Nitrogen Fertilizer Reduction Combined with Biochar Application Maintain the Yield and Nitrogen Supply of Rice but Improve the Nitrogen Use Efficiency
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Experimental Material
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. Rice Plant Sampling and Analysis
2.5. Soil Sampling and Analysis
2.6. Yield and N Fertilizer Use Efficiency
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
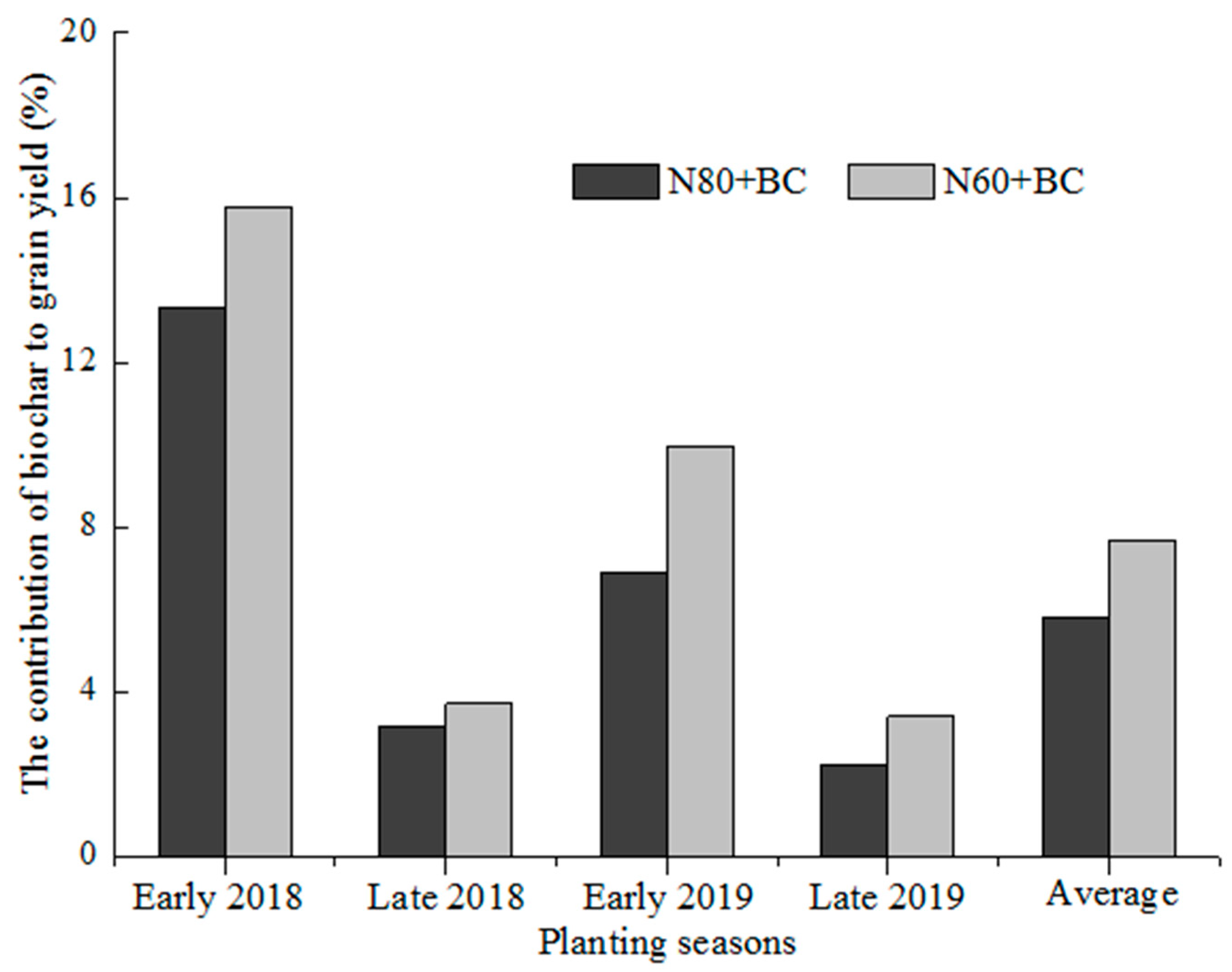
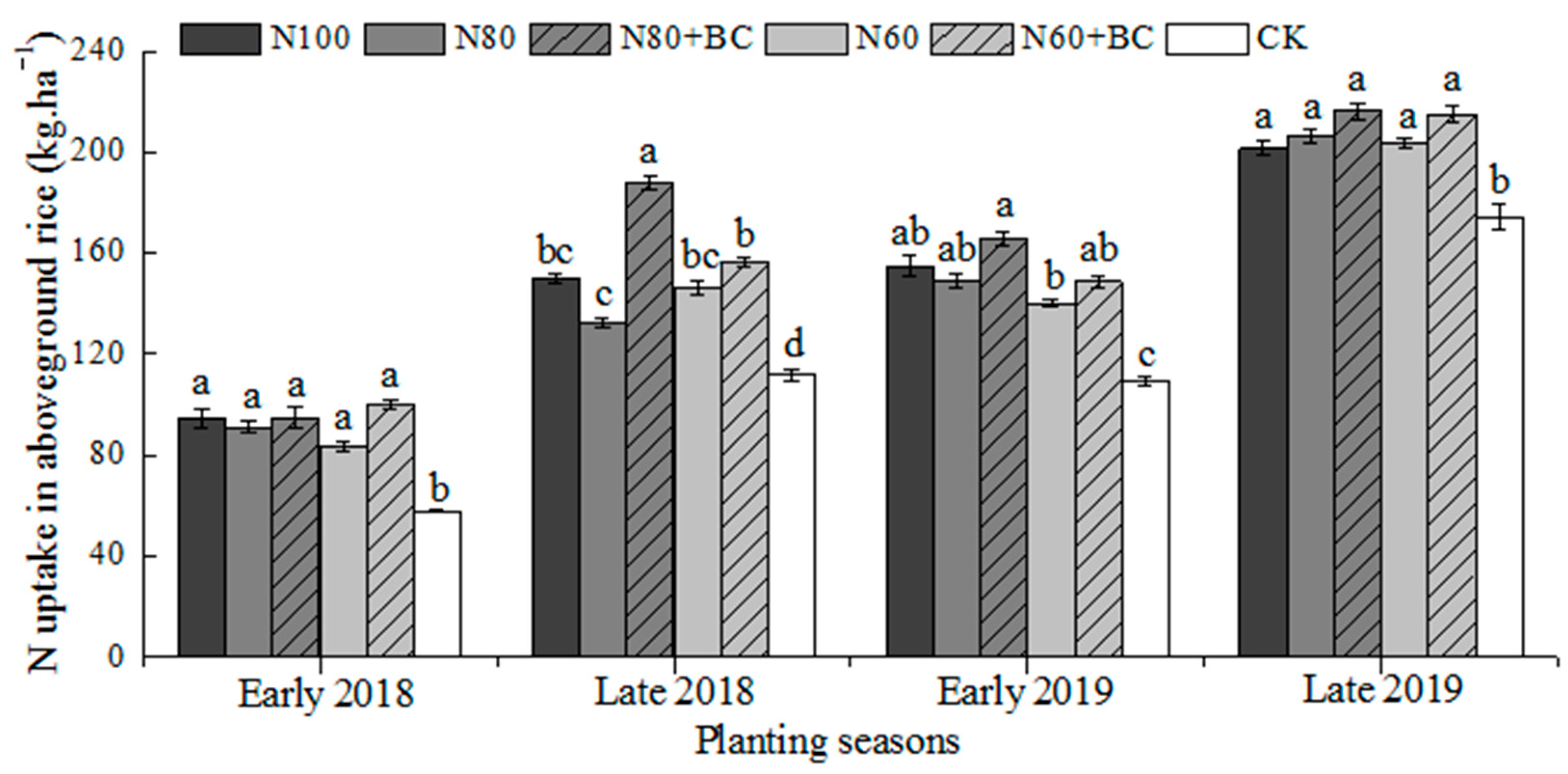
3.1. Effects of Fertilization Regimes on the Aboveground Biomass, Grain Yield, and N Uptake of Rice
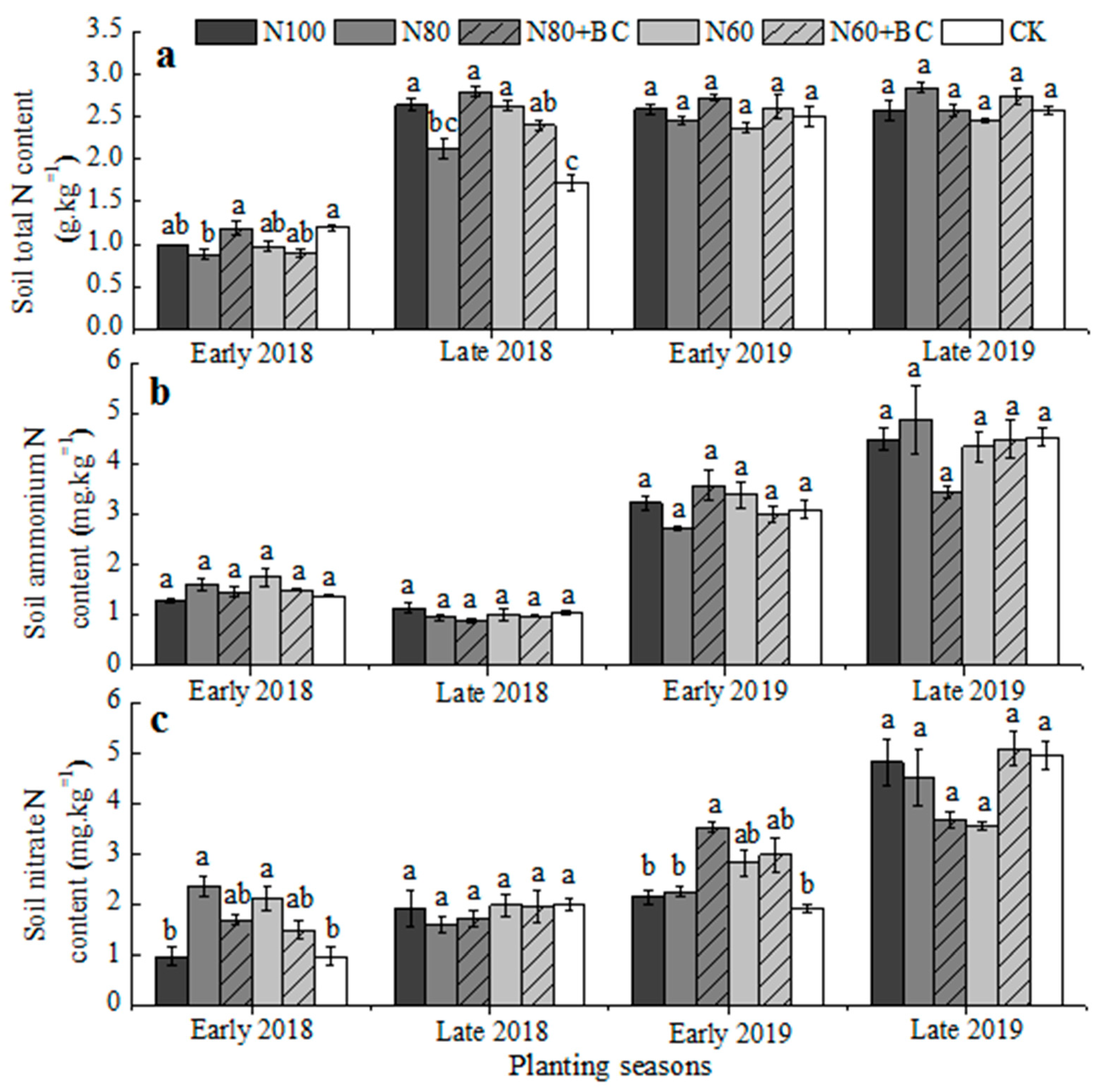
3.2. Effects of Fertilization Regimes on Soil Nutrient Fertility
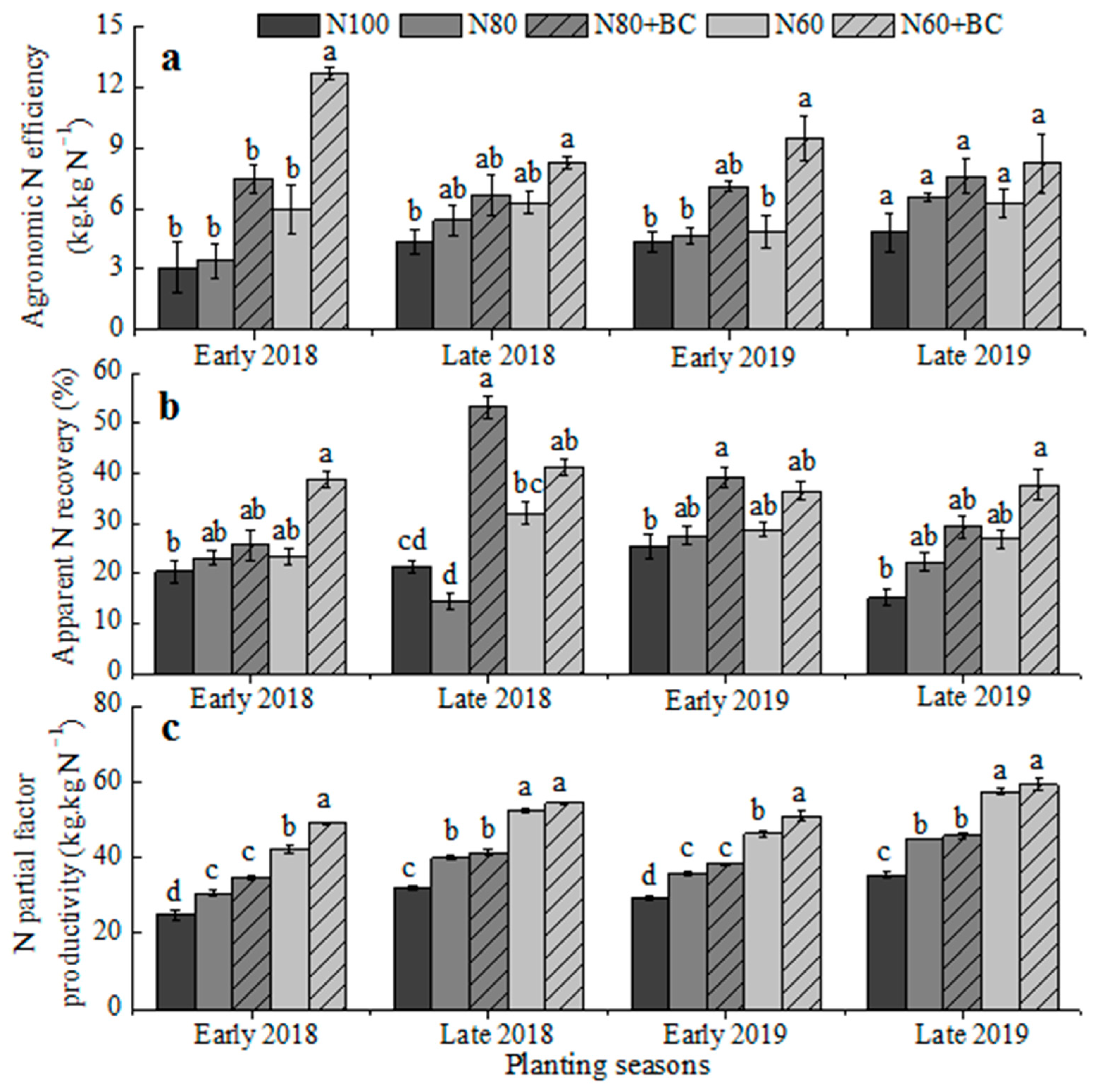
3.3. Effects of Fertilization Regimes on N Use Efficiency of Fertilizers
4. Discussion
4.1. Biochar Incorporation Improve the Grain Yield of Rice
4.2. Biochar Incorporation Maintain N Balance and Improve Soil Fertility
4.3. Biochar Incorporation Improve the N Use Efficiency of Fertilizers
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tsukaguchi, T.; Nitta, S.; Matsuno, Y. Cultivar differences in the grain protein accumulation ability in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Field Crop. Res. 2016, 192, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladha, J.K.; Reddy, P.M. Nitrogen fixation in rice systems: State of knowledge and future prospects. Plant Soil 2003, 252, 151–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, A.K.; Sharma, N.; Dosanjh, N.K.; Goyal, M.; Mahajan, G. Variation in the nutritional quality of rice straw and grain in response to different nitrogen levels. J. Plant Nutr. 2018, 41, 1946–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Ortiz, R.; Naranjo, M.Á.; Ruiz-Navarro, A.; Atares, S.; García, C.; Zotarelli, L.; San Bautista, A.; Vicente, O. Enhanced agronomic efficiency using a new controlled-released, polymeric-coated nitrogen fertilizer in rice. Plants 2020, 9, 1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ata-Ul-Karim, S.T.; Zhu, Y.; Cao, Q.; Rehmani, M.I.A.; Cao, W.; Tang, L. In-season assessment of grain protein and amylose content in rice using critical nitrogen dilution curve. Eur. J. Agron. 2017, 90, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wu, L.; Wu, X.; Ding, Y.; Li, G.; Li, J.; Weng, F.; Liu, Z.; Tang, S.; Ding, C.; et al. Lodging resistance of japonica rice (Oryza Sativa L.): Morphological and anatomical traits due to top-dressing nitrogen application rates. Rice 2016, 9, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.F.; Cheng, C.; Luo, F.; Chang, Y.Y.; Teng, Q.; Men, D.Y.; Liu, L.; Yang, M.Y. Effects of different fertilization practices on the incidence of rice pests and diseases: A three-year case study in Shanghai, in subtropical southeastern China. Field Crop. Res. 2016, 196, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchet, G.; Gavazov, K.; Bragazza, L.; Sinaj, S. Responses of soil properties and crop yields to different inorganic and organic amendments in a Swiss conventional farming system. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 230, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, J.Y.; Li, X.X.; Wang, N.N.; Lan, Z.C.; He, J.Z.; Bai, Y.F. Contrasting effects of nitrogen forms and soil pH on ammonia oxidizing microorganisms and their responses to long-term nitrogen fertilization in a typical steppe ecosystem. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2017, 107, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Han, W.; Tang, A.; Shen, J.; Cui, Z.; Vitousek, P.; Erisman, J.W.; Goulding, K.; Christie, P. Enhanced nitrogen deposition over China. Nature 2013, 494, 459–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayefeh, M.; Sadeghi, S.M.; Noorhosseini, S.A.; Bacenetti, J.; Damalas, C.A. Environmental impact of rice production based on nitrogen fertilizer use. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 15885–15895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, N.; Cai, M.; Zhang, X.; Abdelhafez, A.A.; Zhou, L.; Sun, H.; Chen, G.; Zou, G.; Zhou, S. Runoff loss of nitrogen and phosphorus from a rice paddy field in the east of China: Effects of long-term chemical N fertilizer and organic manure applications. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 22, e01011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Ma, K.; Ciais, P.; Polasky, S. Reducing human nitrogen use for food production. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, G.P.; Paul, E.A.; Harwood, R.R. Greenhouse gases in intensive agriculture: Contributions of individual gases to the radiative forcing of the atmosphere. Science 2000, 289, 1922–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Ji, H.; Liu, H.; Feng, Y.; Guo, Z. Nitrogen fertilizer reduction in combination with Azolla cover for reducing ammonia volatilization and improving nitrogen use efficiency of rice. PeerJ 2021, 9, e11077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.; Ahmad, S.; Ahmad, I.; Han, Q. Nitrogen fertilization affects maize grain yield through regulating nitrogen uptake, radiation and water use efficiency, photosynthesis and root distribution. PeerJ 2020, 8, e10291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Li, Z.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, B.; Duan, M.; Liu, B. Effects of biochar combined with nitrogen fertilizer reduction on rapeseed yield and soil aggregate stability in upland of purple soils. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health. 2020, 17, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, C.C.; Gao, P.D.; Wang, B.Q.; Lin, W.P.; Jiang, N.H.; Cai, K.Z. Impacts of chemical fertilizer reduction and organic amendments supplementation on soil nutrient, enzyme activity and heavy metal content. J. Integr. Agric. 2017, 16, 1819–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghdadi, A.; Halim, R.A.; Ghasemzadeh, A.; Ramlan, M.F.; Sakimin, S.Z. Impact of organic and inorganic fertilizers on the yield and quality of silage corn intercropped with soybean. PeerJ 2018, 6, e5280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Cao, G.; Wang, L.; Wang, S. Effects of equal chemical fertilizer substitutions with organic manure on yield, dry matter, and nitrogen uptake of spring maize and soil nitrogen distribution. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omondi, M.O.; Xia, X.; Nahayo, A.; Liu, X.; Korai, P.K.; Pan, G. Quantification of biochar effects on soil hydrological properties using meta-analysis of literature data. Geoderma 2016, 274, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Win, K.T.; Okazaki, K.; Ookawa, T.; Yokoyama, T.; Ohwaki, Y. Influence of rice-husk biochar and Bacillus pumilus strain TUAT-1 on yield, biomass production, and nutrient uptake in two forage rice genotypes. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0220236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohan, D.; Sarswat, A.; Ok, Y.S.; Pittman, C.U., Jr. Organic and inorganic contaminants removal from water with biochar, a renewable, low cost and sustainable adsorbent-a critical review. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 160, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duwiejuah, A.B.; Abubakari, A.H.; Quainoo, A.K.; Amadu, Y. Review of biochar properties and remediation of metal pollution of water and soil. J. Health Pollut. 2020, 10, 200902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, X.; Ye, L.L.; Wang, C.H.; Zhou, H.; Sun, B. Temperature-and duration-dependent rice straw-derived biochar: Characteristics and its effects on soil properties of an Ultisol in southern China. Soil Tillage Res. 2011, 112, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.G.; Sun, F.F.; Zong, Y.T. Effect of rice husk biochar and coal fly ash on some physical properties of expansive clayey soil (Vertisol). Catena 2014, 114, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, W.Y.; Lai, C.M.; Ke, G.R.; Chung, R.S.; Chen, C.T.; Cheng, C.H.; Pai, C.W.; Chen, S.Y.; Chen, C.C. The effects of woodchip biochar application on crop yield, carbon sequestration and greenhouse gas emissions from soils planted with rice or leaf beet. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2013, 44, 1039–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaza, C.; Giannetta, B.; Fernández, J.M.; López-de-Sá, E.G.; Polo, A.; Gascó, G.; Méndez, A.; Zaccone, C. Response of different soil organic matter pools to biochar and organic fertilizers. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 225, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.L.; Edwards-Jones, G.; Murphy, D.V. Biochar mediated alterations in herbicide breakdown and leaching in soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 804–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchimiya, M.; Wartelle, L.H.; Klasson, K.T.; Fortier, C.A.; Lima, I.M. Influence of pyrolysis temperature on biochar property and function as a heavy metal sorbent in soil. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 2501–2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Chen, L.; He, L.Y.; Sheng, X.F. Increased biomass and reduced heavy metal accumulation of edible tissues of vegetable crops in the presence of plant growth-promoting Neorhizobium huautlense T1-17 and biochar. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 228, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malińska, K.; Zabochnicka-Świątek, M.; Dach, J. Effects of biochar amendment on ammonia emission during composting of sewage sludge. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 71, 474–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorentino, N.; Sánchez-Monedero, M.A.; Lehmann, J.; Enders, A.; Fagnano, M.; Cayuela, M. Interactive priming of soil N transformations from combining biochar and urea inputs: A 15N isotope tracer study. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 131, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Tang, S.; Gong, J.; Zeng, G.; Tang, W.; Song, B.; Zhang, P.; Yang, Z.; Luo, Y. Responses of enzymatic activity and microbial communities to biochar/compost amendment in sulfamethoxazole polluted wetland soil. J. Hazard Mater. 2020, 385, 121533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Wang, Z.; Deng, X.; Herbert, S.; Xing, B. Impacts of adding biochar on nitrogen retention and bioavailability in agricultural soil. Geoderma 2013, 206, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Fan, L.; Chen, J.; Jiang, L.; Zou, Y. Continuous applications of biochar to rice: Effects on nitrogen uptake and utilization. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavalloni, C.; Alberti, G.; Biasiol, S.; DelleVedove, G.; Fornasier, F.; Liu, J.; Peressotti, A. Microbial mineralization of biochar and wheat straw mixture in soil: A short-term study. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2011, 50, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clough, T.J.; Condron, L.M.; Kammann, C.; Müller, C. A review of biochar and soil nitrogen dynamics. Agronomy 2013, 3, 275–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelissen, V.; Saha, B.K.; Ruysschaert, G.; Boeckx, P. Effect of different biochar and fertilizer types on N2O and NO emissions. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 70, 244–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.H.; Liu, J.L.; Zhang, J.B.; Zhao, F.T.; Wang, W.P. Effects of nitrogen application rates on translocation of dry matter and nitrogen utilization in rice and wheat. Acta Agron. Sinica 2010, 36, 1736–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Wang, Z.X.; Luo, X.M.; Song, J.X.; Huang, B. Effects of straw incorporation on Rhizoctoniasolani inoculum in paddy soil and rice sheath blight severity. J. Agric. Sci. 2014, 152, 741–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Jiao, X.Y.; Li, H.D.; Hu, T.S.; Jiang, H.Z.; Mahmoud, A. Effects of biochar on water quality and rice productivity under straw returning condition in a rice-wheat rotation region. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 819, 152063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, D.; Feng, Q.; Mcgrouther, K.; Yang, M.; Wang, H.; Wu, W. Effects of biochar amendment on rice growth and nitrogen retention in a waterlogged paddy field. J. Soil Sediment. 2015, 15, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoakwah, E.; Arthur, E.; Frimpong, K.A.; Islam, K.R. Biochar amendment influences tropical soil carbon and nitrogen lability. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2021, 21, 3567–3579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendershot, W.H.; Duquette, M. A simple barium chloride method for determining cation exchange capacity and exchangeable cations. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1986, 50, 605–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walkley, A.; Black, I.A. An examination of the Degtjareff method for determining soil organic matter, and a proposed modification of the chromic acid titration method. Soil Sci. 1934, 37, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, S.R.; Sommers, L.E. Phosphorus. In Methods of Soil Analysis. Part 2. Chemical and Microbiological Properties, 2nd ed.; Page, A.L., Miller, R.H., Keeney, D.R., Eds.; Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 1982; pp. 403–430. [Google Scholar]
- Page, A.L.; Miller, R.H.; Keeney, D.R. Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 2: Chemical and Microbiological Properties, 2nd ed.; American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 1982; pp. 595–624. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, G.X.; Shen, Q.R.; Cao, J.L. Nitrogen fixation and N transfer from peanut to rice cultivated in aerobic soil in an intercropping system and its effect on soil N fertility. Plant Soil 2004, 263, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Li, J.M.; Ma, Y.; Hao, X.Y.; Li, X.Y. Phosphorus efficiency in long-term (15 years) wheat–maize cropping systems with various soil and climate conditions. Field Crop. Res. 2008, 108, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.L.; Huang, S.B.; Tian, B.J.; Ren, J.H.; Meng, Q.F.; Wang, P. Manipulating planting density and nitrogen fertilizer application to improve yield and reduce environmental impact in Chinese maize production. Front Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vos, J. Nitrogen responses and nitrogen management in potato. Potato Res. 2009, 52, 305–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, J.; Yang, L.; Yan, T.; Xue, F.; Zhao, D. Nitrogen fertilizer reduction in rice production for two consecutive years in the Taihu Lake area. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2012, 146, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Major, J.; Rondon, M.; Molina, D.; Riha, S.J.; Lehmann, J. Maize yield and nutrition during 4 years after biochar application to a Colombian savanna oxisol. Plant Soil 2010, 333, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Yang, L.; Qin, H.; Jiang, L.; Zou, Y. Fertilizer nitrogen uptake by rice increased by biochar application. Biol. Fert. Soils 2014, 50, 997–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguera, D.; Barot, S.; Laossi, K.R.; Cardoso, J.; Lavelle, P.; de Carvalho, M.C. Biochar but not earthworms enhances rice growth through increased protein turnover. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2012, 52, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.; Ullah, S.; He, L.; Zhao, Q.; Iqbal, A.; Wei, S.; Shah, T.; Ali, N.; Bo, Y.; Adnan, M. Combined application of biochar and nitrogen fertilizer improves rice yield, microbial activity and N-metabolism in a pot experiment. PeerJ 2020, 8, e10311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Meng, J.; Liang, X.; Yang, E.; Chen, W.F. Biochar’s leacheates affect the abscisic acid pathway in rice seedlings under low temperature. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 646910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guntzer, F.; Keller, C.; Meunier, J.D. Benefits of plant silicon for crops: A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2012, 32, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Tombeur, F.; Cooke, J.; Collard, L.; Cisse, D.; Saba, F.; Lefebvre, D.; Burgeon, V.; Nacro, H.B.; Cornelis, J.T. Biochar affects silicification patterns and physical traits of rice leaves cultivated in a desilicated soil (Ferric Lixisol). Plant Soil 2021, 460, 375–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, D.; Niu, S. A global analysis of soil acidification caused by nitrogen addition. Environ. Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 024019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Lu, S.; Fan, M.; Li, X.; Kuzyakov, Y. Integrated management systems and N fertilization: Effect on soil organic matter in rice-rapeseed rotation. Plant Soil 2013, 372, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaser, B.; Wiedner, K.; Seelig, S.; Schmidt, H.P.; Gerber, H. Biochar organic fertilizers from natural resources as substitute for mineral fertilizers. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2015, 35, 667–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bista, P.; Ghimire, R.; Machado, S.; Pritchett, L. Biochar effects on soil properties and wheat biomass vary with fertility management. Agronomy 2019, 9, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, B.; Lehmann, J.; Solomon, D.; Kinyangi, J.; Grossman, J.; O’Neill, B.; Skjemstad, J.O.; Thies, J.; Luizão, F.J.; Petersen, J. Black carbon increases cation exchange capacity in soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2006, 70, 1719–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.Y.; Jiang, J.; Xu, R.K.; Li, Z. Adsorption of Pb (II) on variable charge soils amended with rice-straw derived biochar. Chemosphere 2012, 89, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaskin, J.W.; Speir, R.A.; Harris, K.; Das, K.; Lee, R.D.; Morris, L.A.; Fisher, D.S. Effect of peanut hull and pine chip biochar on soil nutrients, corn nutrient status, and yield. Agron. J. 2010, 102, 623–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angst, T.; Sohi, S. Establishing release dynamics for plant nutrients from biochar. GCB Bioenergy 2013, 5, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laird, D.; Fleming, P.; Wang, B.; Horton, R.; Karlen, D. Biochar impact on nutrient leaching from a Midwestern agricultural soil. Geoderma 2010, 158, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Bian, R.; Pan, G.; Cui, L.; Hussain, Q.; Li, L.; Zheng, J.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, X.; Han, X. Effects of biochar amendment on soil quality, crop yield and greenhouse gas emission in a Chinese rice paddy: A field study of 2 consecutive rice growing cycles. Field Crop. Res. 2012, 127, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, B.; Lehmann, J.; Sohi, S.P.; Thies, J.E.; O’Neill, B.; Trujillo, L.; Gaunt, J.; Solomon, D.; Grossman, J.; Neves, E.G. Black carbon affects the cycling of non-black carbon in soil. Org. Geochem. 2010, 41, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oladele, S.O.; Adeyemo, A.J.; Awodun, M.A. Influence of rice husk biochar and inorganic fertilizer on soil nutrients availability and rain-fed rice yield in two contrasting soils. Geoderma 2019, 336, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.Y.; Jiang, J.J.; Chen, W.; Han, F.P. Effect of biochar on soil properties on the Loess Plateau: Results from field experiments. Geoderma 2020, 369, 114323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.N.; Xu, C.Y.; Tahmasbian, I.; Che, I.; Xu, Z.H.; Zhou, X.H.; Wallace, H.M.; Bai, S.H. Effects of biochar on soil available inorganic nitrogen: A review and meta-analysis. Geoderma 2017, 288, 79–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Xue, L.H.; Petropoulos, E.; Qian, C.; Hou, P.F.; Xu, D.F.; Yang, L.Z. Nutrient loss by runoff from rice-wheat rotation during the wheat season is dictated by rainfall duration. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 285, 117382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Zwieten, L.; Kimber, S.; Morris, S.; Chan, K.; Downie, A.; Rust, J.; Joseph, S.; Cowie, A. Effects of biochar from slow pyrolysis of papermill waste on agronomic performance and soil fertility. Plant Soil 2010, 327, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petter, F.A.; de Lima, L.B.; Júnior, B.H.M.; de Morais, L.A.; Marimon, B.S. Impact of biochar on nitrous oxide emissions from upland rice. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 169, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knicker, H.; Skjemstad, J.O. Nature of organic carbon and nitrogen in physically protected organic matter of some australian soils as revealed by solid-state 13C and 15N nmr spectroscopy. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 2000, 23, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.Q.; He, T.Y.; Cao, T.; Yang, T.X.; Meng, J.; Chen, W.F. Effects of biochar application on nitrogen leaching, ammonia volatilization and nitrogen use efficiency in two distinct soils. J. Soil. Sci. Plant. Nut. 2017, 17, 515–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Planting Seasons | Treatments | Number of Tillers | Aboveground Dry Biomass (kg·ha−1) | Grain Yield (kg·ha−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Early season in 2018 | N100 | 8.3 ± 0.3ab | 10,609.7 ± 459.1a | 4488.9 ± 228.1bc |
| N80 | 7.5 ± 0.1ab | 10,281.3 ± 266.6a | 4422.2 ± 121.9bc | |
| N80+BC | 9.2 ± 0.3a | 11,244.1 ± 519.3a | 5011.1 ± 100.8ab | |
| N60 | 8.2 ± 0.3ab | 10,692.9 ± 225.6a | 4577.8 ± 127.8bc | |
| N60+BC | 9.3 ± 0.3a | 11,277.5 ± 226.1a | 5300.0 ± 33.3a | |
| CK | 7.0 ± 0.2b | 8796.2 ± 105.6a | 3933.3 ± 19.2b | |
| Late season in 2018 | N100 | 11.2 ± 0.2a | 15,146.3 ± 208.5ab | 5766.7 ± 112.8a |
| N80 | 10.0 ± 0.2ab | 13,909.1 ± 214.4b | 5766.7 ± 106.0a | |
| N80+BC | 11.3 ± 0.3a | 16,750.9 ± 259.6a | 5950.0 ± 140.9a | |
| N60 | 10.5 ± 0.2ab | 15,544.5 ± 254.8ab | 5666.7 ± 58.8a | |
| N60+BC | 10.8 ± 0.2ab | 14,756.3 ± 187.5b | 5877.8 ± 32.1a | |
| CK | 9.2 ± 0.2b | 11,217.7 ± 269.9c | 4988.9 ± 115.7b | |
| Early season in 2019 | N100 | 10.7 ± 0.4a | 15,874.3 ± 446.7a | 5277.8 ± 90.5ab |
| N80 | 10.8 ± 0.4a | 15,521.6 ± 287.1a | 5155.6 ± 61.2ab | |
| N80+BC | 10.0 ± 0.1a | 16,131.3 ± 286.0a | 5511.1 ± 39.0a | |
| N60 | 10.3 ± 0.1a | 14,751.5 ± 148.6a | 5011.1 ± 89.1b | |
| N60+BC | 9.8 ± 0.3a | 15,643.9 ± 202.6a | 5511.1 ± 121.9a | |
| CK | 8.7 ± 0.2a | 12,422.8 ± 216.4b | 4488.9 ± 55.9c | |
| Late season in 2019 | N100 | 12.7 ± 0.5a | 19,601.4 ± 239.2a | 6388.9 ± 167.2a |
| N80 | 13.0 ± 0.1a | 20,614.1 ± 260.2a | 6466.7 ± 33.3a | |
| N80+BC | 13.5 ± 0.4a | 20,465.5 ± 294.5a | 6611.1 ± 122.4a | |
| N60 | 13.3 ± 0.4a | 19,366.5 ± 205.3a | 6200.0 ± 77.8a | |
| N60+BC | 12.3 ± 0.3a | 20,362.8 ± 310.7a | 6411.1 ± 157.7a | |
| CK | 11.3 ± 0.3a | 15,549.3 ± 447.9b | 5522.2 ± 105.0b |
| Planting Seasons | Treatments | pH | CEC (cmol·kg−1) | Organic Matter (g·kg−1) | Available P (mg·kg−1) | Available K (mg·kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Early season in 2018 | N100 | 6.03 ± 0.03a | 5.18 ± 0.15a | 30.37 ± 0.98a | 23.67 ± 0.96a | 52.92 ± 0.49a |
| N80 | 6.10 ± 0.02a | 5.36 ± 0.12a | 27.91 ± 0.71ab | 20.75 ± 1.76a | 69.92 ± 4.88a | |
| N80+BC | 6.11 ± 0.03a | 5.43 ± 0.12a | 26.77 ± 0.31ab | 19.83 ± 1.11a | 72.83 ± 5.69a | |
| N60 | 6.02 ± 0.03a | 5.21 ± 0.19a | 27.17 ± 0.79ab | 20.67 ± 0.97a | 70.11 ± 0.48a | |
| N60+BC | 5.93 ± 0.05a | 5.61 ± 0.03a | 24.88 ± 0.81b | 21.75 ± 1.04a | 58.44 ± 4.26a | |
| CK | 5.92 ± 0.01a | 5.11 ± 0.15a | 28.29 ± 0.77ab | 22.92 ± 0.39a | 70.50 ± 5.56a | |
| Late season in 2018 | N100 | 5.13 ± 0.03ab | 4.99 ± 0.06a | 36.99 ± 0.21ab | 20.08 ± 0.81ab | 37.35 ± 2.17a |
| N80 | 5.11 ± 0.13b | 4.93 ± 0.11a | 36.42 ± 1.11ab | 17.54 ± 1.24b | 43.17 ± 3.28a | |
| N80+BC | 5.62 ± 0.13a | 5.35 ± 0.09a | 32.07 ± 0.74bc | 19.21 ± 0.99ab | 46.03 ± 3.58a | |
| N60 | 5.19 ± 0.02ab | 5.19 ± 0.18a | 35.29 ± 1.30abc | 19.09 ± 0.87ab | 41.08 ± 0.58a | |
| N60+BC | 5.23 ± 0.05ab | 5.42 ± 0.12a | 39.80 ± 2.14a | 21.14 ± 1.12ab | 47.56 ± 1.72a | |
| CK | 5.15 ± 0.07ab | 4.85 ± 0.11a | 29.38 ± 0.65c | 24.17 ± 0.56a | 40.86 ± 0.72a | |
| Early season in 2019 | N100 | 5.30 ± 0.06a | 6.13 ± 0.13a | 31.68 ± 0.70c | 15.67 ± 0.97bc | 40.99 ± 1.00a |
| N80 | 5.43 ± 0.08a | 5.74 ± 0.18a | 29.58 ± 1.08c | 14.38 ± 0.69c | 44.99 ± 3.47a | |
| N80+BC | 5.63 ± 0.12a | 6.15 ± 0.20a | 36.51 ± 1.33ab | 21.92 ± 0.59a | 47.71 ± 0.46a | |
| N60 | 5.30 ± 0.00a | 6.14 ± 0.02a | 31.91 ± 0.90bc | 17.83 ± 1.02bc | 51.74 ± 1.04a | |
| N60+BC | 5.37 ± 0.02a | 5.87 ± 0.09a | 40.47 ± 0.47a | 18.54 ± 0.35ab | 48.03 ± 1.65a | |
| CK | 5.23 ± 0.11a | 5.90 ± 0.02a | 28.80 ± 0.15c | 15.92 ± 0.33bc | 47.07 ± 4.04a | |
| Late season in 2019 | N100 | 4.90 ± 0.03b | 6.13 ± 0.20ab | 30.47 ± 0.31b | 23.00 ± 0.53a | 46.98 ± 1.18a |
| N80 | 4.83 ± 0.04b | 4.25 ± 0.26b | 31.30 ± 0.33b | 21.38 ± 0.58a | 53.97 ± 4.57a | |
| N80+BC | 5.20 ± 0.03a | 7.22 ± 0.25a | 38.99 ± 0.08a | 24.46 ± 0.82a | 56.50 ± 1.85a | |
| N60 | 4.93 ± 0.04b | 5.38 ± 0.48ab | 30.09 ± 0.59b | 21.08 ± 0.89a | 51.31 ± 3.09a | |
| N60+BC | 5.27 ± 0.05a | 5.40 ± 0.48ab | 39.03 ± 0.36a | 24.38 ± 1.10a | 52.12 ± 0.51a | |
| CK | 4.80 ± 0.06b | 5.37 ± 0.24ab | 30.62 ± 0.79b | 23.42 ± 0.19a | 52.70 ± 3.77a |
| Parameters of N Use Efficiency | Pearson Correlation Coefficient | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | CEC | SOM | TN | NH4+-N | NO3−-N | N Uptake | Grain Yield | |
| AEN | 0.249 | 0.190 | 0.289 * | −0.251 | −0.261 * | −0.195 | 0.320 * | 0.375 ** |
| ARN | 0.870 ** | 0.570 ** | 0.891 ** | −0.835 ** | −0.871** | −0.591 ** | 0.883 ** | 0.911** |
| PFPN | 0.144 | −0.024 | 0.146 | −0.140 | −0.101 | 0.136 | 0.164 | 0.204 |
| Partial correlation coefficient | ||||||||
| pH | CEC | SOM | TN | NH4+-N | NO3−-N | N uptake | Grain yield | |
| AEN | −0.491** | 0.143 | −0.182 | −0.216 | 0.325 * | −0.367 ** | 0.092 | 0.683 ** |
| ARN | −0.203 | 0.316 * | 0.205 | −0.443 ** | 0.455 ** | −0.383 ** | 0.496 ** | 0.298* |
| PFPN | −0.061 | −0.121 | −0.061 | −0.041 | 0.124 | 0.085 | −0.012 | 0.349 ** |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ning, C.; Liu, R.; Kuang, X.; Chen, H.; Tian, J.; Cai, K. Nitrogen Fertilizer Reduction Combined with Biochar Application Maintain the Yield and Nitrogen Supply of Rice but Improve the Nitrogen Use Efficiency. Agronomy 2022, 12, 3039. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12123039
Ning C, Liu R, Kuang X, Chen H, Tian J, Cai K. Nitrogen Fertilizer Reduction Combined with Biochar Application Maintain the Yield and Nitrogen Supply of Rice but Improve the Nitrogen Use Efficiency. Agronomy. 2022; 12(12):3039. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12123039
Chicago/Turabian StyleNing, Chuanchuan, Rui Liu, Xizhi Kuang, Hailang Chen, Jihui Tian, and Kunzheng Cai. 2022. "Nitrogen Fertilizer Reduction Combined with Biochar Application Maintain the Yield and Nitrogen Supply of Rice but Improve the Nitrogen Use Efficiency" Agronomy 12, no. 12: 3039. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12123039
APA StyleNing, C., Liu, R., Kuang, X., Chen, H., Tian, J., & Cai, K. (2022). Nitrogen Fertilizer Reduction Combined with Biochar Application Maintain the Yield and Nitrogen Supply of Rice but Improve the Nitrogen Use Efficiency. Agronomy, 12(12), 3039. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12123039











