Orderly Mechanical Seedling-Throwing: An Efficient and High Yielding Establishment Method for Rice Production
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Observations
2.3.1. Grain Yield and Yield Components
2.3.2. Growth Analysis
2.3.3. Tiller Numbers
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
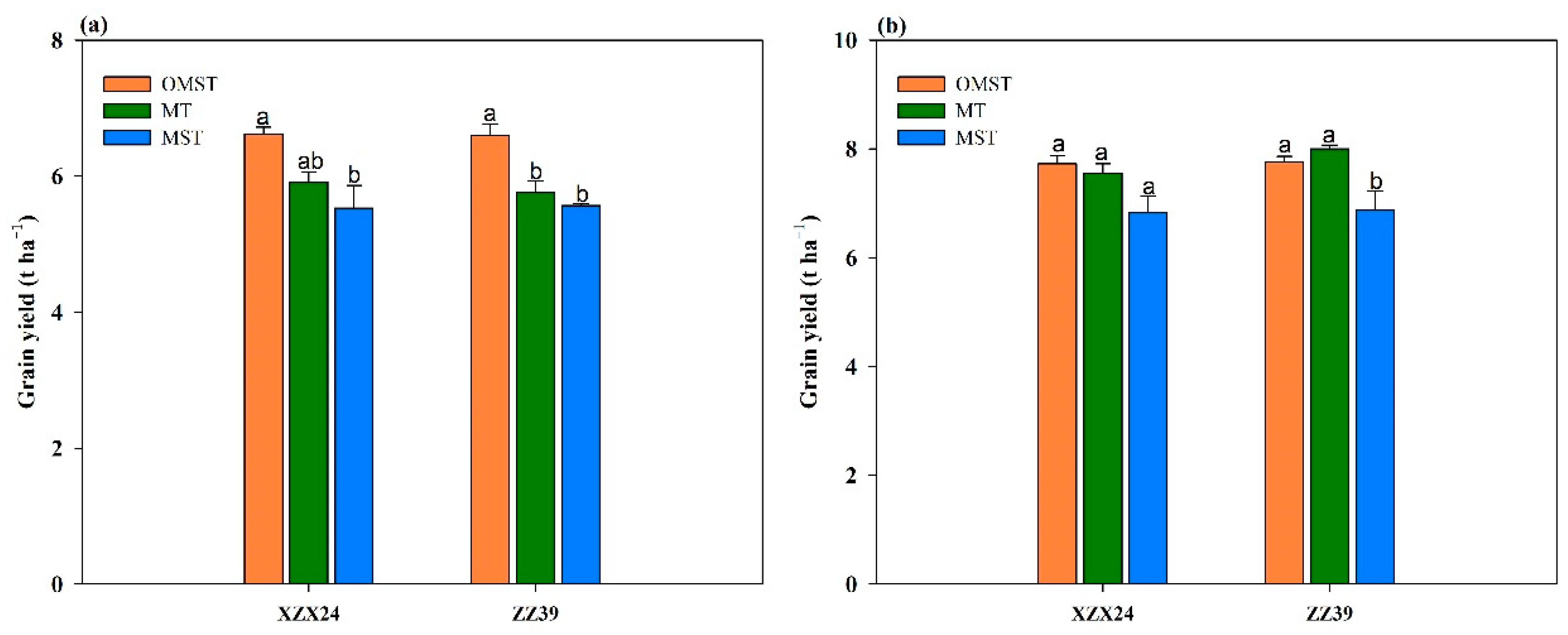
3.1. Grain Yield and Yield Components
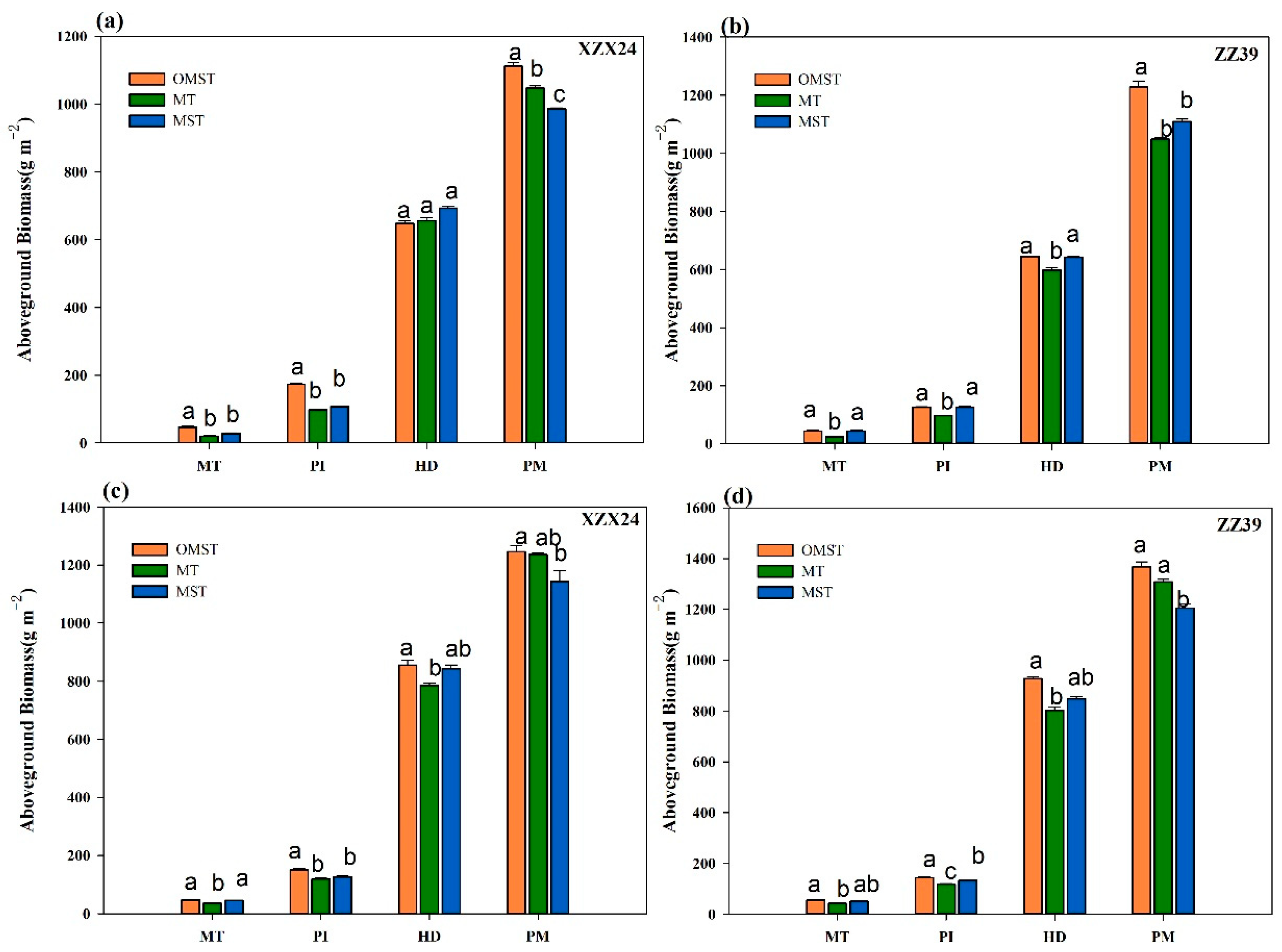
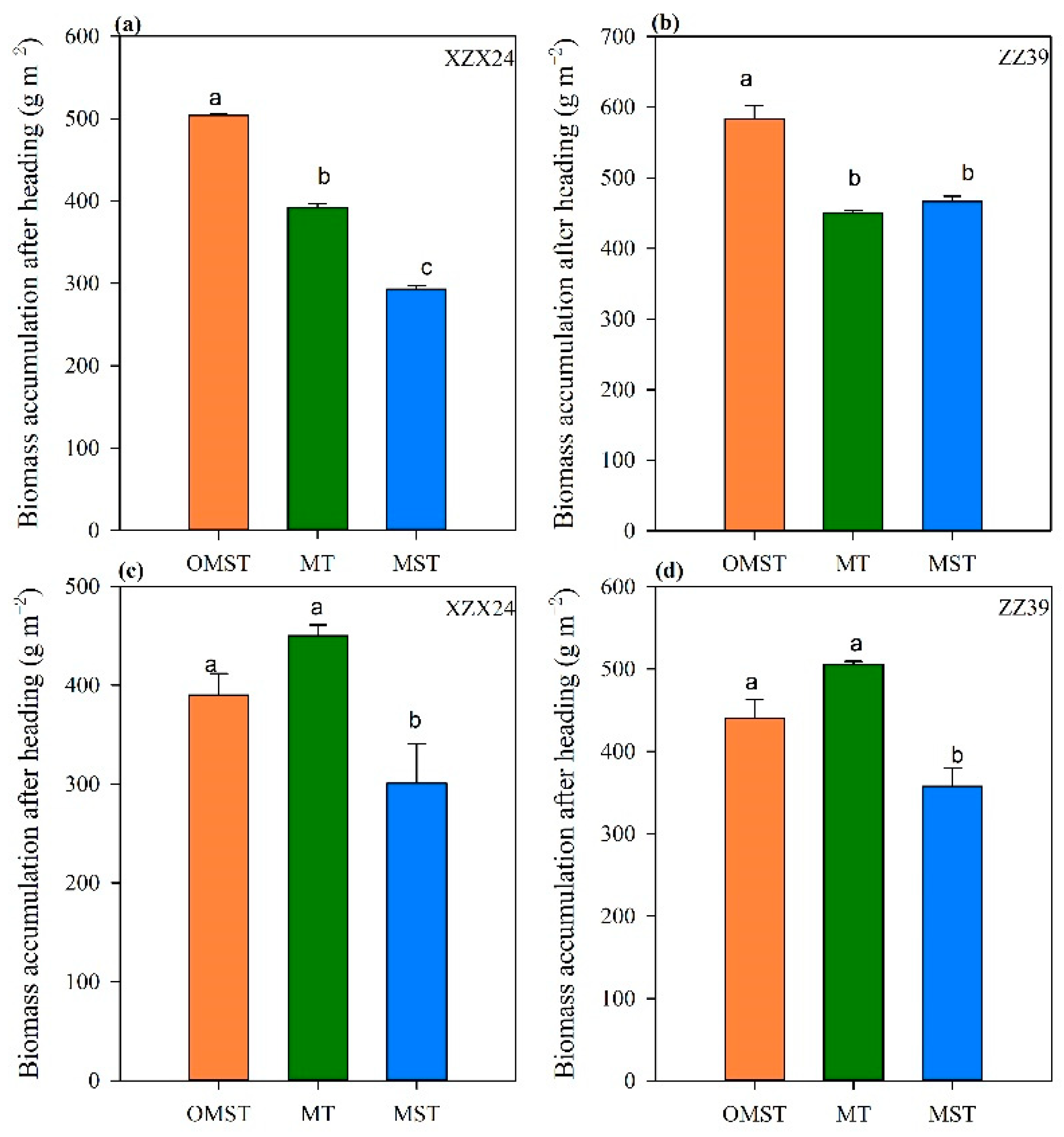
3.2. Aboveground Biomass
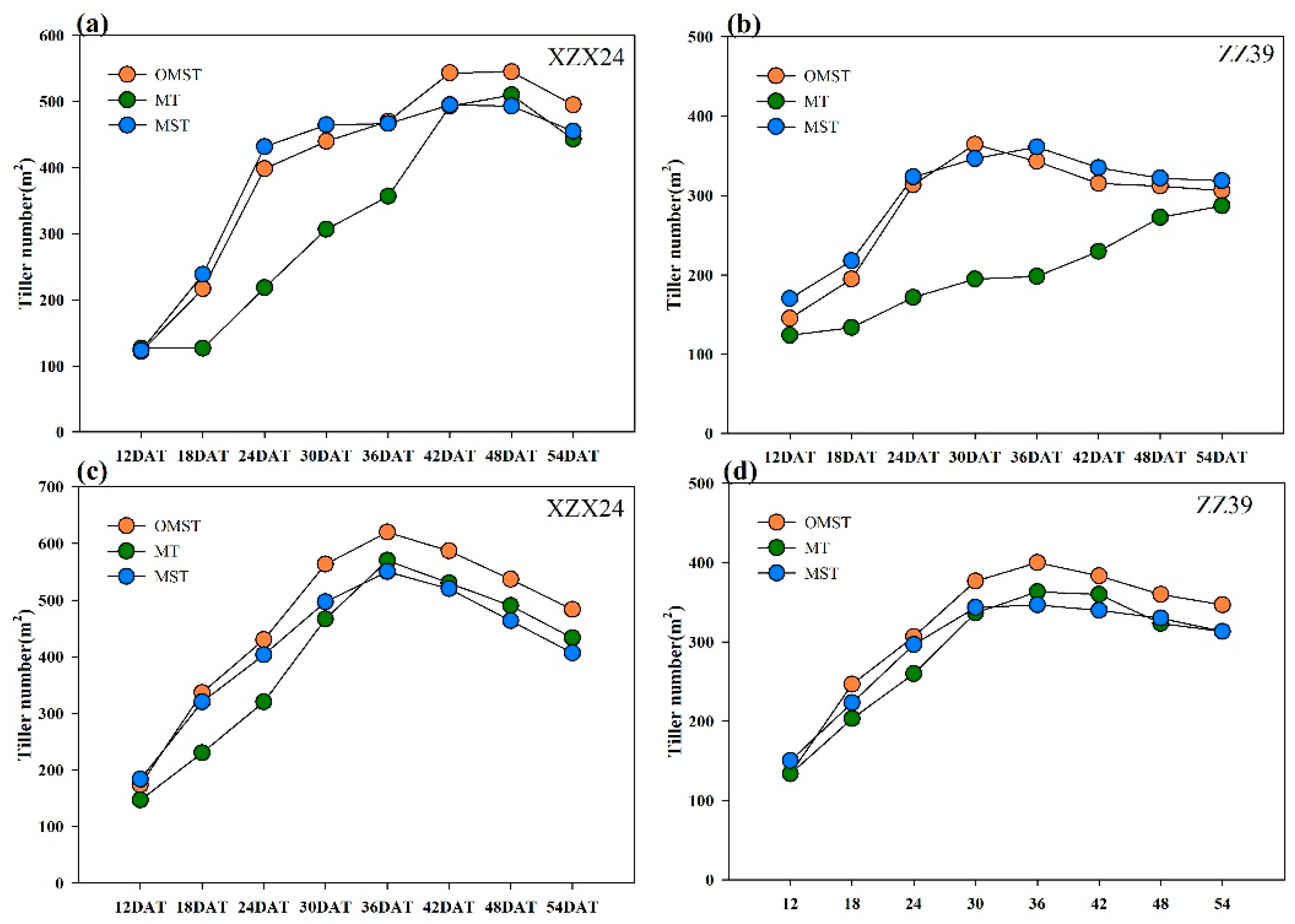
3.3. The Dynamics of Tiller Number
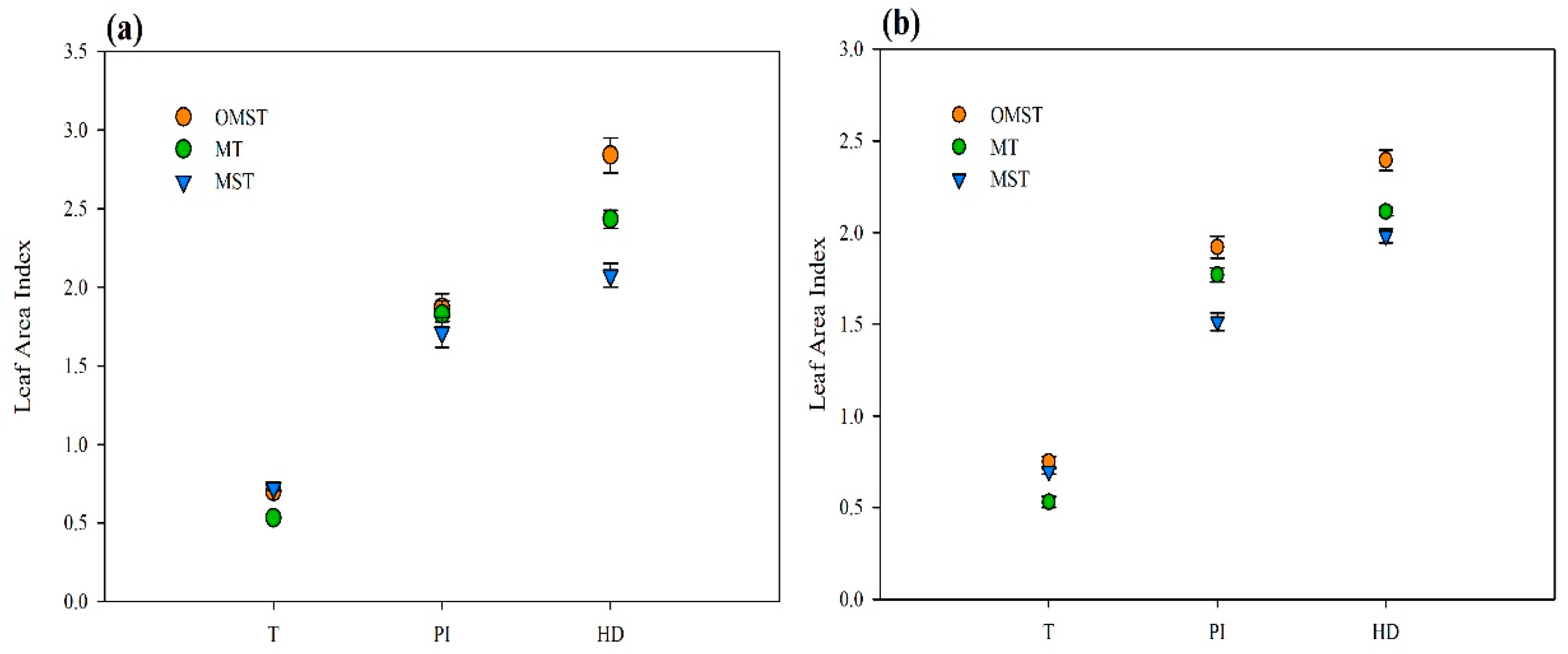
3.4. Leaf Area Index
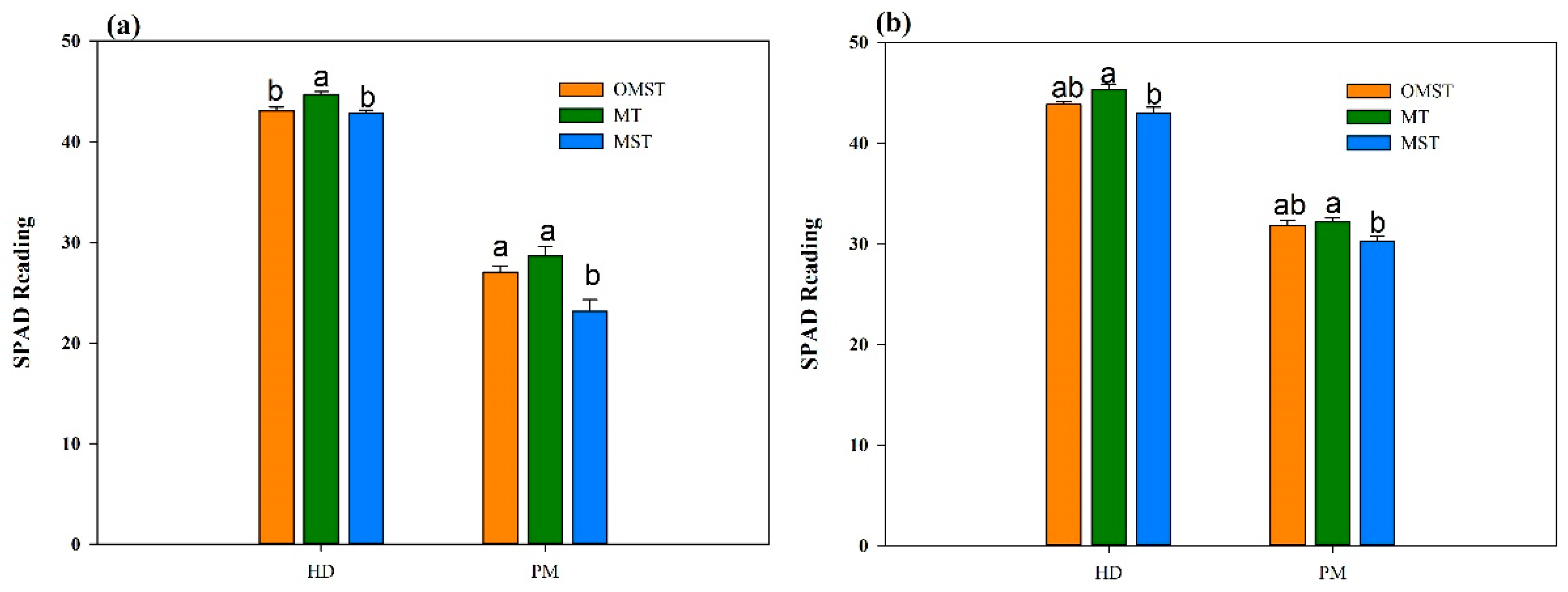
3.5. Leaf SPAD Reading
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, L.; Zhan, X.; Yu, T.; Nie, L.; Huang, J.; Cui, K.; Wang, F.; Li, Y.; Peng, S. Yield performance of direct-seeded, double-season rice using varieties with short growth durations in central China. Field Crop. Res. 2018, 227, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Tang, Q.; Zou, Y. Current status and challenges of rice production in China. Plant Prod. Sci. 2009, 12, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, W.; He, A.; Jiang, G.; Sun, H.; Jiang, M.; Man, J.; Nie, L. Ratoon rice technology: A green and resource-efficient way for rice production. Adv. Agron. 2020, 159, 135–167. [Google Scholar]
- Bu, R.; Ren, T.; Lei, M.; Liu, B.; Li, X.; Cong, R.; Lu, J. Tillage and straw-returning practices effect on soil dissolved organic matter, aggregate fraction and bacteria community under rice-rice-rapeseed rotation system. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 287, 106681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Zou, Y. Integrating mechanization with agronomy and breeding to ensure food security in China. Field Crop. Res. 2018, 224, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; He, P.; Yin, X.; Struik, P.C.; Ding, W.; Liu, K.; Huang, Q. Simultaneously improving yield and nitrogen use efficiency in a double rice cropping system in China. Eur. J. Agron. 2022, 137, 126513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, L.; Yuan, K. Estimating effects of cooperative membership on farmers’ safe production behaviors: Evidence from the rice sector in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 25400–25418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, F.; Xiao, X.; Dong, J. Large increases of paddy rice area, gross primary production, and grain production in Northeast China during 2000–2017. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 711, 135183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Hussain, S.; Zheng, M.; Peng, S.; Huang, J.; Cui, K.; Nie, L. Dry direct-seeded rice as an alternative to transplanted-flooded rice in Central China. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2015, 35, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tao, Y.; Chen, Q.; Peng, S.; Wang, W.; Nie, L. Lower global warming potential and higher yield of wet direct-seeded rice in Central China. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2016, 36, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, M.; Chen, J.; Cao, F.; Zou, Y. Increased hill density can compensate for yield loss from reduced nitrogen input in machine-transplanted double-cropped rice. Field Crop. Res. 2018, 221, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, J.; Xing, X.; Li, G.; Ding, Y.; Dou, F.; Wang, S.; Chen, L. Effects of different controlled-release nitrogen fertilisers on ammonia volatilisation, nitrogen use efficiency and yield of blanket-seedling machine-transplanted rice. Field Crop. Res. 2017, 205, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, C.; Fang, B.; Fang, Y.; Chen, K.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H. Potential for high yield with increased seedling density and decreased N fertilizer application under seedling-throwing rice cultivation. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiang, L.; Tang, Q.; Wang, W.; Zheng, H.; Zheng, Z. Effects of Orderly Mechanical Seedling-Broadcasting on Disaster Reduction of Double Cropping Late Rice Production under Autumn Low Temperature. Chin. J. Agrometrorol. 2022, 2, 500–508, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Deng, X.; Chen, B.; Chen, Y. Variations in root morphological indices of rice (Oryza sativa L.) induced by seedling establishment methods and their relation to arsenic accumulation in plant tissues. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 281, 116999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, Y.; Singh, V.P.; Singh, G.; Yadav, D.S.; Sinha, R.K.P.; Johnson, D.E.; Mortimer, A.M. The implications of land preparation, crop establishment method and weed management on rice yield variation in the rice—Wheat system in the Indo-Gangetic plains. Field Crop. Res. 2011, 121, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S. Seedling broadcasting in China: An overview. In Direct Seeding: Research Strategies and Opportunities, 1st ed.; Pandey, S., Mortimer, M., Wade, L., Tuong, T.P., Lopez, K., Hardy, B., Eds.; International Rice Research Institute: Los Baños, Philippines, 2002; pp. 177–185. [Google Scholar]
- Ai, Z.; Guo, X.; Liu, W.; Ma, G.; Qing, X. Changes of safe production dates of double-season rice in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River. Acta Agron. Sin. 2014, 40, 1320–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Tang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Jia, W.; Luo, Y.; Wang, X.; Zheng, H.; Xiong, J. Evaluation of orderly mechanical seedling-broadcasting on yield formation and growth characteristics of rice. Acta Agron. Sin. 2021, 47, 942–951. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.; Yang, W.; Ren, W. Effects of rice seedlings horizontal distribution on the dynamics of rice population, canopy light transmittance rate and panicle characteristics. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2017, 18, 359–365. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, F.; Huang, J.; Nie, L.; Cui, K.; Peng, S.; Wang, F. Dry matter and N contributions to the formation of sink size in early- and late-maturing rice under various N rates in central China. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2016, 18, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, P.; Lal, B.; Nayak, A.K.; Raja, R.; Panda, B.B.; Tripathi, R.; Shahid, M.; Kumar, U.; Baig, M.J.; Swai, C.K.; et al. Inter-relationship between intercepted radiation and rice yield influenced by transplanting time, method, and variety. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2019, 63, 337–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acevedo-Siaca, L.G.; Dionora, J.; Laza, R.; Paul, Q.W.; Long, S.P. Dynamics of photosynthetic induction and relaxation within the canopy of rice and two wild relatives. Food Energy Secur. 2021, 10, e286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Masclaux-Daubresse, C. Current Understanding of Leaf Senescence in Rice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Wang, W.; Zheng, H.; Liu, G.; Chao, Y.; Xu, C.; Zheng, Z.; Li, X.; Wei, Y.; Tang, Q. Influences of Different Mechanical and Orderly Planting Methods on Growth Characteristics and Yield of rice. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2021, 23, 162–171. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; He, A.; Jiang, G.; Hussain, S.; Wang, W.; Sun, H.; Nie, L. Faster leaf senescence after flowering in wet direct-seeded rice was mainly regulated by decrease in cytokinin content as compared with transplanted-flooded rice. Food Energy Secur. 2020, 9, e232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horgan, F.G.; Figueroa, J.Y.; Almazan, M.L.P. Seedling broadcasting as a potential method to reduce apple snail damage to rice. Crop Prot. 2014, 64, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishwakarma, A.; Singh, J.K.; Sen, A.; Bohra, J.S.; Singh, S. Effect of transplanting date and age of seedlings on growth, yield and quality of hybrids under system of rice (Oryza sativa) intensification and their effect on soil fertility. Indian J. Agric. Sci. 2016, 86, 679–685. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Ge, Q.; Chu, G.; Xu, C.; Yan, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, D. Seasonal differences in the rice grain yield and nitrogen use efficiency response to seedling establishment methods in the Middle and Lower reaches of the Yangtze River in China. Field Crop. Res. 2017, 205, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, B.S.; Abeysekera, A.S.K.; Wickramarathe, M.S.; Kulatunga, S.D.; Wickrama, U.B. Effect of rice establishment methods on weedy rice (Oryza sativa L.) infestation and grain yield of cultivated rice (O. sativa L.) in Sri Lanka. Crop Prot. 2014, 55, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Zhou, X.F.; Cao, F.B.; Xia, B.; Zou, Y.B. No-tillage effect on rice yield in China: A meta-analysis. Field Crop Res. 2015, 183, 126–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanbagavalli, S.; Kandasamy, O.S. Nitrogen management and economic returns of seedling throwing method of rice planting in dry season. Agric. Sci. Dig. 2000, 20, 42–45. [Google Scholar]
- Senguttuvel, P.; Sravanraju, N.; Jaldhani, V.; Divya, B.; Beulah, P.; Nagaraju, P.; Manasa, Y.; Hari Prasad, A.S.; Brajendra, P.; Subrahmanyam, D.; et al. Evaluation of genotype by environment interaction and adaptability in low land irrigated rice hybrids for grain yield under high temperature. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 15825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
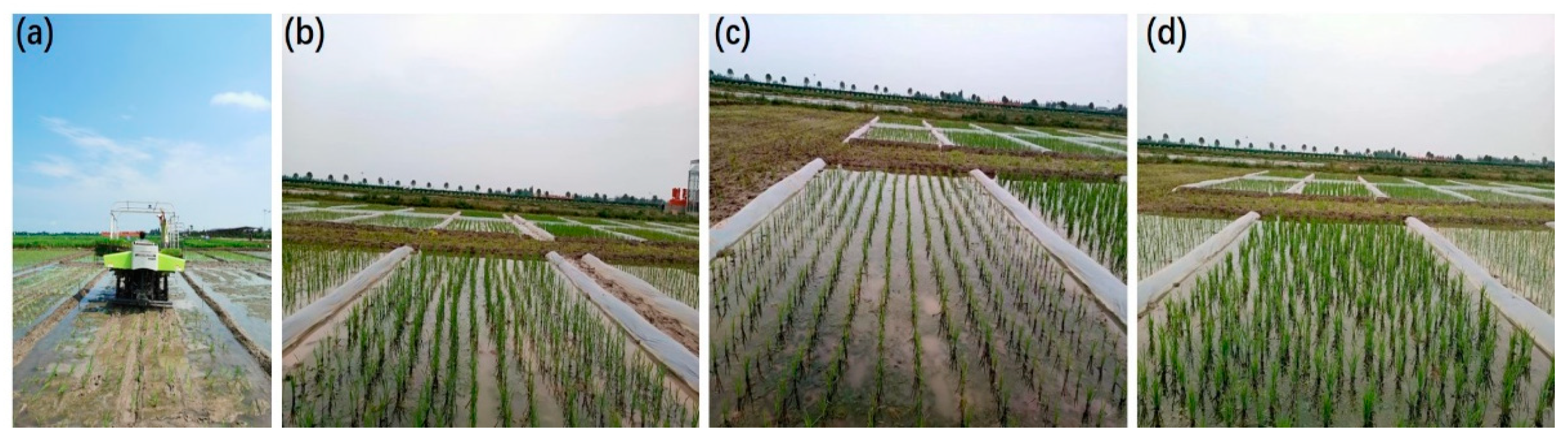

| Variety | Establishment Method | Panicle Number (No. m−2) | Spikelet Per Panicle | Grain Filling Percentage (%) | 1000-Grain Weight (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| XZX24 | OMST | 371.7 a | 103.4 b | 80.0 a | 23.8 a |
| MT | 340 b | 115.8 a | 78.1 a | 23.6 a | |
| MST | 326.9 b | 111.5 a | 78.1 a | 23.3 a | |
| ZZ39 | OMST | 285.2 a | 110.9 b | 85.1 a | 25.9 a |
| MT | 237.1 b | 121.1 a | 83.9 a | 25.7 a | |
| MST | 248.5 b | 109.1 b | 87.5 a | 26.1 a | |
| T | ** | ** | ns | ns | |
| V | ** | ns | ** | ** | |
| T*V | ns | ns | ns | ns |
| Variety | Establishment Method | Panicle Number (No. m−2) | Spikelet Per Panicle | Grain Filling Percentage (%) | 1000-Grain Weight (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| XZX24 | OMST | 360.0 a | 127.6 a | 79.1 b | 23.0 a |
| MT | 320.0 b | 122.1 ab | 85.0 a | 23.3 a | |
| MST | 323.3 b | 120 b | 74.7 c | 23.1 a | |
| ZZ39 | OMST | 287.8 a | 132.4 a | 79.9 b | 26.5 a |
| MT | 274.4 b | 130.4 a | 81.6 a | 26.5 a | |
| MST | 283.3 ab | 115.8 b | 67.8 c | 26.5 a | |
| T | ** | ** | ** | ns | |
| V | ** | ** | ** | ** | |
| T*V | ** | ** | ** | ns |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, W.; Xiang, L.; Zheng, H.; Tang, Q. Orderly Mechanical Seedling-Throwing: An Efficient and High Yielding Establishment Method for Rice Production. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2837. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12112837
Wang W, Xiang L, Zheng H, Tang Q. Orderly Mechanical Seedling-Throwing: An Efficient and High Yielding Establishment Method for Rice Production. Agronomy. 2022; 12(11):2837. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12112837
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Weiqin, Li Xiang, Huabin Zheng, and Qiyuan Tang. 2022. "Orderly Mechanical Seedling-Throwing: An Efficient and High Yielding Establishment Method for Rice Production" Agronomy 12, no. 11: 2837. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12112837
APA StyleWang, W., Xiang, L., Zheng, H., & Tang, Q. (2022). Orderly Mechanical Seedling-Throwing: An Efficient and High Yielding Establishment Method for Rice Production. Agronomy, 12(11), 2837. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12112837








