Impact of Sowing Time on Chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) Biomass Accumulation and Yield
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Locations and Seasonal Conditions
2.2. Plant Material and Experimental Conditions
2.3. Measurements at Physiological Maturity
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Correlation between Traits
3.2. Biomass and Related Traits
3.3. Yield and Yield Components
3.3.1. Mean Grain Yield
3.3.2. Pod Number and Pod Fill
3.4. Contribution of Yield Components to Final Grain Yield
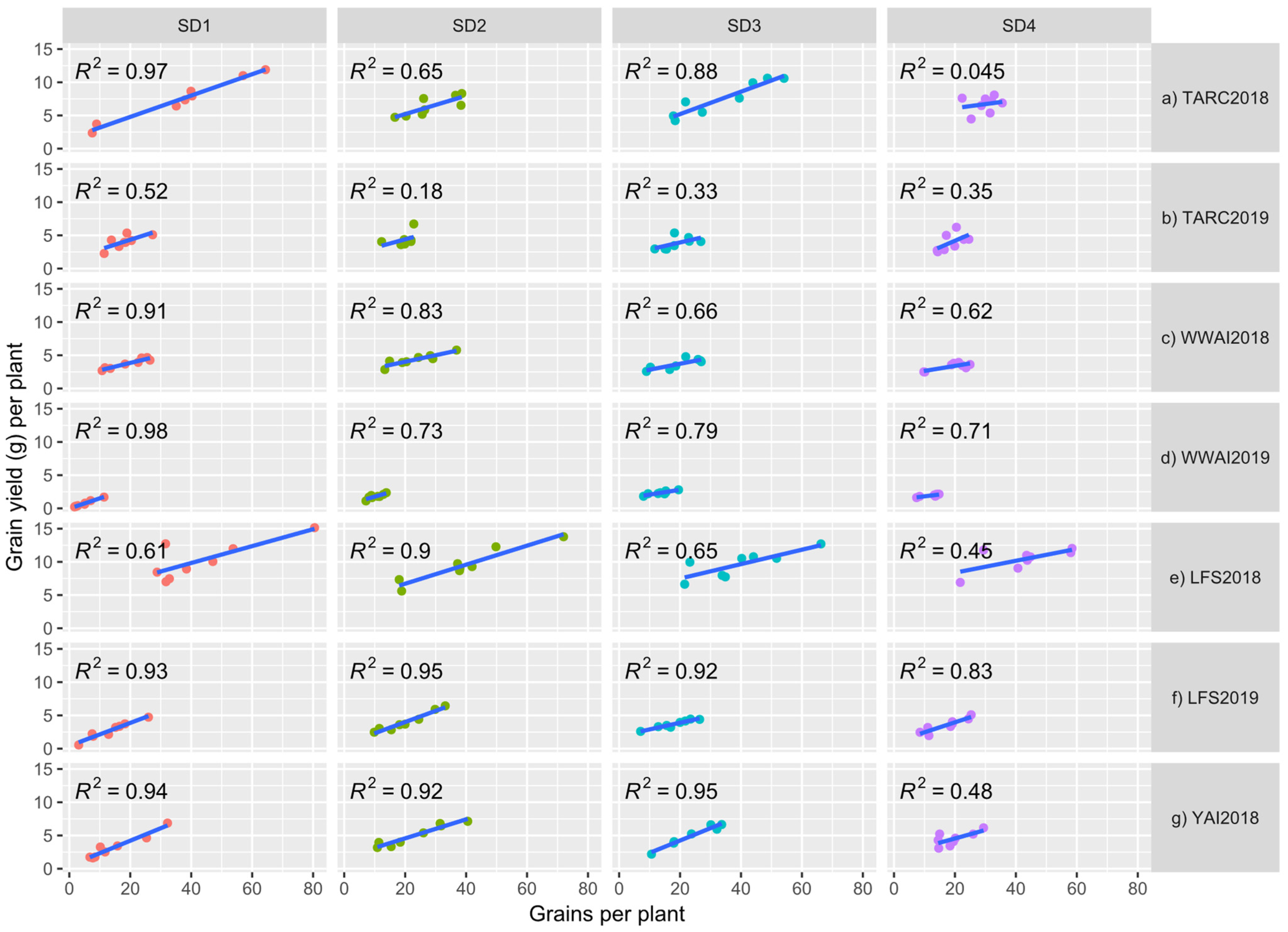
3.5. Relationship between Biomass and Grain Yield
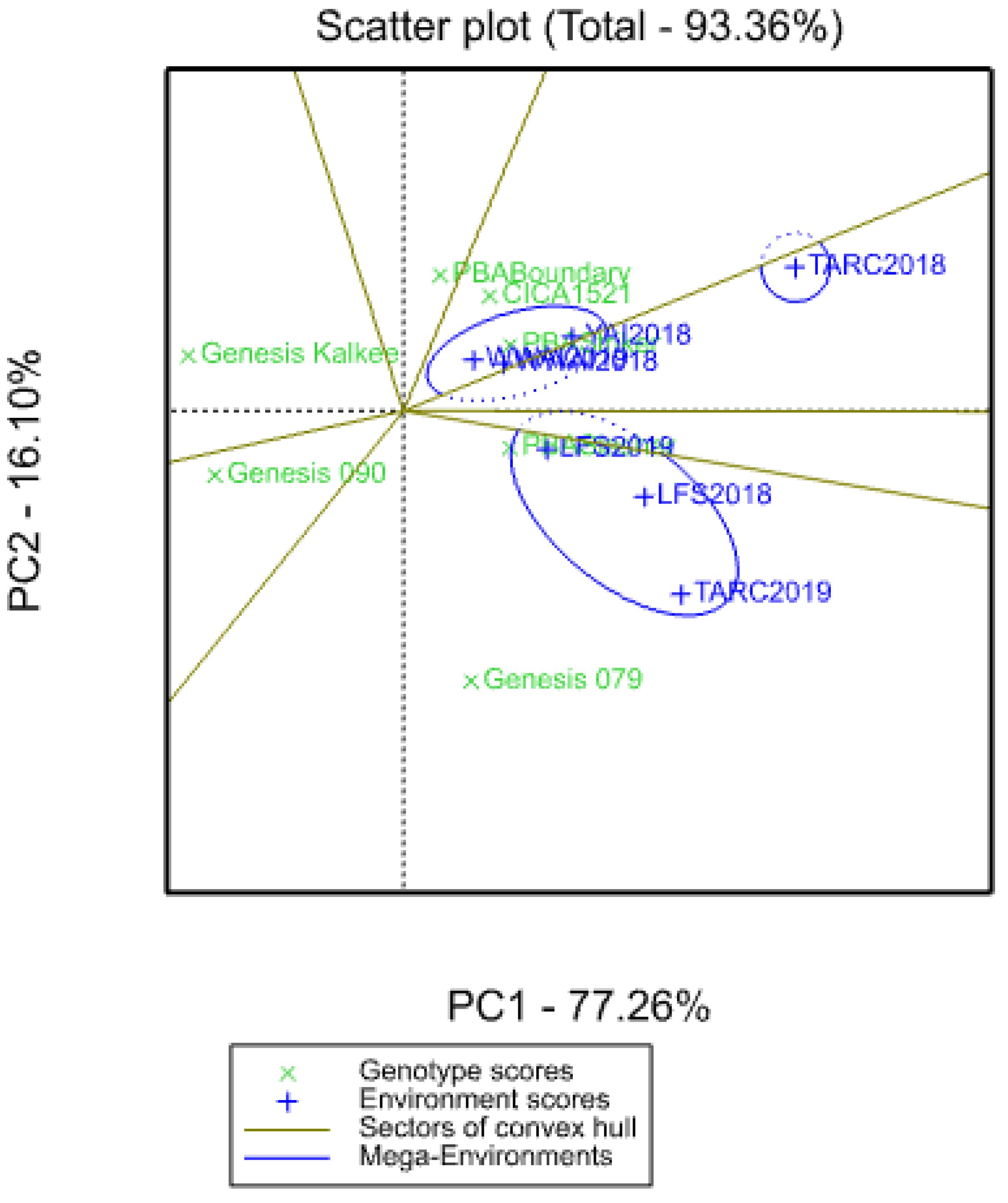
3.6. Environmental Correlations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jukanti, A.K.; Gaur, P.M.; Gowda, C.L.L.; Chibbar, R.N. Nutritional quality and health benefits of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.): A review. Brit. J. Nutr. 2012, 108, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bampidis, V.A.; Christodoulou, V. Chickpeas (Cicer arietinum L.) in animal nutrition: A review. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2011, 168, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAOSTAT. 2020. Available online: https://faostat.fao.org/faostat/ (accessed on 14 November 2021).
- Croser, J.S.; Clarke, H.J.; Siddique, K.H.M.; Khan, T.N. Low-temperature stress: Implications for chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) improvement. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2003, 22, 185–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaur, P.M.; Samineni, S.; Thudi, M.; Tripathi, S.; Sajja, S.B.; Jayalakshmi, V.; Mannur, D.M.; Vijayakumar, A.G.; Ganga Rao, N.V.P.R.; Ojiewo, C.; et al. Integrated breeding approaches for improving drought and heat adaptation in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). Plant Breed. 2019, 138, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sadras, V.; Dreccer, M.F. Adaptation of wheat, barley, canola, field pea and chickpea to the thermal environments of Australia. Crop Pasture Sci. 2015, 66, 1137–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, J.D.; Turner, N.C.; Siddique, K.H.M.; Knights, E.J.; Brinsmead, R.B.; Mock, I.; Edmondson, C.; Khan, T.N. Genotype by environment studies across Australia reveal the importance of phenology for chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) improvement. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 2004, 55, 1071–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, H.J.; Siddique, K.H.M. Response of chickpea genotypes to low temperature stress during reproductive development. Field Crops Res. 2004, 90, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devasirvatham, V.; Gaur, P.M.; Mallikarjuna, N.; Raju, T.N.; Trethowan, R.M.; Tan, D.K.Y. Reproductive biology of chickpea response to heat stress in the field is associated with the performance in controlled environments. Field Crops Res. 2013, 142, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Devasirvatham, V.; Gaur, P.M.; Mallikarjuna, N.; Tokachichu, R.N.; Trethowan, R.M.; Tan, D.K.Y. Effect of high temperature on the reproductive development of chickpea genotypes under controlled environments. Funct. Plant Biol. 2012, 39, 1009–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Devasirvatham, V.; Gaur, P.M.; Raju, T.N.; Trethowan, R.M.; Tan, D.K.Y. Field response of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) to high temperature. Field Crops Res. 2015, 172, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Devasirvatham, V.; Tan, D.K.Y.; Gaur, P.M.; Raju, T.N.; Trethowan, R.M. High temperature tolerance in chickpea and its implications for plant improvement. Crop Pasture Sci. 2012, 63, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gaur, P.M.; Jukanti, A.K.; Varshney, R.K. Impact of genomic technologies on chickpea breeding strategies. Agronomy 2012, 2, 199–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sadras, V.O.; Slafer, G.A. Environmental modulation of yield components in cereals: Heritabilities reveal a hierarchy of phenotypic plasticities. Field Crops Res. 2012, 127, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, J.A.; Knights, E.J.; Harden, S.; Hobson, K.B. Seed quality and the effect of introducing Cicer echinospermum to improve disease and pest resistance in desi chickpea. Legum. Sci. 2019, 1, e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pushpavalli, R.; Berger, J.D.; Turner, N.C.; Siddique, K.H.M.; Colmer, T.D.; Vadez, V. Cross-tolerance for drought, heat and salinity stresses in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2020, 206, 405–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tricker, P.J.; ElHabti, A.; Schmidt, J.; Fleury, D. The physiological and genetic basis of combined drought and heat tolerance in wheat. J. Exp. Bot. 2018, 69, 3195–3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maphosa, L.; Richards, M.F.; Norton, S.L.; Nguyen, G.N. Breeding for abiotic stress adaptation in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.): A comprehensive review. Crop Breed. Genet. Genom. 2020, 2, e200015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shunmugam, A.S.K.; Kannan, U.; Jiang, Y.; Daba, K.A.; Gorim, L.Y. Physiology based approaches for breeding of next-generation food legumes. Plants 2018, 7, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lake, L.; Sadras, V.O. The critical period for yield determination in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). Field Crop Res. 2014, 168, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, M.F.; Preston, A.L.; Napier, T.; Jenkins, L.; Maphosa, L. Sowing date affects the timing and duration of key chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) growth phases. Plants 2020, 9, 1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebetzke, G.J.; Fischer, R.A.; van Herwaarden, A.F.; Bonnett, D.G.; Chenu, K.; Rattey, A.R.; Fettell, N.A. Plot size matters: Interference from intergenotypic competition in plant phenotyping studies. Funct. Plant Biol. 2014, 41, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VSN International. Genstat for Windows, 20th ed.; VSN International: Hemel Hempstead, UK, 2019; Available online: https://vsni.co.uk/software/genstat (accessed on 20 May 2021).
- Canci, H.; Toker, C. Evaluation of yield criteria for drought and heat resistance in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2009, 195, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamurthy, L.; Gaur, P.M.; Basu, P.S.; Chaturvedi, S.K.; Tripathi, S.; Vadez, V.; Rathore, A.; Varshney, R.K.; Gowda, C.L.L. Large genetic variation for heat tolerance in the reference collection of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) germplasm. Plant Genet. Resour. 2011, 9, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Upadhyaya, H.D.; Dronavalli, N.; Gowda, C.L.L.; Singh, S. Identification and evaluation of chickpea germplasm for tolerance to heat stress. Crop Sci. 2011, 51, 2079–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parent, B.; Bonneau, J.; Maphosa, L.; Kovalchuk, A.; Langridge, P.; Fleury, D. Quantifying wheat sensitivities to environmental constraints to dissect genotype × environment interactions in the field. Plant Physiol. 2017, 174, 1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roorkiwal, M.; Jain, A.; Kale, S.M.; Doddamani, D.; Chitikineni, A.; Thudi, M.; Varshney, R.K. Development and evaluation of high-density Axiom((R)) CicerSNP Array for high-resolution genetic mapping and breeding applications in chickpea. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2018, 16, 890–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, M.R.; Rao, I.M.; Merchant, A. Source-Sink Relationships in crop plants and their influence on yield development and nutritional quality. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manning, B.K.; Adhikari, K.N.; Trethowan, R. Impact of sowing time, genotype, environment and maturity on biomass and yield components in faba bean (Vicia faba). Crop Pasture Sci. 2020, 71, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramamoorthy, P.; Lakshmanan, K.; Upadhyaya, H.D.; Vadez, V.; Varshney, R.K. Shoot traits and their relevance in terminal drought tolerance of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). Field Crop Res. 2016, 197, 10–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramamoorthy, P.; Lakshmanan, K.; Upadhyaya, H.D.; Vadez, V.; Varshney, R.K. Root traits confer grain yield advantages under terminal drought in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). Field Crop Res. 2017, 201, 146–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Slafer, G.A.; Savin, R.; Sadras, V.O. Coarse and fine regulation of wheat yield components in response to genotype and environment. Field Crop Res. 2014, 157, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malosetti, M.; Ribaut, J.-M.; van Eeuwijk, F.A. The statistical analysis of multi-environment data: Modeling genotype-by-environment interaction and its genetic basis. Front. Physiol. 2013, 4, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


| Experiment | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TARC18 | Rainfall (mm) | 26.2 | 13 | 7.8 | 3 | 14.2 | 27.2 | 0.8 | 23.8 | 9.2 | 59 | 50 | 28.8 |
| Irrigation (mm) | 0 | 0 | 40 | 15 | 30 | 0 | 20 | 20 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Min Temp. (°C) | 20.6 | 19.1 | 17.5 | 14.7 | 7.4 | 5.5 | 2.7 | 3.8 | 7.9 | 13.5 | 15.5 | 19.3 | |
| Max Temp. (°C) | 36.9 | 34.8 | 33.4 | 30.1 | 21.7 | 17.8 | 18.1 | 18.9 | 23.7 | 27.5 | 29.2 | 34.8 | |
| WWAI18 | Rainfall (mm) | 60.3 | 46.5 | 7.7 | 3.9 | 26.8 | 40.1 | 15.2 | 19 | 25.3 | 22.3 | 91.3 | 48.4 |
| Irrigation (mm) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 16 | 18 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Min Temp. (°C) | 18.2 | 16.3 | 13.6 | 11 | 5.5 | 3.9 | 1.4 | 2.7 | 3.8 | 9.3 | 13 | 17.5 | |
| Max Temp. (°C) | 34.5 | 32.6 | 30.2 | 27.9 | 18.6 | 15 | 14.2 | 15.1 | 19.5 | 26.3 | 26.7 | 32.6 | |
| LFS18 | Rainfall (mm) | 24.2 | 1 | 4.2 | 2 | 23.2 | 29.2 | 5.8 | 8.8 | 12.4 | 7.4 | 57.6 | 22.6 |
| Irrigation (mm) | 0 | 0 | 220 | 0 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 12 | 12 | 0 | 0 | |
| Min Temp. (°C) | 19 | 17.7 | 14.4 | 11.4 | 6.1 | 3.8 | 2.1 | 3.3 | 4.8 | 10.4 | 13.6 | 18.6 | |
| Max Temp. (°C) | 35.8 | 33.9 | 31 | 28.9 | 19.6 | 15.4 | 15.9 | 16.9 | 21.2 | 27 | 27.9 | 33.8 | |
| YAI18 | Rainfall (mm) | 24.2 | 1 | 4.2 | 2 | 23.2 | 29.2 | 5.8 | 8.8 | 12.4 | 7.4 | 57.6 | 22.6 |
| Irrigation (mm) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 11 | 11 | 0 | 0 | 16 | 48 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Min Temp. (°C) | 19 | 17.7 | 14.4 | 11.4 | 6.1 | 3.8 | 2.1 | 3.3 | 4.8 | 10.4 | 13.6 | 18.6 | |
| Max Temp. (°C) | 35.8 | 33.9 | 31 | 28.9 | 19.6 | 15.4 | 15.9 | 16.9 | 21.2 | 27 | 27.9 | 33.8 | |
| TARC19 | Rainfall (mm) | 58 | 16.8 | 17.6 | 0 | 18.6 | 5.8 | 9.8 | 3.2 | 5.4 | 2.2 | 20.2 | 2.4 |
| Irrigation (mm) | 0 | 60 | 60 | 49 | 24 | 0 | 25 | 20 | 30 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Min Temp. (°C) | 24.6 | 19.8 | 18 | 14.5 | 8.6 | 5 | 5.2 | 3.6 | 7.8 | 12.9 | 15.5 | 19.6 | |
| Max Temp. (°C) | 39.7 | 34.2 | 31.9 | 28.2 | 21.5 | 17.9 | 18.3 | 19.2 | 24.3 | 29.1 | 30.7 | 36.4 | |
| WWAI19 | Rainfall (mm) | 25.5 | 11.4 | 39.7 | 23 | 53.9 | 44.3 | 25.5 | 18.4 | 19 | 8.7 | 54.9 | 7.7 |
| Irrigation (mm) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Min Temp. (°C) | 22.1 | 16.7 | 15.2 | 11.4 | 6.3 | 2.8 | 3.6 | 1.1 | 3.8 | 8.1 | 11.4 | 15.9 | |
| Max Temp. (°C) | 38 | 31.8 | 28.6 | 25 | 17.7 | 14.5 | 14 | 14.4 | 19.9 | 26.1 | 27.3 | 34 | |
| LFS19 | Rainfall (mm) | 10.6 | 28.4 | 14.8 | 33.4 | 34 | 37.4 | 28.8 | 13.2 | 13.2 | 7 | 41.2 | 4.9 |
| Irrigation (mm) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 200 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Min Temp. (°C) | 21.9 | 17.1 | 15.5 | 12 | 6.7 | 3.2 | 4.2 | 1.6 | 4.9 | 9.4 | 12.2 | 16.7 | |
| Max Temp. (°C) | 38.9 | 33 | 30.1 | 26.1 | 19 | 15.4 | 14.9 | 15.8 | 21.4 | 27.6 | 28.6 | 34.6 |
| Branch Number (BN) | - | |||||||||||||
| Dry matter (DM) (t/ha) | 0.19 | - | ||||||||||||
| Filled pods per plant (FPP) | 0.69 | 0.16 | - | |||||||||||
| 100 grain weight (100 GW) (g) | 0.18 | −0.09 | −0.07 | - | ||||||||||
| Harvest index (HI) | 0.22 | −0.38 | 0.53 | 0.08 | - | |||||||||
| Plant height (PH) (cm) | −0.05 | 0.73 | 0.00 | −0.35 | −0.45 | - | ||||||||
| Bottom pod height (BPH) (cm) | −0.23 | 0.58 | −0.25 | −0.33 | −0.50 | 0.78 | - | |||||||
| Top pod height (TPH) (cm) | 0.06 | 0.81 | 0.15 | −0.29 | −0.35 | 0.88 | 0.78 | - | ||||||
| Pod number per plant (PNP) | 0.70 | 0.23 | 0.99 | −0.04 | 0.49 | 0.03 | −0.22 | 0.19 | - | |||||
| Grains per plant (GPPl) | 0.67 | 0.26 | 0.92 | −0.01 | 0.51 | 0.06 | −0.18 | 0.24 | 0.93 | - | ||||
| Grains per pod (GPP) | 0.27 | 0.14 | 0.15 | 0.22 | 0.17 | 0.03 | −0.04 | 0.08 | 0.18 | 0.40 | - | |||
| Grain yield per plant (GYP) | 0.68 | 0.34 | 0.85 | 0.08 | 0.49 | 0.07 | −0.13 | 0.27 | 0.88 | 0.93 | 0.41 | - | ||
| Unfilled pods per plant (UPP) | 0.42 | 0.46 | 0.43 | 0.17 | 0.07 | 0.18 | 0.02 | 0.31 | 0.58 | 0.52 | 0.22 | 0.56 | - | |
| Grain yield (GY) (t/ha) | 0.42 | 0.42 | 0.67 | 0.04 | 0.64 | 0.11 | −0.07 | 0.29 | 0.69 | 0.74 | 0.33 | 0.81 | 0.47 | - |
| BN | DM | FPP | 100 GW | HI | PH | BPH | TPH | PNP | GPPl | GPP | GYP | UPP | GY |
| Experiment | Sowing Date | Branch Number per Plant | Bottom Pod Height (cm) | Top Pod Height (cm) | Plant Height (cm) | Biomass (t/ha) | Harvest Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TARC18 | SD1 | 5.29 | 20.26 | 38.33 b | - | 3.87 | 0.34 |
| SD2 | 5.24 | 19.37 | 34.82 a | - | 3.25 | 0.33 | |
| SD3 | 6.07 | 18.78 | 38.64 b | - | 2.99 | 0.37 | |
| SD4 | 4.73 | 19.24 | 36.99 ab | - | 2.52 | 0.40 | |
| p-value | ns | ns | * | - | ns | ns | |
| TARC19 | SD1 | 5.39 | 31.70 b | 49.97 b | 52.71 b | 5.45 c | 0.34 a |
| SD2 | 4.84 | 28.31 b | 45.67 b | 55.47 b | 4.69 bc | 0.41 bc | |
| SD3 | 4.38 | 24.16 a | 38.06 a | 45.49 a | 3.82 ab | 0.39 b | |
| SD4 | 4.64 | 21.47 a | 33.73 a | 39.99 a | 3.24 a | 0.44 c | |
| p-value | ns | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | |
| WWAI18 | SD1 | 9.02 c | 27.69 d | 42.91 c | 45.37 c | 3.49 c | 0.35 a |
| SD2 | 8.53 c | 25.90 c | 42.03 c | 45.19 c | 3.23 c | 0.41 b | |
| SD3 | 6.55 b | 23.30 b | 35.62 b | 39.25 b | 2.91 b | 0.48 c | |
| SD4 | 5.49 a | 21.50 a | 31.96 a | 35.64 a | 2.35 a | 0.51 c | |
| p-value | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | |
| WWAI19 | SD1 | 6.31 d | 33.42 d | 43.80 d | 51.71 d | 4.58 d | 0.04 a |
| SD2 | 5.79 c | 29.46 c | 44.15 c | 47.35 c | 3.53 c | 0.17 b | |
| SD3 | 4.48 b | 27.20 b | 39.74 b | 42.13 b | 2.69 b | 0.31 c | |
| SD4 | 3.55 a | 24.56 a | 34.28 a | 36.99 a | 1.95 a | 0.38 d | |
| p-value | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | |
| LFS18 | SD1 | 11.73 | 33.05 c | 58.01 d | 57.89 c | 7.66 d | 0.29 a |
| SD2 | 10.92 | 30.24 b | 49.77 c | 47.21 b | 5.85 c | 0.38 b | |
| SD3 | 10.47 | 27.07 a | 46.87 b | 45.83 b | 5.01 b | 0.49 c | |
| SD4 | 10.91 | 25.55 a | 44.31 a | 42.61 a | 4.38 a | 0.55 d | |
| p-value | ns | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | |
| LFS19 | SD1 | 4.74 b | 41.62 d | 63.11 d | 63.63 d | 7.36 d | 0.13 a |
| SD2 | 5.39 c | 37.09 c | 57.97 c | 58.21 c | 6.97 c | 0.23 b | |
| SD3 | 4.41 ab | 29.77 b | 48.91 b | 48.38 b | 5.23 b | 0.30 c | |
| SD4 | 4.00 a | 25.05 a | 41.53 a | 41.75 a | 3.96 a | 0.37 d | |
| p-value | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | |
| YAI18 | SD1 | 9.47 | 20.93 a | 35.53 | 35.69 | 4.05 c | 0.22 a |
| SD2 | 10.33 | 19.66 a | 38.65 | 39.61 | 4.31 c | 0.32 b | |
| SD3 | 7.42 | 20.18 a | 35.78 | 41.15 | 3.53 b | 0.41 c | |
| SD4 | 5.12 | 24.36 b | 36.22 | 37.76 | 2.95 a | 0.41 c | |
| p-value | ns | * | ns | ns | *** | *** |
| Experiment | Sowing Date | Filled Pods per Plant | Unfilled Pods per Plant | Pods per Plant | Grains per Pod | Grains per Plant | 100 Grain Weight (g) | Grain Yield (t/ha) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TARC18 | SD1 | 32.6 | 10.2 a | 42.8 a | 1.1 | 38.5 | 22.9 | 1.302 |
| SD2 | 23.6 | 5.9 b | 29.5 b | 1.2 | 27.5 | 23.0 | 1.071 | |
| SD3 | 27.8 | 4.1 b | 31.8 b | 1.2 | 34.3 | 23.5 | 1.095 | |
| SD4 | 25.1 | 3.7 b | 28.8 b | 1.3 | 32.0 | 23.23 | 1.001 | |
| p-value | ns | *** | * | ns | ns | ns | ns | |
| TARC19 | SD1 | 15.2 | 4.0 | 19.2 | 1.2 | 18.1 | 23.7 a | 1.868 a |
| SD2 | 15.5 | 3.2 | 18.7 | 1.3 | 19.6 | 23.3 a | 1.903 a | |
| SD3 | 15.1 | 3.5 | 18.5 | 1.2 | 18.9 | 21.9 b | 1.473 b | |
| SD4 | 15.3 | 3.6 | 18.9 | 1.2 | 18.8 | 20.7 c | 1.438 b | |
| p-value | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | *** | * | |
| WWAI18 | SD1 | 22.8 bc | 1.7 a | 24.6 bc | 0.9 a | 19.1 a | 22.2 | 1.216 |
| SD2 | 25.6 c | 1.8 a | 27.4 bc | 0.9 a | 23.3 b | 22.3 | 1.306 | |
| SD3 | 20.4 ab | 1.4 ab | 21.8 a | 1.0 ab | 19.5 a | 22.3 | 1.377 | |
| SD4 | 17.0 c | 1.1 b | 18.1 ab | 1.1 b | 18.8 a | 22.0 | 1.209 | |
| p-value | ** | * | ** | * | * | ns | ns | |
| WWAI19 | SD1 | 4.6 a | 0.5 | 5.0 a | 1.2 a | 4.7 a | 5.0 a | 0.173 a |
| SD2 | 9.9 b | 1.0 | 10.9 b | 1.1 ab | 10.3 b | 15.9 b | 0.600 b | |
| SD3 | 12.6 c | 1.0 | 13.6 c | 1.0 ab | 13.6 c | 17.5 c | 0.812 c | |
| SD4 | 10.6 b | 1.4 | 12.0 bc | 1.0 b | 12.4 c | 15.8 b | 0.747 d | |
| p-value | *** | ns | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | |
| LFS18 | SD1 | 34.0 | 7.0 b | 41.0 b | 1.3 a | 43.1 | 25.1 a | 2.221 a |
| SD2 | 28.6 | 4.7 a | 33.3 a | 1.4 ab | 39.2 | 26.2 b | 2.190 a | |
| SD3 | 28.8 | 4.0 a | 32.8 a | 1.4 ab | 39.5 | 26.1 b | 2.422 b | |
| SD4 | 29.7 | 3.7 a | 33.4 a | 1.5 b | 42.5 | 26.0 b | 2.335 ab | |
| p-value | ns | *** | ** | *** | ns | *** | * | |
| LFS19 | SD1 | 10.1 a | 2.7 | 12.8 a | 1.0 | 13.4 a | 21.5 | 0.983 a |
| SD2 | 15.0 b | 3.4 | 18.4 b | 1.1 | 20.3 b | 20.8 | 1.593 b | |
| SD3 | 13.7 b | 3.7 | 17.5 b | 1.0 | 18.0 b | 23.8 | 1.552 b | |
| SD4 | 13.4 ab | 3.3 | 16.7 ab | 1.0 | 17.2 ab | 21.2 | 1.475 b | |
| p-value | * | ns | * | ns | * | ns | *** | |
| YAI18 | SD1 | 11.2 | 2.8 | 14.0 a | 1.3 | 14.8 a | 18.1 b | 0.871 a |
| SD2 | 17.2 | 4.5 | 21.6 b | 1.3 | 23.2 b | 17.5 b | 1.384 bc | |
| SD3 | - | - | - | - | - | 16.3 a | 1.439 c | |
| SD4 | 14.6 | 2.1 | 16.7 ab | 1.4 | 19.7 ab | 15.2 a | 1.225 ab | |
| p-value | ns | ns | * | ns | * | ** | *** |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Richards, M.F.; Maphosa, L.; Preston, A.L. Impact of Sowing Time on Chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) Biomass Accumulation and Yield. Agronomy 2022, 12, 160. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12010160
Richards MF, Maphosa L, Preston AL. Impact of Sowing Time on Chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) Biomass Accumulation and Yield. Agronomy. 2022; 12(1):160. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12010160
Chicago/Turabian StyleRichards, Mark F., Lancelot Maphosa, and Aaron L. Preston. 2022. "Impact of Sowing Time on Chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) Biomass Accumulation and Yield" Agronomy 12, no. 1: 160. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12010160
APA StyleRichards, M. F., Maphosa, L., & Preston, A. L. (2022). Impact of Sowing Time on Chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) Biomass Accumulation and Yield. Agronomy, 12(1), 160. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12010160





