Studies on the Removal of Phenol and Nitrophenols from Water by Activated Carbon Developed from Demineralized Kraft Lignin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of Contact Time and Initial Concentration
3.2. Effect of Solution pH on Adsorption
3.3. Effect of Temperature
3.4. Adsorption Isotherms
3.5. Thermodynamic Studies
3.6. Kinetic Studies
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ali, I.; Asim, M.; Khan, T.A. Low cost adsorbents for the removal of organic pollutants from wastewater. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 113, 170–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M. A current global view of environmental and occupational cancers. J. Environ. Sci. Health C Environ. Carcinog. Ecotoxicol. Rev. 2011, 29, 223–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- US EPA. Toxic and Priority Pollutants Under the Clean Water Act. US EPA. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/eg/toxic-and-priority-pollutants-under-clean-water-act (accessed on 24 January 2021).
- Honarmandrad, Z.; Javid, N.; Malakootian, M. Removal efficiency of phenol by ozonation process with calcium peroxide from aqueous solutions. Appl. Water Sci. 2021, 11, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Chen, D.; Li, N.; Xu, Q.; Li, H.; He, J.; Lu, J. Surface-Nanoengineered Bacteria for Efficient Local Enrichment and Biodegradation of Aqueous Organic Wastes: Using Phenol as a Model Compound. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 2916–2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heitkamp, M.A.; Camel, V.; Reuter, T.J.; Adams, W.J. Biodegradation of p-nitrophenol in an aqueous waste stream by immobilized bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1990, 56, 2967–2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadam, H.K.; Tilve, S.G. Advancement in methodologies for reduction of nitroarenes. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 83391–83407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Ma, Y.; Gao, N.; Chu, W.; Li, C. Removal of phenol by powdered activated carbon adsorption. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2013, 7, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adebayo, M.A.; Areo, F.I. Removal of phenol and 4-nitrophenol from wastewater using a composite prepared from clay and Cocos nucifera shell: Kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic studies. Resour. Environ. Sustain. 2021, 3, 100020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, M.; Joly, G.; Renaud, A.; Magnoux, P. Removal of Phenol from Water by Adsorption Using Zeolites. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2004, 43, 5275–5280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Yang, F.; Zou, Y.; Peng, Y. Adsorption of Phenol and p-Nitrophenol from Aqueous Solutions on Metal–Organic Frameworks: Effect of Hydrogen Bonding. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2014, 59, 1476–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, N.; Fakhruddin, A.N.M. Removal of phenol from aqueous solution using rice straw as adsorbent. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 1459–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillejos-López, E.; Nevskaia, D.M.; Muñoz, V.; Guerrero-Ruiz, A. On the interactions of phenol, aniline and p-nitrophenol on activated carbon surfaces as detected by TPD. Carbon 2008, 46, 870–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, G.; Liang, D.; Qu, D.; Huang, Y.; Liu, T.; Mao, H.; Ji, P.; Huang, D. Simultaneous removal of cadmium ions and phenol from water solution by pulsed corona discharge plasma combined with activated carbon. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 228, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robau-Sánchez, A.; Aguilar-Elguézabal, A.; de la Torre-Sáenz, L.; Lardizábal-Gutiérrez, D. Radial distribution of porosity in spherical activated carbon particles. Carbon 2003, 41, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, M.; Suhas; Singh, R.; Tyagi, I.; Ahmed, J.; Chaudhary, S.; Kushwaha, S. Microporous activated carbon as adsorbent for the removal of noxious anthraquinone acid dyes: Role of adsorbate functionalization. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgharnia, H.; Nasehinia, H.; Rostami, R.; Rahmani, M.; Mehdinia, S.M. Phenol removal from aqueous solution using silica and activated carbon derived from rice husk. Water Pract. Technol. 2019, 14, 897–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisal, A.; Daud, W.M.A.W.; Ahmad, M.A.; Radzi, R. Using cocoa (Theobroma cacao) shell-based activated carbon to remove 4-nitrophenol from aqueous solution: Kinetics and equilibrium studies. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 178, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahya, A.A.; Rashid, K.T.; Ghadhban, M.Y.; Mousa, N.E.; Majdi, H.S.; Salih, I.K.; Alsalhy, Q.F. Removal of 4-Nitrophenol from Aqueous Solution by Using Polyphenylsulfone-Based Blend Membranes: Characterization and Performance. Membranes 2021, 11, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, S.J.; Koumanova, B.; Kircheva, Z.; Nenkova, S. Adsorption of 2-nitrophenol by technical hydrolysis lignin: Kinetics, mass transfer, and equilibrium studies. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2005, 44, 2281–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaoui, M.; Achard, C.; Rogalski, M. Solubility as a function of temperature of selected chlorophenols and nitrophenols in aqueous solutions containing electrolytes or surfactants. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2002, 47, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.K.; Gupta, V.K.; Jain, S.; Suhas. Removal of Chlorophenols Using Industrial Wastes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 1195–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhas; Carrott, P.; Carrott, M.R.; Singh, R.; Singh, L.; Chaudhary, M. An innovative approach to develop microporous activated carbons in oxidising atmosphere. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 156, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albadarin, A.B.; Collins, M.N.; Naushad, M.; Shirazian, S.; Walker, G.; Mangwandi, C. Activated lignin-chitosan extruded blends for efficient adsorption of methylene blue. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 307, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Xin, Q.; Wu, X.; Chen, Z.; Yan, Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, M.; Xu, Q. Selective adsorption and separation of organic dyes from aqueous solution on polydopamine microspheres. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 461, 292–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojoudi, N.; Mirghaffari, N.; Soleimani, M.; Shariatmadari, H.; Belver, C.; Bedia, J. Phenol adsorption on high microporous activated carbons prepared from oily sludge: Equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J. Phenol Removal from Water with Potassium Permanganate Modified Granular Activated Carbon. J. Environ. Prot. 2013, 4, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, S.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X. Removal behaviors and mechanisms of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solution by cephalosporin residue and derived chars. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 238, 484–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksu, Z.; Akın, A.B. Comparison of Remazol Black B biosorptive properties of live and treated activated sludge. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 165, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayranci, E.; Duman, O. Adsorption behaviors of some phenolic compounds onto high specific area activated carbon cloth. J. Hazard. Mater. 2005, 124, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotoruelo, L.; Marqués, M.D.; Díaz, F.J.; Rodríguez-Mirasol, J.; Rodríguez, J.J.; Cordero, T. Adsorbent ability of lignin-based activated carbons for the removal of p-nitrophenol from aqueous solutions. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 184, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, S.; Sumanjit, K.; Mahajan, R. Comparative study of surface modified carbonized Eichhornia crassipes for adsorption of dye safranin. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2015, 50, 2436–2447. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Cheng, P.; Wang, H.; Xu, H.; Dang, L.; Liu, Z.; Lei, Z. Activation of graphene aerogel with phosphoric acid for enhanced electrocapacitive performance. Carbon 2015, 92, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Han, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, L. CO2-activated porous carbon derived from cattail biomass for removal of malachite green dye and application as supercapacitors. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 317, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sözüdoğru, O.; Fil, B.A.; Boncukcuoğlu, R.; Aladağ, E.; Kul, S. Adsorptive removal of cationic (BY2) dye from aqueous solutions onto Turkish clay: Isotherm, kinetic, and thermodynamic analysis. Part. Sci. Technol. 2016, 34, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotoruelo, L.M.; Marqués, M.D.; Díaz, F.J.; Rodríguez-Mirasol, J.; Rodríguez, J.J.; Cordero, T. Lignin-based activated carbons as adsorbents for crystal violet removal from aqueous solutions. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2012, 31, 386–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, B. A combined experiment and molecular dynamics simulation study of hydrogen bonds and free volume in nitrile-butadiene rubber/hindered phenol damping mixtures. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 12339–12348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraj, R.; Moon, S.-H.; Sivabalan, R.; Arabindoo, B.; Murugesan, V. Removal of phenol from aqueous solution and resin manufacturing industry wastewater using an agricultural waste: Rubber seed coat. J. Hazard. Mater. 2002, 89, 185–196. [Google Scholar]
- Langmuir, I. The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1918, 40, 1361–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freundlich, H. Over the adsorption in solution. J. Phys. Chem. 1906, 57, 1100–1107. [Google Scholar]
- Temkin, M. Kinetics of ammonia synthesis on promoted iron catalysts. Acta Physiochim. URSS 1940, 12, 327–356. [Google Scholar]
- Dubinin, M.M. The Equation of the Characteristic Curve of Activated Charcoal. Proc. USSR Acad. Sci. 1947, 55, 327–329. [Google Scholar]
- Rincón-Silva, N.G.; Moreno-Piraján, J.C.; Giraldo, L.G. Thermodynamic Study of Adsorption of Phenol, 4-Chlorophenol, and 4-Nitrophenol on Activated Carbon Obtained from Eucalyptus Seed. J. Chem. 2015, 2015, 569403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salimi, M.; Salehi, Z.; Heidari, H.; Vahabzadeh, F. Production of activated biochar from Luffa cylindrica and its application for adsorption of 4-Nitrophenol. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dąbrowski, A.; Podkościelny, P.; Hubicki, Z.; Barczak, M. Adsorption of phenolic compounds by activated carbon—A critical review. Chemosphere 2005, 58, 1049–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supong, A.; Bhomick, P.C.; Karmaker, R.; Ezung, S.L.; Jamir, L.; Sinha, U.B.; Sinha, D. Experimental and theoretical insight into the adsorption of phenol and 2, 4-dinitrophenol onto Tithonia diversifolia activated carbon. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 529, 147046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattson, J.A.; Mark Jr, H.B.; Malbin, M.D.; Weber Jr, W.J.; Crittenden, J.C. Surface chemistry of active carbon: Specific adsorption of phenols. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1969, 31, 116–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotoruelo, L.; Marqués, M.; Leiva, A.; Rodríguez-Mirasol, J.; Cordero, T. Adsorption of oxygen-containing aromatics used in petrochemical, pharmaceutical and food industries by means of lignin based active carbons. Adsorption 2011, 17, 539–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lua, A.C. A detailed study of pyrolysis conditions on the production of steam-activated carbon derived from oil-palm shell and its application in phenol adsorption. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2020, 10, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lütke, S.F.; Igansi, A.V.; Pegoraro, L.; Dotto, G.L.; Pinto, L.A.A.; Cadaval, T.R.S. Preparation of activated carbon from black wattle bark waste and its application for phenol adsorption. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, B.H.; Rahman, A.A. Removal of phenol from aqueous solutions by adsorption onto activated carbon prepared from biomass material. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 160, 576–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, S.; Gupta, D.V. Adsorption of phenol and 4-nitrophenol on granular activated carbon in basal salt medium: Equilibrium and kinetics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 147, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rincón-Silva, N.G.; Moreno-Piraján, J.C.; Giraldo, L. Equilibrium, kinetics and thermodynamics study of phenols adsorption onto activated carbon obtained from lignocellulosic material (Eucalyptus globulus Labill seed). Adsorption 2016, 22, 33–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, S.Z.; Darijani, Z.; Karimi, M.A. Fast and efficient removal of phenol by magnetic activated carbon-cobalt nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 832, 154942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, N.F.; Netto, M.S.; Silva, L.F.O.; Mallmann, E.S.; Lima, E.C.; Ferrari, V.; Dotto, G.L. Composite carbon materials from winery composted waste for the treatment of effluents contaminated with ketoprofen and 2-nitrophenol. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magdy, Y.M.; Altaher, H.; ElQada, E. Removal of three nitrophenols from aqueous solutions by adsorption onto char ash: Equilibrium and kinetic modeling. Appl. Water Sci. 2018, 8, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isichei, T.; Okieimen, F. Adsorption of 2-Nitrophenol onto Water Hyacinth Activated Carbon-Kinetics and Equilibrium Studies. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 3, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arasteh, R.; Masoumi, M.; Rashidi, A.M.; Moradi, L.; Samimi, V.; Mostafavi, S.T. Adsorption of 2-nitrophenol by multi-wall carbon nanotubes from aqueous solutions. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 256, 4447–4455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasilewska, M.; Marczewski, A.W.; Deryło-Marczewska, A.; Sternik, D. Nitrophenols removal from aqueous solutions by activated carbon—Temperature effect of adsorption kinetics and equilibrium. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renault, F.; Morin-Crini, N.; Gimbert, F.; Badot, P.-M.; Crini, G. Cationized starch-based material as a new ion-exchanger adsorbent for the removal of C.I. Acid Blue 25 from aqueous solutions. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 7573–7586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu’azu, N.D.; Zubair, M.; Ihsanullah, I. Process Optimization and Modeling of Phenol Adsorption onto Sludge-Based Activated Carbon Intercalated MgAlFe Ternary Layered Double Hydroxide Composite. Molecules 2021, 26, 4266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umpierres, C.S.; Thue, P.S.; Lima, E.C.; Reis, G.S.d.; de Brum, I.A.S.; de Alencar, W.S.; Dias, S.L.P.; Dotto, G.L. Microwave-activated carbons from tucumã (Astrocaryum aculeatum) seed for efficient removal of 2-nitrophenol from aqueous solutions. Environ. Technol. 2018, 39, 1173–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Deng, G.; Shi, X. Adsorption characteristics and mechanism of p-nitrophenol by pine sawdust biochar samples produced at different pyrolysis temperatures. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhorabe Prashant, T.; Lataye Dilip, H.; Ingole Ramakant, S. Adsorptive Removal of 4-Nitrophenol from Aqueous Solution by Activated Carbon Prepared from Waste Orange Peels. J. Hazard. Toxic Radioact. Waste 2017, 21, 04016015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achari, V.S.; Jayasree, S.; Rajalakshmi, A. Adsorption of p–nitrophenol on coconut shell granular activated carbon: Isotherms, kinetics and thermodynamics. Indian J. Chem. Technol. 2018, 24, 471–478. [Google Scholar]
- Lagergren, S. About the theory of so-called adsorption of soluble substances. K. Sven. Vetensk. Handl. 1898, 24, 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, Y.-S.; McKay, G. Sorption of dye from aqueous solution by peat. Chem. Eng. J. 1998, 70, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elovich, S. Proceedings of the Second International Congress on Surface Activity; Academic Press Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1959. [Google Scholar]
- Weber, W.; Morris, J. Advances in water pollution research. In Proceedings of the First International Conference on Water Pollution Research; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Weber, W.J., Jr. Evolution of a technology. J. Environ. Eng. 1984, 110, 899–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

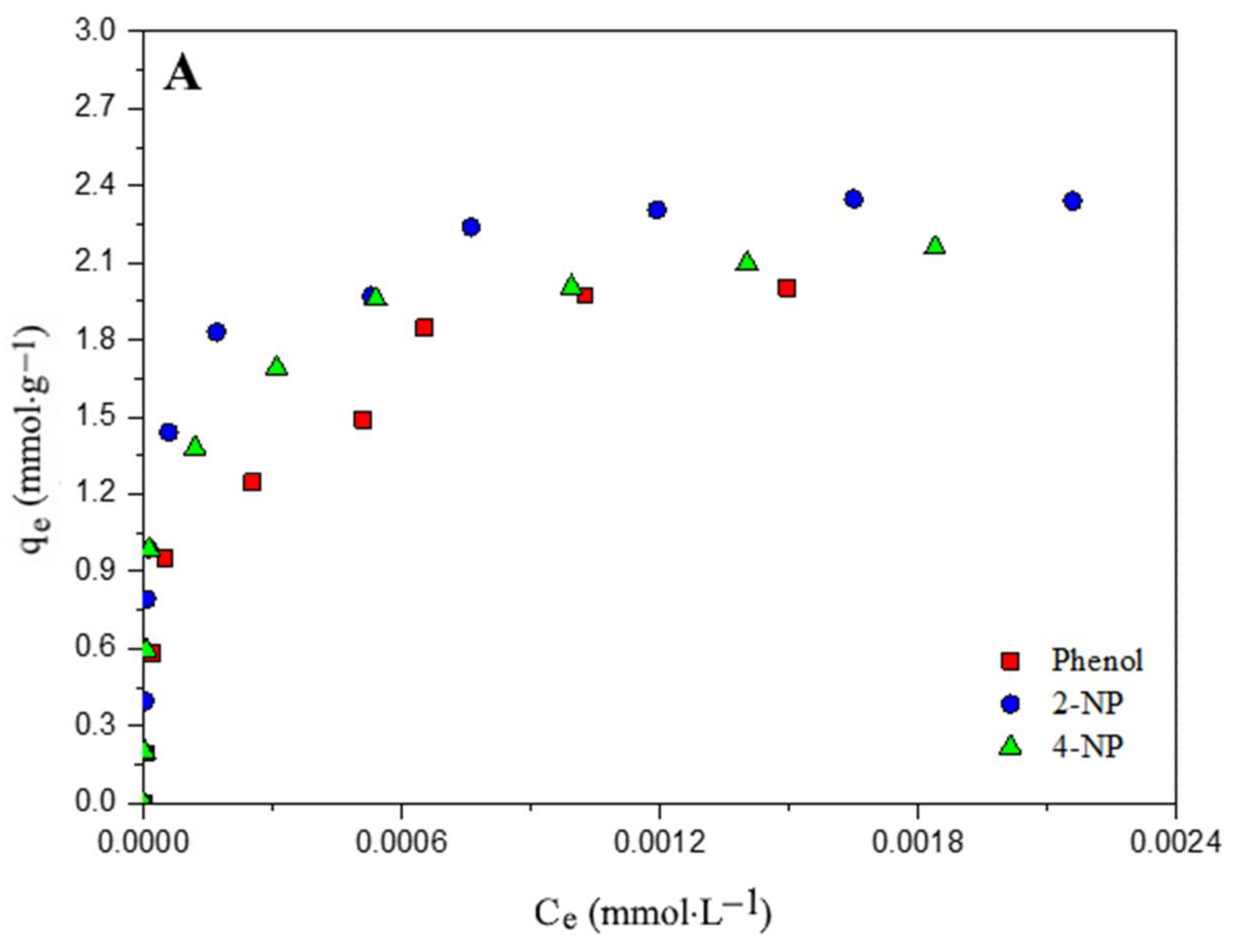
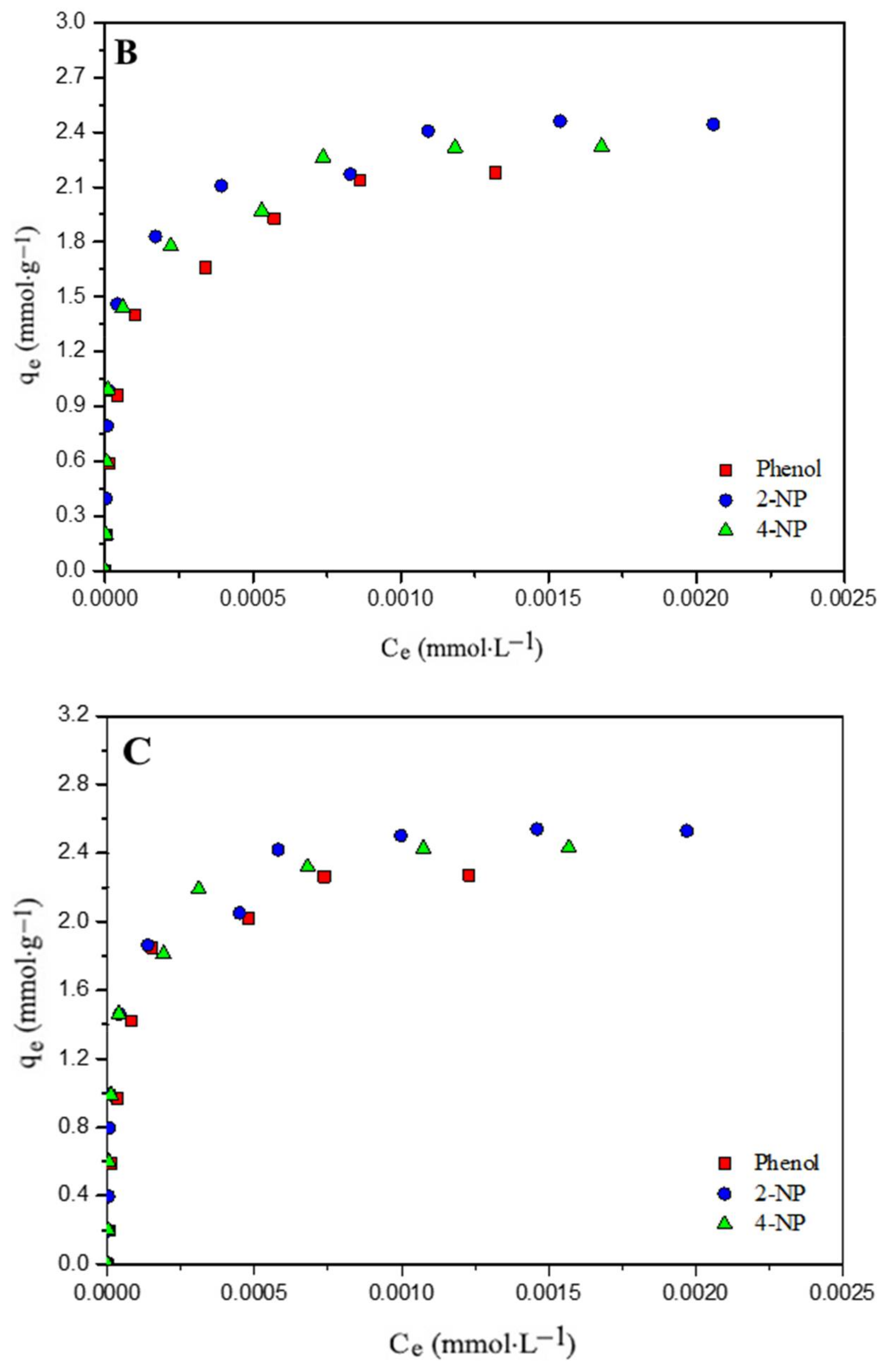
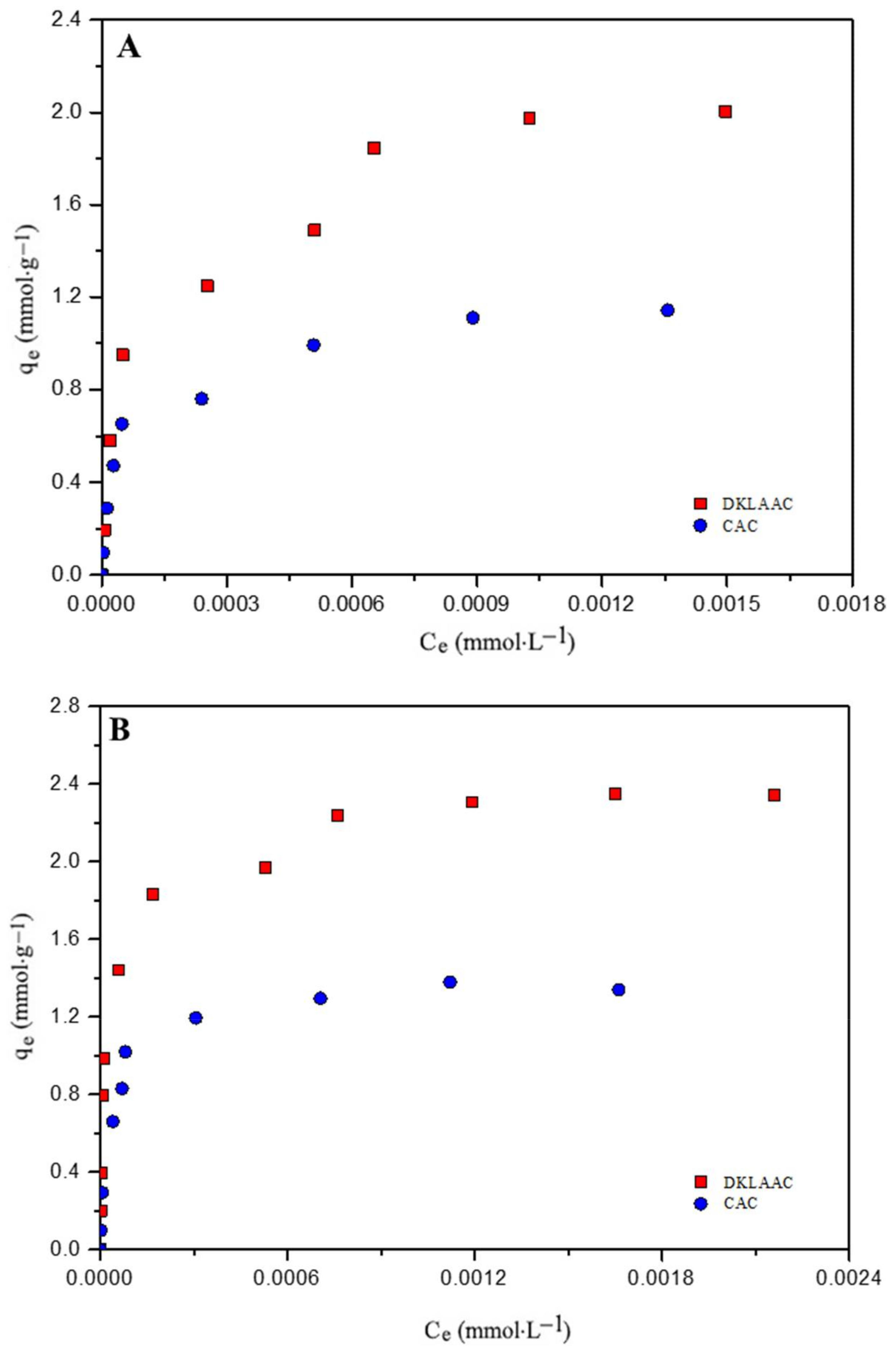
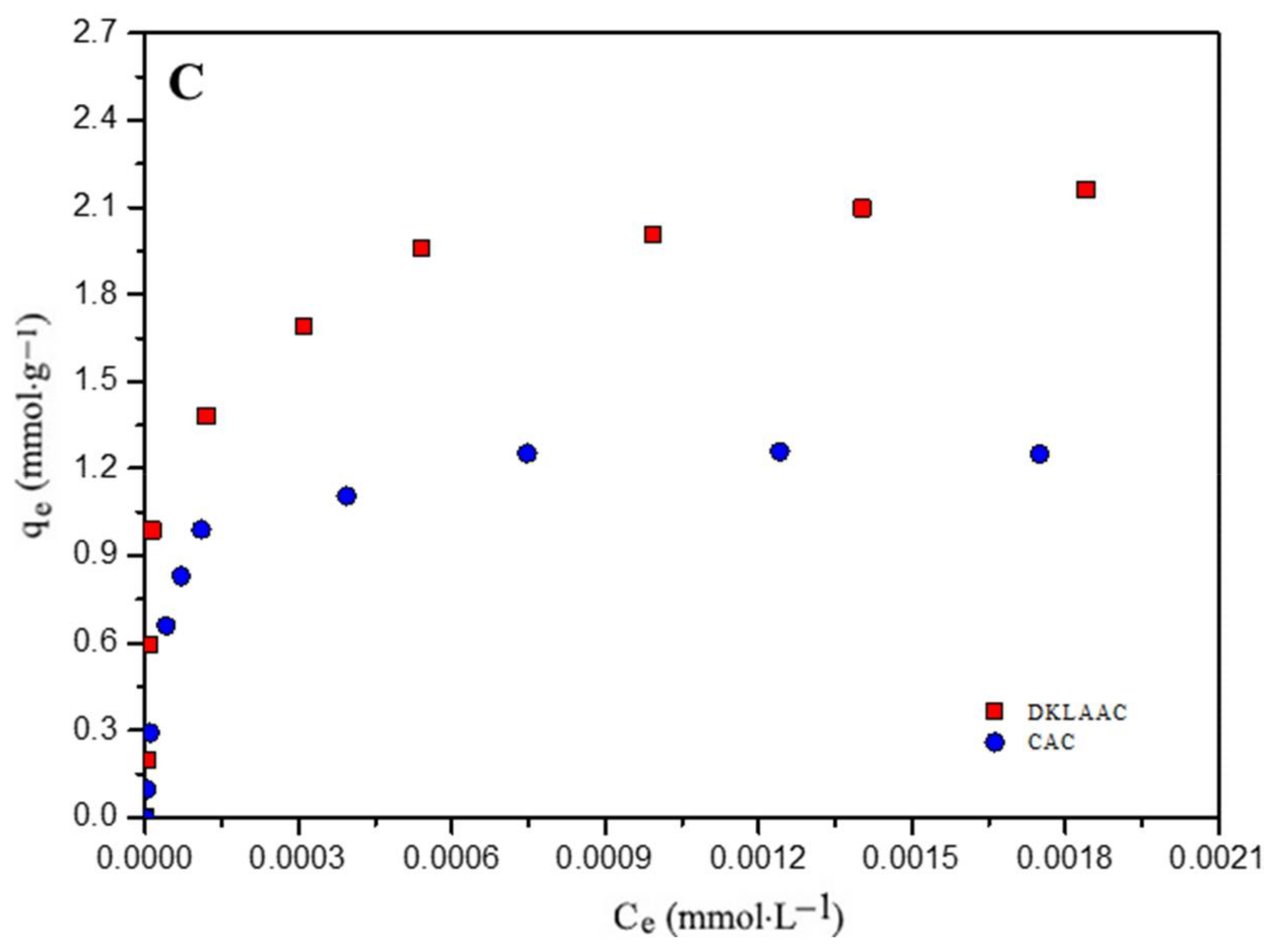
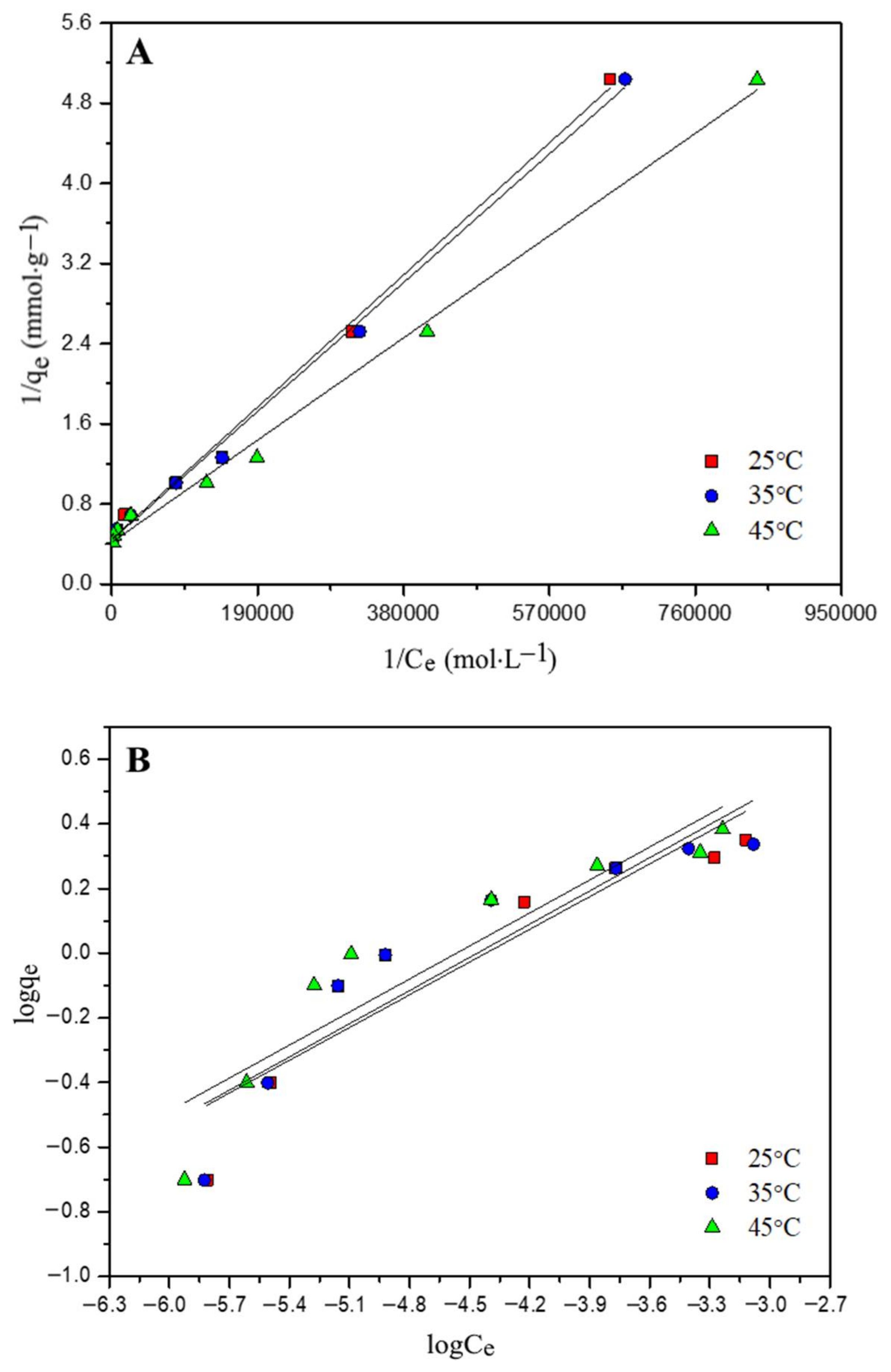

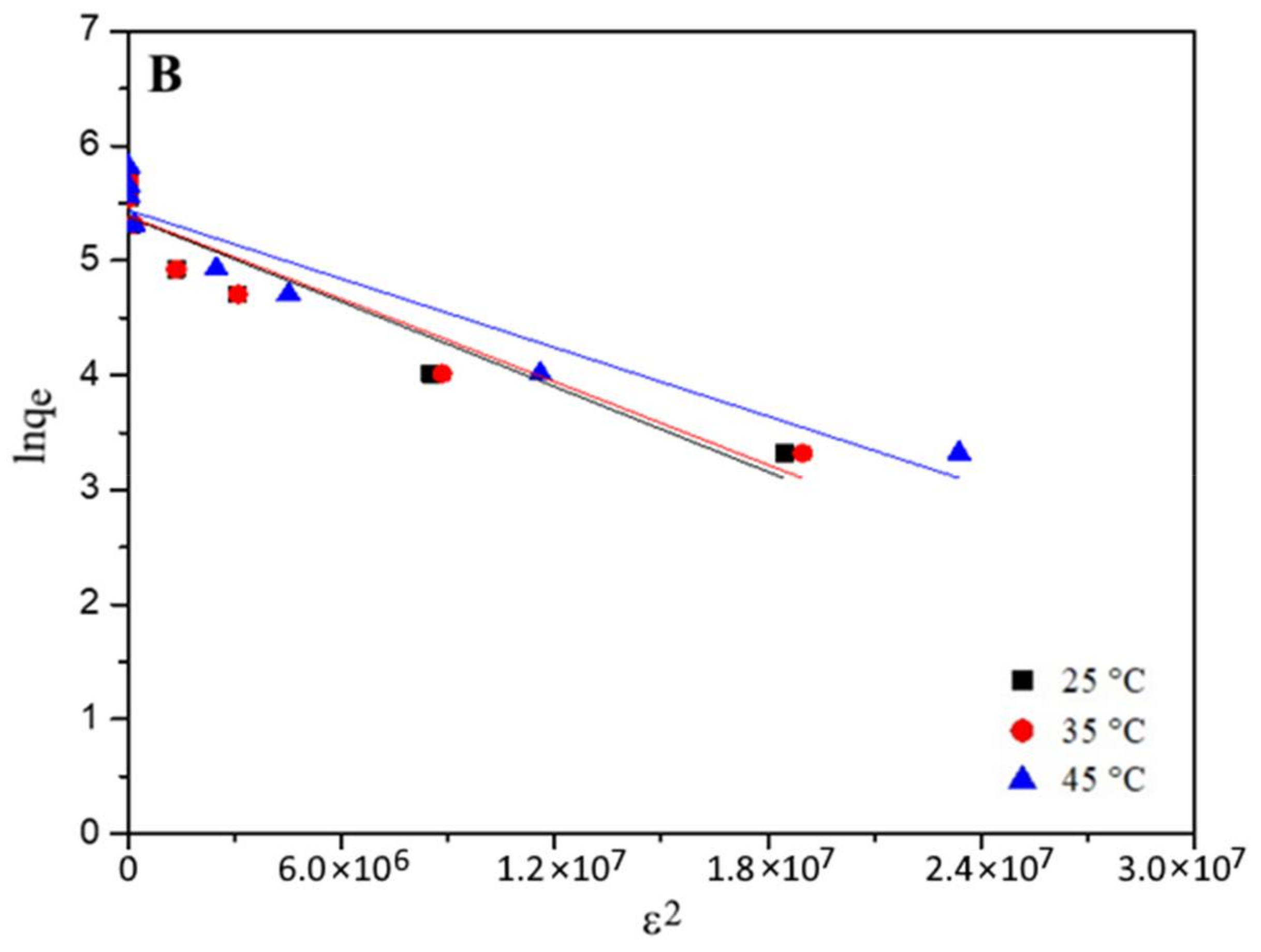
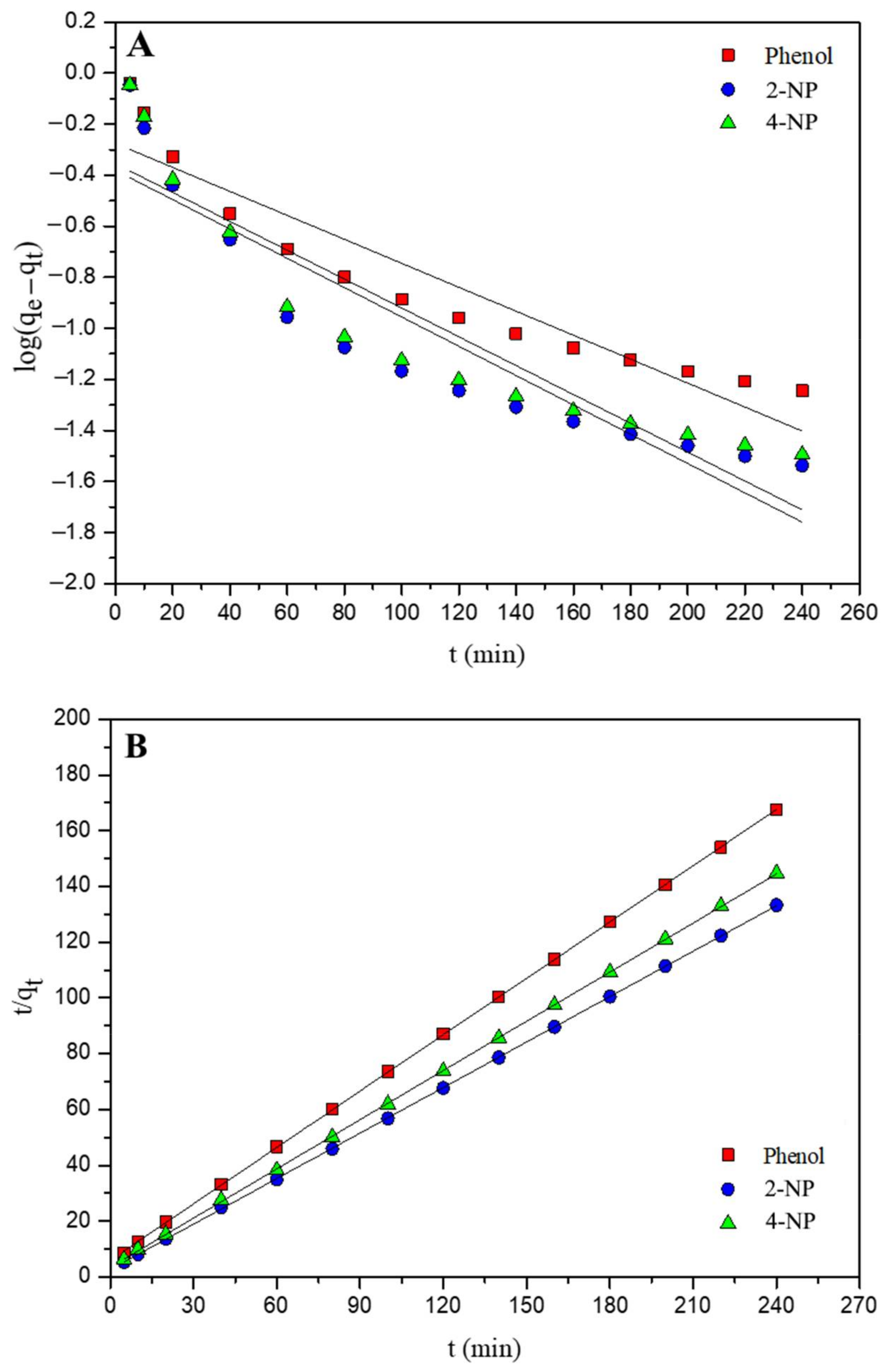
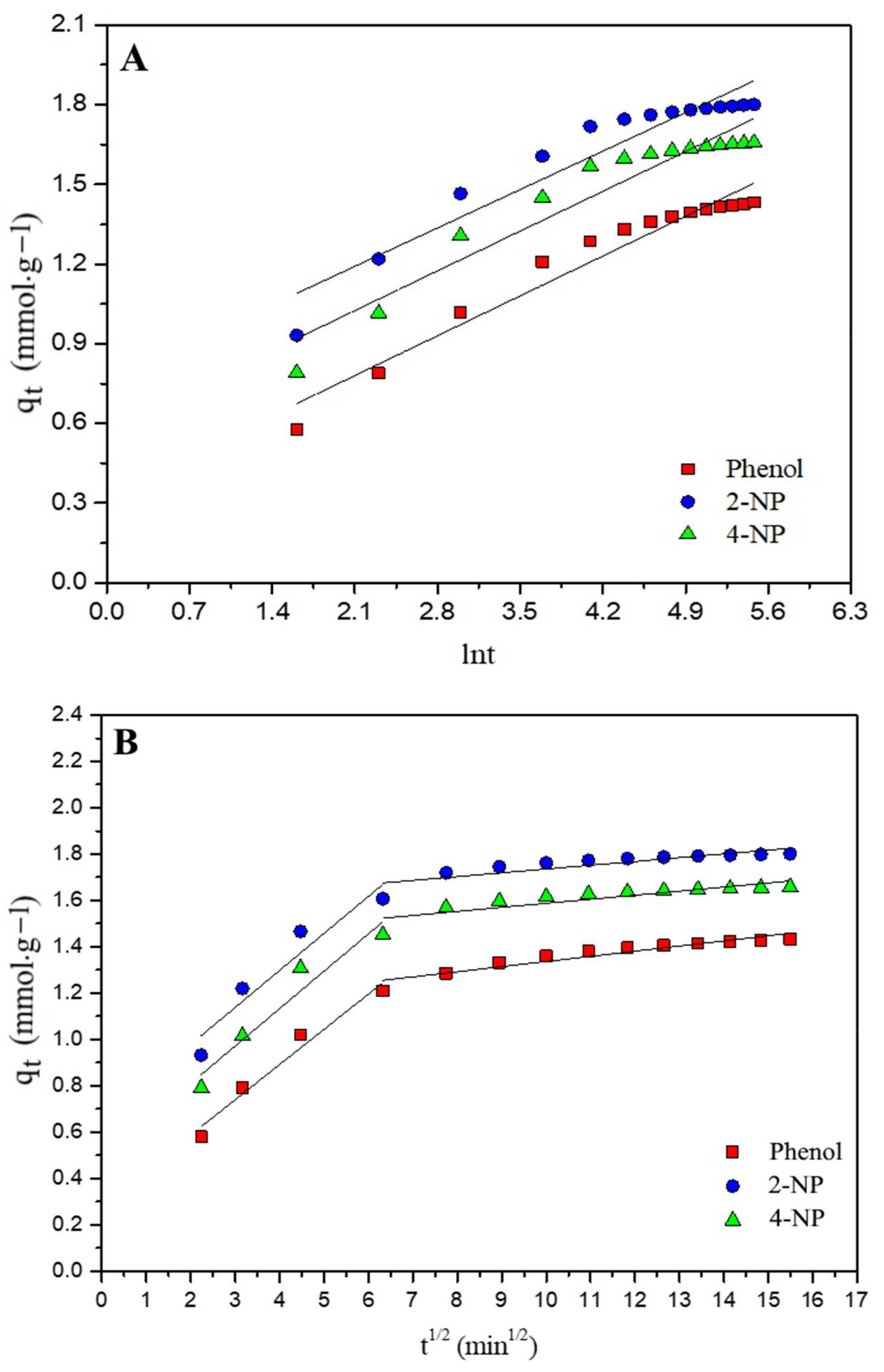
| Parameters | Phenol | 2-NP | 4-NP | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 °C | 35 °C | 45 °C | 25 °C | 35 °C | 45 °C | 25 °C | 35 °C | 45 °C | |
| Experimental | |||||||||
| qexp (mmol·g−1) | 2.09 | 2.18 | 2.27 | 2.34 | 2.46 | 2.53 | 2.2 | 2.32 | 2.43 |
| qexp (mg·g−1) | 189 | 205 | 214 | 326 | 342 | 352 | 306 | 323 | 338 |
| Langmuir model | |||||||||
| qmax (mmol·g−1) | 1.88 | 2.15 | 2.37 | 2.22 | 2.27 | 2.39 | 2.10 | 2.28 | 2.29 |
| qmax (mg·g−1) | 177 | 202 | 223 | 309 | 315 | 333 | 292 | 317 | 319 |
| b (L·mol−1) | 1.90 × 104 | 2.22 × 104 | 2.25 × 104 | 6.49 × 104 | 6.53 × 104 | 7.78 × 104 | 5.43 × 104 | 6.31 × 104 | 6.45 × 104 |
| R2 | 0.993 | 0.995 | 0.999 | 0.996 | 0.997 | 0.995 | 0.992 | 0.994 | 0.998 |
| Freundlich model | |||||||||
| Kf (mmol·g−1) | 39.9 | 106 | 119 | 31.0 | 33.7 | 36.0 | 18.4 | 27.8 | 41.2 |
| n | 2.42 | 2.06 | 2.05 | 2.96 | 2.92 | 2.77 | 3.31 | 3.05 | 2.78 |
| R2 | 0.897 | 0.899 | 0.905 | 0.864 | 0.857 | 0.864 | 0.859 | 0.852 | 0.872 |
| Temkin model | |||||||||
| b (KJ·mol−1) | 0.084 | 0.075 | 0.058 | 0.056 | 0.055 | 0.053 | 0.063 | 0.058 | 0.051 |
| AT (L·mg−1) | 3.37 | 4.14 | 3.36 | 10.25 | 10.50 | 12.54 | 9.97 | 11.5 | 9.36 |
| R2 | 0.965 | 0.989 | 0.982 | 0.988 | 0.986 | 0.985 | 0.983 | 0.983 | 0.989 |
| D-R model | |||||||||
| E (KJ·mol−1) | 1.25 | 1.57 | 1.73 | 2.01 | 2.04 | 2.24 | 1.83 | 2.03 | 2.06 |
| qm (mg·g−1) | 119 | 116 | 121 | 217 | 219 | 231 | 213 | 226 | 230 |
| R2 | 0.886 | 0.914 | 0.890 | 0.895 | 0.894 | 0.909 | 0.909 | 0.907 | 0.887 |
| Adsorbent | Adsorbate | Surface Area | Adsorption Capacity (mg·g−1) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oil palm shell-based activated carbon | phenol | 988 | 168 | [49] |
| Black wattle bark waste-based activated carbon | phenol | 414 | 98.6 | [50] |
| Rattan sawdust-based activated carbon | phenol | 1083 | 149.25 | [51] |
| Granular activated carbon | phenol | 579.23 | 165.80 | [52] |
| Eucalyptus globulus labill seed-based activated carbon | phenol | 300 | 55.566 | [53] |
| Magnetic activated carbon | phenol | 942.9 | 107.5 | [54] |
| DKLAAC | phenol | 1305 | 177 | This study |
| Raw winery residue based activated carbon | 2-NP | 227 | 376 | [55] |
| Animal bone based char ash | 2-NP | 72.9 | 8.624 | [56] |
| water hyacinth activated carbon | 2-NP | - | 47.62 | [57] |
| Acid assisted multi wall carbon nanotube | 2-NP | 197.83 | 256.41 | [58] |
| DKLAAC | 2-NP | 1305 | 309 | This study |
| Granular activated carbon | 4-NP | 900 | 904.21 | [59] |
| Cocoa shell-based activated carbon | 4-NP | 248.75 | 166.67 | [18] |
| Granular activated carbon | 4-NP | 579.23 | 206.3 | [52] |
| Eucalyptus globulus labill seed-based activated carbon | 4-NP | 300 | 137.005 | [53] |
| DKLAAC | 4-NP | 1305 | 317 | This study |
| Phenols | Temperature (°C) | −ΔG° (kJ·mol−1) | ΔS° (J·mol−1·K−1) | ΔH° (kJ·mol−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| phenol | 25 35 45 | 24.4 25.6 26.5 | 104.6 | 6.8 |
| 2-NP | 25 35 45 | 27.5 28.4 29.8 | 116.1 | 7.1 |
| 4-NP | 25 35 45 | 27.0 28.3 29.3 | 113.5 | 6.9 |
| Adsorbent | Adsorbate | Free Energy (kJ·mol−1) | Enthalpy (kJ·mol−1) | Entropy (J·mol−1·K−1) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon slurry-based activated carbon | phenol | −23.0 | 1.1 | 80.9 | [22] |
| Magnetic activated carbon | phenol | −8.12 | 43.57 | 173.14 | [54] |
| Sludge-based activated carbon | phenol | −5.33 | 16.52 | 105 | [61] |
| Black wattle bark-based activated carbon | phenol | −12.20 | 7.89 | 70 | [50] |
| DKLAAC | phenol | −24.4 | 6.8 | 104.6 | This study |
| Granular activated carbon | 2-NP | −3.30 | 5.92 | 90 | [59] |
| Raw winery residue-based activated carbon | 2-NP | −17.35 | −5.53 | 30 | [55] |
| Tucuma seed-based carbon activated with ZnCl2 (1:1) | 2-NP | −16.66 | 105.40 | 405.2 | [62] |
| Tucuma seed-based carbon activated with ZnCl2 (1:1.5) | 2-NP | −16.89 | 50.18 | 224.9 | [62] |
| Tucuma seed-based carbon activated with ZnCl2 (1:2) | 2-NP | −17.76 | 36.30 | 181.3 | [62] |
| DKLAAC | 2-NP | −27.5 | 7.1 | 116.1 | This study |
| Pine sawdust-based Activated carbon | 4-NP | −4.31 | 13.068 | 49.908 | [63] |
| Orange waste peel-based activated carbon | 4-NP | −21.10 | 7.78 | 95 | [64] |
| Granular activated carbon | 4-NP | −10.48 | 11.00 | 20 | [59] |
| Coconut shell-based granular activated carbon | 4-NP | −5.17 | 6.02 | 38.18 | [65] |
| Luffa cylindrica fruit-based activated biochar | 4-NP | −26.84 | 17.54 | 145 | [44] |
| DKLAAC | 4-NP | −27.0 | 6.9 | 113.5 | This study |
| Parameters | Phenol | 2-NP | 4-NP |
|---|---|---|---|
| Experimental | |||
| C0 (mol·L−1) | 2 × 10−3 | 2 × 10−3 | 2 × 10−3 |
| qe(exp) (mmol·g−1) | 1.49 | 1.83 | 1.69 |
| PFO | |||
| qe(cal) (mmol·g−1) | 0.530 | 0.416 | 0.442 |
| K1 (min−1) | 0.011 | 0.013 | 0.013 |
| R2 | 0.900 | 0.855 | 0.858 |
| PSO | |||
| qe(cal) (mmol·g−1) | 1.48 | 1.84 | 1.70 |
| K2 (g·mmol−1·min−1) | 0.076 | 0.112 | 0.100 |
| R2 | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.999 |
| IPD | |||
| Kid1 | 0.152 | 0.160 | 0.162 |
| C1 | 0.284 | 0.659 | 0.487 |
| R2 | 0.969 | 0.914 | 0.937 |
| Kid2 | 0.022 | 0.016 | 0.018 |
| C2 | 1.11 | 1.57 | 1.41 |
| R2 | 0.900 | 0.742 | 0.752 |
| Elovich | |||
| α (mmol·g−1·min−1) | 0.999 | 8.05 | 3.15 |
| β (g·mmol−1) | 4.66 | 4.84 | 4.67 |
| R2 | 0.952 | 0.908 | 0.917 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chaudhary, M.; Suhas; Kushwaha, S.; Chaudhary, S.; Tyagi, I.; Dehghani, M.H.; Stephen Inbaraj, B.; Goscianska, J.; Sharma, M. Studies on the Removal of Phenol and Nitrophenols from Water by Activated Carbon Developed from Demineralized Kraft Lignin. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2564. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12102564
Chaudhary M, Suhas, Kushwaha S, Chaudhary S, Tyagi I, Dehghani MH, Stephen Inbaraj B, Goscianska J, Sharma M. Studies on the Removal of Phenol and Nitrophenols from Water by Activated Carbon Developed from Demineralized Kraft Lignin. Agronomy. 2022; 12(10):2564. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12102564
Chicago/Turabian StyleChaudhary, Monika, Suhas, Sarita Kushwaha, Shubham Chaudhary, Inderjeet Tyagi, Mohammad Hadi Dehghani, Baskaran Stephen Inbaraj, Joanna Goscianska, and Minaxi Sharma. 2022. "Studies on the Removal of Phenol and Nitrophenols from Water by Activated Carbon Developed from Demineralized Kraft Lignin" Agronomy 12, no. 10: 2564. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12102564
APA StyleChaudhary, M., Suhas, Kushwaha, S., Chaudhary, S., Tyagi, I., Dehghani, M. H., Stephen Inbaraj, B., Goscianska, J., & Sharma, M. (2022). Studies on the Removal of Phenol and Nitrophenols from Water by Activated Carbon Developed from Demineralized Kraft Lignin. Agronomy, 12(10), 2564. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12102564











