Abstract
Little is known about the best management systems for seed production of Italian ryegrass. The main objective of this study was to determine the influence of management systems on the first-year seed crop grown under various nitrogen fertilization (0, 60, 120 and 180 kg ha−1). Management systems of single-purpose crops were with (SeedPGR-crop) and without (Seed-crop) plant growth regulator application. The dual-purpose crops incorporated early spring forage cut during stem elongation (EF-seed-crop) and late cut at the onset of heading (LF-seed-crop) followed by seed harvest. Compared to the single-purpose crops, the dual purpose-crops shattered much less seeds but still yielded less because their plants had lower number of visible nodes on stems, shorter ears, fewer spikelets per ear, fewer flowers per spikelet in various ear sections and lighter seeds. Despite similar lodging incidence, the SeedPGR-crop produced relatively small, but significantly larger seed yield than the Seed-crop because plants in the SeedPGR-crop had shorter stems with fewer vegetative tillers, and shattered seeds slightly less. Nitrogen fertilization consistently improved seed yields in all management systems regardless of associated increases in lodging and seed shedding. These yield increments were mainly associated with the increased number of early- and late-formed reproductive tillers, and partly due to improved number of florets per spikelet and slightly heavier seed in early-formed reproductive ears. In spite of larger seed losses through shattering, the single-purpose crops largely out-yielded and had higher seed germination than the dual-purpose crops at all nitrogen fertilization rates, with maximized yields produced in the SeedPGR-crop.
1. Introduction
Italian ryegrass (Lolium multiflorum Lam.) is the most important grass forage crop in Croatia but can be also grown for seed under dual-purpose (combined forage-seed) and single purpose (pure-seed) management systems. Limited information is available about best management practices and operations for seed crop of Italian ryegrass. For seed production, harvest may be by swathing and picking up later with a combine, or by combining direct. In climates where good weather at harvest (hot and dry summers) is normal (e.g., Villamete Valey in Oregon, USA), swathing is preferred [1]. Ryegrasses are cut and windrowed at approximately 40% seed moisture, left to dry in the field to 12% moisture, and then threshed [2]. This allows more seed to continue ripening while reducing seed losses due to shattering. However, in area with unstable weather at harvest such as in continental Croatia, direct combining and artificial drying of harvested seed are necessary. Nitrogen (N) is the most critical mineral element affecting seed yield of grass crops, primarily through its influence on tillering and fertile (reproductive) tiller number. The effect of N fertilization on perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.) is well documented, whereas information for Italian ryegrass crop is scarce. In Atlantic Canada, ref. [3] reported that more intensive N fertilization increased tiller number per unit area and spikelets per spike, and consequently, seed yield of Westerwold ryegrass. In two field trials in New Zealand, ref. [4] reported seed yields greater than 3500 kg ha−1 under N fertilization rate of 180 kg ha−1 for Italian ryegrass crop.
Increasing N supply increases growth and stem elongation, making plants prone to lodging. In perennial ryegrass, lodging was found to reduce seed yield as a result of reduced seed number [5], but in contrast with the findings of [6], seed weight was increased by lodging. Furthermore, when combined with favourable weather conditions, lodging supports the growth of new tillers (secondary regrowth), which leads to difficulties in harvesting. Previous research indicated that the application of plant growth regulator (PGR) has a great potential of improving Italian ryegrass seed yields by significantly reducing stem height, and therefore, reducing lodging and secondary regrowth at harvest [7]. In addition, ref. [4] found that after applying PGR seed yields increased by 29 to 64% compared to the untreated control. The seed yield response was associated with stem shortening, and reduction in lodging, resulting in more saleable seeds per unit area. Similar results were obtained by [8] in perennial ryegrass, whereby PGR consistently reduced lodging and stem height, but had no effect on the number of spikes per unit area, spikelets per spike and florets per spikelet.
The incidence of lodging in the dual-purpose (combined forage-seed) management system for Italian ryegrass crop may be lowered by using the first cut for forage. Early studies on the opportunity cost of grazing annual ryegrass grown for seed indicated that benefits of grazing could outweigh possible reductions in seed yield [9]. In Great Britain, fertile tiller number was not significantly influenced by cutting annual ryegrass as late as 21 May, although seed yield declined significantly [10]. However, defoliation management recommendations for grasses should be based on stages of phenological development rather than on calendar days because of variations in crop development from year to year. Cutting prior to internode extension results in the removal of leaf material only, and subsequent regrowth arises from the extension of leaf primordia from the terminal meristem and from the meristem of axillary tillers [11]. Once internode extension has begun, cutting may remove the terminal meristem and thus the unexpanded leaves. The critical stage for spring cutting appears to be few weeks after ear formation, when the inflorescences reach a vulnerable height within the sheaths [12]. Thus, a new knowledge is needed about the effects of timing of spring cuts on Italian ryegrass seed yield to underpin the decisions on when to cut the dual-purpose (combined forage-seed) crops to optimize seed production.
The main objective of this study was to determine the influence of various management systems on seed production of first-year Italian ryegrass crop grown under various N fertilization.
2. Materials and Methods
Field trial was conducted at Maksimir experimental field (45°49′ N, 16°2′ E, 123 m above sea level) on silt loam soil (Eutric Cambisol). Experimental site has the 30-Yr (1997–2016) average annual temperature of 10.3 °C and precipitation of 852 mm. A two-factorial experiment (management system and N fertilization) was conducted in the growing season of 2011/2012 with weather data presented in Table 1. Management systems consisted of the single purpose (pure-seed) and the dual-purpose (combined forage-seed) crops. In addition, the single-purpose crops consisted of management with (SeedPGR-crop) and without (Seed-crop) application of PGR. The dual-purpose crops had early (EF-seed-crop) and late (LF-seed-crop) spring forage cut followed by seed harvest. Nitrogen fertilization was applied at total rates of 0, 60, 120 and 180 kg ha−1.

Table 1.
Monthly mean temperatures and total rainfall during the growing season of 2011–2012.
Previous crop on experimental site was winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Soil tests prior to tillage indicated satisfactory phosphorus (P) and potassium (K) levels to maintain adequate soil quality and crop production. Field was ploughed at 25 cm depth four weeks before sowing, and rotary harrowed for seedbed preparation. Tillage operations and sowing were delayed from early October until early November because of dry weather. Italian ryegrass tetraploid variety Mir was sown on 3 November 2011 at 450 seeds m−2 in a 20 cm wide rows with a small plot drill (Wintersteiger, Ried im Innkreis, Austria). Field trial was conducted at Maksimir experimental field (45°49′ N, 16°2′ E, 123 m above sea level) on silt loam soil (Eutric Cambisol).
Plots were free of weeds, pests and diseases throughout experimentation. Granular N fertilization, as calcium ammonium nitrate (27% N) was top-broadcast in split applications. Dates of N application with corresponding crop growth stages are shown in Table 2. Plant growth regulator trinexapac-ethyl (Moddus EC 250, Syngenta Crop Protection, Cambridge, UK) was applied with a backsprayer at a dose of 1.0 L/ha (250 g a.i. L−1) during stem elongation (ZCK 32–33) [13] in the SeedPGR-crop (Table 2). For plots with forage cut management, early spring forage cut date was also during stem elongation stage (ZCK 32–33), whereas late forage cut was at the beginning of heading (ZCK 52–53). Plants were cut at a height of 7 cm, and forage and dry matter yield was determined in the central six rows of each plot on each day of cutting.

Table 2.
Summary of management, growth stages, and weather conditions for the first-production year of biannual Italian ryegrass crop grown for seed production.
Number of emerged plants was counted in 1.0 m length of two adjacent rows at three sites in each plot. Total number of ears per unit area was based on the sample that was taken 10 days after full anthesis (ZCK 65) from each plot at 30 cm length of two adjacent rows where all tillers were cut off at ground level. The total ear number in each sample was recorded; afterwards, each sample was divided into the vegetative (unproductive) tillers (no ears), early-formed reproductive (fertile) tillers and late-formed reproductive tillers (greenheads). The difference between the late-formed reproductive tillers (greenheads) and the early-formed reproductive tillers was that the former had ears that had not yet begun anthesis (ZCK 61). In the early-formed reproductive tillers the following measurements were carried out: stem length to the ear, number of visible nodes on the stem, number of spikelets per ear, and the number of florets per spikelet in the lower, middle and upper section of ear. Paired spikelets from the lower, middle and upper sections of each early-formed reproductive tillers were selected for determination of the number of florets per spikelet.
Crop lodging severity was assessed visually and scored as a percentage of plot lodged where 0 was not lodged (plants fully upright) and 100% was most severe lodging (plants were laying flat on the ground). Lodging was observed daily following anthesis until harvest. One week after anthesis two tin containers (15.0 cm width, 60.0 cm length and 5.0 cm depth) with an overall surface area of 1800 cm2 were placed on the ground between the adjacent central rows of each plot to determine the weight of shed seed. Containers were removed at harvest, and the weight of shed seed was determined.
Italian ryegrass crop was harvested by direct combining when seed moisture content reached approximately 40–45%. Mature seed was harvested with a small-plot combine (Wintersteiger, Ried im Innkreis, Austria) with drum speed and concave settings to simulate commercial farm practice. Only six central rows were harvested from the middle of each plot (excluding the 0.3 m length at each end) to avoid a border effect. Harvest dates were given in Table 2. Growing degree days were calculated from the data of weather station located 300 m from the experimental site using a base temperature of 0 °C. After harvest, samples were taken for determination of seed moisture content for harvested as well as shed seed. Seed was dried at room temperature for several weeks, and then cleaned of impurities to determine clean seed weight (yield). In this paper seed yield and shattered seed were expressed with 14% w/w moisture content. Samples for the determination of seed moisture content were oven dried at 60 °C for 48 h.
Thousand-seeds weight was determined by counting 500 seeds and weighing. Germination was determined approximately 90 days after harvest in accordance with the International Seed Testing Association (ISTA) rules [14] by placing 100 seeds on a moist germination paper for imbibition. After a chilling treatment for 5 days at 5 °C, the seeds were germinated at 20 °C. The final seedling count was made after 14 days.
Field trail was arranged in a strip-plot design with four replicates. Management systems were horizontal plots, while N fertilization was assigned to vertical plots. Data were analysed using Mixed Model procedures in a SAS/STAT Software [15]. Analysis of variance was computed with management system and N fertilization considered fixed. Means separation was calculated using the Fisher’s Least Significant Difference (LSD) test at p ≤ 0.05.
3. Results
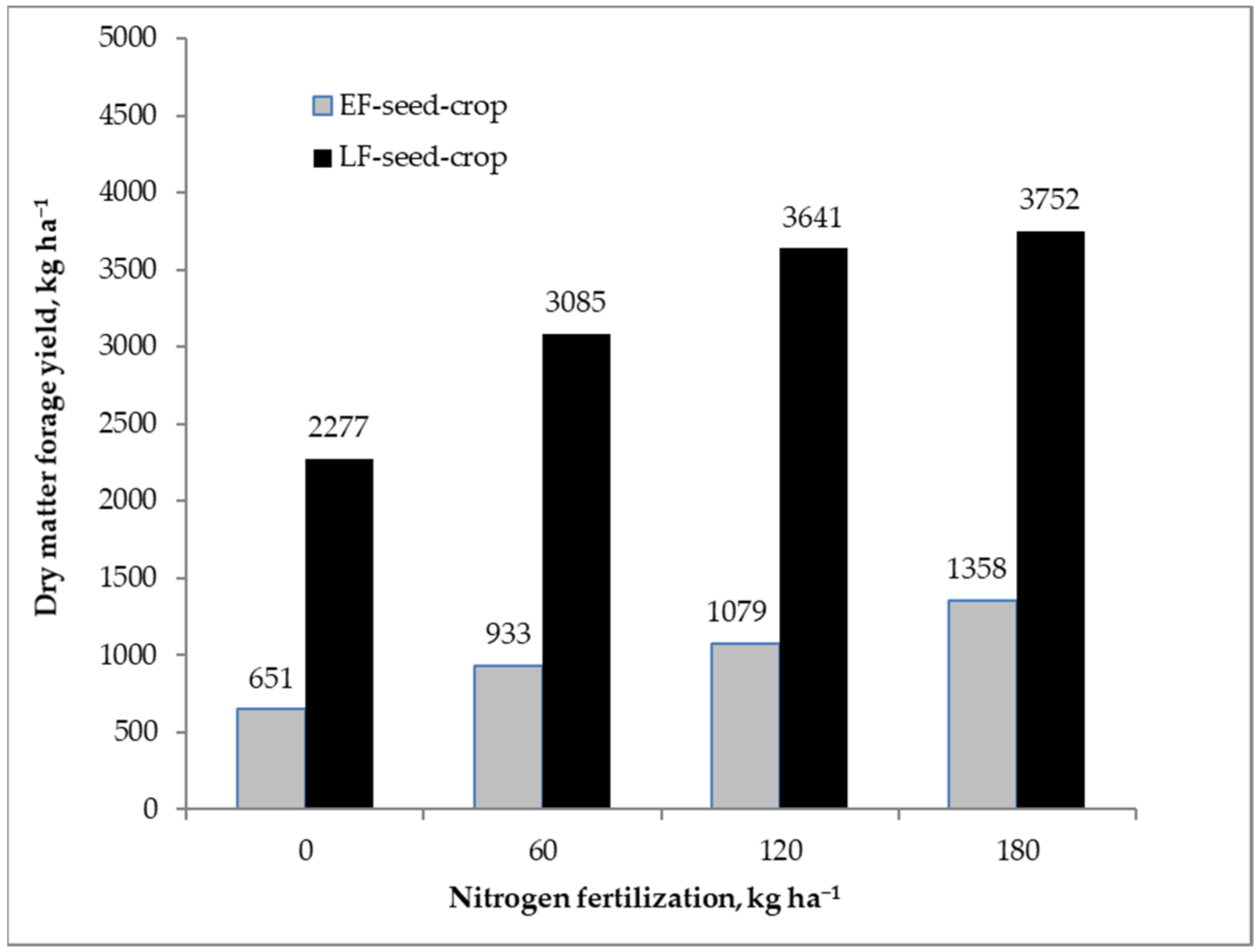
There was no difference in plant number per unit area among investigated treatments (Table 3). Forage yields were significantly affected by N fertilization and management system in the combined forage-seed crops (data not shown). Forage dry matter yield averaged 1005 kg ha−1 in the EF-seed-crop, whereas the LF-seed-crop produced larger forage yield (3189 kg ha−1). Forage yield increments with higher N fertilization rates were larger in the LF-seed-crop than the EF-seed-crop, as indicated by a significant management system × N fertilization interaction (Figure 1).

Table 3.
Seed yield, yield components, seed shedding and other traits of Italian ryegrass crop as affected by management system and nitrogen fertilization.
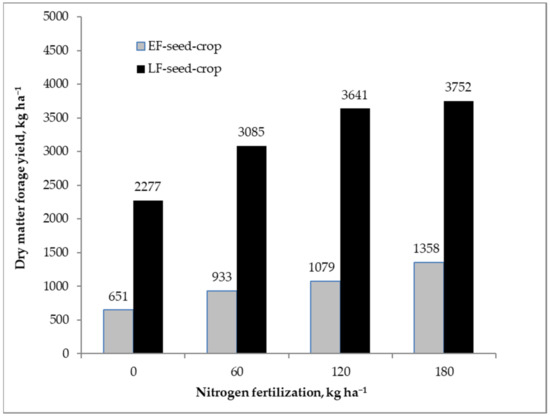
Figure 1.
Effect of nitrogen fertilization on forage yield in the dual-purpose crops of Italian ryegrass at early (EF-seed-crop) and late (LF-seed-crop) spring cutting date. LSD (0.05) = 357 kg ha−1 for comparing means within the same management system, LSD (0.05) = 928 kg ha−1 for comparing means within the same N fertilization, LSD (0.05) = 913 kg ha−1 for comparing means across management system and N fertilization.
Management system significantly affected most measured traits except the number of early- and late-formed, and consequently, the total reproductive tillers (ears) per unit area (Table 3). Average seed moisture content at harvest ranged from 40.0% in the Seed-crop to 44.3% in the EF-seed-crop. The single-purpose crops had the greatest seed shedding averaging 793 kg ha−1 in the Seed-crop and 577 kg ha−1 in the SeedPGR-crop. The dual-purpose crops had lower seed shedding (averaging 161 kg ha−1 in the EF-seed-crop and 347 kg ha−1 in the LF-seed-crop). The application of PGR in the SeedPGR-crop significantly increased seed yield compared to (unsprayed) Seed-crop despite no differences in the lodging score at harvest (Table 3). The 1000-seed weight as well as other yield components did not differ significantly between these two management systems, but plants treated with growth regulator had shorter stems on early-formed reproductive tillers (Table 4) and fewer vegetative tillers (Table 3). The dual-purpose crops produced significantly lower average seed yields than the single-purpose crops (Table 3). The smallest average seed yield of 1127 kg ha−1 was produced by the LF-seed-crop, which also had the lowest lodging occurrence at harvest (49.7%). Seed germination averaged relatively high 94.6%, and the dual-purpose crops had significantly lower (albeit by a small absolute margin) seed germination than the single-purpose crops (Table 3).

Table 4.
Characteristics of early-formed reproductive tillers in Italian ryegrass crop as affected by management system and nitrogen fertilization.
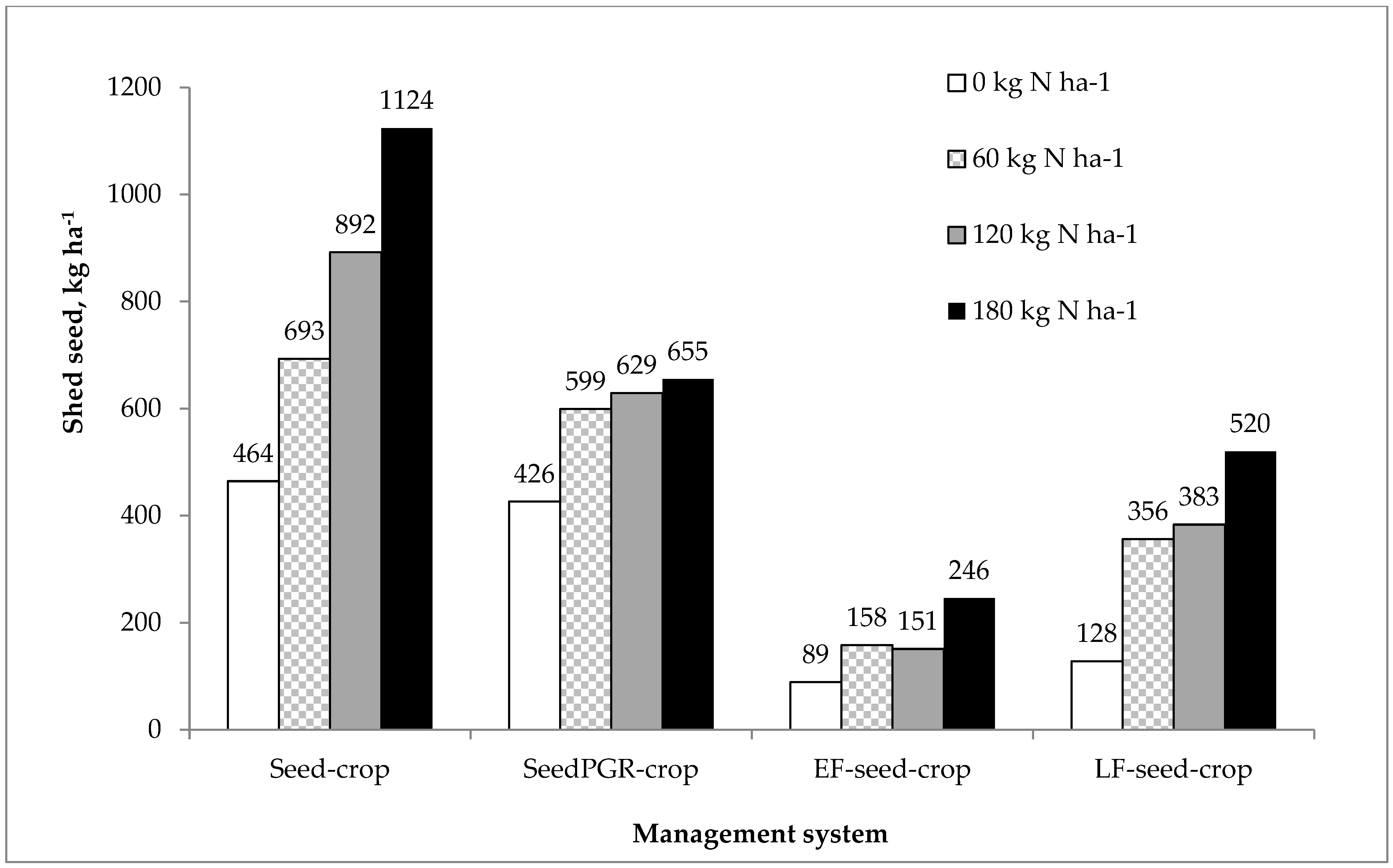
Similar to management system, N fertilization had an effect on most measured traits (Table 3 and Table 4). The number of early-formed and late-formed reproductive tillers increased following spring applications of N fertilizer (Table 3), but the proportion of reproductive tillers was similar under all N fertilization rates. The early-formed ears in fertilized plots were significantly longer than those from unfertilized plots, even though they had similar spikelet numbers (Table 4). Moreover, N fertilization significantly increased the number of florets per spikelet in early-formed ears, as well as the 1000-seed weight. In contrast, seed germination was unaffected by N fertilization (Table 3). Nitrogen fertilization slightly increased seed moisture content at harvest (Table 3), but had significant effect on seed shattering. Seed shedding averaged 277 kg ha−1 in unfertilized plots while the largest seed shattering (averaging 611 kg ha−1) was found at the highest N fertilization, which also had the highest crop lodging (92.8%) at harvest. As expected, the lowest seed yields occurred in unfertilized plots and averaged 961 kg ha−1. Nitrogen fertilization consistently improved seed yields, with N rate of 60 kg ha−1 producing the largest increment (Table 3). Higher N application rates brought about relatively small yield improvements; however, seed yields maximized at the highest N rate of 180 kg ha−1 and averaged 1611 kg ha−1. The absence of management system × N fertilization interaction for seed yield (Table 3) indicated that seed yield increments with higher N fertilization rates existed under all crop managements. In contrast, shed seed responses to N fertilization varied under management systems. Nitrogen fertilization tended to increase seed shedding in all management systems, except in the SeedPGR-crop where the amount of shattered seed at harvest did not differ across N fertilization rates (Figure 2). Consequently, seed yields were maximized at the highest N fertilization in the SeedPGR-crop (2002 kg ha−1). The largest seed shedding was measured in the Seed-crop grown at the highest N fertilization (1124 kg ha−1), which in turn, was the main reason for slightly lower seed yield when compared to that produced at lower N rate of 120 kg ha−1 (data not shown). The lowest seed yield (639 kg ha−1) was produced in unfertilized plots of the LF-Seed-crop, with seed shedding amounting 128 kg ha−1 (Figure 2).
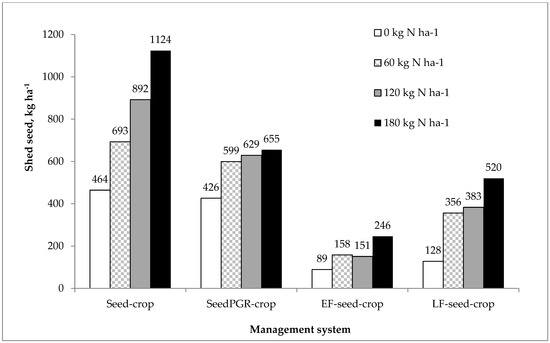
Figure 2.
Effect of nitrogen (N) fertilization on seed shattering of Italian ryegrass crop grown under various management systems. LSD (0.05) = 240 kg N ha−1 for comparing means within the same management system, LSD (0.05) = 318 kg N ha−1 for comparing means within the same N fertilization, LSD (0.05) = 311 kg N ha−1 for comparing means across management system and N fertilization.
4. Discussion
4.1. Crop Establishment, Forage Yield and Seed Harvest
Weather conditions following sowing were unfavourable for crop establishment because insufficient rain (Table 1) caused delayed and uneven emergence with stand density averaging 216 plants m−2 (Table 3). No information about optimum stand (plant) density for Italian ryegrass seed crop could be found in the literature. Seedling densities of approximately 500 per sqm are usually required for satisfactory stands and early forage production of Westerwolds ryegrass [16]. Compared to the EF-seed-crop, the LF-seed-crop produced larger forage yield because of being cut 2 weeks later (Table 2). Higher N fertilization consistently increased forage yields in these two dual-purpose (combined forage-seed) crops, suggesting that N availability was the most limiting factor for growth. Forage dry matter content at cutting significantly declined with higher N fertilization (data not shown), as reported by [17].
One of the undesirable features of Italian ryegrass is its inability to retain seed until the time of harvest; therefore, it is generally direct combine-harvested at higher moisture content than perennial ryegrass [18]. Direct combining is not usually advisable at seed moisture concentrations above 40%, but seed crop of tetraploid Italian ryegrass can be successfully combined directly starting at around 45% moisture as long as combine drum speeds are adjusted correctly [19]. Despite being grown under various management systems and harvested on various dates (Table 2), Italian ryegrass was successfully direct-combined within the optimum harvesting window (40–45% seed moisture content at harvest). Across all treatments, seed moisture content at harvest averaged 41.3%, with seed yield averaging 1411 kg ha−1. In Atlantic Canada, crop of tetraploid Westerworlds ryegrass produced about 1000 kg ha−1 [3]. In Serbia, seed yield of the first-year Italian ryegrass crop harvested by hand averaged 1035 kg ha−1 [20]. Seed yields of 2000 kg ha−1 are common in the Willamette Valley in Oregon where mild, moist winters and dry summers provide an ideal environment for grass seed production [1]. However, seed yields have been lower than 1000 kg ha−1 and more erratic under climatic conditions in the south-eastern USA because of year-round rainfall, especially during seed maturation [21]. The non-significance of the interaction management system × N fertilization for seed yield in the first-production year of Italian ryegrass crop (Table 3) allowed us to discuss the effects of these two factors independently.
4.2. Effect of Management System
The number of reproductive (fertile) tillers was similar under all management systems (Table 3), but the dual-purpose crops produced significantly lower average seed yields than the single-purpose crops. These results clearly showed the negative effect of spring forage cuts on the seed yield potential of Italian ryegrass from regrowth (secondary growth). In practice, it is usually the number of reproductive tillers that has the most important influence on yield. The tillers of the earliest origin are the most fertile, produce the largest inflorescences, and have the highest seed set and heaviest seed in a seed crop. In our experiment, spring cutting for forage removed those oldest tillers and left seed crop to be produced from later-formed tillers of lower yield and quality. In addition, plants in the dual-purpose crops developed and grew under warmer temperatures and drier conditions (Table 1 and Table 2) compared to plants in the single-purpose crops. Consequently, plants from the dual-purpose crops had a significantly smaller number of visible nodes, shorter ears, fewer spikelets per ear, and fewer florets per spikelet in the basal, middle and upper section of the early-formed reproductive ears (Table 4). In addition, the dual-purpose crops produced significantly lighter seed weights than the single-purpose crops (Table 3). For example, seeds produced in the SeedPGR-crop were 38% heavier than those in the LF-seed-crop. In Britain, ref. [10] reported that fertile tiller number was not influenced by cutting annual ryegrass as late as 21 May, but seed yield declined significantly. In contrast, ref. [22] found that annual ryegrass might be grazed up to the time when all primary tillers had their apical meristems removed (early to mid-April in Oregon) without any deleterious effect on seed yield. In their research, the beneficial effect of grazing was to increase the number of fertile tillers per unit area, which was not observed in our experiment. In New Zealand, ref. [23] found that grazing annual ryegrass reduced the number of spikelets per ear.
Our findings showed that considerable seed yield losses (up to 800 kg ha−1) in the single-purpose Italian ryegrass crop may occur before harvest. Despite the greatest seed shedding (Table 3), the single-purpose crops succeeded in achieving the highest seed yields. Crop lodging has been identified as one of the major factors accounting for reduced seed yields due to shattering in Italian ryegrass crop [24]. In glasshouse conditions, Lombardy populations of Lolium multiflorum lost approximately 30% of their seed at seed moisture concentration of 43%, and the yield loss has increased to 40% at a seed moisture concentration of just under 40% [25]. In our experiment, lodging incidence in the single-purpose crops occurred late in the growing season (Table 2) because of windy weather few days before harvest. This adverse weather conditions just before harvest and differences in maturity (moisture content) among seeds of the same spike or among plants were probably the major factors accounting for large seed losses due to shattering in the single-purpose crops. The dual-purpose crops had more favourable weather conditions before harvest, which resulted in less lodging (Table 3), and consequently, lower seed shedding (averaging 161 kg ha−1 in the EF-seed-crop and 347 kg ha−1 in the LF-seed-crop). The glasshouse test of [26] showed that artificially-induced shedding losses of Italian ryegrass began at moisture content of around 48%, after which shedding proceeded at the same rate between the investigated genotypes. Although it is not possible to relate seed shedding under glasshouse conditions to field environments with any precision, the smallest seed shedding in the EF-seed-crop was most likely associated with the highest seed moisture content at harvest (Table 3). Similar to the single-purpose crops, the LF-seed-crop had relatively large seed shattering caused by windy weather one day before harvest that also brought about considerable lodging (Table 2).
The application of PGR in the SeedPGR-crop significantly increased seed yield compared to (unsprayed) Seed-crop despite no differences in the lodging score at harvest (Table 3). The 1000-seed weight as well as other yield components did not differ significantly between these two management systems, but plants treated with growth regulator had shorter stems on early-formed reproductive tillers (Table 4) and fewer vegetative tillers (Table 3). In Belgium, ref. [7] reported that application of PGR significantly reduced stem height of Italian ryegrass. In glasshouse experiment [27], it was found that competition for carbohydrates or nitrogen between the seeds and new vegetative tillers that develop after the onset of anthesis was not a major cause of the low seed yields in Lolium perenne L. seed crops. However, competition for assimilates between seeds and new vegetative tillers has been suggested as a major cause of the low and variable seed yield in Lolium perenne [28] as the growth of new tillers requires carbohydrate support from the older tillers. Thus, it appears that assimilates from the reproductive and vegetative tillers might have been translocated more efficiently into seeds in the SeedPGR-crop when compared to the Seed-crop. In addition, the SeedPGR-crop had slightly higher seed moisture content at harvest (Table 3) and slightly less seed shedding than the Seed-crop. Thus, observed differences in seed shattering between the single-purpose crops treated or not treated with PGR could be related to differences in seed moisture content at harvest.
Seed germination averaged relatively high 94.6% and was affected by management systems (Table 3). The dual-purpose crops had significantly lower (albeit by a small absolute margin) seed germination than the single-purpose crops, and these differences in germination were most probably associated with relatively large differences in seed weights (Table 3). Researchers generally agree that seed viability is acquired at an early stage of development, for instance, just 7 days after anthesis for perennial ryegrass [29]. In North Italian ecotypes of Lolium multiflorum [25], it was reported that germination values reached a maximum 27 days after anthesis because the 1000-seed weight increased until approximately 27–30 days after anthesis. A small decrease in seed germination in the dual-purpose crops might have been a result of the formation of lighter and physiologically unripe seeds by the later-formed tillers. In a study of [29] it seemed likely that some viable but immature and low-weight seeds of perennial ryegrass contained insufficient food reserves to maintain their viability after 3 months in storage. Ref. [30] showed that increasing seed weight, both between and within seed lots of tetraploid Italian ryegrass, increased seedling growth, emergence at 5 and 10 °C, and vigour. The author concluded that seeding rates should be adjusted to take account of differences in 1000-seed weight to ensure that the best production is obtained from seed sown.
4.3. Effect of N Fertilization
Seed shedding consistently increased with higher N fertilization rates (Figure 2) presumably due to higher potential yields accompanied with increases in crop lodging. Increases in crop lodging at higher N fertilization rate (Table 3) were primarily attributed to longer stem height of early-formed reproductive tillers (Table 4). In addition, stems from fertilized plots had more aboveground nodes than those from unfertilized plots indicating larger length to basal internode. It is well-known that in grass seed crops N fertilization before the onset of stem elongation increases the length of basal internodes, which in turn, along with higher stem height, may result in crop more susceptible to lodging.
Yield increases with higher N fertilization rates were achieved despite the associated increases in lodging and seed shedding (Table 4), once more indicating the importance of N for seed yield build-up. However, lodging occurred very late in the growing season (Table 2) and most likely had a limited effect on crop performance. [4] reported positive correlation between seed yields and days to 50% lodging; with each days delay increasing seed yield by 45 kg ha−1. In Belgium, Italian ryegrass seed yield increased up to 90 kg N ha−1, and no difference was found between 90, 120 and 150 kg N ha−1 [31]. However, the highest recorded seed yields in New Zealand (greater than 3500 kg ha−1) were produced under N fertilization with around 180 kg ha−1 [4]. Improved seed yields at higher N fertilization rates were mainly due to more reproductive (fertile) tillers per unit area (Table 3). [32] reported that seed head number was one of the major determinants of perennial ryegrass seed yield responses to N fertilizer application rates. In contrast, ref. [33] found that seed yields of perennial ryegrass were not associated with the number of ears per unit area. [3] also showed there was no firm relationship between fertile tillers or spikelets numbers and the seed yields of Westerwolds ryegrass. However, seed yields in most seed crops depend strongly on the number of reproductive (fertile) ears per unit area, and early-formed tillers are largely responsible for producing those ears. In our research, the number of early-formed and late-formed reproductive tillers increased following spring applications of N fertilizer (Table 3). Thus, N applied in the spring stimulated tiller formation and survival, but apparently not influencing the proportion of tillers becoming fertile (reproductive), which averaged 71.0%. Moreover, N fertilization increased the number of florets per spikelet in early-formed ears. In addition to the increased number of reproductive ears per unit area, seed yield increments in fertilized plots were also partly related to heavier seed weight (Table 3), supporting our contention that, except for seed shattering, the late occurrence of lodging had a limited effect on crop performance. Nitrogen fertilization also had little influence on spikelet number and seed weight of Westerwolds ryegrass in research by [3], whereas increased seed weight of perennial ryegrass at higher N fertilization rates was found by [32]. Nitrogen fertilization had no effect on seed germination (Table 3) as also found by [32] on perennial ryegrass.
The effect of management systems and N fertilization in the second-production year of biannual Italian ryegrass crop with contrasting growing conditions is presented and discussed in a companion paper [34].
5. Conclusions
Crop lodging in the first-production year of biannual Italian ryegrass occurred late in the growing season, and consequently, had limited effect on crop performance. Delayed lodging in the single purpose-crops was caused by strong winds few days before harvest, which in turn, resulted in large seed yield losses through shattering. The dual-purpose crops had more favourable weather conditions before harvest, and consequently, less lodging and smaller seed shedding at harvest, but still failed to achieve seed yields at the level of the single-purpose crops. The application of PGR in the single-purpose crop increased seed yield compared to unsprayed single-purpose crop despite no differences in the lodging score at harvest. Nitrogen fertilization consistently improved seed yields, with N fertilization rate of 60 kg ha−1 producing the largest increment. These yield improvements with higher N fertilization rates were achieved despite the associated increases in lodging and seed shedding, which ranged from 2.5% and 277 kg ha−1 in unfertilized plots to 92.8% and 636 kg ha−1 at the highest N rate, respectively. Seed yield increments with higher N fertilization rates were noted under all management systems, and consequently, seed yields were maximized in the SeedPGR-crop coupled with the highest N fertilization rate. Seed germination was unaffected by N fertilization, but the dual-purpose crops had lower seed germination than the single-purpose crops, most likely due to large differences in seed weight.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.S., Z.P., D.J. and D.U.; methodology, Z.S.; software, Z.S. and A.M.-L.; formal analysis, Z.S., D.J. and A.M.-L.; investigation, Z.S., D.J. and D.D.P.; writing—original draft preparation, Z.S. and D.J.; writing—review and editing, A.M.-L., D.U., Z.P. and D.D.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
All relevant data for this study are reported in this article.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Stjepan Svečnjak for his technical assistance.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Young, W.C., III; Barker, R.E. Ryegrass seed production in Oregon. In Ecology, Production, and Management of Lolium for Forage in the USA; Rouquette, F.M., Jr., Nelson, L.R., Eds.; No. 24; CSSA Special Publish: Madison, WI, USA, 1997; pp. 123–138. [Google Scholar]
- Silberstein, T.B.; Mellbye, M.E.; Chastain, T.G.; Young, W.C., III. Response of seed yield to swathing time in annual and perennial ryegrasss. In 2004 Seed Production Research at Oregon State University USDA-ARS Co-Operating; Young, W.C., III, Ed.; Oregon State University Extension Service: Corvallis, OR, USA, 2005; pp. 27–30. [Google Scholar]
- Kunelius, H.T.; McRae, K.B.; Dürr, G.H.; Fillmore, S.A.E. Seed and herbage production of Westerwolds ryegrass as influenced by applied nitrogen. Can. J. Plant. Sci. 2004, 84, 791–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolston, M.P.; Trethewey, J.A.K.; Chynoweth, R.J.; McCloy, B.L. Italian ryegrass seed yield: Trinexapac-ethyl and closing date interaction. Agron. N. Z. 2012, 42, 119–127. [Google Scholar]
- Griffith, S.M. Changes in dry matter, carbohydrate and seed yield resulting from lodging in three temperate grass species. Ann. Bot. 2000, 85, 675–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebblethwaite, P.D.; Burbidge, A.; Wright, D. Lodging studies in Lolium perenne grown for seed. 1. Seed yield and yield components. J. Agric. Sci. 1978, 90, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rijckaert, G.A. Effects of trinexapac-ethyl (Moddus) in seed crops of Italian ryegrass and timothy. Bioforsk Fokus 2007, 2, 231–235. [Google Scholar]
- Chastain, T.G.; Young III, W.C.; Silberstein, T.B.; Garbacik, C.J. Performance of trinexapac-ethyl on Lolium perenne seed crops in diverse lodging environments. Field Crops Res. 2014, 157, 104–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herron, G.R. Influence of Grazing and Nitrogen Fertilization on Winter Growth, Seed and Straw Production of Lolium multiflorum Lam. Master’s Thesis, Oregon State University, Corvallis, OR, USA, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Bean, E.W.; Carr, A.J.H.; Griffiths, D.J.; Lewis, J.; Pegler, R.H.D.; Roberts, H.M.; Stoddart, J.L. Principles of Herbage Seed Production; Technical Bulletin; Welsh Plant Breeding Station: Aberystwyth, UK, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Jewiss, O.R. Tillering in grasses: Its significance and control. J. Br. Grassl. Soc. 1972, 27, 65–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, H.M. The effect of defoliation on the seed-producing capacity of bred varieties of grasses: III. Varieties of perennial ryegrass, coksfoot, meadow fescue and timothy. J. Br. Grassl. Soc. 1965, 20, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadoks, J.C.; Chang, T.T.; Konzak, C.F. A decimal code for growth stages of cereals. Weed Res. 1974, 14, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISTA. International Rules for Seed Testing; International Association for Seed Testing: Zurich, Switzerland, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- SAS Institute. SAS/STAT Software: Changes and Enhancements through Rel. 6.12; SAS Institute: Cary, NC, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Evers, G.W.; Nelson, L.R. Overseeding bermudagrass with annual ryegrass. In Proceedings of the American Forage and Grassland Conference, Lancaster, PA, USA, 6–10 March 1994; pp. 190–193. [Google Scholar]
- Binnie, R.C.; Harrington, F.J.; Murdoch, J.C. The effect of cutting height and nitrogen level on the yield, in vitro digestibility and chemical composition on Italian ryegrass swards. J. Br. Grassl. Soc. 1974, 29, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwynne, W.G. Grassland Practice No. 8. Harvesting Grass Seed. Short Term Leaflet, No. 158; Ministry of Agriculture, Fisheries and Food: London, UK, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, H.M. Harvesting tetraploid ryegrass for seed. Grass Forage Sci. 1971, 26, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simić, A.; Vučković, S.; Sokolović, D.; Stanisavljević, R.; Mandić, V.; Duronić, G. Response of Italian ryegrass seed crop to spring nitrogen application in the first harvest year. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2012, 11, 6826–6831. [Google Scholar]
- Weihing, R.M.; Evatt, N.S. Seed and Forage Yields of Gulf Ryegrass as Influenced by Nitrogen Fertilization and Simulated Winter Grazing; PR-2139; Texas Agricultural Experiment Station: College Station, TX, USA, 1960. [Google Scholar]
- Young III, W.C.; Chilcote, D.O.; Youngberg, H.W. Annual ryegrass seed yield response to grazing during early stem elongation. Agron. J. 1996, 88, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, K.R. Seed production in New Zealand ryegrass: I. Effect of grazing. N. Z. J. Agric. Res. 1980, 8, 27–32. [Google Scholar]
- Griffith, S.M.; Alderman, S.C.; Streeter, D.J. Italian ryegrass and nitrogen fertilization in western Oregon in two contrasting climatic years. I. Growth and seed yield. J. Plant. Nutr. 1997, 20, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja Harun, R.M.; Bean, E.W. Seed development and shedding in North Italian ecotypes of Lolium multiflorum. Grass Forage Sci. 1979, 48, 181–188. [Google Scholar]
- Hides, D.H.; Kute, C.A.; Marshall, A.H. Seed development and seed yield potential of Italian ryegrass (Lolium multiflorum Lam.) populations. Grass Forage Sci. 1993, 48, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warringa, J.W.; Kreuzer, A.D.H. The effect of new tiller growth on carbohydrates, nitrogen and seed yield per ear in Lolium perenne L. Ann. Bot. 1996, 78, 749–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Clemence, T.G.A.; Hebblethwaite, P.D. An appraisal of ear, leaf and stem 14CO2 assimilation, 14C-assimilate distribution and growth in a reproductive seed crop of amenity Lolium perenne. Ann. Appl. Biol. 1984, 105, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, M.J.; Watkin, B.R. Seed production studies on perennial ryegrass, timothy, and prairie grass. II. Changes in physiological components during seed development and time and method of harvesting for maximum seed yield. J. Br. Grassl. Soc. 1975, 30, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampton, J.G. Effect of seed and seed lot 1000-seed weight on vegetative and reproductive yields of ‘Grasslands Moata’ tetraploid Italian ryegrass (Lolium multiflorum). N. Z. J. Exp. Agr. 1986, 14, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vleugels, T.; Rijckaert, G.; Gislum, R. Seed yield response to N fertilization and potential of proximal sensing in Italian ryegrass seed crops. Field Crops Res. 2017, 211, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cookson, W.R.; Rowarth, J.S.; Cameron, K.C. The response of a perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.) seed crop to nitrogen fertilizer application in the absence of moisture stress. Grass Forage Sci. 2000, 55, 314–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgersma, A. Seed yield related to crop development and to yield components in nine cultivars perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.). Euphytica 1990, 49, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svečnjak, Z.; Kovačević, M.; Jareš, D.; Týr, Š.; Jama-Rodzeńska, A.; Milanović-Litre, A. Management Systems for Biannual Seed Crop of Italian Ryegrass (Lolium multiflorum Lam.) Grown at Various Nitrogen Fertilization. II. Second-Production Year Characterized by Considerable Crop Lodging and Limited Seed Shattering Before Direct Combine-Harvesting. Agronomy 2022. in review. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).