosel, K.; Van Vugt, S. The MSP Guide: How to Deswign and Facilitate Multi-Stakeholder Partnerships; Centre for Development Innovation: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2015; ISBN 978-94-6257-542-4. [Google Scholar]
- MDF Training and Consultancy. Tango Toolkit for Organisations; MDF Training and Consultancy BV: Ede, The Netherlands, 2008; ISBN 90-808685-1-5. [Google Scholar]
- ISSD Uganda Brief 4: Evidence of Policy Change in Uganda; ISSD Uganda: Kampala, Uganda, 2015.
- ISSD Uganda Brief 13: Seed System Development in the West Nile Region of Uganda; ISSD Uganda: Kampala, Uganda, 2015.
- ISSD Uganda Brief 1: Towards a Vibrant, Pluralistic and Market-Oriented Seed Sector in Uganda; ISSD Uganda: Kampala, Uganda, 2015.
- ISSD Uganda Brief 6: Quality Declared Seed Class for Farmer Groups; ISSD Uganda: Kampala, Uganda, 2015.
- Mubangizi, E.; Ntamu, D.N.; Thembo, W.M.; Thijssen, M. ISSD Briefing Note—September 2012 Uganda Seed Sector Assessment; Centre for Development Innovation: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- ISSD Uganda Brief 2: Status of the Seed Sector in Uganda; ISSD Uganda: Kampala, Uganda, 2015.
- ISSD Uganda. Brief 14: Facilitation of Seed Sector Innovations in West Nile: Using Multi-Stakeholder Platforms; ISSD Uganda: Kampala, Uganda, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- ISSD. Baseline Study on Farmers’ Access to Seed and other Planting Materials; Wageningen UR Uganda: Kampala, Uganda, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Muhhuku, F. Seed Industry Development and Seed Legislation in Uganda. J. New Seeds 2002, 4, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TASAI Uganda Policy Brief; The African Seed Access Index, 2015; Available online: https://tasai.org/wp-content/themes/tasai2016/img/briefs_Uganda_TASAI_Policy_Brief_2015.pdf (accessed on 5 May 2021).
- Joughin, J. The Political Economy of Seed Reform in Uganda: Promoting a Regional Seed Trade Market; Africa Trade Practice Working Paper Series; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Marechera, G.; Muinga, G.; Irungu, P. Assessment of Seed Maize Systems and Potential Demand for Climate-Smart Hybrid Maize Seed in Africa. J. Agric. Sci. 2016, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bold, T.; Kaizzi, K.C.; Svensson, J.; Yanagizawa-Drott, D. Lemon Technologies and Adoption: Measurement, Theory and Evidence from Agricultural Markets in Uganda*. Q. J. Econ. 2017, 132, 1055–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Erenstein, O.; Kassie, G.T. Seeding eastern Africa’s maize revolution in the post-structural adjustment era: A review and comparative analysis of the formal maize seed sector. Int. Food Agribus. Manag. Rev. 2018, 21, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Government of Uganda Seed and Plant Regulations; Ministry of Agriculture, Animal Industry and Fisheries: Entebbe, Uganda, 2016.
- Mastenbroek, A.; Oyee, P.; Gildemacher, P.R. ISSD Uganda: Bridging the Gap of Quality Seed; Final Programme Report for the Integrated Seed Sector Development Programme in Uganda; Wageningen Centre for Development Innovation: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Mugisha, J.; Ntakyo, P.R.; Bangizi, R.; Namwanje, D.; Mutambira, B. Access to Quality Seed in Uganda: The Contribution of Farmers’ Local Seed Businesses to the Seed Sector; DataCapital: Kampala, Uganda, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Government of Uganda National Seed Policy. Ministry of Agriculture, Animal Industry and Fisheries: Entebbe, Uganda, 2018. Available online: https://www.agriculture.go.ug/wp-content/uploads/2019/05/Ministry-of-Agriculture-Animal-Industry-and-Fisheries-National-Seed-Policy.pdf (accessed on 5 May 2021).


| Characteristics | Certified Seed | Quality Declared Seed |
|---|---|---|
| Crops | Cereals, legumes, oil seed crops, roots, and tubers | Same as certified, except for maize and sunflower, which are excluded |
| Producers | Registered national and multinational seed companies | Registered farmer groups and individual farmers (local seed businesses) |
| Marketing | Direct marketing and through agro-dealer networks | Sold within the communities where seed is produced and not stocked with agro dealers |
| Input material | Basic seed | Basic seed |
| Field inspection | Minimum of three field inspections of all seed fields | Maximum of two field inspections of 10% of seed fields of the same variety |
| Inspectors | National level government seed inspection and certification agency | District level authorized government field inspectors |
| Seed testing | Multiple seed lots, depending on volume | One seed lot per variety, after bulking |
| Standards | Germination, genetic purity, moisture content, and seed health | Same standards as certified seed |
| Government Agency issued quality mark |  |  |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mastenbroek, A.; Otim, G.; Ntare, B.R. Institutionalizing Quality Declared Seed in Uganda. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1475. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11081475
Mastenbroek A, Otim G, Ntare BR. Institutionalizing Quality Declared Seed in Uganda. Agronomy. 2021; 11(8):1475. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11081475
Chicago/Turabian StyleMastenbroek, Astrid, Geoffrey Otim, and Bonny R. Ntare. 2021. "Institutionalizing Quality Declared Seed in Uganda" Agronomy 11, no. 8: 1475. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11081475
APA StyleMastenbroek, A., Otim, G., & Ntare, B. R. (2021). Institutionalizing Quality Declared Seed in Uganda. Agronomy, 11(8), 1475. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11081475






