Synthesis and Characterization of Nano Fe and Mn (hydr)oxides to Be Used as Natural Sorbents and Micronutrient Fertilizers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Synthesis of Nano-Amorphous Metal Oxides
2.3. Characterization of Nano Metal Oxides
2.4. Heavy Metal Interactions and Nutrients Releasing
2.5. Plant Experiment
2.6. Plant Material
2.7. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of Nano-Amorphous Metal Oxides
3.1.1. Infrared Spectroscopy
3.1.2. Crystallinity
3.1.3. Particle Size
3.1.4. Specific Surface-Area
3.1.5. Point of Zero Charge (PZC)
3.1.6. Mössbauer Spectrometry
3.2. Heavy Metals Interactions and Nutrients Releasing
3.3. Plant Experiment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AMO | amorphous Mn oxide |
| FMBO | Fe-Mn binary oxide |
| 2L-Fh | two-line ferrihydrite |
| Fe-EDDHA | Fe (III) ethylenediamine bis (o-hydroxyphenyl acetic acid) |
| Fe-EDDHMA | (Fe (III) ethylenediamine di-(o-hydroxy-p-methyl-phenylacetic) acid), iron (III) N,N’-bis(o-hydroxybenzyl)-ethylenediamine-N,N’-diacetic acid |
| FTIR | Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, ICP MS: inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry, XRD X-ray diffraction |
| ANOVA | analysis of variance |
References
- Gillispie, E.C.; Taylor, S.E.; Qafoku, N.P.; Hochella, M.F. Impact of iron and manganese nano-metal-oxides on contaminant interaction and fortification potential in agricultural systems—A review. Environ. Chem. 2019, 16, 377–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pariona, N.; Camacho-Aguilar, K.I.; Ramos-González, R.; Martinez, A.I.; Herrera-Trejo, M.; Baggio-Saitovitch, E. Magnetic and structural properties of ferrihydrite/hematite nanocomposites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2016, 406, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michálková, Z.; Martínez-Fernández, D.; Komárek, M. Interactions of two novel stabilizing amendments with sunflower plants grown in a contaminated soil. Chemosphere 2017, 186, 374–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornell, R.M.; Schwertmann, U. The Iron Oxides: Structures, Properties, Reactions, Occurrences and Uses, 2nd ed.; WILEY-VHC. GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.; Pigna, M.; Cozzolino, V.; Caporale, A.G.; Violante, A. Competitive sorption of copper(II), chromium(III) and lead(II) on ferrihydrite and two organomineral complexes. Geoderma 2010, 159, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalobos, M.; Antelo, J. A unified surface structural model for ferrihydrite: Proton charge, electrolyte binding, and arsenate adsorption. Rev. Int. Contam. Ambient. 2011, 27, 139–151. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, S.J.; Page, K.; Kim, H.; Campbell, B.J.; Boerio-Goates, J.; Woodfield, B.F. Novel synthesis and structural analysis of ferrihydrite. Inorg. Chem. 2012, 51, 6421–6424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villacís-García, M.; Ugalde-Arzate, M.; Vaca-Escobar, K.; Villalobos, M.; Zanella, R.; Martínez-Villegas, N. Laboratory synthesis of goethite and ferrihydrite of controlled particle sizes. Bol. Soc. Geol. Mex. 2015, 67, 433–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, A.; Banerjee, S.; Mani, R.; Chattopadhyaya, M.C. Synthesis, characterization, and application of goethite mineral as an adsorbent. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2013, 1, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitrakar, R.; Tezuka, S.; Sonoda, A.; Sakane, K.; Ooi, K.; Hirotsu, T. Phosphate adsorption on synthetic goethite and akageneite. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2006, 298, 602–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Puppa, L.; Komárek, M.; Bordas, F.; Bollinger, J.C.; Joussein, E. Adsorption of copper, cadmium, lead and zinc onto a synthetic manganese oxide. J. Colloid. Interf. Sci. 2013, 399, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ettler, V.; Knytl, V.; Komárek, M.; Della Puppa, L.; Bordas, F.; Mihaljevič, M.; Klementová, M.; Šebek, O. Stability of a novel synthetic amorphous manganese oxide in contrasting soils. Geoderma 2014, 214–215, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataria, N.; Garg, V.K. Green synthesis of Fe3O4 nanoparticles loaded sawdust carbon for cadmium (II) removal from water: Regeneration and mechanism. Chemosphere 2018, 208, 818–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xu, F.; Li, F.; Li, L. Synthesis, application, and mechanisms of ferro-manganese binary oxide in water remediation: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 388, 124313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chugh, G.; Siddique, K.H.M.; Solaiman, Z.M. Nanobiotechnology for agriculture: Smart technology for combating nutrient deficiencies with nanotoxicity challenges. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizwan, M.; Ali, S.; Qayyum, M.F.; Ok, Y.S.; Adrees, M.; Ibrahim, M.; Zia-ur-Rehman, M.; Farid, M.; Abbas, F. Effect of metal and metal oxide nanoparticles on growth and physiology of globally important food crops: A critical review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 322, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marschner, P.; Rengel, Z. Chapter 12: Nutrient availability in soils. In Marschner’s Mineral Nutrition in Higher Plants, 3rd ed.; Marschner, P., Ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2012; pp. 315–330. ISBN 9780123849052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 3696:1987. Water for Analytical Laboratory Use–Specification and Test Methods. 1987. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/9169.html (accessed on 8 June 2021).
- Luo, J.; Zhang, Q.; Suib, S.L. Mechanistic and kinetic studies of crystallization of birnessite. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 1999, 33, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lui, H.; Yang, Y.; Kang, J.; Fan, M.; Qu, J. Removal of tetracycline from water by Fe-Mn binary oxide. J. Environ. Sci. 2012, 24, 242–247. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Chen, Y.; Long, J.; Li, X.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, P.; Qi, J.; Huang, X.; Liu, J.; Xu, R.; et al. Removal of thallium from aqueous solutions using Fe-Mn binary oxides. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 338, 296–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Qua, J.; Liu, H.; Liu, R.; Wu, R. Preparation and evaluation of a novel Fe–Mn binary oxide adsorbent for effective arsenite removal. Water Res. 2007, 41, 1921–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwertmann, U.; Cornell, R.M. Iron Oxides in the Laboratory: Preparation and Characterization; Wiley: Weinheim, Germany, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Antelo, J.; Fiol, S.; Pérez, C.; Marinño, S.; Arce, F.; Gondar, D.; López, R. Analysis of phosphate adsorption onto ferrihydrite using the CD-MUSIC model. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 347, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eljamala, R.; Eljamala, O.; Khalilb, A.M.E.; Sahac, B.B.; Matsunagaa, N. Improvement of the chemical synthesis efficiency of nano-scale zero-valent iron particles. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 4727–4735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand, R.A. Improving the validity of hyperfine field distributions from magnetic alloys. Part I: Unpolarized source. In Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physic Research Section B Beam Interaction with Materials and Atoms; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1987; Volume 28, pp. 398–416. [Google Scholar]
- Zornoza, P.; Sánchez-Pardo, B.; Carpena, R.O. Interaction and accumulation of manganese and cadmium in the manganese accumulator Lupinus albus. J. Plant. Physiol. 2010, 167, 1027–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blamey, F.P.C.; Hernandez-Soriano, M.C.; Cheng, M.; Tang, C.; Paterson, D.J.; Lombi, E.; Wang, W.H.; Scheckel, K.G.; Kopittke, P.M. Synchrotron-based techniques shed light on mechanisms of plant sensitivity and tolerance to high manganese in the root environment. Plant. Physiol. 2015, 169, 2006–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lozano-Rodríguez, E.; Luguera, M.; Lucena, J.J.; Carpena-Ruiz, R.O. Evaluation of two different acid digestion methods in closed systems of trace elements determination in plants. Quim. Anal. 1995, 14, 27–30. [Google Scholar]
- Pradhan, S.; Patra, P.; Das, S.; Chandra, S.; Mitra, S.; Dey, K.K.; Akbar, S.; Palit, P.; Goswami, A. Photochemical modulation of biosafe manganese nanoparticles on Vigna radiata: A detailed molecular, biochemical, and biophysical study. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 13122–13131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hausner, D.B.; Bhandari, N.; Pierre-Louis, A.M.; Kubicki, J.D.; Strongin, D.R. Ferrihydrite reactivity toward carbon dioxide. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 337, 492–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, D.; Wilson, L.D. Synthesis and characterization of cellulose-goethite composites and their adsorption properties with roxarsone. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 169, 282–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouředníček, P.; Hudcová, B.; Trakal, L.; Pohořelý, M.; Komárek, M. Synthesis of modified amorphous manganese oxide using low-cost sugars and biochars: Material characterization and metal(loid) sorption properties. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 670, 1159–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Lan, H.; Wang, H.; Liu, H.; Qu, J. Comparing the adsorption behaviors of Cd, Cu and Pb from water onto Fe-Mn binary oxide, MnO2 and FeOOH. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2015, 9, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Leo, P.; Pizzigallo, M.D.R.; Anconac, V.; Di Benedetto, F.; Mesto, E.; Schingaro, E.; Ventruti, G. Mechanochemical transformation of an organic ligand on mineral surfaces: The efficiency of birnessite in catechol degradation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 201–202, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, K.; Maity, A.; Ghosh, U.C. Manganese associated nanoparticles agglomerate of iron(III) oxide: Synthesis, characterization and arsenic(III) sorption behavior with mechanism. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 184, 832–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laxmipathiraj, P.; Narshimhan, B.R.V.; Prabhakar, S.; Bhaskarraju, G. Adsorption studies of arsenic on manganese substituted iron oxyhydroxide. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 304, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Zhou, J.; Lou, Z.; Zhou, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Baig, S.A.; Xu, X. Removal of Sb(V) from aqueous solutions using Fe-Mn binary oxides: The influence of iron oxides forms and the role of manganese oxides. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 354, 577–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappell, H.F.; Thom, W.; Bowron, D.T.; Faria, N.; Hasnip, P.J.; Powell, J.J. Structure of naturally hydrated ferrihydrite revealed through neutron diffraction and first-principles modeling. Phys. Rev. Mater. 2017, 1, 036002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gu, X.; Yue, J.; Li, L.; Xue, H.; Yang, J.; Zhao, X. General synthesis of MnOx (MnO2, Mn2O3, Mn3O4, MnO) hierarchical microspheres as lithium-ion battery anodes. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 184, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Shen, Y.; Jia, Z.; Qiu, G.; Liu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, X.; Cai, C. Interaction mechanisms and kinetics of ferrous ion and hexagonal birnessite in aqueous systems. Geochem. Trans. 2015, 16, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Valezi, D.F.; Bau, J.P.T.; Zaia, D.A.M.; Costa, A.C.S.; Urbano, A.; Tupan, L.F.S.; Paesano, A., Jr.; Piccinato, M.T.; Di Mauro, E. Enhanced magnetic component in synthetic goethite (α-FeOOH) and its relationship with morphological and structural characteristics. Phys. Status Solidi B 2019, 256, 1800578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.; Mosa, I.M.; Poyraz, A.S.; Biswas, S.; El-Sawy, A.M.; Song, W.; Luo, Z.; Chen, S.; Rusling, J.F.; He, J.; et al. Robust mesoporous manganese oxide catalysts for water oxidation. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 1693–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Liu, F.; Feng, X.; Hub, T.; Zheng, L.; Qiu, G.; Koopal, L.K.; Tan, W. Effects of Fe doping on the structures and properties of hexagonal birnessites—Comparison with Co and Ni doping. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2013, 117, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Zhang, W.; Tao, L.; Liu, F.; Zhang, J. Enhanced removal of antimony by acid birnessite with doped iron ions: Companied by the structural transformation. Chemosphere 2019, 226, 834–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.; Lu, S.; Liu, F.; Feng, X.; He, J.; Koopal, L.K. Determination of the point-of-zero charge of manganese oxides with different methods including an improved salt titration method. Soil Sci. 2008, 173, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, H.; Keqiang, S.; Daiping, H.; Boqing, X. Amorphous manganese oxide for catalytic aerobic oxidation of benzyl alcohol. Chin. J. Catal. 2007, 28, 1025–1027. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.; Wu, P.; Yu, L.; Liu, S.; Ruan, B.; Hu, H.; Zhu, N.; Lin, Z. FeOOH-loaded MnO2 nano-composite: An efficient emergency material for thallium pollution incident. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 192, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyittah, M.K.; Tsyawo, F.W.; Kumah, K.K.; Stanley, C.D.; Rechcigl, J.E. Suitability of two methods for determination of point of zero charge (PZC) of adsorbents in soils. Comm. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2015, 47, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husnain, S.M.; Asim, U.; Yaqub, A.; Shahzad, F.; Abbas, N. Recent trends of MnO2-derived adsorbents for water treatment: A review. New J. Chem. 2020, 44, 6096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komulski, M. Compilation of PZC and IEP of sparingly soluble metal oxides and hydroxides from literature. Adva. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 152, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, B.; Zhao, D. Immobilization of as (III) in soil and groundwater using a new class of polysaccharide stabilized Fe–Mn oxide nanoparticles. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 211–212, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, M.; Hanna, K.; Abdelmoula, M.; Zegeye, A.; Faure, P.; Ruby, C. Formation of green rust via mineralogical transformation of ferric oxides (ferrihydrite, goethite and hematite). Appl. Clay Sci. 2012, 64, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsyth, J.B.; Hedleys, I.G.; Johnson, C.E. The magnetic structure and hyperfine field of goethite (a-FeOOH). J. Phys. C Solid State Phys. 1968, 1, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.A.; Leckie, J.O. Effect of adsorbed complexing ligands on trace metal uptake by hydrous oxides. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1978, 12, 1309–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coup, K.M.; Swedlund, P.J. Demystifying the interfacial aquatic geochemistry of thallium(I): New and old data reveal just a regular cation. Chem. Geol. 2015, 398, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, A.R.; McBride, M.B.; Baveye, P.; Steenhuis, T.S. Environmental factors determining the trace-level sorption of silver and thallium to soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 345, 191–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akter, M.; Sikder, M.T.; Rahman, M.M.; Ullah, A.A.; Hossain, K.F.B.; Banik, S.; Hosokawa, T.; Saito, T.; Kurasaki, M. A systematic review on silver nanoparticles-induced cytotoxicity: Physicochemical properties and perspectives. J. Adv. Res. 2018, 9, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, B.J.; Jenne, E.A.; Chao, T.T. The sorption of silver by poorly crystallized manganese oxides. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1973, 37, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasany, S.M.; Rehman, H.U.; Rashid, A. Adsorption of microamounts of silver on manganese dioxide from acid solutions. Sep. Sci. Technol. 1989, 24, 1363–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Apaolaza, L.; Lucena, J.J. Influence of the soil/solution ratio, interaction time, and extract on the evaluation of iron chelate sorption/desorption by soils. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 2493–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Apaolaza, L.; Lucena, J.J. Fe(III)-EDDHA and -EDDHMA sorption on Ca-montmorillonite, ferrihydrite, and peat. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 5258–5264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Rayo, S.; Hernández, D.; Lucena, J.J. Chemical evaluation of HBED/Fe3+ and the novel HJB/Fe3+ chelates as fertilizers to alleviate iron chlorosis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 8504–8513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Alcalá, I.; Bellón, F.; del Campillo, M.C.; Barrón, V.; Torrent, J. Application of synthetic siderite (FeCO3) to the soil is capable of alleviating iron chlorosis in olive trees. Sci. Hortic. 2012, 138, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

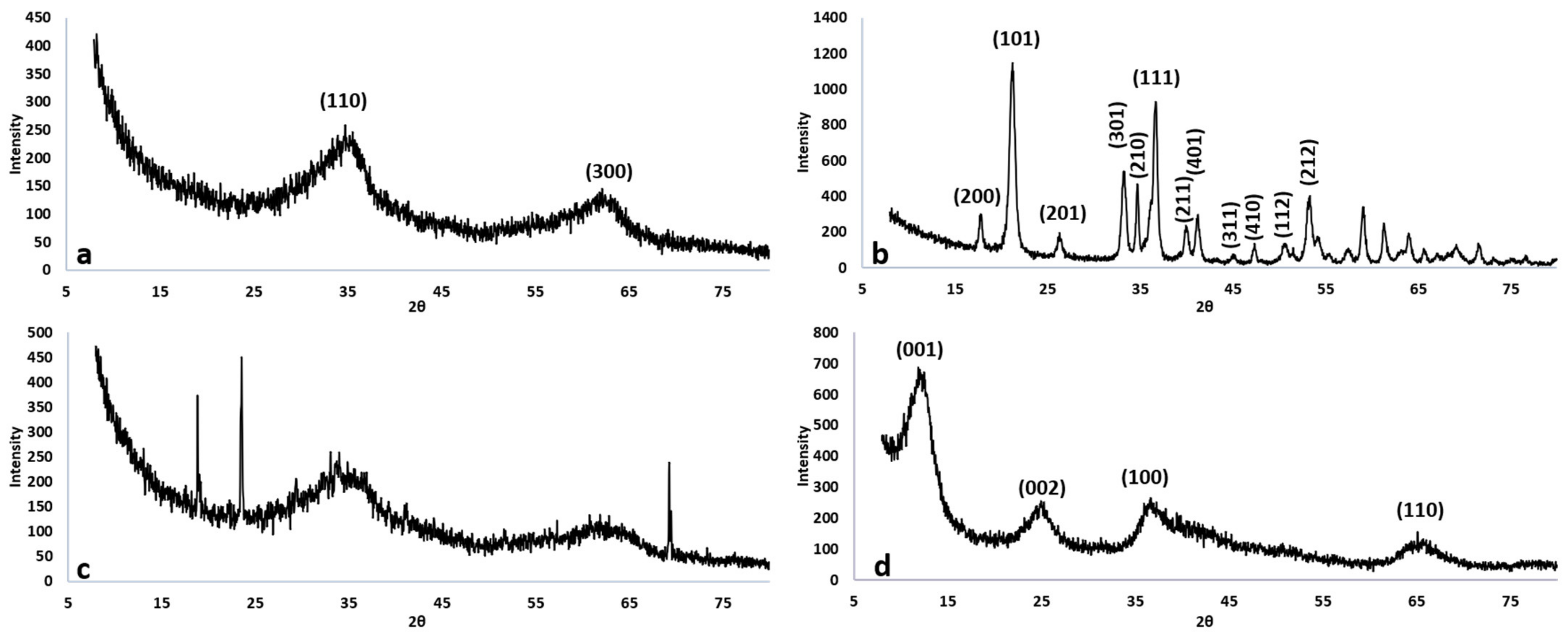
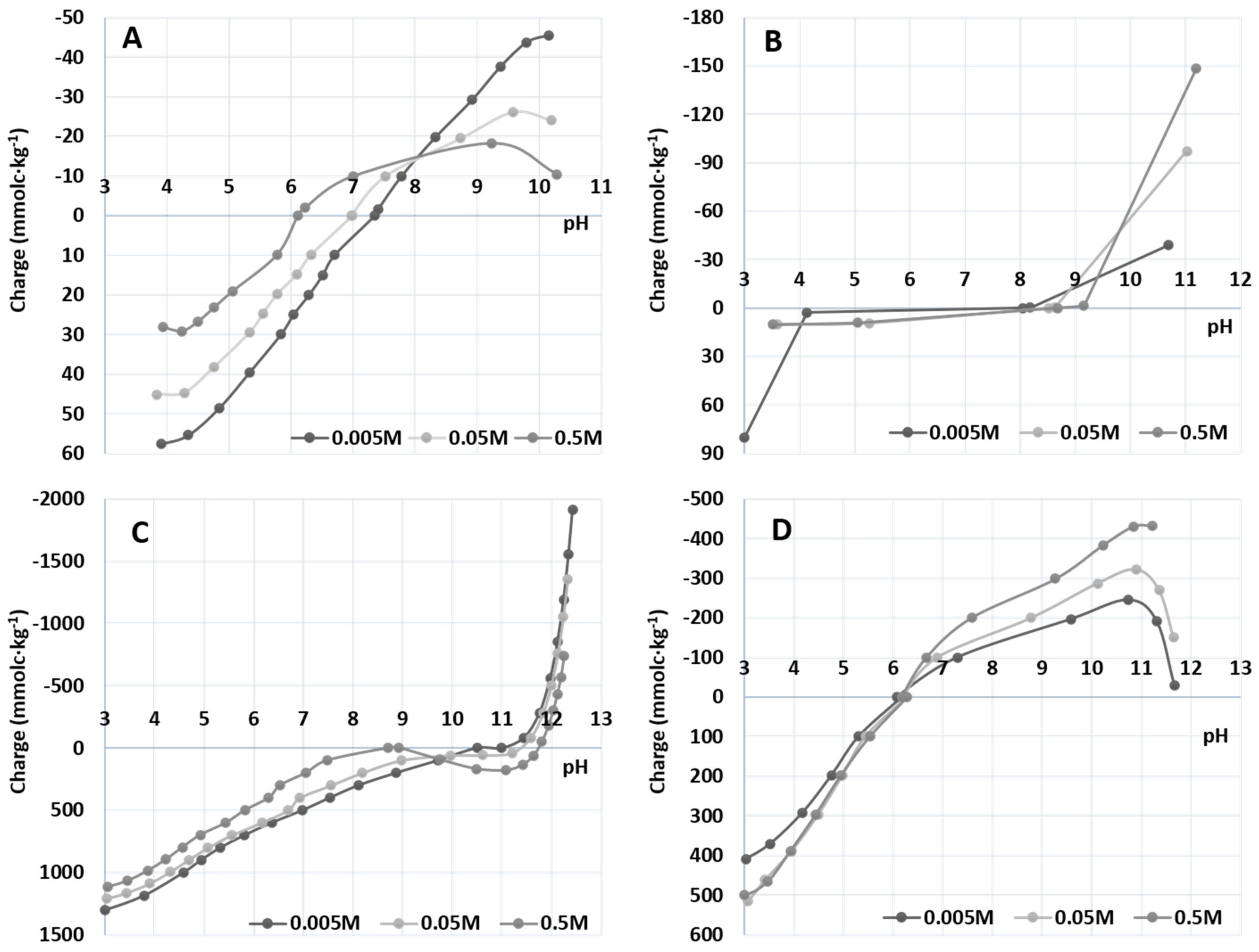





| Nanomaterial | Crystallographic Plane | Size (nm) | BET (m2 g−1) | PZC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2L-Fh | (110) | 1.20 | 297 ± 1.9 | 8.00 |
| (300) | 1.44 | |||
| Goethite | (200) | 18.5 | 79.1 ± 0.4 | 8.10 |
| (101, 201, 301, 401) | 25.9 | |||
| (111, 211) | 18.9 | |||
| AMO | Peaks at 2θ = 19°, 24°,70° | 39.1 | 118 ± 0.9 | 9.80 |
| FMBO | (002, 100, 110) | 2.81 | 396 ± 1.8 | 6.20 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cieschi, M.T.; de Francisco, M.; Herrero, P.; Sánchez-Marcos, J.; Cuevas, J.; Esteban, E.; Lucena, J.J.; Yunta, F. Synthesis and Characterization of Nano Fe and Mn (hydr)oxides to Be Used as Natural Sorbents and Micronutrient Fertilizers. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1876. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11091876
Cieschi MT, de Francisco M, Herrero P, Sánchez-Marcos J, Cuevas J, Esteban E, Lucena JJ, Yunta F. Synthesis and Characterization of Nano Fe and Mn (hydr)oxides to Be Used as Natural Sorbents and Micronutrient Fertilizers. Agronomy. 2021; 11(9):1876. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11091876
Chicago/Turabian StyleCieschi, María Teresa, Marina de Francisco, Paula Herrero, Jorge Sánchez-Marcos, Jaime Cuevas, Elvira Esteban, Juan José Lucena, and Felipe Yunta. 2021. "Synthesis and Characterization of Nano Fe and Mn (hydr)oxides to Be Used as Natural Sorbents and Micronutrient Fertilizers" Agronomy 11, no. 9: 1876. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11091876
APA StyleCieschi, M. T., de Francisco, M., Herrero, P., Sánchez-Marcos, J., Cuevas, J., Esteban, E., Lucena, J. J., & Yunta, F. (2021). Synthesis and Characterization of Nano Fe and Mn (hydr)oxides to Be Used as Natural Sorbents and Micronutrient Fertilizers. Agronomy, 11(9), 1876. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11091876








