Improvement of Root Characteristics Due to Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Potassium Interactions Increases Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Yield and Nitrogen Use Efficiency
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material and Growth Conditions
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Sampling and Measurements
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
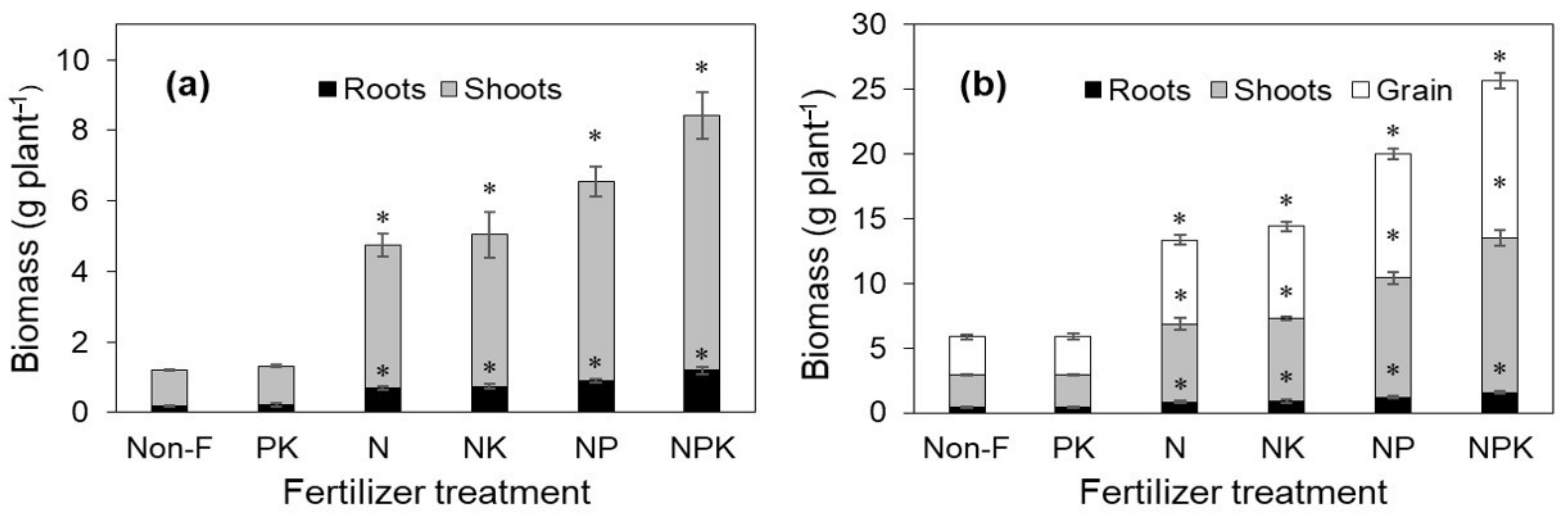
3.1. Plant Growth and Grain Yield
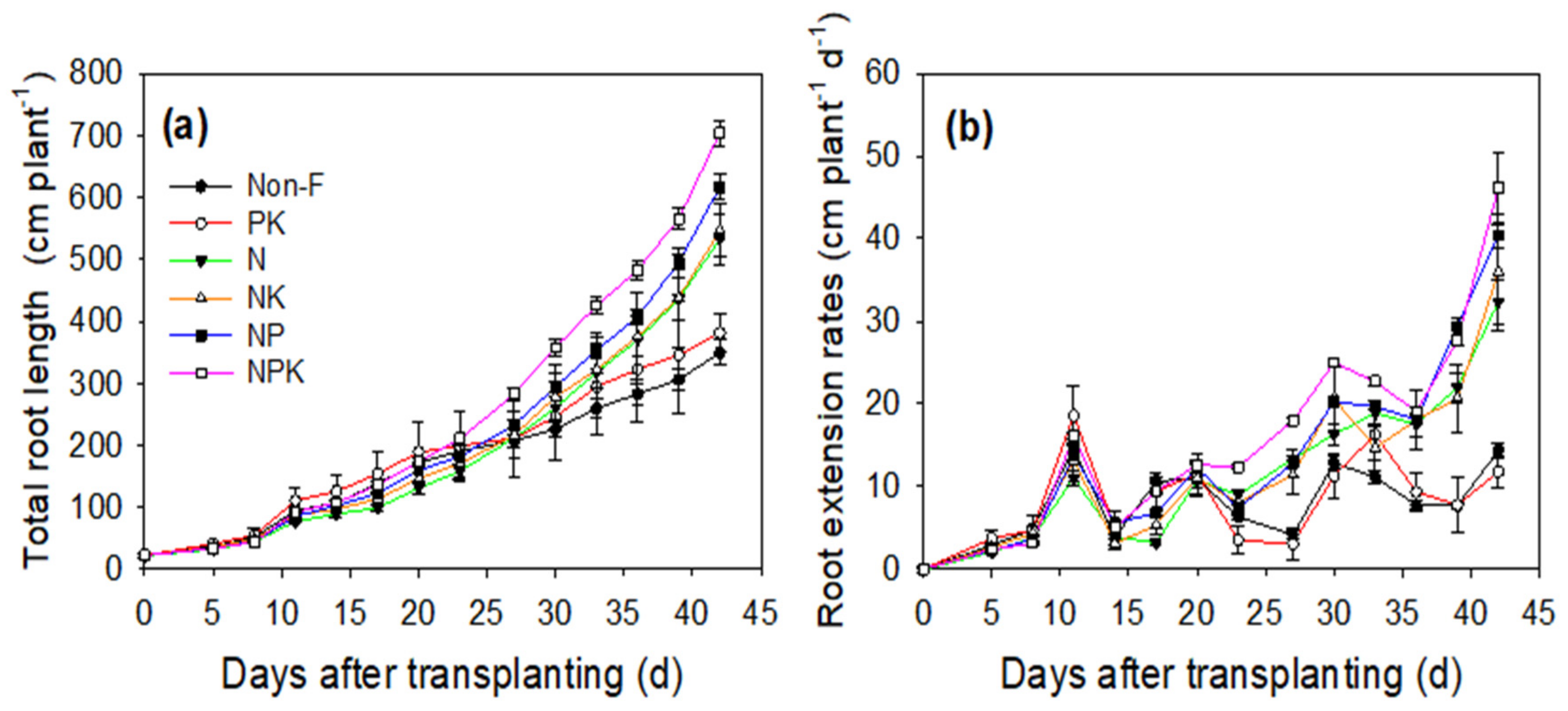
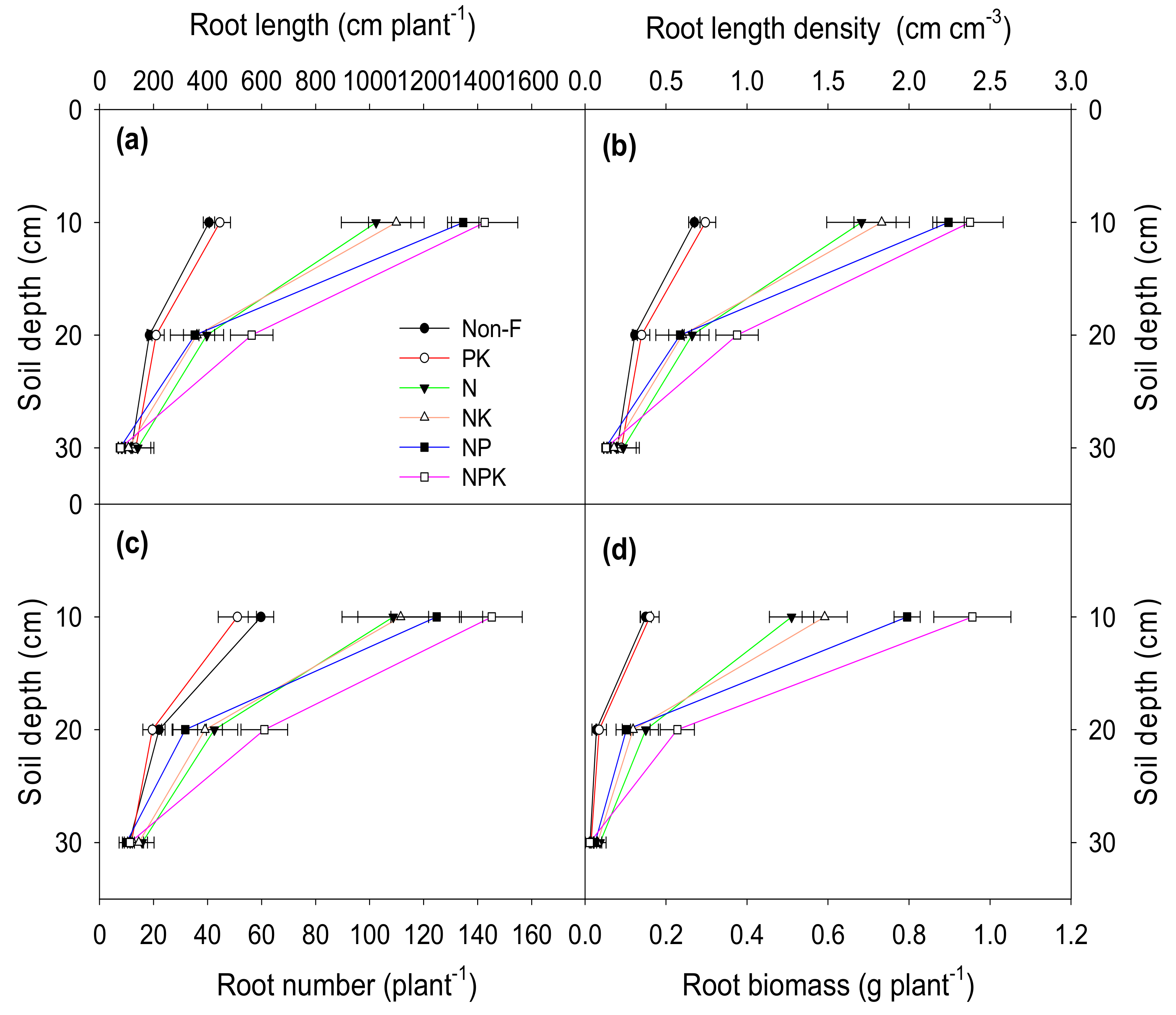
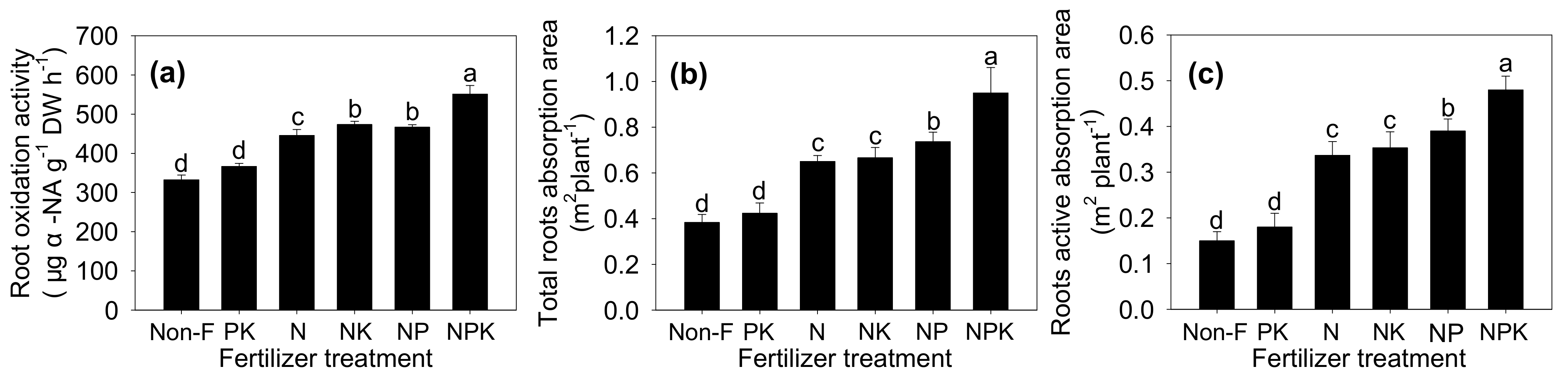
3.2. Root Morphology and Physiology
3.3. Nitrogen Uptake and Utilization Efficiency
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of N, P, and K Interactions on Root Growth
4.2. Increase in Yield and NUE Due to N, P, and K Interactions Are Associated with Improved Root Morphological and Physiological Traits
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Duncan, E.G.; O’Sullivan, C.A.; Roper, M.M.; Biggs, J.S.; Peoples, M.B. Influence of Co-Application of Nitrogen with Phosphorus, Potassium and Sulphur on the Apparent Efficiency of Nitrogen Fertiliser Use, Grain Yield and Protein Content of Wheat: Review. Field Crops Res. 2018, 226, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAOStat. Available online: https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/ (accessed on 8 November 2021).
- Sun, H.; Zhang, H.; Powlson, D.; Min, J.; Shi, W. Rice production, nitrous oxide emission and ammonia volatilization as impacted by the nitrification inhibitor 2- chloro-6-(trichloromethyl)-pyridine. Field Crops Res. 2015, 173, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fageria, N.K.; Oliveira, J.P. Nitrogen, Phosphorus and Potassium Interactions in Upland Rice. J. Plant Nutr. 2014, 37, 1586–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somaweera, K.A.T.N.; Suriyagoda, L.D.B.; Sirisena, D.N.; De Costa, W.A.J.M. Accumulation and Partitioning of Biomass, Nitrogen, Phosphorus and Potassium among Different Tissues during the Life Cycle of Rice Grown under Different Water Management Regimes. Plant Soil 2016, 401, 169–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, G.; Chen, S.; Xu, C.; Wang, D.; Zhang, X. Agronomic and physiological performance of indica/japonica hybrid rice cultivar under low nitrogen conditions. Field Crops Res. 2019, 243, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Yu, C.; Li, C.; Xin, Q.; Huang, X.; Zhang, J.; Yue, Y.; Huang, G.; Li, X.; Wang, W. Modeling the impacts of water and fertilizer management on the ecosystem service of rice rotated cropping systems in China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 219, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cormier, F.; Foulkes, J.; Hirel, B.; Gouache, D.; Moënne-Loccoz, Y.; Le Gouis, J. Breeding for Increased Nitrogen-Use Efficiency: A Review for Wheat (T. Aestivum L.). Plant Breed. 2016, 135, 255–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godfrey, D.; Hawkesford, M.J.; Powers, S.J.; Millar, S.; Shewry, P.R. Effects of Crop Nutrition on Wheat Grain Composition and End Use Quality. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 3012–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, W.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, M.; Shi, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Sun, Y.; Zhou, H.; Li, C.; Yang, Y.; Geng, J. Improving Crop Yields, Nitrogen Use Efficiencies, and Profits by Using Mixtures of Coated Controlled-Released and Uncoated Urea in a Wheat-Maize System. Field Crops Res. 2017, 205, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, E.G.; O’Sullivan, C.A.; Roper, M.M.; Palta, J.; Whisson, K.; Peoples, M.B. Yield and Nitrogen Use Efficiency of Wheat Increased with Root Length and Biomass Due to Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Potassium Interactions. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2018, 181, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, W.; Deng, Y.; Chen, X.; Xu, X.; Chen, R.; Lv, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, X.; He, X.; Li, B.; et al. Characterization of root response to phosphorus supply from morphology to gene analysis in field-grown wheat. J. Exp. Bot. 2013, 64, 1403–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Teng, W.; Tong, Y.; Chen, X.; Zou, C. Phosphorus Efficiency Mechanisms of Two Wheat Cultivars as Affected by a Range of Phosphorus Levels in the Field. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fageria, N.K.; Moreira, A.; Moraes, L.A.C.; Moraes, M.F. Root Growth, Nutrient Uptake, and Nutrient-Use Efficiency by Roots of Tropical Legume Cover Crops as Influenced by Phosphorus Fertilization. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2014, 45, 555–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blevins, D.G.; Barnett, N.M.; Frost, W.B. Role of Potassium and Malate in Nitrate Uptake and Translocation by Wheat Seedlings. Plant Physiol. 1978, 62, 784–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, A.J.; Cramer, M.D. Root Nitrogen Acquisition and Assimilation. In Root Physiology: From Gene to Function; Plant Ecophysiology; Lambers, H., Colmer, T.D., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2005; Volume 4, pp. 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metho, L.A.; Hammes, P.S.; de Beer, J.M.; Groeneveld, H.T. Interaction between Cultivar and Soil Fertility on Grain Yield, Yield Components and Grain Nitrogen Content of Wheat. S. Afr. J. Plant Soil 1997, 14, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Shi, X.; Li, S.; Sun, X.; He, X. Nitrogen Use Efficiency as Affected by Phosphorus and Potassium in Long-Term Rice and Wheat Experiments. J. Integr. Agric. 2014, 13, 588–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlegel, A.J.; Havlin, J.L. Irrigated grain sorghum response to 55 years of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium fertilization. Agron. J. 2020, 113, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Bom, F.; Magid, J.; Jensen, L.S. Long-Term P and K Fertilisation Strategies and Balances Affect Soil Availability Indices, Crop Yield Depression Risk and N Use. Eur. J. Agron. 2017, 86, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colwell, J.; Grove, T. Assessments of Potassium and Sulphur Fertilizer Requirements of Wheat in Western Australia. Aust. J. Exp. Agric. 1976, 16, 748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertic, B.; Loncaric, Z.; Vukadinovic, V.; Vukobratovic, Z.; Vukadinovic, V. Winter Wheat Yield Responses to Mineral Fertilization. Cereal Res. Commun. 2007, 35, 245–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.K.; Dwivedi, B.S.; Tiwari, K.N.; Majumdar, K.; Rani, M.; Singh, S.K.; Timsina, J. Optimizing Nutrient Management Strategies for Rice–Wheat System in the Indo-Gangetic Plains of India and Adjacent Region for Higher Productivity, Nutrient Use Efficiency and Profits. Field Crops Res. 2014, 164, 30–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkesford, M.J. Genetic Variation in Traits for Nitrogen Use Efficiency in Wheat. J. Exp. Bot. 2017, 68, 2627–2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, M.; Palta, J.A.; Fillery, I.R.P. Root Characteristics of Vigorous Wheat Improve Early Nitrogen Uptake. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 2006, 57, 1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Zhang, H.; Blumwald, E.; Li, H.; Cheng, J.; Dai, Q.; Huo, Z.; Xu, K.; Guo, B. Different Characteristics of High Yield Formation between Inbred Japonica Super Rice and Inter-Sub-Specific Hybrid Super Rice. Field Crops Res. 2016, 198, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Hu, L.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, D.; Zheng, L.; Chen, Z.; Hu, Y.; Cui, P.; Guo, B.; Dai, Q.; et al. Different Characteristics of Nutrient Absorption and Utilization between Inbred Japonica Super Rice and Inter-Sub-Specific Hybrid Super Rice. Field Crops Res. 2018, 218, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, J.; Milroy, S.P.; Rebetzke, G.J.; Palta, J.A. The Influence of Shoot and Root Size on Nitrogen Uptake in Wheat Is Affected by Nitrate Affinity in the Roots during Early Growth. Funct. Plant Biol. 2015, 42, 1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyassar, M.A.; Jairo, A.; Palta, J.A.; Kadambot, H.M.S.; Victor, O.S. Five decades of selection for yield reduced root length density and increased nitrogen uptake per unit root length in Australian wheat varieties. Plant Soil. 2016, 413, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurtrie, R.E.; Iversen, C.M.; Dewar, R.C.; Medlyn, B.E.; Näsholm, T.; Pepper, D.A.; Norby, R.J. Plant Root Distributions and Nitrogen Uptake Predicted by a Hypothesis of Optimal Root Foraging. Ecol. Evol. 2012, 2, 1235–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palta, J.A.; Chen, X.; Milroy, S.P.; Rebetzke, G.J.; Dreccer, M.F.; Watt, M. Large Root Systems: Are They Useful in Adapting Wheat to Dry Environments? Funct. Plant Biol. 2011, 38, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epie, K.E.; Maral, E. Shoot and Root Biomass, Phosphorus and Nitrogen Uptake of Spring Wheat Grown in Low Phosphorus and Moisture Content Conditions in a Pot Experiment. J. Plant Nutr. 2018, 41, 2273–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benlloch-Gonzalez, M.; Berger, J.; Bramley, H.; Rebetzke, G.; Palta, J.A. The Plasticity of the Growth and Proliferation of Wheat Root System under Elevated CO2. Plant Soil 2014, 374, 963–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, D.W.; Sommers, L.E. Total Nitrogen Analysis of Soil and Plant Tissues. J. AOAC Int. 1980, 63, 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xue, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yang, J.; Zhang, J. Morphological and Physiological Traits of Roots and Their Relationships with Shoot Growth in “Super” Rice. Field Crops Res. 2009, 113, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, G.; Chen, T.; Wang, Z.; Yang, J.; Zhang, J. Reprint of Morphological and physiological traits of roots and their relationships with water productivity in watersaving and drought-resistant rice. Field Crops Res. 2014, 165, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Bi, Y.; Tao, J.; Huang, S.; Hou, M.; Xue, R.; Liang, Z.; Gu, P.; Yoneyama, K.; Xie, X.; et al. Strigolactones Are Required for Nitric Oxide to Induce Root Elongation in Response to Nitrogen and Phosphate Deficiencies in Rice: Modulation of Root Elongation by N and P Supply. Plant Cell Environ. 2016, 39, 1473–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eissenstat, D.M. Costs and Benefits of Constructing Roots of Small Diameter. J. Plant Nutr. 1992, 15, 763–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boring, T.J.; Thelen, K.D.; Board, J.E.; De Bruin, J.L.; Lee, C.D.; Naeve, S.L.; Ross, W.J.; Kent, W.A.; Ries, L.L. Phosphorus and Potassium Fertilizer Application Strategies in Corn–Soybean Rotations. Agronomy 2018, 8, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodd, J.R.; Mallarino, A.P. Soil-test phosphorus and crop grain yield response to long-term phosphorus fertilization for corn-soybean rotations. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2005, 69, 1118–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, W.; Liu, H.; Zhao, H.; Wang, J.; Zheng, H.; Jia, Y.; Yang, L.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Li, X.; et al. The response of grain yield and root morphological and physiological traits to nitrogen levels in paddy rice. Front Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Treatments | N (g box−1) | P (g box−1) | K (g box−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Non−F | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| P | 0 | 4 | 0 |
| K | 0 | 0 | 0.8 |
| PK | 0 | 4 | 0.8 |
| N | 2.08 | 0 | 0 |
| NK | 2.08 | 0 | 0.8 |
| NP | 2.08 | 4 | 0 |
| NPK | 2.08 | 4 | 0.8 |
| Treatment | Total N Uptake (mg Plant−1) | N Uptake per Unit Root Length (mg m−1) | N Uptake per Unit Root Biomass (mg g−1) | NRE (%) | Root to Shoot Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non−F | 6.9 ± 0.1 d | 0.98 ± 0.01 d | 36.3 ± 0.4 c | na | 0.187 ± 0.005 a |
| PK | 7.6 ± 0.1 d | 0.96 ± 0.01 d | 36.2 ± 0.4 c | na | 0.190 ± 0.007 a |
| N | 44.1 ± 0.3 c | 2.82 ± 0.02 c | 63.3 ± 0.4 b | 9.7 ± 0.1 c | 0.172 ± 0.014 b |
| NK | 48.7 ± 0.4 c | 3.11 ± 0.02 c | 65.6 ± 0.5 b | 10.4 ± 0.1 c | 0.172 ± 0.005 b |
| NP | 73.7 ± 0.3 b | 4.15 ± 0.01 b | 81.9 ± 0.3 a | 17.4 ± 0.1 b | 0.163 ± 0.007 b |
| NPK | 95.6 ± 0.9 a | 4.63 ± 0.05 a | 79.9 ± 0.8 a | 23.0 ± 0.2 a | 0.165 ± 0.009 b |
| Treatment | Total N Uptake (mg Plant−1) | NRE (%) | NAE (g g−1) | NPE (g g−1) | NIE (g g−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non−F | 66.1 ± 1.1 d | ns | ns | ns | 44.1 ± 1.3 a |
| PK | 67.4 ± 2.2 d | ns | ns | ns | 44.3 ± 2.5 a |
| N | 152.0 ± 6.9 c | 18.0 ± 0.6 c | 7.5 ± 0.5 c | 41.5 ± 1.2 a | 42.8 ± 1.0 b |
| NK | 164.3 ± 5.5 c | 20.5 ± 1.3 c | 8.7 ± 1.0 c | 42.2 ± 2.4 a | 43.2 ± 2.6 b |
| NP | 224.4 ± 8.9 b | 33.1 ± 1.8 b | 13.9 ± 1.4 b | 42.0 ± 1.9 a | 42.8 ± 3.2 b |
| NPK | 298.8 ± 11.4 a | 48.4 ± 1.5 a | 19.2 ± 1.0 a | 39.0 ± 1.0 b | 40.1 ± 1.4 c |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Du, M.; Zhang, W.; Gao, J.; Liu, M.; Zhou, Y.; He, D.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, S. Improvement of Root Characteristics Due to Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Potassium Interactions Increases Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Yield and Nitrogen Use Efficiency. Agronomy 2022, 12, 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12010023
Du M, Zhang W, Gao J, Liu M, Zhou Y, He D, Zhao Y, Liu S. Improvement of Root Characteristics Due to Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Potassium Interactions Increases Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Yield and Nitrogen Use Efficiency. Agronomy. 2022; 12(1):23. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12010023
Chicago/Turabian StyleDu, Ming, Wenzhong Zhang, Jiping Gao, Meiqiu Liu, Yan Zhou, Dawei He, Yanze Zhao, and Shiming Liu. 2022. "Improvement of Root Characteristics Due to Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Potassium Interactions Increases Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Yield and Nitrogen Use Efficiency" Agronomy 12, no. 1: 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12010023
APA StyleDu, M., Zhang, W., Gao, J., Liu, M., Zhou, Y., He, D., Zhao, Y., & Liu, S. (2022). Improvement of Root Characteristics Due to Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Potassium Interactions Increases Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Yield and Nitrogen Use Efficiency. Agronomy, 12(1), 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12010023





