Research Progress in Leaf Related Molecular Breeding of Cucurbitaceae
Abstract
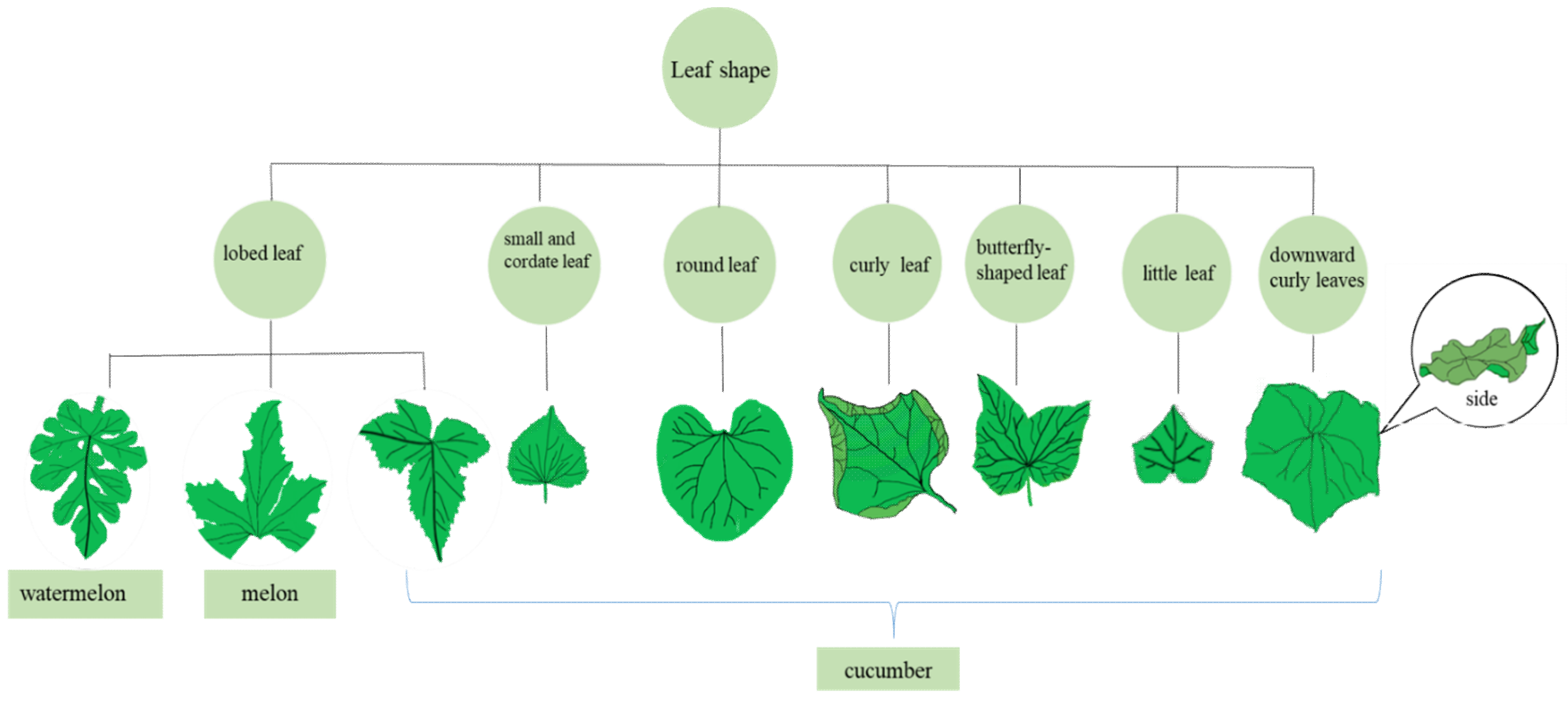
:1. Introduction
2. Genes Affect Leaf Development
2.1. Leaf Shape Mutant
2.1.1. Lobed Leaf
2.1.2. Round Leaf
2.1.3. Curly Leaf
2.1.4. Small and Cordate Leaf
2.1.5. Little Leaf
2.1.6. Downward Curly Leaves
2.1.7. Butterfly-Shaped Leaves
2.2. Leaf Color Mutants
2.3. Plant Hormones Affect Leaf Development
| Mocular Marker | Gene Name | Species | Traits | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| —— | CsHAN1 | Cucumber | Lobed leaf | Ding et al. (2015) [7] |
| G69 and 784RS | Pll (MELO3C010784) | Melon | Lobed leaf | Gao et al. (2014) [8] |
| W07164 and W07061 | Cl LL1 (Cla018360) | Watermelon | Lobed leaf | Chen (2018) [9] |
| Chr1: 16 164 573–21 583 426 | CsPID1 (Csa1G537400) | Cucumber | Round leaf | Zhang et al. (2018) [10] Liu et al. (2019) [11] |
| dCAPS-01 and NWSSR0024 | CsPHB (Csa6G525430) | Cucumber | Curly leaf | Rong et al. (2018) [13] |
| SNP7G3596452 | scl1 (Csa7G062760) | Cucumber | Small and cordate leaf | Gao et al. (2017) [14] |
| SSR21758 and UW083795 | ORF4 | Cucumber | Littleleaf | Yang et al. (2018) [15] |
| —— | CsIVP | Cucumber | Downward curly leaves | Yan et al. (2020) [16] |
| UW026993 and UW027011 | CsWOX1 (Csa1G042780) | Cucumber | Butterfly-shaped leaves | Niu et al. (2018) [6] Wang et al. (2020) [17] |
3. Environmental Factors
3.1. Temperature Affects Leaf Development
3.2. Effect of Light on Leaf Development
3.3. Influence of CO2
4. Prospect
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rolnik, A.; Olas, B. Vegetables from Cucurbitaceae family and their products; positive effect on human health. Nutrition 2020, 78, 110788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsukaya, H. Leaf shape: Genetic controls and environmental factors. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2005, 49, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mingyue, F.U.; Cheng, S.; Feng, X.U.; Chen, Z.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Zheng, J.; Wang, L. Advance in mechanism of plant leaf colour mutation. Not. Bot. Horti Agrobot. Cluj-Napoca 2021, 49, 12071. [Google Scholar]
- Moon, J.; Hake, S. How a leaf gets its shape. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2011, 14, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dkhar, J.; Pareek, A. What determines a leaf’s shape? EvoDevo 2014, 5, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niu, H.; Liu, X.; Tong, C.; Wang, H.; Li, S.; Lu, L.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Weng, Y.; Li, Z. The WUSCHEL-related homeobox1 gene of cucumber regulates reproductive organ development. J. Exp. Bot. 2018, 69, 5373–5387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ding, L.; Yan, S.; Jiang, L.; Liu, M.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, W.; Han, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, X. HANABA TARANU regulates the shoot apical meristem and leaf development in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 7075–7087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, X.; Ning, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Yan, W.; Zhang, Z.; Li, G. Fine mapping of a gene that confers palmately lobed leaf (pll) in melon (Cucumis melo L.). Euphytica 2014, 200, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X. Fine Mapping and Cloning of Watermelon Split Leaf Gene ClLL1. Master’s Thesis, Northwest University of Agriculture and Forestry Science and Technology, Shaanxi, China, 2018. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Chen, F.; Zhao, Z.; Hu, L.; Liu, H.; Cheng, Z.; Weng, Y.; Chen, P.; Li, Y. Mutations in CsPID encoding a Ser/Thr protein kinase are responsible for round leaf shape in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). Tag.Theor. Appl. Genetics.Theor. Und Angew. Genet. 2018, 131, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Hao, N.; Li, H.; Ge, D.; Du, Y.; Liu, R.; Wen, C.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wu, T. PINOID is required for lateral organ morphogenesis and ovule development in cucumber. J. Exp. Bot. 2019, 70, 5715–5730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Cheng, F.; Wang, J.; Wei, Q.; Fu, W.; Yu, X.; Li, J.; Chen, J.; Lou, Q. A leaf shape mutant provides insight into PINOID Serine/Threonine Kinase function in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). J Integr. Plant Biol. 2019, 61, 1000–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rong, F.; Chen, F.; Huang, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, C.; Hou, D.; Cheng, Z.; Weng, Y.; Chen, P.; Li, Y. A mutation in class III homeodomain-leucine zipper (HD-ZIP III) transcription factor results in curly leaf (cul) in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2018, 132, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, S.; Hu, B.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, S. Mutation in a novel gene SMALL AND CORDATELEAF 1 affects leaf morphology in cucumber. J. Bot. Engl. Ed. 2017, 59, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Liu, H.; Zhao, J.; Pan, Y.; Cheng, S.; Lietzow, C.D.; Wen, C.; Zhang, X.; Weng, Y. LITTLELEAF (LL) encodes a WD40 repeat domain-containing protein associated with organ size variation in cucumber. Plant J. 2018, 95, 834–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yan, S.; Ning, K.; Wang, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhong, Y.; Ding, L.; Zi, H.; Cheng, Z.; Li, X.; Shan, H.; et al. CsIVP functions in vasculature development and downy mildew resistance in cucumber. PLoS Biol. 2020, 18, e3000671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Niu, H.; Li, C.; Shen, G.; Liu, X.; Weng, Y.; Wu, T.; Li, Z. WUSCHEL-related homeobox1 (WOX1) regulates vein patterning and leaf size in Cucumis sativus. Hortic. Res. 2020, 7, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, C.; Liu, Q.; Wang, M.; Hou, L.; Zhao, C.; Wang, X.; Xia, H. Research Progress on Molecular Mechanisms of Leaf Color Variation in Plants. Shandong Agric. Sci. 2021, 53, 127–134. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, H.; Gu, X.; Zhang, S.; Wang, X. Research Progress of vegetable Leaf Color Mutants. Chin. Veg. 2007, 6, 39–42. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Ma, S.; Shang, J.; Cheng, S. Leaf Colour Mutants in Cucurbits and Their Research Progress. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2011, 39, 16039–16040+16116. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hang, K.; Li, Y.; Zhu, W.; Wei, Y.; Njogu, M.K.; Lou, Q.; Li, J.; Chen, J. Fine Mapping and Transcriptome Analysis of Virescent Leaf Gene v-2 in Cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 1458. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, H.; Zhang, S.; Wang, M.; Wang, Y.; Weng, Y.; Gu, X. Molecular sciences fine mapping of virescent leaf gene v-1 in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1602. [Google Scholar]
- Pierce, L.K.; Wehner, T.C. Review of Genes and Linkage Groups in Cucumber. HortScience: A publication of the American Society for Horticultural Science. HortScience 1990, 25, 605–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.M.; Gu, X.F.; Zhang, C.Z.; Fang, X.J.; Zhang, S.P.; Xu, C.Q. Genetic mechanism of the cucumber leaf mutant. Acta Hortic. Sin. 2003, 30, 409–412. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, H.; Gu, X.; Zhang, S.; Wang, X.; Fang, Z.; Zhang, Z. Changes of the Photosynthetic Pigment and Differential Expression of the Correlated Genes in a Chlorophyll-Deficient Cucumber Mutant (Cucumis sativus L.). Chin. Agric. Sci. 2010, 43, 4027–4035. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Cui, L.; Cheng, J. Chlorophyll Biosynthesis and Metabolism Analyses of Reciprocal Interspecific Hybrid between Cucumis hystrix and C. sativus. Plant Physiol. J. 2013, 49, 452–456. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Wei, Q.; Wang, J.; Fu, W.; Qin, X.; Lu, X.; Cheng, F.; Yang, K.; Zhang, L.; Yu, X.; et al. Fine Mapping of CsVYL, Conferring Virescent Leaf Through the Regulation of Chloroplast Development in Cucumber. Front. Plant Ence 2018, 9, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.; Du, H.; Zhang, K.; Lv, D.; He, H.; Pan, J.; Cai, R.; Wang, G. A Mutation in CsYL2.1 Encoding a Plastid Isoform of Triose Phosphate Isomerase Leads to Yellow Leaf 2.1 (yl2.1) in Cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 22, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Li, Z. Characteristic and fine-mapping of albino cotyledons(al) mutant in cucumber(Cucumis sativus L.). J. Northwest AF Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2021, 49, 88–95+122. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, H.; Chen, F.; Zhang, C.; Rong, F.; Chen, P.; Li, Y. Photosynthetic characteristics of analysis of new leaf color mutant in cucumber. Acta Agric. Boreali-Occident. Sin. 2018, 27, 1622–1628. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Gao, B.; Yang, J.; Chen, P.; Li, Y. Physiological characteristics of analysis a new leaf color yellow mutant in cucumber. Acta Agric. Boreali-Occident. Sin. 2015, 24, 98–103. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ma, S.; Zhang, L. Discovery of mutant strains carrying watermelon albino lethal gene. Chin. Watermelon Muskmelon 1990, 4, 22. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Yang, J.; Li, Q.; Wu, S.; He, C.; Ma, Y. Phenotypic characteristics and genetic analysis of pumpkin (Cucurbita moschata Duch.) silver leaf mutant 48a. Chin. Cucurbita 2020, 33, 12–16. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.; Fu, Q.; Lv, J.; Zhou, M.; He, M.; Xu, W.; Wang, H.; Huang, Z. Analysis of Physiological Characteristics and Chloroplast Ultrastructure of A New Leaf Color Mutant in Melon. J. Sichuan Agric. Univ. 2018, 36, 372–379. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Xing, G.; Li, M.; Li, S. Integrating physiology, genetics, and transcriptome to decipher a new thermo-sensitive and light-sensitive virescent leaf gene mutant in cucumber. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 972620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Zhang, H.; Xie, C.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, H.; Weng, Y.; Chen, P.; Li, Y. A mutation in CsHD encoding a histidine and aspartic acid domain-containing protein leads to yellow young leaf-1 (yyl-1) in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). Plant Sci. 2020, 293, 110407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shwartz, I.; Levy, M.; Ori, N.; Bar, M. Hormones in tomato leaf development. Dev. Biol. 2016, 419, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Jiao, Y. The Diverse Roles of Auxin in Regulating Leaf Development. Plants 2019, 8, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pekker, I.; Alvarez, J.P.; Eshed, Y. Auxin Response Factors Mediate Arabidopsis Organ Asymmetry via Modulation of KANADI Activity. Plant Cell 2005, 17, 2899–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chitwood, D.H.; Headland, L.R.; Ranjan, A.; Martinez, C.C.; Braybrook, S.A.; Koenig, D.P.; Kuhlemeier, C.; Smith, R.S.; Sinha, N.R. leaf asymmetry as a developmental constraint imposed by auxin-dependent phyllotactic patterning oa. Plant Cell 2017, 24, 2318–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donner, T.J.; Scarpella, E. Auxin-transport-dependent leaf vein formation. Botany 2009, 87, 678–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangerth, K.-F. Basipetal auxin versus acropetal cytokinin transport, and their interaction with NO3 fertilisation in cotyledon senescence and sink:source relationships in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). Plant Biol. 2015, 17, 1135–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, D.; Ding, F.; Wu, J.; Gan, D. Expression of CsaIAAs gene in cucumber induced by 6-BA treatment. J. Anhui Agric. Univ. 2014, 41, 260–264. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Wang, W.; Bo, K.; Miao, H.; Song, Z.; Wei, S.; Zhang, S.; Gu, X. Quantitative Trait Loci Mapping and Candidate Gene Analysis of Low Temperature Tolerance in Cucumber Seedlings. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, H.; Wang, M.; Xie, J.; Xiong, X.; Hu, X.; Qin, Y. Advances in response and research methods of plant low temperature stress. Jiangsu Agric. Sci. 2019, 47, 31–36. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xu, H.; Wang, S.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, D. Effects of low temperature stress on physiological indexes of cucumber seedlings. Jiangsu Agric. Sci. 2013, 41, 126–127. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Lu, Y.; Dai, Z. Cold Tolerance of the Cucumber in Differ ent Development Period. Hubei Agric. Sci. 2008, 544, 548. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Q. Research Advances on Physiological Responses and Tolerant Mechanism to High Temperature Stress in Rice. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2015, 31, 249–258. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xue, S.; Yang, Z.; Zhu, L.; Li, J. Effects of high temperature stress on senescence and endogenous hormone of cucumber during flowering period. Chin. J. Ecol. 2018, 37, 409–416. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Q.; Wu, L.; Chen, F.; Feng, X. Effect of High Temperature Stress on Physiological and Biochemical Characteristics and Photosynthesis of Cucumissativus L. Seedlings. J. Yanan Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2021, 40, 23–26+31. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.; Chen, X.; Chen, C.; Xu, Q. Effects of Supplemental Different Light Qualities on Growth, Photosynthesis, Biomass Partition and Early Yield of Greenhouse Cucumber. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2009, 42, 2615–2623. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Ban, T.; Ma, C.; Wang, Q.; Yang, H.; Lu, J. Effects of light supplement on respiratory enzymes in leaves of cucumber seedling. Guizhou Agric. Sci. 2021, 49, 111–115. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, Y.; Diao, J.; Xue, X.; Lu, X.; Zhang, J. Effects of Continuous Overcast Weather on Cucumber Growth and Antioxidant Enzyme Activities in Glasshouse. A Chin. J. Agrometeorol. 2017, 38, 537–547. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Qin, L. Effects of Light time on Leaf structure and photosynthetic characteristics of Cucumber. J. Chifeng Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2016, 32, 25–27. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Dickinson, R.E.; Dai, Y.; Zhou, L. Sensitivity of simulated terrestrial carbon assimilation and canopy transpiration to different stomatal conductance and carbon assimilation schemes. Clim. Dyn. 2011, 36, 1037–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, T.; Dabuxi, T. Effects of CO2 enrichment and different potassium levels on stomatal state of cucumber. Jiangsu Agric. Sci. 2018, 46, 110–113. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Dong, Y.; Cui, Q.; Zhang, W.; Ai, X.; Liu, B.; Li, Q. Effects of water-nitrogen coupling on the metabolites and key enzyme activities of carbon and nitrogen metabolism in cucumber leaves under doubled CO2 concentration. Plant Physiol. J. 2017, 53, 1717–1727. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Xing, Y.; Wang, X.; Ma, H. Effects of CO2 Enrichment on the Microstructure and Ultrastructure of Leaves in Cucumber. Acta Hortic. Sin. 2002, 29, 30–34. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Rong, F.; Qin, Y.; Chen, F.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, Z.; Hu, L.; Li, Y. The leaf structure in cucumber slightly curly leaf mutant of resistance to powdery mildew. China Cucurbits Veg. 2017, 30, 11–14. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Xu, H.; Wang, H.; Feng, S. Research Progress in Leaf Related Molecular Breeding of Cucurbitaceae. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2908. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12112908
Liu Y, Xu H, Wang H, Feng S. Research Progress in Leaf Related Molecular Breeding of Cucurbitaceae. Agronomy. 2022; 12(11):2908. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12112908
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yafei, Huinan Xu, Huasen Wang, and Shengjun Feng. 2022. "Research Progress in Leaf Related Molecular Breeding of Cucurbitaceae" Agronomy 12, no. 11: 2908. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12112908
APA StyleLiu, Y., Xu, H., Wang, H., & Feng, S. (2022). Research Progress in Leaf Related Molecular Breeding of Cucurbitaceae. Agronomy, 12(11), 2908. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12112908







