Mitigating Soil Salinity Stress with Gypsum and Bio-Organic Amendments: A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
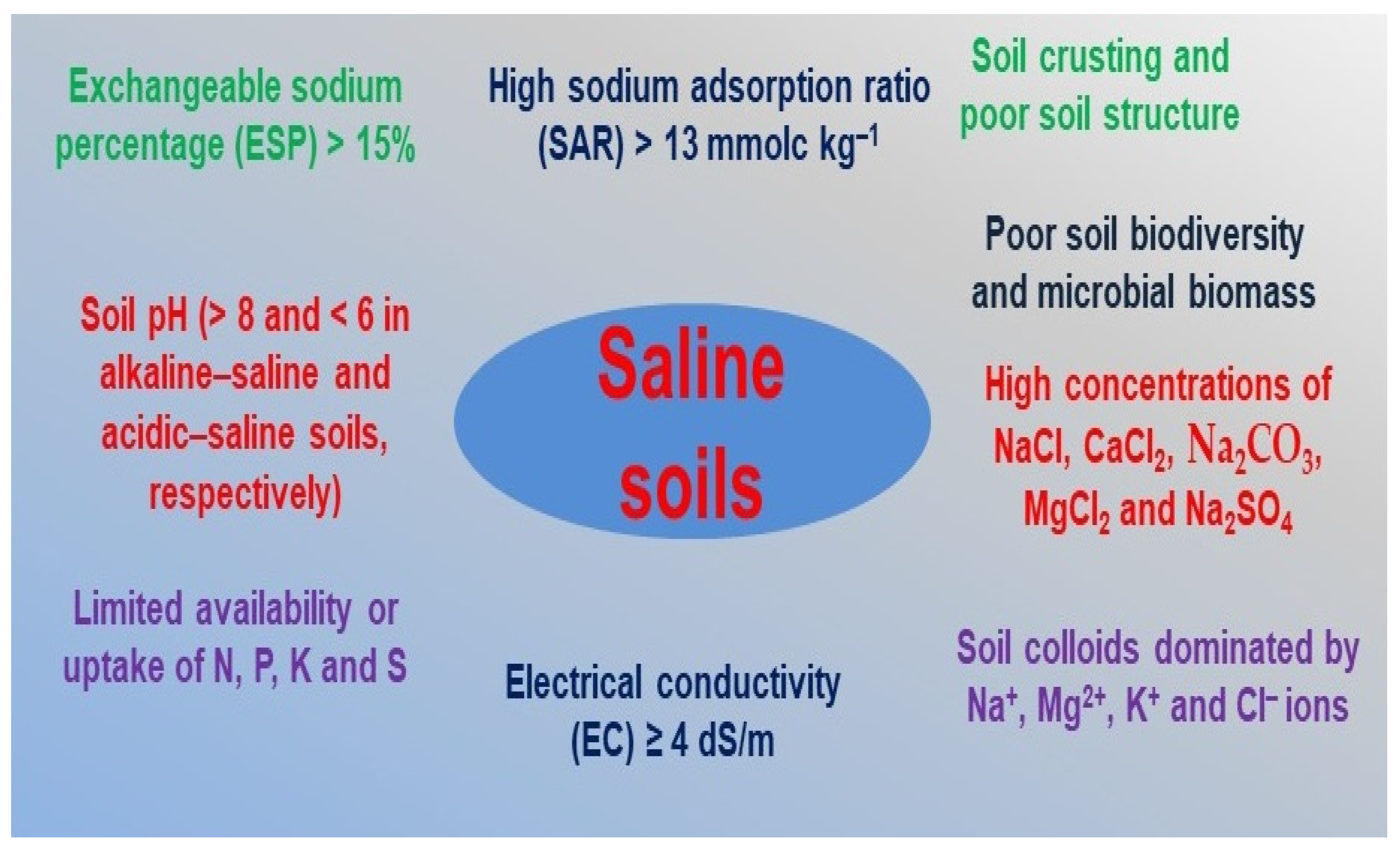
2. Effect of Salinity on Soil Properties and Productivity
Plants Response to Salinity Stress
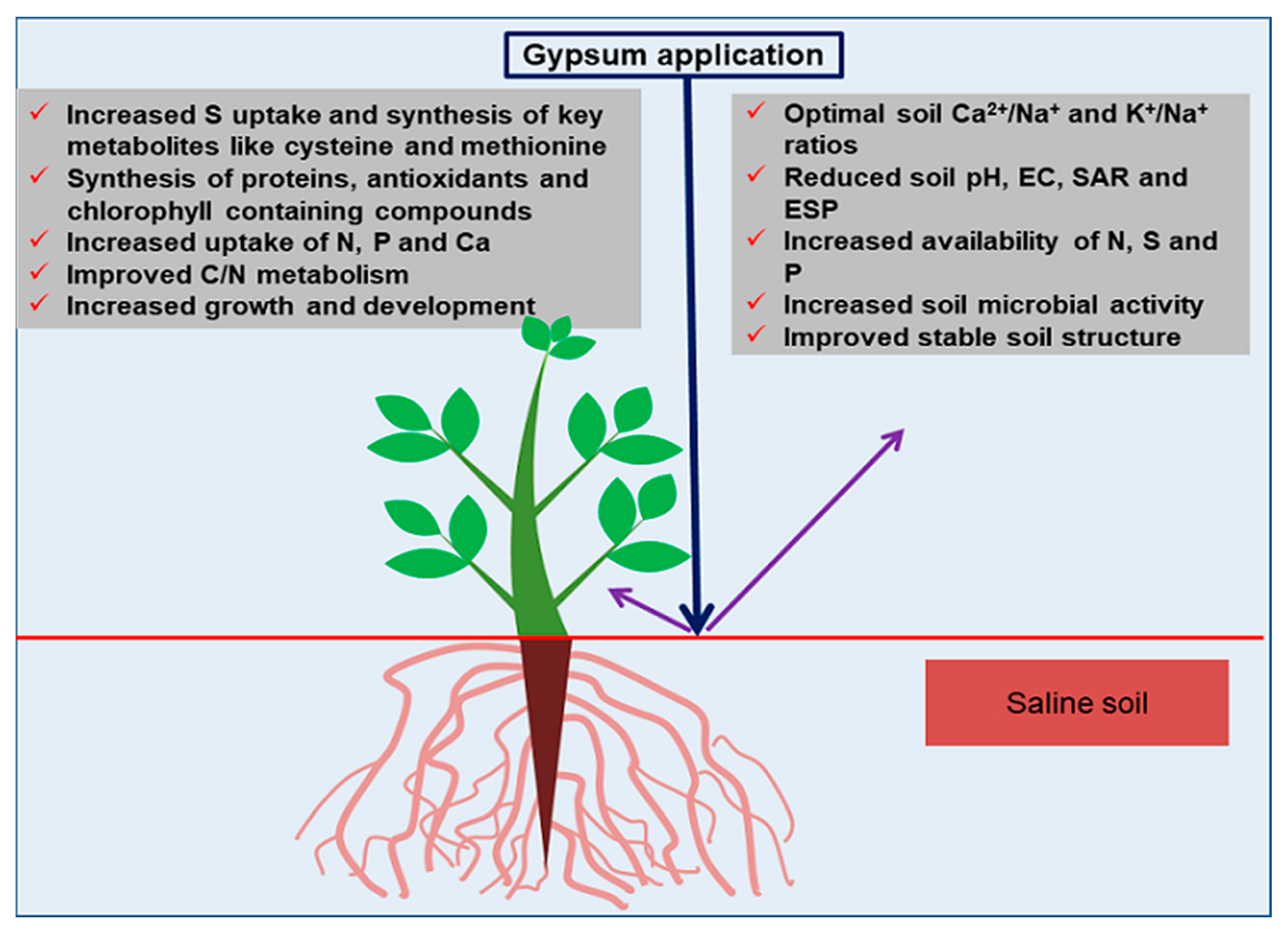
3. Importance of Gypsum in Saline Soils
3.1. Mechanisms of Gypsum Efficacy in Saline Soils
3.2. Regulatory Roles of Sulfur in Plants under Salinity Stress
| S-Containing Compound | Optimal Application Rate | Crop | Impact on Soil and Crop Productivity | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Elemental S | 700 kg S ha−1 | Red Cabbage (Brassica oleracea var. capitata L.) | Increased head weight and total yield; Increased S, P, N and K uptake; Reduced leaf Na+ content | [71] |
| Elemental S | 1120 kg S ha−1 | Sugarcane (Saccharum sp. var. CP87-3388) | Increased available soil P and S; Increased leaf area index | [22] |
| Elemental S | 500 kg S ha−1 | Pea (Pisum sativum L.) | Increased growth and yield; Increased uptake of N, P and K; Reduced leaf Na+ content | [100] |
| Agricultural sulfur (98% S) | 600 kg S ha−1 | Rice (Oryza sativa L. cv. Sakha 106) | Decreased soil pH, EC and bulk density; Increased growth and yield | [101] |
| Gypsum | 5 t ha−1 | Berseem clover (Trifolium alexandrinum L. cv. Helaly) | Decreased soil pH and EC; Increased soil available K; Increased growth, herbage production and forage quality | [102] |
| Gypsum | 10.52 t ha−1 | Fodder beet (Beta vulgaris cv. Kawai terma) | Decreased soil pH, SAR, EC and bulk density; increased root and shoot biomass production | [103] |
| Gypsum | 4 t ha−1 | Onion (Allium cepa L. cv. Adama red) | Decreased soil EC and ESP; increased exchangeable Ca2+ and onion yield | [104] |
| Gypsum | 12 t ha−1 | Grapevine (Vitis vinifera) | Decreased soil ESP, improved root growth, water penetration and fruit yield. | [70] |
| Gypsum | 9.2 t ha−1 | Wheat (Triticum aestivum L. cv. Gemmeiza 11) | Increased grain yield and reduced soil and irrigation water salinity | [66] |
4. Emerging Perspectives in the Amelioration of Salt-Affected Soils
4.1. Effects of Bio-Organic Amendments on Saline Soils
4.2. Complementary Use of Gypsum and Bio-Organic Amendments in the Management of Saline Soils
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Young, J.; Udeigwe, T.K.; Weindorf, D.C.; Kandakji, T.; Gautam, P.; Mahmoud, M.A. Evaluating management-induced soil salinization in golf courses in semi-arid landscapes. Solid Earth 2015, 6, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akram, S.; Siddiqui, M.N.; Hussain, B.M.N.; Al Bari, M.A.; Mostofa, M.G.; Hossain, M.A.; Tran, L.-S.P. Exogenous glutathione modulates salinity tolerance of soybean [Glycine max (L.) Merrill] at reproductive stage. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2017, 36, 877–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, A.S.; Zaman, M.; Heng, L. Soil salinity: Historical perspectives and a world overview of the problem. In Guideline for Salinity Assessment, Mitigation and Adaptation Using Nuclear and Related Techniques; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 43–53. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, P.; Ahanger, M.A.; Alam, P.; Alyemeni, M.N.; Wijaya, L.; Ali, S.; Ashraf, M. Silicon (Si) supplementation alleviates NaCl toxicity in mung bean [Vigna radiata (L.) Wilczek] through the modifications of physio-biochemical attributes and key antioxidant enzymes. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2018, 38, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, M.D.; Oliveira, M.M.; Saibo, N.J.M. Regulation of Na+ and K+ homeostasis in plants: Towards improved salt stress tolerance in crop plants. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2017, 40 (Suppl. S1), 326–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Murphy, B.R.; Jadwiszczak, M.J.; Soldi, E.; Hodkinson, T.R. Endophytes from the crop wild relative Hordeum secalinum L. improve agronomic traits in unstressed and salt stressed barley. Cogent Food Agric. 2018, 4, 1549195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, S.H.; Kumar, V.; Khare, T.; Guddimalli, R.; Parveda, M.; Solymosi, K.; Suprasanna, P.; Kavi Kishor, P.B. Engineering salinity tolerance in plants: Progress and prospects. Planta 2020, 251, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, P.; Lata, C.; Kumar, S. Effect of individual and interactive alkalinity and salinity on physiological, biochemical and nutritional traits of Marvel grass. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 2018, 56, 573–581. [Google Scholar]
- Pitman, M.G.; Läuchli, A. Global impact of salinity and agricultural ecosystems. In Salinity: Environment-Plants-Molecules; Läuchli, A., Lüttge, U., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Rengasamy, P. Soil processes affecting crop production in salt-affected soils. Funct. Plant Biol. 2010, 37, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, K.; Qadir, G.; Jami, A.R.; Saqib, A.I.; Nawaz, M.Q.; Kamal, M.A.; Haq, E. Strategies for Soil Amelioration Using Sulphur in Salt Affected Soils. Cercet. Agron. Mold. 2016, 49, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-shareef, O.N.; Tester, M. Plant salinity tolerance. In eLS; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.-K. Plant salt stress. In eLS; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.J.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.Y.; Oh, D.H.; Dassanayake, M.; Liu, B.; Huang, Q.; Sun, H.X.; Xia, R.; Wu, Y.; et al. Insights into salt tolerance from the genome of Thellungiella salsuginea. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 12219–12224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahanger, M.A.; Alyemeni, M.N.; Wijaya, L.; Alamri, S.A.; Alam, P.; Ashraf, M.; Ahmad, P. Potential of exogenously sourced kinetin in protecting Solanum lycopersicum from NaCl-induced oxidative stress through up-regulation of the antioxidant system, ascorbate-glutathione cycle and glyoxalase system. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0202175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldesuquy, H.; Baka, Z.; Mickky, B. Kinetin and spermine mediated induction of salt tolerance in wheat plants: Leaf area, photosynthesis and chloroplast ultrastructure of flag leaf at ear emergence. Egypt. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2014, 1, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Wang, W.H.; Wu, F.H.; He, E.M.; Liu, X.; Shangguan, Z.P.; Zheng, H.L. Hydrogen sulfide enhances salt tolerance through nitric oxide-mediated maintenance of ion homeostasis in barley seedling roots. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abdelhamid, M.; Eldardiry, E.; El-Hady, M.A. Ameliorate salinity effect through sulphur application and its effect on some soil and plant characters under different water quantities. Agric. Sci. 2013, 4, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Assaha, D.V.M.; Ueda, A.; Saneoka, H.; Al-Yahyai, R.; Yaish, M.W. The role of Na+ and K+ transporters in salt stress adaptation in glycophytes. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Fattah, M.K. Potential use of halophytes in combination with gypsum to reclaim and restore saline-sodic soils in Egypt. Malays. J. Soil Sci. 2015, 19, 131–139. [Google Scholar]
- Capaldi, F.R.; Gratão, P.L.; Reis, A.R.; Lima, L.W.; Azevedo, R.A. Sulfur metabolism and stress defense responses in plants. Trop. Plant Biol. 2015, 8, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wiedenfeld, B. Sulfur application effects on soil properties in calcareous soil and on sugarcane growth and yield. J. Plant Nutr. 2011, 34, 1003–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas, J.; Daliakopoulos, I.N.; del Moral, F.; Hueso, J.J.; Tsanis, I.K. A review of soil-improving cropping systems for soil salinization. Agronomy 2019, 9, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gonçalo Filho, F.; da Silva Dias, N.; Suddarth, S.R.P.; Ferreira, J.F.S.; Anderson, R.G.; dos Santos Fernandes, C.; de Lira, R.B.; Neto, M.F.; Cosme, C.R. Reclaiming tropical saline-sodic soils with gypsum and cow manure. Water 2019, 12, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nan, J.; Chen, X.; Chen, C.; Lashari, M.S.; Deng, J.; Du, Z. Impact of flue gas desulfurization gypsum and lignite humic acid application on soil organic matter and physical properties of a saline-sodic farmland soil in Eastern China. J. Soils Sediments 2016, 16, 2175–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadir, M.; Ghafoor, A.; Murtaza, G. Amelioration strategies for saline soils: A review. Land Degrad. Dev. 2000, 11, 501–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abhayawickrama, B.; Gimhani, D.; Kottearachchi, N.; Herath, V.; Liyanage, D.; Senadheera, P. In Silico identification of QTL-based polymorphic genes as salt-responsive potential candidates through mapping with two reference genomes in rice. Plants 2020, 9, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, W.-W.; Wang, C.; Xue, R.; Wang, L. Effects of salinity on the soil microbial community and soil fertility. J. Integr. Agric. 2019, 18, 1360–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Wang, Z.; Meixner, F.X.; Yang, F.; Wu, H.; Chen, X. Biogeochemical characterizations and reclamation strategies of saline sodic soil in Northeastern China. CLEAN-Soil Air Water 2010, 38, 1010–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheeseman, J.M. The evolution of halophytes, glycophytes and crops, and its implications for food security under saline conditions. New Phytol. 2015, 206, 557–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastava, P.; Kumar, R. Soil salinity: A serious environmental issue and plant growth promoting bacteria as one of the tools for its alleviation. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2015, 22, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tavakoli Kivi, S.; Bailey, R.T. Modeling sulfur cycling and sulfate reactive transport in an agricultural groundwater system. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 185, 78–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello, S.K. An overview of the morphological, genetic and metabolic mechanisms regulating phosphorus efficiency via root traits in soybean. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2021, 21, 1013–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, A. Predicting the interaction between the effects of salinity and climate change on crop plants. Sci. Hortic. 1999, 78, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanji, K.K.; Kielen, N.C. Salinity in the soil environment. In Salinity: Environment-Plants-Molecules; Läuchli, A., Lüttge, U., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherland, 2002; pp. 21–51. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, A.; Khan, A.L.; Muneer, S.; Kim, Y.H.; Al-Rawahi, A.; Al-Harrasi, A. Silicon and salinity: Crosstalk in crop-mediated stress tolerance mechanisms. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Safdar, H.; Amin, A.; Shafiq, Y.; Ali, A.; Yasin, R.; Shoukat, A.; Hussan, M.U.I.; Sarwar, M.I. A review: Impact of salinity on plant growth. Nat. Sci. 2019, 17, 34–40. [Google Scholar]
- Ahanger, M.A.; Agarwal, R.M. Salinity stress induced alterations in antioxidant metabolism and nitrogen assimilation in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) as influenced by potassium supplementation. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 115, 449–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lastiri-Hernández, M.A.; Alvarez-Bernal, D.; Bermúdez-Torres, K.; Cárdenas, G.C.; Ceja-Torres, L.F. Phytodesalination of a moderately saline soil combined with two inorganic amendments. Bragantia 2019, 78, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roy, S.J.; Negrao, S.; Tester, M. Salt resistant crop plants. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2014, 26, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munns, R.; Tester, M. Mechanisms of salinity tolerance. Annu. Rev. Plant. Biol. 2008, 59, 651–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.-L.; Flowers, T.J.; Wang, S.-M. Mechanisms of sodium uptake by roots of higher plants. Plant Soil 2009, 326, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keisham, M.; Mukherjee, S.; Bhatla, S.C. Mechanisms of sodium transport in plants-progresses and challenges. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Byrt, C.S.; Zhao, M.; Kourghi, M.; Bose, J.; Henderson, S.W.; Qiu, J.; Gilliham, M.; Schultz, C.; Schwarz, M.; Ramesh, S.A. Non-selective cation channel activity of aquaporin AtPIP2;1 regulated by Ca(2+) and pH. Plant Cell Environ. 2017, 40, 802–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Garciadeblás, B.; Senn, M.E.; Bañuelos, M.A.; Rodríguez-Navarro, A. Sodium transport and HKT transporters: The rice model. Plant J. 2003, 34, 788–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo, J.; Rubio, F. Na+ and K+ transporters in plant signaling. In Transporters and Pumps in Plant Signaling; Geisler, M., Venema, K., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; Volume 7, pp. 65–98. [Google Scholar]
- Maathuis, F.J.; Ahmad, I.; Patishtan, J. Regulation of Na(+) fluxes in plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gupta, B.; Huang, B. Mechanism of salinity tolerance in plants: Physiological, biochemical, and molecular characterization. Int. J. Genom. 2014, 2014, 701596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayakannan, M.; Bose, J.; Babourina, O.; Rengel, Z.; Shabala, S. Salicylic acid improves salinity tolerance in Arabidopsis by restoring membrane potential and preventing salt-induced K+ loss via a GORK channel. J. Exp. Bot. 2013, 64, 2255–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Netondo, G.W.; Onyango, J.C.; Beck, E. Sorghum and salinity: II. gas exchange and chlorophyll fluorescence of sorghum under salt stress. Crop. Sci. 2004, 44, 806–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marschner, P. Mineral nutrition of higher plants. In Special Publications of the Society for General Microbiology, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Peleg, Z.; Apse, M.P.; Blumwald, E. Engineering salinity and water-stress tolerance in crop plants. In Plant Responses to Drought and Salinity Stress-Developments in a Post-Genomic Era; Elsevier Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2011; pp. 405–443. [Google Scholar]
- Hasegawa, P.M.; Bressan, R.A.; Zhu, J.K.; Bohnert, H.J. Plant cellular and molecular responses to high salinity. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 2000, 51, 463–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shabala, S.; Pang, J.; Zhou, M.; Shabala, L.; Cuin, T.A.; Nick, P.; Wegner, L.H. Electrical signalling and cytokinins mediate effects of light and root cutting on ion uptake in intact plants. Plant Cell Environ. 2009, 32, 194–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flowers, T.J.; Colmer, T.D. Salinity tolerance in halophytes. New Phytol. 2008, 179, 945–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamford, N.P.; Figueiredo, M.V.B.; Junior, S.S.; Freitas, A.D.S.; Santos, C.E.R.S.; Junior, M.A.L. Effect of gypsum and sulfur with Acidithiobacillus on soil salinity alleviation and on cowpea biomass and nutrient status as affected by PK rock biofertilizer. Sci. Hortic. 2015, 192, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Xu, Y.; Chen, T.; Xing, L.; Xu, K.; Xu, Y.; Ji, D.; Chen, C.; Xie, C. Regulatory mechanisms underlying the maintenance of homeostasis in Pyropia haitanensis under hypersaline stress conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 662, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.J.; Chen, Q.; Li, Y.; Zhuo, Y.Q.; Xu, L.Z. Research on saline-alkali soil amelioration with FGD gypsum. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2017, 121, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Kim, K.-R.; Lee, S.-H.; Kunhikrishnan, A.; Kim, W.-I.; Kim, K.-H. Effect of gypsum on exchangeable sodium percentage and electrical conductivity in the Daeho reclaimed tidal land soil in Korea—A field scale study. J. Soils Sediments 2016, 18, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcívar, M.; Zurita-Silva, A.; Sandoval, M.; Muñoz, C.; Schoebitz, M. Reclamation of saline–sodic soils with combined amendments: Impact on quinoa performance and biological soil quality. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shainberg, I.; Sumner, M.E.; Miller, W.P.; Farina, M.P.W.; Pavan, M.A.; Fey, M.Y. Use of Gypsum on Soils: A Review. Adv. Soil Sci. 1989, 9, 1–111. [Google Scholar]
- Abd El-Hady, M.; Shaaban, S.M. Acidification of saline irrigation water as a water conservation technique and its effect on some soil properties. Am.-Eurasian J. Agric. Environ. Sci. 2010, 7, 463–470. [Google Scholar]
- Cifuentes, F.R.; Lindemann, W.C. Organi matter stimulation of elemental sulfur oxidation in a calcareous soil. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1993, 57, 727–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weil, R.R.; Brady, N.C. The Nature and Properties of Soils, 15th ed.; Pearson: England, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmoodabadi, M.; Yazdanpanah, N.; Sinobas, L.R.; Pazira, E.; Neshat, A. Reclamation of calcareous saline sodic soil with different amendments (I): Redistribution of soluble cations within the soil profile. Agric. Water Manag. 2013, 120, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboelsoud, H.; Engel, B.; Gad, K. Effect of planting methods and gypsum application on yield and water productivity of wheat under salinity conditions in North Nile Delta. Agronomy 2020, 10, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cramer, G.R. Kinetics of maize leaf elongation. J. Exp. Bot. 1992, 43, 857–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grieve, C.; Grattan, S. Mineral nutrient acquisition and response by plants grown in saline environments. In Handbook of Plant and Crop Stress, 2nd ed.; Pessarakli, M., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1999; pp. 203–229. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, J.; Rengasamy, P. Diagnosis and Management of Soil Constraints: Transient Salinity, Sodicity and Alkalinity; The University of Adelaide and Grain Research and Development Corporation: Adelaide, Australia, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Wheaton, A.D.; McKenzie, B.M.; Tisdall, J.M. Management of a sodic soil for wine grape production. Aust. J. Exp. Agric. 2002, 42, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalaby, O.A.E.-S. Alleviation of salinity stress in red cabbage plants by urea and sulfur applications. J. Plant Nutr. 2018, 41, 1597–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riffat, A.; Ahmad, M.S.A. Alleviation of adverse effects of salt stress on growth of maize (Zea mays L.) by sulfur supplementation. Pak. J. Bot. 2020, 52, 763–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.L.d.S.; Trevizam, A.R.; Piccolo, M.C.; Furlan, G. Tomato production in function of sulfur doses application. Rev. Bras. Tecnol. Apl. Ciências Agrárias 2014, 7, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, B.A.; Kopittke, P.M.; Macfarlane, D.C.; Dalzell, S.A.; Menzies, N.W. Changes in soil chemistry after the application of gypsum and sulfur and irrigation with coal seam water. Geoderma 2019, 337, 782–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, S.J.; Norton, J.B.; Strom, C.F.; Kelleners, T.J.; Aboukila, E.F. Gypsum, langbeinite, sulfur, and compost for reclamation of drastically disturbed calcareous saline–sodic soils. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 16, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherer, H.W. Sulphur in crop production—Invited paper. Eur. J. Agron. 2001, 14, 81–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanuzzaman, M.; Bhuyan, M.; Mahmud, J.A.; Nahar, K.; Mohsin, S.M.; Parvin, K.; Fujita, M. Interaction of sulfur with phytohormones and signaling molecules in conferring abiotic stress tolerance to plants. Plant Signal Behav. 2018, 13, e1477905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazar, R.; Iqbal, N.; Masood, A.; Syeed, S.; Khan, N.A. Understanding the significance of sulfur in improving salinity tolerance in plants. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2011, 70, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatma, M.; Masood, A.; Per, T.S.; Rasheed, F.K.; Nafees, A. Interplay between nitric oxide and sulfur assimilation in salt tolerance in plants. Crop. J. 2016, 4, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lewandowska, M.; Sirko, A. Recent advances in understanding plant response to sulfur-deficiency stress. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2008, 55, 457–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koralewska, A.; Stuiver, C.E.E.; Posthumus, F.S.; Kopriva, S.; Hawkesford, M.J.; de Kok, L.J. Regulation of sulfate uptake, expression of the sulfate transporters Sultr1;1 and Sultr1;2, and APS reductase in Chinese cabbage (Brassica pekinensis) as affected by atmospheric H2S nutrition and sulfate deprivation. Funct. Plant Biol. 2008, 35, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazid, M.; Khan, T.M.; Mohammad, F. Response of crop plants under sulphur stress tolerance. J. Stress Physiol. Biochem. 2011, 7, 25–57. [Google Scholar]
- Hawkesford, M.J.; de Kok, L.J. Managing sulphur metabolism in plants. Plant Cell Environ. 2006, 29, 382–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fatma, M.; Khan, M.I.R.; Masood, A.; Khan, N.A. Coordinate changes in assimilatory sulfate reduction are correlated to salt tolerance: Involvement of phytohormones. Annu. Rev. Res. Biol. 2013, 3, 267–295. [Google Scholar]
- Iqbal, N.; Masood, A.; Khan, M.I.; Asgher, M.; Fatma, M.; Khan, N.A. Cross-talk between sulfur assimilation and ethylene signaling in plants. Plant Signal Behav. 2013, 8, e22478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nazar, R.; Umar, S.; Khan, N.A. Exogenous salicylic acid improves photosynthesis and growth through increase in ascorbate-glutathione metabolism and S assimilation in mustard under salt stress. Plant Signal Behav. 2015, 10, e1003751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chan, K.X.; Phua, S.Y.; van Breusegem, F. Secondary sulfur metabolism in cellular signalling and oxidative stress responses. J. Exp. Bot. 2019, 70, 4237–4250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Spadaro, D.; Yun, B.W.; Spoel, S.H.; Chu, C.; Wang, Y.Q.; Loake, G.J. The redox switch: Dynamic regulation of protein function by cysteine modifications. Physiol. Plant 2010, 138, 360–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, S.S.; Tuteja, N. Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant machinery in abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2010, 48, 909–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz, J.M.; Blumwald, E. Salinity-induced glutathione synthesis in Brassica napus. Planta 2002, 214, 965–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Mageed, T.A.; Rady, M.M.; Taha, R.S.; Abd El Azeam, S.; Simpson, C.R.; Semida, W.M. Effects of integrated use of residual sulfur-enhanced biochar with effective microorganisms on soil properties, plant growth and short-term productivity of Capsicum annuum under salt stress. Sci. Hortic. 2020, 261, 108930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruse, C.; Jost, R.; Lipschis, M.; Kopp, B.; Hartmann, M.; Hell, R. Sulfur-enhanced defence: Effects of sulfur metabolism, nitrogen supply, and pathogen lifestyle. Plant Biol. (Stuttg.) 2007, 9, 608–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjum, N.A.; Gill, R.; Kaushik, M.; Hasanuzzaman, M.; Pereira, E.; Ahmad, I.; Tuteja, N.; Gill, S.S. ATP-sulfurylase, sulfur-compounds, and plant stress tolerance. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khan, N.A.; Nazar, R.; Anjum, N.A. Growth, photosynthesis and antioxidant metabolism in mustard (Brassica juncea L.) cultivars differing in ATP-sulfurylase activity under salinity stress. Sci. Hortic. 2009, 122, 455–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koprivova, A.; North, K.A.; Kopriva, S. Complex signaling network in regulation of adenosine 5’-phosphosulfate reductase by salt stress in Arabidopsis roots. Plant Physiol. 2008, 146, 1408–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fatma, M.; Asgher, M.; Masood, A.; Khan, N.A. Excess sulfur supplementation improves photosynthesis and growth in mustard under salt stress through increased production of glutathione. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2014, 107, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perveen, S.; Iqbal, N.; Saeed, M.; Zafar, S.; Arshad, Z. Role of foliar application of sulfur-containing compounds on maize (Zea mays L. var. Malka and hybrid DTC) under salt stress. Braz. J. Bot. 2018, 41, 805–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ur Rehman, H.; Iqbal, Q.; Farooq, M.; Wahid, A.; Afzal, I.; Basra, S.M.A. Sulphur application improves the growth, seed yield and oil quality of canola. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2013, 35, 2999–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krischan, J.; Makaruk, A.; Harasek, M. Design and scale-up of an oxidative scrubbing process for the selective removal of hydrogen sulfide from biogas. J. Hazard Mater. 2012, 215–216, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osman, A.S.; Rady, M.M. Ameliorative effects of sulphur and humic acid on the growth, anti-oxidant levels, and yields of pea (Pisum sativum L.) plants grown in reclaimed saline soil. J. Hortic. Sci. Biotechnol. 2015, 87, 626–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zayed, B.; Abdelaal, M.; Deweedar, G. Response of rice yield and soil to sulfur application under water and salinity stresses. Egypt. J. Agron. 2017, 39, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Naby, Z.M.; Hafez, W.A.E.-K.; Hashem, H.A. Remediation of salt-affected soil by natural and chemical amendments to improve berseem clover yield and nutritive quality. Afr. J. Range Forage Sci. 2018, 36, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, K.; Qadir, G.; Jami, A.-R.; Nawaz, M.Q.; Rehim, A.; Jabran, K.; Hussain, M. Gypsum and farm manure application with chiseling improve soil properties and performance of fodder beet under saline-sodic conditions. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2015, 17, 1225–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitila, K.; Chala, A.; Workina, M. Effect of Gypsum and compost Application in Reclaiming Sodic soils at Small Scale Irrigation Farm in Bora District of East Shewa Zone, Oromia, Ethiopia. Agriways 2020, 08, 28–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouri, H.; Chavoshi Borujeni, S.; Nirola, R.; Hassanli, A.; Beecham, S.; Alaghmand, S.; Saint, C.; Mulcahy, D. Application of green remediation on soil salinity treatment: A review on halophytoremediation. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2017, 107, 94–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanji, K.; Kielen, N. Agricultural drainage water management in arid and semi-arid areas. In FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper 61, Annex 1: Crop Salt Tolerance Data; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Chartzoulakis, K.S. Salinity and olive: Growth, salt tolerance, photosynthesis and yield. Agric. Water Manag. 2005, 78, 108–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuazo, V.H.D.; Raya, A.M.n.; Ruiz, J.A. Impact of salinity on the fruit yield of mango (Mangifera indica L. cv. ‘Osteen’). Eur. J. Agron. 2004, 21, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paranychianakis, N.V.; Chartzoulakis, K.S. Irrigation of Mediterranean crops with saline water: From physiology to management practices. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2005, 106, 171–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panta, S.; Flowers, T.; Lane, P.; Doyle, R.; Haros, G.; Shabala, S. Halophyte agriculture: Success stories. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2014, 107, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abate, S.; Belayneh, M.; Ahmed, F.; Tejada Moral, M. Reclamation and amelioration of saline-sodic soil using gypsum and halophytic grasses: Case of Golina-Addisalem irrigation scheme, Raya Kobo Valley, Ethiopia. Cogent Food Agric. 2021, 7, 1859847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello, S.K.; Yusuf, A.A. Phosphorus influences the performance of mycorrhiza and organic manure in maize production. J. Plant Nutr. 2021, 44, 679–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbarki, S.; Cerda, A.; Brestic, M.; Mahendra, R.; Abdelly, C.; Pascual, J.A. Vineyard compost supplemented with Trichoderma Harzianum T78 improve saline soil quality. Land Degrad. Dev. 2017, 28, 1028–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamoorthy, R.; Kim, K.; Subramanian, P.; Senthilkumar, M.; Anandham, R.; Sa, T. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and associated bacteria isolated from salt-affected soil enhances the tolerance of maize to salinity in coastal reclamation soil. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 231, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Tang, X.; Shao, H.; Wang, H. The foliar spray of Rhodopseudomonas palustris grown under Stevia residue extract promotes plant growth via changing soil microbial community. J. Soils Sediments 2015, 16, 916–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacilio, M.; Moreno, M.; Bashan, Y. Mitigation of negative effects of progressive soil salinity gradients by application of humic acids and inoculation with Pseudomonas stutzeri in a salt-tolerant and a salt-susceptible pepper. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2016, 107, 394–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, K.; Apostolakis, A.; Daliakopoulos, I.; Tsanis, I. Can tomato inoculation with Trichoderma compensate yield and soil health deficiency due to soil salinity? In Proceedings of the EGU (European Geosciences Union) General Assembly Conference, Vienna, Austria, 17–22 April 2016; Geophysical Research Abstracts; EGU2016–1007; EGU: Vienna, Austria, 2016.
- Daliakopoulos, I.N.; Apostolakis, A.; Wagner, K.; Deligianni, A.; Koutskoudis, D.; Stamatakis, A.; Tsanis, I.K. Effectiveness of Trichoderma harzianum in soil and yield conservation of tomato crops under saline irrigation. Catena 2019, 175, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leithy, S.; Gaballah, M.; Goma, A. Associative impact of bio- and organic fertilizers on geranium plants grown under saline conditions. Int. J. Acad. Res. 2009, 1, 17–23. [Google Scholar]
- Jha, Y.; Subramanian, R.B. PGPR regulate caspase-like activity, programmed cell death, and antioxidant enzyme activity in paddy under salinity. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants 2014, 20, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miltner, A.; Richnow, H.-H.; Kopinke, F.-D.; Kästner, M. Incorporation of carbon originating from CO2 into different compounds of soil microbial biomass and soil organic matter. Isot. Environ. Health Stud. 2005, 41, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ontl, T.; Schulte, L. Soil Carbon Storage. Nat. Educ. Knowl. 2012, 3, 35. Available online: https://www.nature.com/scitable/knowledge/library/soil-carbon-storage-84223790/ (accessed on 20 August 2021).
- Khatun, M.; Shuvo, M.A.R.; Salam, M.T.B.R.; Hafizur, S.M. Effect of organic amendments on soil salinity and the growth of maize (Zea mays L.). Plant Sci. Today 2019, 6, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ondrasek, G.; Rengel, Z. Environmental salinization processes: Detection, implications & solutions. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 754, 142432. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gómez, I.; Navarro-Pedreño, J.; Mataix, J. The influence of saline irrigation and organic waste fertilisation on the mineral content (N, P, K, Na, Ca and Mg) of tomatoes. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1992, 59, 483–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Fattah, M.K. Role of gypsum and compost in reclaiming saline-sodic soils. J. Agric. Vet. Sci. 2012, 1, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaaban, M.; Abid, M.; Abou, S. Amelioration of salt affected soils in rice paddy system by application of organic and inorganic amendments. Plant Soil Environ. 2013, 59, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vance, W.H.; Tisdall, J.M.; McKenzie, B.M. Residual effects of surface applications of organic matter and calcium salts on the subsoil of a red-brown earth. Aust. J. Exp. Agric. 1998, 38, 595–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, U.; Eroğlu, S.; Sahin, F. Microbial application with gypsum increases the saturated hydraulic conductivity of saline–sodic soils. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2011, 48, 247–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayoumy, M.; Khalifa, T.; Aboelsoud, H. Impact of some organic and inorganic amendments on some soil properties and wheat production under saline-sodic soil. J. Soil Sci. Agric. Eng. 2019, 10, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bello, S.K.; Alayafi, A.H.; AL-Solaimani, S.G.; Abo-Elyousr, K.A.M. Mitigating Soil Salinity Stress with Gypsum and Bio-Organic Amendments: A Review. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1735. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11091735
Bello SK, Alayafi AH, AL-Solaimani SG, Abo-Elyousr KAM. Mitigating Soil Salinity Stress with Gypsum and Bio-Organic Amendments: A Review. Agronomy. 2021; 11(9):1735. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11091735
Chicago/Turabian StyleBello, Suleiman K., Abdullah H. Alayafi, Samir G. AL-Solaimani, and Kamal A. M. Abo-Elyousr. 2021. "Mitigating Soil Salinity Stress with Gypsum and Bio-Organic Amendments: A Review" Agronomy 11, no. 9: 1735. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11091735
APA StyleBello, S. K., Alayafi, A. H., AL-Solaimani, S. G., & Abo-Elyousr, K. A. M. (2021). Mitigating Soil Salinity Stress with Gypsum and Bio-Organic Amendments: A Review. Agronomy, 11(9), 1735. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11091735








